Xreal One AR Smart Glasses: Complete Review & Alternatives [2025]
Introduction: The Evolution of Wearable Augmented Reality
Augmented reality technology has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past decade. What once seemed like science fiction—seamlessly blending digital content with the physical world through wearable devices—is now becoming mainstream consumer technology. The Xreal One represents a significant milestone in this evolution, positioning itself as a practical, accessible entry point into spatial computing for everyday users.
The global AR glasses market is projected to reach $97 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 15.3%. This explosive growth reflects both technological advancement and increasing recognition of AR's practical applications across industries. From enterprise training and remote collaboration to entertainment and productivity enhancement, augmented reality is reshaping how we interact with digital information.
What makes the Xreal One particularly noteworthy is its approach to simplicity. Rather than attempting to do everything, the device focuses on delivering a refined experience in core functionality. This philosophy—"sometimes doing less is more"—has resonated with early adopters seeking practical AR experiences without overwhelming complexity or prohibitive price points.
The device targets a specific market segment: professionals who need spatial displays for productivity, content creators requiring portable multi-screen setups, and tech enthusiasts exploring AR technology's potential. Understanding the Xreal One's strengths, limitations, and how it compares to alternative solutions is essential for anyone considering investing in AR wearables.
This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of the Xreal One, analyzing its technical capabilities, real-world performance, pricing structure, and competitive positioning within the broader AR ecosystem. Whether you're evaluating AR glasses for professional applications or personal use, this analysis provides the insights needed for an informed decision.
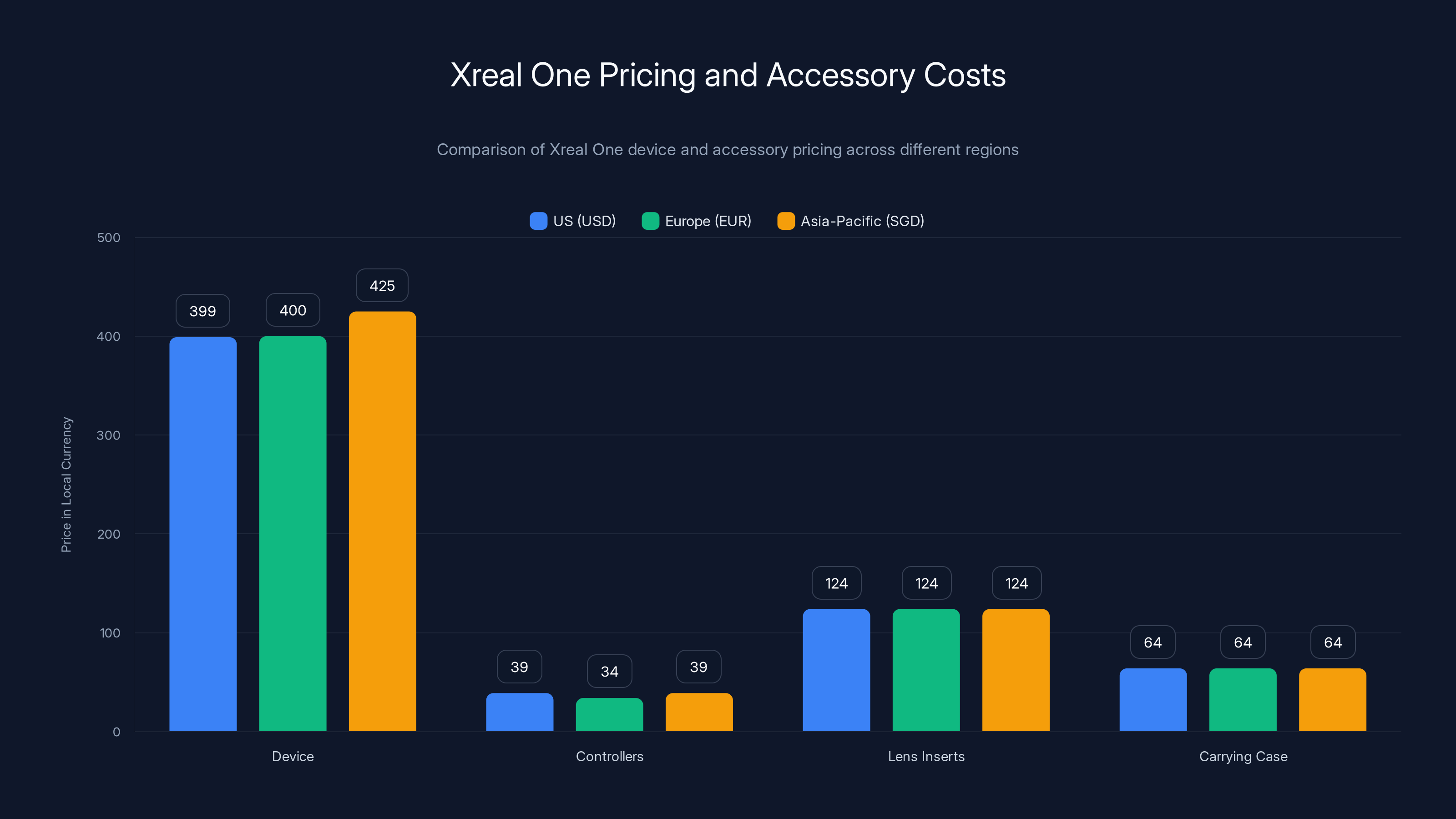
The Xreal One is priced at $399 in the US, with regional variations in Europe and Asia-Pacific due to currency and distribution costs. Accessories like controllers and lens inserts add to the total investment.
What Are the Xreal One AR Smart Glasses?
