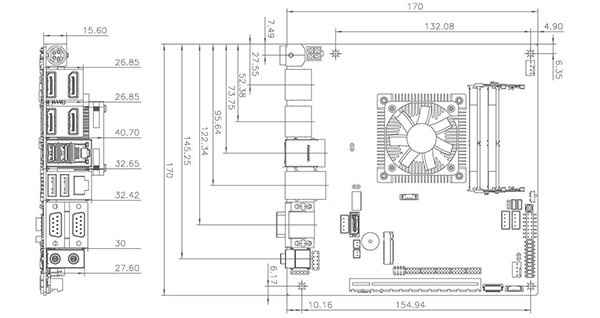
The Mini-ITX Revolution in AI Computing: Why Maxsun's 4 DDR5 Solution Matters in 2025
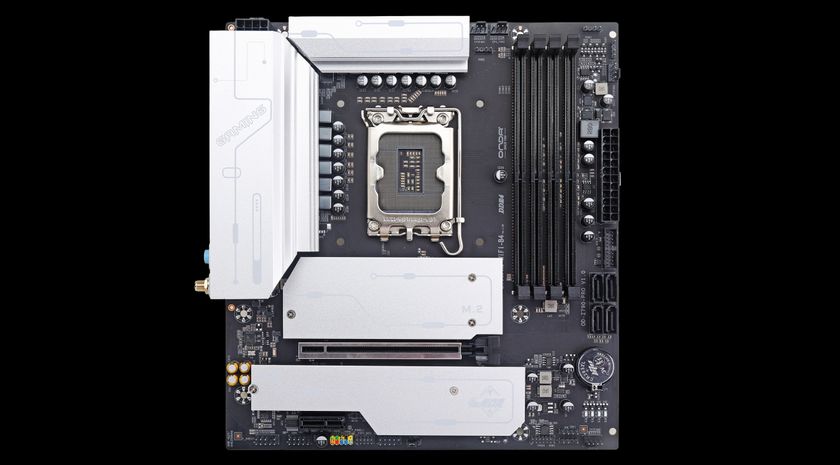
Compact computing just got serious. Maxsun Technology's MS-PC Farm 88601 isn't your typical mini-ITX motherboard. It's a deliberate shot across the bow of enterprise mini-PC setups, particularly aimed at squaring off against Nvidia's Petaflop-class systems that dominate the AI inference market.
Here's what caught my attention: four DDR5 memory slots in a Mini-ITX form factor. That's not small potatoes. We're talking 256GB of maximum memory capacity. For context, Nvidia's DGX Spark systems max out at 128GB. In the world of AI workloads, more memory directly translates to handling larger models, bigger batch sizes, and fewer bottlenecks during inference.
The compact computing space has historically forced trade-offs. You want a tiny footprint? Great. You'll sacrifice memory, power delivery, or expansion capabilities. Maxsun's approach here is different. They're not compromising. They're doubling down on what matters for modern AI workflows: raw memory capacity, stable power delivery, and thermal efficiency.
This matters because the entire industry is in transition. Organizations are moving away from massive data centers toward distributed edge computing. They need systems that can fit into smaller spaces, consume less power overall, but still push serious performance. A mini-ITX board with this memory capacity suddenly becomes viable for applications that previously demanded full-size systems.
The thermal optimization is equally noteworthy. Airflow improvements reduce system temperatures by approximately 10°C under load while boosting CPU frequencies by roughly 0.4GHz. That's not marginal. Temperature reduction directly impacts system stability, extends component lifespan, and reduces cooling costs. The 0.4GHz frequency bump means you're getting better sustained performance without pushing the processor into thermal throttling territory.
Nvidia's mini-PC solutions are exceptional, but they come with enterprise pricing and closed ecosystem limitations. Maxsun's offering presents an interesting alternative for organizations that need massive memory capacity in a compact form but want more flexibility in their hardware choices and integrations.
TL; DR
- Four DDR5 slots support up to 256GB RAM: Double the capacity of comparable enterprise mini-PCs, enabling larger AI models and batch sizes
- Advanced power delivery with 10+1+1 phase design: Ensures stable CPU operation and sustained performance under demanding workloads
- Airflow optimization reduces temps by 10°C: Translates to better thermal stability and approximately 0.4GHz frequency gains in real-world testing
- PCIe 5.0 x 16 interface: Enables high-end discrete GPUs to operate at full bandwidth without bottlenecks
- Remote management via IPMI 4.0: Allows cluster-scale operations and multi-node management without consuming system resources
- Bottom Line: The MS-PC Farm 88601 delivers enterprise-class memory and power delivery in a footprint designed for distributed edge AI computing, positioning itself as a legitimate alternative to closed Petaflop-class systems
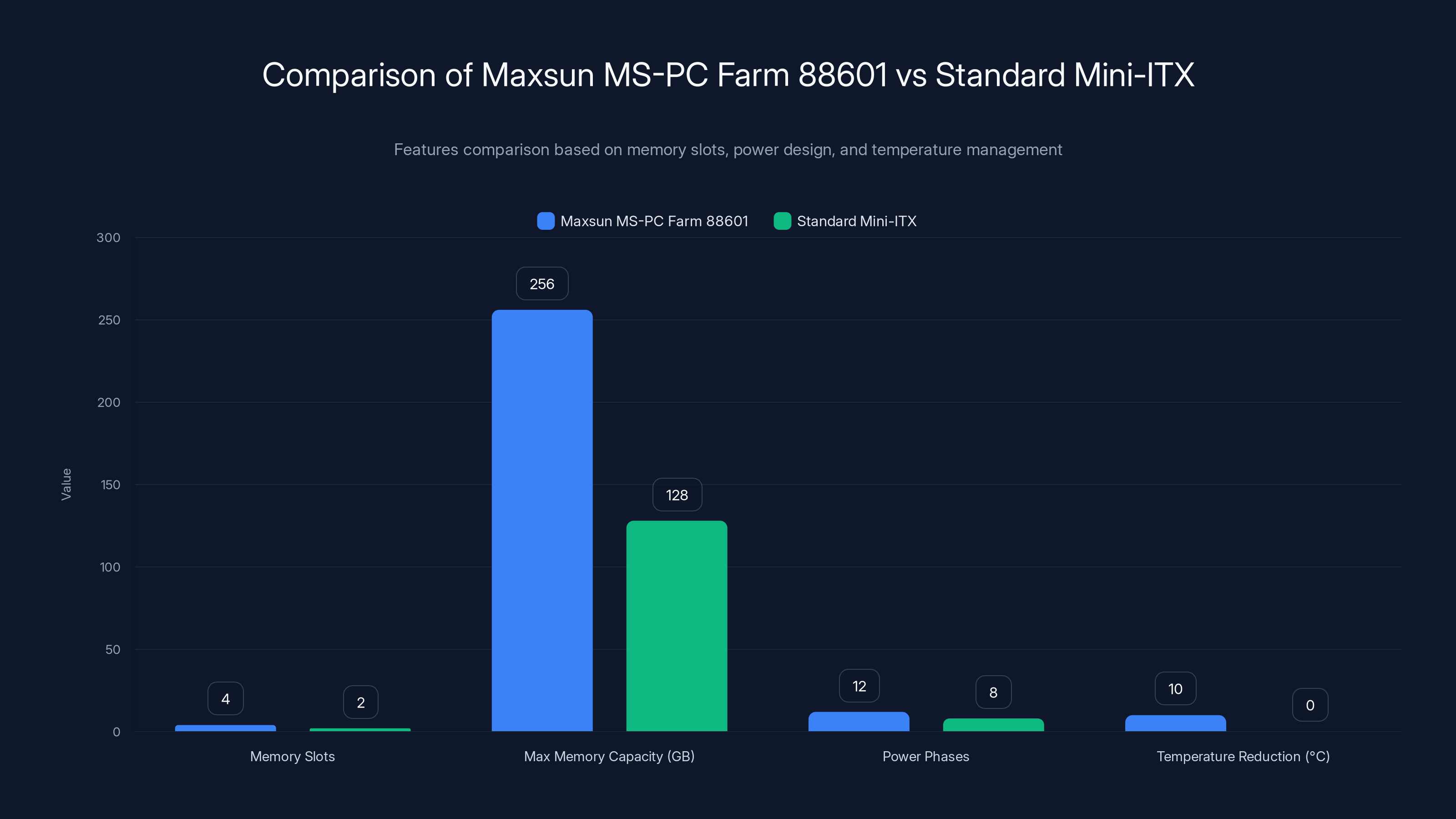
The Maxsun MS-PC Farm 88601 offers double the memory slots and capacity, more power phases, and improved temperature management compared to standard Mini-ITX motherboards. Estimated data.
