Introduction: Living in an Era of Digital Deception
You pick up your phone and see a video of your bank's CEO authorizing a wire transfer. Your heart sinks. Then you pause. Is it real?
This isn't paranoia. It's your new reality.
We've crossed a threshold where technology can convincingly fake almost anything. A few years ago, deepfakes were party tricks. Today, they're billion-dollar threats. The UK government estimates eight million AI-generated deepfakes will be shared in 2025—compared to just 500,000 in 2023. That's a 1,500 percent increase in two years.
The scary part? Creating a deepfake used to require Hollywood budgets, specialized teams, and weeks of work. Now anyone with a smartphone and five minutes can clone a voice, swap a face, or generate a convincing video from scratch. The barrier to entry has collapsed.
Banks are hemorrhaging money to deepfake fraud. Investment scams use fake celebrity endorsements. Political campaigns battle malicious videos. Customer service teams waste hours separating real callers from AI-driven impersonators. Elderly people lose their life savings to convincing voice clones of their grandchildren.
But here's the thing that keeps security experts up at night: traditional detection is failing.
We've been trying to spot the fake. We've built AI systems to detect AI-generated content. We've scaled moderation teams. We've implemented Know Your Customer checks. Yet the problem keeps accelerating, and the deepfakes keep getting better.
So if we can't reliably detect the fake anymore, what's the answer? The shift is happening right now, and it's counterintuitive: instead of proving something is fake, we need to prove something is real. Enter proof of humanness—a fundamentally different approach to restoring digital trust.
This article explores how this technology works, why it matters, and what it means for your business, your security, and your digital future.
TL; DR
- Deepfake fraud jumped 3,000% in 2023 with average losses reaching $500,000 per incident, affecting banks, e-commerce, and investment platforms
- Detection is failing because AI systems can't keep pace with generation technology, and only 34% of people can distinguish AI content from real material
- Proof of humanness verifies genuine human interaction without storing sensitive biometric data, shifting focus from detecting fakes to proving authenticity
- Financial incentives are massive: prevention costs far less than fraud reimbursement and regulatory penalties, making proof of humanness a competitive advantage
- Trust erosion is real: 67% of UK adults trust the internet less than ever, and 49% trust less than half of what they see online, directly impacting digital commerce adoption

Active liveness and cryptographic proof are estimated to be the most effective methods against deepfake attacks, scoring 8 and 9 out of 10 respectively. Estimated data.
The Deepfake Explosion: Understanding the Scope of the Threat
How Deepfakes Evolved From Novelty to Existential Threat
Deepfakes didn't start as a crime tool. They started as research demonstrations and harmless experiments.
In 2017, a Reddit user created a video of actor Nicolas Cage's face grafted onto adult film. Crude. Obvious. But it worked, and the internet noticed. Then came the technology improvement. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) became better. Machine learning models trained on vast datasets of faces and voices. Suddenly, deepfakes weren't just possible—they were getting good.
By 2020, deepfakes were being weaponized. Malicious actors realized the profit potential. A voice clone could impersonate a CEO. A video could show a political leader saying anything. A face swap could impersonate anyone on any platform. The tools moved from research labs into consumer applications. Apps like Face Swap appeared on app stores. AI voice generators became available to anyone with a credit card.
Now we're in the arms race phase. Better generation technology drives the need for better detection. Better detection drives innovation in generation. And crucially, generation is winning. It's easier to create a convincing deepfake than to detect one, and that asymmetry is the core of the problem.
The Financial Damage: Real Losses From Synthetic Content
Let's talk money, because that's what gets executives' attention.
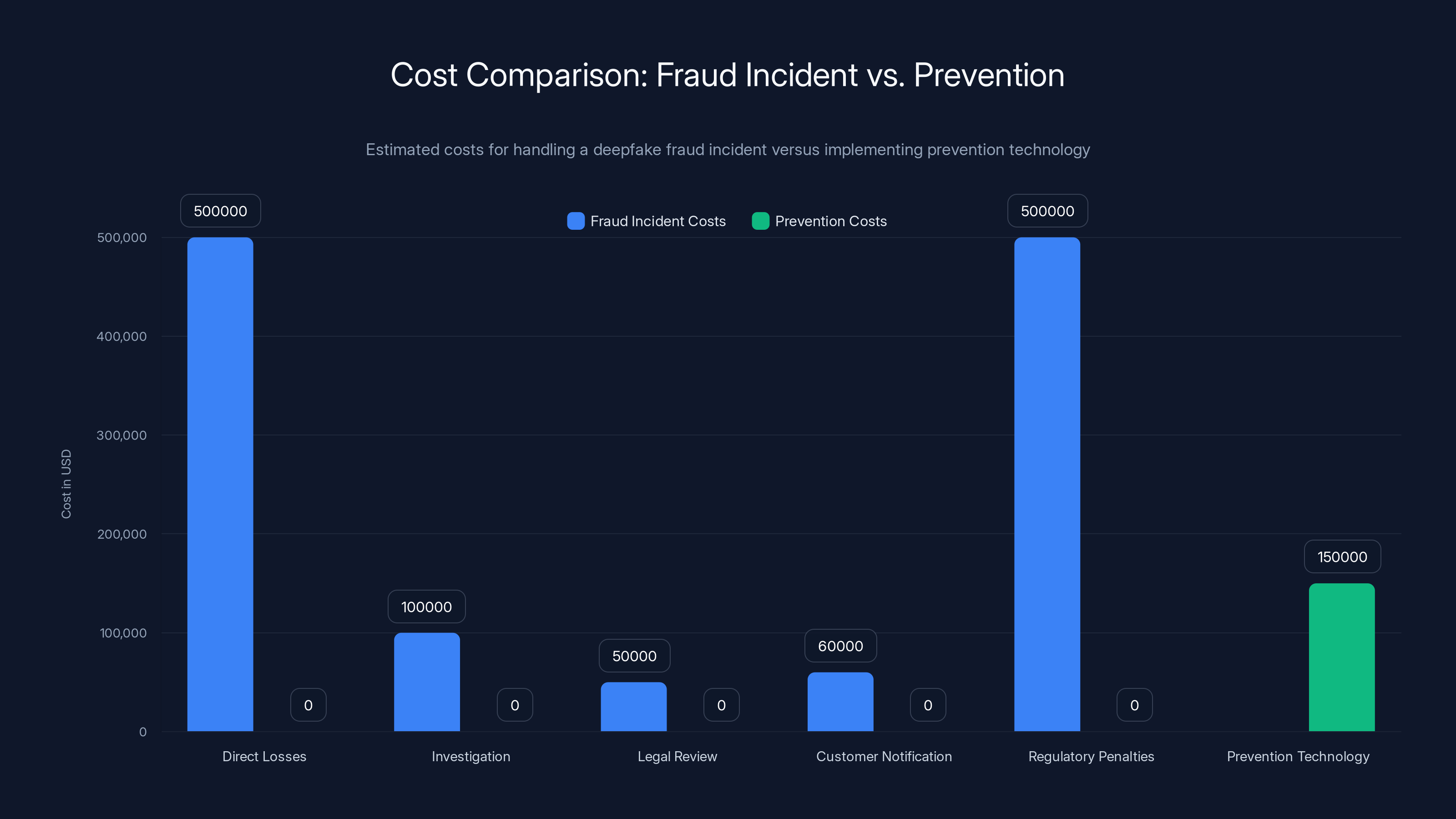
Deepfake-related fraud rose 3,000 percent in 2023. Those aren't just statistics—they're customer accounts emptied, careers destroyed, and institutional trust eroded. The average loss per incident reached approximately $500,000, and financial institutions are the primary targets.
