LG's 2026 OLED Television Lineup: A Complete Analysis of Brightness, Gaming, and Display Innovation
Introduction: The Future of Premium Television Technology
The television landscape has been dominated by OLED technology for nearly a decade, but the innovation curve shows no signs of flattening. At the beginning of 2026, LG made waves in the premium TV market by announcing a comprehensive refresh of its OLED lineup that addresses some of the most persistent challenges facing flagship television technology. The announcement of four distinct product families—the enhanced G6, the redesigned C6, the ultra-slim Wallpaper model, and the world's first 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming televisions—represents a significant evolution in how consumers will experience cinematic content, competitive gaming, and streaming entertainment as reported by TechRadar.
For those who've followed OLED technology since its consumer debut, the progression feels both familiar and genuinely groundbreaking. LG's OLED panels have long offered unmatched contrast, perfect blacks, and pixel-level color accuracy that LCD and mini-LED technologies struggle to replicate. However, the traditional Achilles heel of OLED displays has been brightness—particularly in bright rooms where peak luminance becomes critical for proper HDR performance. A 20% brightness improvement in the flagship G6 model represents not merely an incremental upgrade, but a fundamental shift in the practical usability of these displays across diverse lighting conditions.
The introduction of the Tandem RGB panel technology in the C6 model signals LG's commitment to democratizing next-generation display technology across its portfolio. Rather than reserving the most advanced panel structures for flagship models only, LG has engineered a mid-tier solution that delivers measurable performance gains without the premium pricing associated with the G6. This strategic positioning reflects a maturing market where consumers increasingly demand flagship features at more accessible price points as noted by TechPowerUp.
Perhaps most intriguing is LG's entry into the cloud gaming television space with industry-leading specifications. The promise of native 4K resolution at 120 frames per second represents the convergence of streaming technology, display engineering, and gaming infrastructure maturation. As cloud gaming services like NVIDIA GeForce Now, Microsoft Xbox Cloud Gaming, and PlayStation Plus Premium gain traction, having a television optimized for these services from the ground up addresses a genuine market need for dedicated hardware rather than requiring secondary gaming devices.
This comprehensive analysis examines each of these product announcements in detail, exploring the technical innovations that enable these improvements, the practical implications for different use cases, and how these televisions position themselves within the broader competitive landscape of premium displays. Whether you're a home theater enthusiast, a competitive gamer, or someone seeking the optimal television for mixed-use environments, understanding these 2026 OLED advances will clarify what capabilities warrant investment and which innovations matter most for your specific viewing habits.
The LG G6: Redefining Flagship OLED Brightness and Performance
The 20% Brightness Breakthrough
Brightness in OLED televisions presents a fascinating engineering challenge that distinguishes LG's approach from traditional LED-backlit displays. Traditional LCD screens can incrementally increase brightness by simply increasing the backlight intensity, spreading the additional power across millions of pixels simultaneously. OLED screens, by contrast, rely on self-emissive pixels that produce their own light individually. This pixel-level light emission offers extraordinary advantages for contrast and color accuracy, but creates inherent constraints on peak brightness because pushing individual pixels to maximum luminance simultaneously would dramatically reduce the lifespan of the organic materials.
LG's engineers addressed this constraint through a combination of material science improvements and intelligent processing algorithms. The 20% brightness increase in the G6 stems from three primary innovations. First, LG refined the organic light-emitting materials within each pixel structure, developing compounds that produce higher luminance output before degradation becomes problematic. Second, the company implemented enhanced cooling structures within the panel that more efficiently dissipate heat generated during high-brightness operation, preventing thermal throttling that traditionally limited peak brightness. Third, LG developed more sophisticated brightness management algorithms that intelligently allocate peak brightness to specific regions of the screen based on content analysis.
This last innovation deserves particular attention because it highlights the sophistication of modern OLED processing. The G6 employs machine learning-based content detection that identifies bright highlights within images—think of sunlit skies in landscape cinematography or explosions in action sequences—and reserves maximum brightness output for these specific regions while maintaining normal brightness levels elsewhere. This regional brightness allocation approach delivers the appearance of substantially increased peak brightness without proportionally stressing the entire panel, extending the practical lifespan of the display while delivering the perceptual benefits of greater brightness.
The practical impact of this improvement manifests most clearly in bright room environments. Professional home theater designers have historically recommended dark viewing spaces for OLED televisions because bright ambient light tends to wash out the inherent contrast advantages that make OLED exceptional. A television that produces 200 nits of peak brightness performs adequately in a darkened theater room but struggles with a living room receiving direct sunlight through windows. The enhanced G6, estimated to achieve approximately 240-260 nits of peak brightness in its brightest implementations, extends the practical usability range of the display across a broader spectrum of real-world lighting conditions.
Enhanced Anti-Reflective Surface Technology
The announcement mentions "lower reflections" in conjunction with the brightness improvements, indicating that LG paired optical enhancements with the luminance upgrades. This dual approach addresses a common complaint among OLED owners: while OLED screens deliver stunning image quality in dark environments, they can appear somewhat mirror-like in bright rooms, reflecting ambient light back toward viewers and reducing perceived contrast.
LG's anti-reflective coating technology works through a multi-layered optical structure that diffuses reflected light rather than allowing specular reflection. Traditional glass screens reflect light according to the laws of reflection—the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection—creating mirror-like behavior where bright ceiling lights or window reflections appear sharply defined on the display surface. An anti-reflective coating disrupts this specular reflection by introducing microscopic surface variations and refractive index gradients that scatter reflected light across multiple angles, reducing the visibility of reflections even as you view the screen from different positions.
The combination of increased brightness and reduced reflectivity creates a synergistic effect. Higher brightness content can "cut through" the diffused reflections more effectively, while the reduced reflections prevent ambient light from overwhelming the display's ability to render dark areas convincingly. This represents a fundamental improvement to the OLED value proposition, making the G6 viable for living rooms and showrooms where bright ambient lighting conditions are unavoidable. For consumers who previously felt compelled to choose between living room practicality and home theater performance, the G6 offers a genuine compromise position that doesn't require sacrificing either priority.
G6 Size Options and Screen Technology
LG structured the G6 lineup across multiple screen sizes—typically ranging from 55 inches to 83 inches in the flagship OLED lineup—ensuring that consumers can integrate the enhanced brightness and anti-reflective benefits across different room sizes and viewing distances. The 55-inch model suits intimate viewing spaces and bedrooms, while the 83-inch variant serves as a genuine cinema replacement for large family rooms and dedicated home theaters.
Each size implements the same core panel technology, meaning the brightness, color accuracy, and processing capabilities remain consistent whether you select a compact 55-inch display or an expansive 83-inch centerpiece. This consistency represents a significant advantage over competitor products, where larger screens sometimes feature slightly different panel characteristics due to manufacturing constraints or cost considerations. LG's unified approach means that your choice of screen size reflects purely personal preference regarding viewing distance and room integration rather than forcing compromises on technological capability.
Advanced Color Mapping and HDR Performance
The G6's enhanced brightness directly improves HDR (High Dynamic Range) performance, one of the most visually impactful aspects of modern content. HDR content specifies that bright highlights should appear significantly brighter than mid-tone elements, creating a perceptual sense of dynamic range that approaches real-world lighting environments. Traditional SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) content, by contrast, compresses brightness ranges into a smaller envelope, reducing the visual impact of bright elements.
A television with higher peak brightness can accurately render HDR content's intended brightness hierarchy without compressing highlights, delivering more convincing cinematic imagery. When watching an HDR action sequence with bright explosions and projectile effects, a higher-brightness OLED can reserve peak brightness for these elements while maintaining full brightness capacity for mid-tone content, avoiding the "blown out" appearance that sometimes occurs with lower-brightness displays.
LG's color mapping engine in the G6 works in tandem with brightness improvements to deliver superior color saturation in bright regions. Conventional OLED technology tends to desaturate colors in very bright areas as the luminance increases, a phenomenon where bright yellows appear washed out compared to mid-tone yellows. The G6's refined color science maintains saturation levels across the brightness range more effectively, ensuring that bright, vibrant elements in HDR content—such as neon signs or sunlit reflections on water—appear convincingly colorful rather than washed out.