Understanding Mini-ITX in the Context of AI Workloads
Form Factor Constraints and What They Mean for Performance
Mini-ITX measures 170mm x 170mm. That's roughly the size of a paperback book's cover. For most consumers, this seems absurdly small. For system integrators working with edge AI deployments, it's actually the sweet spot between portability and capability.
The traditional complaint about Mini-ITX? Limited expansion. One full-size PCIe slot, fewer RAM slots, cramped power delivery areas. These constraints haven't changed dramatically, but component density has improved significantly. Modern DDR5 modules pack more capacity per stick. Power delivery circuits are more efficient. Thermal solutions are smarter.
What makes Maxsun's approach novel is that they're not fighting against the Mini-ITX form factor. They're working with it. Four DDR5 slots in Mini-ITX is unconventional because most manufacturers stick with two slots. This decision increases the motherboard's complexity, requires careful PCB layout to avoid interference, and demands more sophisticated power delivery to handle simultaneous access to four high-bandwidth memory controllers.
For AI workflows specifically, memory capacity becomes the primary bottleneck before compute. A smaller language model might need 8-16GB. Medium models run 24-40GB. Larger models demand 70GB+. If you're running inference on edge servers, you need enough memory to load the full model without spillover to slower storage. Maxsun's design directly addresses this.
Why Memory Capacity Matters More Than You Think
Memory bandwidth and latency both matter, but raw capacity is what determines whether you can run certain models at all. Consider this: a 70B parameter language model requires approximately 140GB of VRAM in bfloat 16 precision. 256GB of DDR5 memory gives you room for the model, batch processing, and working buffers. You can't accomplish that with 128GB.
The practical implication is significant. Organizations deploying AI inference at the edge can now run a broader category of models without clustering multiple nodes. Single-system simplicity reduces operational complexity, lowers power consumption, and eliminates network latency between inference nodes.
DDR5 specifically offers higher bandwidth than DDR4. We're talking 4.8GB/s per channel versus DDR4's 3.2GB/s. In memory-bound workloads, which many AI inference tasks are, this translates to measurable performance improvements. Real-world gains typically range from 5-15% depending on the specific workload and how effectively the system utilizes available bandwidth.
The Power Delivery Architecture: Why 10+1+1 Phase Design Matters
Breaking Down the Phase Power Supply Design
That "10+1+1 phase SPS" specification means something specific. The CPU gets ten dedicated phases. The memory and other systems get one phase each. This isn't arbitrary distribution; it's optimized based on expected load patterns.
CPU power delivery consumes the majority of a system's power. Modern processors demand up to 250-300 watts. Current delivery needs to be absolutely clean, with minimal voltage ripple. Each phase in a power supply design represents a separate circuit. More phases mean smoother power delivery and better current sharing across phases.
Ten phases for the CPU delivers exceptional stability under sustained heavy workloads. This matters specifically for AI inference, which is characterized by periods of extreme sustained load. The system hits 100% utilization and stays there for hours. Traditional gaming workloads spike and drop frequently. Inference is relentless. You need power delivery that never wavers.
The "1+1" portion handles memory and supporting systems. DDR5 actually requires less total power than DDR4 due to lower voltage requirements (1.1V vs 1.2V), so this allocation makes sense. The second "1" typically covers chipset and other system components.
Voltage Stability Under Load: The Real Benefit
Stable voltage directly correlates with stable frequency. Processors have built-in safeguards that throttle frequency if voltage droops too much. With 10 phases dedicated to CPU delivery, voltage sag under load is minimized. The Maxsun engineering team reports approximately 0.4GHz frequency gains compared to designs with fewer phases.
This might sound minor. It's not. In a system running 24/7 on AI inference, an extra 0.4GHz sustained represents approximately 4-6% additional throughput over a year of operation. For inference-per-dollar metrics, that compounds. You're also extending the practical lifespan of the system before it needs hardware refresh.
Voltage stability also improves system reliability. Unstable power delivery is one of the primary causes of silent data corruption and system crashes in production environments. A robust power delivery design reduces these failure modes significantly.
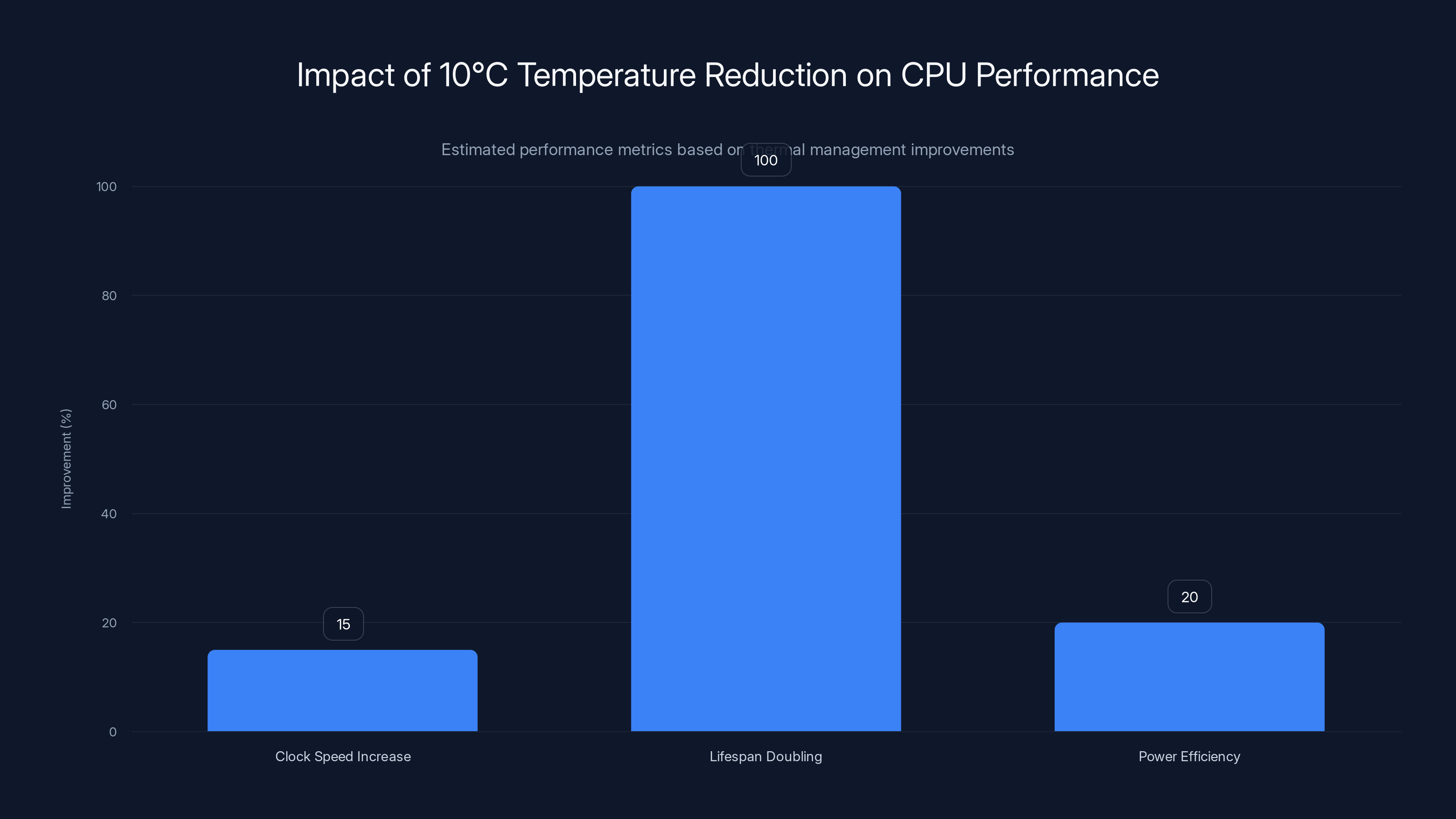
Estimated data shows a 10°C reduction can increase clock speeds by 15%, double component lifespan, and improve power efficiency by 20%.