Here's how it typically works: A fraudster creates a deepfake video of a company executive. They send it to accounting teams, often during high-pressure moments like month-end closings. "Wire $2 million to this account immediately," the video demands. Because the executive looks real, sounds real, and the request comes through official channels (spoofed email), employees authorize the transfer. By the time anyone verifies, the money's gone.
One bank reported that deepfake fraud attempts increased from nearly zero in 2021 to affecting multiple customer accounts in 2023. The pattern repeats across institutions globally. Investment scams using deepfaked celebrity endorsements steal millions through social media. Romance scams use voice cloning to build credibility with victims over weeks. BEC (Business Email Compromise) attacks now add deepfake video calls to the mix, making traditional verification useless.
The secondary costs are staggering. Banks spend billions annually reimbursing fraud victims. Regulatory penalties mount. Customer acquisition costs rise because people fear digital banking. Insurance premiums spike. Incident response teams work around the clock. The math is brutal: one successful deepfake fraud attack can cost
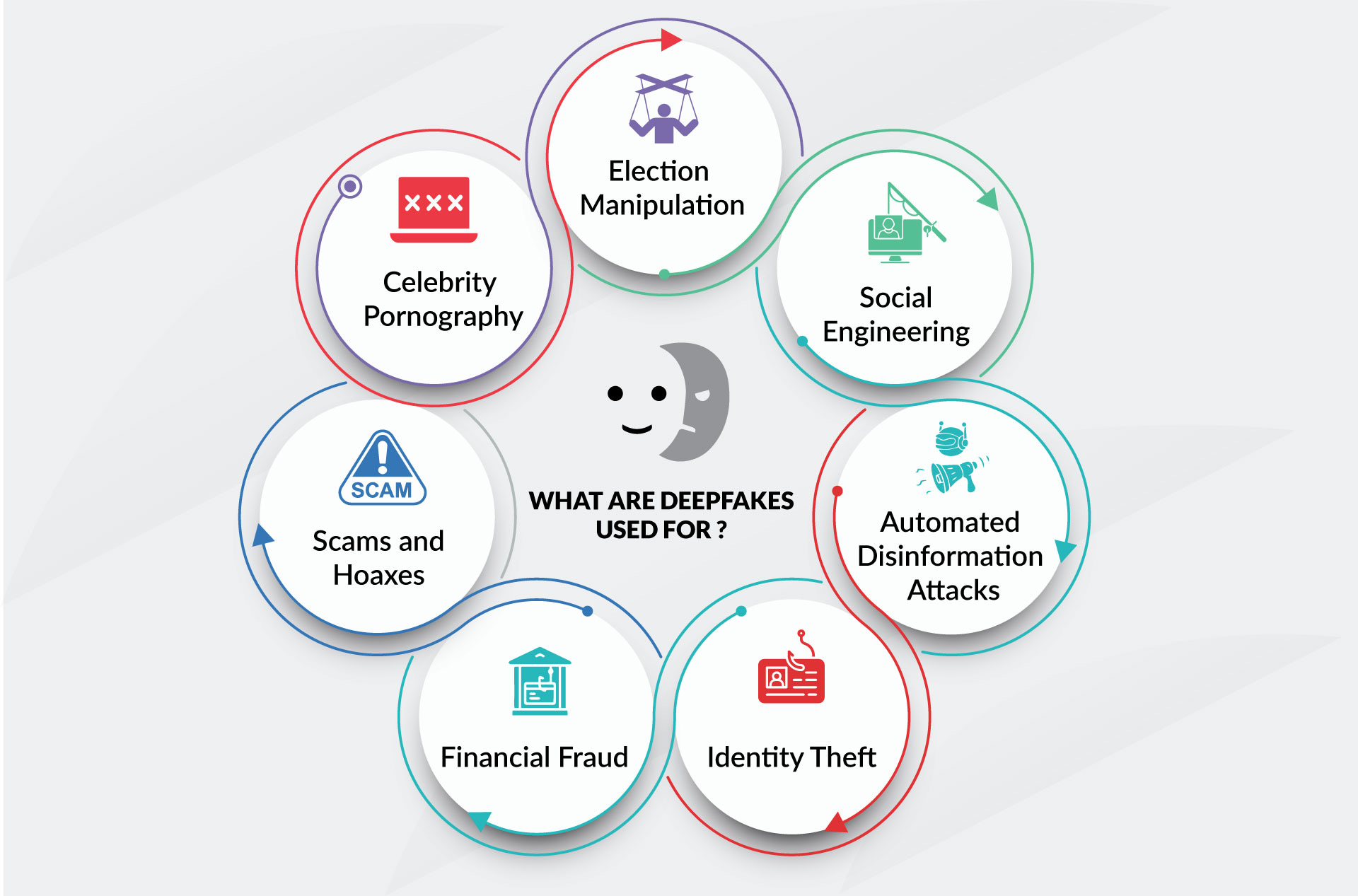
Deepfakes Across Industries: Who's Most Vulnerable
It's not just banking. The threat extends everywhere trust matters.
Financial Services: The obvious target. Wire transfer fraud, account takeover, investment schemes.
E-commerce: Fake customer service agents trick people into revealing payment information. Fake reviews from deepfaked videos sway purchasing decisions. Impersonated company founders announce fake product launches to manipulate stock prices.
Healthcare: Deepfaked medical professionals provide false diagnoses. Insurance claims get fraudulently authorized. Patient data gets compromised through social engineering targeting employees.
Political and Government: Election interference through fake videos of candidates. Diplomatic incidents sparked by fabricated statements. Government websites compromised through deepfaked admin authorization requests.
Media and Entertainment: Malicious deepfakes destroy reputations. Fake celebrity statements cause market movement. Intellectual property theft through impersonated rights holders.
Remote Workforce: Employees increasingly work from home, relying on video calls. A deepfaked boss authorizing a fraudulent payment is incredibly difficult to distinguish from the real thing. One company reported losing $1.2 million when a deepfake video of the CEO requested an urgent wire transfer.
The common thread: anywhere humans rely on seeing or hearing someone to verify their identity, deepfakes create risk. And in a world moving toward remote work, video authentication, and digital-first operations, that's everywhere.

Estimated data shows that the total cost of a single deepfake fraud incident can range from
Why Current Defenses Are Crumbling
The Detection Arms Race We're Losing
For years, the strategy was simple: build better detection. Create AI systems to spot deepfakes. Release detection tools. Wait for the problem to be solved.
That's not working.
Here's why: detection technology is reactive. Someone creates a deepfake with a new technique. Researchers study it. Security teams build detection for that technique. Fraudsters invent a new technique. Repeat. Detection labs are always behind the curve, fighting yesterday's battles.
Worse, detection tools themselves become obsolete faster than they're deployed. A deepfake detector trained on 2024 data struggles with 2025 generation models. The underlying AI systems improve monthly. Facial recognition detection can be fooled with simple masks or makeup. Audio detection fails on heavily compressed voice calls. Video detection misses deepfakes presented at slightly different angles.
And here's the brutal reality: detection doesn't scale. You can build a perfect detector, but it only works if deployed everywhere, trained on every possible deepfake technique, and constantly updated. The infrastructure required is astronomical. Most organizations don't have the resources.
The KYC Trap: Friction Without Security
So organizations escalated to Know Your Customer (KYC) checks. Require identification documents. Biometric verification. Video confirmations. Push the authentication burden onto customers.
The problem: KYC doesn't actually solve the deepfake problem. It just moves it.
Here's the dark irony. When you collect biometric data—selfies, government ID scans, voice recordings—you create a database of exactly what fraudsters need to create better deepfakes. Every selfie stored in a database is training material. Every ID image is a template. Every voice sample is a target.