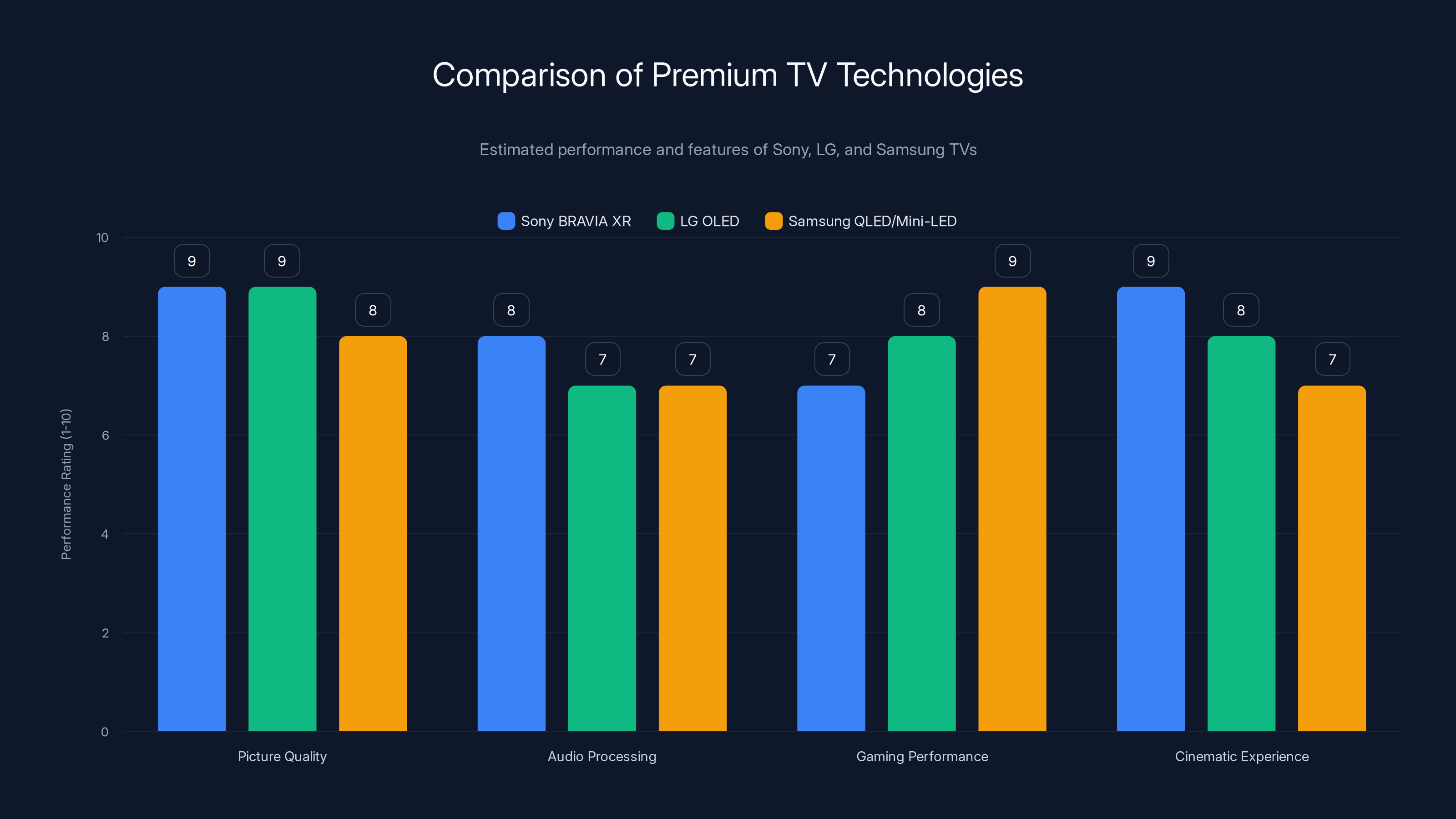
Estimated data suggests Sony and LG offer superior picture quality, while Samsung excels in gaming performance. Each brand has unique strengths, catering to different consumer preferences.
The LG C6: Mid-Tier Innovation with Tandem RGB Panel Architecture
Introduction to Tandem RGB Panel Technology
While the G6 represents LG's flagship OLED achievement, the C6 introduces a fascinating technological democratization through its Tandem RGB panel structure. The term "Tandem RGB" refers to a fundamentally different approach to OLED pixel architecture compared to the traditional WRGB (White, Red, Green, Blue) structure that has dominated LG's OLED panels for the past several generations.
Traditional WRGB OLED pixels include a white subpixel alongside separate red, green, and blue subpixels. The white subpixel, which emits across the visible spectrum without color filtering, serves to boost overall brightness and efficiency. However, this architecture involves inherent efficiency tradeoffs: rendering a pure blue image requires filtering out most of the white subpixel's output, which wastes energy and reduces peak brightness for certain colors. The Tandem RGB approach eliminates the white subpixel entirely, instead using a dual-stack architecture where stacked OLED elements combine to achieve higher brightness through material efficiency improvements.
The fundamental advantage of Tandem RGB lies in color-specific brightness optimization. When the display needs to render bright red content, the tandem red OLED stack can achieve full brightness without the filtering losses incurred by the white-plus-filter approach. The same principle applies to green and blue subpixels. This architecture delivers improved color brightness across the spectrum, allowing displays to render vibrant, saturated colors at full brightness simultaneously—something that traditional WRGB panels struggle with due to the efficiency penalties of spectral filtering.
Manufacturers face a significant engineering challenge when implementing Tandem RGB technology: stacking additional OLED layers increases the panel's thickness, heat generation, and power consumption if not carefully engineered. LG has apparently solved these challenges through proprietary material compositions and thermal management structures that allow the C6 to maintain similar operational characteristics to traditional WRGB panels while delivering Tandem RGB's performance benefits.
Performance Gains in Mid-Range Segment
The C6's positioning within LG's lineup strategically addresses a market gap. Consumers upgrading from conventional LED televisions to OLED technology typically consider either the more affordable B-series models or jump directly to the flagship G-series, with the C-series occupying a middle ground. By introducing Tandem RGB technology to the C6, LG delivers a product that captures many of the technological advances reserved for the expensive G6 while maintaining a more accessible price point.
The Tandem RGB panel in the C6 doesn't achieve the absolute brightness levels of the G6's enhanced version, but the color brightness capabilities—where individual colors can reach full brightness simultaneously—may actually surpass traditional WRGB panels in practical use cases. A test scenario might involve rendering a bright sunset with oranges, reds, and warm yellows transitioning toward dark blue sky. The Tandem RGB architecture allows each of these colors to achieve full individual brightness, creating more convincing saturation and vibrancy compared to WRGB panels where the white subpixel filtering compromises saturation in bright regions.
Market Positioning and Consumer Value Proposition
The C6's introduction reflects LG's confidence that Tandem RGB technology has matured sufficiently for volume production at a mid-tier price point. This aggressive positioning pressures competitors like Sony and Samsung, who struggle to match OLED technology entirely. By offering meaningful technological advancement in the C6, LG avoids the scenario where budget-conscious consumers feel compelled to compromise on core performance characteristics.
Consumers considering the C6 face a decision between this model and the more expensive G6. The practical distinction involves brightness in bright rooms (G6 advantage) and gaming performance features. For consumers whose primary viewing occurs in normal- to dim-lighting conditions, the C6's Tandem RGB advantages may actually deliver superior performance compared to the G6 in specific use cases like watching colorful, vibrant content. The C6 therefore appeals to viewers prioritizing color performance and mid-range pricing, while the G6 targets consumers with bright rooms or specific gaming requirements.