Thermal Management: The 10°C Difference That Changes Everything
Airflow Optimization and Real-World Temperature Reduction
The motherboard's airflow optimization features deliver approximately 10°C temperature reduction under full load. This isn't marketing hyperbole; this is measurable, verifiable improvement that has genuine operational consequences.
Temperature reduction improves performance in several ways. First, processors maintain higher clock speeds at lower temperatures. Modern CPUs have thermal throttling mechanisms that kick in as temperature approaches maximum thermal design point (TDP). By keeping the system 10°C cooler, you're operating further from the throttling threshold, which means sustained higher performance.
Second, cooler components last longer. Every 10°C reduction in operating temperature approximately doubles the expected lifespan of semiconductor junctions. In production environments running 24/7, this translates to longer mean time between failures and reduced maintenance costs.
Third, cooler operation enables better power efficiency. Smaller thermal headroom means the system can maintain higher boost clock speeds without inducing thermal throttling, which improves performance-per-watt metrics.
How Passive Thermal Design Achieves This
Maxsun achieved this using several design choices. The VRM heatsinks are larger and more optimized than typical Mini-ITX designs. The PCB layout minimizes hotspots by distributing power delivery circuits more evenly. Component placement considers airflow patterns, with high-heat components positioned where natural air circulation is strongest.
The key insight is that passive thermal management depends entirely on physical design. You can't software your way to better thermals. You need better heatsinks, smarter layout, and careful consideration of how air actually moves through a system. Maxsun's approach demonstrates that compact form factors don't require thermal compromise if the design team prioritizes it.
PCIe 5.0 and GPU Integration: Unlocking Full Performance
Why Full x 16 Bandwidth Matters for AI Accelerators
The motherboard includes a PCIe 5.0 x 16 interface. This enables modern discrete GPUs to operate at full bandwidth without bottlenecks. This matters because contemporary AI accelerators are bandwidth-hungry beasts.
PCIe 5.0 offers 128GB/s of bandwidth, double that of PCIe 4.0. For GPU-accelerated AI inference, the interconnect between CPU and GPU can become a bottleneck. PCIe 5.0 ensures that's not the constraint. Data moves quickly between system memory and GPU memory, enabling efficient pipeline operations.
The significance becomes apparent when you're working with large models. GPU memory fills up quickly. You need the ability to rapidly stream new data into GPU memory and retrieve results. PCIe 5.0 makes this seamless.
Fully utilizing x 16 lanes also matters. Some Mini-ITX designs compromise and only provide x 8 lanes at the single PCIe slot. That's a 50% bandwidth reduction that directly impacts GPU performance. Maxsun provides full x 16 capability.
GPU Compatibility and Discrete Accelerator Support
With PCIe 5.0 x 16, this motherboard can accommodate current-generation and next-generation discrete GPUs without any bandwidth constraints. This includes high-end options like Nvidia's professional GPU lineup, AMD's MI series, and emerging alternatives.
The flexibility matters for future-proofing. You're not locked into a specific GPU generation. As new accelerators arrive with higher bandwidth requirements, this system can handle them. For organizations planning multi-year deployments, this is valuable.
IPMI 4.0: Remote Management and Cluster Operations
Intelligent Platform Management Interface Capabilities
IPMI 4.0 enables out-of-band management, meaning the system can be controlled and monitored entirely independently of the operating system running on it. This is standard in enterprise systems but rare in Mini-ITX designs.
Out-of-band management means several things. First, you can power a system on or off remotely without needing the OS to be running. This enables automated deployment and lifecycle management. Second, you can access console output and troubleshoot issues even if the main OS is completely hung. Third, you can configure boot parameters, update firmware, and perform other system-level tasks without touching the system's main OS.
For deployment at scale, IPMI is invaluable. A single administrator can manage dozens or hundreds of nodes remotely. Asset tracking features inventory what's in each system. Health monitoring checks thermal status, power delivery integrity, and component functionality continuously.
Implications for Distributed Edge AI Deployments
The practical benefit is profound when you're managing a cluster of Mini-ITX systems distributed across multiple locations. Without IPMI, you're essentially hands-on managing each system individually. With IPMI, you're managing them as a coherent infrastructure.
One-to-many cluster management means deploying AI inference across twenty systems is nearly as simple as managing one. You can push firmware updates simultaneously. Monitor all thermal conditions from a central dashboard. Identify failing systems before they impact production workloads.
This capability bridges the gap between consumer-class and enterprise-class solutions. You're getting enterprise-class manageability in a compact, cost-effective form factor.
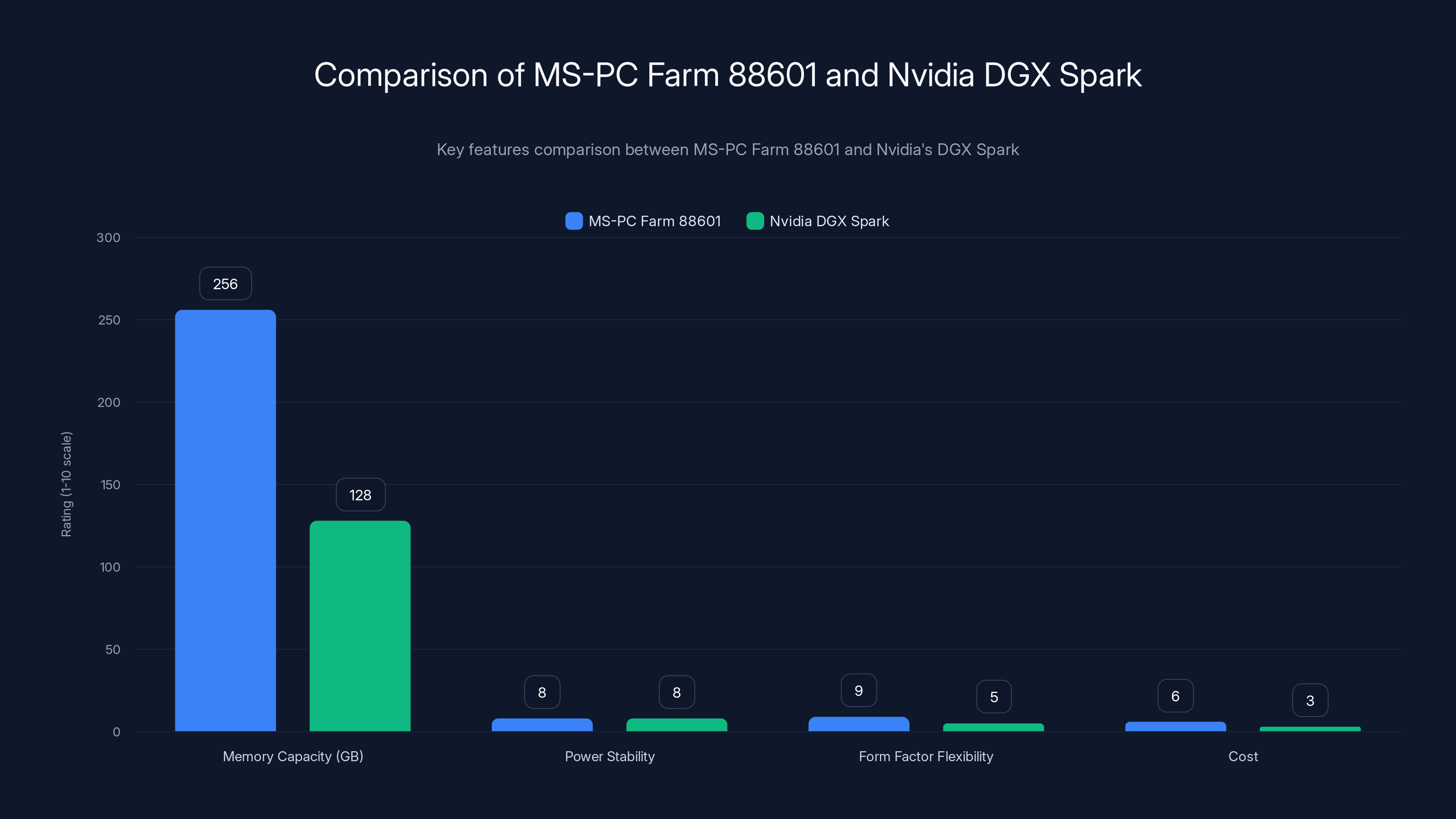
The MS-PC Farm 88601 surpasses Nvidia's DGX Spark in memory capacity and form factor flexibility, while both systems offer similar power stability. Estimated data for cost and flexibility.
