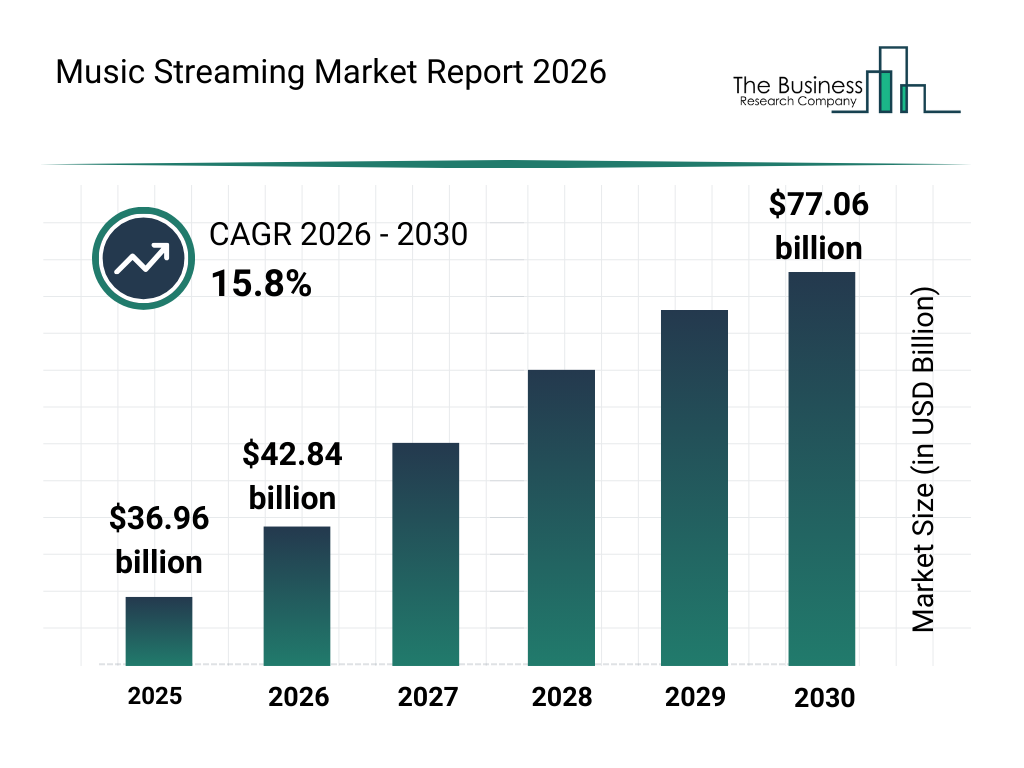
Why Music Streaming Alternatives Matter in 2025
The landscape of music streaming has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past few years. While Spotify remains the market leader with over 600 million users worldwide, the platform's repeated price increases—with the most recent adjustment pushing premium plans to $12.99 per month—have sparked a genuine exodus among budget-conscious listeners and audiophiles seeking premium sound quality. This shift represents more than just frustration with pricing; it reflects a fundamental change in how listeners evaluate value in the streaming music ecosystem.
The competitive music streaming market has matured significantly. What was once Spotify's exclusive advantage—an intuitive interface and superior algorithm-driven recommendations—is now table stakes across the industry. Today's streaming platforms compete on multiple dimensions: audio quality, exclusive content, integration with existing technology ecosystems, pricing flexibility, and support for artists. For developers and content creators building applications that integrate music services, the decision becomes even more nuanced, requiring consideration of API capabilities, cost structures, and feature completeness.
Understanding your listening habits and priorities becomes crucial when evaluating alternatives. Are you primarily concerned with cost? Do you value lossless audio quality like an audiophile? Are you entrenched in an Apple or Android ecosystem? Do you need family sharing capabilities? Are you interested in supporting independent artists directly? Each of these questions points toward different streaming solutions, each with distinct strengths and limitations.
The stakes have shifted considerably since music streaming first emerged. Labels have become more sophisticated in negotiating licensing deals, artists have learned to leverage multiple platforms simultaneously, and technology has enabled higher-quality audio streaming at lower bitrates. Meanwhile, the consolidation of tech giants—Apple, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft—into the music streaming space has created a dynamic where these services often function as retention tools for broader ecosystem lock-in rather than standalone revenue generators.
This comprehensive guide examines not just the obvious Spotify alternatives, but explores emerging platforms, niche services, and hybrid approaches that serve specific listener communities. Whether you're seeking to save money, improve audio quality, support independent musicians, or integrate music services into applications, this analysis provides the insight needed to make an informed decision aligned with your actual needs and values.
The Spotify Standard: Understanding What You're Moving Away From
Current Spotify Ecosystem and Recent Changes
Spotify's market dominance stems from decisions made over more than a decade of operation. The platform established user experience standards that competitors still reference: the seamless playlist creation experience, the "Discover Weekly" algorithmic recommendation engine, the ability to follow friends and see what they're listening to, and the freemium model that introduced millions to paid streaming. However, the company's 2024-2025 strategic shifts reveal a platform optimizing for profitability over market share expansion.
The price increases represent a calculated decision. Spotify's management recognizes that the user base has sufficient switching costs—saved playlists, listening history, connected devices—that they can afford modest price resistance. The third major price increase in two years (Premium now at
Simultaneously, Spotify has introduced new features designed to increase engagement and justify premium pricing: AI DJ features, music video integration (beta), audiobook functionality for select markets, and collaborative playlists with enhanced social features. These additions blur traditional service boundaries—music streaming alone is no longer the competitive advantage.
Why Listeners Are Reconsidering
The decision to explore alternatives often follows specific trigger events. A price increase notification, discovery of a competitor's superior audio quality, or frustration with Spotify's algorithm during a personal preference shift catalyzes change. Research indicates that approximately 35% of streaming subscribers maintain accounts with multiple services simultaneously, suggesting that the "winner-take-all" prediction of early streaming industry analysis has proven false.
Meaningfully, the switching costs have declined. Playlist migration tools now exist (though still imperfect), music discovery has decentralized through social media and artist direct promotion, and interface familiarity is no longer a competitive barrier—most modern listeners can navigate any streaming app interface within minutes. This commoditization of basic functionality means competitors can compete effectively by emphasizing differentiation points: sound quality, user interface philosophy, pricing structure, or artist support mechanisms.
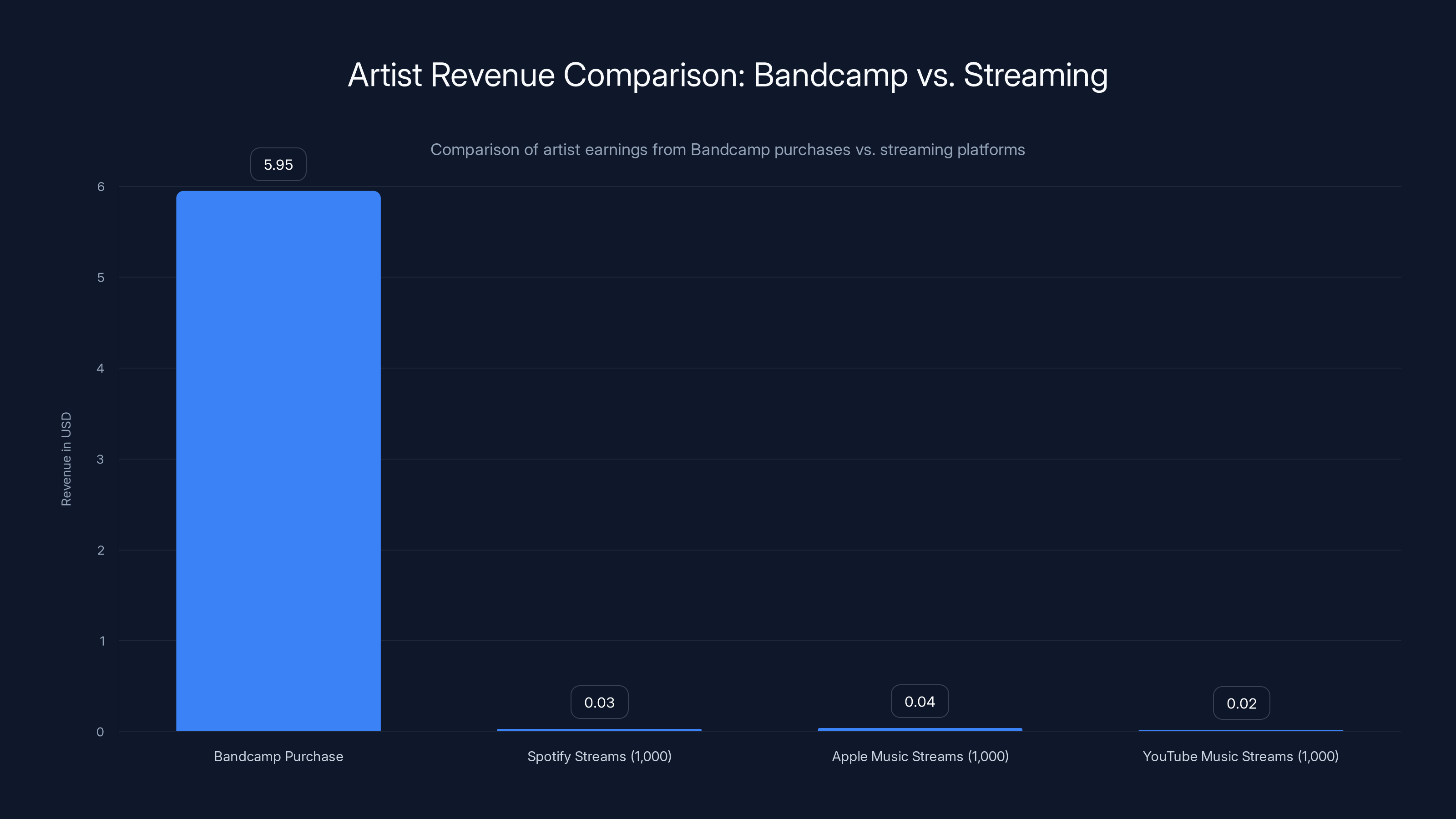
Artists earn significantly more from a single Bandcamp purchase compared to 1,000 streams on major platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music. Estimated data for streaming platforms.