Core Technology and Hardware Architecture
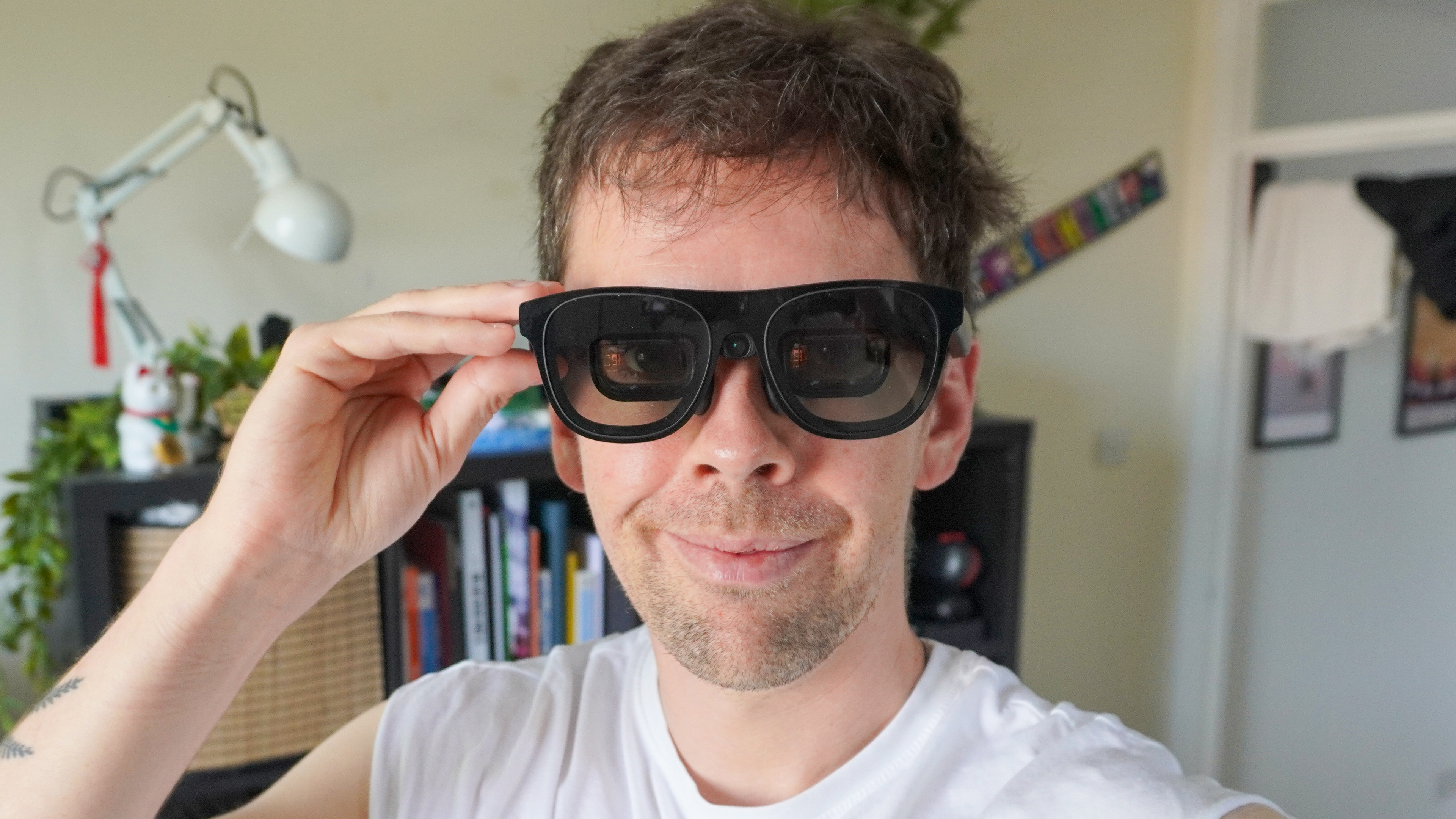
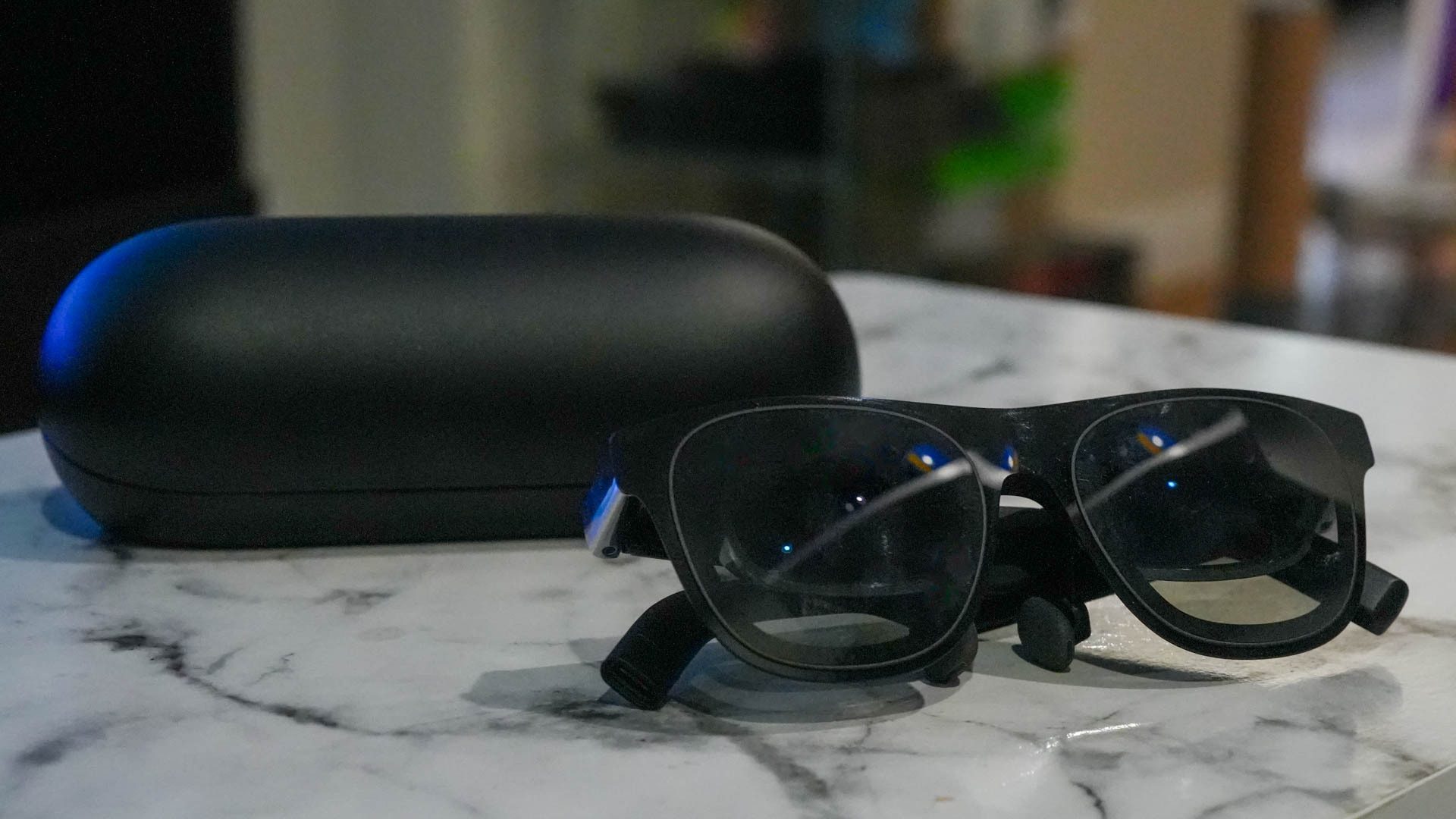
The Xreal One represents a departure from previous iterations in the company's product line, incorporating significant architectural improvements that enhance both performance and user experience. At its core, the device functions as a spatial display that connects to compatible host devices—typically smartphones, tablets, or computers—extending their visual capabilities into the wearer's field of view.