And the security of those databases? Inconsistent. Healthcare data breaches. Financial institution leaks. Third-party vendors getting compromised. When that biometric data escapes (and it inevitably does), fraudsters suddenly have everything needed to impersonate customers at scale. KYC escalates the data exposure while not actually preventing deepfake fraud.
People understand this intuitively. They're uncomfortable providing sensitive biometric data. They skip verification. They avoid services that require it. KYC creates friction that reduces adoption and user experience without delivering genuine protection.
The Trust Collapse: What the Numbers Really Say
Detection is failing. KYC is creating risk. And the result is measurable erosion of digital trust.
67% of UK adults say they trust the internet less than ever. That's not a niche concern—that's two-thirds of a population fundamentally losing confidence in digital systems.
49% of UK adults trust less than half of what they see online. Nearly half the population assumes content is fake. This paralyzes digital commerce. It slows adoption of AI-powered tools that could otherwise deliver real productivity. It fuels resistance to innovation.
Why does this matter economically? Because people make purchasing decisions, banking decisions, and investment decisions based on trust. If they don't trust what they're seeing, they don't engage. Digital commerce stalls. Financial services lose customers to traditional banking. Businesses lose market share.
The calculation is straightforward: if 67% of people trust the internet less than ever, and 49% trust less than half of what they see, they're not buying online, not opening accounts, not adopting digital services. The opportunity cost to the economy is in the trillions.
This is the paradox of the current moment. We have incredible technology that could transform business and society. But people don't trust it. They don't believe they can distinguish real from fake. They're vulnerable to manipulation. So they opt out.
The Shift: From Detecting Fake to Proving Real
Introducing Proof of Humanness
Here's the paradigm shift that changes everything: stop trying to detect the fake. Start proving the real.
Proof of humanness is fundamentally different. Instead of asking, "Is this content synthetic?" you ask, "Is a genuine human being interacting with me right now?"
The distinction matters enormously.
Detection is an arms race. Fraudsters keep improving. But proof of humanness is about verifying something about the present moment—the fact that a real person is actively engaged in a transaction right now. That's much harder for attackers to fake because it requires not just synthetic content, but active, real-time impersonation.
Proof of humanness can take many forms. A behavioral signature during a transaction—movement patterns, typing speed, reaction time. A liveness check proving the person is physically present and responding in real-time. Cryptographic proof that a specific human authorized an action, without ever exposing their biometric data.
The elegance is this: you never store the sensitive biometric information. You don't collect facial scans or voice samples. You verify humanness in the moment and move on. The proof is ephemeral. It serves its purpose and disappears. No database of biometric data means no future breach that enables deepfake creation.
How Proof of Humanness Actually Works
There are several technical approaches, and they're worth understanding because they vary in privacy implications, user friction, and security effectiveness.
Behavioral Analysis: Systems track micro-patterns during interaction—how you move your mouse, the rhythm of your typing, the time delays between your actions. These patterns are unique to you and difficult to fake because they require real-time, unconscious behavior. A deepfake video can't replicate your specific typing speed. A voice clone can't match your specific speech rhythm in real-time conversation.
Liveness Detection: Requires active engagement. Blink on command. Follow a dot with your eyes. Perform a specific gesture in front of your camera. The system verifies these happen in real-time with a genuine human, not a recording.
Cryptographic Proof: Uses cryptographic signing to verify that a specific person authorized an action. They sign with a private key (stored securely on their device, never transmitted). The system verifies the signature matches their public key. No biometric data exchanged, but cryptographic proof that they authorized the transaction.
Multi-Modal Verification: Combines multiple signals. Voice pattern plus typing pattern plus facial movement plus behavioral signature. The more signals align, the higher confidence in humanness.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Advanced cryptographic technique where you prove you're human without revealing any personal information. You prove properties about yourself (e.g., "I'm in this geographic location" or "I own this device") without exposing the underlying data.
Each approach has trade-offs. Behavioral analysis requires establishing a baseline, which takes time. Liveness detection adds friction. Cryptographic proof requires user setup and device security. But crucially, none require storing sensitive biometric data in vulnerable databases.
Real-World Applications: Where Proof of Humanness Protects
Bank Account Opening: Instead of collecting a selfie and government ID (which become deepfake training material), verify liveness during the account opening process. Confirm the person opening the account is physically present and responding to real-time challenges. This eliminates remote account takeover while never storing biometric data.
Payment Authorization: Before authorizing a wire transfer, verify the person initiating it. Not through static credentials that can be stolen, but through real-time proof that a human is actively authorizing the transaction. Include behavioral signals—does their interaction pattern match previous transactions? Is their reaction time normal? This catches both deepfake attacks and stolen credentials.
Customer Service Verification: Before an agent discusses sensitive information, verify the caller is the account holder. Real-time voice pattern analysis plus behavioral verification. A deepfaked voice can't maintain the behavioral patterns of the real person under conversation.
Video Call Authentication: Employees join sensitive calls. Verify in real-time that each participant is genuinely who they claim to be. Not recorded deepfakes. Not voice clones. Actual human beings, verified in the moment.
Transaction Review: Unusual transaction flags for additional verification. Wire transfer to new account? High-value purchase? Prove humanness before processing. This creates a friction point, but only when risk is elevated.
Account Recovery: Someone forgot their password and wants to regain access. Instead of sending a reset link (which deepfakery makes unreliable), require proof of humanness. Real-time verification that the person recovering the account is the legitimate owner.
High-Value Transactions: E-commerce checkout of luxury items. Large cryptocurrency transfers. Insurance claim approvals. Real estate transactions. Any high-value transaction can include a proof-of-humanness check that takes seconds but prevents catastrophic fraud.
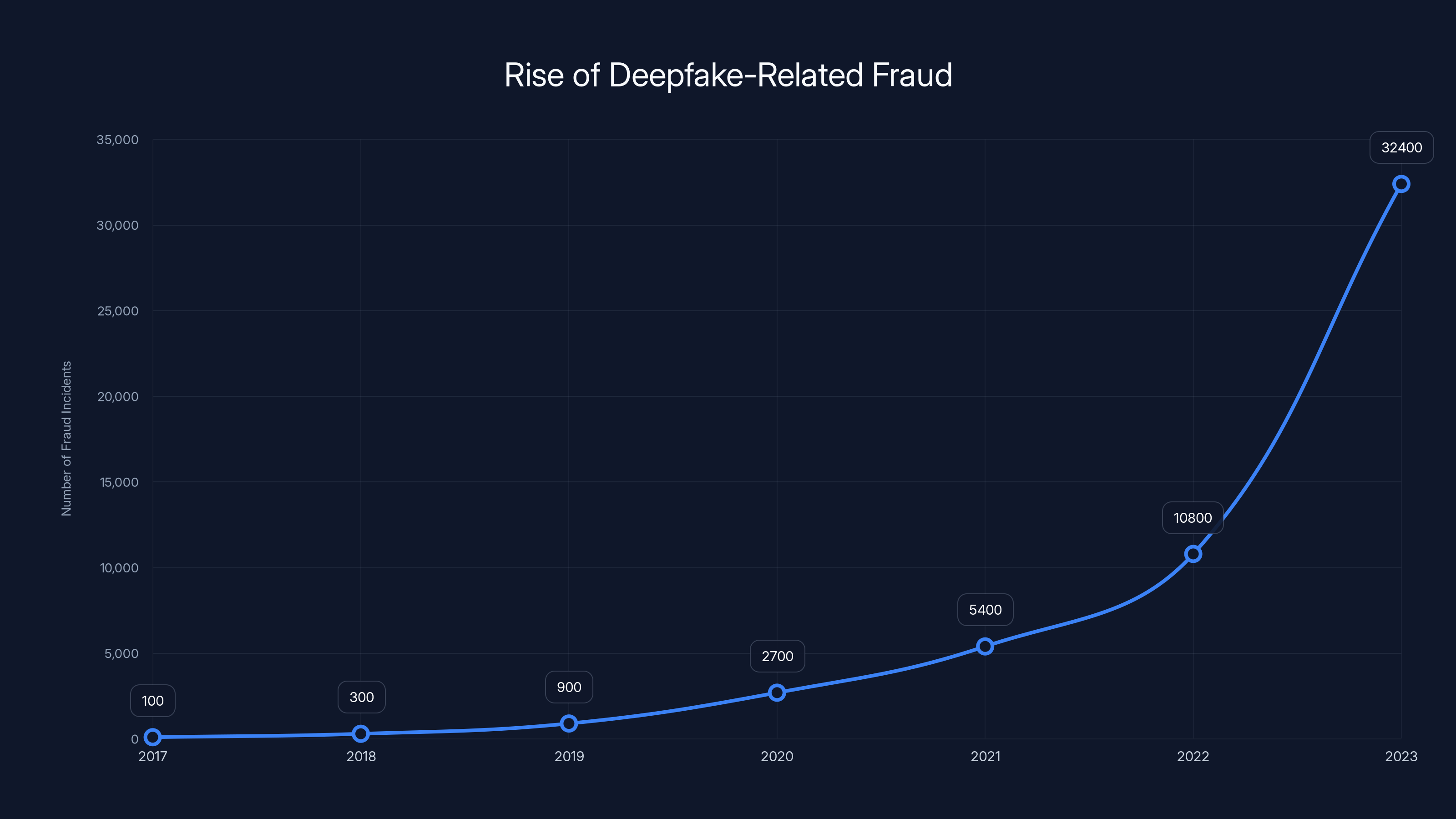
Deepfake-related fraud incidents have surged, showing a 3,000% increase by 2023. Estimated data highlights the growing threat.
