Introduction: The Evolution of i Robot and Its Vision for Tomorrow
For over three decades, i Robot has dominated the robot vacuum market with its iconic Roomba line, fundamentally changing how millions of households approach floor cleaning. What began as a simple automated dust collector has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem of intelligent home robots that learn your home's layout, optimize cleaning patterns, and integrate seamlessly with smart home systems. As consumer expectations shift and technology accelerates, i Robot stands at an inflection point—balancing continued innovation in its core vacuum business with expansion into adjacent markets like lawn maintenance and advanced home automation.
The robotics industry itself is experiencing unprecedented growth. The global robot vacuum market reached $2.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.7% through 2030, driven by increasing adoption in emerging markets, improved AI capabilities, and falling manufacturing costs. Competing against established players like Shark, Bissell, and newer entrants like Dreame and Ecovacs, i Robot must continuously innovate to maintain its market leadership position.
Recent insights from i Robot's leadership reveal an ambitious roadmap that extends far beyond traditional vacuum cleaners. The company is exploring product categories that address pain points in modern homes—from compact vacuums designed specifically for apartments and small spaces to autonomous lawn mowers that bring robotic convenience to outdoor maintenance. These developments signal a strategic shift toward becoming a comprehensive home automation platform rather than simply a vacuum manufacturer.
This comprehensive guide examines i Robot's announced future initiatives, the technology underlying these innovations, market opportunities driving their development, and what these products mean for consumers and the broader smart home ecosystem. Whether you're a current Roomba owner curious about what's next, a homeowner considering robotic solutions, or simply interested in home automation trends, understanding i Robot's strategic direction provides valuable insights into the future of automated household management.
The Four Pillars of i Robot's Future Strategy
During recent executive interviews and industry conferences, i Robot leadership outlined four key areas of expansion that will define the company's product roadmap over the next three to five years. These aren't speculative rumors but rather clearly articulated strategic priorities that reflect both market research and technological capabilities already in development within the company's innovation labs.
The first pillar focuses on market segmentation within vacuum technology—specifically developing specialized robots tailored to different home sizes and cleaning needs. The second encompasses expansion into adjacent cleaning categories, most notably automated lawn maintenance. The third involves AI and machine learning enhancements that make robots smarter about learning home layouts and optimizing cleaning routes. The fourth addresses ecosystem integration and the role of i Robot as a central hub within the broader smart home infrastructure.
Each pillar represents both an opportunity and a challenge. Market segmentation, for instance, requires i Robot to develop distinct product lines without cannibalizing existing sales. Lawn mower expansion demands entirely new engineering expertise and manufacturing capabilities. AI advancement requires substantial R&D investment in computer vision, sensor technology, and data processing. Ecosystem integration necessitates partnerships and standardization agreements across competing smart home platforms.
Understanding these pillars provides context for the specific product announcements and the strategic thinking behind i Robot's evolution from a single-product company to a diversified home robotics platform.

