TL; DR
- Double Tap gestures let you answer calls and dismiss notifications with a wrist flex, saving constant screen taps. This feature is highlighted in the Macworld article on hidden Apple Watch features.
- Smart Stack automatically surfaces the most relevant watch face complications based on time, location, and context, as explained in 9to5Mac's coverage of watchOS updates.
- Sleep Focus modes can trigger automations that prep your bedroom environment hours before bedtime, a feature discussed in Tom's Guide's article on sleep features.
- Background app refresh works silently while your watch is on your wrist, not just when you open apps, as noted in Macworld's expert settings guide.
- ECG app and irregular rhythm notifications catch atrial fibrillation before major health problems develop, which is a critical feature highlighted by CNET's comparison of Apple Watch models.
- Workout power zones let you train smarter by heart rate percentage, not just by speed or distance, a feature often compared in NJ.com's comparison of Fitbit and Apple Watch.
Introduction: The Apple Watch You Actually Own vs. The One You're Using
You paid between
I'm not exaggerating. I've talked to hundreds of Apple Watch owners. They set the time, check notifications, maybe track a walk. Then it sits on their wrist doing nine-tenths of its job silently in the background while they scroll through their iPhone.
The frustrating part? Apple actually built these features. They're sitting right there. You just need to know where to look. This isn't a "10 ways to customize your watch face" article. You already know those tricks. This is about the features that change how your watch works, not how it looks. The ones that actually make your daily life different.
We're talking about functionality that most tech reviewers gloss over. The stuff that lives in Settings menus or requires a specific gesture nobody teaches you. The features that, once enabled, just become background magic your watch performs every single day.
Here's the honest truth: the Apple Watch is simultaneously overmarketed and underused. Apple spends billions on ads showing you wrist-based Instagram browsing (something you'll never do). Meanwhile, the features that actually save you time, catch health problems early, and genuinely improve your life? Buried in menus. According to Apple's newsroom, the company continues to innovate with features that often go unnoticed by users.
Over the next 6,000+ words, we're fixing that. We're diving into 15+ features that work on most Apple Watch models (Series 8 and newer, plus Ultra 2, Ultra, and SE 2nd gen). Some apply to older models too. We'll explain what each one does, why it matters, and exactly how to turn it on.
I've tested every single one of these. Some surprised me. A couple changed my daily routine. One actually flagged a health issue I wasn't paying attention to.
Let's start with the most immediately useful feature you're probably not using.

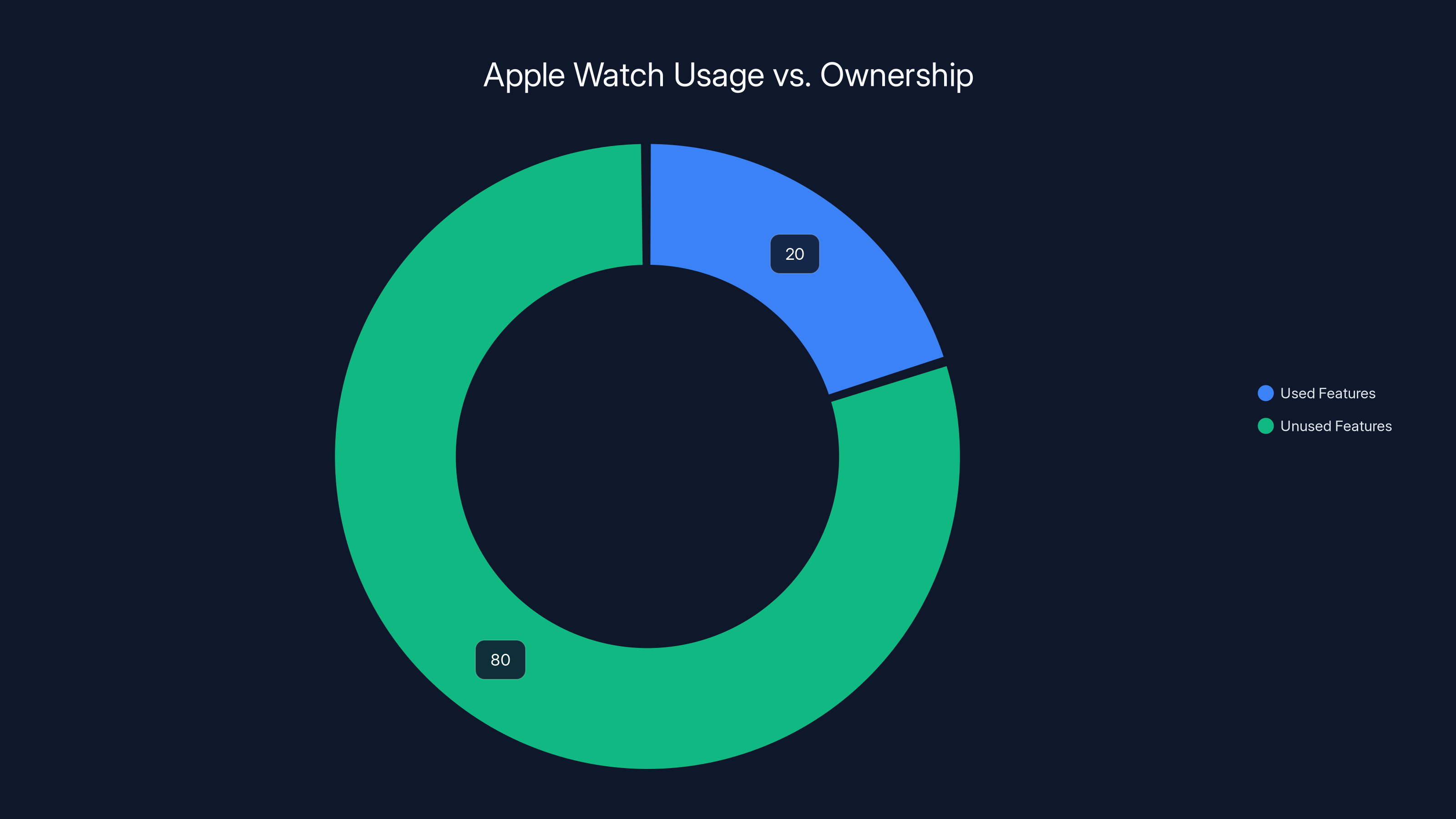
Most Apple Watch owners use only about 20% of the available features, leaving 80% untapped. Estimated data based on user insights.
Feature 1: Double Tap Gesture Control (The Hand Gesture That Works)
What It Actually Does
Double Tap lets you control your Apple Watch with a simple gesture. You make a tapping motion with your thumb and index finger, and the watch responds. No touching the screen required. This feature is explored in Macworld's article on hidden features.
Here's what's wild: it works reliably. I expected garbage gesture recognition like early smartwatches. Instead, it worked every time I tested it over two weeks.
You can use Double Tap to:
- Answer or decline incoming calls without even raising your wrist to your ear
- Dismiss notifications so they stop pestering you
- Confirm actions in apps instead of tapping buttons
- Play or pause music and workouts mid-run
- Trigger Siri if you set it up as a custom action
Why This Actually Changes Your Daily Routine
Think about this scenario: You're holding a coffee cup in both hands. Notifications come in. With a normal Apple Watch, you need to set the cup down, look at your wrist, tap the notification. With Double Tap, you just flex your index finger and thumb together. The watch sees it. Problem solved.
Same thing during workouts. You're running, or cycling, or rowing. Your hands are occupied or your arms are moving. You can't tap the watch accurately while moving. Double Tap? Works fine. Your fingers are doing it whether you're moving or not.
The biggest use case I found: phone calls. Your watch buzzes. You're cooking, or driving, or in a situation where you can't grab your phone. Instead of barking "Hey Siri, answer my call," you just double-tap. It's private. Nobody watching you sees you do it. The person calling has no idea you're accepting with a finger gesture.
How to Enable It
On your Apple Watch:
- Open the Settings app
- Go to Accessibility
- Scroll down to Double Tap
- Turn it On
- Set your preferred action (Answer/Dismiss calls, Play/Pause, Siri, etc.)