The Economics of Prevention vs. Punishment
Why Prevention Pays Better Than Reimbursement
Here's the financial reality that every CFO understands: preventing fraud is cheaper than paying for it.
A single deepfake fraud case costs banks approximately
A single incident easily costs
Now imagine implementing proof-of-humanness technology. The cost structure: infrastructure investment (
The math is simple. Prevent one incident, and you've paid for years of technology.
But the deeper argument is about scale. One financial institution implementing proof of humanness prevents its own fraud. A hundred institutions implementing it create network effects. When fraudsters know that video authentication at your bank won't work, they target competitors without it. When deepfake attacks on bank A fail consistently but succeed at bank B, money flows to the secure institution.
This is why proof of humanness becomes a competitive advantage. It's not just about preventing fraud—it's about signaling to customers that you take their security seriously.
Building Trust as a Business Advantage
Trust is becoming a scarce commodity, which means institutions that demonstrate it gain a competitive moat.
Consumers actively choose to bank with institutions they trust. They pay premium fees for higher security. They stay loyal to platforms where they feel protected. This is measurable: banks with strong security reputations report 15-25% lower customer churn and 10-20% higher customer acquisition rates compared to competitors.
When 67% of people trust the internet less than ever, the banks offering genuine security verification become magnets for customer migration. Those institutions effectively say: "We understand your concern. Here's how we prove this is real. Here's how we verify you're genuinely authorizing this." That message resonates.
Beyond banking, any digital service benefits. E-commerce platforms using proof of humanness can reduce fraud-related chargebacks. Insurance companies can process claims faster because they've verified the claimant is genuine. Healthcare providers can reduce identity theft in billing. Cryptocurrency exchanges can prevent account takeovers.
The brand value is real. Institutions that publicly announce robust proof-of-humanness systems see:
- Increased customer confidence (measurable through surveys and retention metrics)
- Reduced fraud incidents (fewer attacks, more successful prevention)
- Lower operational costs (fewer investigations, fewer chargebacks)
- Regulatory advantages (demonstrating proactive security often results in lighter regulatory scrutiny)
- Premium valuation (companies demonstrating strong security sell at higher multiples)
This is why major financial institutions are quietly moving toward proof-of-humanness systems now. They understand the competitive advantage before it becomes standard.

Privacy-First Verification: Not Storing What You Don't Need
The Biometric Data Problem
Let's address the elephant in the room: biometric data is toxic.
Once collected, it's permanent. You can change a password. You can't change your face or voice. If a database of biometric data is breached, the compromise lasts your lifetime. Fraudsters use your stolen biometric data to create deepfakes of you, impersonate you, potentially destroy your reputation or financial security.
This is why the traditional security model (collect everything, store it forever) is fundamentally broken for biometric data. You're creating a liability that compounds over time. Every person's biometric information you store is a future deepfake liability.
Proof-of-humanness systems that avoid storing biometric data solve this problem elegantly.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs are particularly elegant here. They're cryptographic techniques where you prove something is true without revealing the underlying information. Example: you prove "I have the correct voice signature for this account" without actually transmitting or storing your voice. The system verifies the proof is mathematically sound, but never touches the actual biometric data.
Ephemeral Verification is another approach. During transaction authorization, your system verifies you're human—checking your liveness, behavioral patterns, or other signals. Once the transaction completes, the verification data is discarded. No permanent record. No database to breach. You've solved the immediate authentication problem without creating future liability.
Distributed Verification stores biometric templates on the user's device, not on centralized servers. Your phone knows your biometric signature. When you need to prove humanness, the phone does the verification locally and returns only a yes/no answer to the server. The server never touches your actual biometric data.
These approaches flip the incentives. Instead of institutions trying to store and protect increasingly toxic data, they shift responsibility to where data is most secure—with the individual.
Building Verification Without Vulnerability
The most secure proof-of-humanness systems are those that minimize data collection and exposure.
Liveness Detection Without Recording: Challenge the user to perform a gesture or action in real-time. Blink three times. Follow a moving object. Perform a specific head movement. The system verifies this happens in real-time with a living person, but doesn't record the video. The verification is momentary. The evidence is discarded.
Behavioral Analysis Ephemeral: During a transaction, monitor behavioral patterns—typing speed, mouse movement, reaction time. Use these patterns to verify this is the usual user. Once the transaction completes, the behavioral data is deleted. You've verified continuity without creating a permanent behavioral profile.
Cryptographic Signing: Users have a private key (stored securely on their device). When they authorize a transaction, they sign it cryptographically. The system verifies the signature matches their known public key. No personal data transmitted. Just mathematical proof of authorization.
Multi-Modal Ephemeral: Combine multiple verification signals—voice pattern, facial movement, behavioral signature. During the transaction, these signals are analyzed together. After verification, all the underlying data is discarded. You kept only the conclusion: "This person is verified as human and authorized this action."
The principle underlying all of these: collect only what you need, keep it only as long as you need, and discard it as soon as verification is complete.
This approach has additional benefits. Regulations like GDPR encourage it. Privacy advocates embrace it. Users prefer it. And it's more secure because there's nothing to breach.