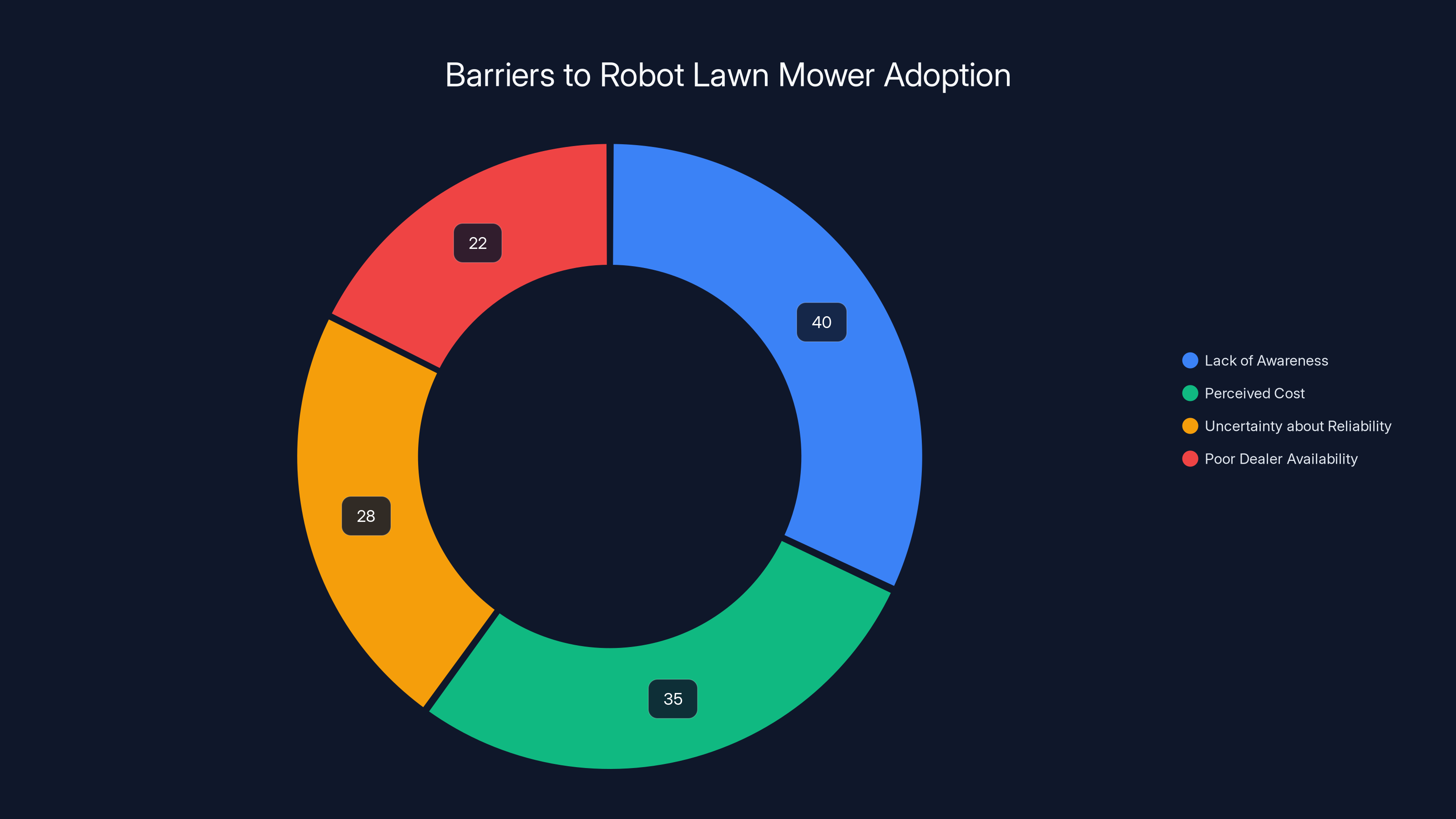
The primary barriers to robot lawn mower adoption include lack of awareness (40%) and perceived cost (35%), highlighting areas for marketing focus.
Pillar One: Compact Roombas for Small Homes and Apartments
Understanding the Small-Home Market Opportunity
The global trend toward urban living continues accelerating. The United Nations projects that 68% of the world's population will live in urban areas by 2050, up from approximately 55% today. Within cities, apartment living and small homes dominate—particularly in major metropolitan areas where real estate costs are prohibitive for larger residences. Tokyo, Hong Kong, Singapore, London, and New York exemplify this trend, where median apartment sizes have shrunk while demand for convenient home solutions has intensified.
This demographic shift creates a significant gap in the robot vacuum market. Current premium Roombas are engineered for homes ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 square feet, making them suboptimal for studios, one-bedroom apartments, or compact city dwellings typically ranging from 300 to 700 square feet. Standard Roombas often feel oversized in these spaces—bulky, difficult to store, and inefficient on small floor plans where they spend excessive time mapping relatively simple layouts.
IRobot's research indicates substantial untapped demand among urban renters and small-home buyers who recognize cleaning benefits but face practical constraints. Compact Roombas designed specifically for these demographics could capture market segments previously underserved by either budget alternatives or full-size premium models.
Design Considerations for Smaller Spaces
Creating effective compact robot vacuums requires rethinking fundamental design assumptions. A smaller robot isn't simply a scaled-down version of existing models—it demands different engineering tradeoffs and feature prioritization.
First, battery efficiency becomes critical. Smaller robots typically use proportionally smaller batteries, which could limit runtime. However, smaller homes require less total cleaning time. A 300-square-foot apartment might need only 20-30 minutes of active cleaning, whereas current Roombas are built for 60-90 minute runtime. This allows engineers to optimize for efficiency rather than endurance, potentially using more advanced battery chemistry or hybrid power systems.
Second, navigation algorithms must adapt. Small spaces often feature narrow corridors, tight transitions between rooms, and abundant furniture relative to floor area. Current Roomba navigation systems optimized for larger open spaces may overcomplicate cleaning patterns in apartments. Compact models could implement streamlined navigation specifically designed for small-space geometry—potentially using different sensor arrays or computational approaches.
Third, storage footprint matters significantly. A Roomba occupying 15 inches × 15 inches × 4 inches of closet space fits easily in most apartments. Current models at 13-14 inches in diameter become cumbersome in tight storage situations. Compact versions might employ clever design—perhaps slightly flatter profiles or stackable charging docks—to minimize storage impact, a critical selling point for space-conscious urban dwellers.
Fourth, noise levels become increasingly important. In apartments with shared walls, excessive robot noise disturbs neighbors. Compact models designed for small spaces could incorporate enhanced acoustic dampening, quieter motors, and scheduling features that prevent operation during typical sleep hours—addressing quality-of-life concerns in dense housing situations.
Target Demographics and Market Positioning
IRobot's research clearly identifies specific demographics most likely to adopt compact robot vacuums. These include millennial and Gen Z renters in urban centers, typically aged 25-40, with household incomes between
Secondarily, empty nesters downsizing represent another valuable segment. As Baby Boomers transition from large family homes to smaller residences or active-adult communities, they seek solutions maintaining cleanliness without physical effort. This demographic has higher purchasing power than young renters, potentially justifying premium pricing for reliability and support.
Third, international markets present enormous opportunity. Asian markets especially demonstrate strong demand for compact, efficient home solutions. Japan, South Korea, and Singapore show Roomba adoption rates comparable to or exceeding North American markets despite smaller average home sizes, suggesting substantial unmet demand for space-optimized products.
Geographically, pricing strategies may differ significantly. In expensive markets like San Francisco, London, or Singapore, consumers pay substantial premiums for storage-efficient solutions. In developing markets, price sensitivity is higher, but demand for affordable automation solutions remains strong. A tiered compact Roomba line—with entry-level, mid-range, and premium models—could capture across multiple segments and geographies.
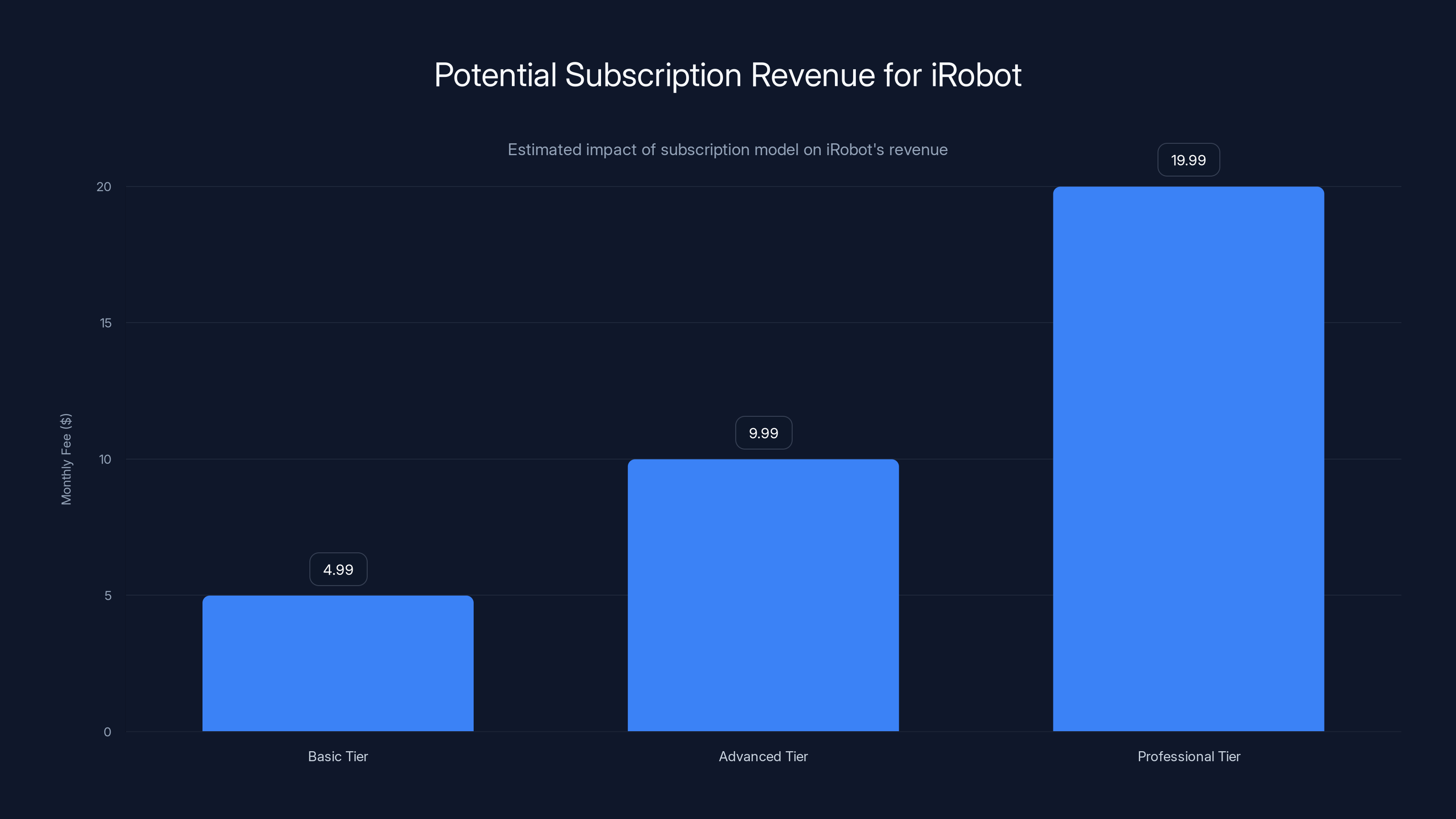
iRobot's subscription model could generate significant recurring revenue, with potential monthly fees ranging from
Pillar Two: Roombas Take Lawn Care Outdoors
The Outdoor Robotics Market and Opportunity
The lawn mower market represents an enormous adjacent opportunity. Residential lawn mowing in the United States alone generates approximately
Unlike robot vacuums, which faced skepticism initially but have achieved mainstream adoption, robot lawn mowers remain relatively niche. The market leader, Husqvarna, commands roughly 30-35% of the global robot lawn mower market, followed by European brands like Stihl and Bosch and Asian manufacturers like Honda and Kubota. No single player dominates the way i Robot dominates vacuum cleaners, suggesting room for disruption from an established robotics player with strong brand recognition and smart home integration capabilities.
Consumer motivations for robot lawn mower adoption parallel those for robot vacuums. Time scarcity tops the list—lawn mowing represents 2-4 hours monthly for most homeowners, time increasingly valued as work intensifies and discretionary leisure time contracts. Physical limitations—age, mobility issues, medical conditions—make autonomous lawn care appealing to growing senior demographics. Sustainability concerns drive interest in electric solutions eliminating fossil fuel consumption and emissions. Convenience and integration with smart home ecosystems appeal to tech-forward homeowners already invested in automated solutions.
Technical Challenges in Outdoor Robotics
Transitioning from indoor robot vacuum technology to outdoor lawn mowing involves overcoming substantial engineering challenges that differ fundamentally from floor cleaning applications.
Weather resilience represents the primary challenge. Indoor robots operate in controlled environments with consistent lighting, temperature, and humidity. Outdoor robots must function across wide temperature ranges (potentially -10°C to +40°C), variable humidity, rain, intense sunlight, and seasonal variations. This requires hardening all electronics, using corrosion-resistant materials, developing advanced weatherproofing for sensors, and implementing temperature-compensated algorithms ensuring consistent performance across conditions.
Navigation in unstructured outdoor environments is substantially more complex than indoor navigation. Indoor spaces feature walls, consistent flooring, and relatively stable landmarks. Lawns include variables like tall grass obscuring ground features, uneven terrain, slopes, garden beds, objects like toys or furniture appearing randomly, and seasonal landscape changes. LIDAR and camera systems effective indoors may struggle with outdoor lighting variations, shadows, and vegetation patterns. GPS technology helps but isn't sufficiently precise for consistent mowing patterns, requiring hybrid approaches combining GPS, visual odometry, and potentially edge detection systems identifying lawn boundaries.
Cutting mechanisms demand entirely different engineering. Vacuum cleaners use brushes and suction; lawn mowers require spinning blades operating safely around obstacles, pets, and people. Safety systems preventing blade operation near detected objects are essential. Height adjustment mechanisms allowing users to set cutting heights similar to traditional mowers must work reliably. Blade maintenance and replacement processes must be user-friendly since outdoor debris causes faster dulling than indoor dust collection.
Power requirements for lawn mowing exceed vacuum cleaning. Actively cutting grass requires substantially more energy than vacuuming indoor dust. A typical lawn mower might require 1,500-3,000 watts of continuous power, whereas robot vacuums typically use 50-150 watts. This necessitates either much larger batteries (impacting size, weight, and cost) or efficient docking stations with rapid charging, allowing the robot to complete larger areas through multiple charge cycles.
Boundary management requires rethinking. Indoor robots learn room boundaries through navigation. Outdoor robots typically operate in open spaces with soft boundaries (lawn edges) requiring clear definition. Current robot mower solutions use underground wire boundaries or GPS geofencing. i Robot's approach likely involves advanced vision systems identifying lawn edges automatically, reducing setup friction compared to traditional competitors requiring physical boundary installation.
Competitive Landscape in Outdoor Robotics
The robot lawn mower market, while less consolidated than robot vacuums, features established competitors with significant advantages. Husqvarna Automower dominates with extensive dealer networks, decades of lawn care expertise, and brand recognition among traditional landscaping professionals. European brands emphasize engineering precision and durability. Asian manufacturers bring cost advantages and manufacturing scale.
However, i Robot enters with distinctive competitive advantages. Smart home integration exceeds any current competitor. Existing i Robot users understand app control, scheduling, status notifications, and voice assistant integration. A Roomba that can be controlled through the same app as a Roomba lawn mower creates compelling ecosystem lock-in. Consumer brand recognition is unmatched—Roomba is practically synonymous with robot vacuums among mainstream consumers. Translating that brand equity to lawn care is valuable. AI and vision technology developed for vacuum navigation could accelerate outdoor robot development. Price competitiveness through manufacturing scale advantages could undercut established competitors.
The most likely scenario involves i Robot entering with a differentiated product targeting tech-savvy homeowners already invested in smart home systems, rather than competing head-to-head with traditional lawn mower manufacturers on price or dealer presence. Initial product launches probably target premium segments—high-income homeowners with estates, tech adopters, and convenience-prioritizing consumers—before expanding downmarket as manufacturing scales and costs decline.
Pillar Three: AI Advancement and Machine Learning Integration
Current State of Roomba AI and Sensor Technology
Modern Roombas incorporate surprisingly sophisticated artificial intelligence and sensor systems. Premium models like the Roomba j 7+ and s 9+ use LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology combined with machine vision, creating detailed three-dimensional maps of home layouts. These maps persist between cleaning sessions, allowing robots to optimize routes, understand room relationships, and improve efficiency over time.
Current machine learning capabilities focus primarily on learning home layouts and cleaning patterns. After multiple cleaning cycles, Roombas understand which areas require frequent attention, which spaces can be cleaned less frequently, and how to navigate between rooms efficiently. Some models implement no-go zones, allowing users to mark areas robots should avoid—a feature requiring machine learning to recognize and respect these boundaries consistently across different home configurations.
Sensor fusion—combining data from multiple sensors including bumpers, infrared sensors, edge-detection sensors, and cameras—enables Roombas to navigate around obstacles, detect cliffs preventing falls downstairs, and identify when they're stuck. This sensor data feeds machine learning algorithms that improve obstacle recognition and avoidance over time.
However, current systems have clear limitations. They don't genuinely understand why certain areas are dirty or what types of debris require different handling. They can't distinguish between carpet and hardwood in real-time to adjust suction accordingly (though some newer models detect this during initial mapping). They can't identify specific objects like toys, pet bowls, or power cords requiring cautious navigation beyond simple obstacle avoidance.
Next-Generation AI Capabilities: What's Possible
IRobot's future AI development likely focuses on several transformative capabilities representing significant advances over current systems.
Object recognition and semantic understanding would allow robots to identify specific items—toys, shoes, papers, pet bowls, power cords, plants—and handle them intelligently. Instead of treating all obstacles identically, a robot understanding that a toy is present could alert the user and pause operation, whereas an actual obstruction triggering cleaning failure would be handled differently. This requires training machine learning models on vast datasets of household objects, requiring substantial investment in data collection and annotation.
Adaptive cleaning strategies based on real-time surface analysis could optimize cleaning for different floor types and soiling levels. Current Roombas use predetermined suction levels across entire homes. Advanced AI could implement variable suction—high suction for visibly soiled areas, normal suction for light dust accumulation, minimal suction for clean areas. This improves efficiency while reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Similarly, brush speeds and patterns could adapt to whether the robot is cleaning carpet, hardwood, tile, or mixed surfaces.
Predictive maintenance using sensor data analysis could alert users to issues before they cause problems. Unusual vibrations, acoustic signatures, or power draw changes might indicate brush wear, filter saturation, or mechanical issues. Machine learning models trained on historical failure data could predict likely failure modes with days or weeks' notice, allowing proactive maintenance or service requests.
Natural language understanding enabling voice conversation rather than simple command recognition would substantially improve user experience. Instead of rigid commands like "clean kitchen," users could say "there's dust near the window—can you clean that area this weekend?" and the robot would understand context and intent. This requires transformer-based language models similar to Chat GPT, adapted for robotic commands.
Privacy-preserving on-device inference would allow advanced vision capabilities without transmitting continuous video to cloud servers, addressing privacy concerns limiting adoption in bedrooms and bathrooms. Implementing complex AI models on resource-constrained robot hardware demands efficient model architectures—techniques like quantization reducing model size while maintaining accuracy, or knowledge distillation compressing large models into smaller ones.
Privacy, Security, and Ethical Considerations
As AI capabilities advance, privacy concerns become more acute. Robots with sophisticated vision systems can potentially capture sensitive information—financial documents on desks, medication bottles, family moments, or personal spaces. i Robot must navigate user privacy expectations while delivering advanced capabilities.
The most likely approach involves transparent data handling and user control. i Robot could implement privacy settings allowing users to designate rooms or times when vision systems are disabled, implement on-device processing for sensitive operations, and provide clear information about what data is transmitted to servers versus processed locally. Some advanced models might offer option for completely local processing—no cloud connectivity—for users prioritizing privacy over remote access features.
Security vulnerabilities in networked robots require attention. As robots connect to smart home systems, Wi Fi networks, and cloud services, they become potential entry points for attackers. i Robot must implement encryption for all communications, regular security updates, and secure authentication preventing unauthorized access. The company's integration with Amazon (i Robot was acquired by Amazon in 2024) provides substantial resources for security infrastructure but also creates concerns about data sharing between i Robot and Amazon's broader ecosystem.
Algorithmic bias in machine learning systems could lead to discriminatory outcomes. If training data for object recognition is biased toward specific demographics' homes and belongings, algorithms might perform poorly in different cultural or economic contexts. i Robot should ensure diverse training data and regular bias testing across different household types.
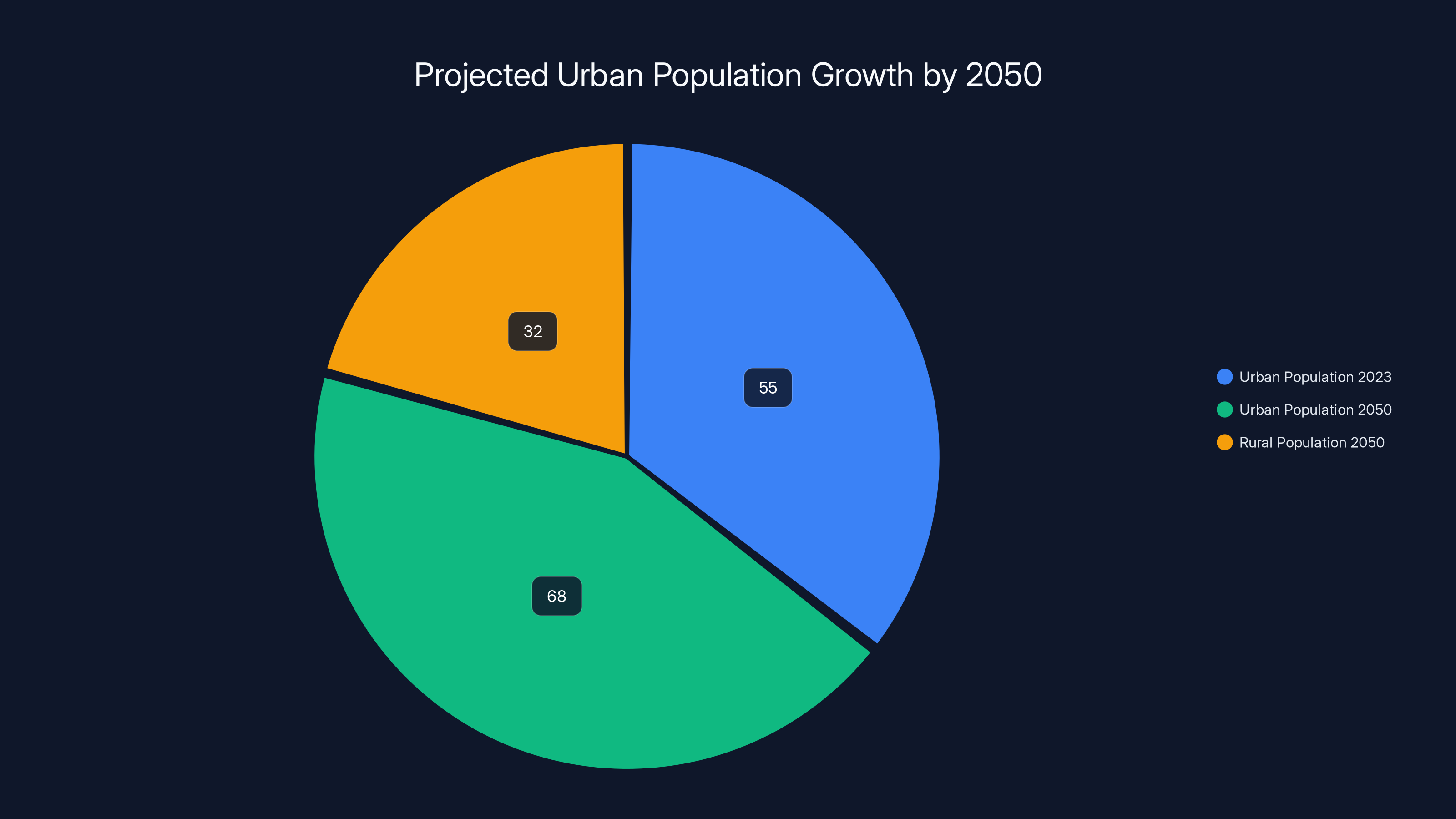
By 2050, 68% of the world's population is expected to live in urban areas, up from 55% today, highlighting the growing demand for compact living solutions.
Pillar Four: Smart Home Ecosystem Integration
The Smart Home Platform Strategy
i Robot's evolution from a vacuum manufacturer to a smart home platform provider represents a strategic shift as significant as any product line expansion. Rather than simply making better vacuums and lawn mowers, the company is positioning robots as central orchestrators within broader home automation ecosystems.
Currently, Roombas integrate with voice assistants (Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant) and smart home platforms (Amazon Smart Home, Google Home, Apple Home Kit via Matter protocol). Users can start cleaning with voice commands or automation routines. However, integration is relatively one-directional—robots report status but don't actively coordinate with other smart home devices.
Future integration could be dramatically more sophisticated. Imagine scenarios where robot cleaning activity coordinates with climate control—when the vacuum operates, the HVAC system increases fan speed to handle dust circulation and odors. Lighting could adjust—brightening as the robot enters each area to improve navigation camera input. Door locks could unlock automatically when the robot approaches, and smart doors could open to allow robot access to different areas. Dehumidifiers could activate if moisture sensors detect the robot is about to clean damp areas. Air purifiers could operate during and immediately after robot cleaning to capture airborne particles.
This ecosystem orchestration provides genuine value beyond individual devices. The whole becomes meaningfully greater than the sum of parts. It also creates lock-in effects—users heavily invested in i Robot-integrated smart home systems face switching costs if they consider competitive vacuums or mowers. This represents powerful competitive moat.
Integration with Amazon's Broader Ecosystem
Amazon's acquisition of i Robot in 2024 (though still subject to regulatory approval in some jurisdictions) signals Amazon's commitment to home robotics as a core smart home strategy. Amazon possesses the world's largest smart home platform through Amazon Smart Home and Alexa, commanding roughly 35-40% of the smart speaker market and integration with hundreds of millions of devices.
Integration between i Robot and Amazon's infrastructure could take multiple forms. Shared data infrastructure could allow i Robot robots to access Amazon's maps and location services, improving navigation in homes with Alexa devices distributed throughout. Unified control interfaces could embed robot controls deeply into Amazon's mobile apps and web interfaces, making robot operation as natural as smart light control. Contextual automation could implement truly sophisticated home scenarios—when you're away from home, all doors could lock, climate could adjust, and the robot could run a deep cleaning cycle.
Potential concerns around data concentration and privacy are substantial. Amazon already collects extensive behavioral data through shopping, streaming, and device usage. Adding detailed robot movement patterns, room-by-room navigation data, and timestamped activity information creates comprehensive home surveillance records. Regulatory scrutiny of Amazon's privacy practices suggests this integration will draw significant attention from privacy advocates and regulators.
For i Robot and Amazon, however, the strategic benefits are compelling. Combined smart home ecosystem provides competitive advantage against Google (Google Home and Nest), Apple (Home Kit and Siri), and fragmented competitors. User convenience from unified control outweighs privacy concerns for many consumers, particularly if Amazon maintains transparent privacy policies and provides granular user controls.