Apple Music: The Ecosystem Play
Core Philosophy and Positioning
Apple's entry into music streaming differs fundamentally from Spotify's approach. Rather than seeking universal adoption, Apple Music exists as a retention mechanism for the iOS ecosystem, bundled into Apple's growing services strategy alongside iCloud, Apple TV+, Apple News+, and Apple Fitness+. This ecosystem-first mentality manifests in every aspect of Apple Music's design and feature set.
Audio Quality and Immersive Features
Apple aggressively markets superior audio quality as a competitive differentiator. The platform offers lossless audio and Hi-Res Lossless for songs from participating labels, theoretically enabling bitrate-transparent music playback. However, this feature carries a significant asterisk: most Apple devices don't support lossless playback. The iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch all compress lossless audio back to lossy formats (AAC) for playback, making the lossless catalog essentially inaccessible to the majority of Apple Music subscribers. Only users with specific Mac models or AirPods Max (Apple's $549 premium headphones) can experience true lossless quality.
More successfully, Apple has implemented spatial audio with dynamic head tracking, a technology that creates three-dimensional sound fields through your speakers or headphones. Early adopter feedback suggests the feature creates genuinely immersive listening experiences for specific content—orchestral recordings, certain hip-hop productions, and live concert recordings benefit substantially from spatial audio rendering. Dynamic head tracking (available on AirPods Pro and AirPods Max) makes spatial audio move as you move your head, adding another layer of engagement.
For classical music enthusiasts and soundtrack lovers, Apple Music has invested in curated content from classical music experts, recognizing that algorithm-driven recommendations perform poorly for niche genres requiring genuine musicological understanding.
Integration and Ecosystem Features
The HomeKit integration enables voice-controlled playback through Siri, arguably Apple's strongest competitive advantage. Speaking "Hey Siri, play my Focus playlist" while cooking or exercising represents frictionless interaction that competitors struggle to match. For users deeply invested in Apple's smart home ecosystem, this hands-free control becomes genuinely valuable.
Apple Music's lyrics feature, integrated directly into the playback interface, allows users to follow along with song lyrics in real-time across iOS, watchOS, and tvOS. The presentation feels native rather than bolted-on, suggesting genuine product integration rather than feature checkbox completion.
Pricing and Family Plans
However, Apple Music's lack of a genuine free tier—the platform requires a paid subscription or Apple Music Voice subscription ($4.99/month, limited to voice control only)—creates a barrier for trial and discovery that Spotify and other competitors have leveraged successfully.
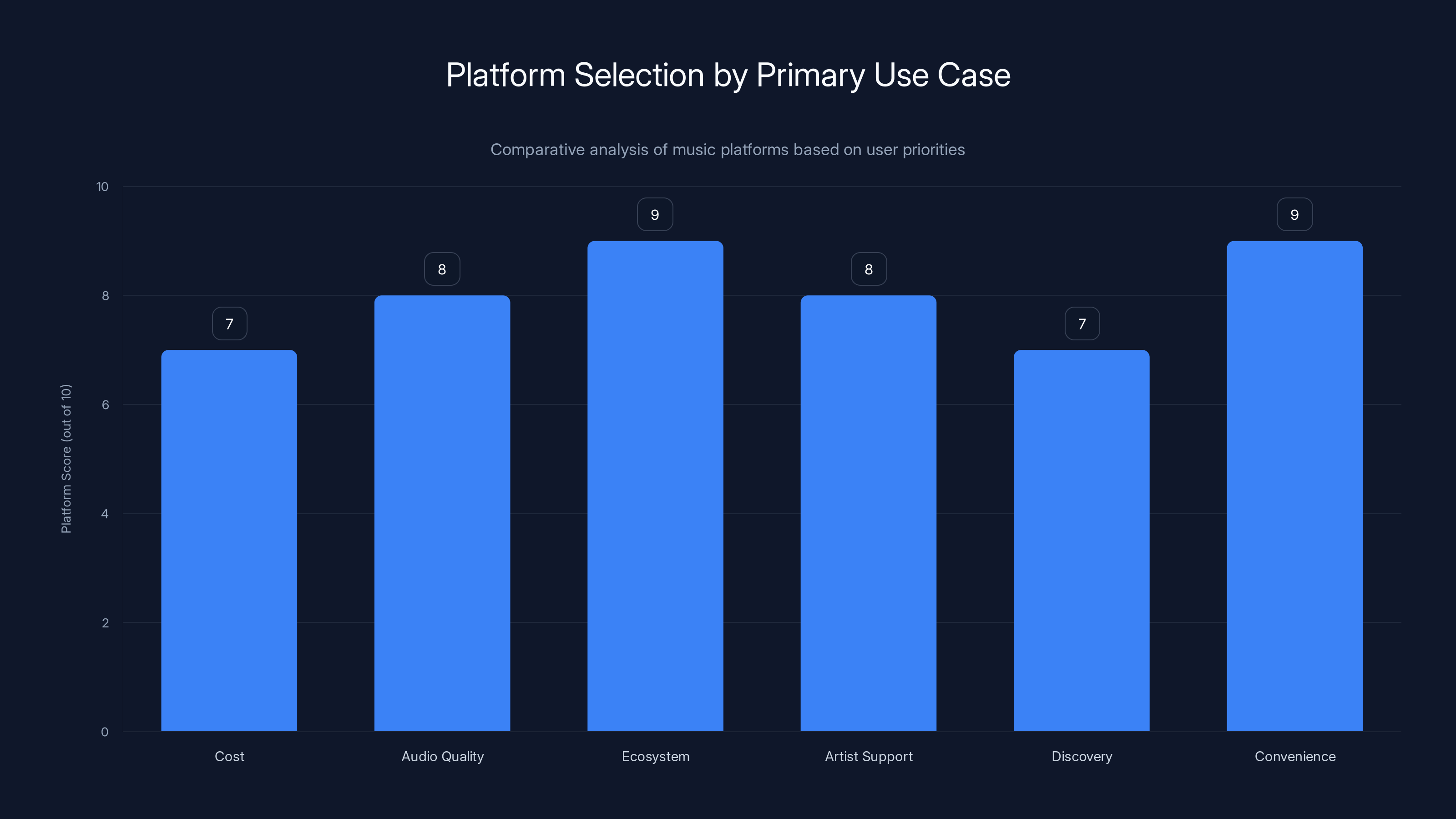
Estimated data shows platforms excel in different areas: Spotify leads in convenience, while Tidal excels in audio quality.
Amazon Music: The Integrated Play
Understanding Amazon's Tiered Approach
Amazon's music strategy reflects the company's broader service philosophy: create an integrated ecosystem where music becomes one component of a larger value proposition. Unlike Spotify's focused approach (music and podcasts) or Apple's bundling strategy, Amazon treats music as one thread in the Prime membership tapestry.
The layered approach creates genuine confusion initially. Amazon Music Free provides access to curated playlists and radio stations with approximately 2 million songs (versus 100+ million for premium tiers), supported by advertisements. This serves as discovery and trial functionality. For Prime members, Amazon Music Prime includes access to the full library with individual song selection, no advertisements, and the ability to download content—accessible at no additional cost beyond Prime membership (
The distinction matters: Prime membership has become so economically attractive for retail shopping, video streaming, and fast shipping that music inclusion functions as a profit multiplier on existing spending rather than a standalone value proposition. For existing Prime members evaluating music streaming services, Amazon Music Prime essentially costs zero dollars, making it a rational default choice regardless of quality considerations.
Amazon Music Unlimited: Premium Tier Analysis
The audio quality positioning is notable. Amazon Music Unlimited subscribers receive access to millions of lossless audio tracks, significantly more extensive than Apple Music's lossless catalog. However, most consumer-grade headphones and speakers cannot meaningfully reproduce lossless quality—studies suggest listener preference for high-quality lossy compression exceeds preference for lossless quality in blind A/B testing. This feature serves more as marketing differentiation than practical advantage for most listeners.
The spatial audio support across both Dolby Atmos and Sony 360 Reality Audio formats provides broader compatibility than Apple's proprietary implementation, though the actual adoption of these immersive audio formats remains limited across music production and consumer speaker hardware.
Integration with Amazon Ecosystem
Where Amazon Music demonstrates clear advantage is integration depth with Amazon hardware. Every Echo device becomes a music controller with voice command compatibility. The Alexa ecosystem—comprising hundreds of thousands of smart home devices—all directly interface with Amazon Music without the friction that characterizes Apple or Spotify integration on non-native platforms.
For households already committed to Alexa-based smart homes, or for users primarily listening through Echo devices, Amazon Music Unlimited becomes the logical choice. The friction drops to zero when your voice-controlled lighting, thermostats, and security systems all tie into the same ecosystem managing music playback.