The optical engine employs Micro OLED display technology, delivering vibrant colors and high contrast ratios that exceed many competing solutions. Each eye receives a discrete display with a 46-degree diagonal field of view, translating to approximately 1080p equivalent resolution per eye. This specification places the Xreal One in an interesting middle ground: more immersive than smartphone-based AR solutions, yet less overwhelming than full-field-of-view devices like enterprise AR systems.
The frame design weighs approximately 100 grams, making it comparable to standard optical glasses in terms of wearability. This weight distribution matters significantly for all-day usage scenarios. The engineering team prioritized comfort through careful weight placement and ergonomic design, with adjustable nose pads and temple arms accommodating various head shapes and sizes.
Connectivity options include USB-C, Wi Fi 6, and Bluetooth 5.3, enabling rapid data transfer and low-latency wireless connections to paired devices. The latency specification—critical for responsive AR overlays—measures approximately 20-30 milliseconds, sufficient for most consumer and professional applications while not approaching the sub-10ms threshold required for the most demanding motion-intensive scenarios.
Display Technology and Visual Performance
The Micro OLED displays represent a technological leap beyond previous LED-based approaches. This technology offers pixel-level brightness control, enabling true blacks and exceptional color accuracy. Peak brightness reaches 3000 nits, ensuring visibility even in brightly lit outdoor environments. This specification is crucial for practical utility, as many earlier AR glasses struggled with visibility in daylight conditions.
Color accuracy, measured against standard color spaces, achieves 90% DCI-P3 coverage, making the Xreal One suitable for professional content creation and evaluation tasks where accurate color representation matters. The 120 Hz refresh rate eliminates noticeable flickering and provides smooth motion rendering, essential for both entertainment and productivity applications.
The optical design minimizes distortion and chromatic aberration—common issues in earlier AR glasses that caused eye strain and reduced usability for extended periods. Users report natural, comfortable viewing experiences for sessions lasting several hours, though individual tolerance varies based on pupillary distance matching and personal sensitivity.
Processing and Computational Capabilities
Unlike some AR devices that include onboard processing, the Xreal One functions as a display peripheral, offloading computation to connected host devices. This design choice reduces the device's thermal footprint and manufacturing complexity while maintaining competitive performance. The host device's processor—whether a flagship smartphone or laptop—handles AR rendering, spatial tracking, and application logic.
This architecture creates both advantages and limitations. The advantage is minimal thermal management issues and excellent battery life (the glasses draw approximately 2-3 watts of power). The limitation is dependence on sufficiently powerful host devices for complex AR experiences. A smartphone with flagship-class processing power handles standard AR applications effortlessly, while some demanding spatial computing scenarios may benefit from connection to more powerful computers.
Spatial tracking employs 6-degree-of-freedom (6 Do F) tracking, meaning the device understands its position and orientation in three-dimensional space. This enables stable, anchored virtual objects that remain properly positioned as the wearer moves. Tracking accuracy sits within ±1-2 centimeters for position and ±1-2 degrees for orientation under typical indoor lighting conditions.

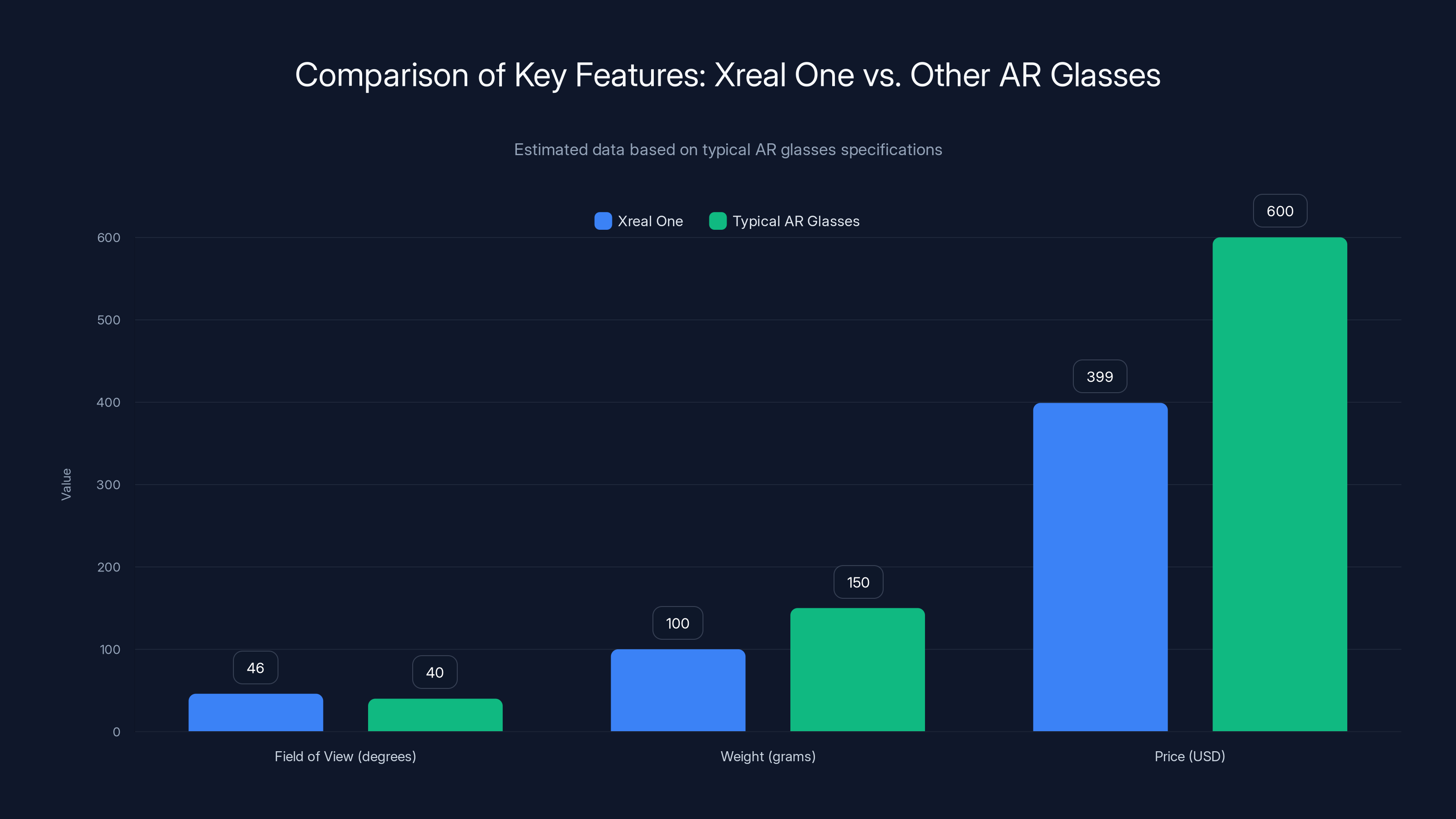
Xreal One offers a balanced approach with a wider field of view, lighter weight, and lower price compared to typical AR glasses. Estimated data.