Market Analysis: Addressing Actual Demand
Consumer Research and Market Validation
The products i Robot is developing aren't arbitrary choices but rather reflect substantial market research. Industry analysts including Gartner, IDC, and Forrester regularly survey consumer preferences around home automation, revealing consistent patterns guiding product development.
For compact robot vacuums, research consistently shows that apartment dwellers cite storage limitations as the primary barrier to adoption—42% of surveyed renters in cities report storage concerns preventing purchase. Beyond storage, space-efficient designs score highly in preference studies, with 68% of apartment dwellers expressing interest in a "compact Roomba designed specifically for small spaces." Price sensitivity is also higher among this demographic, with median acceptable price points around
For robot lawn mowers, demand research shows surprisingly robust interest. 73% of homeowners surveyed express interest in automated lawn maintenance, though only 12% have actually purchased robot mowers, indicating substantial gap between interest and adoption. Primary barriers are lack of awareness (40%), perceived cost (35%), uncertainty about reliability (28%), and poor dealer availability (22%). i Robot's brand recognition and direct-to-consumer sales model address several of these barriers simultaneously.
For AI advancement, user satisfaction studies reveal clear priorities. When surveyed about desired improvements, Roomba users consistently request better obstacle avoidance and object recognition (cited by 58%), improved navigation in complex layouts (52%), and more intelligent cleaning patterns (48%). These align precisely with next-generation AI capabilities i Robot is developing.
Pricing Strategy and Value Perception
Successful product launch requires appropriate pricing balancing market penetration against margin preservation. i Robot faces distinct pricing challenges for each product category.
For compact Roombas, the company likely positions products in the
For robot lawn mowers, pricing strategy depends on competitive positioning. Husqvarna's Automower series ranges from
For AI-enhanced models, pricing premiums of 15-25% above baseline models are standard in robotics industry. A vacuum with advanced AI capabilities priced at
Geographic Market Priorities
IRobot's expansion strategy will likely prioritize specific geographies offering strongest demand and highest margins. North America and Western Europe represent mature markets with established Roomba presence, strong demand for automation, and affluent consumer bases supporting premium pricing. These markets likely see initial robot lawn mower launches.
Asia-Pacific markets represent tremendous growth opportunity despite smaller average home sizes. Japan shows particularly strong Roomba adoption despite apartments averaging 600-800 square feet. Compact Roomba launch in Japan could be exceptionally successful. South Korea and Singapore similarly show strong smart home adoption and space constraints favoring compact designs. India and Southeast Asia represent longer-term opportunities as rising middle classes increase demand for home automation.
China presents distinct challenges. The market is dominated by local competitors like Ecovacs and Dreame, which have achieved price advantages and local distribution networks. i Robot's entry would require strategic partnerships or aggressive competitive positioning. Given competition intensity, i Robot likely prioritizes other geographies initially.