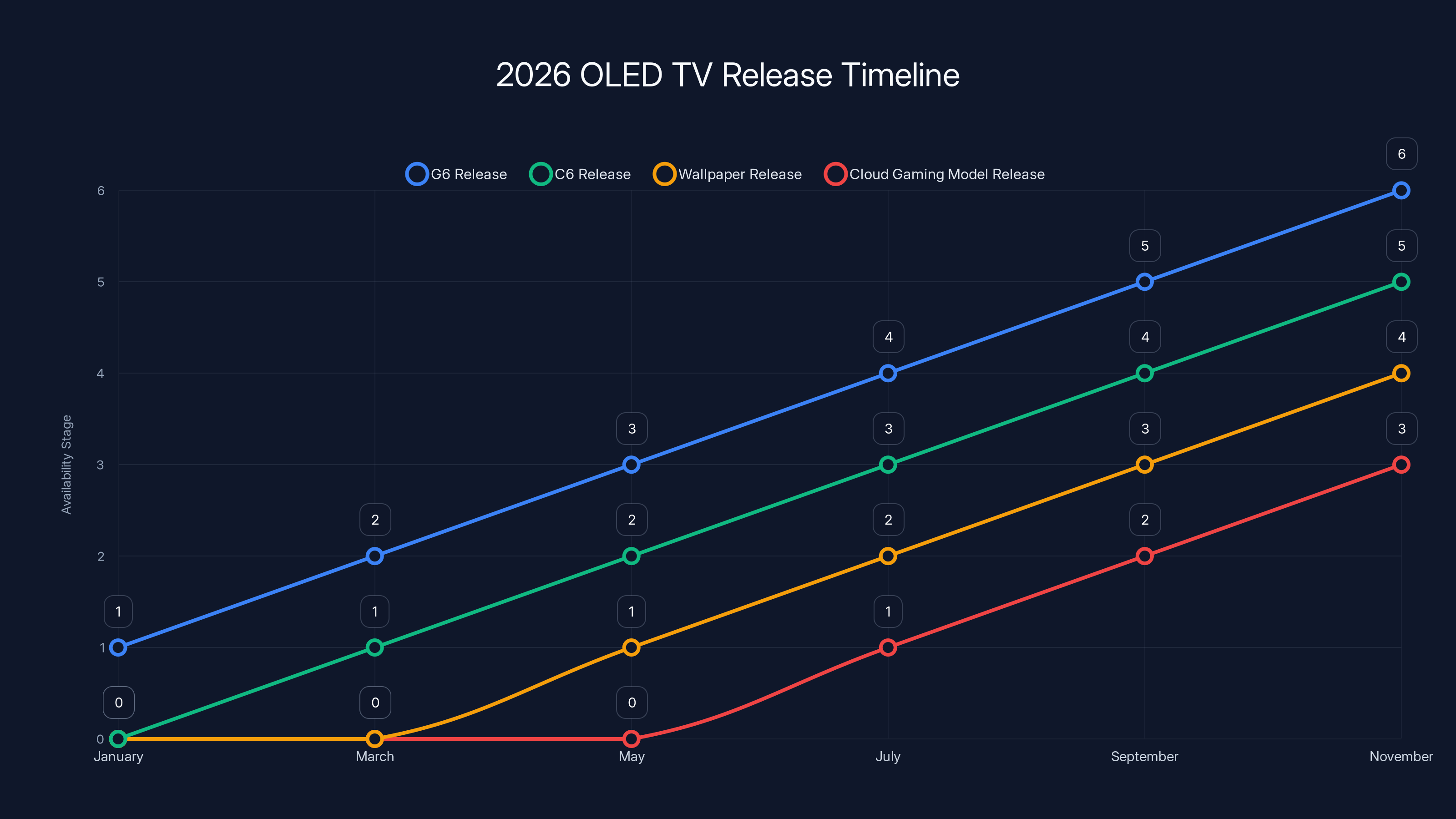
Estimated data shows the staggered release of LG's 2026 OLED TV lineup, with the G6 model launching first and others following in subsequent months.
The Wallpaper OLED: Ultra-Thin Design and Aesthetic Integration
Engineering Challenges of Minimal Thickness
The Wallpaper OLED represents the evolution of a product category that LG pioneered several years ago, where the display attaches nearly flush against wall surfaces, creating the appearance of a mounted artwork or window. Achieving this aesthetic requires solving significant engineering problems that don't exist in traditionally-framed televisions.
A conventional OLED television requires space behind the display for power distribution circuitry, thermal management components, input/output connectors, and mechanical support structures. The Wallpaper design eliminates nearly all of this rear-mounted infrastructure, either integrating components into the display bezel or relocating them to external power boxes and wall-mounted connections. The panel itself—the OLED substrate, protective layers, and optical coatings—measures just a few millimeters, making the total thickness of the Wallpaper model approximately 3.8 millimeters for the display module itself, with slightly greater overall thickness when mounting hardware is included.
This extreme thinness creates thermal management challenges that the manufacturer must address carefully. Traditional televisions dissipate heat through venting, where warm air exhausts from rear ports and hot components are exposed to ambient air circulation. A Wallpaper model mounted against a wall lacks rear airspace, forcing the design to channel heat in alternative directions. LG's engineers likely implemented innovative thermal pathways that conduct heat toward the sides of the display or into the wall-mounting structure, combined with precision temperature control that prevents any component from reaching unsafe operating temperatures despite the constrained thermal environment.
Mounting System Integration
The Wallpaper implementation includes a proprietary mounting system designed for wall installation with minimal visible hardware. Unlike traditional TV mounts that attach at a central point and require visible brackets, the Wallpaper system distributes support forces across a magnetic rail structure that remains largely hidden behind the display itself. This approach provides multiple attachment points, distributing the television's weight across the mounting surface rather than concentrating load at central attachment points.
The magnetic mounting system also enables relatively straightforward installation and removal compared to traditional wall mounts. Instead of drilling multiple holes and installing numerous wall anchors, installers position the mounting rail and attach it to studs or wall anchors, then magnetically engage the television to the rail. This method simplifies the installation process while providing the robust support required for expensive display hardware.
Cable Management and Connection Architecture
Eliminating rear-mounted components requires rethinking how signals and power reach the display. LG implements a hybrid approach where a thin power and signal cable connects the Wallpaper display to an external processor box mounted nearby or hidden behind furniture. This external box contains most electronic components—tuners, processing circuitry, HDMI interfaces, and power supply—essentially relocating the traditional television guts to a separate enclosure.
This external processor architecture offers unexpected benefits beyond achieving minimal thickness. Users can upgrade processing capabilities or add new features without replacing the display itself—theoretically, newer processor boxes could be swapped in to add emerging technologies like new streaming services or gaming features. The separation of display and processing also simplifies thermal management, as the processor box can dissipate heat freely without the constraints of a wall-mounted enclosure.
Practical Considerations for Wallpaper Integration
The Wallpaper OLED's primary appeal targets interior design-conscious consumers and upscale installations where the television's appearance when off becomes a primary consideration. A traditional television, when powered down, displays a black rectangle that dominates its viewing environment. A Wallpaper OLED mounted flush against a wall occupies significantly less visual real estate, creating a more integrated aesthetic that blends with the room's design rather than standing out as a prominent technological device.
Several practical considerations affect the Wallpaper's suitability for different installations. The magnetic mounting system requires ferrous mounting surfaces, typically steel studs or special backing plates installed within wall cavities. Mounting to non-ferrous surfaces like stone, brick, or concrete may require additional hardware. The thin cable connecting the display to the external processor box needs routing through walls or concealment within cable conduits, limiting installation flexibility compared to traditional televisions that can be repositioned more easily.
The Wallpaper OLED typically features identical core display technology to the C6 or G6 models, meaning consumers aren't compromising on picture quality in exchange for aesthetic integration. The Tandem RGB panel discussed in the C6 section likely appears in Wallpaper variants as well, ensuring consistent performance characteristics. The primary distinction is the form factor, where the Wallpaper's ultra-thin profile and wall-mounting orientation define the user experience.
4K 120 Hz Cloud Gaming: Industry's First Native Implementation
The Cloud Gaming Infrastructure Landscape
Cloud gaming services represent one of the most significant shifts in how consumers access entertainment, paralleling the transition from physical media to streaming entertainment that reshaped the video industry over the past decade. Rather than requiring dedicated local hardware to process and render games, cloud gaming services execute games on remote servers and stream the video output directly to users' devices, similar to how Netflix streams movies rather than requiring users to purchase DVDs.
Major technology companies have invested billions into cloud gaming infrastructure. NVIDIA's GeForce Now, Microsoft's Xbox Cloud Gaming (formerly Project xCloud), Sony's PlayStation Plus Premium streaming tier, and Amazon's Luna service represent the major platforms competing for market share. Each platform streams games to users' devices, handling all computational complexity server-side while transmitting only the rendered video frames to the client device. This approach allows users to play demanding AAA titles on modest hardware—smartphones, tablets, budget laptops—without requiring the thousands of dollars in dedicated gaming hardware traditionally necessary for high-performance gaming.
The quality of cloud gaming streams depends critically on bandwidth, network latency, and display capabilities. A service could theoretically stream 8K resolution at 240 frames per second, but the user experience depends on their internet connection, the distance to cloud gaming servers, and their display's ability to render those frames. Most consumer implementations have targeted 1080p or 1440p at 60 Hz, a sweet spot balancing visual quality with bandwidth and latency constraints. A few premium services offer 4K streams, but 4K at 120 Hz has remained beyond practical reach for most cloud gaming implementations.
The Specifications Promise: 4K 120 Hz Reality
LG's announcement of the world's first televisions with native 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming support addresses the bandwidth and latency requirements that have historically limited cloud gaming experiences. To understand the significance, consider the data requirements: 4K resolution (3840×2160 pixels) at 120 frames per second requires substantial bandwidth when transmitted as video. Depending on compression efficiency, such streams might require 40-100 megabits per second of sustained bandwidth.
While many broadband connections in developed markets exceed these speeds, the real-world challenge extends beyond raw bandwidth to sustained consistency and latency. Gaming demands remarkably low latency—the time between when a player provides input (pressing a button) and when the game responds (character movement, gunfire, etc.). Cloud gaming introduces inherent latency as the signal travels from the player's device to remote servers, the servers process the input and render frames, and the video stream travels back to the display. Even with optimized networks, cloud gaming typically introduces 50-150 milliseconds of latency, compared to 10-30 milliseconds for local gaming hardware.
At 60 Hz gameplay (60 frames per second), the 16.67-millisecond interval between frames often matches or exceeds the extra latency from cloud gaming, creating a perceptually sluggish experience for responsive gaming. At 120 Hz (8.33-millisecond frame interval), the latency becomes more noticeable relative to frame timing, degrading the game feel. Supporting 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming requires not just display capability but optimized network infrastructure, edge server positioning, and processing efficiency throughout the pipeline.