Pricing Structure and Student Plans
Amazon's promotional pricing aggressively targets student audiences and budget-conscious listeners. The Single Device Plan at $5.99/month (approximately 54% cheaper than standard Unlimited pricing) addresses a specific use case: listening primarily on one Echo device or through a single point of access. This granular pricing approach acknowledges that not all listening occurs on unlimited devices, and enables price discrimination that captures additional price-sensitive segments.
The Student Plan (
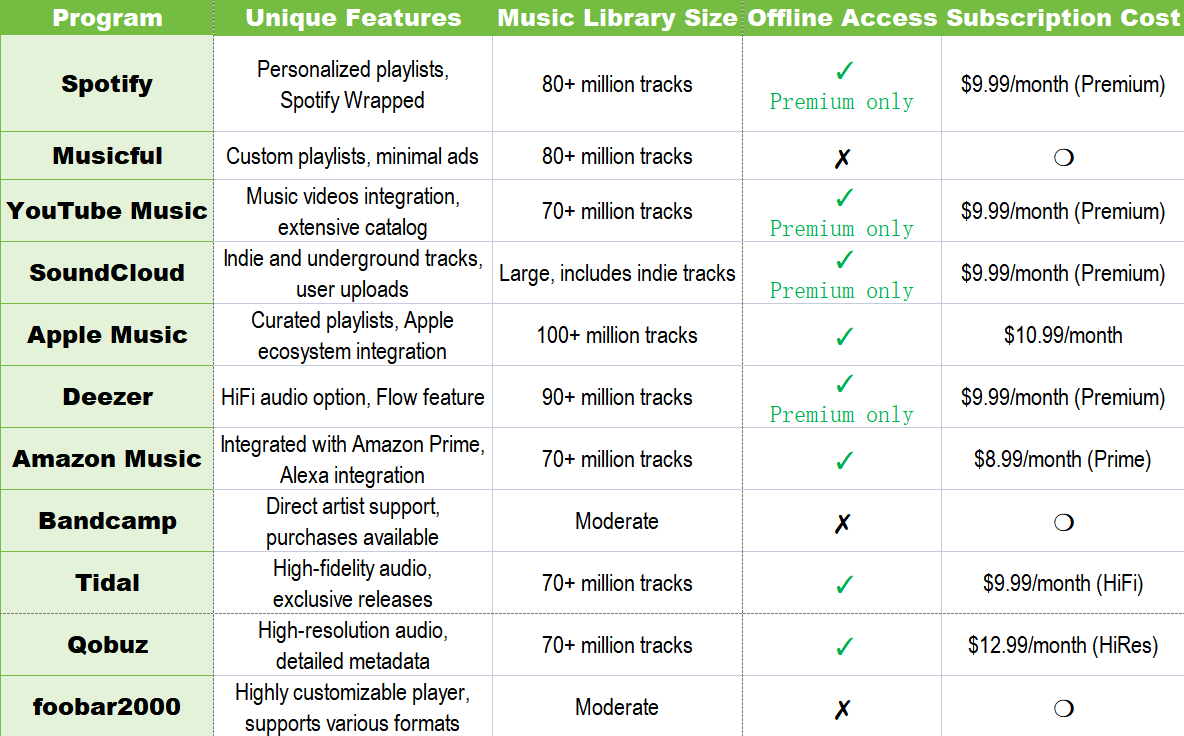
YouTube Music: Google's Streaming Platform
The Unique Positioning and Advantages
YouTube Music represents Google's answer to music streaming, but with a fundamentally different underlying asset base. Rather than licensing music specifically for streaming (as Spotify and Apple do), YouTube Music leverages the existing YouTube video library, transforming music videos and artist performances into streaming content. This philosophical difference creates both advantages and limitations that shape the service's competitive position.
The platform exists in two tiers: YouTube Music (free with ads,
Uniquely, YouTube Music Premium subscribers gain YouTube Premium's full feature set: background playback (playing music while using other apps), offline downloads, and an ad-free experience across both music and video content. The simultaneous access to music and music video content from a unified ecosystem represents genuine functional advantage versus competitors requiring separate platforms for audio and video consumption.
Audio Quality and Technical Implementation
YouTube Music's audio quality positioning occupies a middle ground. The service streams audio at various bitrates depending on user settings (ranging from approximately 24 kbps for low quality to 256 kbps for highest quality). While not approaching lossless quality like Amazon Music Unlimited or Apple Music's theoretical lossless catalog, the highest YouTube Music quality tier (256 kbps) approaches audible equivalence to Spotify's premium tier (320 kbps) for most listeners on consumer hardware.
This quality ceiling reflects YouTube's original video optimization focus. Investing in lossless audio infrastructure makes limited sense when the platform's primary value—music video access—has historically delivered quality ceilings around 1080p video resolution. Improving audio beyond lossy compression represents diminishing returns on infrastructure investment.
Discovery and Content Integration
YouTube Music's killer feature is algorithmic discovery powered by the YouTube recommendation engine—arguably the most sophisticated recommendation system in consumer technology. The algorithm's underlying data includes not just listening behavior (like Spotify) but actual video viewing patterns, search queries, watch time across millions of content categories, and social signals from likes, comments, and shares. This creates recommendation quality that many users find superior to Spotify for discovery scenarios.
Further, YouTube Music surfaces artist-created content (official music videos, live performances, covers, behind-the-scenes) within the streaming experience. Discovering that your favorite artist released live concert footage or a cover version of another artist's work creates engagement depth that audio-only platforms struggle to match. For younger audiences particularly (Gen Z primarily discovers music through video content), this native integration feels natural rather than forced.
Unique Challenges and Limitations
YouTube Music's major limitation is library completeness—not all artists publish to YouTube. Independent artists, certain niche genres, and some established artists with complex licensing agreements may have incomplete catalogs. The platform's strength (leveraging video content) simultaneously creates its weakness: artists without video content have reduced visibility within the platform.
UX navigation has evolved through multiple iterations, with users frequently reporting confusion about the distinction between YouTube Music and YouTube Premium, or difficulty finding specific features. The interface optimization reflects YouTube's broader design philosophy rather than music-service-specific UX best practices, creating friction for users transitioning from Spotify's focused music interface.
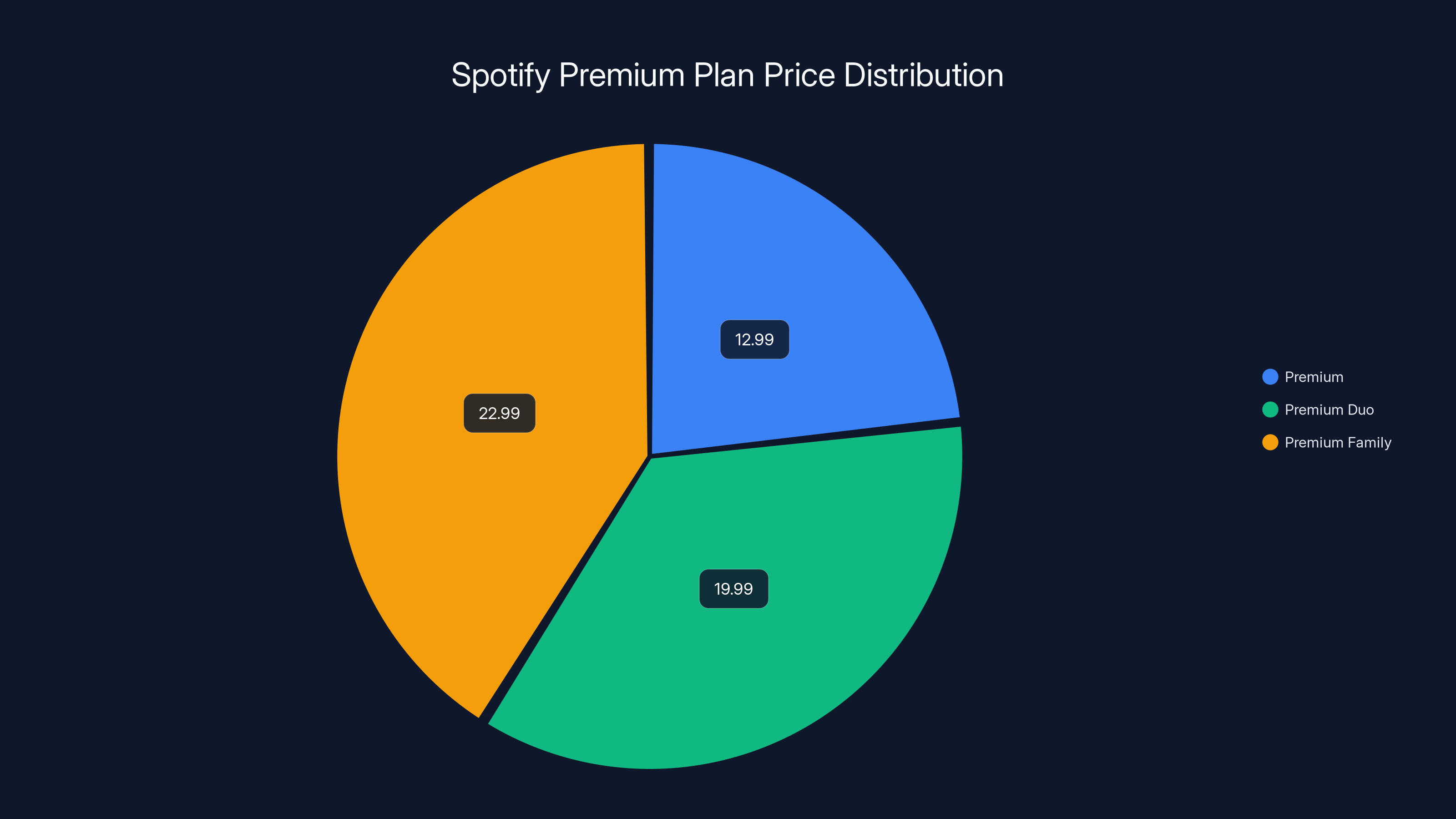
Spotify's pricing strategy positions it as a premium service with the Premium Family plan being the most expensive at $22.99/month.