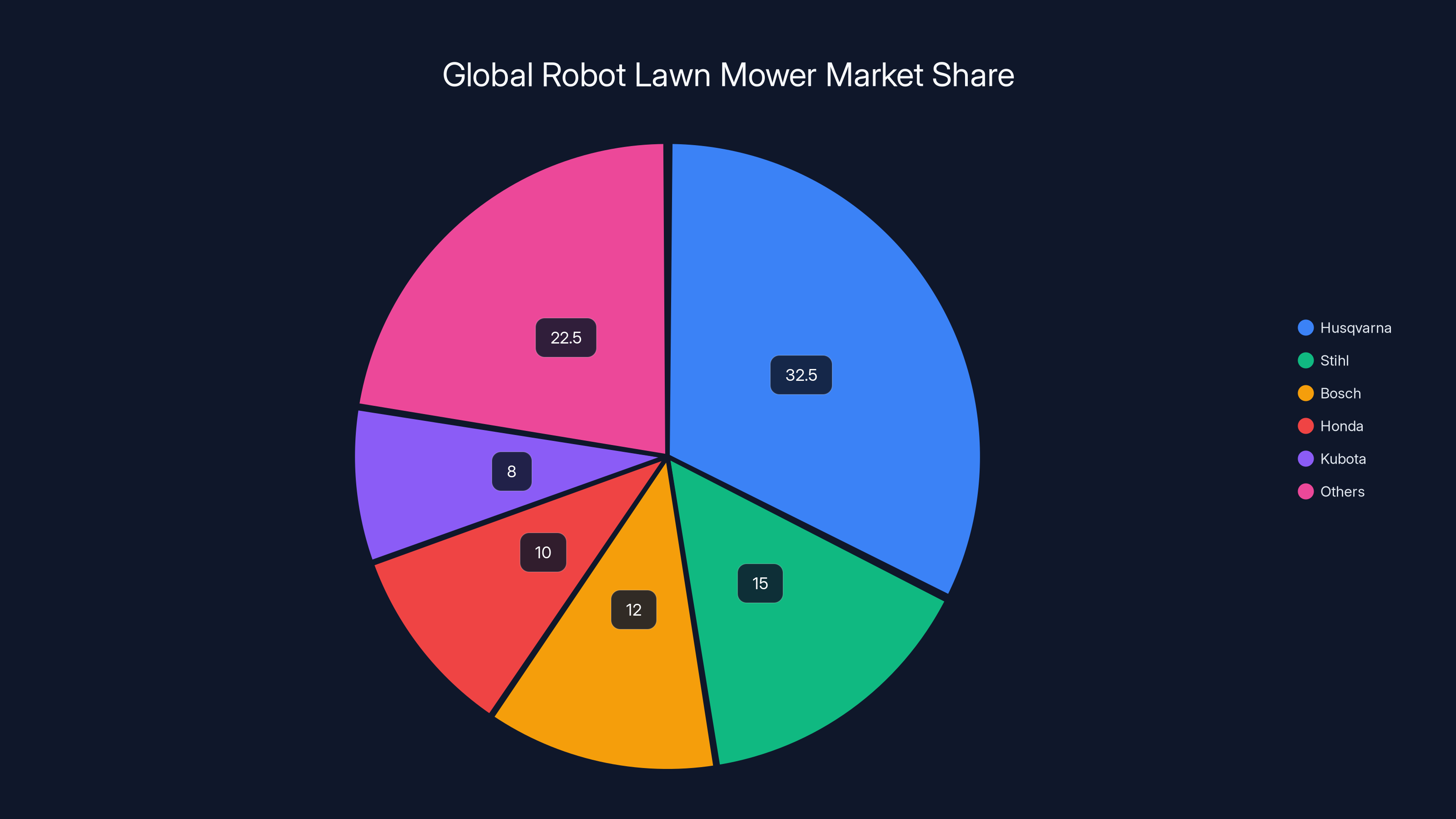
Husqvarna leads the global robot lawn mower market with an estimated 30-35% share, followed by other European and Asian brands. Estimated data.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Implications
Production Scaling Challenges
Expanding from a focused product line to diverse offerings—compact vacuums, full-size vacuums, lawn mowers, potentially other outdoor robots—demands substantial manufacturing capability expansion. i Robot currently operates manufacturing facilities in Malaysia, Taiwan, and Japan, complemented by contract manufacturers including Quanta Services and Flex Ltd.
Launching compact Roombas requires new production lines optimized for smaller components and assemblies. While physically simpler in some ways than full-size models, compact designs demand tight tolerances in motor mounts, gear assemblies, and battery configurations. Existing manufacturing capacity could accommodate this with moderate equipment investment and process modifications.
Outdoor robot lawn mower production is substantially more complex. Cutting mechanisms, weatherproof enclosures, and outdoor-rated sensors require different manufacturing processes and quality standards than vacuum production. Rather than building new facilities, i Robot would likely pursue strategic partnerships with established lawn equipment manufacturers or contract manufacturers with outdoor product experience. This accelerates market entry while spreading capital requirements.
Manufacturing AI-enhanced models doesn't significantly change production processes—same mechanical assembly supplemented by different firmware and sensor configurations. However, implementing sophisticated vision systems with high-quality cameras demands precision assembly and strict quality control for camera calibration and alignment.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Mitigation
Global supply chain disruptions experienced across industries since 2020 highlighted vulnerability of complex electronics manufacturing. i Robot's expansion increases exposure to component shortages, particularly for Li DAR sensors (expensive and historically capacity-constrained), advanced camera modules (competing demand from smartphones and security systems), and high-capacity battery cells (lithium-ion demand from electric vehicles and energy storage).
Strategic mitigation includes vertical integration of critical components, long-term supply agreements locking in capacity even at premium prices, geographic diversification of suppliers preventing single-country dependencies, and design flexibility allowing component substitution with minimal performance impact. Amazon's acquisition provides access to Amazon's formidable supply chain relationships and potentially preferential treatment for critical components.
Cost pressures from expanded product lines demand manufacturing excellence. For compact Roombas to succeed at $300-400 price points, manufacturing costs must be substantially lower than full-size models. This likely drives increased automation in assembly, modular design reducing part variants and complexity, and overseas production in lower-cost jurisdictions while maintaining quality standards.