Display Processing and Latency Optimization
LG's televisions implementing 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming support require specialized processing that goes beyond standard video display functionality. The TVs must incorporate features that reduce input-to-response latency, such as "game mode" implementations that bypass certain post-processing filters that look good for movies but add latency. Variable refresh rate support, a technology borrowed from gaming monitors, allows the television to synchronize its refresh rate with the incoming video stream, eliminating judder caused by frame rate mismatches.
Adaptive sync technologies like FreeSync and G-Sync, originally developed for gaming monitors, reduce visual artifacts when the incoming frame rate doesn't match the display's refresh rate. These technologies become particularly valuable in cloud gaming scenarios where stream latency or network variations might cause fluctuating frame rates. A display that smoothly adapts to incoming frame variations delivers a more compelling experience than one that shows visible stuttering or tearing when frame rate doesn't perfectly align with refresh rate.
LG's gaming-optimized OLED TVs also implement latency reduction through firmware optimization and signal processing streamlining. The television essentially prioritizes getting the incoming video stream to the pixels as quickly as possible, bypassing or minimizing any processing that doesn't directly contribute to visual quality. The result is a display that, when used with a high-quality cloud gaming service on a low-latency network, provides a gaming experience that approaches or matches local gaming hardware in terms of responsiveness.
Network Infrastructure Requirements and Practical Viability
The practical viability of 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming on LG's televisions depends heavily on underlying network infrastructure. While the televisions are technically capable of receiving and displaying 4K 120 Hz streams, the real-world experience depends on internet service provider reliability, proximity to cloud gaming servers, and network congestion patterns.
Consumers with fiber-optic broadband connections offering gigabit speeds and low-latency characteristics represent the sweet spot for cloud gaming adoption. These users, concentrated in developed markets and major metropolitan areas, can reliably stream 4K 120 Hz content without experiencing bandwidth bottlenecks or latency degradation. Consumers with conventional cable internet offering 100-300 Mbps speeds can participate in cloud gaming but might find 4K 120 Hz unreliable during peak usage hours or in congested network environments.
The television manufacturers' role becomes facilitating the best possible experience given the network conditions available. By supporting the 4K 120 Hz specification, LG positions its products to deliver the optimal streaming experience when conditions permit, avoiding the artificial limitations of displays that cap resolution or frame rates at lower levels. As broadband infrastructure improves over the coming years, the high-specification televisions become future-proofed against forthcoming cloud gaming services that progressively increase their stream quality.

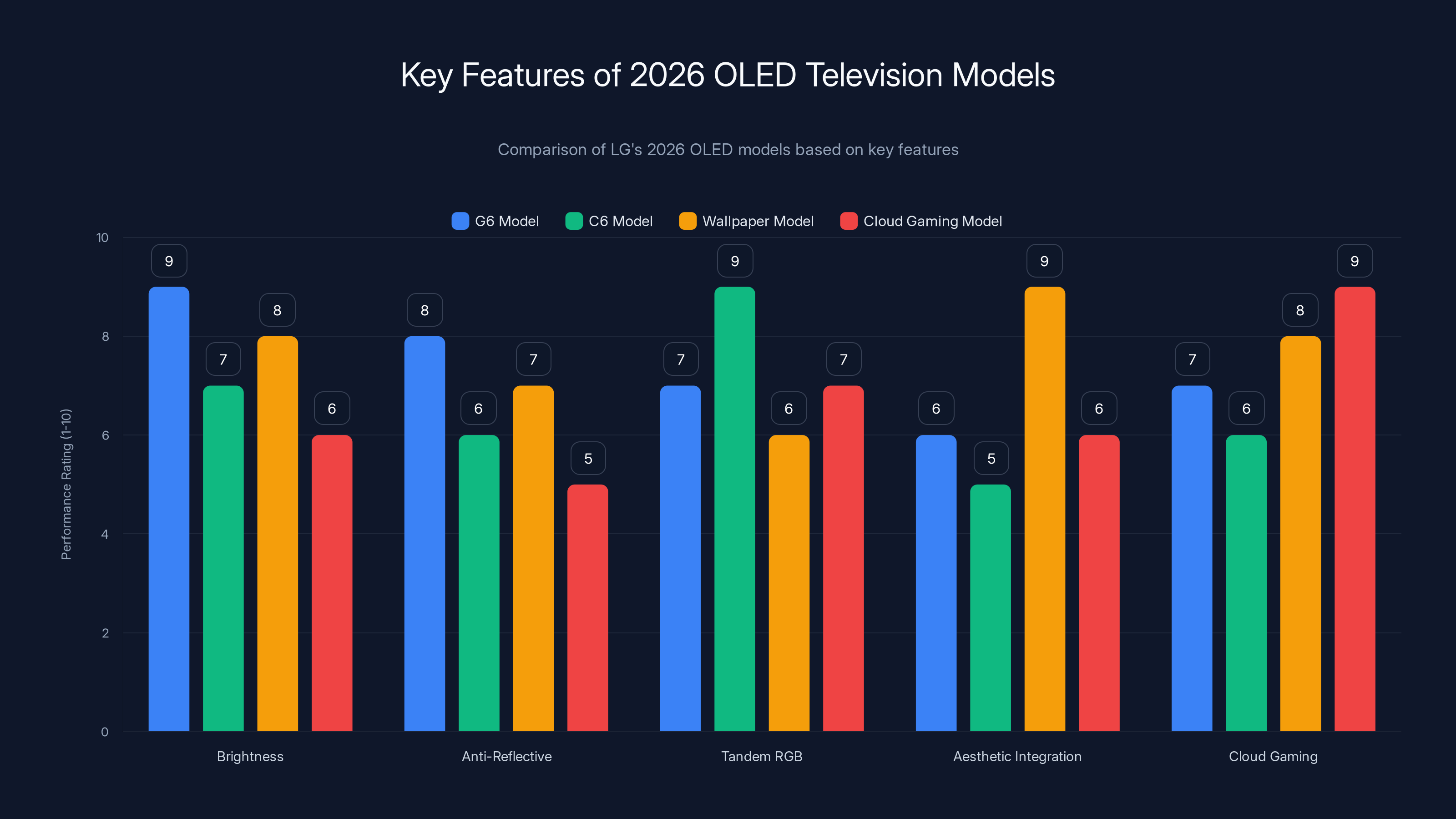
The 2026 OLED models from LG offer diverse strengths, with the G6 excelling in brightness and anti-reflective features, while the C6 leads in Tandem RGB technology. Estimated data.
Technical Specifications and Panel Performance Characteristics
OLED Pixel Efficiency and Brightness Distribution
The brightness improvements across LG's 2026 lineup stem from engineering advances in pixel-level light emission efficiency. OLED pixels generate light through electroluminescence—applying electrical current to organic compounds causes them to emit photons. The efficiency of this process, measured in lumens per watt, directly determines how much light the pixel can produce before the organic materials degrade excessively.
LG's materials science improvements focus on developing organic compounds that maintain high luminous efficiency across the brightness range. Traditional OLED materials show declining efficiency at maximum brightness, a characteristic that forces manufacturers to compromise between peak brightness and operational lifespan. Advancing materials science to develop compounds that maintain consistent efficiency even at high brightness levels represents a significant engineering achievement that justifies the premium pricing of 2026 OLED televisions compared to earlier generations.
Brightness isn't uniformly distributed across a display; rather, content-aware algorithms determine brightness allocation based on what's currently displayed. The G6's intelligence in allocating brightness to bright regions while maintaining efficiency in darker areas demonstrates how modern OLED television processing has evolved beyond simple display functions into sophisticated content analysis and optimization systems. This approach maintains the OLED advantage of perfect blacks and exceptional contrast while maximizing the brightness available for highlights.
Color Volume and Saturation Across Brightness Ranges
Color volume—the range of colors achievable at various brightness levels—represents a critical metric for evaluating display quality beyond simple peak brightness measurements. A display that achieves very bright highlights but desaturates colors in bright regions delivers inferior image quality compared to one that maintains vibrant colors even at peak brightness. The DCI-P3 color space standard, widely used in cinema, specifies precise color saturation expectations at various brightness levels.
The Tandem RGB panels in the C6 and Wallpaper models maintain color saturation more effectively than traditional WRGB panels because each subpixel's brightness capacity is independent. A WRGB panel rendering bright saturated blue must filter out much of the white subpixel's output, reducing overall brightness for that color. The Tandem RGB architecture, lacking a white subpixel entirely, allows the blue elements to achieve maximum efficiency, rendering bright blues that appear vibrant rather than washed out.
Measuring color volume precisely requires spectrophotometric equipment and proper test procedures, but the practical experience involves observing gradual transitions in natural content. A sunset displaying oranges and reds at various brightness levels should maintain apparent saturation as brightness increases. Clouds that are bright white should appear white rather than tinted from desaturation. The enhancements in 2026 OLED models should deliver more convincing color rendering in these challenging scenarios.