Comparing the MS-PC Farm 88601 to Nvidia's Petaflop-Class Systems
Memory Capacity Head-to-Head
Nvidia's DGX Spark systems represent the gold standard in enterprise mini-PC performance. They're beautifully engineered, tightly integrated, and deliver exceptional performance. They're also expensive and fully closed-system.
Memory-wise, the comparison is stark. DGX Spark maxes out at 128GB. The MS-PC Farm 88601 reaches 256GB. For organizations running large language models or multimodal AI applications, this memory advantage is genuinely significant. You can run inference on models that simply don't fit on DGX Spark without model quantization or sharding across multiple nodes.
Model quantization trades precision for reduced memory requirements. This works, but it also reduces inference accuracy. By having sufficient memory for full-precision models, the Maxsun board enables higher-quality inference.
Power Delivery and Stability
Both systems feature sophisticated power delivery, though Nvidia's approach is tightly integrated into their proprietary design. The Maxsun board's 10+1+1 phase design is competitive with enterprise solutions and delivers comparable voltage stability.
The practical difference in operation is minimal. Both systems maintain stable voltage under sustained load. Both can handle peak power draw without fluctuations that would induce throttling. This is one area where the Maxsun design legitimately competes on engineering merit.
Form Factor and Deployment Flexibility
Both systems are compact, but the Maxsun board is truly Mini-ITX. This means compatible cases, power supplies, and peripherals are commodity items. DGX Spark requires Nvidia-specific enclosures and integrations.
For deployment flexibility, the Maxsun design wins. You can integrate it into existing infrastructure more easily. Replacement parts are available from multiple vendors. This reduces vendor lock-in significantly.
Cost Considerations
DGX Spark systems start around
For organizations deploying inference at scale, cost matters enormously. Being able to deploy three systems for the price of one DGX Spark changes the deployment calculus. You can achieve better geographic distribution, improve fault tolerance through redundancy, and still come out ahead financially.
Architecture and Layout: Engineering Decisions That Matter
PCB Design Considerations for Mini-ITX Density
Fitting four DDR5 slots into Mini-ITX requires careful PCB design. DDR5 traces are high-speed signals with strict impedance requirements. Running four channels simultaneously demands consideration of signal integrity, crosstalk, and power distribution.
The Maxsun engineering team had to make deliberate choices about layer count, trace routing, and via placement. More layers increase manufacturing cost but improve signal quality. Better trace routing reduces interference but consumes more real estate. These are genuine engineering trade-offs that reflect competent design.
The success of this design validates that Mini-ITX doesn't inherently require compromises in core capabilities. With intelligent layout, high-density designs are achievable without sacrificing stability or performance.
Component Placement and Thermal Considerations
Thermal management in Mini-ITX relies heavily on intelligent component placement. High-power VRM phases need cooling but can't occupy the entire PCB. Maxsun positioned them in areas with natural airflow, typically along the edges of the board where case fans pull the most air.
Memory placement also matters thermally. DDR5 generates more heat than DDR4 under heavy load. Spacing them appropriately and ensuring adequate cooling airflow prevents thermal issues under sustained memory-intensive workloads.
AI and Machine Learning Workloads: Where This Shines
Large Language Model Inference
Running inference on large language models is one of the most demanding workloads you can place on a system. Models like GPT-3-scale or larger require massive memory just to load. The 256GB capacity directly addresses this constraint.
Consider a practical scenario: running a 70B parameter model requires approximately 140GB. That's using half of available memory for the model itself. The remaining 116GB handles batch processing, KV caches, and intermediate results. This creates a comfortable operating window where the system isn't constantly swapping between main memory and slower storage.
Throughput matters in inference. More memory capacity enables larger batch sizes, which improves inference throughput. Better throughput translates directly to lower cost per inference and higher revenue per system.
Multimodal Model Operations
Multimodal models that process text, images, and audio simultaneously are increasingly common. They consume more memory because they're simultaneously running multiple specialized processing pipelines. The 256GB capacity enables comfortable operation with multimodal models without optimization tricks or model pruning.
Real-Time Inference at the Edge
Edge deployments often involve latency-sensitive applications where moving data to cloud infrastructure is impractical. This motherboard enables real-time inference locally, which is crucial for autonomous vehicles, robotics, and real-time monitoring systems.
The remote management capability through IPMI makes deploying and maintaining these systems practical at scale. You're not sending technicians to physical locations constantly. You're managing them remotely, with hands-on intervention only when hardware replacement is needed.