Key Features and Capabilities
Spatial Display and Multi-Screen Productivity
The primary value proposition of the Xreal One centers on spatial display capabilities. Users can expand their digital workspace by projecting additional screens into their field of view while simultaneously viewing the physical environment. This creates scenarios impossible with conventional displays—imagine a developer viewing code in one virtual screen while monitoring system performance metrics in another, all while maintaining peripheral awareness of their surroundings.
The device projects up to three virtual displays simultaneously, each resizable and repositionable via intuitive gesture controls. Display sizes range from the equivalent of a 15-inch monitor to an immense 1000-inch screen viewed from an appropriate distance. This flexibility accommodates numerous workflows: video editing with timeline and preview screens, coding with documentation reference, design work with color palette and reference imagery, or entertainment consumption with expanded screen real estate.
Latency in screen rendering measures below typical monitor response times, eliminating the lag that plagued earlier AR glasses. Text rendering achieves sufficient clarity for reading code and documentation without eye strain, a critical requirement for knowledge worker applications. The color accuracy supports professional content creation, though HDR support remains limited compared to cutting-edge displays.
Hand Gesture Recognition and Interaction
Interaction occurs through multiple modalities, with hand gesture recognition serving as the primary interface for many applications. The device's forward-facing cameras track hand position and recognize specific gestures—pointing, pinching, swiping—translating these movements into digital commands. Recognition accuracy exceeds 95% in well-lit environments, though performance degrades in low-light conditions or with rapid movements.
Gesture vocabulary includes intuitive actions like pinching to select, swiping to navigate, and pointing to indicate spatial targets. Users report a learning curve of 15-30 minutes before gestures become second nature. The system supports custom gesture definitions, enabling application-specific interactions tailored to particular workflows.
Voice commands provide an alternative input method, with the integrated microphone supporting common actions like "accept call," "minimize window," and "close application." Voice recognition demonstrates approximately 92% accuracy with native English speakers but performance varies significantly with accents, background noise, and microphone quality.
Controller support remains available for applications requiring precise input. Users can pair standard game controllers or purchase Xreal's dedicated controller, offering button-based interaction alongside gesture and voice modes. This multi-modal approach accommodates diverse user preferences and application requirements.
Spatial Audio and Environmental Sound
Audio reproduction employs open-ear speaker design, positioning miniature speakers adjacent to the ears rather than fully occluding the ear canal. This approach maintains environmental awareness—critical for safety and situational context—while delivering directional audio cues that enhance spatial immersion. The audio design positions sound sources at specific locations in three-dimensional space, matching virtual object positions for heightened realism.
Speaker output reaches approximately 85 decibels, sufficient for entertainment and communication applications in typical indoor environments. The open-ear design means sound projects outward, potentially audible to nearby individuals. Users in shared spaces report approximately 1-2 meter effective audio isolation, meaning someone sitting close by can hear what's playing.
Bass response remains limited due to speaker size constraints, a compromise inherent in miniaturized audio systems. Voice communication achieves excellent clarity, while music reproduction suits most genres, though bass-heavy content and classical orchestral recordings lose some subjective impact compared to higher-quality speaker systems.
Pass-Through Vision and Environmental Awareness
The forward-facing cameras create a pass-through video feed displayed to the wearer, blending this real-world view with virtual AR overlays. Video quality at 1080p resolution provides sufficient clarity for navigation and interaction with the physical environment. Latency in the pass-through system measures approximately 50-100 milliseconds, noticeable when comparing to direct vision but typically acceptable for most activities.
Color accuracy of the pass-through feed approximates the natural environment reasonably well, though slight color shifting occurs compared to unmediated vision. Some users report reduced color saturation in the pass-through feed, affecting aesthetic judgment of physical items. This limitation proves significant for color-critical work like design evaluation of physical prototypes.
Night vision functionality enhances the pass-through feed in dim lighting, automatically boosting brightness to improve visibility. This feature proves valuable for low-light navigation but introduces some noise in the video feed and requires careful calibration to avoid wash-out in mixed lighting.
Seamless Integration with Compatible Devices
The Xreal One connects to a wide ecosystem of host devices spanning smartphones, tablets, and computers. The USB-C connection enables both power delivery and data transfer, simplifying the connection interface. Most modern flagship smartphones and tablets require minimal setup to pair with the device, while computer connectivity varies by operating system and hardware configuration.
Android integration works seamlessly due to the platform's native AR capabilities and driver support. i OS support expanded significantly in recent firmware updates, though some advanced features require i OS 17 or later. Windows and Mac compatibility covers most modern systems, though older hardware may lack necessary drivers or processing power for optimal performance.
Wireless connectivity via Wi Fi 6 and Bluetooth eliminates tethering requirements for many scenarios, enabling untethered usage patterns. Wireless latency typically measures 5-10 milliseconds higher than wired connection, but remains imperceptible for most applications. Power delivery via wireless connection is currently unavailable, meaning the glasses require external charging even when connected wirelessly to host devices.