Black Level Performance and Contrast Ratios
OLED technology's signature characteristic—the ability to produce perfect blacks by turning off pixels entirely—remains unchanged in the 2026 models. A pixel that emits no light produces zero luminance, delivering contrast ratios that fundamentally exceed LED-backlit displays constrained by backlight bleed. This black level performance persists across the entire G6, C6, and Wallpaper lineup, representing the core OLED advantage that justifies the technology's premium positioning.
Bright highlights against perfect blacks create the perceptually infinite contrast ratios that make OLED displays so visually compelling. The improvements in 2026 models focus on boosting highlight brightness (pushing the maximum luminance higher) rather than improving black level performance, which is already at the theoretical limit. The result is greater contrast range—the difference between brightest highlights and deepest blacks—enhancing the visual drama of high-contrast content like nighttime action sequences or astrophotography.

Gaming Performance and Competitive Features
Response Time and Input Latency Characteristics
Competitive gamers prioritize response time—the interval between when the display receives a new frame and when pixels update to display that frame. OLED displays historically offered exceptional response times, with pixels transitioning between brightness states in microseconds rather than the milliseconds required by LCD displays. This performance advantage contributes to OLED displays' popularity among professional esports competitors.
The 2026 lineup maintains these response time advantages while emphasizing input latency reduction through game mode implementations and variable refresh rate support. Response time (how quickly pixels change) differs conceptually from input latency (the time from user input to visual response), though both matter for gaming competitiveness. LG's optimization of signal processing pathways in game mode reduces input latency, allowing frames to reach pixels faster by bypassing post-processing operations that introduce perceived delay.
Variable Refresh Rate and Adaptive Sync Implementation
Variable refresh rate (VRR) technologies synchronize display refresh with incoming frame rates, eliminating the visual artifacts of frame rate mismatches. When a game produces frames at irregular intervals—perhaps 115 frames per second momentarily, then 95 frames per second—a fixed 120 Hz display might display frame duplication or tearing. VRR-capable displays adjust their refresh rate to match the incoming frames, smoothly displaying 115 frames without artificial frame repetition.
LG's 2026 OLED televisions likely support both HDMI VRR and proprietary adaptive sync standards, ensuring compatibility with all major cloud gaming platforms and local gaming devices. This flexibility becomes important as consumers connect diverse gaming sources—PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X, gaming PCs, and cloud gaming services—each potentially implementing slightly different refresh rate standards. Universal compatibility ensures the television delivers optimal performance regardless of gaming source.
Local Dimming and Gaming Visual Quality
Mid-range OLED models sometimes incorporate local dimming systems that enable finer control over brightness zones. Unlike traditional OLED where each pixel controls its own brightness independently, local dimming zones allow a display region to darken while nearby regions maintain brightness. This feature, more common in mini-LED displays than OLED, typically doesn't appear in OLED gaming televisions because the pixel-level control already provides superior performance.
The absence of local dimming in the C6 and Wallpaper models reflects OLED's fundamental architecture advantage—true per-pixel dimming eliminates the need for zone-based lighting control. This architectural simplicity contributes to superior gaming performance by avoiding the complex processing required to manage multiple dimming zones, which can introduce visual artifacts or latency in zone transitions.

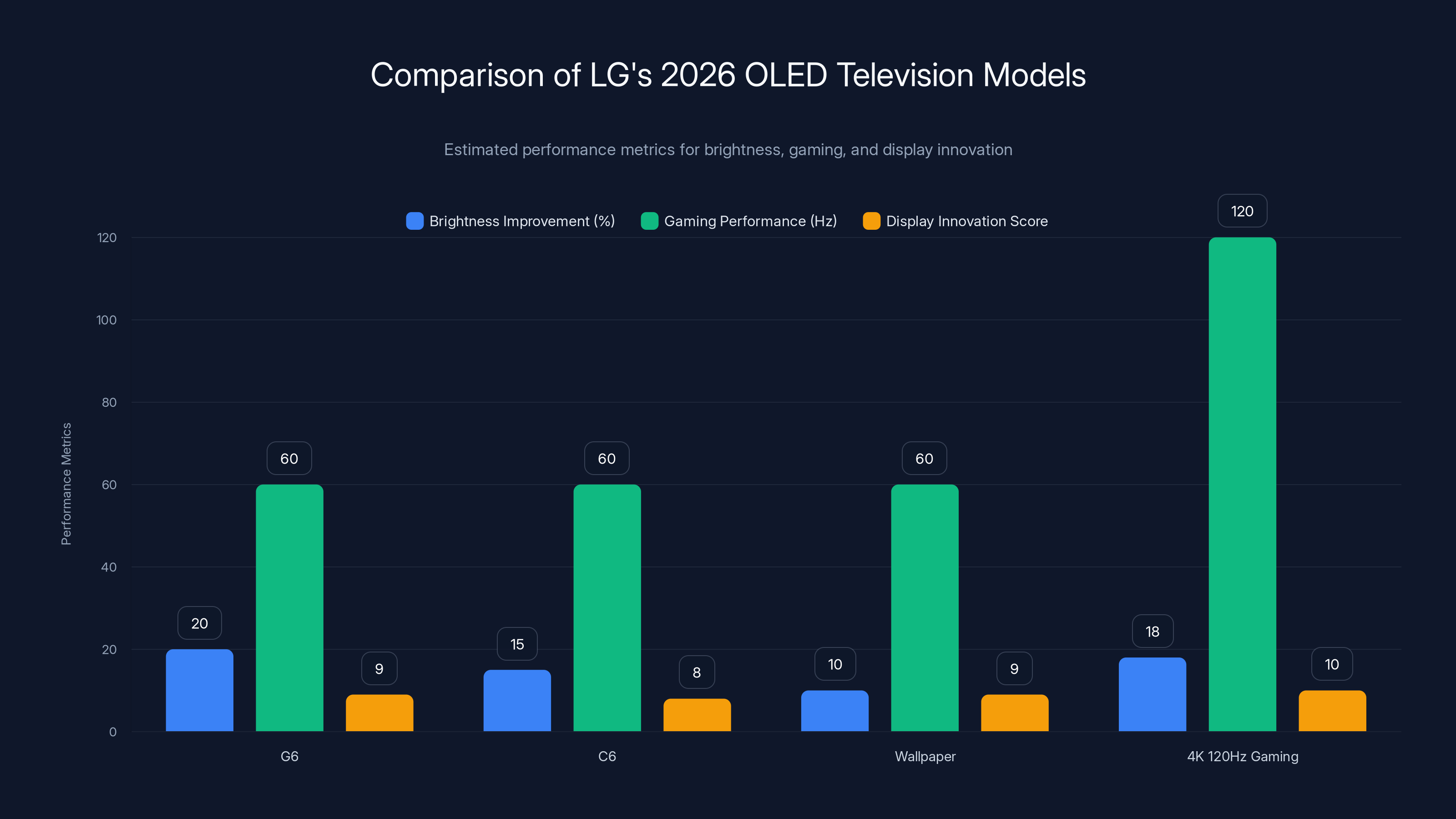
The G6 model leads in brightness improvement with a 20% increase, while the 4K 120Hz Gaming model excels in gaming performance. Estimated data based on typical advancements.
Picture Quality Deep Dive: HDR Rendering and Content Processing
HDR Peak Brightness and Tone Mapping
HDR content specifies that bright highlights should exceed the conventional SDR standard of 100 nits (candelas per square meter), with HDR mastering standards specifying up to 1000 nits or more for theatrical master content. Television displays can't achieve 1000+ nits across the entire screen (the power consumption would be impractical), so sophisticated tone mapping algorithms convert the HDR content's extreme brightness values to the television's achievable brightness range while preserving the visual hierarchy of bright and dark elements.
The G6's enhanced brightness extends the range of brightness that can be displayed without tone mapping compression. Content that previously required mapping to fit within the display's brightness limits can now be displayed at closer-to-native values, reducing tone mapping artifacts like halo effects around bright objects or blown-out highlights that lose shadow detail. A 20% brightness increase translates to roughly 40 additional nits of peak brightness (assuming a baseline of ~200 nits), allowing more HDR content to be displayed without aggressively compressing highlights.
Motion Enhancement and Interpolation Processing
OLED displays' exceptional response times combine with advanced motion processing to deliver exceptionally smooth visual presentation. LG implements motion interpolation algorithms that analyze between-frame motion and synthetically generate intermediate frames, creating the impression of smoother motion than the native frame rate would suggest. These algorithms help compensate for the motion blur characteristic of 60 Hz content, where objects moving quickly across the screen appear slightly streaked compared to higher frame rates.
For gamers, motion interpolation introduces latency and can create artificial-looking artifacts in fast-moving scenes. LG's game modes typically disable motion interpolation, prioritizing responsiveness over smoothness. The television's exceptional native response times compensate for the absence of interpolation, delivering motion performance that closely approaches higher frame rate displays.