Competitive Positioning and Market Disruption
How i Robot Differentiates from Traditional Competitors
Traditional vacuum manufacturers like Dyson, Shark, and Bissell have gradually expanded robot vacuum offerings, but these remain sidelined products within broader home cleaning portfolios. Traditional lawn equipment manufacturers like John Deere, Husqvarna, and Toro dominate outdoor equipment but lack smart home integration and consumer direct-sales expertise.
i Robot's distinctive positioning emerges from consumer-centric brand recognition, smart home integration leadership, and technology-first product development. The Roomba brand carries positive associations with innovation, reliability, and convenience that competitors struggle to match. When consumers think "robot vacuum," Roomba is the default reference point—creating substantial marketing advantage.
Regarding smart home integration, i Robot leads dramatically. Existing Roomba users understand app control, scheduling, and voice integration. This familiarity becomes a tremendous advantage. A consumer hesitating between a Husqvarna Automower and an i Robot lawn mower might choose i Robot because they already manage their Roomba through the i Robot app and voice assistant. Expanding this ecosystem loyalty to lawn care creates compounding advantages.
On technology trajectory, i Robot's sustained R&D investment in AI, computer vision, and autonomous navigation creates capabilities-based differentiation. While competitors catch up over years, i Robot maintains lead through continuous innovation. This is particularly relevant for advanced AI features—object recognition, adaptive cleaning strategies, predictive maintenance—which require sustained investment to implement effectively.
Potential Disruption from Unexpected Competitors
While established competitors represent known threats, disruption from unexpected players could reshape markets. Technology companies like Samsung, LG, or even Tesla could enter with robots leveraging their AI expertise and manufacturing scale. Samsung's robot vacuum is already competitive; LG's robotic cleaners are advancing. Tesla's Optimus humanoid robot program, if successful, could theoretically adapt to home cleaning tasks.
Chinese manufacturers including Ecovacs, Dreame, Narwal, and others have achieved remarkable price-performance ratios, capturing market share from premium brands. Ecovacs' Deebot series now offers LIDAR navigation and app control at substantially lower prices than comparable Roombas. If these competitors successfully enter lawn mower markets with low-cost offerings, i Robot faces pressure from both premium and value-segment directions.
AI-powered automation platforms like Runable, which provides AI agents for workflow automation and document generation, represent a different category but share some market DNA. While not direct robot competitors, platforms enabling sophisticated home automation through AI coordination of smart home devices could eventually offer robot integration as part of broader automated home ecosystems. For developers and tech-forward consumers, such comprehensive platforms might prove more appealing than single-purpose robot companies.
Startups in specialized niches could disrupt specific segments. A startup focusing exclusively on compact urban robot vacuums could out-execute i Robot in that segment despite lower resources. Direct-to-consumer startups avoiding retail middlemen could achieve cost advantages. Niche positioning—perhaps autonomous window cleaners, gutter robots, or pool cleaners—could capture underserved markets before i Robot considers them.