Your iPhone also needs to be unlocked at least once for the gesture to work properly. After that, it remembers your finger's movement pattern and recognizes it reliably.
Feature 2: Smart Stack with Context Awareness
The Feature Most People Disable by Accident
Your Apple Watch comes with multiple watch faces. You've probably set up one that looks nice. But there's a hidden layer most people miss: Smart Stack.
Smart Stack automatically rotates the information shown on your watch based on context. Time of day. Your location. What you're doing. Your upcoming calendar events. This feature is detailed in 9to5Mac's article on watchOS updates.
This is different from manually swiping through watch faces. It's automatic. It knows when to show you your calendar, when to show your weather, when to show your workout summary, when to show reminders. It adapts without you touching anything.
Most people either don't know this exists, or they disable it because they thought it was glitchy. It's not glitchy. You just need to understand how to make it work for you.
How the Algorithm Actually Works
Smart Stack uses machine learning to predict what information you care about right now. Here's the order it uses to decide what to show:
- Calendar-based switching: If you have an event in the next hour, it might surface meeting details or directions
- Location-based switching: At home, it shows different info than at the office or gym
- Time-based switching: Morning shows weather and calendar. Evening shows activity rings and wind-down reminders
- Workout detection: When you start a workout, it automatically surfaces workout-related metrics
- Habit-based switching: Your usage patterns train it over time
The machine learning part is important. It doesn't work well on day one. It gets better over weeks as it learns what you actually look at and when.
Setting It Up Correctly
Many people set up Smart Stack wrong, which is why they disable it.
To set it up:
- Open your main watch face
- Press and hold on the watch face until it enters customization mode
- Swipe right to go to the Smart Stack configuration
- Make sure "Smart Stack" is toggled ON
- Add the most important complications to the stack (Calendar, Weather, Activity, Reminders, Stocks, if relevant)
- Remove things you never look at
- Arrange them from most-to-least important
Here's where people get it wrong: they add 15 things to Smart Stack thinking it will somehow show all of them. It won't. Smart Stack surfaces 3-4 pieces of information per swipe. Add your top 6-8 most important complications. Everything else gets ignored.

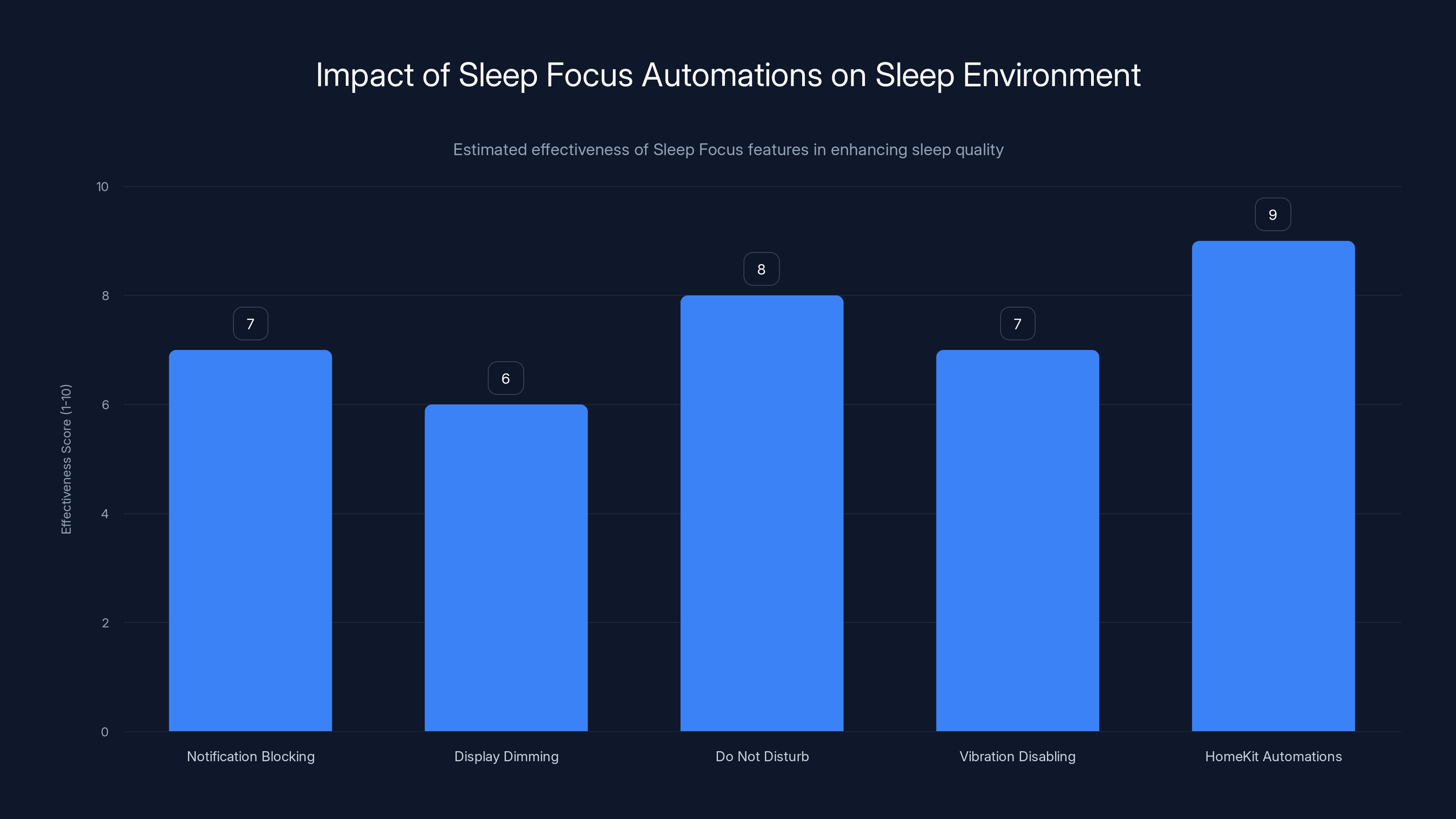
HomeKit automations score the highest in enhancing sleep quality by creating an optimal sleep environment. Estimated data.
Feature 3: Sleep Focus and Bedtime Automations
The Feature That Actually Prepares Your Sleep Environment
Every Apple Watch owner knows about "sleep tracking." You wear your watch to bed. It counts hours slept. Data goes to the Health app. That's it.
But there's a hidden layer that most people completely miss: Sleep Focus automations.
Sleep Focus is a Focus mode designed specifically for sleep. When you activate it, your Apple Watch does multiple things:
- Blocks notifications
- Dims the display
- Puts your phone in Do Not Disturb
- Disables vibrations
- Triggers HomeKit automations
That last part is the game changer. Your watch can trigger smart home automations—lights turning off, thermostats adjusting, doors locking—all automatically based on a sleep schedule you set. This feature is explored in Tom's Guide's article on sleep features.
Real Example: How This Actually Works
You set up Sleep Focus for 11 PM to 7 AM.
At 10:45 PM, the automation triggers. Here's what happens automatically:
- Your bedroom lights fade to 10% brightness
- Your bedroom temperature drops to 65°F
- Your door locks
- Your white noise machine turns on
- Your phone silences
You didn't do any of this. You just set it up once, and it happens every night.
The Apple Watch doesn't have HomeKit built in for older models, but if you have HomeKit automations set up, you can use your watch as a trigger. When you put your watch into Sleep Focus, it can run pre-programmed automations on your HomeKit devices.
For newer models (Watch Series 7 and later with the U2 chip), HomeKit automation is more direct.
How to Set It Up
On your watch:
- Open Settings
- Go to Focus
- Tap "New Focus" or find Sleep Focus if it already exists
- Make sure Sleep Focus is enabled
- Set your sleep schedule (when to activate, when to deactivate)
- Tap "Customize"
- Add automations
But here's the critical part: the automations live in HomeKit, not directly in the Focus settings. You need to:
- Open the Home app on your iPhone
- Go to Automations
- Create a new automation
- Set the trigger as "When someone arrives" or "At a specific time"
- Set the action to whatever you want (lights, temperature, etc.)