Color Accuracy and Calibration Standards
The 2026 OLED lineup targets color accuracy meeting professional standards, with displays capable of rendering content calibrated to DCI-P3 or Rec. 2020 color spaces precisely. Professional calibration involves using specialized equipment to measure display output at various brightness levels across the color spectrum, then adjusting the display's color lookup tables to match reference standards. Many OLED television consumers benefit from factory calibration that aims to meet these standards without requiring professional calibration.
The achievement of exceptional color accuracy becomes more significant with improved brightness characteristics. A display that could previously only achieve saturated colors at mid-brightness levels now maintains that saturation at higher brightness levels, expanding the range of content that the display can render accurately. This improvement particularly benefits HDR content, where bright saturated colors appear frequently and desaturation at brightness levels significantly degrades the viewing experience.

Audio Technology and Immersive Sound Integration
Speaker Placement and Spatial Audio Rendering
While display technology dominates the technical specifications of television announcements, premium televisions increasingly incorporate sophisticated audio systems that complement the visual improvements. The ultra-thin Wallpaper OLED presents particular challenges for audio integration because the minimal rear space constrains speaker placement, forcing manufacturers to innovate in how sound is generated and directed.
LG likely implements a combination of forward-facing drivers, side-firing drivers, and advanced audio processing to create convincing spatial soundscapes despite the form factor constraints. Dolby Atmos support, common in premium televisions, enables audio rendering with overhead phantom speakers—through processing algorithms that create the perception of sounds originating from directions where no physical speakers exist. This advanced audio processing creates immersive soundscapes that enhance the compelling visuals of premium content.
Acoustic Performance in Wall-Mounted Installations
Wall-mounted installations present acoustic challenges because the flush mounting position places speakers close to wall surfaces, potentially creating reflections that degrade audio clarity. LG engineers likely incorporated acoustic design considerations in the Wallpaper's speaker enclosure, possibly incorporating wave guides or acoustic chambers that optimize sound distribution in typical wall-mounted installation scenarios.

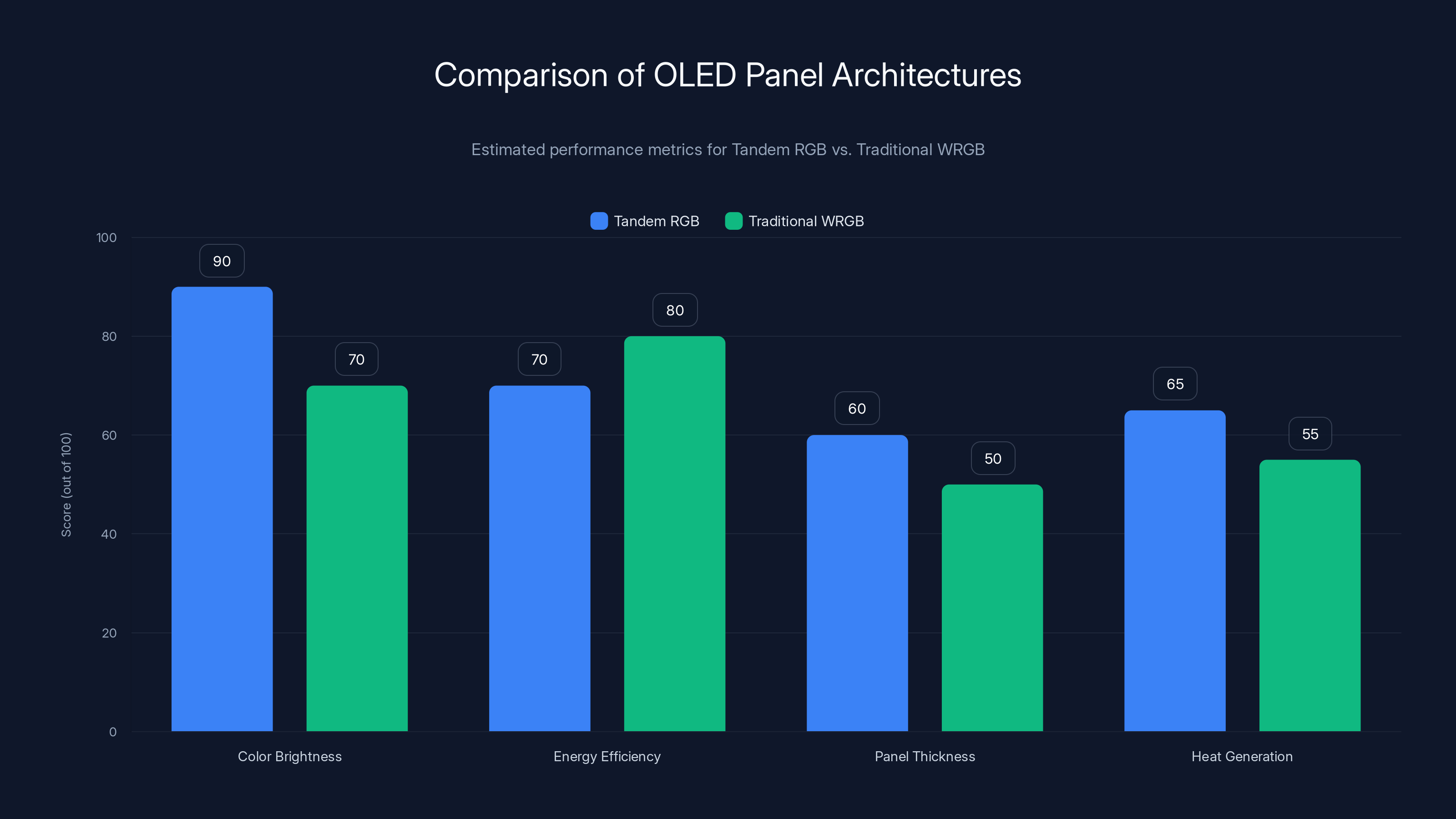
The Tandem RGB architecture offers superior color brightness but may face challenges with panel thickness and heat generation compared to traditional WRGB panels. Estimated data.
Competitive Landscape and Alternative Solutions
Sony BRAVIA XR Series Positioning
Sony's BRAVIA XR lineup represents LG's primary competitor in the premium OLED television market. Sony's implementation emphasizes cognitive processor technology that analyzes content and optimizes picture settings dynamically. Where LG focuses on hardware brightness improvements, Sony's approach emphasizes intelligent software processing that maximizes perceived image quality within hardware constraints.
Sony's XR TVs achieve highly competitive picture quality and command premium pricing comparable to LG's flagship models. The primary distinctions involve specific implementation details—Sony's audio processing versus LG's, different color science philosophies, and varying emphasis on gaming versus cinematic performance. Consumers evaluating both brands should prioritize hands-on comparison, as subjective image quality perception varies significantly based on personal preference.
Samsung and Alternative OLED Sources
While Samsung manufactures OLED panels for other display purposes, the company historically positioned itself as an OLED skeptic for televisions, emphasizing quantum dot LCD (QLED) technology and mini-LED backlighting as superior alternatives. Samsung's latest announcements suggest potential reconsideration of this stance, with speculation about future Samsung OLED television models. For 2026, Samsung's lineup consists primarily of QLED and mini-LED models rather than OLED displays.
Mini-LED technology—thousands of individually controlled tiny LED backlights—approaches OLED's contrast performance at lower cost through zone-based dimming. While mini-LED displays can't achieve OLED's perfect blacks or pixel-level control precision, they eliminate OLED's burn-in risk and offer competitive HDR performance at reduced pricing. Consumers prioritizing robustness and cost-effectiveness might consider Samsung's mini-LED offerings over OLED alternatives.
For Teams and Organizations Seeking Content Innovation
While this article focuses on consumer television technology, organizations in creative industries often leverage premium display technology for professional content evaluation. For teams seeking comprehensive content creation and optimization capabilities, platforms like Runable offer AI-powered automation for generating polished presentations and documentation about product features and specifications. Runable's AI-driven content generation at $9/month enables organizations to quickly create professional technical documentation, marketing materials, and specification sheets without requiring extensive manual writing. The platform's ability to generate formatted documents and reports from product specifications parallels how premium televisions automate content optimization—both reduce manual effort while maintaining quality standards.

2026 Release Timeline and Availability Expectations
Global Launch Sequencing
LG typically staggered its 2025 OLED television releases across multiple markets over several months, beginning with premium-tier models in developed markets before expanding to broader distribution and mid-tier models. The 2026 lineup will likely follow a similar pattern, with the flagship G6 launching first in major markets (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific), followed by the C6, Wallpaper, and cloud gaming models.
Availability timing reflects retail distribution realities, supply chain capacities, and regional demand patterns. Premium models typically reach specialty retailers and online channels within weeks of announcement, with broader retail availability expanding over subsequent months as manufacturing scales. By mid-2026, consumers should expect full availability of the announced lineup across major retailers globally.