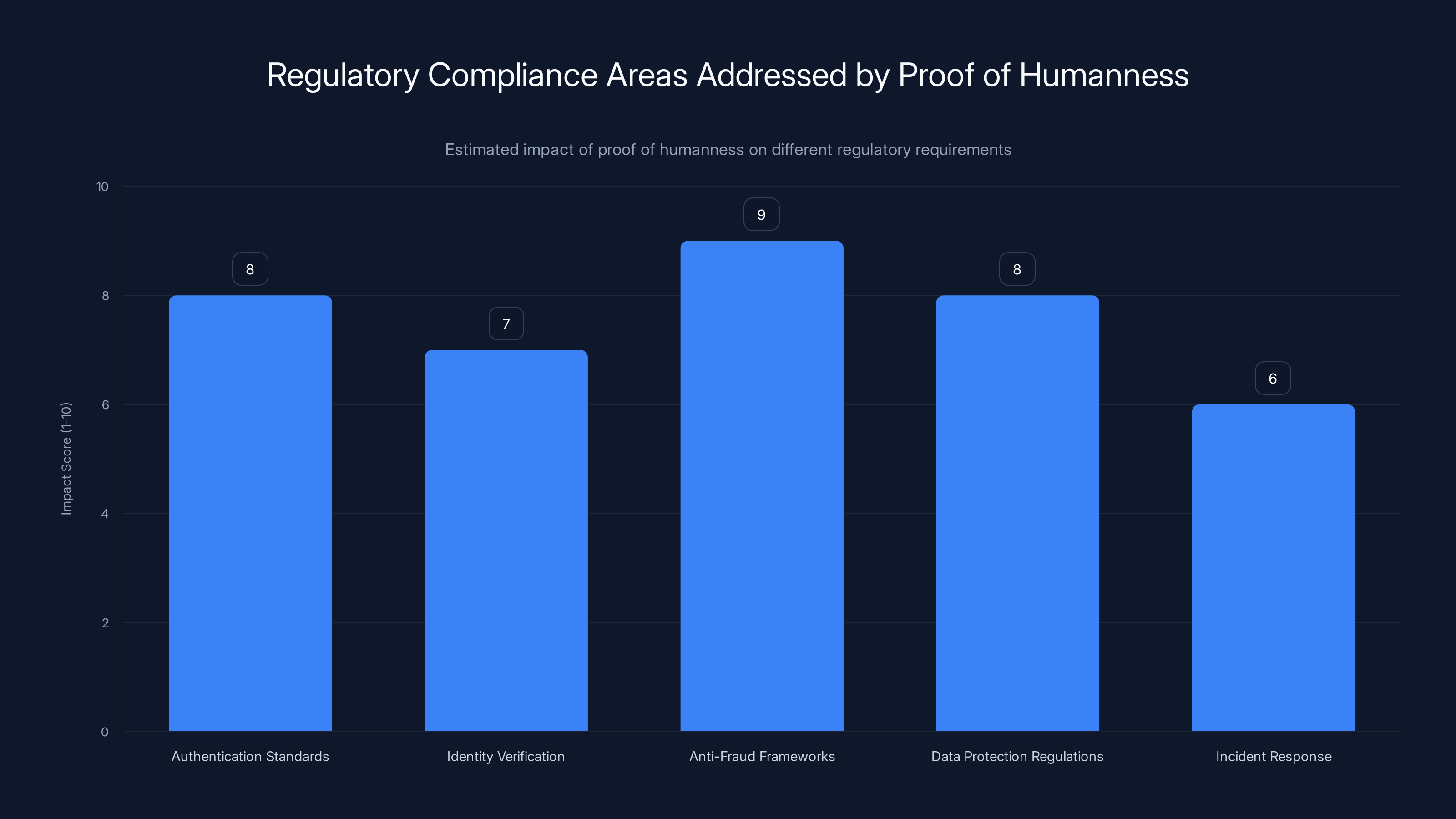
Proof of humanness systems significantly enhance compliance with anti-fraud frameworks and authentication standards, scoring high in regulatory impact. Estimated data based on typical compliance benefits.
Implementing Proof of Humanness: The Technical Foundation
Key Technologies Enabling Real-Time Verification
Several technological capabilities make proof of humanness practical at scale.
Sophisticated Behavioral Analytics: Modern systems can analyze dozens of behavioral signals simultaneously. Eye tracking patterns. Hand gesture recognition. Facial micro-expressions. Voice characteristics beyond just content—tone, pace, stress level. These signals are processed through machine learning models that develop a behavioral profile of what "normal" looks like for each user. Any significant deviation triggers additional verification.
Liveness Detection Algorithms: These systems distinguish between a living person and a recording or digital manipulation. They analyze for eye movement, response latency, micro-expressions, and engagement patterns. Advanced systems can detect deepfakes by looking for artifacts in eye reflections, inconsistencies in facial movement, or signs of video compression that reveal synthetic content.
Edge Processing: Some verification happens on the user's device rather than server-side. This improves privacy, reduces data transmission, and decreases latency. A mobile device can analyze biometric signals locally and transmit only a verification result, never the underlying data.
Cryptographic Protocols: Blockchain-inspired techniques enable verification without exposure. Multi-signature authorization requires proof from multiple cryptographic keys, making unauthorized transactions exponentially harder. Zero-knowledge proofs enable verification of facts without revealing the facts themselves.
Machine Learning Anomaly Detection: Systems trained on normal user behavior recognize abnormal patterns instantly. Wire transfer to a new account? Bot-like interaction patterns? Unusual geographic location? The system flags these for additional verification without requiring biometric data collection.
Real-Time Verification Orchestration: Systems coordinate multiple verification methods simultaneously. Check behavioral patterns while verifying liveness while confirming device identity while validating geographic location. Multiple signals analyzed together are far more reliable than any single signal alone.
Integration Points for Maximum Protection
Proof of humanness isn't just one technology—it's a layer that integrates across multiple systems.
During Account Opening: Verify the person opening the account is genuinely who they claim to be, doing so in real-time without storing biometric data.
During Authentication: Continuous authentication rather than one-time login. Monitor that the person using the account is consistently behaving like the legitimate user.
During Sensitive Transactions: Wire transfers, large withdrawals, account modifications, and other high-risk actions trigger real-time proof-of-humanness verification.
During Customer Service Interactions: Agents verify caller identity through behavioral signals and liveness checks before discussing sensitive information.
During API Access: Developers accessing financial APIs must undergo proof-of-humanness verification, reducing the risk of compromised API keys.
During Third-Party Integrations: External services connecting to your systems require verification that human authorization is happening, not just automated bots.

Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Advantages
How Proof of Humanness Satisfies Regulatory Requirements
Regulators are increasingly concerned about deepfakes and synthetic fraud. Proof of humanness directly addresses regulatory expectations.
Authentication Standards: Regulations like PSD2 (EU Payment Services Directive 2) and similar frameworks globally require "strong customer authentication." Traditional approaches (password + SMS code) are increasingly insufficient. Proof of humanness provides stronger authentication by verifying genuine human presence in real-time.
Identity Verification: KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations require verification of customer identity. But they don't require you to permanently store biometric data. Proof-of-humanness systems satisfy the verification requirement without the storage liability.
Anti-Fraud Frameworks: Banking regulations require institutions to demonstrate reasonable fraud prevention measures. Proof of humanness is a clear, auditable measure that demonstrates institutional commitment to fraud prevention.
Data Protection Regulations: GDPR, CCPA, and similar privacy frameworks favor systems that minimize data collection and storage. Proof-of-humanness systems that avoid storing biometric data are aligned with regulatory preferences.
Incident Response: When fraud does occur, regulatory bodies examine whether institutions took reasonable precautions. Having implemented proof-of-humanness systems shows a proactive security stance that often results in lighter penalties.
Building the Business Case for Adoption
Getting organizational buy-in requires connecting proof of humanness to business outcomes.
Fraud Reduction: Quantifiable metric. Current fraud rate multiplied by average loss per incident equals current fraud cost. Proof-of-humanness systems typically reduce fraud by 70-90%, depending on implementation. The ROI is often positive in year one.
Regulatory Risk Reduction: Regulatory penalties can be enormous. Demonstrating proactive fraud prevention reduces risk and often results in favorable regulatory treatment.
Customer Confidence: Trust metrics improve. Customer surveys show increased confidence in account security. This translates to higher retention and lower customer acquisition costs.