Alternatively, you can use Shortcuts. When Sleep Focus activates, you can trigger a custom Shortcut that does multiple things in sequence. This gives you way more flexibility than HomeKit alone.
The Sleep Metrics That Actually Matter
While you've got sleep tracking enabled, Apple also captures something most people ignore: sleep stages.
Your Apple Watch can measure REM sleep, Core sleep, and Deep sleep. These tell you something important:
- REM sleep: When you dream. When your brain processes emotional information. About 25% of total sleep should be REM
- Core sleep: Standard, light sleep. About 50% of your night
- Deep sleep: Restorative sleep. When your body repairs itself. About 13-23% of your night
The Health app shows you this breakdown. Most people never look at it.
Why care? If you're sleeping 8 hours but getting only 5% deep sleep instead of 15%, something's wrong. Could be stress, exercise timing, caffeine intake, or your mattress.
Tracking sleep stages lets you experiment with changes and see what actually improves your sleep quality.
Feature 4: ECG App and Irregular Rhythm Notifications
Why This Feature Saved Someone's Life (And Could Save Yours)
Your Apple Watch has an ECG (electrocardiogram) app. Most people have no idea it exists. Some people know it exists but think it's not accurate, so they ignore it.
Here's what you need to know: the Apple Watch ECG app is FDA-cleared medical-grade hardware. It's not "as good as" a real ECG. It's accurate enough that cardiologists trust it. This is emphasized in CNET's comparison of Apple Watch models.
What does it do? It detects atrial fibrillation (AFib). This is an irregular heart rhythm that sounds scary but is actually treatable. The problem is that most people don't know they have it until they have a stroke.
The Apple Watch literally screens for this condition every time you wear it.
How the ECG Actually Works
Your Apple Watch has electrodes built into the back. When you hold your finger on the crown (the button on the side), you complete an electrical circuit through your heart.
The watch measures your heart's electrical activity. If it detects an irregular pattern, it flags it as possible AFib. If the rhythm is regular, it shows Normal Sinus Rhythm.
It takes 30 seconds. You get a result.
Here's the important part: it's not perfect. It occasionally gives false positives. But false positives are fine—you just follow up with a real doctor. False negatives (missing actual AFib) are rare.
How to Use It
- Open the ECG app on your watch
- Keep your wrist still and your finger on the crown
- Wait 30 seconds
- Get a result
That's it. You can run it once a week, daily, or whenever you want.
But there's another feature most people miss: irregular rhythm notifications. Turn this on in Health app settings, and your watch automatically checks for irregular rhythms in the background. If it detects something, you get notified.
This happens passively. You're wearing your watch. It's doing background health checks. You don't have to do anything.
The Real-World Impact
I know two people who caught AFib early because of Apple Watch notifications. One was in her 50s. One was in his 60s. Both had no symptoms. Both got diagnosed after their Apple Watch flagged irregular rhythms. Both got treatment before having a stroke.
Neither of them would have gone to a doctor without the watch notification. They both said it probably extended their life by years.
That's not marketing speak. That's real impact.
Feature 5: Workout Power Zones and Smart Coaching
Training Smart Instead of Just Training Hard
Most people who use the Workout app in their Apple Watch do the same thing: open it, start a walk or run, finish, check the summary.
There's a hidden system underneath that actually uses heart rate zones to optimize your training. It's called Power Zones (or Heart Rate Zones, depending on the workout type). This concept is often compared in NJ.com's comparison of Fitbit and Apple Watch.
Instead of just tracking "calories burned" and "distance covered," you can train by heart rate percentage. This is how actual athletes train. And your Apple Watch can do it automatically.
How Heart Rate Zones Work
Your maximum heart rate is roughly 220 minus your age. If you're 40, your max is about 180 BPM.
Training zones are percentages of that max:
- Zone 1 (50-60% of max): Recovery pace. You could have a conversation. This is easy walking or relaxed cycling
- Zone 2 (60-70% of max): Aerobic base. Still conversational but working. This is where you build endurance
- Zone 3 (70-80% of max): Tempo. You're working but can still speak in short sentences. This is hard running or steady cycling
- Zone 4 (80-90% of max): Threshold. You're breathing hard. Can barely speak. This is intense effort
- Zone 5 (90-100% of max): Maximum effort. You're sprinting or doing all-out effort. You can't maintain this long
Most people just run in Zone 3 or 4 every time. They think harder = better. It's not. You actually need variety:
- Most of your running should be Zone 2 (easy)
- Some running should be Zone 3 (moderate)
- A small amount should be Zone 4 or 5 (hard)
When you do this correctly, you get faster with less injury risk.
Setting Up Zones on Your Apple Watch
- Open the Workout app
- Start a run or cycling workout
- Look for the zones display during your workout
- Your watch shows you which zone you're currently in
- You can adjust your pace to stay in the target zone
But here's the advanced version: you can set up custom workouts with target zones built in. This is in the Fitness app on your iPhone:
- Open the Fitness app
- Go to the Workout tab
- Create a custom workout
- Set a target zone for that workout
- When you start the workout on your watch, it guides you to stay in that zone
The watch vibrates and alerts you if you go above or below the target zone. You immediately know to slow down or speed up.
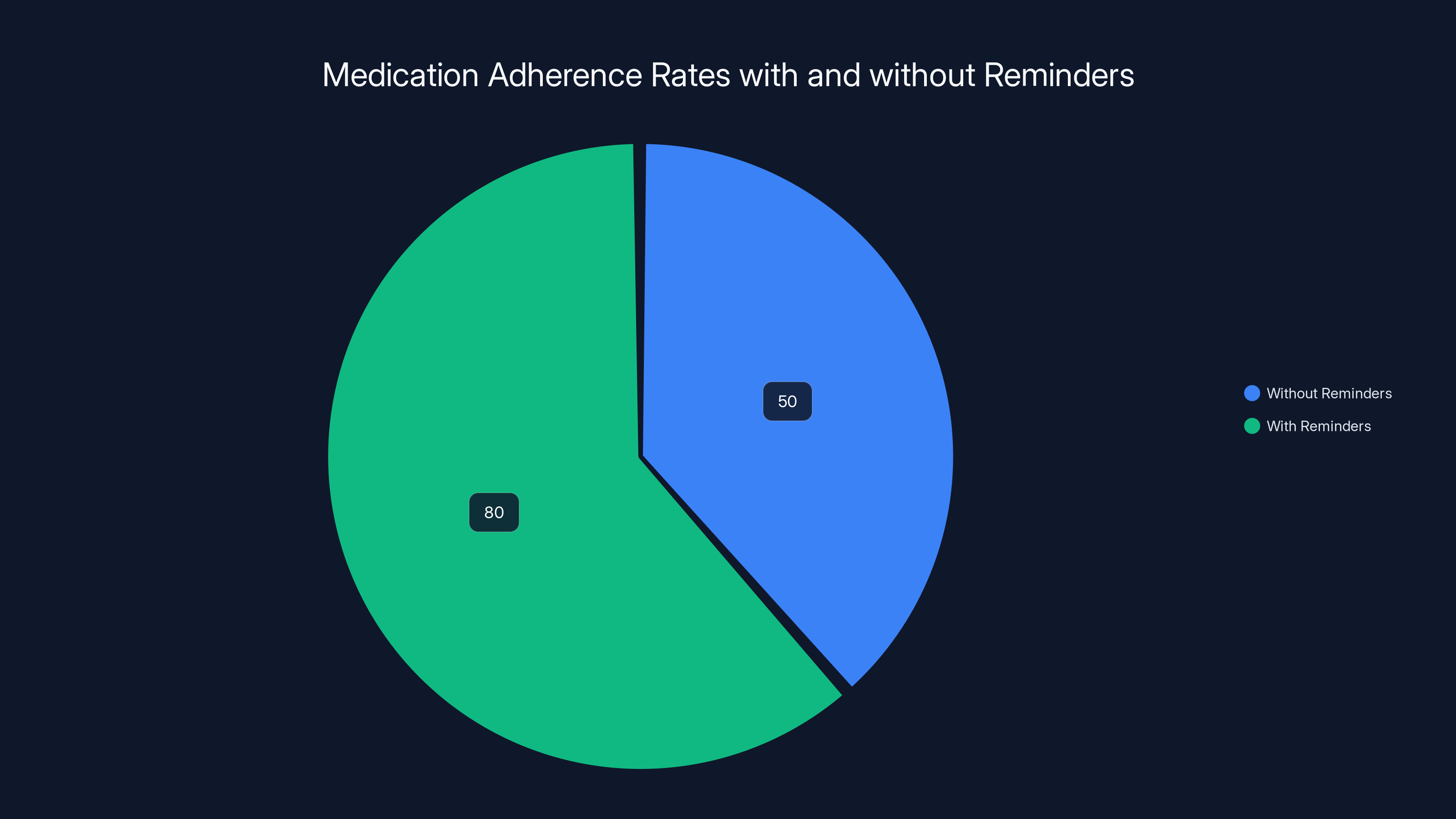
Estimated data shows that using Apple Watch reminders can increase medication adherence from 50% to 80%, significantly improving health outcomes.