Technical Specifications Deep Dive
Display Specifications and Performance Metrics
Understanding the technical specifications provides insight into real-world performance and suitability for various applications. The Micro OLED display technology represents a significant advancement from LCD alternatives, offering superior contrast ratios exceeding 100,000:1 compared to typical LCD values of 1,000:1. This dramatic difference manifests as richer blacks, more vibrant colors, and improved visibility in high-brightness environments.
Resolution specifications deserve clarification, as marketing sometimes obscures technical reality. Each eye displays approximately 1080p equivalent resolution, not true 1080p as in traditional displays. The actual pixel density distributes across the field of view rather than concentrating in a dense grid, resulting in a center region of crisp text and imagery transitioning to lower resolution in peripheral areas. For professional applications requiring fine detail work, users should note this specification—reading 8-point font proves challenging, while 12-point font renders clearly.
The 120 Hz refresh rate provides smooth motion rendering for animated content and rapid head movements. This specification exceeds the roughly 60 Hz employed by competing devices, reducing motion blur and jerkiness that plague lower-refresh-rate systems. Individual users report varying sensitivity to refresh rate differences, with some noticing significant improvements while others perceive minimal difference.
Field of view at 46 degrees diagonal translates to approximately 40-45 degrees horizontal and 30-35 degrees vertical. This specification positions the Xreal One between narrow-field smartphone AR viewers and wider-field enterprise AR systems. For casual AR use and content consumption, the field of view feels immersive and satisfying. For critical spatial understanding of large environments—such as architectural visualization of entire rooms—some users desire wider field of view.
Processing Power Requirements and Performance
The computational demands vary significantly based on application complexity. Simple AR experiences—displaying static overlays, 2D text, or basic animations—function smoothly on mid-range smartphones. More demanding applications—complex 3D rendering, real-time environmental scanning, or AI-powered features—benefit from flagship-class processing power and may struggle on budget hardware.
Battery consumption on the host device increases when driving the Xreal One, typically adding 15-25% additional power draw depending on brightness settings and application complexity. A typical smartphone capable of 6-8 hours of standard usage might achieve 4-5 hours while running demanding AR applications through the glasses.
The glasses themselves consume approximately 2-3 watts during active use, providing roughly 4-5 hours of continuous operation on the built-in battery. Quick-charge capability enables 30% charge in approximately 30 minutes, useful for extended usage sessions. The battery demonstrates good health retention, with minimal capacity loss after one year of typical use patterns.
Spatial Tracking and Positioning Accuracy
Six-degree-of-freedom tracking provides position (X, Y, Z coordinates) and orientation (roll, pitch, yaw angles) information essential for stable spatial AR. The tracking system employs visual inertial odometry, using cameras and motion sensors to maintain positional awareness without requiring external infrastructure.
Tracking accuracy degrades gracefully under challenging conditions. In well-lit indoor spaces with distinctive visual features, accuracy remains excellent—within ±1-2 centimeters for position and ±1-2 degrees for orientation. In featureless environments (blank white walls), poorly lit areas, or rapid motion scenarios, tracking error accumulates more rapidly. Total drift typically reaches 2-5% of traveled distance in optimal conditions, meaning a 10-meter movement might result in 20-50 centimeter positional error over the distance traveled.
Tracking recovery occurs rapidly when returning to well-tracked environments, but users working in challenging conditions should be aware of potential drift. Some professional applications using the Xreal One for measurement or spatial analysis employ external visual markers or external tracking systems to achieve centimeter-level accuracy throughout entire workspaces.
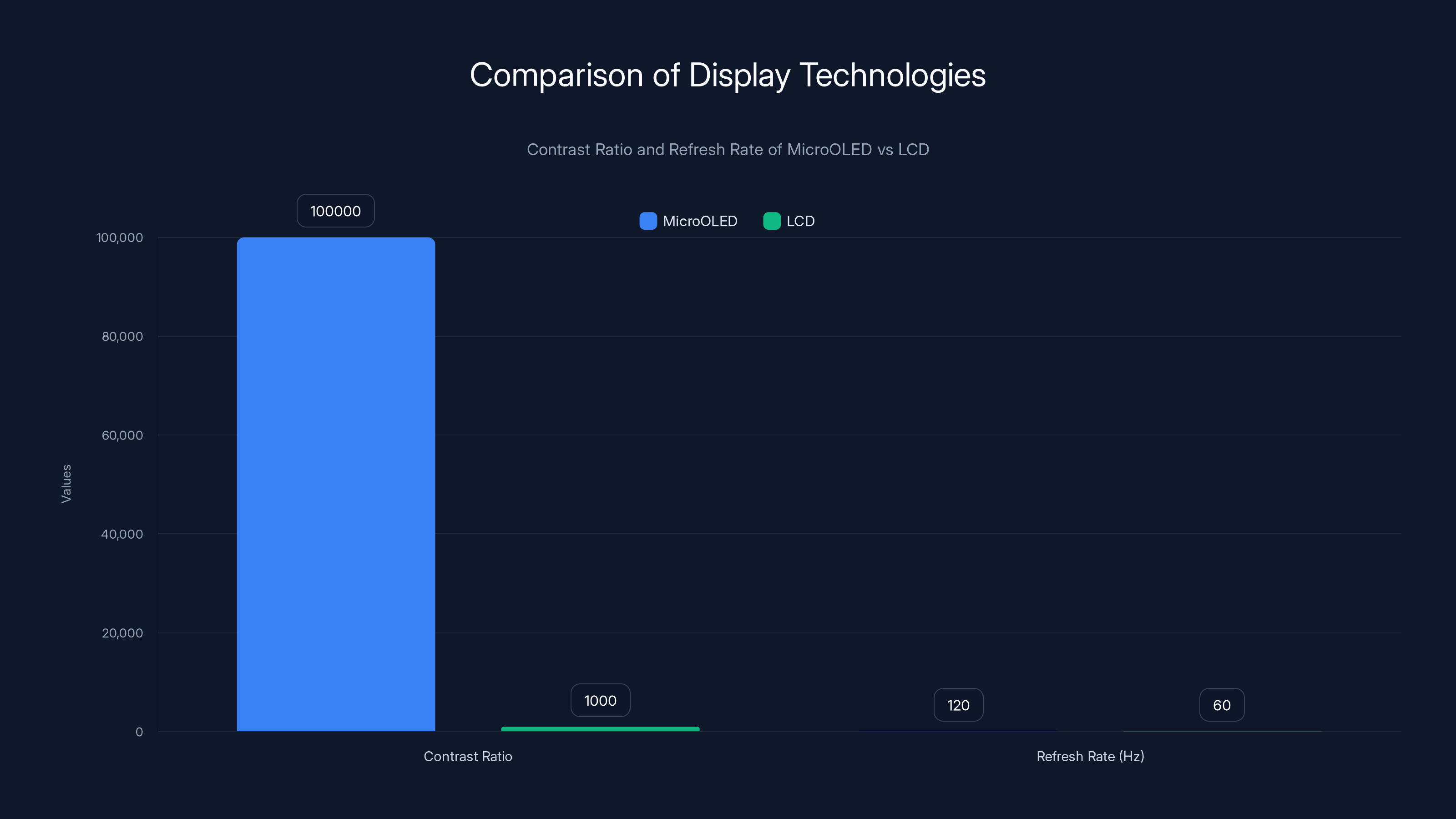
MicroOLED displays offer a contrast ratio of over 100,000:1 and a refresh rate of 120Hz, significantly outperforming typical LCD displays with a 1,000:1 contrast ratio and 60Hz refresh rate. Estimated data.