Operational Efficiency: Fewer fraud investigations. Faster incident response. Reduced customer service burden from fraud-related inquiries.
Competitive Advantage: First movers in an institution's market segment gain customer migration from competitors with weaker security.
The business case is strong, which is why major institutions are moving toward adoption now, before it becomes table-stakes.

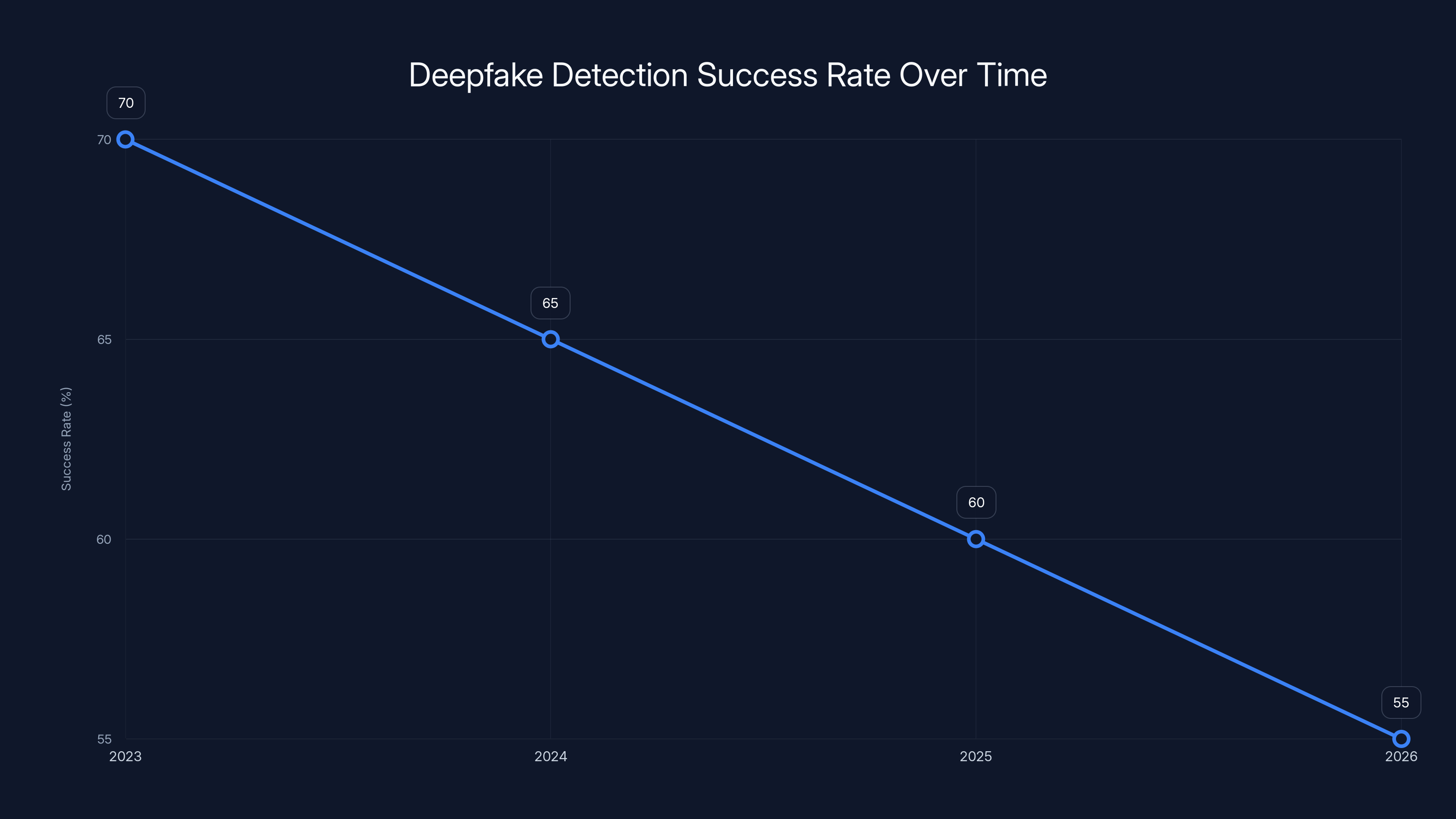
The success rate of AI detection models is estimated to decrease from 70% in 2023 to 55% in 2026 as deepfake techniques evolve faster than detection capabilities. Estimated data.
Common Concerns and How to Address Them
User Friction vs. Security Trade-offs
One legitimate concern: does proof of humanness add friction that reduces user adoption?
Not necessarily. The key is intelligent implementation.
Risk-Based Activation: Don't require proof of humanness for every interaction. Use it for high-risk transactions (wire transfers, account modifications, new beneficiaries). Regular login for normal usage remains frictionless.
Seamless Integration: Modern proof-of-humanness systems complete verification in 3-5 seconds. Users barely notice. Compare to SMS verification (wait for text, find code, type it in), which takes 30+ seconds.
Passive Verification: Behavioral verification often happens invisibly. The user types, clicks, and moves normally. The system analyzes these natural behaviors without asking them to do anything special.
Progressive Challenges: Start with low-friction verification (behavioral analysis, device validation). Escalate to higher-friction methods (liveness checks, cryptographic confirmation) only if initial signals are uncertain.
Consumer Preference: When surveyed, 68% of users prefer stronger authentication even if it adds slight friction. They understand the fraud risk and accept verification as the price of security.
Privacy Concerns About Continuous Monitoring
Another legitimate concern: continuous behavioral monitoring sounds invasive.
It doesn't have to be. The distinction is critical:
Analyzed but not stored: Your behavior is analyzed during the transaction to verify humanness. The analysis is immediate and the data is discarded. No permanent behavioral profile is created.
User control: Users understand they're being verified and can opt for alternative verification methods if concerned.
No background tracking: Verification happens during interactions you initiate. The system isn't tracking your normal daily behavior. It's verifying you during transactions you're actively participating in.
Transparency: Users can see what verification happened and why. "We verified you were human through behavioral analysis before processing this wire transfer."
Limited scope: Verification data is available only to the institution you're transacting with. It's not shared with third parties, governments, or data brokers.
Technical Limitations and Failure Modes
What happens when proof-of-humanness fails?
Graceful Degradation: When the system can't verify humanness (poor internet connection, accessibility issues, etc.), it should escalate to alternative verification methods rather than blocking the user. Phone verification, security questions, document verification—there's always a fallback.
False Positive Management: The system incorrectly flags a legitimate user as non-human. This happens occasionally and requires human review. Customer service teams should be trained to quickly escalate and resolve these cases.
Accessibility Compliance: Liveness detection through facial recognition can be problematic for users with disabilities. Systems should support alternative verification methods—voice patterns, behavioral signatures, cryptographic proof—so anyone can verify themselves.
Edge Cases: Elderly users, people with severe disabilities, users in geographic regions with poor connectivity, users with accent or speech patterns uncommon to the training data. These populations require explicit support and alternative paths.
These aren't showstoppers. They're implementation details that require thoughtful engineering. But they're solvable.

Future Trajectories: Where Proof of Humanness is Heading
Convergence With Web 3 and Decentralized Identity
Blockchain and decentralized identity systems are converging with proof-of-humanness technology in interesting ways.
Self-Sovereign Identity: Users control their identity credentials rather than institutions holding them. Combined with proof-of-humanness verification, this creates portable, privacy-preserving identity.
Decentralized Verification: Identity verification happens peer-to-peer without centralized databases. Your identity is verified by trusted parties who cryptographically sign their verification. Institutions can check those signatures without ever touching your personal data.