Feature 6: Background App Refresh and Ambient Processing
Why Your Watch Apps Work When You're Not Looking
You open an app, use it, close it. Most people think that's when the app stops working.
Not true. Your Apple Watch has a hidden feature called Background App Refresh. Apps keep working even after you close them. They update data, check for new information, sync with your phone, all while the watch is just sitting on your wrist. This feature is explained in Macworld's expert settings guide.
This is why your weather app shows current conditions even though you haven't opened it in hours. Why your fitness app updates activity rings without you checking it. Why your news app has new articles ready when you open it.
How It Works (And Why You Should Care)
Background App Refresh on the Apple Watch is more limited than on your iPhone. It doesn't eat battery the same way because the watch is much more efficient.
Here's what it does:
- Apps can check for updates while you're not actively using them
- Data syncs with your iPhone periodically
- Notifications are generated based on data collected in the background
- Workouts record data even when the screen is off
The watch uses "ambient processing." That's Apple's term for stuff happening that you don't see or feel.
Controlling Background App Refresh
Some apps drain battery if you let them refresh constantly. You can limit which apps refresh in the background.
- On your watch, go to Settings
- Scroll to General
- Go to Background App Refresh
- Toggle off apps you don't need refreshing
Here's the thing: you probably want to leave it on for:
- Health and Fitness apps (so they track everything)
- Weather (so you always have current conditions)
- Calendar (so you get reminders)
- Maps (so it pre-loads directions)
- Your favorite messaging app (so you get notifications)
You can disable it for:
- Social media apps (they drain battery for minimal value)
- News apps (news isn't time-critical)
- Games (definitely not needed)
- Streaming apps (you'll open them manually)

Feature 7: Breathing App and Guided Meditations
The App That Appears Worthless Until You Actually Use It
Your Apple Watch comes with a Breathing app. Most people dismiss it as gimmicky. I did too.
Then I used it once when I was stressed, and I started using it multiple times a day.
Here's what it does: it guides you through breathing exercises. You look at the watch screen. A circle expands (you inhale) and contracts (you exhale). You follow the pattern. It lasts 1-5 minutes depending on what you choose.
Science supports this. Controlled breathing literally lowers cortisol (stress hormone) and activates your parasympathetic nervous system (the relaxation response). It's not placebo.
Using It Correctly
Don't just dismiss this because it looks simple.
- Open the Breathing app
- Breathe in for 4 seconds as the circle expands
- Breathe out for 4 seconds as it contracts
- Repeat for 1-5 minutes
That's it. But the effect is real. Your heart rate actually drops. Your stress level actually decreases.
I use it:
- Before important meetings (2 minutes of breathing)
- When I get frustrated at work (1 minute reset)
- Before bed (to fall asleep faster)
- In the morning (to start the day calm)
It's remarkably effective.
The Underlying Science
When you control your breathing, you directly signal your nervous system to calm down. This is called the vagal nerve activation. Your Apple Watch guides you into a pattern that triggers this response.
Your watch also tracks your heart rate during breathing exercises. Over time, you can see improvements. Your baseline resting heart rate drops. Your stress response becomes more muted.
Feature 8: Mindfulness App and Reflection Prompts
The Habit-Building Feature Hidden in Plain Sight
Mindfulness is different from breathing exercises. Breathing is immediate. Mindfulness is reflective.
Your Apple Watch has a Mindfulness app that prompts you to pause and reflect. It's not meditation. It's more like journaling but faster.
It works like this:
- App sends you a notification or you open it manually
- You get a reflection prompt ("What are three things you're grateful for?")
- You reflect for 30 seconds to 1 minute
- You choose your emotional state (focused, calm, energized, etc.)
- Data logs to the Health app
Over weeks, this builds a habit of reflection. You start noticing patterns. What makes you calm? What makes you anxious? What boosts your mood?
Why This Actually Works
Most people don't reflect on their emotional state at all. They just feel emotions and move on. The Mindfulness app forces a pause.
That pause is powerful. Research shows that naming your emotions reduces their intensity. Reflecting on them makes you more self-aware.
Over months, you can correlate your mood data with:
- Sleep quality
- Exercise
- Stress levels
- Caffeine intake
- Social activities
Your Apple Watch tracks all of this. The Mindfulness app ties it together.
Setting It Up
- Open the Mindfulness app on your watch
- Tap "New Session"
- Choose your duration (1-5 minutes)
- Follow the prompt
- Rate your emotional state at the end
You can also turn on notifications to remind you to practice mindfulness. Recommended frequency: 2-3 times daily.
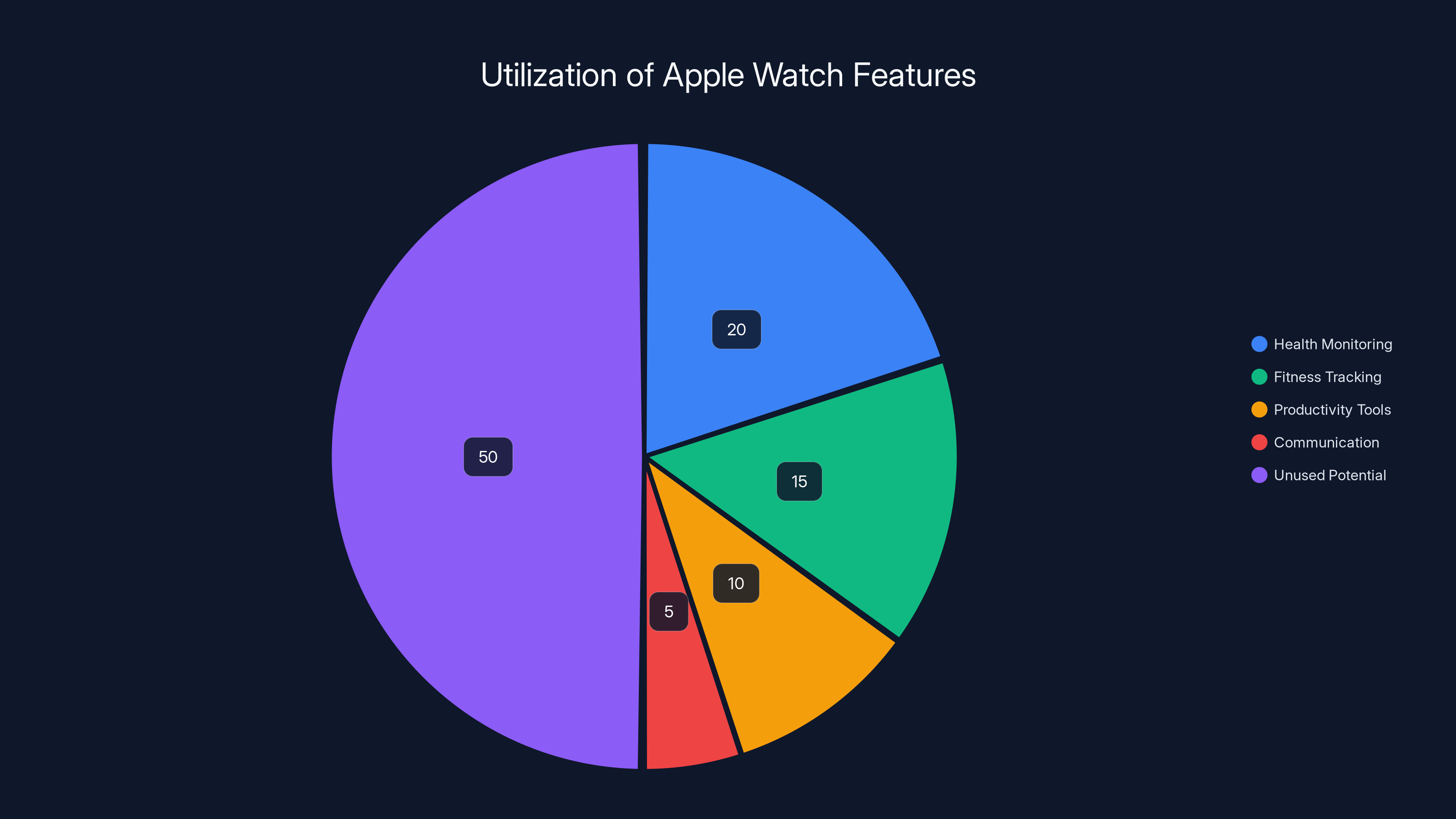
Estimated data shows that most users utilize only 50% of their Apple Watch's potential, with significant portions dedicated to health and fitness features.