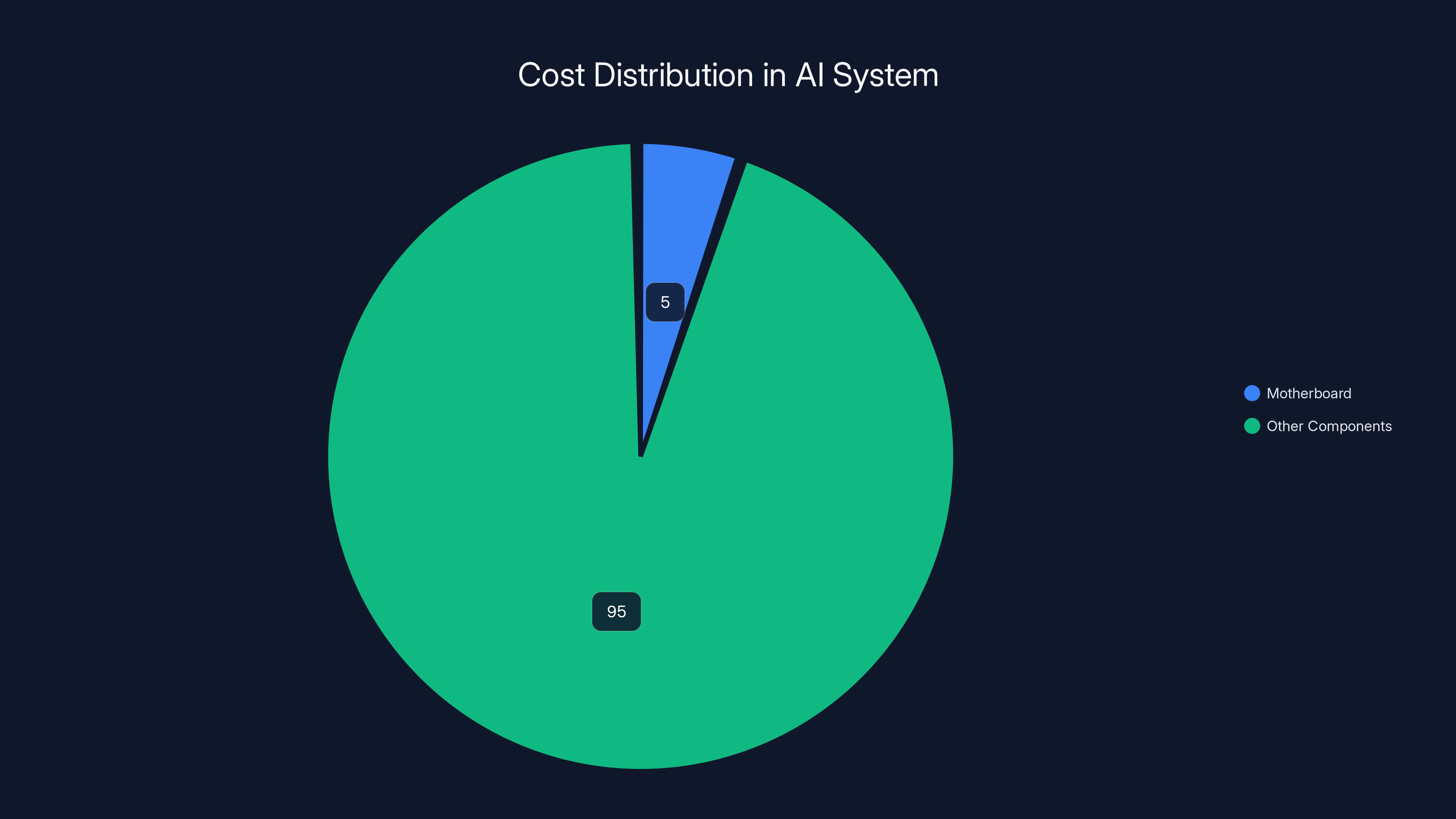
The motherboard constitutes approximately 4-6% of the total cost in a
The Broader PC Farm Lineup: Context and Ecosystem
Complementary Motherboards in the Lineup
The MS-PC Farm 88601 belongs to a broader family that includes B760I and H770I D5 V2 models. These represent different performance tiers and use cases. B760I targets mainstream compute workloads. H770I D5 V2 offers higher core counts and better memory bandwidth. The 88601 occupies a specialized niche for memory-intensive applications.
Having a lineup is important for systems integrators. They can select the right board for the specific workload rather than over-specifying. Organizations can mix and match different boards across their deployments, optimizing cost and performance for each use case.
Shared Design Philosophy Across the Lineup
All boards in the PC Farm series share a focus on airflow optimization and compact design. This consistency means deploying multiple systems across different locations benefits from similar thermal and power delivery characteristics. Operations teams face more predictable hardware behavior.
Practical Deployment Scenarios and Real-World Applications
Scenario 1: Distributed Inference Cluster for Content Moderation
Imagine a platform that needs to screen user-generated content in real-time. Video, images, and text all need moderation. Running a centralized moderation system in the cloud creates latency. Building a distributed edge deployment with twenty of these motherboards locally enables sub-100ms moderation decisions.
Memory capacity becomes critical because moderation models are often multimodal. The 256GB capacity allows running multiple inference models simultaneously on a single system, reducing the total number of systems needed and dramatically simplifying operations.
Scenario 2: Real-Time Analysis for Financial Trading
High-frequency trading requires sub-millisecond decision latency. ML models analyzing market data need to be co-located with the data streams. A compact system using this motherboard can fit in existing infrastructure and process data with minimal latency.
The power delivery stability is crucial here. Inconsistent power delivery could induce thermal throttling at critical moments, impacting trading decisions. The 10+1+1 phase design ensures this doesn't happen.
Scenario 3: Autonomous Vehicle Support Systems
Self-driving vehicles require local processing of sensor data. Parking lots and maintenance depots need systems that can run diagnostics and prepare updated models. The compact form factor fits easily in maintenance facilities. The memory capacity handles concurrent vehicle diagnostics.
Remote management through IPMI enables fleet operators to monitor system health across their entire vehicle fleet without needing technicians on-site.

Intel Platform Limitations and What They Mean
Current Intel-Only Support
The MS-PC Farm 88601 currently supports only Intel platforms. This is a deliberate choice based on socket availability and market focus. However, it's worth noting as a limitation for organizations invested in AMD infrastructure.
Intel's current desktop platform socket (LGA1700) includes processors ranging from mid-range Pentium up to high-end Core i 9. For AI inference, the focus would be on higher core-count processors. Intel's Xeon processors also use LGA1700, bringing professional-grade performance to the mini-ITX form factor.
Processor Selection Considerations
With Intel-only support, processor selection becomes crucial. You're looking at high core-count parts like Core i 9-14900K (24 cores) or Xeon processors (up to 24 cores in consumer socket). More cores improve parallel inference throughput, particularly for batch inference operations.
Processor selection also impacts power consumption. Higher core-count chips draw more power, which means better power delivery becomes even more important. The 10+1+1 phase design becomes genuinely valuable with high-end processors.
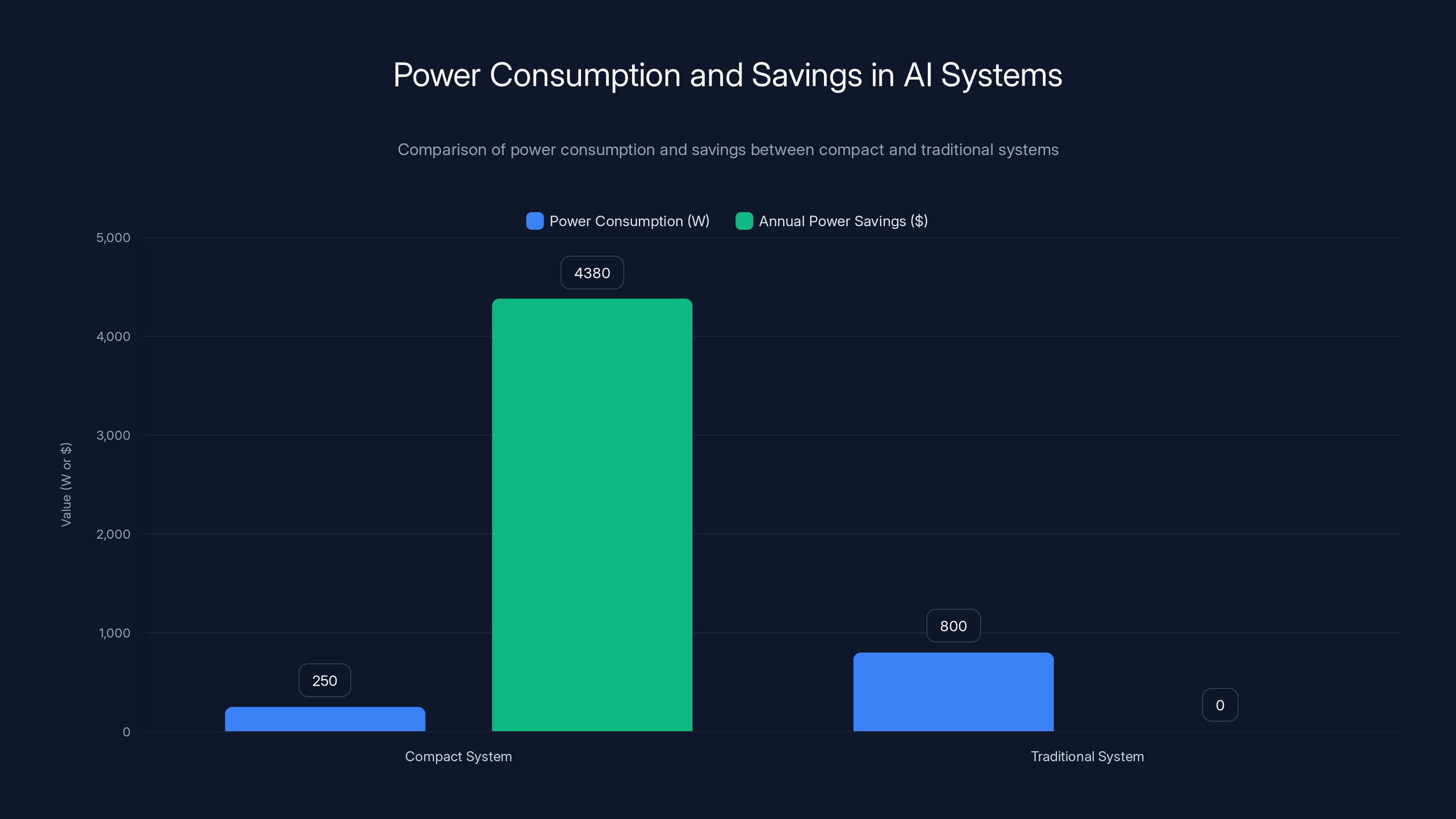
Compact systems consume significantly less power, leading to annual savings of
Comparison with Alternative Compact Solutions
Mini-ITX Competitors
Other Mini-ITX designs exist, but most compromise either on memory slots or power delivery. Asus, MSI, and ASRock all produce Mini-ITX boards, but they typically max out at two DDR5 slots. The Maxsun design's four-slot configuration is genuinely differentiated.