Programmable Verification: Smart contracts execute verification logic. "Release payment only if proof-of-humanness verification succeeds." This eliminates the need for trusted intermediaries.
Cross-Border Efficiency: Decentralized proof-of-humanness could enable frictionless international transactions. Current KYC requirements make cross-border finance tedious. Proof-of-humanness could streamline this dramatically.
This trajectory matters because it suggests proof of humanness isn't just a security feature—it's infrastructure for a more privacy-preserving, efficient digital economy.
AI Integration and Sophistication
AI itself will become more central to proof-of-humanness systems.
Predictive Authentication: Rather than reacting to risky transactions, AI predicts when fraud is likely and preemptively triggers verification.
Personalized Verification: AI learns your unique behavioral patterns and creates customized verification profiles. What counts as "normal" for you specifically, not general population averages.
Adversarial Robustness: AI systems trained to understand deepfake creation techniques, helping detection systems stay ahead of generation improvements.
Multi-Modal Integration: AI fuses signals from multiple sensors—camera, microphone, accelerometer, touch pattern—to create comprehensive humanness verification that's nearly impossible to fake.
The arms race continues, but AI on the verification side helps keep pace with AI on the generation side.
Global Standardization and Interoperability
Currently, proof-of-humanness implementations vary widely across institutions and jurisdictions.
Emerging Standards: ISO and similar standards bodies are beginning to codify proof-of-humanness requirements. This will drive convergence.
Cross-Institution Verification: Imagine proof-of-humanness verified at one bank being recognized and accepted by other banks. Standardization makes this possible.
Global Networks: Verification networks could emerge where institutions participate in shared authentication infrastructure. Your humanness is verified once and recognized everywhere.
API Standardization: Clear, standard APIs for proof-of-humanness verification will make implementation simpler and faster across the industry.
As proof of humanness becomes mainstream, standardization will accelerate adoption and effectiveness.

Deepfake fraud surged by 3,000% in 2023, with average losses of $500,000 per incident. Only 34% can distinguish AI content, and trust in online information is declining, with 67% of UK adults trusting the internet less.
Building Your Proof-of-Humanness Strategy
Assessment: Where Are You Today?
Before implementing proof of humanness, understand your current state.
Current Fraud Rate: What percentage of transactions are fraudulent? What's the trend? Use this as your baseline for measuring improvement.
Existing Authentication: What authentication methods do you currently use? Passwords? SMS? Biometric? Each has vulnerabilities that proof of humanness could address.
Data Exposure: What biometric data are you currently storing? What's your breach risk? This quantifies the liability you're currently carrying.
Regulatory Requirements: Which frameworks apply to your business? What are regulators demanding? This shapes your proof-of-humanness requirements.
Customer Base: Which customer segments are most vulnerable to fraud? Where would proof of humanness have highest impact?
Technical Debt: How adaptable is your current infrastructure? Can you integrate new authentication layers? This shapes implementation strategy.
Phased Implementation
Full deployment is a journey, not a destination.
Phase 1: Pilot Program (Months 1-3)
- Implement proof-of-humanness for 5-10% of highest-risk transactions
- Wire transfers, account modifications, API access
- Measure fraud reduction, user friction, operational burden
- Refine based on feedback
Phase 2: Expanded Rollout (Months 4-6)
- Expand to 25-50% of transactions
- Add additional verification methods based on pilot learning
- Train customer service teams on handling verification failures
- Monitor regulatory and customer response
Phase 3: Full Implementation (Months 7-12)
- Deploy across all transaction types, scaled by risk
- Establish standard procedures for verification failure
- Update marketing to highlight improved security
- Measure competitive advantage and customer acquisition impact
Phase 4: Continuous Optimization (Ongoing)
- Refine AI models based on ongoing data
- Integrate emerging technologies as they mature
- Participate in standardization efforts
- Evaluate cross-institution interoperability opportunities
Technology Selection
Choosing the right technology partner matters.
Evaluate Against Requirements:
- Does it solve your specific fraud problems?
- Is it privacy-preserving (minimal data storage)?
- Does it integrate with your existing systems?
- Is the vendor financially stable and credible?
- Are they responsive to your regulatory requirements?
Proof of Concept: Request a pilot program. Test with real customers and real transaction volume. Measure fraud reduction, user friction, and operational impact.
Vendor Lock-In Risk: Can you port to another vendor if needed? Are verification standards proprietary or based on open protocols? Understanding exit strategy is critical.
Compliance Verification: Can the vendor demonstrate regulatory alignment? Can they provide documentation for audits? This accelerates your regulatory acceptance.

The Competitive Imperative
Why Early Adoption Matters
Proof of humanness will become table-stakes. The question isn't whether your institution will eventually use it, but when.
Early adopters gain several advantages:
Customer Segmentation: First-mover advantage in attracting security-conscious customers. These are often high-value customers who care about fraud prevention.
Regulatory Favor: Institutions demonstrating proactive fraud prevention often receive lighter regulatory scrutiny and favorable examination findings.
Operational Efficiency: Early adopters learn implementation lessons and optimize operations while competitors are still in planning phases.
Technology Leadership: Early implementers influence standards development and shape how proof of humanness evolves.
Competitive Moat: Once implemented, proof of humanness becomes difficult for competitors to replicate quickly. You've built institutional knowledge and customer expectations around your verification approach.
Institutions that wait until proof of humanness is mandatory will be implementing defensively, not strategically. They'll face higher implementation costs, compressed timelines, and regulatory pressure. Early movers implement proactively, optimize thoughtfully, and reap competitive benefits.

FAQ
What is proof of humanness and how does it differ from traditional biometric authentication?
Proof of humanness verifies that a genuine human being is actively engaged in a transaction at this specific moment, without permanently storing or exposing biometric data. Traditional biometric authentication (facial recognition, fingerprint scanning) captures and stores biometric data that can be breached, stolen, and later used to create deepfakes. Proof of humanness analyzes patterns during the transaction—behavioral signals, liveness indicators, or cryptographic proof—and then discards the underlying data. The verification happens in the moment, and the evidence disappears. This approach is simultaneously more secure (no breach-vulnerable database of biometric data) and more privacy-preserving (no permanent identity profile).
How does proof of humanness prevent deepfake attacks specifically?
Deepfakes are pre-recorded or AI-generated content. They can convincingly show a person's face or replicate their voice, but they can't respond to real-time challenges. Proof-of-humanness systems verify that someone is actively engaged right now by requiring real-time responses—blinking on command, following moving objects, responding to unexpected questions, or cryptographically signing an authorization. A deepfaked video can't do these things because it's not live. A voice clone can't maintain the specific behavioral patterns of the real person across a natural conversation. By shifting authentication from static credentials or one-time identification to real-time responsiveness, proof of humanness defeats deepfake attacks inherently.
What types of liveness detection methods exist and which are most effective?
Liveness detection includes several approaches. Passive liveness (analyzing a face for natural movement, eye reflections, and micro-expressions) requires no user action but is vulnerable to sophisticated deepfakes. Active liveness (requiring the user to blink, smile, or follow instructions) is harder to fake but adds minor friction. Behavioral liveness (analyzing reaction time, movement patterns, and interaction consistency) works invisibly but requires baseline training. Cryptographic liveness (requiring real-time digital signatures) is highly secure but requires device security and user understanding. Most effective systems combine multiple approaches. A system might use passive analysis first, escalate to active challenges if signals are uncertain, and require cryptographic confirmation for high-value transactions. This layered approach balances security and usability.
Does proof of humanness require storing personal biometric data?