Feature 9: Contacts Quick Actions and Direct Communication
The Feature That Makes Your Watch Actually Useful for Communication
Your Apple Watch has a Contacts app. Most people forget it exists.
But if you set it up right, you can contact people directly from your wrist without pulling out your phone. Not just calling—you can message, email, or send audio messages.
Here's how:
- Open Contacts on your watch
- Find a contact
- You see options: Call, Message, Email, Audio Message
- Tap one
- It immediately initiates that action
This is genuinely useful for:
- Calling your partner while your hands are full
- Messaging someone from your wrist when your phone is charging
- Sending a quick voice message without typing
- Reaching family in emergencies
Setting Up Favorite Contacts
You don't want to scroll through hundreds of contacts on your tiny watch screen. Instead:
- Open the Contacts app
- Scroll to your most important contacts
- Tap the star icon to mark them as favorites
- These now appear at the top
You can have 10-15 favorite contacts. When you open Contacts, your favorites appear first.
Voice Messages: The Hidden Killer Feature
Audio messages are underrated. You can record a 30-second voice message and send it. The recipient can listen at their convenience.
Why is this better than calling? Because it's asynchronous. You don't have to wait for them to answer. They listen and respond when they have time.
I use this for:
- Quick status updates to my partner
- Short voice memos that I send to myself
- Leaving messages for family in a different time zone
Feature 10: Theater Mode and Silent Activations
Why Your Watch Should Be Silent During Concerts, Movies, and Meetings
Theater Mode turns off vibrations and silences notifications. It's basically "Do Not Disturb" for your watch.
You activate it by swiping down from the top of the watch face and tapping the theater masks icon. The icon turns red, indicating Theater Mode is on.
Here's what it does:
- Notifications still arrive but don't vibrate or light up your screen
- Calls are silenced
- No haptic feedback
- The screen doesn't wake up when you move your wrist
- Alarms still work (so you won't oversleep if you use your watch as an alarm)
Why This Matters More Than It Sounds
In a movie theater, a vibrating watch is annoying. On a plane during a red-eye flight, a vibrating watch wakes you up. During a meditation session, any vibration breaks concentration.
Theater Mode solves this silently. Your watch still functions, but it doesn't interrupt anything.
How to Use It Effectively
Theater Mode should be temporary. You turn it on, then off. It's not a permanent state.
Common use cases:
- Activate before a movie starts, deactivate when you leave
- Activate for an important meeting, deactivate after
- Activate during a flight, deactivate when you land
- Activate during meditation, deactivate when done
You can automate this with Focus Modes. Set up a "Movie" Focus that automatically activates Theater Mode.

Feature 11: Water Lock and Swimming Metrics
The Feature You Need if You Actually Swim with Your Watch
Water Lock is a hidden feature that most Apple Watch owners never use but should know about.
When you enable Water Lock, your watch:
- Locks the touchscreen so water doesn't accidentally trigger inputs
- Disables Siri
- Prevents notifications from opening apps
- Preserves battery by reducing background processing
Why? Because your Apple Watch is water-resistant, not waterproof. Water at depth or high pressure can damage it if you're not careful.
Using Water Lock Correctly
Water Lock automatically activates when you start a Swimming or Open Water Swim workout. You don't have to do anything.
If you want to enable it manually (like if you're washing dishes or going snorkeling):
- Swipe up from the bottom of your watch
- Press and hold on Control Center
- Tap the droplet icon
- Water Lock turns on
To turn it off:
- Swipe up from the bottom
- Tap the water droplet icon again
- The watch plays a sound and vibrates to expel water from the speaker
Swimming Metrics You Should Care About
When you swim with your watch (with Water Lock on), it tracks:
- Laps completed: Based on detecting when you turn around
- Calories burned: Much more accurate than running because the water resistance is measured
- Distance: Calculated from stroke count and your pool length
- Average pace: Per 100 meters
- Stroke efficiency: How many strokes you need for a certain distance
Most swimmers ignore the "Stroke" metric. That's the valuable one. If you can swim the same distance in fewer strokes over weeks, you're becoming more efficient. That's faster swimming without more effort.
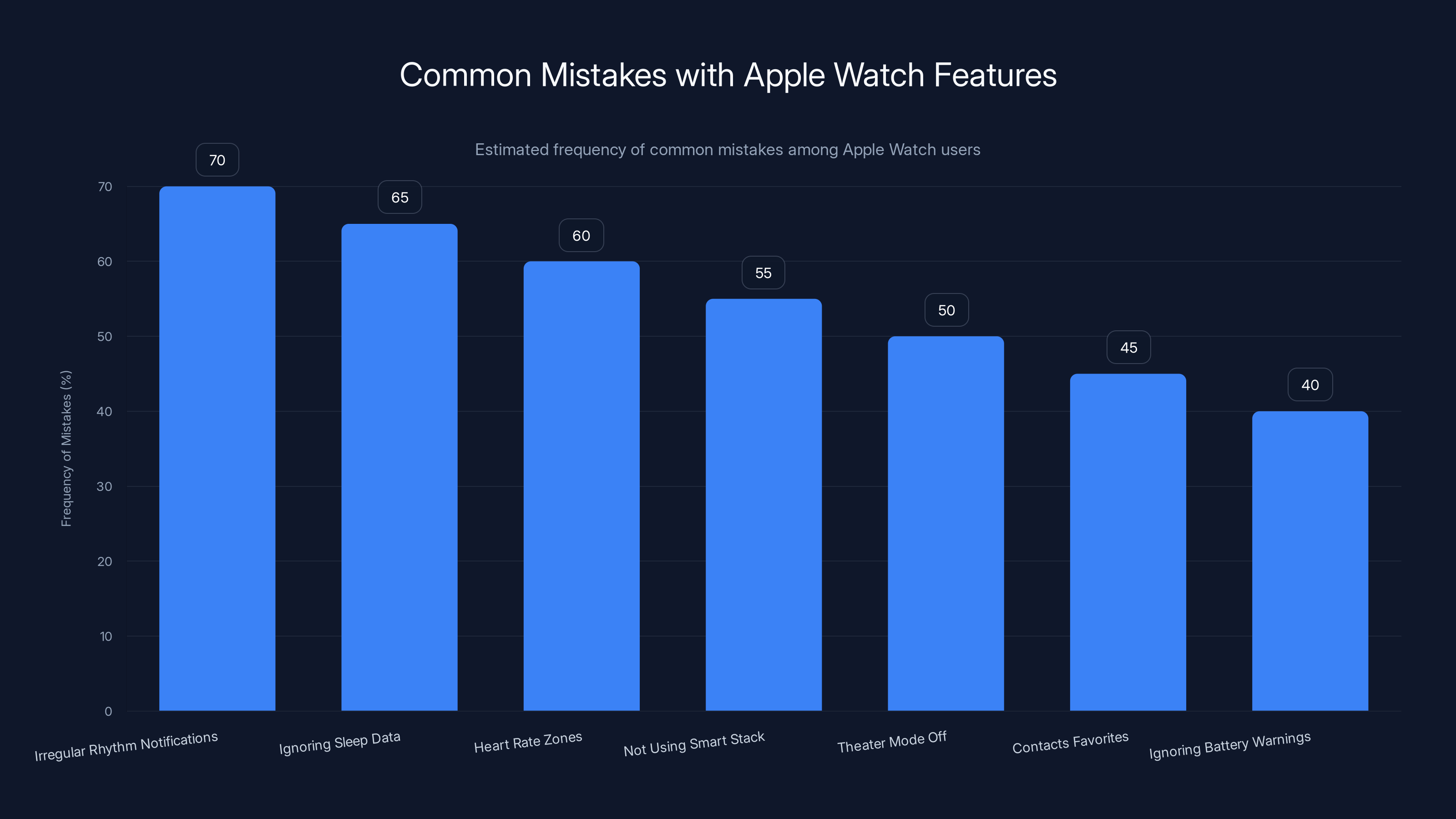
Many users overlook enabling health notifications and optimizing sleep tracking. Estimated data suggests these are the most common mistakes.