Google Play Music Sunset and YouTube Music Migration: A Case Study in Service Transitions
What Happened and Industry Implications
Google's 2020 decision to sunset Google Play Music in favor of consolidating functionality into YouTube Music provides instructive lessons about streaming service consolidation and user migration complexity. Google provided 12 months advance notice and extensive tooling to migrate playlists and preferences to YouTube Music, yet the transition encountered significant user friction and dissatisfaction.
The consolidation made strategic sense: eliminating duplicate music infrastructure and consolidating around YouTube's larger ecosystem removed technological redundancy. However, execution challenges revealed misalignments between user expectations (Google Play Music's straightforward music-focused interface) and the consolidated platform's video-first orientation. Users who deliberately chose Google Play Music's simplicity over YouTube's complexity felt forced into an unwanted transition.
This precedent creates legitimate concerns for users choosing Google's music services: platform consolidations and shut-downs, while sometimes inevitable, create real disruption to music libraries, playlists, and listening history. Users considering YouTube Music should recognize they're dependent on Google's continued commitment to the service within its broader strategy.
The Transition Lessons
The Google Play Music sunset offered free playlist migration tooling, yet many users reported incomplete transfers, playlist metadata loss, or difficulty replicating recommendations and discovery preferences. Third-party migration services emerged to fill gaps, suggesting Google underestimated the psychological and practical friction of transitioning music services.
This historical precedent influences current platform selection decisions. Rational users considering long-term commitments to Google's music services factor in platform stability risk—Google has demonstrated willingness to consolidate services when strategic priorities shift. This risk premium doesn't apply equally to all platforms (Spotify and Apple have committed publicly to long-term music service focus, making consolidation less probable) but meaningfully impacts value calculations.
Bandcamp: Supporting Independent Artists
Philosophy and Operating Model
Bandcamp occupies a fundamentally different position in music distribution and commerce than streaming platforms. Operating as an "online record store and music community," Bandcamp functions simultaneously as a marketplace, publishing platform, and discovery engine where artists earn substantially more revenue per transaction than traditional streaming arrangements.
The economic model creates genuine differentiation: artists receive approximately 85% of the revenue from direct purchases (with Bandcamp taking 15%), compared to streaming payouts that typically range from
Bandcamp distinguishes between purchasing music (downloads in MP3, FLAC, AAC, and Vorbis formats) and streaming functionality. The platform launched a Bandcamp app (Bandcamp for Artists and general listeners) incorporating streaming features alongside purchase options, blending marketplace and subscription streaming in a hybrid model designed to serve artist sustainability.
Unique Features and Community Aspects
Bandcamp functions as genuine community platform rather than algorithm-driven recommendation engine. Users follow artists and labels, participate in genre-specific communities, and discover new music through manual browsing and artist recommendations rather than algorithmic suggestion. This creates a fundamentally different listening experience: more intentional, more community-oriented, and less passive recommendation-driven than Spotify or YouTube Music.
The platform introduced Bandcamp Fridays, a monthly commerce initiative where Bandcamp waives its service fee and all proceeds go directly to artists. This recurring promotional event has generated millions in artist revenue and demonstrates the platform's commitment to artist economics beyond baseline revenue distribution. During single Bandcamp Friday events, the platform has reported transferring
For listeners seeking to support specific artists while obtaining high-quality music files, Bandcamp's purchase model enables sustainable artist support. The platform particularly serves independent rock, hip-hop, electronic, and experimental music communities where artists maintain direct fan relationships.
Limitations and Adoption Challenges
Bandcamp's major limitation is library completeness—the platform hosts artists who choose to publish there, which excludes many major label releases and artists preferring traditional distribution. Discovering obscure artists on Bandcamp works remarkably well; discovering mainstream contemporary pop music proves more challenging.
The hybrid model (purchases + streaming) creates complexity in usage patterns. Casual listeners seeking unlimited streaming access may find Bandcamp's model awkward compared to traditional subscription services. The pricing structure (purchasing specific albums versus unlimited monthly access) requires different financial planning and listening commitment than streaming subscriptions.
Additionally, Bandcamp's interface prioritizes artist discovery and community participation over algorithmic personalization. Users accustomed to Spotify's "Discover Weekly" playlists may find Bandcamp's recommendation approach frustratingly manual and limited. The tradeoff between algorithm-driven convenience and community-driven intentionality benefits certain listeners while disadvantaging others.
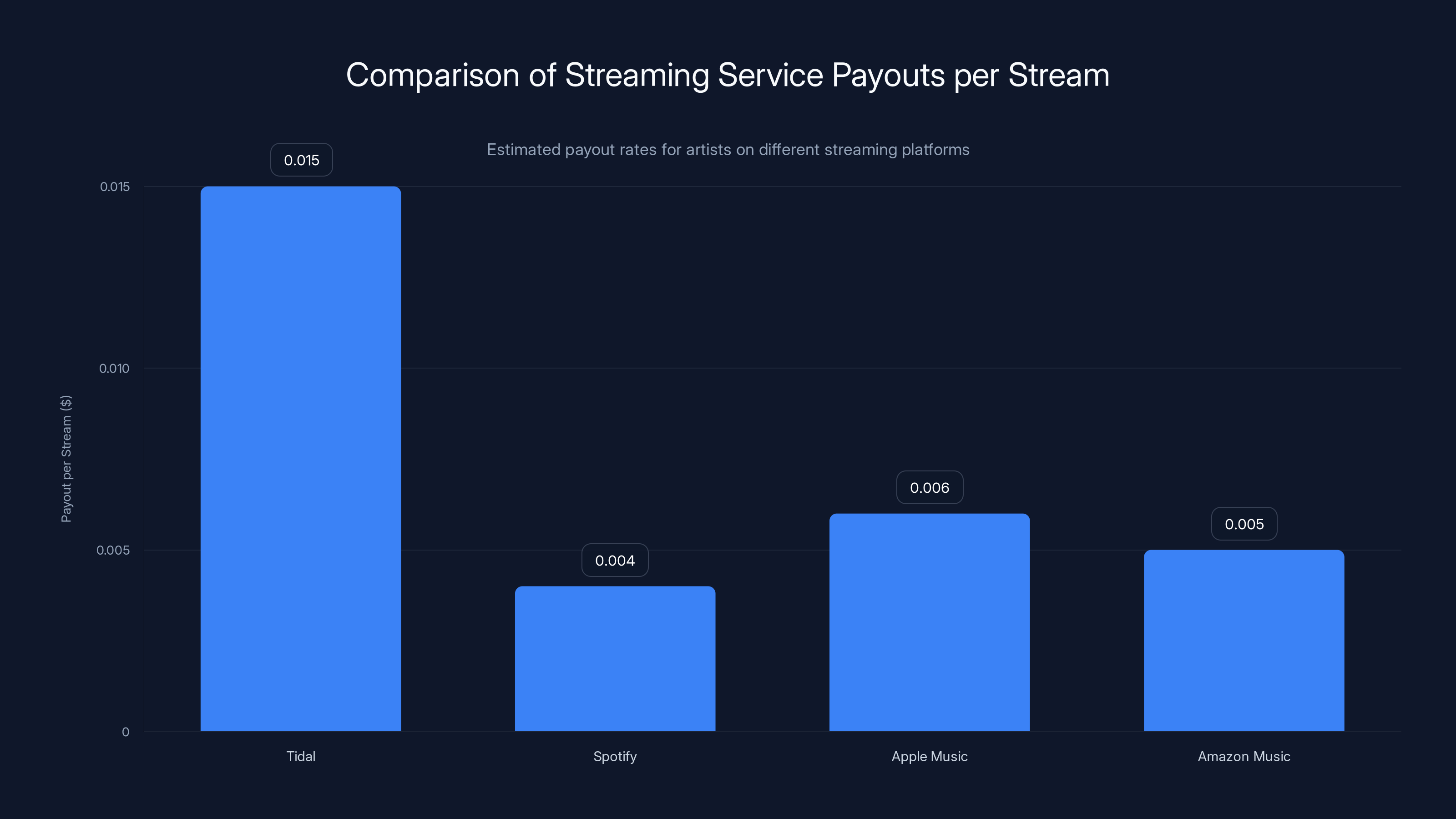
Tidal offers higher payouts per stream, estimated between
Tidal: Premium Audio Quality and Artist-Centric Compensation
High-Fidelity Audio as Core Differentiator
Tidal, acquired by Jay-Z and rebranded as an artist-focused platform, explicitly positions high-fidelity audio as its primary competitive differentiation. Tidal HiFi Plus ($22.99/month) delivers lossless audio and spatial audio across the platform's library, representing the most comprehensive high-fidelity implementation among mainstream streaming services. Unlike Apple Music (which offers lossless but limited device support) or Amazon Music Unlimited (which offers lossless but limited adoption), Tidal integrates lossless audio as core feature with substantial support across devices and headphones.
For audiophiles using high-end audio equipment, Tidal's codec support (MQA, ALAC, FLAC) and commitment to quality create genuine technical advantage. Measurements confirm that Tidal's lossless streams demonstrate measurable audio quality improvement over lossy competitors when played through quality playback systems. The magnitude of this improvement depends on listener audio equipment and hearing capability, but the technical advantage persists.