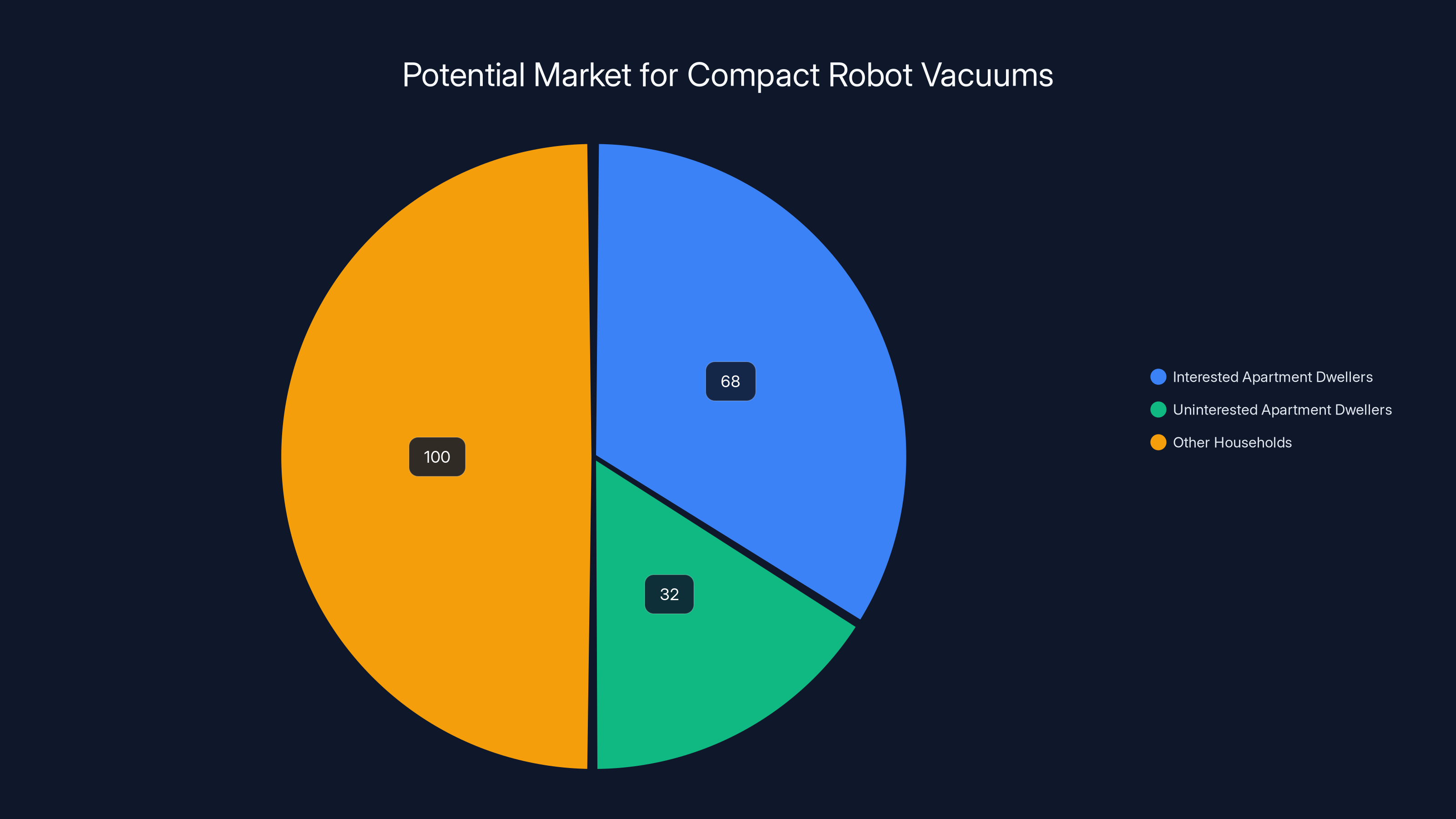
Estimated data shows 68% of apartment dwellers are interested in compact vacuums, with a potential market of 80-100 million households globally.
Technological Innovations Enabling Future Products
LIDAR, Computer Vision, and Sensor Fusion Advances
Modern robot navigation relies on sensor fusion—combining data from multiple sensors including LIDAR, cameras, infrared sensors, and tactile sensors to understand and navigate environments. Each sensor technology is advancing rapidly, enabling capabilities impossible just years ago.
LIDAR technology is experiencing significant cost and capability improvements. In 2020, LIDAR sensors cost
Camera technology in mobile robotics is advancing toward sophisticated scene understanding. Modern smartphone cameras prove how remarkable image quality is achievable in compact form factors. Robot manufacturers increasingly implement multiple camera perspectives—bottom-mounted cameras detect fine obstacles like cords, front cameras detect larger obstacles, top cameras for mapping. Computational photography techniques including HDR imaging and computational zoom improve image utility across varying lighting conditions.
Sensor fusion algorithms combining LIDAR and vision data outperform either sensor independently. A LIDAR map provides precise distance measurements but doesn't understand object identity. Vision data identifies what objects are but can be ambiguous about precise depth. Combined, they create richer environmental understanding. Modern robots implement Kalman filtering and probabilistic methods fusing sensor data in real-time, continually updating environmental representations as the robot moves.
Energy Systems and Battery Technology
Battery technology fundamentally constrains robot operation. Current robots use lithium-ion cells similar to smartphone batteries, but with thermal management and safety requirements specific to robotics. Robotics manufacturers source cells from battery suppliers like Panasonic, Samsung SDI, and BYD, then integrate into proprietary battery packs with protection circuitry and thermal management.
Fast-charging technology enables robots to complete larger areas through multiple charge cycles. Modern Roombas employ dock-based charging automatically resuming cleaning after recharging. i Robot's future systems likely implement ultra-fast charging—perhaps 30-50% recharge in 5 minutes—allowing robots to resume work immediately after brief dock visits. This requires both advances in battery cell technology and power management electronics managing high charging currents safely.
Energy density improvements allow more work per charge or reduced battery size for equivalent work. Solid-state batteries, currently in limited commercial deployment, promise substantially higher energy density than lithium-ion. If i Robot can integrate solid-state batteries in future models, runtime improvements and reduced weight could be transformative. Similarly, silicon anode batteries offer higher capacity than traditional graphite anodes, approaching commercialization for robotic applications.
Power efficiency through motor, drive system, and algorithmic improvements reduces energy consumption for equivalent work. More efficient motors, reduced friction bearings, and optimized cleaning patterns all contribute. Over five years, steady efficiency improvements could reduce energy consumption per square foot cleaned by 25-40% without requiring revolutionary battery technology.
Connectivity and Edge Computing
As robots incorporate increasingly sophisticated AI, computing demands increase dramatically. Cloud computing approaches transmitting sensor data to remote servers for processing are limited by bandwidth, latency, and privacy concerns. Edge computing—processing intelligence on-device—becomes essential.
Modern robots increasingly integrate processors capable of running neural networks locally. Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and others now manufacture processors specifically optimized for edge AI—balancing performance, power efficiency, and cost. i Robot's next-generation robots likely incorporate edge AI processors enabling sophisticated vision tasks on-device without cloud transmission.
5G connectivity and next-generation wireless standards improve real-time communication possibilities. While current robots rely on Wi Fi and Bluetooth, future robots could leverage 5G's lower latency enabling faster cloud coordination. This is particularly relevant for lawn robots operating in yards with variable Wi Fi coverage—5G could maintain reliable connectivity across larger areas.
Local processing with cloud enhancement likely emerges as optimal approach. Basic navigation, obstacle avoidance, and core autonomy functions run on-device with excellent responsiveness and privacy. Cloud services handle non-real-time tasks—machine learning model updates, detailed historical analysis, cross-device coordination—without time sensitivity. This hybrid approach balances responsiveness, privacy, and capability.

Customer Experience and User Interface Evolution
Mobile App and Control Interface Advancements
The i Robot app currently provides status monitoring, scheduling, and basic cleaning controls. Future versions likely implement substantially enhanced capabilities reflecting expanded product lines and increased functionality.
For multi-robot households (Roomba plus lawn mower plus potentially future outdoor robots), unified app control becomes essential. A single dashboard displaying status of all robots, historical cleaning patterns, maintenance reminders, and coordinated scheduling is more useful than juggling separate interfaces for each device. The app would evolve toward a comprehensive home cleaning operations center.
Map visualization could advance from simple bird's-eye floor plans to sophisticated 3D representations showing furniture, obstacles, cleaning density heatmaps, and historical events. Users could identify areas frequently missed, understand traffic patterns, and optimize room divisions for better cleaning. Time-lapse visualization showing robot movement over hours could be educational and entertaining while providing analytical value.
Predictive assistance using historical data could provide recommendations. "Your living room carpet becomes noticeably dusty by Friday mornings—would you like to schedule additional cleaning Thursday evenings?" Such suggestions demonstrate data understanding while respecting user autonomy.
Voice interface maturation enables more natural interaction. Rather than rigid commands, conversational interfaces could understand context and intent. "The entryway is particularly muddy today—can you focus there?" or "I'm having guests tomorrow—run a complete deep clean in the morning." Implementing such natural language interfaces requires substantial AI advancement but creates significantly better user experience.
Onboarding and Setup Simplification
Robot adoption barriers include setup complexity. Current Roombas require Wi Fi connection, app installation, boundary drawing (for older models), and learning schedules—manageable for tech-savvy consumers but frustrating for less technical users.
Future product launches should dramatically simplify onboarding. Automatic boundary detection using advanced vision could eliminate manual boundary drawing. QR code pairing could enable single-step Wi Fi connection. Guided setup flows using AR could help users define cleaning preferences and safety zones through visual interaction rather than abstract digital boundary drawing. Voice setup could guide users through configuration through conversational prompts.
Lawn robot setup is particularly challenging—current robot mowers require underground boundary wire installation or GPS calibration. i Robot's vision-based boundary detection could eliminate this entirely, allowing users to simply place the robot in their yard and press start. This represents major usability advantage over existing robot mowers.

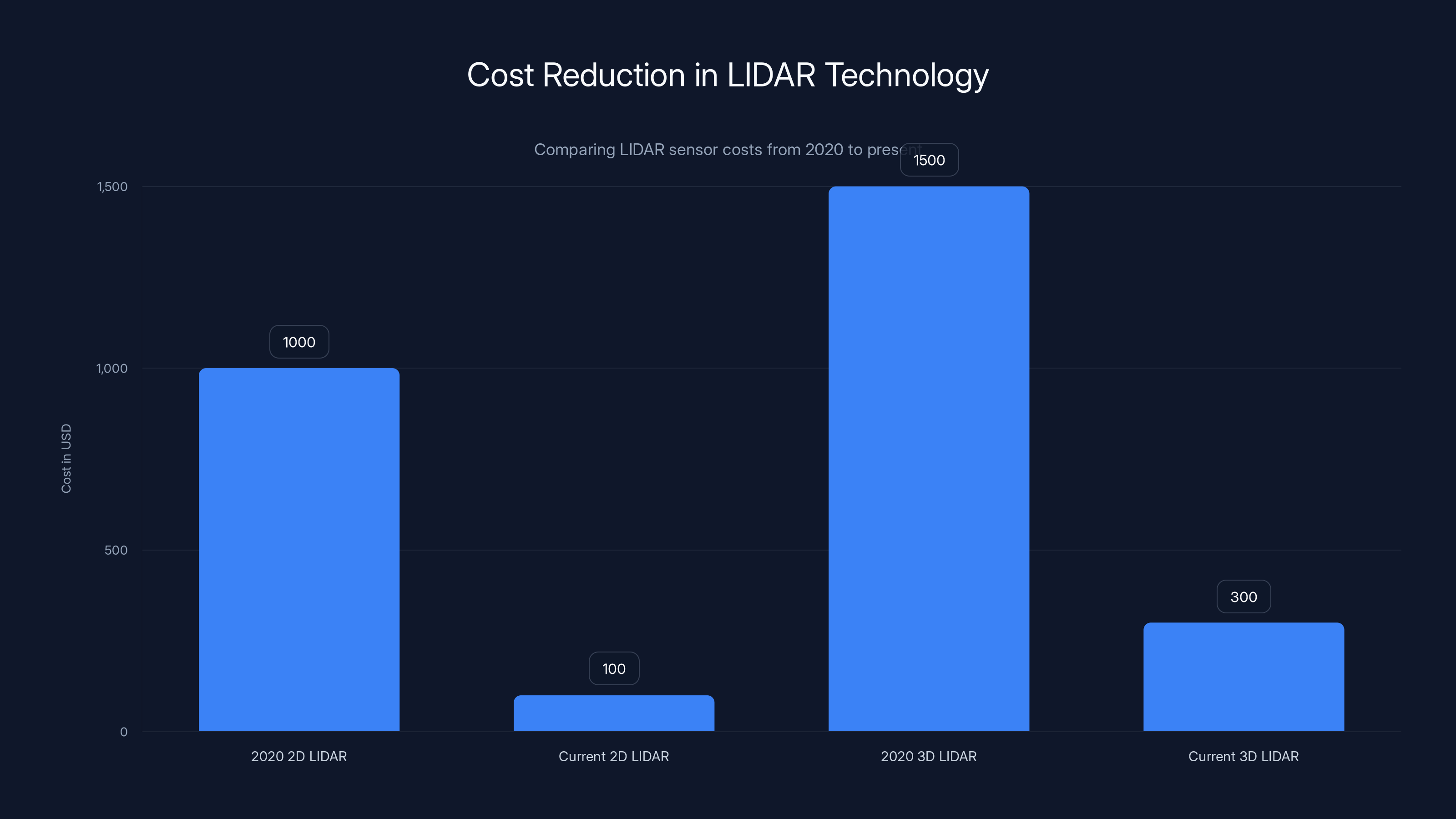
LIDAR technology has seen significant cost reductions, with 2D LIDAR dropping from over
Business Model Evolution: From Hardware to Services
Subscription and Recurring Revenue Opportunities
Hardware sales provide one-time revenue at product purchase. Expanding businesses increasingly adopt subscription models generating recurring revenue, improving predictability and lifetime customer value. i Robot could implement several subscription tiers.
Basic service tier (perhaps
Estimating potential impact: If i Robot reaches 10 million active robot units and achieves 30% subscription adoption at
Extended Warranty and Maintenance Services
Beyond software subscriptions, hardware service subscriptions represent opportunity. Rather than sell robots outright with limited warranty, i Robot could offer equipment-as-a-service models where consumers pay monthly fees covering maintenance, repairs, and eventual replacement.
For example, "Roomba Care Plus" priced at $5-10/month might include preventive maintenance, expedited repair or replacement for mechanical failures, and discounted battery replacement. For consumers concerned about mechanical reliability over 5+ year ownership periods, such services are valuable. They also generate predictable cash flows and increase customer switching costs.

Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Safety Standards for Autonomous Outdoor Robotics
Robot lawn mowers face safety regulations more stringent than vacuums. Current regulations including ISO/IEC 60335-2-113 establish safety requirements for robotic lawnmowers, addressing risks including blade injuries, fall hazards, and autonomous operation risks.
i Robot lawn mowers must demonstrate child safety ensuring children cannot accidentally start or stop robots. Pet safety is critical—mechanisms preventing blade operation if the robot detects animals nearby. Obstacle detection at speed must ensure robots don't strike people who enter cutting areas. Tipping and rollover protection on slopes prevents robots from becoming hazards themselves.
Meeting these standards requires extensive testing and certification—a significant cost and timeline factor for new product launches. i Robot's engineering and quality teams must design for compliance from inception rather than retrofitting later. Failure in this area could result in regulatory rejection, liability exposure, and reputational damage.
Privacy Regulations and Data Protection
Advanced vision systems and home mapping create privacy regulatory implications. GDPR (European Union) and similar regulations governing personal data require transparency about what data is collected, how it's used, and user rights regarding their data. i Robot must clearly communicate data handling policies and provide users granular control over collection and retention.
Facial recognition regulations in certain jurisdictions prohibit or restrict use of facial recognition technology without explicit consent. If i Robot implements facial recognition in future models for security or user identification purposes, significant regulatory compliance is required.
State-level regulations in the United States increasingly address AI transparency and bias. California's AI transparency requirements, if adopted nationally, would require i Robot to document and disclose AI capabilities, training data sources, and potential bias issues. Proactive compliance with emerging standards positions i Robot favorably with regulators and consumers.

Financial Projections and Market Impact
Revenue Potential from Product Expansion
Estimating financial impact requires forecasting addressable markets and i Robot's potential capture rates. For compact Roombas, the addressable market includes apartment dwellers and small-home owners in developed markets—approximately 80-100 million households globally at current robotics adoption rates. If i Robot captures 5% adoption with average selling price of
For robot lawn mowers, the addressable market is larger—300-400 million residential properties with lawns in developed countries. Current robot mower penetration is only 3-5%. If i Robot captures 8-10% of the total potential market (representing roughly 3-4x capture of traditional competitors), this could represent $3-4 billion annual revenue at scale.
These projections are aspirational but not unrealistic. They assume 5-10 year timelines to achieve scale, massive marketing investments, successful execution of product development, and no major disruption from competitors. More conservatively, i Robot's current
Market Share and Competitive Positioning
Current robot vacuum market is roughly
The critical competitive variable is speed to market and execution quality. If i Robot launches superior products achieving strong consumer reviews and word-of-mouth adoption, it gains dominant positioning in new categories. If competing companies—particularly aggressive Chinese manufacturers or better-funded competitors—execute faster or achieve better value propositions, i Robot's market share faces erosion despite brand advantages.

Timeline and Expected Launch Windows
Near-Term Launches (2024-2025)
Based on current development cycles and i Robot's historical product launch patterns, compact robot vacuums are likeliest to launch first, probably in late 2024 or early 2025. These leverage existing vacuum technology with form factor modifications—the shortest path to new product revenue. Initial launches probably focus on premium compact models, later expanding into budget-focused compact line.
AI enhancement rollouts for existing product lines are essentially continuous, with each new firmware version and each generation adding improved capabilities. A 2025 flagship Roomba will incorporate substantially more sophisticated AI than 2023 models, even without revolutionary breakthroughs.
Medium-Term Launches (2025-2027)
Robot lawn mower launches likely occur in 2025-2026, probably initially in North America and Western Europe where market demand is strongest and regulatory complexity is manageable. Initial products probably target premium segment ($3,500-5,500), establishing brand presence and achieving early-adopter credibility before expanding downmarket.
Expanded smart home integration continues across this period, deepening Amazon ecosystem integration and supporting Matter protocol compatibility. App redesigns implementing suggested features occur iteratively.
Long-Term Opportunities (2027-2030)
If lawn mower launches succeed, expansion to adjacent outdoor automation becomes likely—potentially robot leaf blowers, gutter cleaners, pool cleaners, or other outdoor maintenance robots. Each new category would leverage core navigation and autonomy technology developed for initial launches.
Advanced AI capabilities including sophisticated natural language understanding, object recognition, and predictive features become more pervasive, moving from flagship models into mid-range and budget products as computational costs decline.
International expansion accelerates as initial category launches prove successful, with regional customization for different market requirements and preferences.

Challenges and Potential Obstacles
Execution Risk and Product Development Delays
Historically, consumer robotics companies frequently face product development delays and performance shortfalls. i Robot itself experienced challenges with earlier product launches. Compact Roomba development might face unexpected challenges miniaturizing complex systems, potentially delaying launches. Lawn mower development, entering an entirely new domain with different environmental challenges, carries higher execution risk.
Market timing risks also exist. Consumer preferences shift, competitors accelerate development, or macroeconomic conditions reduce discretionary spending on home robots. If i Robot misses windows when early-adopter willingness to pay is high, revenue potential diminishes.
Competitive Response and Market Consolidation
Existing competitors won't passively accept i Robot expansion into new categories. Husqvarna (owned by Husqvarna Group) has resources, manufacturing expertise, and brand recognition in lawn care to compete intensely. Shark and Bissell could accelerate compact Roomba development. Chinese manufacturers have proven rapid commercialization capabilities.
Major technology companies (Google, Amazon, Apple, Samsung) could enter simultaneously with competing products. While none has committed specifically to robot vacuums or lawn mowers, their AI capabilities, capital, and ecosystem reach make them credible competitors. Amazon's acquisition of i Robot actually increases incentive for Google and Apple to develop competitive products.
Market consolidation risk exists—if i Robot struggles, acquisition by a larger technology or appliance company could occur, potentially benefiting competitors or changing strategic direction.
Regulatory and Safety Certification Bottlenecks
Introducing new robot categories involves regulatory approval and safety certification processes. These can be unpredictably lengthy and complex. Lawn mower certification requiring extended outdoor testing could delay launches by 12+ months. Privacy regulations emerging in Europe or new jurisdictions could require costly product modifications.