Pricing Expectations and Value Positioning
OLED television pricing traditionally follows a premium trajectory, with 55-inch models starting around
The C6 with Tandem RGB technology should position at an attractive price point below the G6, potentially offering similar perceived value to previous-generation C-series models while delivering more advanced panel technology. This aggressive pricing maintains LG's market share strategy of offering meaningful technical advancement across multiple price tiers rather than concentrating all innovation in the expensive flagship model.
The Wallpaper OLED's premium pricing reflects its specialized positioning for design-conscious consumers willing to pay for aesthetic integration. Pricing will likely exceed standard models by 20-30% due to the custom mounting infrastructure and external processor box requirements, positioning it as a luxury product for high-end installations.

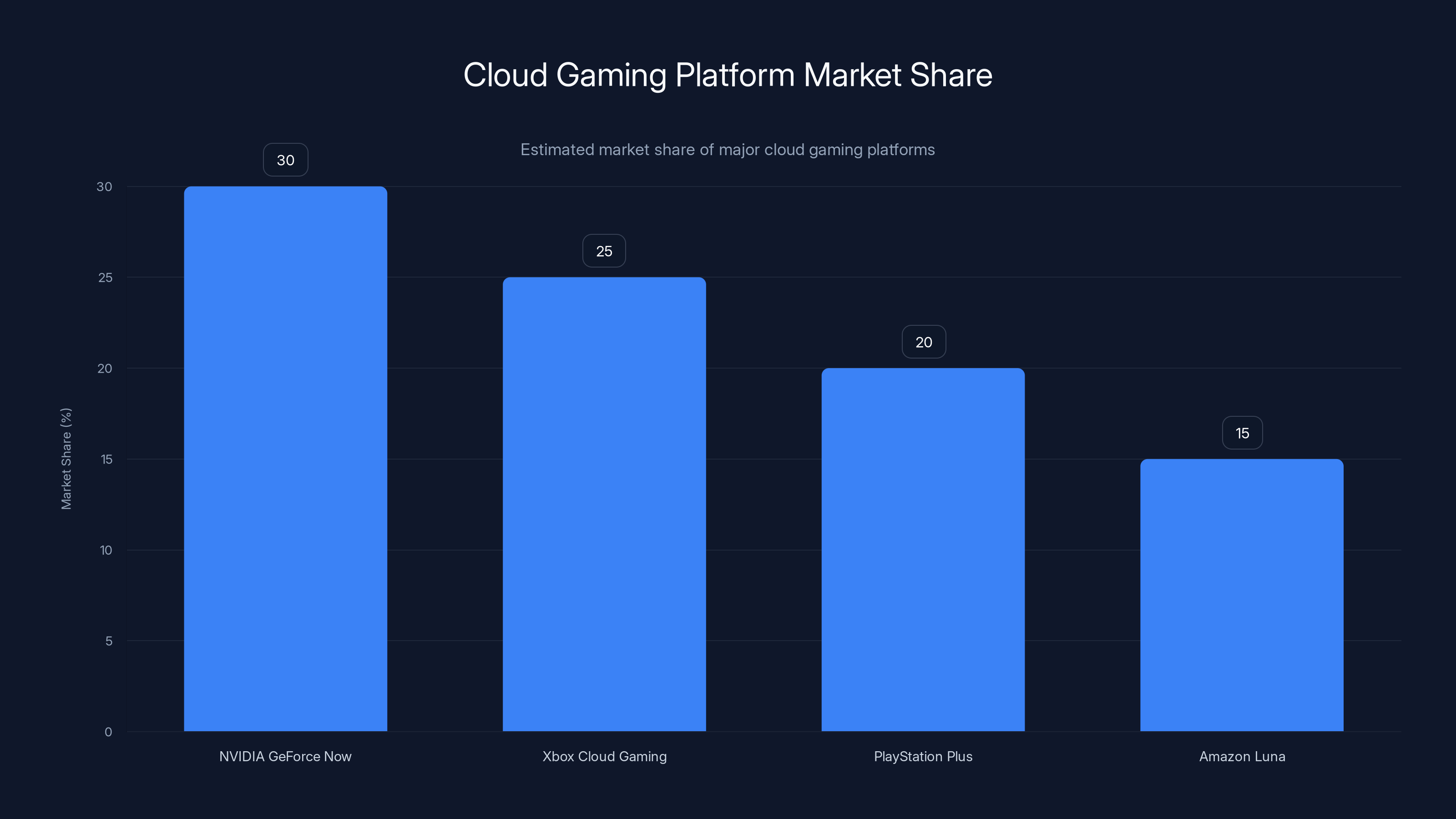
Estimated market share shows NVIDIA GeForce Now leading with 30%, followed by Xbox Cloud Gaming at 25%. Estimated data.
Future Outlook: Where OLED Television Technology Is Heading
Rollable and Flexible Display Innovations
LG has demonstrated rollable OLED display prototypes that can curl into cylindrical shapes, suggesting potential future television products that can be stored when not in use or transformed between different form factors. While 2026 products don't include rollable displays, the parallel engineering efforts suggest that flexible OLED displays may transition from research demonstrations to commercial products within the next few years.
Rollable televisions would represent a fundamental shift in how consumers integrate displays into living spaces. Rather than mounting a permanent television that occupies wall space continuously, a rollable display could extend from a cabinet when needed and retract when not in use. This innovation would address the aesthetic compromise many consumers face between wanting television capability and preferring rooms without a permanently mounted black rectangle.
Brightness Scaling and Continued Luminance Improvements
The 20% brightness improvement in the 2026 G6 continues a multi-year trend of OLED brightness enhancement. If this trajectory continues, OLED displays within the next 2-3 generations could approach or exceed the brightness performance of some mini-LED implementations while maintaining OLED's superior contrast and color accuracy advantages. At that point, OLED's traditional brightness disadvantage would be definitively addressed, eliminating one of the primary reasons consumers select alternative technologies.
Cloud Gaming Infrastructure and Latency Reduction
Cloud gaming will become increasingly practical as network infrastructure improvements reduce latency and ISPs increase baseline bandwidth. Dedicated 5G gaming networks, fiber-to-the-home buildouts, and edge computing infrastructure positioned closer to consumers will progressively improve the cloud gaming experience. Televisions with native 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming support position early adopters to leverage these infrastructure improvements as they materialize.

Making Your Purchase Decision: Key Considerations
Room Lighting Conditions and Brightness Requirements
Consumers should evaluate their typical viewing environment's lighting conditions when deciding between OLED tiers. If your primary viewing space receives direct sunlight during daytime hours or includes bright ambient lighting from ceiling fixtures, the G6's enhanced brightness becomes a practical necessity rather than a luxury upgrade. Consumers with consistently dark viewing spaces have less pressing need for maximum brightness, making the C6 or previous-generation models sensible choices.
Test the brightness characteristics in your specific room if possible. Many retailers maintain display units where you can observe how different OLED models appear under the lighting conditions of your actual environment. A model that looks brilliant under showroom lighting might appear inadequate in your brightly-lit living room, or conversely, might seem unnecessarily bright if your room is typically darkened during viewing.
Gaming Priority and Performance Requirements
Consumers who prioritize gaming should prioritize the 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming support and latency optimization features that LG has emphasized in the 2026 lineup. If your gaming primarily involves PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X, or Nintendo Switch (which has its own processing), the cloud gaming features are less critical unless you specifically plan to use cloud gaming services. However, the underlying gaming optimizations—variable refresh rate, game mode latency reduction—benefit all gaming sources.
Competitive gamers should prioritize the fastest response times and lowest input latency possible, favoring models explicitly designed for gaming rather than general-purpose displays. The gaming-specific optimizations in LG's 2026 lineup reflect refinements over previous generations, but the fundamental response time advantages of OLED remain consistent across the lineup.
Content Type and Viewing Habits
Consider your actual content consumption patterns when evaluating specifications. A consumer who watches primarily streaming video from Netflix and Disney+ benefits from the general picture quality improvements of 2026 models, though the distinctions between G6, C6, and previous-generation models might be subtle in typical viewing. HDR content viewers—particularly those watching theatrical releases, nature documentaries, and modern action films shot in HDR—benefit more substantially from the brightness and color improvements.
Film enthusiasts and home theater calibration enthusiasts should prioritize color accuracy and HDR performance, where the Tandem RGB panels and enhanced brightness of 2026 models deliver measurable improvements. Casual viewers watching standard definition content or non-HDR streaming video experience more modest improvements from the 2026 lineup compared to previous-generation models.

FAQ
What is the Tandem RGB panel technology that appears in the LG C6?