However, Tidal's pricing reflects this quality premium. At
Artist-Centric Compensation Model
Tidal aggressively markets artist-friendly economics as distinguishing philosophy. The platform maintains higher payout-per-stream rates than competitors (ranging from approximately
Beyond per-stream payouts, Tidal offers artist-focused features like lossless audio mastering assistance, artist collaboration tools, and analytics dashboards designed for creator revenue optimization. The platform explicitly brands itself as artist-first in positioning, appealing to listeners who prioritize sustainable artist compensation in platform selection.
Integration and Ecosystem Position
Tidal operates as standalone platform without bundling into broader ecosystems. This independence creates both advantages and disadvantages. The platform avoids the ecosystem lock-in dynamics that benefit Apple and Amazon, but simultaneously lacks retention mechanisms that drive user stickiness in competitor platforms.
Device compatibility has improved substantially—Tidal supports iOS, Android, web, various smart speakers, and consumer audio devices—but integration depth remains limited compared to Apple's HomeKit integration or Amazon's Alexa ecosystem. For users outside the Apple ecosystem or without Amazon devices, this represents a neutral positioning rather than disadvantage.

Pandora: Internet Radio Legacy and Personalization
Historical Context and Evolution
Pandora predates Spotify by a decade, pioneering internet radio and algorithmic music discovery through the Music Genome Project—a proprietary system that analyzes songs by hundreds of musical attributes and recommends similar music based on these structural characteristics. While Spotify's recommendation algorithm prioritizes user listening behavior, Pandora's approach emphasizes musical similarity, creating meaningfully different discovery experiences.
For listeners who appreciate radio-like serendipity rather than algorithm-driven personalization based on previous choices, Pandora's discovery experience often proves superior. The platform facilitates discovering unknown artists with similar musical characteristics to known preferences without requiring explicit listening history to drive recommendations.
Pricing and Tier Structure
Pandora Premium ($11.99/month) includes unlimited skips, ad-free playback, offline downloads across platforms, and explicit song selection (choosing exactly what to hear rather than accepting radio-like algorithmic sequences). This tier competes with standard streaming competitors, though Pandora's interface emphasizes radio and personalized station creation over playlist-based browsing.
Technical Implementation and Device Support
Pandora supports all major platforms (iOS, Android, web, Alexa, smart televisions), though integration depth varies. The platform functions excellently on smart speakers and automotive systems where voice-based station creation and playback suits user behavior patterns. On mobile and web platforms, competitors offer more sophisticated playlist management and social features.
The streaming quality defaults to approximately 32-64 kbps bitrate for standard service tiers, inferior to competitors' offerings. Premium tiers improve quality but still cap at approximately 192 kbps lossy compression. For casual listeners on lower-tier paid plans, this represents acceptable compromise; for quality-focused listeners, the bitrate limitation creates preference for competitors.

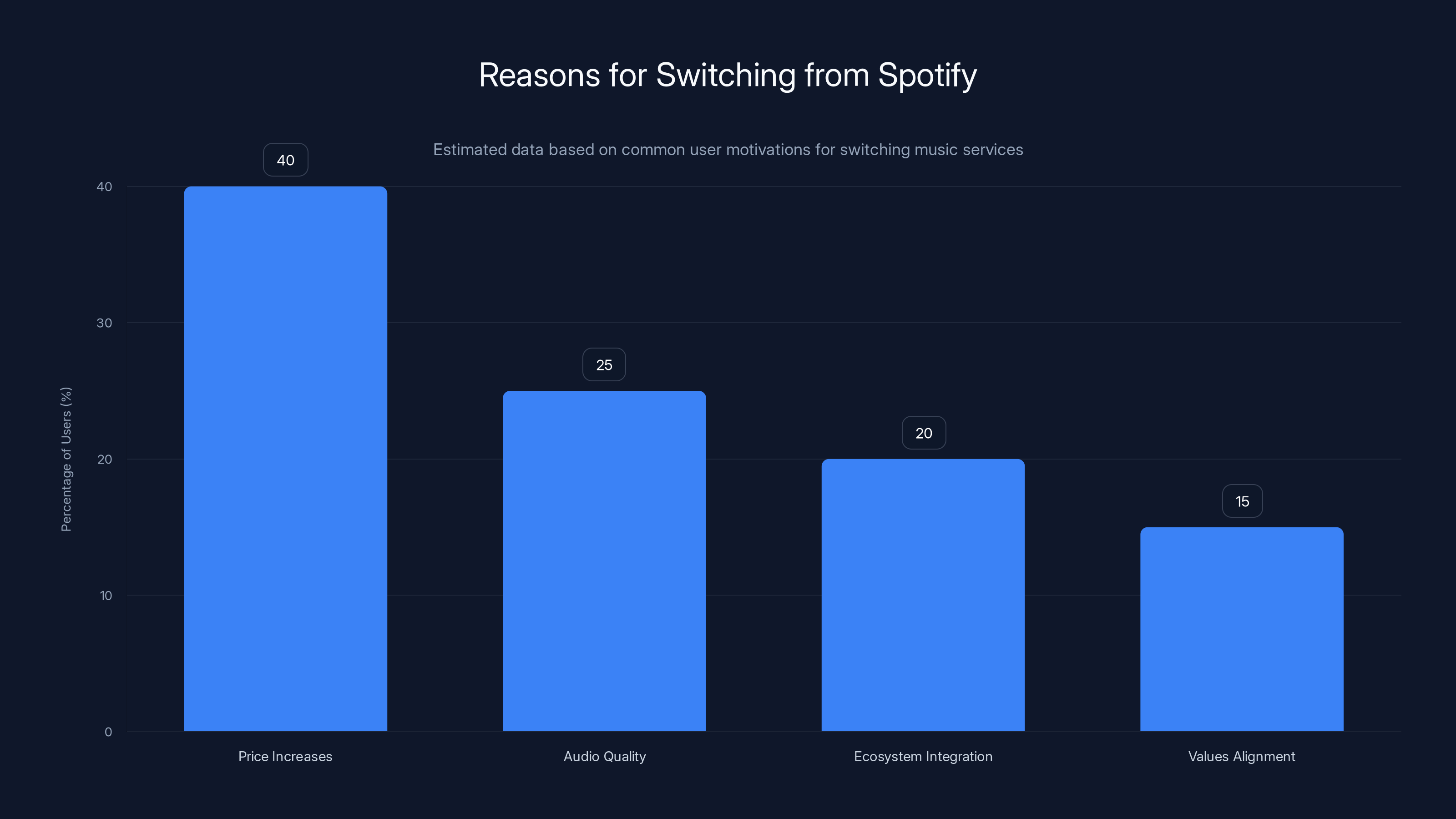
Estimated data suggests that price increases are the primary reason users switch from Spotify, followed by audio quality and ecosystem integration.
Emerging Alternatives: SoundCloud, Deezer, and Subsonic
SoundCloud: Creator-Focused Platform
SoundCloud operates as hybrid between social music platform and streaming service, emphasizing content creator access and community interaction. The platform enables independent producers, DJs, and musicians to upload and distribute music directly to listeners, bypassing traditional label gatekeeping. For electronic music, hip-hop, and underground genres particularly, SoundCloud's creator community delivers content unavailable through other streaming services.
SoundCloud Go+ ($12.99/month) provides ad-free listening, offline downloads, and access to the full artist catalog. The pricing matches premium competitors, but the value proposition differs: instead of encyclopedic mainstream catalogs, SoundCloud offers depth in alternative and independent genres that appeal to specific listener communities.
The platform's social features—following creators, commenting on specific timestamps within tracks, reposting content—create engagement mechanics beyond passive listening that appeal to listeners viewing music consumption as community participation rather than individual entertainment consumption.
Deezer: International and Feature-Rich Offering
Deezer operates primarily outside North America, achieving significant adoption in Europe and Latin America. The platform offers competitive features: Flow (an algorithmic discovery feature), high-quality audio at various tiers, and family plans comparable to competitors. Pricing varies by region but generally aligns with Spotify's international positioning.
Uniquely, Deezer implemented artificial intelligence-powered features earlier than competitors—the platform pioneered AI-based DJ personalities that provide personalized commentary between songs, a feature now common across services. Deezer's international presence provides advantage in regional music cataloging and artist relationships outside North American focus areas.
Subsonic and Self-Hosted Alternatives
For users seeking complete control over streaming infrastructure, self-hosted options like Subsonic, Airsonic, and Jellyfin provide capabilities for streaming personal music libraries across devices. These solutions require technical sophistication and ongoing server maintenance but eliminate dependency on commercial platforms and provide absolute privacy for music consumption data.
The self-hosted approach appeals primarily to users with substantial personal music libraries (extensively collected or purchased music files) seeking to manage access infrastructure independently. For casual streaming users relying on commercial catalogs, the technical overhead exceeds benefits. However, for technologically capable users prioritizing privacy and independence, this category warrants consideration.

Comparative Analysis: Feature Parity and Differentiation
Audio Quality Hierarchy
Defining audio quality requires understanding technical specifications and perceptual reality. Specifications indicate bitrate and codec, but audible differences depend on listener hearing capability, audio equipment quality, and content mastering characteristics.