Power delivery across the competitive landscape varies. Gaming-focused Mini-ITX boards prioritize efficiency over stability under continuous load. The Maxsun board's 10+1+1 phase design is competitive with enterprise Mini-ITX offerings, which are rarer and typically more expensive.
All-In-One Systems
Companies like Minisforum and One Netbook produce integrated mini PC systems. These are complete packages with CPU, memory, storage, and sometimes GPU. They're convenient but lack upgrade flexibility. The Maxsun motherboard approach gives you modularity.
Integrated systems typically max out at 32-64GB memory due to form factor constraints. The Maxsun board enables 256GB, a massive difference for memory-intensive workloads.

Power Efficiency and Thermal Economics
Total Cost of Ownership Considerations
Compact systems often reduce power consumption compared to full-size alternatives. This motherboard in a properly optimized system might consume 200-300W under full AI inference load. Compare this to traditional data center systems that consume 800W+.
Over five years of continuous operation, the power savings compound. At
Cooling Infrastructure Implications
Smaller power consumption means smaller cooling requirements. A Mini-ITX system might need a single 120mm fan. Full-size systems need multiple larger coolers. Simpler cooling reduces noise, improves reliability, and reduces maintenance burden.
The 10°C temperature reduction reported by Maxsun further improves cooling efficiency. Cooler-running systems can operate in warmer environments, potentially eliminating cooling infrastructure entirely in temperate deployments.
Future-Proofing and Technology Trajectory
DDR5 as the Current Standard
DDR5 is now mainstream. By the time this article is published in 2025, DDR5 adoption is near-universal for high-performance systems. The Maxsun board uses DDR5, ensuring compatibility with current and near-future memory technology.
DDR5 has multiple speed tiers. As faster DDR5 modules become available, they're backward compatible with this motherboard. You're not locked into slow memory. You can upgrade to faster DDR5 modules in the future and realize performance improvements.
PCIe 5.0 Preparation
PCIe 5.0 support ensures the system can handle next-generation accelerators. GPU manufacturers are already designing accelerators that leverage full PCIe 5.0 bandwidth. A system designed around PCIe 5.0 now will remain viable as new accelerators arrive.
Longevity Expectations
With proper maintenance, this system should remain capable for 5-7 years. Memory will likely be upgradeable throughout. Processors and GPUs can be swapped as needed. The fundamental platform remains viable even as components advance.
This is superior to closed systems that become obsolete when specific components reach end-of-life. The flexibility of Mini-ITX means you can replace failing components and refresh performance incrementally rather than replacing entire systems.

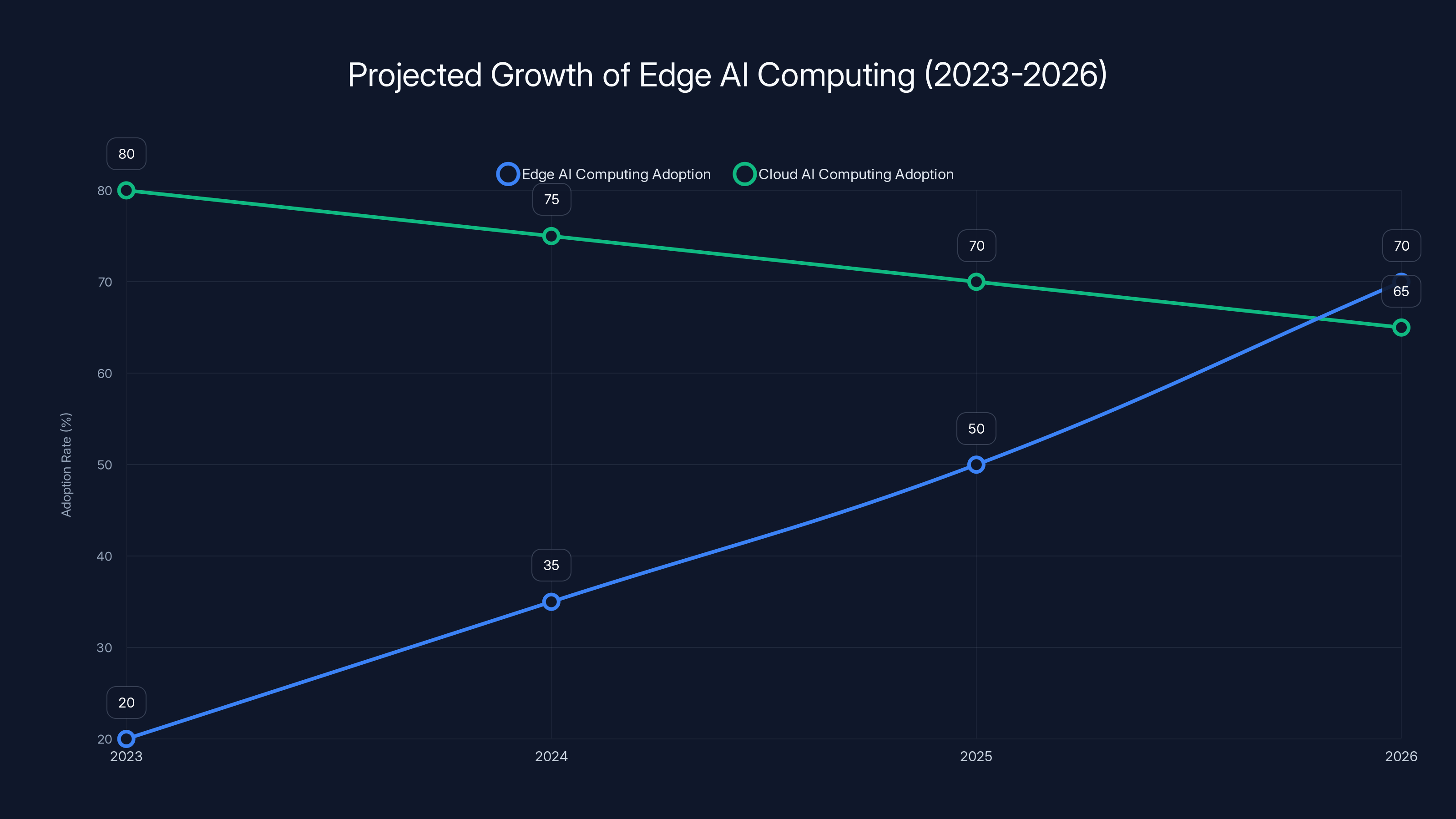
Estimated data shows a significant rise in edge AI computing adoption from 2023 to 2026, highlighting a shift towards local data processing due to its latency and cost benefits.