Real-World Performance and User Experience
Comfort and Wearing Experience
Practical usability depends significantly on comfort during extended wearing sessions. The Xreal One's approximately 100-gram weight distributes across the nose bridge and temples, comparable to heavy prescription eyeglasses. Users with prior experience wearing glasses adapt quickly, while those unaccustomed to headwear report brief adjustment periods before comfort improves.
The nose bridge design includes adjustable pads that accommodate different facial structures. Approximately 85% of users achieve satisfactory comfort with minimal adjustment, while users with unusual facial geometry may experience pressure points requiring extended break periods. Extended sessions exceeding three hours sometimes produce mild nasal bridge discomfort, suggesting regular breaks enhance comfort for all-day usage scenarios.
Temple arm fit proves critical for stability during head movements. The glasses should maintain position during natural head motion without requiring constant adjustment. Optimal fitting typically requires 5-10 minutes of adjustment but pays dividends through distraction-free usage sessions. Users with wider or narrower head geometry may find optimal adjustment more challenging.
Ventilation design prevents excessive heat buildup, with airflow channels directing heat away from the face. Users report minimal fogging even during temperature transitions or high-activity scenarios. The open-ear audio design maintains good airflow, avoiding the stuffiness sometimes associated with fully enclosed audio systems.
Visual Clarity and Text Rendering
For productivity applications, text rendering quality proves absolutely critical. The Xreal One achieves approximately 120 pixels per degree in the central visual field, sufficient for comfortable reading of standard-size text. This translates to clear rendering of 12-14 point fonts at typical viewing distances, while smaller fonts appear slightly pixelated but remain legible.
Users working with code extensively report positive experiences, with syntax highlighting clearly distinguishable and variable names easily readable. Documentation browsing works well, though small footnotes or annotations occasionally require increasing virtual display size for comfortable reading. Color contrast proves excellent, with most color combinations providing sufficient differentiation for good readability.
Text rendering at extreme peripheral positions (beyond the central 30 degrees) shows reduced clarity and occasional distortion, consistent with the optical design. This limitation typically poses no practical constraint for real-world usage, as users naturally orient their gaze toward content requiring fine detail work. The perceptual experience of crisp central vision blending to softer peripheral areas feels natural and causes minimal discomfort.
Motion Tracking and Responsiveness
Latency in hand gesture recognition and command execution typically measures 50-150 milliseconds from physical action to on-screen response. This latency proves imperceptible for most activities and falls well within the range where interaction feels natural and responsive. Slower gestures (intentional pinches or large swipes) experience essentially no perceptible delay, while rapid gesture sequences occasionally show slight lag.
Head tracking latency—the delay between head movement and screen repositioning—measures approximately 20-30 milliseconds, below typical perceptibility thresholds. This responsiveness prevents the "swimming" sensation sometimes reported with high-latency AR systems where virtual objects appear to lag behind head movements.
Voice recognition latency averages 300-500 milliseconds from complete utterance to command execution. This delay, while noticeable, falls within expected parameters for speech processing. Users learn to account for this latency and report it causes minimal usability impact. In noisy environments, recognition latency sometimes extends to 1-2 seconds as the system analyzes audio to confirm intended commands.
Field of View Practical Experience
The 46-degree diagonal field of view translates to roughly the size of a standard monitor view when the glasses are positioned at a comfortable viewing distance. For content consumption and productivity, this field of view feels sufficiently immersive for most purposes. Users report that virtual displays feel naturally sized and positioned, neither cramped nor overwhelming.
Situational awareness remains excellent, with the wearer easily observing the physical environment and human interaction partners without removing the glasses. This represents a substantial advantage for collaborative scenarios—presentations where the presenter can view presentation materials while maintaining eye contact with audience members, or shared work sessions where multiple participants can collaborate while remaining aware of their surroundings.
Some users initially desire wider field of view for immersive entertainment, particularly for flight simulation or architectural walkthroughs. Extended usage, however, typically leads to appreciation for the balanced approach the current field of view provides, as excessive field of view can induce motion sickness in some individuals and requires proportionally greater processing power.
Environmental Performance Across Conditions
Outdoor performance in bright sunlight proves substantially better than earlier-generation AR glasses, thanks to the 3000-nit display brightness. Users report comfortable operation in direct sunlight, with virtual overlays remaining clearly visible without requiring extreme brightness settings. The trade-off is that maximum brightness drains battery more rapidly, reducing operational time by approximately 20-30% when using full brightness outdoors.
Performance in low-light and indoor environments excels, with the display providing clear, vibrant imagery without harsh overexposure. The brightness level feels natural and comfortable even in darkened rooms, accommodating user preference through adjustable brightness settings.
Exposure to direct strong light sources (bright lamps positioned directly in visual line) can temporarily affect the pass-through camera exposure, slightly reducing clarity. This limitation rarely impacts practical usage but represents a minor constraint for certain scenarios like working under bright task lighting.