Premium Audio Quality Tier:
- Tidal HiFi Plus: Lossless (ALAC/FLAC/MQA) and spatial audio across full catalog
- Apple Music: Lossless and spatial audio (limited device support)
- Amazon Music Unlimited: Lossless and spatial audio (extensive catalog)
Standard Quality Tier:
- Spotify: 320 kbps AAC (premium), 160 kbps AAC (normal), 96 kbps AAC (low)
- YouTube Music: 256 kbps (high quality), variable lower tiers
- Apple Music: 256 kbps AAC lossy (premium devices)
Budget Quality Tier:
- Pandora Plus/Premium: 192 kbps (premium tier), lower quality standard
- Amazon Music Free: SD quality (standard definition)
- Spotify Free: 160 kbps AAC
For listeners with average hearing capability and consumer-grade headphones or speakers, the perceptual difference between 256 kbps and lossless quality approaches imperceptibility. Meaningful quality preference requires specific circumstances: professional audio equipment, trained listening capability, or specific genres (classical, jazz, acoustic) where dynamic range advantages benefit from lossless reproduction.
Pricing Comparison Matrix
| Service | Individual Monthly | Family Monthly | Student Monthly | Audio Quality | Ad-Free |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spotify | $12.99 | $16.99 | $6.99 | 320 kbps | Yes |
| Apple Music | $10.99 | $16.99 | $5.99 | Lossless (limited) | Yes |
| Amazon Music Unlimited | $10.99* | $19.99 | $5.99 | Lossless | Yes |
| YouTube Music | $11.99 | N/A | $6.99** | 256 kbps | Yes |
| Tidal | $10.99 | N/A | $5.99 | 320 kbps | Yes |
| Tidal HiFi Plus | $22.99 | N/A | N/A | Lossless | Yes |
| Pandora Plus | $6.99 | N/A | N/A | 320 kbps | Yes |
| SoundCloud Go+ | $12.99 | N/A | N/A | 256 kbps | Yes |
*Amazon Music Unlimited for Prime members; $11.99 for non-members **YouTube Premium student pricing; bundled with YouTube Music
Ecosystem Integration Analysis
Ecosystem lock-in increasingly determines streaming service selection among committed platform users:
Apple Ecosystem: Seamless integration with iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, HomePod. Siri voice control, AirPlay streaming, native app integration creates friction-free experience for Apple users. Family Sharing enables coordinated access and device management.
Amazon Ecosystem: Alexa integration across Echo devices, Fire tablets, and connected home devices. Voice control and device coordination across smart home infrastructure. Prime membership bundling creates economic efficiency for existing Prime users.
Google Ecosystem: YouTube integration combines music and video streaming. Google Home voice control integration enables hands-free playback. Android platform native integration, though less deep than iOS Apple Music integration.
Platform Agnostic: Spotify, Tidal, SoundCloud, Pandora operate across all platforms without ecosystem preference. This independence creates flexibility but sacrifices integration depth that ecosystem-native services offer.
Users deeply invested in specific ecosystems face switching costs that overwhelm price and feature comparisons. An Apple user with extensive Apple device collection, iCloud photo and file integration, and HomeKit smart home infrastructure may rationally choose Apple Music at
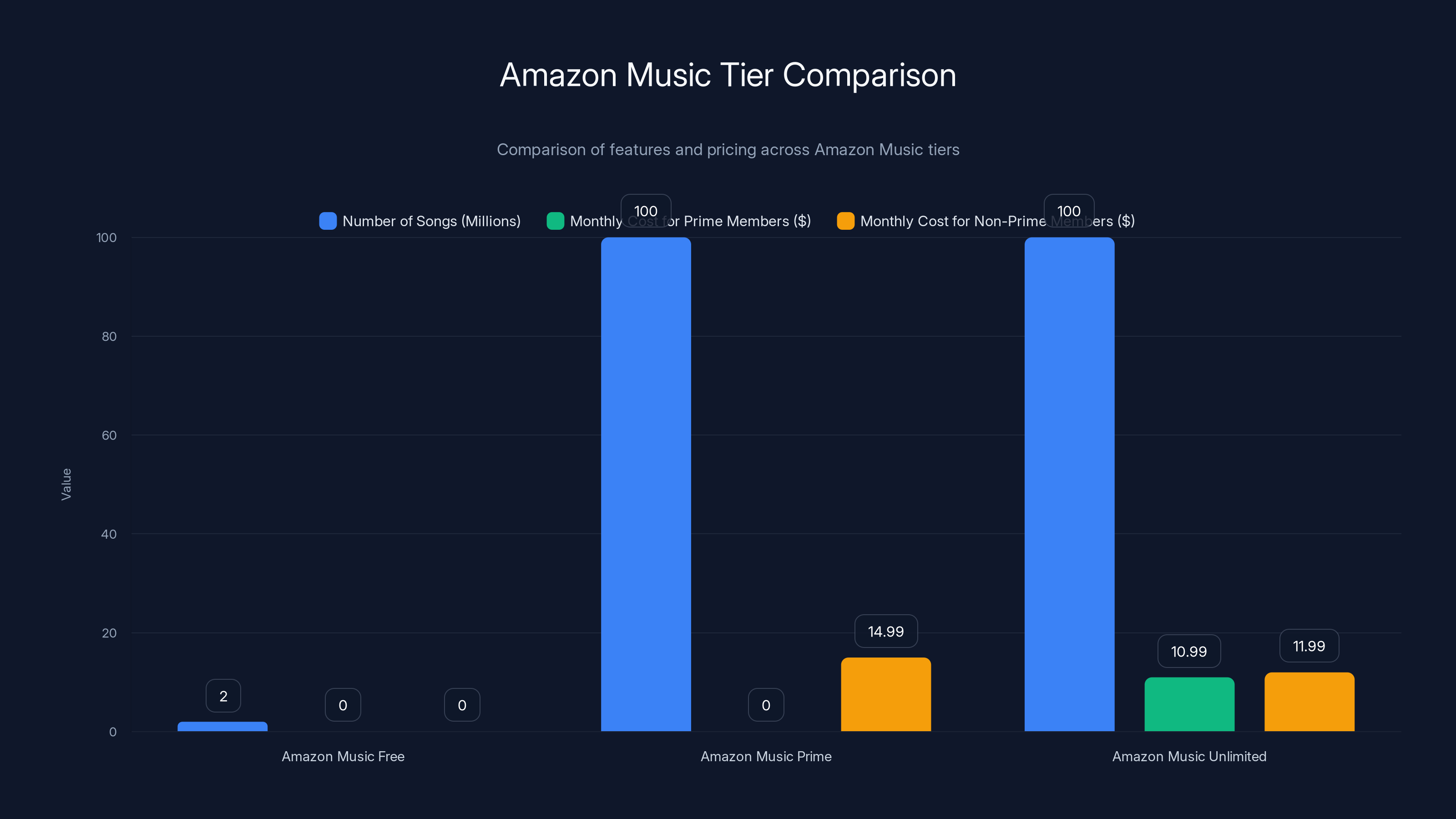
Amazon Music offers a tiered approach with varying features and pricing. Amazon Music Free provides limited access, while Amazon Music Prime and Unlimited offer extensive libraries with additional benefits for Prime members.
Discovery Mechanisms: How Different Services Find New Music
Algorithmic Recommendation Approaches
Modern streaming services employ distinct algorithmic philosophies reflecting underlying data and design priorities:
Collaborative Filtering (Spotify Model): Analyzes listener behavior patterns across millions of users to identify similarity clusters. Users with similar listening histories receive similar recommendations. The strength lies in discovering new artists within genres users actively consume. The limitation appears when seeking genre expansion—the algorithm rarely recommends music dramatically different from established preferences, limiting serendipity.
Content-Based Analysis (Pandora/Tidal Model): Analyzes musical characteristics (instrumentation, tempo, harmonic complexity, vocal timbre) to recommend musically similar content regardless of listening history patterns. Strengths appear in genre exploration and discovering unknown artists with similar sound profiles. Limitations emerge in unexpected juxtapositions—artists with different audiences but similar musical attributes may create jarring recommendations.
Hybrid Approaches (YouTube Music/Apple Music): Combine collaborative filtering with content analysis, contextual data (time of day, user device, playlist context), and explicit user signals (likes, shares, playlist additions). YouTube Music additionally leverages YouTube video viewing patterns, search behavior, and social signals from the broader YouTube ecosystem, creating substantially richer data for recommendation.
User-Driven Discovery
Beyond algorithmic recommendations, streaming platforms facilitate manual music discovery through:
Curated Playlists: Editorial teams or AI curation create thematic collections ("Morning Motivation," "Deep Focus," "Throwback Hip-Hop") enabling users to explore music organized by context or mood. Spotify pioneered this approach; all services now emphasize curated playlists as discovery mechanisms.
Radio Stations: Pandora and other services enable creating station-based listening experiences where users choose seed artist or song, then listen to algorithmically generated sequences of similar music. This recreates traditional radio's serendipitous discovery model in digital context.
Social Discovery: Following friends or curators, viewing shared playlists, and seeing what others listen to creates discovery through social proof rather than algorithmic inference. Spotify particularly emphasizes these social features.
Artist/Label Following: Direct relationships with artists and independent labels enable discovering new releases from known sources. Bandcamp particularly emphasizes this model, enabling fans to follow favorite artists and receive notifications of new releases.
The discovery mechanism choice reveals fundamental platform philosophy: Spotify and YouTube emphasize passive algorithmic recommendations requiring minimal user effort; Pandora and Bandcamp emphasize user intention and community participation; Apple and Amazon lean toward editorial curation bundled within broader ecosystem services.