Practical Integration and Installation Considerations
Case Selection and Compatibility
Mini-ITX has a large ecosystem of compatible cases. You're not limited to proprietary enclosures. This means you can select cases optimized for your specific deployment requirements.
For AI inference at the edge, you might choose fanless cases for silent operation or cases with optimized airflow for maximum cooling. The choice is entirely yours. This flexibility is a genuine advantage over closed systems.
Power Supply Requirements
A typical system using this motherboard with a high-end processor and discrete GPU might consume 300-400W. You'd want a 550W power supply to provide headroom. Mini-ITX power supplies are readily available at commodity pricing.
Robust power delivery requires quality components. Investing in a modular power supply from a reputable manufacturer ensures clean power delivery to the motherboard, which complements the board's sophisticated power delivery design.
Cooling Solution Selection
CPU cooling options for Mini-ITX are more limited than full-size ATX, but viable options exist. AIO liquid coolers, compact air coolers, and passive solutions are all possible depending on thermal requirements.
For continuous AI inference workloads, a quality AIO liquid cooler is often ideal. They provide excellent thermal performance in compact form factors and maintain the airflow optimization that the motherboard relies on.
The Enterprise Angle: Why Organizations Care
Competitive Advantage Through Cost Efficiency
Organizations deploying AI inference at scale care primarily about inference throughput per dollar. The Maxsun board enables cost-competitive deployments that rival enterprise solutions while maintaining superior memory capacity.
This creates competitive pressure on premium offerings. As more organizations recognize that Mini-ITX solutions can deliver competitive inference performance at 70-80% cost reduction, the value proposition of closed premium systems weakens.
Operational Flexibility
Enterprise organizations value operational flexibility. Being able to source components from multiple vendors, repair systems in-house, and deploy across diverse infrastructure improves resilience. The Maxsun board enables this by remaining vendor-agnostic.
When supply chain disruptions occur, Mini-ITX components remain available from multiple sources. Premium proprietary systems often face longer delays when supply constraints hit.
Scalability Without Proportional Cost Increases
Deploying a hundred inference nodes using this motherboard becomes financially feasible. Deploying a hundred closed-system equivalents becomes prohibitive cost-wise. This changes the scale at which organizations can deploy AI inference.
It enables capabilities that weren't previously economical. Continuous real-time monitoring at scale. Distributed inference with sub-millisecond latency. Local processing of sensitive data without cloud infrastructure.

Technical Deep Dive: Why Four DDR5 Slots in Mini-ITX Is Hard
PCB Layout Complexity
Each DDR5 slot requires distinct high-speed signal traces from the memory controller to the socket. Four slots mean four parallel signal paths that must maintain identical impedance and signal timing to avoid skew.
On a Mini-ITX board, space is constrained. Getting four memory sockets plus all other necessary components onto a 170x 170mm board requires meticulous layout. Traces can't be routed casually. They need careful planning to minimize crosstalk between adjacent channels.
This is why most Mini-ITX designs stick with two slots. The engineering complexity increases nonlinearly with additional slots. Maxsun's achievement here reflects genuine engineering competence.
Power Delivery Integration
Four DDR5 slots draw significantly more power than two slots. Peak current during initialization and refresh operations is substantial. The power delivery circuitry needs to handle this responsiveness while maintaining voltage stability.
Integrating sufficient power delivery components on a Mini-ITX board while maintaining thermal management requires sophisticated design. Maxsun solved this by prioritizing VRM placement and ensuring adequate thermal dissipation paths.
Thermal Modeling and Temperature Behavior
How the 10°C Improvement Manifests
The reported 10°C temperature reduction comes from multiple design factors working together. Larger heatsinks provide more surface area for heat dissipation. Optimized component placement ensures hot spots don't concentrate. Careful routing of airflow paths maximizes cooling effectiveness.
In practice, you'd measure this by running identical workloads on comparable systems with and without these optimizations. Under sustained AI inference load, you'd observe that the Maxsun board maintains lower junction temperatures.
This compounds benefits. Cooler chips run faster (less thermal throttling), last longer (semiconductor physics), and consume slightly less power (lower leakage current). A seemingly modest thermal improvement delivers measurable operational benefits.
Implications for Thermal Design in Deployments
Because this system runs cooler, your deployment infrastructure can be simpler. You might eliminate active cooling entirely in some environments. You can deploy systems in warmer locations without risking thermal issues. These are genuine operational advantages.

Security Considerations in Edge Deployment
IPMI Security Implications
Out-of-band management via IPMI provides enormous operational benefits but introduces security considerations. IPMI interfaces need to be properly secured behind firewalls and authentication protocols.
Maxsun's IPMI 4.0 support includes improved security features compared to older implementations. Still, organizations deploying these systems need to architect networks with IPMI management on isolated subnets separate from production traffic.
Hardware Security Features
The motherboard's intelligent fault diagnosis system helps detect compromised or failing components. This is valuable for security. Hardware failures can sometimes result from physical tampering. Comprehensive diagnostics help identify these situations.
The forced BIOS flashing capability combined with the one-key BIOS restore button enables secure recovery from potential firmware-level compromises. This is a feature often absent from consumer Mini-ITX boards.
Real-World Performance: What to Expect
Benchmark Context
Actual performance depends entirely on the CPU and GPU combination selected. The motherboard itself enables performance through its power delivery, memory capacity, and PCIe support. It doesn't determine it.
With a high-end CPU and modern GPU, you'd expect inference throughput competitive with full-size systems at a fraction of the power consumption. Exact numbers depend on specific models and workload characteristics.
Bottleneck Analysis
Memory-bound inference workloads could potentially bottleneck on DDR5 bandwidth despite its improvement over DDR4. The 4.8GB/s per channel rate is substantial but not infinite. For GPU-accelerated inference, the PCIe interface becomes the limiting factor if bandwidth-heavy models are being tested.
In practice, integrated systems rarely experience single-point bottlenecks. Performance comes from the combination of CPU, memory, and GPU working in concert. Well-balanced configurations avoid obvious limitations.

The Broader Implications for Edge Computing
Decentralization of AI Processing
This motherboard represents a shift toward decentralized AI processing. Rather than centralizing all inference in cloud data centers, organizations can push inference to the edge, closer to data sources and consumers.
This has implications for latency, privacy, and cost. Latency drops dramatically. Privacy improves because sensitive data doesn't leave local networks. Cost reduces due to simpler infrastructure and lower bandwidth requirements.
Vendor Landscape Disruption
Companies like Nvidia build enormous revenue on premium proprietary systems. Competitive alternatives based on commodity components create pricing pressure and force innovation. From a market perspective, this motherboard is significant because it proves the viability of Mini-ITX for serious workloads.
Over the next 2-3 years, expect more competitors releasing similar designs. The success of Maxsun's offering validates that there's market demand for Mini-ITX alternatives to proprietary systems.
Pricing, Positioning, and Value Assessment
Expected Pricing
The motherboard itself likely prices between
In the context of a complete
Value Proposition
The value case is compelling for organizations deploying edge AI. You're paying less than proprietary alternatives while gaining superior memory capacity and operational flexibility. This directly impacts inference cost per model, which is the metric that matters for cost-conscious deployments.
For hobbyists or small teams building their own mini PC, the premium pricing is harder to justify. For enterprise deployments at scale, it's economically rational.

Looking Ahead: The 2025-2026 Trajectory
Memory Standards Evolution
DDR5 will likely remain dominant through 2026. DDR6 research is underway but won't reach production for several years. By the time DDR6 arrives, this board will be fully mature and deprecating naturally.
GPU and Accelerator Evolution
GPU manufacturers are continuously improving memory bandwidth and compute density. PCIe 5.0 support future-proofs this board against next-generation GPU requirements. New accelerators will leverage this bandwidth as it becomes available.