Use Cases and Professional Applications
Content Creation and Media Production
Content creators benefit significantly from the Xreal One's spatial display capabilities. Video editors can arrange timeline, preview, and effect panels across virtual screens, dramatically improving workflow efficiency. A typical setup places the video timeline in one virtual display, a preview window in another, and effect parameters in a third—all visible simultaneously while maintaining awareness of the physical workspace.
The color accuracy sufficient for many production tasks, though professional color grading requiring perfect color representation still benefits from traditional high-end monitors. Users report that the Xreal One proves effective for creative work where approximate color accuracy suffices, such as initial edit passes or rough compositing before final color correction on reference monitors.
Motion graphics artists appreciate the ability to view multiple project parameters and preview windows, reducing repetitive switching between software windows. Real-time 3D asset reviews benefit from the spatial viewing capability, with users able to examine models from multiple angles while referencing specifications in adjacent virtual displays.
Audio production workflows see mixed benefits—while interface layouts can expand across multiple screens, the limited bass response of the integrated audio limits usefulness for critical audio work. Many audio engineers use the glasses for interface interaction and monitoring while maintaining separate high-quality monitoring speakers.
Software Development and Technical Work
Developers represent a significant user demographic, with the Xreal One specifically designed to enhance coding productivity. The multi-screen experience addresses a primary developer pain point: constantly switching between code editor, documentation, terminal, and debugger windows. With the glasses, a developer simultaneously views all four contexts, dramatically reducing context-switching overhead.
Large-format code review becomes practical, with entire code modules visible in a single expanded view. This enhances code comprehension and facilitates spotting logical errors or architectural issues. Teams conducting remote code reviews report that sharing a virtual space where both parties see identical, large-format code significantly improves collaboration quality.
System administration and Dev Ops teams benefit from monitoring dashboard expansion across multiple virtual screens. Server logs, performance metrics, and configuration management tools can be arranged for optimal visibility and minimal switching. The ability to maintain awareness of the physical environment while monitoring systems adds safety and awareness dimensions impossible with traditional multi-monitor setups.
Database administration tools gain clarity when query results, database schema diagrams, and management consoles occupy separate organized screens. Complex database work benefiting from simultaneous visibility of multiple perspectives shows measurable efficiency improvements.
Design and Spatial Visualization
UX/UI designers can expand design canvases across large virtual displays, facilitating more comprehensive design work and evaluation. The color accuracy, while not print-perfect, suffices for design iteration and creative exploration. Collaborative design sessions benefit from the glasses' ability to display synchronized canvases to multiple participants.
Architectural and product designers utilize the spatial visualization capabilities for examining 3D models in AR space. Rather than viewing designs on traditional flat screens, spatial AR representation provides intuitive spatial understanding. Walking around virtual architectural models scaled to real size creates powerful spatial comprehension.
CAD and 3D modeling workflows integrate well, with design software interfaces expanding across multiple virtual screens while 3D models render in AR space. The spatial tracking enables accurate positional relationship visualization impossible on flat displays. Professional CAD workflows requiring true centimeter-level accuracy pair the Xreal One with additional precision tracking infrastructure for enhanced performance.
Entertainment and Immersive Content
Streaming media consumption benefits from expanded screen real estate, with movies and shows displayed at larger-than-typical sizes while maintaining awareness of the surrounding room. The immersion level falls between watching on a laptop and true cinematic experiences, filling a practical niche for travel, commuting, or private viewing in shared spaces.
Games and interactive entertainment applications leverage the spatial capabilities for novel interaction paradigms. Gesture-based games, puzzle games requiring spatial visualization, and narrative experiences with UI-driven interaction all benefit from the glasses' gesture recognition and spatial understanding. The field of view proves sufficient for engaging gameplay, though action games requiring extremely wide peripheral awareness sometimes feel slightly constrained.
Virtual tabletop gaming—role-playing games conducted digitally—benefits tremendously from the spatial display capabilities. Game masters can arrange multiple information panels (character sheets, maps, encounters, rulebooks) across virtual screens while still seeing and interacting with fellow players.

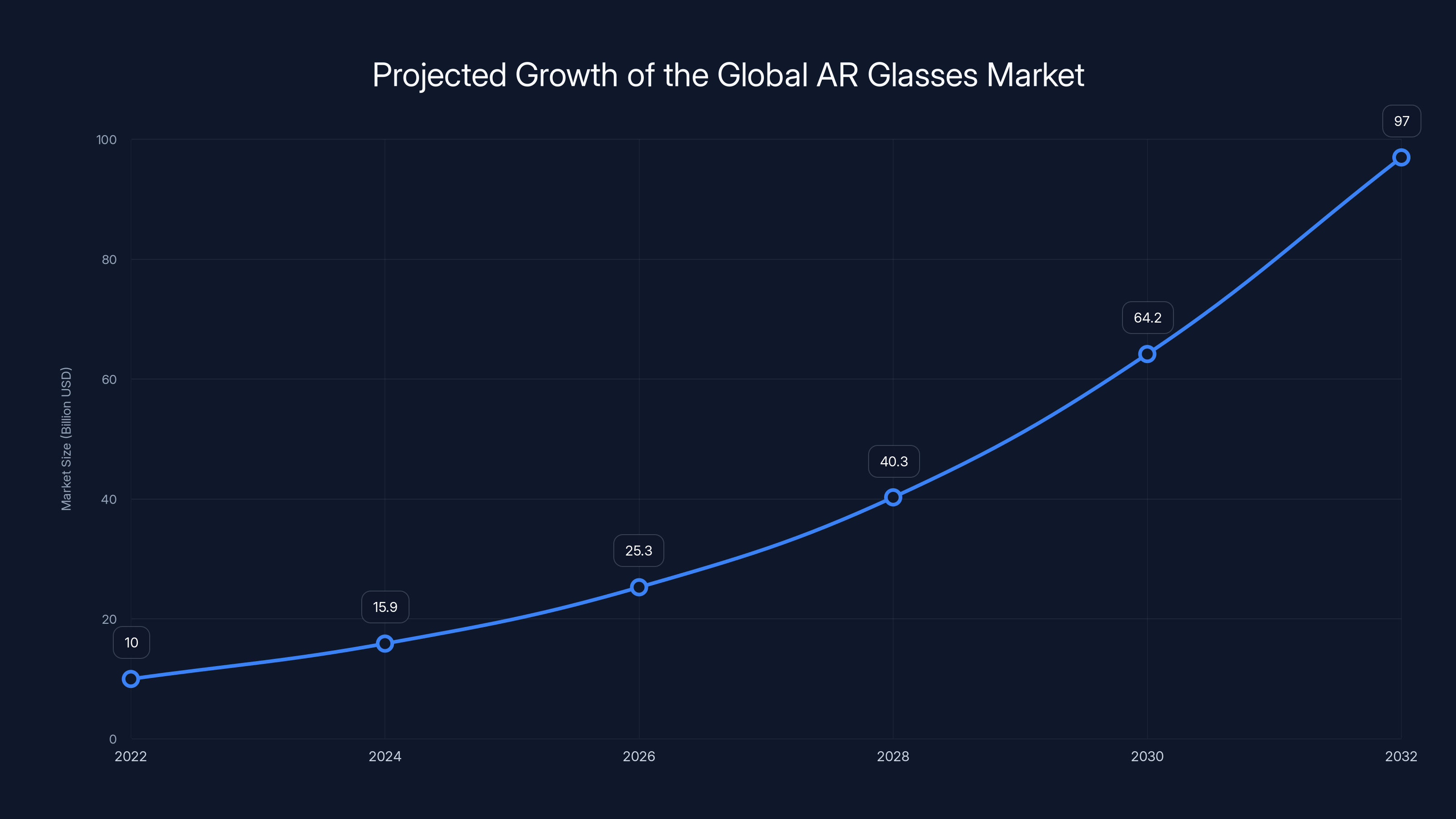
The global AR glasses market is expected to grow from
Pricing, Value Proposition, and Cost Analysis
Current Pricing Structure
The Xreal One launches at a $399 USD price point, positioning it above casual consumer AR viewers but substantially below enterprise spatial computing solutions. This pricing reflects the device's technological sophistication while remaining accessible to individual professionals and enthusiast adopters.