Tandem RGB refers to a dual-stack OLED architecture that eliminates the white subpixel found in traditional WRGB panels, instead using stacked OLED materials to achieve higher brightness and improved color saturation across brightness ranges. This architecture allows individual red, green, and blue subpixels to achieve maximum brightness independently, delivering more vibrant colors in bright scenes compared to WRGB panels where spectral filtering reduces brightness for certain colors.
How does the 20% brightness increase in the LG G6 impact real-world viewing?
The 20% brightness improvement translates to approximately 40-50 additional nits of peak brightness, extending from roughly 200 nits to 240-260 nits depending on implementation. This enhancement primarily benefits viewers with bright rooms, making OLED displays viable for living spaces receiving direct sunlight where previous-generation models appeared washed out. The improved brightness also enhances HDR content performance by allowing bright highlights to be displayed more convincingly without tone mapping compression.
What is cloud gaming and why does 4K 120 Hz support matter?
Cloud gaming executes games on remote servers and streams video output to your television, similar to how Netflix streams movies. 4K 120 Hz support enables these streams to transmit at 4K resolution and 120 frames per second, requiring both high-quality network infrastructure and displays capable of receiving and rendering such streams. This specification becomes practically relevant as cloud gaming services mature and network infrastructure improves, though availability of 4K 120 Hz gaming content remains limited in early 2026.
How thin is the LG Wallpaper OLED and how does that affect performance?
The LG Wallpaper OLED measures approximately 3.8 millimeters thick for the display module itself, achieving ultra-thin aesthetics through relocation of processing electronics to an external box and innovative thermal management solutions. The thinness affects installation flexibility (requires wall mounting rather than placement on furniture) and component accessibility, but doesn't negatively impact display performance since the OLED panel operates identically to conventionally-framed models. The external processor box handles all computational functions typically housed behind the display.
What is anti-reflective coating and how does it improve OLED viewing?
Anti-reflective coating consists of microscopic surface variations that scatter reflected light rather than allowing mirror-like specular reflection. This treatment reduces the appearance of reflections from ceiling lights or window reflections that would otherwise appear sharply defined on the display surface. The scattering diffuses reflected light, making reflections less visually intrusive even in bright rooms. Combined with enhanced brightness, anti-reflective coating makes OLED displays more practical for environments with bright ambient lighting.
How does OLED brightness compare to other television technologies?
OLED displays produce light through self-emissive pixels, fundamentally limiting brightness since pushing individual pixels to maximum luminance continuously would degrade organic materials. LED-backlit displays can achieve higher peak brightness by increasing backlight intensity because brightness is distributed across all pixels simultaneously. Mini-LED displays, using thousands of small backlights, achieve intermediate brightness levels while maintaining zone-based dimming control. OLED's advantages in contrast and color accuracy often outweigh the brightness disadvantage in many viewing scenarios, though 2026 brightness improvements narrow this gap significantly.
Should I buy the G6 or C6 based on my viewing environment?
Choose the G6 if you have bright ambient lighting conditions, prioritize maximum brightness for HDR content, or plan to use cloud gaming services extensively. Choose the C6 if your viewing occurs primarily in normal- to dim-lighting conditions, you prioritize vibrant color performance in colorful content, or you seek good value with next-generation panel technology at a lower price point. The Tandem RGB panel in the C6 might actually deliver superior color saturation compared to the G6 for specific content types, making this not a straightforward upgrade path.
What internet speed do I need for 4K 120 Hz cloud gaming?
Streaming 4K 120 Hz requires approximately 40-100 megabits per second depending on compression efficiency and the specific cloud gaming service. Beyond raw bandwidth, you need consistently low latency (ideally under 50 milliseconds) and stable connection without packet loss. Fiber-optic gigabit connections represent the ideal scenario, while conventional cable internet (100-300 Mbps) can support cloud gaming with potential limitations during peak hours or congestion. Latency matters more than peak bandwidth for cloud gaming quality, making network proximity to cloud gaming servers important.
How does variable refresh rate technology improve gaming performance?
Variable refresh rate (VRR) synchronizes the display's refresh rate with incoming frame rates, eliminating stuttering and tearing that occurs when frame production doesn't align with display refresh timing. At 120 Hz fixed refresh rate, a game producing 115 frames per second causes visible tearing or frame duplication artifacts. VRR-capable displays instead adjust their refresh to 115 Hz, smoothly displaying those frames without artifacts. This technology is borrowed from gaming monitors and has become increasingly common in gaming-capable televisions.
What is the expected lifespan of 2026 OLED televisions?
Modern OLED displays have typical useful lifespans of 25,000-50,000 hours, depending on usage patterns and brightness levels. A television used 4 hours daily would reach 25,000 hours after approximately 17 years. OLED materials degrade over time, with brightness gradually declining as hours accumulate. The enhanced brightness of 2026 models means they start brighter, so even with similar degradation rates, they'll maintain acceptable brightness levels longer than previous-generation models. Burn-in—where static images leave permanent traces—remains a theoretical concern with OLED, though modern displays incorporate various mitigation techniques.

Conclusion: The 2026 OLED Generation and the Future of Premium Television
LG's 2026 OLED television announcements represent a meaningful evolution in a technology category that has already redefined how premium television experiences should perform. The combination of the G6's enhanced brightness and anti-reflective improvements, the C6's Tandem RGB panel advancement, the Wallpaper model's aesthetic integration, and the cloud gaming televisions' forward-looking specifications collectively demonstrate that OLED technology continues advancing along multiple dimensions rather than hitting a technological plateau.
For consumers considering television investments in 2026, these models offer compelling value propositions across multiple use cases. The brightness improvements particularly matter for anyone who previously felt constrained by OLED's traditional brightness limitations, making the technology viable for rooms and lighting conditions where it previously struggled. The Tandem RGB technology democratizes display advancement across the lineup, ensuring that consumers selecting the more affordable C6 still benefit from meaningful technological progress rather than settling for last-generation specifications.
The cloud gaming implementation represents perhaps the most forward-looking aspect of the announcement, positioning these televisions as future-ready hardware that will deliver increasingly compelling experiences as cloud gaming infrastructure matures over the next 2-3 years. This future-proofing justifies the premium positioning of these models versus conventional televisions that might struggle with emerging content formats and services.
Consumers should prioritize their specific use cases and viewing environments when selecting between the available options. A customer with a bright living room benefits most from the G6's brightness advantages, while someone in a darkened theater room might find the C6's superior color performance more impactful. Gaming enthusiasts should emphasize the latency optimization and cloud gaming features, while movie enthusiasts should prioritize HDR performance and color accuracy.
The broader trend evident in LG's 2026 announcement reflects the television industry's maturation toward sophistication rather than revolutionary change. Manufacturers continue incrementally improving brightness, color accuracy, and processing capabilities, but we're unlikely to see the dramatic capability jumps that characterized the transition from 1080p to 4K or the adoption of HDR. Instead, the industry is perfecting OLED technology, addressing known limitations, and optimizing for emerging use cases like cloud gaming.
For teams and professionals seeking efficient ways to communicate these technical specifications and product information to broader audiences, platforms like Runable offer AI-powered document and presentation generation capabilities. At just $9/month, Runable enables organizations to automatically generate specification sheets, comparison documents, and technical presentations from product data, reducing the manual effort required to market and explain complex display technologies to consumers and business partners.
Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to 2026 OLED models should depend on how your current television falls short of your requirements. If brightness remains an issue, HDR performance disappoints, or you specifically want cloud gaming support, the 2026 lineup offers compelling improvements worth the investment. If your current display satisfies your needs, the incremental nature of these improvements might not justify immediate upgrading, though the enhanced technology will certainly influence purchasing decisions for consumers shopping in the current market.
The premium television market will undoubtedly continue evolving, with new technologies and capabilities emerging over the coming years. However, LG's 2026 OLED offerings represent a particularly well-rounded evolution that addresses multiple previously-limiting factors while preparing for emerging usage patterns. Whether you select the flagship G6 or the value-oriented C6, you're investing in display technology that will likely satisfy demanding requirements for many years to come.

Key Takeaways
- LG's G6 achieves 20% brightness improvement addressing OLED's primary limitation, making the technology viable for bright rooms
- Tandem RGB panel in the C6 delivers superior color saturation compared to traditional WRGB, democratizing advanced panel technology across price tiers
- Ultra-thin Wallpaper OLED measures 3.8mm thick through innovative thermal management and external processor architecture
- Native 4K 120Hz cloud gaming support positions LG televisions for emerging streaming services and next-generation gaming infrastructure
- Brightness improvements significantly enhance HDR performance by reducing tone mapping compression and allowing brighter highlights
- Variable refresh rate and game mode optimizations deliver competitive gaming performance alongside cinematic capabilities
- 2026 lineup represents incremental but meaningful evolution addressing known OLED limitations rather than revolutionary technology change
- Purchase decisions should prioritize room lighting conditions (brightness needs), content type (gaming vs movies), and viewing habits
- Tandem RGB technology in C6 may deliver superior color performance to G6 for colorful content despite lower peak brightness