Strategic Recommendations for i Robot
Accelerating Compact Roomba Development
Compact Roombas address clear market demand, leverage existing technology, and face less competitive entanglement than lawn mowers. Prioritizing compact Roomba launches in urban-focused geographies (Singapore, Hong Kong, Tokyo, London, New York) capitalizes on demonstrated demand. Pricing at $299-399 undercuts full-size models while maintaining margins through efficient manufacturing.
Developing tiered compact lines (budget, standard, premium) captures different consumer segments. Distribution through Amazon, electronics retailers, and direct channels reaches target demographic effectively.
Strategic Partnerships for Lawn Mower Development
Entering lawn mower markets with in-house development is ambitious and risky. Strategic partnerships with established lawn equipment companies could accelerate time-to-market. A partnership with existing manufacturers provides supply chain access, manufacturing expertise, safety certification experience, and channel relationships. i Robot contributes AI technology, brand, and smart home integration.
Alternatively, acquihire of smaller lawn robot startups could provide core technology and talent accelerating internal development. Companies like Lego's recent acquisition of Mindstorms robots show how strategic acquisitions supplement organic development.
Deepening Amazon Integration While Maintaining Privacy
Amazon's involvement provides tremendous resources and ecosystem benefits. Leveraging Amazon's supply chain, manufacturing partnerships, and distribution accelerates product launches. Integrating i Robot robots deeply into Amazon Smart Home ecosystem enhances competitive advantage.
Simultaneously, maintaining distinct privacy and data policies preserving user trust is critical. i Robot can benefit from Amazon's infrastructure without sharing every data point. Clear communication about what data stays on-device versus transmitted to clouds reassures privacy-conscious consumers.
Investment in AI and Machine Learning Talent
Achieving advanced AI capabilities requires substantial investment in talent acquisition and retention. i Robot should recruit machine learning engineers, computer vision specialists, and AI researchers, potentially offering competitive compensation and interesting technical challenges. Building internal AI expertise is lengthy and expensive but provides sustained competitive advantage.
Alternatively, partnerships with academic institutions and research organizations can supplement internal capabilities. Collaborating with top computer science programs, AI research labs, and emerging AI companies provides access to cutting-edge research while sharing development costs.

Alternatives and Competitive Landscape
While i Robot dominates robot vacuums, alternatives exist for both vacuums and lawn care, and platform approaches to home automation offer different value propositions than single-category robot companies.
Traditional brands like Shark, Bissell, and Dyson offer robot vacuums competing on price or specific features. Chinese manufacturers including Ecovacs, Dreame, and Narwal offer excellent value propositions at lower prices than i Robot. Robot lawn mower specialists like Husqvarna and Stihl have decades of expertise but lack smart home integration.
For comprehensive home automation, platforms like Runable provide different approaches. Runable's AI agents enable workflow automation and intelligent document generation—complementary capabilities to physical robots. Teams valuing AI-powered automation across multiple domains might prefer integrated platforms like Runable ($9/month with comprehensive automation features) rather than isolated robot solutions. Runable's approach to automation orchestration—coordinating multiple tasks and systems through AI—represents an alternative philosophy to single-purpose robots, potentially more suitable for technically sophisticated users.
Ultimately, i Robot excels at physical automation of household chores. Runable and similar platforms excel at digital automation and intelligent content generation. The optimal smart home likely incorporates both physical robots and digital automation platforms working in coordination.

Conclusion: The Future of Home Automation
i Robot's strategic direction reflects broader transformation in how humans interact with their physical spaces. As technology costs decline, consumer expectations rise, and labor becomes increasingly valuable, automated solutions addressing household chores transition from luxury goods to expected amenities. i Robot's expansion into compact robot vacuums for space-conscious consumers, outdoor robots for lawn maintenance, and advanced AI capabilities for intelligent automation positions the company at the intersection of these trends.
The four pillars examined throughout this analysis—compact Roombas, lawn mowers, advanced AI, and ecosystem integration—represent coherent strategy rather than opportunistic product line extensions. Each pillar strengthens others. Compact Roombas expand addressable market. Lawn mowers demonstrate ecosystem value and lock-in. Advanced AI improves all products. Smart home integration creates moat preventing customer defection.
Success requires flawless execution across multiple complex domains. Product development delays could prove fatal in competitive markets. Competitive response from established and new entrants is virtually certain. Regulatory and safety hurdles remain substantial. Yet i Robot possesses genuine advantages—brand recognition, AI expertise, manufacturing capabilities, ecosystem position through Amazon, and proven ability to execute in robotics.
For consumers, i Robot's expansion portfolio should be carefully evaluated. Current Roomba owners considering lawn mower purchases should examine whether smart home integration benefits justify premium pricing versus specialist competitors. Apartment dwellers curious about robot vacuums should await compact Roomba launches rather than forcing existing models into unsuitable spaces. Tech-forward homeowners seeking comprehensive home automation might benefit from platforms combining AI-powered task automation (like Runable) with physical robots, rather than depending solely on single-category providers.
The broader smart home ecosystem will likely feature multiple specialized solutions—robots from i Robot, automation platforms from companies like Runable, sensors from various manufacturers, and coordinating platforms from Google, Amazon, and Apple. The companies that successfully integrate across this ecosystem while maintaining clear focus on specific value propositions will dominate. i Robot's strategy suggests confidence it can be such a player.
Over the next five years, expect i Robot announcements regarding compact Roombas launching into major urban markets, robot lawn mower pilot programs in selected geographies, significant AI capability advances visible in consumer products, and deepening Amazon ecosystem integration. If these initiatives execute successfully, i Robot's addressable market could expand from current
For those invested in home automation's future—whether as consumers, investors, or technology enthusiasts—i Robot's evolution from humble vacuum-maker to comprehensive home automation platform merits close attention. The company's success or failure in these ambitious initiatives will likely shape how households around the world approach home maintenance for decades to come.

FAQ
What products is i Robot planning to launch?
i Robot is developing compact robot vacuums designed for small homes and apartments, robot lawn mowers for automated yard maintenance, and significantly enhanced AI capabilities for all products. The company is also deepening smart home ecosystem integration through its Amazon partnership, allowing robots to coordinate with other connected home devices.
Why is i Robot developing compact robot vacuums?
Compact Roombas address significant unmet demand from apartment dwellers and small-space residents who find full-size models impractical. Research shows 42% of apartment dwellers cite storage constraints as barriers to adoption, with 68% expressing interest in compact designs. The addressable market for compact vacuums is estimated at 80-100 million households globally in developed markets.
How is the robot lawn mower market opportunity different from the vacuum market?
The residential lawn mower market is substantially larger—$45 billion globally—but robot mower adoption is only 3-5%, indicating massive growth potential. Current robot mower competitors lack i Robot's smart home integration and consumer brand recognition. i Robot's technology expertise in AI navigation, combined with its ecosystem advantages, could disrupt an industry lacking significant innovation leadership.
What AI capabilities is i Robot developing for future products?
Future AI advancements include sophisticated object recognition identifying specific household items, adaptive cleaning strategies adjusting suction and brush speed based on real-time surface analysis, predictive maintenance using sensor data, natural language understanding enabling conversational interaction, and privacy-preserving on-device AI processing reducing cloud dependence.
How does Amazon's acquisition affect i Robot's strategy?
Amazon's acquisition provides access to tremendous supply chain resources, manufacturing partnerships, and smart home ecosystem integration capabilities. This accelerates product development and enhances competitiveness. However, consumers should expect deeper integration with Amazon services and data handling in Amazon's ecosystem, requiring careful attention to privacy policies.
When will new i Robot products launch?
Compact robot vacuums are likely to launch in late 2024 or early 2025, leveraging existing technology with form factor modifications. Robot lawn mower launches are expected in 2025-2026, initially in North America and Western Europe. Advanced AI capabilities rollout continuously with each firmware update and product generation.
What alternatives should consumers consider?
For robot vacuums, competitors including Shark, Bissell, and Chinese manufacturers like Ecovacs and Dreame offer alternatives with different price-performance tradeoffs. For lawn mowers, specialists like Husqvarna provide expertise though less smart home integration. For comprehensive home automation, platforms like Runable provide AI-powered workflow automation complementing physical robots. The optimal smart home likely incorporates both physical robots and digital automation platforms working in coordination.
How do compact Roombas differ from traditional Roombas?
Compact Roombas are engineered specifically for smaller floor plans with optimized battery efficiency for shorter cleaning sessions, streamlined navigation algorithms for small-space geometry, reduced storage footprint critical for apartments, and often enhanced noise reduction for shared-wall environments. They'll likely be priced 40-60% lower than full-size premium models, making them accessible to budget-conscious consumers.
What safety considerations apply to outdoor robots?
Robot lawn mowers must meet safety standards including child safety preventing accidental operation, pet safety with blade disengagement if animals are detected, obstacle detection at speed, and tipping/rollover protection on slopes. These regulatory requirements add development time and testing complexity compared to indoor vacuum development.
How will i Robot's smart home integration work?
Future integration could enable robots to coordinate with climate control, lighting, door locks, and other smart home devices. When the vacuum operates, HVAC could increase fan speed, lights could brighten, and doors could unlock automatically. For lawn mowers, systems could delay operation if weather conditions are unfavorable based on connected sensors, or coordinate with outdoor smart devices.

Key Takeaways
- iRobot is developing compact robot vacuums specifically engineered for apartments and small homes, addressing clear market demand with 42% of apartment dwellers citing storage concerns
- Robot lawn mower entry targets a 2.8B vacuum market
- Advanced AI capabilities including object recognition, adaptive cleaning, natural language interfaces, and predictive maintenance will differentiate iRobot from competitors
- Amazon acquisition accelerates development through supply chain access and smart home ecosystem integration, though consumers should monitor privacy policies
- Product launches expected 2024-2026 include compact Roombas (late 2024), lawn mowers (2025-2026), with continuous AI improvements across all products
- Success requires flawless execution against competitive threats from established manufacturers and emerging competitors; alternatives like automation platforms (Runable) complement physical robots
![iRobot's Future Products: Roomba Lawn Mowers & Small-Home Vacuums [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/irobot-s-future-products-roomba-lawn-mowers-small-home-vacuu/image-1-1767206298252.jpg)