Making the Decision: Platform Selection Framework
Decision Tree by Primary Use Case
If You Prioritize Cost: Start with free tiers (Spotify, YouTube Music, Amazon Music Free) or lowest-cost paid plans (Pandora Plus at
If You Prioritize Audio Quality: Tidal HiFi Plus (
If You Prioritize Ecosystem Integration: Match platform selection to primary device ecosystem (Apple Music for Apple users, Amazon Music for Alexa users, YouTube Music for Google ecosystem users). The integration value often exceeds feature differences for ecosystem-committed users.
If You Prioritize Artist Support: Bandcamp provides the most direct artist compensation (85% revenue to artist). Tidal prioritizes higher per-stream payouts than competitors. Both represent meaningful artist-support mechanisms compared to streaming platforms optimizing listener experience.
If You Prioritize Discovery: YouTube Music's algorithm incorporates the most comprehensive data sources. Spotify remains excellent for collaborative filtering within established genre preferences. Pandora excels for serendipitous genre exploration. Bandcamp suits intentional community-driven discovery.
If You Prioritize Convenience: Spotify, as the market leader, offers the most intuitive interface for most casual users, extensive device compatibility, and the largest user community for collaborative playlists. Integration across third-party services and smart home devices benefits from Spotify's ubiquitous adoption.
Migration Complexity and Switching Costs
Before switching services, understand true switching costs:
Playlist Migration: Tools like Soundiiz, Tunemymusic, and platform-native transfer tools enable playlist migration between services, though imperfect with occasional song-matching failures. Plan 2-3 hours for complete library transfer including manual curation corrections.
Listening History Loss: Switching services means abandoning historical listening data, recommendations derived from that history, and algorithmic suggestions calibrated to your preferences. Expect 2-4 weeks for new platform's recommendation algorithm to recalibrate after establishing listening patterns.
Feature Familiarity: Users accustomed to specific service interfaces require adjustment time learning new navigation paradigms. Spotify users transitioning to Tidal or Pandora may find interface philosophy misaligned with behavioral expectations.
Social Graph Recalibration: Playlists shared with friends, collaborative playlists, or social features tied to specific services don't migrate. Users prioritizing social music experiences should consider network effects—which friends use which service?
Device Integration: Existing device integrations (Sonos systems, car audio, smart speakers) may require reconfiguration or feature loss when switching services. Verify compatibility before committing to platform switch.
These switching costs are non-zero but quantifiable. For users in services with minimal playlist investment or social features, switching is low-friction. For long-term Spotify users with extensive playlists, saved songs, and social connections, switching requires meaningful transition effort.

Alternative Approaches: Hybrid and Multi-Service Strategies
The Multi-Service Model
Approximately 35% of streaming users maintain active subscriptions across multiple services, suggesting the optimal strategy for many listeners involves strategic service combination rather than single-platform commitment.
Optimal combinations might include:
Budget + Quality Combination: Amazon Music Prime (free with Prime membership) for everyday listening + Tidal HiFi Plus ($22.99) for critical listening sessions. Total investment: Prime membership cost only, maintaining high-quality option for specific use cases.
Discovery + Convenience Combination: Spotify Premium (
Ecosystem + Independent Combination: Apple Music (
Multi-service strategies optimize for specific use cases while accepting cost increase. The economics make sense if price paid for complementary features exceeds switching friction and mental overhead. For users spending $25-50 monthly on music, multi-service strategies often maximize satisfaction relative to single-platform constraints.
Budget Hacking Strategies
Price-conscious users employ several approaches to reduce effective costs:
Student Discounting: Multiple services offer 50%+ discounts for verified students (Spotify
Family Plan Sharing: Spotify, Apple, Amazon, and YouTube Music offer family plans supporting 4-6 users. The per-person cost drops substantially when amortized across multiple household members. A
Free Tier Commitment: Spotify, YouTube Music, and Amazon Music offer ad-supported free tiers. For casual listeners accepting advertisement interruption, free tiers eliminate monthly cost while accessing substantial music libraries.
Promotional Pricing: New user promotions frequently offer 50% discount for first three months, or free trials lasting 30-60 days. Systematic rotation through new user promotions (ethically, using different email addresses or household members) can provide continuous discounted access. This approach requires attention to auto-renewal management to avoid unexpected charges.

The Technology Integration Angle: APIs and Developer Access
For Developers Building Music-Integrated Applications
While primary Spotify comparison targets individual listeners, developers integrating music services face distinct evaluation criteria requiring technical analysis.
Spotify Web API: Provides comprehensive access to music catalog, user data, playback control, and playlist management. Authentication via OAuth enables secure user authorization. Rate limiting (429 Too Many Requests) impacts high-volume applications. Documentation quality is excellent; community adoption is extensive. Pricing involves partnership negotiation rather than transparent per-request costs.
Apple Music API: Recently formalized access via MusicKit JS and server-side APIs. Implementation requirements include signing agreements with Apple and configuring app identifiers. Rate limiting exists but published limits are unclear. Documentation quality is adequate but noticeably less comprehensive than Spotify. Adoption remains lower, creating fewer third-party integration examples.
YouTube Music API: Undocumented for third-party developers. Official API access requires special partnership agreements. This creates friction for developers seeking to integrate YouTube Music, pushing them toward unsupported reverse-engineered libraries with inherent stability risks.
Amazon Music API: Limited public API availability; AWS Amplify provides some integration capabilities for AWS developers. Official Amazon Music API access requires partnership negotiation.
General Principle: Spotify provides the most developer-friendly integration due to comprehensive API documentation, transparent rate limiting, and extensive third-party adoption. Developers prioritizing third-party music service integration should evaluate whether Spotify's capabilities meet requirements before seeking alternative implementations. If ecosystem lock-in demands specific platforms (Apple for iOS apps requiring HLS compliance, YouTube for video-integrated experiences), integration complexity increases substantially.

Long-Term Sustainability and Platform Risk Assessment
Company Financial Health and Commitment Signals
Evaluating streaming platform longevity requires assessing financial sustainability and corporate commitment:
Spotify: Profitable since 2019, with consistent revenue growth from 500M+ users generating $13+ billion annual revenue (2023 figures). Stock market listing and consistent quarterly profitability indicate strong long-term viability. The company has demonstrated commitment to streaming as core business rather than ancillary offering.
Apple Music: Embedded within Apple Services segment, estimated at $85+ billion annual revenue (2023), with music representing small but growing portion. Apple's financial strength is unquestionable; however, music remains ancillary to broader services strategy. Service consolidation risk (like Google Play Music shutdown) is non-zero but relatively low given Apple's commitment to services revenue.
Amazon Music: Integrated within broader Prime ecosystem valued at $100+ billion annual revenue. Similarly to Apple, Amazon's financial strength is unquestionable. Music serves as Prime retention mechanism rather than standalone revenue generator, reducing commitment risk compared to Spotify.
YouTube Music: Embedded within Alphabet's $306+ billion annual revenue (2023) with music as small component. Financial strength is absolute; strategic commitment depends on YouTube Music's performance within broader Google Music strategy. The Google Play Music sunset suggests willingness to consolidate services.
Tidal: Privately held by square (formerly Spotify minority investor), with unclear financial health publicly. The platform's smaller user base and higher cost structure create uncertainty about long-term profitability and sustainability. Strategic importance to Square/Block remains secondary compared to payments and point-of-sale services.
Pandora: Operated by Sirius XM, generating approximately $3+ billion annual revenue through combination of satellite radio and streaming services. Streaming represents smaller portion of overall business, reducing strategic priority.
Service Discontinuation Risk
Historical precedent suggests streaming consolidation will continue. Google Play Music's sunsetting occurred with reasonable migration notice (12 months), enabling users to migrate data. However, disruption still occurred, and not all metadata transferred cleanly.
Rational users should prioritize services demonstrating long-term strategic commitment (Spotify, Apple, Amazon) over smaller platforms with less clear financial sustainability (Tidal, Pandora). This risk assessment shouldn't be primary decision factor but warrants consideration for users building extensive music libraries or playlists with service-specific metadata.

Emerging Trends and Future Considerations
Spatial Audio and Immersive Formats
Apple Music's spatial audio with dynamic head tracking and YouTube/Amazon's Dolby Atmos support represent emerging quality standard. Investment in immersive audio formats is likely to accelerate, with potential for spatial audio becoming default quality tier within 3-5 years as production infrastructure matures.
For audiophile-focused listeners, spatial audio capability is becoming selection criteria alongside traditional audio quality metrics. Current support remains inconsistent across services and devices, creating advantage for early-adopter platforms.
AI-Generated and Voice-Cloned Music
AI music generation tools (AIVA, OpenAI Jukebox, Google's MusicLM) create potential disruption in music distribution. Streaming platforms will likely integrate AI music generation, enabling users to create personalized soundtrack experiences. Commercial implications remain unclear—whether AI-generated music counts as licensed content, how royalties distribute, and whether listeners embrace AI music remains unresolved.
This emerging domain could disrupt traditional artist compensation models, particularly affecting independent musicians. Early adoption of AI music features may differentiate platforms, though consumer adoption remains nascent.
Spatial Computing Integration
Apple Vision Pro and emerging spatial computing platforms suggest future streaming experience extension beyond traditional audio playback. Immersive audio environments, virtual concert venues, and spatial music experiences represent potential future differentiation vectors. Current platforms have barely begun exploring spatial computing integration.
Direct Artist-to-Listener Platforms
Blockchain-based music platforms and artist-centric distribution models (Audius, Royal) explore reducing streaming intermediaries. While adoption remains minimal currently, future fragmentation into artist-native platforms could create permanent shift away from centralized streaming services. Rational users following specific artists should monitor whether artists migrate to artist-native platforms, potentially requiring adoption of multiple specialized platforms.