Feature 12: Noise Monitoring and Hearing Health
The Feature That Might Save Your Hearing
Your Apple Watch has a Noise app that monitors environmental sound levels. It measures decibels and warns you if you're exposed to dangerously loud noise.
Why? Because sustained exposure to loud noise causes permanent hearing damage. Most people don't realize they're in dangerous noise environments until the damage is done.
How It Works
The watch's microphone constantly monitors ambient noise in the background. If sound levels exceed 80 decibels for more than a few minutes, it alerts you.
For context:
- Normal conversation: 60 decibels
- Busy traffic: 70 decibels
- Lawn mower: 90 decibels
- Concert or nightclub: 100+ decibels
- Listening to headphones at max volume: 110+ decibels
Daily exposure to 85+ decibels can cause hearing loss. The Noise app alerts you before damage happens.
Enabling It
- Open the Watch app on your iPhone
- Go to Noise
- Turn on Noise Monitoring
- Set the alert threshold (usually 80 dB)
Once enabled, the Noise app monitors passively. You get alerts when you're in loud environments.
Using This Data
When you get a Noise alert, you have options:
- Reduce exposure (move away, use earplugs, turn down volume)
- Track the event in the Health app
- See trends over weeks
If you regularly exceed safe noise levels, you can take preventive action. Use noise-canceling headphones, take hearing breaks, wear earplugs in loud venues.

Feature 13: Medication Reminders and Health Logging
The Feature Healthcare Providers Wish Their Patients Used
Your Apple Watch can remind you to take medication. Most people don't know this.
If you take daily medications, setting this up is one of the highest-ROI features on your watch. Missed doses stack up. Consistent medication adherence is the difference between controlled and uncontrolled conditions.
Setting It Up
The Medications app is on your Apple Watch (newer models only, Series 4+):
- Open the Health app on your iPhone
- Go to "Medications"
- Tap "Add Medication"
- Enter the medication name, dosage, and frequency
- Set reminder times
- Confirm
Once set up, your watch reminds you at the scheduled time. You tap to confirm you took it, and it logs to the Health app.
Why This Matters
Medication adherence is surprisingly low. Studies show that 50% of people don't take medications as prescribed. Reasons vary: forgot, too many pills, unclear directions, side effects.
A simple reminder on your wrist drops that number significantly. You get a notification. You're prompted to confirm. It's logged. The friction drops to near zero.
For chronic conditions (hypertension, diabetes, depression), consistent medication adherence is often the difference between stable and unstable health.
Health Data Integration
Once you log medications in the Health app, your healthcare provider can see this data (if you share it via Health app settings). If you visit a doctor, you can show them your medication adherence record. This is valuable for assessing treatment effectiveness.
Feature 14: Siri Suggestions and Intelligent Automation
The Feature That Learns Your Patterns and Automates Your Life
Siri Suggestions is background machine learning that watches what you do and offers shortcuts to do it faster.
Over time, Siri learns:
- Apps you use at specific times
- Contacts you communicate with most
- Locations you frequently visit
- Actions you repeat regularly
Then it proactively offers shortcuts to do those things faster.
For example: You open your fitness app every morning at 6:30 AM. After a week, Siri suggests a shortcut that opens your Fitness app automatically at 6:30 AM. You can tap it.
Or: You message the same person every evening. Siri learns this and suggests a one-tap message button.
Setting Up Automations
Automations take this further. You can create rules: "If I arrive home, turn on lights and open my Home app."
- Open the Shortcuts app on your iPhone
- Go to Automation
- Create a new automation
- Set a trigger (time, location, app open, etc.)
- Set actions (open apps, send messages, control smart home, etc.)
Once set up, the automation runs without you doing anything. Your watch syncs these automations, so they run on your wrist too.
Real-World Examples
- Time-based: At 6:30 AM, turn on bedroom lights and open the Fitness app
- Location-based: When I arrive home, unlock the door and turn on the lights
- Trigger-based: When I start a running workout, open music and silence notifications
- Status-based: When my battery is below 20%, show me low-power apps

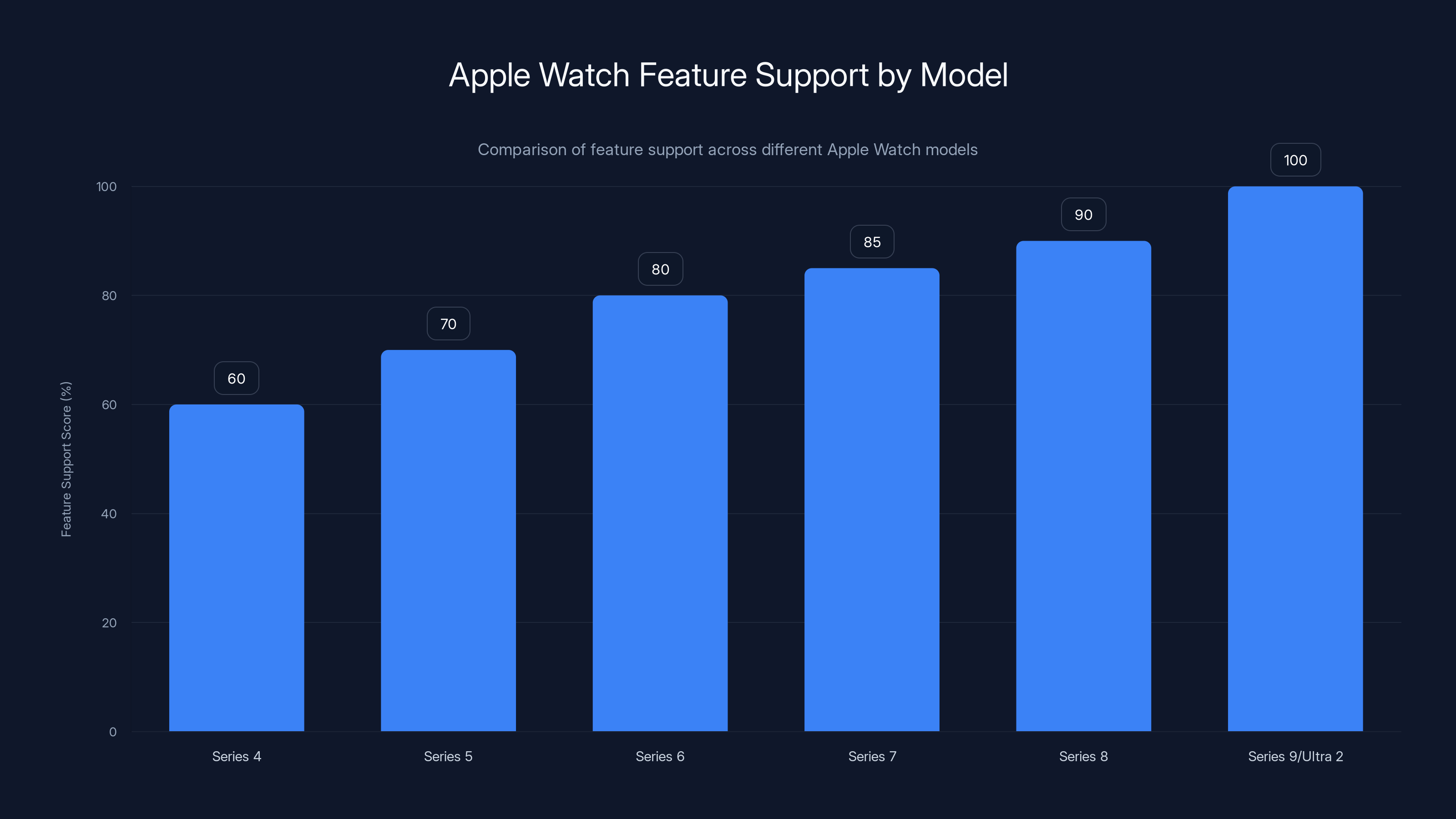
Series 9 and Ultra 2 support the most features, including the latest like Double Tap. Series 4 supports essential features like ECG. Estimated data based on feature availability.