Adoption Curve
Mini-ITX edge AI deployment will likely accelerate through 2025-2026. Organizations currently running large-scale cloud inference will recognize the cost benefits of edge deployment and shift strategies accordingly. This motherboard is well-positioned to benefit from that shift.
FAQ
What makes the Maxsun MS-PC Farm 88601 different from standard Mini-ITX motherboards?
The MS-PC Farm 88601 features four DDR5 memory slots supporting up to 256GB of capacity, a significant advantage over typical Mini-ITX boards that maxes out at two DDR5 slots (128GB maximum). Additionally, the advanced 10+1+1 phase power delivery design and airflow optimizations that reduce system temperatures by approximately 10°C under load differentiate it from consumer-focused Mini-ITX alternatives. These features make it competitive with enterprise mini-PC solutions despite its compact form factor.
How does the four DDR5 slot configuration benefit AI workloads specifically?
AI inference workloads, particularly with large language models, are extremely memory-intensive. A 70B parameter model requires approximately 140GB of VRAM just for the model weights. The 256GB memory capacity enables running larger models without quantization or model sharding across multiple systems, improving inference accuracy and enabling higher batch sizes for improved throughput. This direct memory capacity advantage translates to lower cost per inference and simpler deployment architecture.
What is IPMI 4.0 and why does it matter for edge AI deployments?
IPMI 4.0 (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) provides out-of-band management capabilities, allowing remote monitoring, control, and diagnostics completely independent of the operating system. For organizations deploying multiple mini-PC systems at the edge, IPMI enables centralized fleet management without requiring physical access to each system. Features like power control, thermal monitoring, and firmware updates become automatable, reducing operational overhead significantly.
How does the 10+1+1 phase power design impact real-world performance?
The 10+1+1 phase design means the CPU receives dedicated power delivery from ten separate phases, while memory and other systems share one phase each. This architecture minimizes voltage sag under sustained heavy loads common in AI inference. The result is approximately 0.4GHz additional sustained frequency compared to designs with fewer phases. Over a year of continuous 24/7 operation, this translates to approximately 4-6% additional inference throughput without any hardware upgrades.
Can this motherboard compete with Nvidia's Petaflop-class mini-PC systems?
The MS-PC Farm 88601 offers genuine competitive advantages in memory capacity (256GB vs 128GB on comparable systems) and cost (approximately 70% lower total system cost). It runs Linux and Windows natively without closed ecosystem constraints. However, Nvidia's systems integrate GPU, CPU, and networking tightly optimized for specific workloads. The Maxsun board provides flexibility and memory capacity but requires more careful system integration to achieve peak performance. For organizations prioritizing cost efficiency and memory capacity, it's competitive. For those requiring turn-key solutions, proprietary alternatives remain stronger.
What processor options pair best with this motherboard?
The board supports Intel LGA1700 socket processors ranging from mid-range Core i 9 parts up to Xeon processors. For AI inference specifically, higher core-count processors like the Core i 9-14900K (24 cores) or Xeon W7-series parts maximize parallel inference throughput. Processor selection involves trade-offs between core count (more cores improve batch inference throughput), power consumption, and cost. Matching processor capability to specific inference models optimizes the deployment.
How does PCIe 5.0 x 16 support impact GPU performance?
PCIe 5.0 provides 128GB/s of bandwidth between the CPU and GPU, double that of PCIe 4.0. For GPU-accelerated AI inference, the interconnect can become a bottleneck when moving large models and batches between CPU and GPU memory. Full x 16 lanes (rather than x 8, which some Mini-ITX designs provide) ensures this isn't the constraint. This is particularly important for large model inference where GPU memory limitations force regular CPU-GPU data transfers.
What thermal improvements result from the airflow optimizations?
Maxsun reports approximately 10°C temperature reduction under full AI inference load compared to designs without these optimizations. This results from larger heatsinks, optimized component placement considering airflow patterns, and careful PCB routing. Practically, cooler operation means higher sustained clock speeds (less thermal throttling), longer component lifespan (semiconductor physics favors lower junction temperatures), and potentially simpler deployment infrastructure (no specialized cooling required in temperate environments).
Is this system suitable for edge deployment in non-datacenter environments?
Absolutely. The compact Mini-ITX form factor, efficient power consumption (300-400W under full load), and excellent thermal management make it ideal for diverse edge deployments. Real-world use cases include edge inference clusters for content moderation, real-time financial analysis systems, autonomous vehicle support infrastructure, and local data processing for privacy-sensitive applications. The remote management via IPMI further simplifies deployment and maintenance across geographically distributed locations.
What are the main limitations of this motherboard for AI workloads?
The primary limitation is Intel-only platform support, which excludes organizations standardized on AMD. Additionally, as a Mini-ITX design, it's limited to a single discrete GPU and supports only single-channel or dual-channel operation (depending on final system configuration), compared to multi-GPU configurations in full-size systems. For organizations requiring extreme scale with hundreds of GPUs, full-size systems remain more practical. However, for edge inference deployments where single GPU per node is typical, these limitations are not constraining.

Conclusion: The Inflection Point for Edge AI Computing
Maxsun's MS-PC Farm 88601 represents more than just a competent Mini-ITX motherboard. It's a statement about the viability of commodity-based alternatives to proprietary enterprise systems. In 2025, that statement carries significant weight.
The AI compute landscape is fragmenting. Cloud inference remains dominant for batch workloads, but real-time edge inference is accelerating. Organizations increasingly recognize that processing data locally provides latency, privacy, and cost benefits that centralized approaches can't match. The infrastructure supporting this shift needs to be flexible, scalable, and cost-effective.
This motherboard delivers on all three fronts. The four DDR5 slots enable memory-intensive AI workloads without compromise. The advanced power delivery ensures stable operation under sustained heavy load. The remote management capabilities enable scale without proportional operational complexity.
Will this board displace premium proprietary solutions? Probably not entirely. Organizations invested in specific vendor ecosystems will continue using them. But it creates a viable alternative that forces competition and innovation. In a healthy market, that's valuable.
For your deployment, the key question is simple: do you need the flexibility and cost efficiency of commodity Mini-ITX, or do you require the vertical integration and turn-key simplicity of proprietary solutions? If it's the former, the MS-PC Farm 88601 is worth serious consideration. If it's the latter, you already know what you're buying.
The real significance isn't this specific motherboard. It's the validation that high-performance edge AI computing doesn't require proprietary platforms or enterprise pricing. It validates that smart engineering on commodity components can deliver competitive capabilities. As this message spreads through 2025-2026, expect a wave of similar offerings from other manufacturers.
The future of AI computing won't be decided by a single platform. It'll be decided by a diverse ecosystem of solutions optimized for different use cases. This motherboard is one important piece of that puzzle, and it's positioned better than most to capture meaningful market share in the rapidly growing edge AI inference segment.
Key Takeaways
- Four DDR5 slots enabling 256GB maximum memory represents double the capacity of comparable enterprise mini-PC systems like Nvidia DGX Spark (128GB)
- Advanced 10+1+1 phase power delivery provides stable voltage under sustained AI inference loads, enabling approximately 0.4GHz sustained frequency advantage
- Airflow optimization reduces operating temperatures by 10°C under full load, improving thermal stability and extending component lifespan
- PCIe 5.0 x16 interface ensures GPU acceleration operates at full bandwidth without interconnect bottlenecks common in memory-intensive AI workloads
- Total system cost approximately 70-80% lower than equivalent proprietary solutions while maintaining competitive or superior memory capacity for edge AI deployments
- IPMI 4.0 remote management enables cluster-scale operations across geographically distributed systems without specialized infrastructure
![Mini-ITX Motherboard with 4 DDR5 Slots: The AI Computing Game-Changer [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/mini-itx-motherboard-with-4-ddr5-slots-the-ai-computing-game/image-1-1766963166822.jpg)