No, and this is the key advantage. Properly implemented proof-of-humanness systems verify humanness in the moment and discard the underlying data immediately after. The verification happens, the transaction completes, and the behavioral signals or facial analysis used for verification are deleted. No database of stored biometric data means no centralized target for hackers. No leaked database of facial scans that fraudsters can use to create deepfakes. Some systems use zero-knowledge proofs—cryptographic techniques where you prove facts about yourself without revealing the facts themselves. Others use edge processing where verification happens on your device and only a yes/no result is transmitted to the server. The principle is consistent: verify now, discard data immediately, minimize permanent records.
How much friction does proof of humanness add to user experience?
Minimal friction when implemented intelligently. Liveness detection (blink three times, follow a dot) takes 3-5 seconds. Behavioral verification happens invisibly while you're naturally using the system. Cryptographic signing takes 2-3 seconds if the user's device is properly configured. Compare this to SMS verification (waiting for text, finding code, typing it in), which takes 30+ seconds, or calling customer service (10+ minutes). The key to low friction is risk-based activation: only require verification for genuinely risky transactions (wire transfers, account modifications, API access). Regular login for normal usage remains simple. User surveys show 68% of consumers accept minor friction (5-10 seconds) for meaningful security improvements. Early implementations have reported that friction-related drop-off is negligible when verification is limited to truly sensitive transactions.
How does proof of humanness comply with privacy regulations like GDPR?
Proof of humanness aligns with GDPR's principles better than traditional biometric storage. GDPR requires data minimization (collect only what's necessary) and purpose limitation (use data only for stated purposes). Proof-of-humanness systems collect behavioral or biometric signals only during transaction verification and delete them immediately, satisfying data minimization. They use the data only to verify humanness and authorize the transaction, satisfying purpose limitation. GDPR also gives individuals rights to access, correct, and delete their personal data. Ephemeral verification systems satisfy these rights automatically because there's no stored data to request, correct, or delete. GDPR actually favors proof-of-humanness approaches over traditional biometric databases. This is why the EU is seeing early adoption of these technologies.
What happens if proof of humanness fails or gives a false positive?
Graceful degradation is essential. If the system can't verify humanness through primary methods (poor camera, accessibility issues, etc.), it escalates to alternative verification—security questions, phone verification, agent review. False positives (legitimate user flagged as suspicious) require human review. Customer service teams should be trained to quickly resolve these cases. Well-designed systems use progressive verification: start with low-friction methods, escalate only if uncertain. False positive rates below 1% are standard with modern systems. The fallback options and human review processes ensure users can always complete legitimate transactions, even if automated verification fails.
How does proof of humanness scale to large transaction volumes?
Large-scale implementation requires careful architecture. Cloud infrastructure processes verification in parallel, with typical latency of 200-500ms for most verification methods. Hardware acceleration (GPUs for facial analysis, specialized cryptographic processors) handles high volumes efficiently. Edge processing (verification on user devices before transmission) distributes computation load. Tiered verification (passive analysis first, active challenges only if needed) reduces computational burden for obvious cases. Major financial institutions handle millions of transactions daily and have proven proof-of-humanness can scale to this volume. The per-transaction computational cost is typically under 1 cent, making it economically viable even for institutions with narrow margins.
What is the implementation timeline for proof of humanness?
Pilot programs take 8-12 weeks: select 5-10% of transactions, measure fraud reduction and friction. Limited rollout takes 3-6 months: expand to 25-50% of transactions, train staff, refine processes. Full implementation takes 6-12 months depending on technical complexity and organizational size. A small fintech can implement in 2-3 months. A large bank with complex legacy systems might take 12-18 months. The critical factor is not speed but thoroughness. Rushing implementation increases false positives and user friction. Phased rollout allows learning and optimization at each stage. Most institutions view this as a 12-month program from decision to full deployment.
How does proof of humanness affect fraud rates in practice?
Early implementations report 70-90% reduction in account takeover fraud within six months. Deepfake fraud decreases even more dramatically because the technology directly defeats deepfake attacks. Wire transfer fraud drops significantly because humanness verification is specifically applied to high-risk transactions. However, proof of humanness doesn't eliminate fraud entirely—it shifts it. Some fraudsters abandon your institution for competitors without these protections. Some adapt to alternative fraud vectors that bypass your specific verification. The goal is not zero fraud (impossible) but reducing fraud below the cost of prevention. When fraud reduction saves more than the system costs, the business case is proven.
What's the cost of implementing proof of humanness?
Variable based on approach and scale. Licensing existing solutions:

Conclusion: Rebuilding Digital Trust for the AI Age
We're living through a transition that few fully appreciate. For decades, digital trust was built on a simple premise: we can verify you are who you claim to be through credentials, credentials that are increasingly inadequate against sophisticated fraud.
Deepfakes have broken this model. When video and audio can be convincingly faked, and when 67% of the population has lost trust in digital systems, something fundamental has shifted. The old verification paradigm isn't broken because the technology isn't good enough—it's broken because the problem has fundamentally changed.
You can't out-detect the fakes forever. Detection is reactive. Fraudsters will keep improving. But you can prove the real right now.
Proof of humanness represents a paradigm shift. Instead of asking "Is this content synthetic?" you ask "Is a genuine human actually making this transaction right now?" This is answerable. This is verifiable. This is something that happens in the present moment and can't be circumvented with pre-recorded deepfakes or voice clones.
The technology works. Early implementations prove fraud reduction is dramatic and real. The business case is compelling: prevent one incident and you've justified years of technology investment. The privacy benefits are profound: verification without storing vulnerable biometric data. The regulatory alignment is clear: institutions implementing proof of humanness are demonstrating proactive fraud prevention and compliance.
What's remarkable is that we're still in the early phase. Most financial institutions haven't implemented proof of humanness at scale. Most digital services still rely on static credentials. The technology exists. The need is urgent. But adoption hasn't yet reached critical mass.
This creates a competitive opportunity. Institutions that move now—that implement proof of humanness thoughtfully, iteratively, and at scale—will differentiate themselves in markets where digital confidence has become scarce and valuable. They'll attract security-conscious customers. They'll reduce fraud dramatically. They'll build regulatory goodwill. They'll establish competitive advantages that persist for years.
The future isn't about detecting fakes better. It's about proving the real more convincingly. Organizations that understand this distinction and act on it will lead in the next era of digital commerce, where trust isn't assumed—it's cryptographically verified, behaviorally confirmed, and humanly authenticated in real-time.
The question isn't whether proof of humanness will become standard. It will. The question is whether you'll lead the transition or follow it.

Key Takeaways
- Deepfake fraud rose 3,000% in 2023 with average losses of $500,000 per incident, making traditional detection inadequate
- 67% of UK adults trust the internet less than ever; detection-based approaches are failing because fraudsters keep improving faster than detection tools
- Proof of humanness verifies genuine human interaction in real-time without storing vulnerable biometric data, shifting from detecting fakes to proving authenticity
- Single fraud prevention through proof of humanness typically pays for itself in six months while providing competitive advantage in trust-depleted markets
- Phased implementation starting with 5-10% of high-risk transactions allows institutions to measure impact and optimize before scaling organization-wide
Related Articles
- AI-Generated Reddit Hoax Exposes Food Delivery Crisis [2025]
- Grok Business and Enterprise: Elon Musk's Answer to ChatGPT [2025]
- Covenant Health Breach Exposes 500K Patients: What Happened [2025]
- Ultraloq Bolt Sense Smart Lock: Face & Palm Recognition [2025]
- Lockin V7 Max: The Future of Wireless-Charging Smart Locks [2025]
- SwitchBot Lock Vision: Facial Recognition Smart Deadbolt [2025]
![Deepfakes & Digital Trust: How Human Provenance Rebuilds Confidence [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/deepfakes-digital-trust-how-human-provenance-rebuilds-confid/image-1-1767713863883.jpg)