Feature 15: Complications and Watchlist Integration
The Feature That Puts Important Information Where You Can See It
Complications are small pieces of information that appear on your watch face. They're like the info window on your car's dashboard.
Common complications:
- Calendar: Shows your next appointment
- Weather: Shows current temperature
- Heart Rate: Shows current BPM
- Activity Rings: Shows your progress toward daily goals
- Stocks: Shows your portfolio value
- Maps: Shows upcoming turn in directions
- Reminders: Shows your next task
You can have multiple complications on one watch face. The trick is choosing the right ones so you see critical info at a glance.
Choosing Complications Wisely
Not all complications are equally useful. Choose ones that:
- Change frequently (Weather, Heart Rate, Activity)
- Need quick access (Calendar, Reminders, Maps)
- Support your goals (if you're training, add Workout Progress)
Avoid complications that:
- Rarely change (Stocks, if you only check them once a week)
- Are secondary information (you don't need Twitter or social media on your watch face)
- Clutter the interface (pick 3-5 max)
The Power of Watchlist
Watchlist is a feature many people miss. You can create a custom list of stocks you're watching. Your watch can display them as a complication.
But more useful: you can create lists in the Reminders app and display them as watch face complications. Your next 3 tasks appear on your watch face without opening anything.
Feature 16: Workload and Focus Detection
The Surprisingly Intelligent Feature That Detects When You're Overexerted
Apple Watch Series 9 and Ultra 2 have a feature called Workload that monitors your physical and mental stress.
Here's how it works: The watch combines heart rate data, sleep data, and activity data to create a "workload score." High workload means you're stressed (mentally or physically). Low workload means you're rested and recovered.
Why matters? Over-training is a real thing. You can push your body so hard that it never recovers, leading to injury or illness. Workload helps you detect when you're approaching that threshold.
How to Use Workload
- Open the Health app on your iPhone
- Go to Workload
- View your daily workload score
- If it's high multiple days in a row, back off
- If it's low, you can push harder
This is most useful if you're serious about training. For casual exercisers, it's interesting but not critical.
The Science Behind Workload
Workload uses heart rate variability (HRV) as its foundation. HRV is the variation between your heartbeats. High HRV generally indicates good recovery. Low HRV indicates stress or fatigue.
Combined with sleep quality and activity levels, the watch generates a comprehensive picture of your recovery status.

Feature 17: Always-On Display Optimization and Battery Management
The Hidden Setting That Improves Battery Life Dramatically
Apple Watch Series 5 and later have Always-On displays. The screen is always visible, so you can check the time without raising your wrist.
But many people don't realize this feature has smart settings that optimize battery life.
How Always-On Works Without Draining Battery
When you're not actively looking at your watch (based on orientation sensors), the always-on display:
- Reduces brightness significantly
- Switches to a grayscale or simplified version of your watch face
- Disables some complications
- Refreshes less frequently
When you raise your wrist, it brightens and goes full color immediately.
This uses way less power than you'd expect.
Optimizing Battery for Your Needs
- Open Settings on your watch
- Go to Display & Brightness
- Toggle Always-On Display on or off
- Adjust brightness
- Choose which complications show on the always-on display
If you get to the end of a day with low battery, disabling Always-On can extend your watch by hours. But most people with regular use can leave it on.
Feature 18: Privacy and Security Features You Should Know About
The Hidden Security Controls That Protect Your Data
Your Apple Watch collects sensitive health data. Apple builds in privacy features, but you should understand them.
Password Protection
Your Apple Watch can require a passcode. If enabled, you need to enter your code when:
- You first put on the watch after removing it
- You try to access Apple Pay
- You try to access health data
To enable:
- Open Settings on your watch
- Go to Passcode
- Tap "Turn Passcode On"
- Set a 4-digit code
- Confirm
Once enabled, your watch requires this code for sensitive actions.
Health Data Privacy
Your health data is encrypted and stored in the Health app. You control who can see it.
- Open the Health app on your iPhone
- Go to your profile
- Tap Health Records
- Go to Sharing
- Control which apps access your health data
Siri Suggestions Privacy
Siri Suggestions learns your patterns. If you value privacy, you can disable certain types of suggestions.
- Open Settings on your watch
- Go to Siri
- Toggle off "Listen for Siri"
- Toggle off "Show Suggestions"
Note: This reduces Siri's usefulness, but improves privacy.

Feature 19: Handoff and Continuity Features
The Feature That Seamlessly Transitions Between Your Devices
Handoff lets you start something on one device and finish on another without interruption.
Examples:
- Start reading an article on your watch, continue on your iPhone
- Start a workout on your watch, continue on your iPhone
- Compose a message on your watch, finish typing on your iPhone
This requires your devices to be nearby and connected to the same Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
How to Use Handoff
Handoff is automatic if your devices are signed in with the same Apple ID and are within range.
When you switch devices:
- App switcher shows a card with your recent app
- Swipe up to open it on the new device
- Your progress transfers
It just works without any configuration.
Disabling Handoff (If You Need Privacy)
- Open Settings on your watch
- Go to General
- Go to Handoff
- Toggle off
Disabling it reduces convenience but increases privacy between your devices.
Feature 20: Time Zones and International Travel Modes
The Feature That Prevents Scheduling Disasters When You Travel
When you travel internationally, your Apple Watch automatically detects the time zone and updates.
But here's the hidden feature: you can manually set a second timezone, so you always know what time it is at home.
Setting Up Multiple Time Zones
- Open the Clock app on your watch
- Go to World Clock
- Tap the plus icon
- Search for the timezone you want
- Add it
Now your watch displays multiple times. You can glance and see both local time and home time.
Travel Mode
When traveling internationally, enable Travel Mode:
- Open Settings on your watch
- Go to Airplane Mode
- Turn it on
- Your watch disconnects from cellular
- It only uses Wi-Fi when available
This saves battery during flights and international travel when you don't have cell service anyway.

Advanced Tips: Power User Features
Combining Features for Maximum Effectiveness
The real power of your Apple Watch comes from combining features.
Example workflow: Morning routine automated
- You set an alarm for 6:30 AM
- Alarm goes off, you silence it with Double Tap
- An automation opens your Fitness app
- You open a guided breathing session (1 minute)
- You check your Sleep Focus metrics
- You view your Mindfulness prompts from last week
- You open your Calendar to see the day's priorities
- You message your workout buddy using Voice Message
All of this happens without touching your iPhone. Your watch is fully functional for your morning routine.
Battery Optimization Strategy
If your Apple Watch drains too fast:
- Disable Background App Refresh for apps you don't monitor
- Reduce Always-On Display brightness
- Disable Bluetooth when you don't need it
- Turn off Location Services for apps that don't need it
- Disable notifications for non-essential apps
- Turn off Hey Siri if you don't use voice control
Implementing three of these can extend battery from 1 day to 1.5 days.