Conclusion: Making Your Optimal Choice
The streaming music landscape of 2025 differs fundamentally from Spotify's early dominance. Price increases, ecosystem consolidation, audio quality improvements, and artist support mechanisms have created genuine differentiation across competitors. The question is no longer "Is there a viable Spotify alternative?" but rather "Which combination of features, pricing, and values aligns with my listening priorities?"
The decision framework suggested throughout this analysis emphasizes matching service characteristics to personal priorities rather than pursuing "best" or "worst" platforms. Audio quality audiophiles seeking lossless benefits from Tidal HiFi Plus benefit from a fundamentally different service than budget-conscious listeners optimizing for family plan cost efficiency through Spotify Family or Amazon Prime inclusion.
For most casual listeners, Spotify's combination of interface intuitiveness, algorithmic discovery quality, and ecosystem ubiquity remains compelling despite premium pricing. The network effects of Spotify's massive user base—friends using Spotify, playlists created for Spotify, social features optimized around Spotify—create stickiness that competes effectively against feature advantages of alternative services.
However, specific use cases increasingly justify service migration:
- Apple ecosystem users with HomeKit integration benefit meaningfully from Apple Music's native integration
- Alexa-dependent households gain friction reduction from Amazon Music's direct Echo device integration
- Audio quality enthusiasts justify Tidal HiFi Plus's premium pricing through measurable audio quality improvements
- Artist-support prioritizing listeners find Bandcamp's 85% artist revenue share aligns values with consumption
- YouTube integration seekers logically choose YouTube Music's video-music native combination
The consolidation of music streaming around large technology platforms (Apple, Amazon, Google) and premium specialist services (Tidal) suggests future stratification into ecosystem-locked services competing for retention within device ecosystems, versus niche specialists competing on specific dimensions (quality, artist support, discovery mechanics).
Before switching services, honestly assess switching costs and benefits. The effort required to migrate playlists, reestablish recommendation algorithms, and reconfigure device integrations should be weighed against tangible benefits from target service. For many users, these switching costs exceed benefits from incremental service improvements.
For new users evaluating initial platform selection, the analysis simplifies considerably. Choose based on primary priorities (cost, audio quality, ecosystem integration, artist support, discovery), then optimize through promotion trials and multi-service strategies if single-service limitations become apparent.
The streaming music market remains dynamic, with continued innovation around audio quality, AI-powered personalization, and artist compensation models. Monitoring emerging features and periodically reassessing platform selection ensures your chosen service continues meeting evolving needs. However, the incremental differences between services have narrowed substantially—choosing well remains important, but switching costs ensure extended platform commitment regardless of optimization at margins.
FAQ
What are the main reasons people switch from Spotify to alternative services?
Users typically switch from Spotify due to price increases (raising to $12.99/month as of 2024-2025), desire for superior audio quality (lossless audio available on Amazon, Apple, and Tidal), ecosystem integration benefits (Apple users preferring HomeKit integration, Alexa users preferring Amazon Music), or values alignment (artists choosing platforms with better artist compensation like Bandcamp or Tidal). Research indicates the primary trigger remains price increases rather than feature dissatisfaction, suggesting value perception rather than functionality drives switching decisions.
How do audio quality differences actually impact listening experience?
Audio quality impacts are measurable but dependent on both technical capabilities and listener perception. Streaming at 320 kbps (Spotify Premium) versus 256 kbps (YouTube Music) produces imperceptible differences for most listeners on consumer-grade headphones or speakers. Lossless audio quality (available on Amazon Music Unlimited, Tidal HiFi Plus, and Apple Music) provides objective quality improvement but requires quality audio equipment ($200+ headphones or speakers) to perceive meaningful differences. Listeners with trained ears, professional audio equipment, or specific music genres (classical, jazz, acoustic) benefit most from lossless quality; casual listeners on standard equipment realize minimal perceptual benefit from quality tier improvements.
What is the actual cost difference between family plans across services?
Family plan pricing varies substantially: Spotify Family costs
How long does it take to migrate from one streaming service to another?
Playlist migration using third-party tools (Soundiiz, Tunemymusic) typically requires 1-2 hours for complete transfer. However, metadata accuracy is imperfect—approximately 2-5% of songs may fail to match due to title variations, featuring artist differences, or catalog unavailability on target service. Allowing 2-3 additional hours for manual curation corrections and testing is realistic. Algorithm recalibration requires establishing listening patterns on new platform, typically 2-4 weeks for algorithms to generate meaningful recommendations. Complete migration including device integration configuration and feature familiarity development requires 2-4 weeks total effort, making switching most beneficial for users seeking substantial feature improvements rather than incremental optimization.
Which service offers the best music library for specific genres?
Library completeness varies by genre and artist tier. Mainstream contemporary music (pop, hip-hop, rock) has feature parity across all major services—major label releases appear simultaneously across platforms. Independent and experimental music favors SoundCloud and Bandcamp, which host substantial independent artist catalogs unavailable through traditional licensing agreements. Classical music finds superior curator expertise on Apple Music, which invested substantially in classical-specific content and recommendations. Niche genres (electronic, experimental, ambient) find broader independent artist representation on Bandcamp. For standard mainstream music consumption, library differences between Spotify, Apple, Amazon, and YouTube are negligible—differences lie in interface, discovery mechanisms, and feature completeness rather than content availability.
What does "lossless audio" actually mean and do I need it?
Lossless audio refers to compression formats (FLAC, ALAC, WAV) that reduce file size without discarding audio information—theoretically enabling perfect reconstruction of original recording. Lossy compression (MP3, AAC, Opus used by Spotify and most competitors) intentionally discards audio information imperceptible to human hearing, achieving smaller file sizes at cost of removed audio data. Perceptually, high-quality lossy compression (320 kbps AAC or MP3) remains indistinguishable from lossless for most listeners on typical listening equipment. You need lossless audio if: you use professional audio equipment ($500+), you listen to genres with high dynamic range (classical, jazz, acoustic), or you have trained hearing to perceive subtle quality differences. For casual listening through standard headphones or speakers, lossless quality provides no meaningful audible benefit.
How do streaming services pay artists and which service pays the most?
Streaming payment models typically operate on per-stream compensation ranging from
Can I use multiple streaming services simultaneously on the same account?
Streaming services don't inherently prevent simultaneous multi-device playback across different services—you can stream Spotify on one device while streaming Apple Music on another without technical conflict. However, most services limit simultaneous streams from the same account: Spotify Premium allows one simultaneous stream, Spotify Family allows six devices (with concurrent playback limits). Maintaining active subscriptions to multiple services (approximately 35% of subscribers globally do so) enables strategic service combination without technical limitations. The practical question becomes whether benefits from multiple services justify monthly cost increases, typically ranging from
What happens to my music if a streaming service shuts down?
Historical precedent suggests platform sunset follows predictable patterns: Google Play Music shutdown provided 12 months notice for user migration, YouTube Music provided migration tools enabling playlist transfer. Spotify has made explicit long-term commitment to streaming business and possesses sufficient financial resources for indefinite operation. Apple, Amazon, and Google have committed to music services as strategic components of broader ecosystems, reducing short-term discontinuation risk. However, smaller services (Tidal, Pandora, SoundCloud) possess lower strategic commitment and less transparent financial stability. If service discontinuation occurs, you lose: algorithmic recommendations calibrated to listening history, saved songs and playlists (unless migration tools enable transfer), and any service-specific features (collaborative playlists, social connections). Mitigation strategies include using platform-agnostic playlist tools (Spotify playlists transferable via Soundiiz), downloading high-quality files for important music (available through some services), and prioritizing financially stable services for long-term music library building.
How do I choose between audio quality and cost when selecting a streaming service?
The decision depends on your audio equipment, listening context, and trained hearing capability. If you listen primarily through phone speakers, car audio, or standard headphones, audio quality tier differences become imperceptible—optimizing for cost savings (Spotify at

Key Takeaways
- Spotify's repeated price increases have sparked genuine exodus, with alternatives offering distinct advantages in audio quality, ecosystem integration, or artist compensation
- Audio quality differences matter primarily for users with professional-grade equipment; casual listeners perceive minimal quality differences between 256-320 kbps lossy compression
- Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music function as ecosystem retention tools for Apple, Amazon, and Google respectively, offering integration depth beyond standalone music services
- Tidal emphasizes high-fidelity lossless audio and higher per-stream artist compensation, positioning as premium alternative for audiophiles and artist-support-prioritizing listeners
- Bandcamp enables artists to earn 85% revenue from direct purchases, creating fundamentally different economic model than streaming services optimized for listener convenience
- Family plans reduce per-person costs substantially—Spotify Family at 3.40/person, Amazon Music Unlimited Family at $4/person, undercutting individual pricing
- Discovery mechanisms vary significantly: Spotify emphasizes collaborative filtering, YouTube Music leverages video and search data, Pandora uses music genome analysis, Bandcamp emphasizes community discovery
- Switching costs include playlist migration (2-3 hours), algorithm recalibration (2-4 weeks), device integration configuration, and metadata accuracy losses—should be weighed against benefits
- Approximately 35% of subscribers maintain multiple concurrent services, suggesting optimal strategy for many listeners involves strategic service combination rather than single-platform commitment
- Long-term platform sustainability varies: Spotify, Apple, and Amazon have strong financial commitments; smaller services like Tidal have uncertain sustainability, creating service discontinuation risk