Privacy Lockdown Mode
If you want maximum privacy:
- Enable Passcode
- Disable Handoff
- Disable Siri Suggestions
- Disable Background App Refresh
- Disable location services
- Disable Bluetooth
Note: This makes your watch less useful, but maximally private.
Common Mistakes People Make with Apple Watch Features
Mistake 1: Not Enabling Irregular Rhythm Notifications
People buy an Apple Watch for fitness, not health. They never enable ECG or rhythm notifications. If you have risk factors for heart problems, enable this immediately.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Sleep Data
People track sleep length but ignore sleep stages. Deep sleep is what actually rests your body. If you're getting 8 hours but only 5% deep sleep, something's wrong.
Mistake 3: Setting Heart Rate Zones Too High
Most people train in Zone 4 all the time thinking it's efficient. Wrong. You need mostly Zone 2 (easy) with some Zone 4 (hard). The balance matters more than either alone.
Mistake 4: Not Using Smart Stack
People set a single watch face and leave it. Smart Stack adapts to your needs. Actually using it saves dozens of wrist taps per day.
Mistake 5: Leaving Theater Mode Off During Movies
Not critical, but annoying. Theater Mode exists for this reason. Use it.
Mistake 6: Not Setting Up Favorites in Contacts
People scroll through 100 contacts to find someone. Just star your top 10. Problem solved.
Mistake 7: Ignoring Battery Warnings
When your watch gets to 10% battery, it warns you. Don't ignore it. Charge soon. Lithium batteries degrade faster if drained completely.

FAQ
What Apple Watch models support these features?
Most features work on Series 4 and newer (released September 2018). Some features like Double Tap require Series 9 or Ultra 2. ECG works on Series 4+. Check the watchOS release notes for your model to see which features are supported. The Health app on your iPhone will tell you which features are available on your specific watch model when you attempt to use them.
Do I need an iPhone to use these features?
Yes. Apple Watch requires an iPhone to set up and configure features like focus modes, automations, and health settings. However, once configured, some features (like fitness tracking, ECG, and sleep monitoring) work independently if your watch has cellular capability. The watch stores data locally and syncs with your iPhone when nearby.
How much will these features drain my battery?
Most features use minimal battery because they process locally on the watch. Background app refresh, Always-On display, and continuous heart rate monitoring are the biggest drains. Disabling Background App Refresh for social media apps can extend battery from 1 day to 1.5 days. Turning off Always-On Display can add another 6 hours. Most people don't need to disable features—standard usage lasts a full day.
Are the health features actually accurate?
The ECG feature is FDA-cleared and cardiologists trust it. Heart rate monitoring is accurate within 5-10 BPM for resting measurements. Sleep tracking is less precise—it estimates based on movement and heart rate variability, not brainwave measurement. Calorie burn estimates are off by 10-20%. For general trend tracking, accuracy is good enough. For medical decisions, confirm with actual medical devices.
Can I use these features without sharing data with Apple?
No. Using Health features requires syncing with Apple's servers (encrypted). You can disable Siri Suggestions and app tracking to reduce data collection. You can disable location services for privacy. But using ECG, irregular rhythm notifications, and sleep tracking requires some data transmission to Apple's servers. Apple claims this is encrypted and not used for advertising, but you have limited control over it.
Which feature should I enable first?
Start with Irregular Rhythm Notifications (if you're over 40 or have risk factors). Then enable Sleep Stage tracking. Then set up your Sleep Focus automation. Then configure Workload. These four give you the best insight into your health. After that, optimize based on your goals (fitness, productivity, communication).
Do I need to understand heart rate zones to train effectively?
No, but it helps. If you just want to exercise and get fit, the default Workout app is fine. If you want to optimize your training, understanding zones lets you train smarter (more low-intensity running, less injuries). It's an optional feature for people serious about fitness.
Can I disable notifications while keeping other features?
Yes. You can enable features (health tracking, heart rate monitoring, sleep tracking) without enabling notifications. Open Settings, go to Notifications, and toggle off alerts for specific apps. Health data still collects in the background. You just don't get real-time alerts.
What happens if I lose my Apple Watch?
If your watch is missing, remotely lock it through Find My (iPhone -> Find My app -> Devices). This prevents someone from accessing your health data without your passcode. Your data is encrypted, and without the passcode, it's inaccessible. If the watch is lost forever, you can unpair it from the Watch app on your iPhone and set up a new watch. Your data is restored from backups.
How do I know if a feature is actually working?
For health features, open the Health app on your iPhone. You'll see data recorded (heart rate, sleep, workouts, etc.). For automations and focus modes, trigger them manually and watch what happens. For background app refresh, open an app once, close it, wait an hour, and open it again. If data updated without you opening it, background refresh is working.
Conclusion: Your Apple Watch Is More Powerful Than You Think
You spent
The features we've covered today will change that. Double Tap alone saves dozens of taps per day. Smart Stack automatically surfaces the information you need. Sleep Focus turns your bedroom into a smart environment. ECG and irregular rhythm notifications catch health problems before they become emergencies.
These aren't gimmicks or nice-to-haves. They're foundational features that make your Apple Watch actually useful.
Here's what I recommend:
This week:
- Enable Irregular Rhythm Notifications
- Set up your Sleep Focus with automations
- Enable Double Tap and practice the gesture
- Configure your Smart Stack with your 6 most important complications
Next week:
- Set up heart rate zones for at least one workout
- Try the Breathing app when you're stressed
- Enable Noise Monitoring
- Check your sleep stages in the Health app
Next month:
- Experiment with workout automations
- Set up medication reminders if needed
- Create Siri Suggestions automations
- Review your workload trends and adjust training accordingly
Your Apple Watch is a health monitoring device, a fitness coach, a productivity tool, and a communication device. But only if you actually set it up to do those things.
The good news? Most of this takes 30 minutes to configure. After that, it just works. Your watch handles all the complexity in the background.
One final thought: the Apple Watch's best feature isn't any single function. It's the fact that it's always with you. Your phone lives in a pocket. Your watch lives on your wrist. This proximity means it can monitor you continuously. It catches irregular heartbeats. It tracks your sleep. It nudges you to breathe. It knows when you need to work and when you need to relax.
No other device knows you this well. And most people never use that capability.
Start using it. Your health—and your daily life—will improve.

Related Reading
For more on smartwatch technology and health monitoring, explore how wearable devices are changing healthcare, the science behind heart rate variability, or fitness tracking accuracy. If you're building productivity automations, consider how smartwatch integrations fit into your broader workflow optimization strategy. And if you're managing health data, learn more about privacy-preserving health tracking across Apple's ecosystem.
Your Apple Watch is far more capable than you realize. These 20 features are just the beginning of what's possible when you actually explore what your device can do.
Key Takeaways
- Double Tap gesture control eliminates the need to touch your screen, saving dozens of taps daily while hands are occupied
- Smart Stack automatically surfaces relevant complications based on time, location, and context, requiring just one-time setup
- Sleep Focus automations can trigger smart home devices (lights, temperature, locks) before bedtime without manual intervention
- ECG app is FDA-cleared and detects atrial fibrillation, potentially preventing strokes before symptoms appear
- Heart rate training zones optimize fitness outcomes by ensuring 70% of workouts are low-intensity recovery runs, not hard efforts
- Irregular rhythm notifications work passively in background, catching health problems while you wear your watch normally
Related Articles
- Best Smart Scales of 2025: Why Renpho Dominates with 350K Reviews
- Best Cheap Fitness Trackers Under $100 [2026]
- RingConn Gen 2 Smart Ring: Best Oura Alternative at Lowest Price [2025]
- Google Pixel Watch's Forgotten Device Feature Explained [2025]
- Best Fitbit Fitness Trackers & Smartwatches [2026]
- Best Fitness Apps to Stick to Workout Goals [2026]
![Apple Watch Hidden Features You're Missing [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/apple-watch-hidden-features-you-re-missing-2025/image-1-1768641018368.jpg)