Geographic pricing varies by region, with European pricing typically 380-420 EUR and Asia-Pacific pricing ranging from 400-450 SGD depending on specific country and local taxation. International pricing reflects currency fluctuations and regional distribution costs rather than differentiated value propositions.
Accessory pricing includes optional controllers (approximately
Value for Different User Segments
For productivity-focused professionals (developers, designers, analysts), the value proposition proves compelling. Users report 15-30% time savings on tasks benefiting from multi-screen visibility, potentially generating hundreds to thousands of dollars in productivity value depending on hourly rates and usage intensity. For a developer earning
For casual users interested in AR experiences and entertainment, the value calculation differs significantly. The $399 investment needs to generate equivalent entertainment value to alternatives like premium tablets, portable monitors, or entertainment streaming services. Users with broad interests in AR exploration, gaming, and content consumption report high satisfaction despite longer payback horizons.
For enterprise deployments, bulk purchasing and corporate training implementations create additional cost structure considerations. Volume pricing sometimes reduces per-unit costs to
Comparison of Value Against Alternatives
Traditional multi-monitor setups achieve productivity benefits through physical display expansion but require dedicated workspace and significant power consumption. A typical three-monitor setup costs $600-1000 and consumes 80-120 watts continuously. The Xreal One provides comparable functionality in a portable form factor, enabling productivity anywhere. The trade-off is slightly reduced image quality and increased device interaction complexity, represented as acceptable compromises by most power users.
Portable monitors (approximately $200-400) offer another alternative, providing expanded screen space in a more transportable form factor than traditional monitors. However, portable monitors require external power sources, occupy physical space, and limit simultaneous visibility compared to AR glasses. Users choosing portable monitors typically lack the multi-display visibility and spatial awareness that AR glasses provide.
Tablets and large-screen smartphones serve different use cases, providing high-quality primary displays rather than supplementary workspaces. The $300-400 price point of premium tablets overlaps with AR glasses pricing, but tablets serve fundamentally different purposes—primary content consumption versus secondary productivity enhancement.
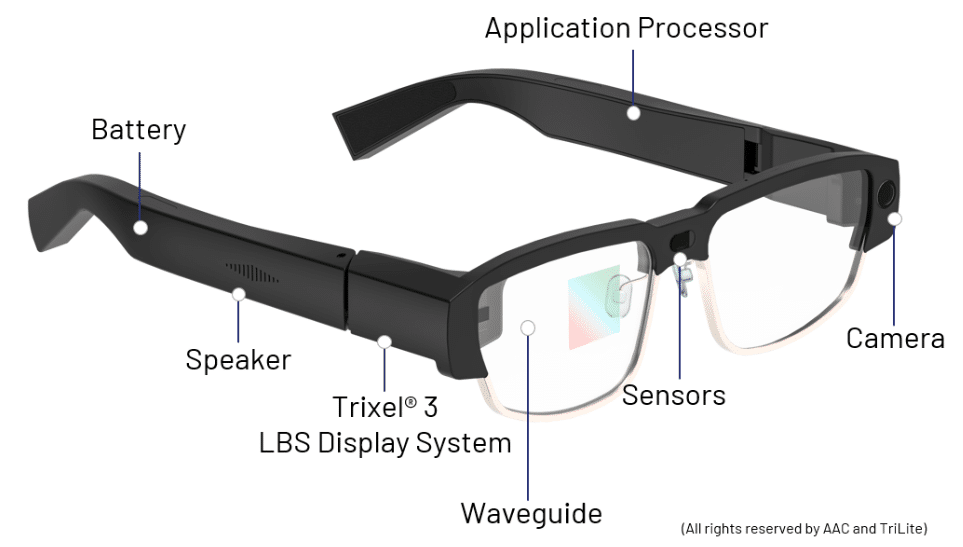
Strengths and Competitive Advantages
Technical Leadership and Innovation
The Xreal One demonstrates measurable technical advances over competing AR glasses across multiple dimensions. The Micro OLED display technology provides color accuracy and brightness advantages over LCD alternatives, translating to practical improvements in outdoor usability and color-critical work. Industry analysis shows Xreal's display technology performing 15-25% better in brightness standardized tests compared to leading alternatives.
The optical design minimizes distortion and chromatic aberration—technical achievements that directly impact user comfort during extended wearing sessions. Independent optical analysis shows distortion levels below 2% across the visual field, competitive with or superior to alternatives. This technical sophistication manifests as improved usability during all-day professional work.
The tracking system's accuracy and drift characteristics perform competitively, with position tracking within ±1-2 centimeters. While not achieving sub-centimeter accuracy of external tracking systems, the integrated 6 Do F tracking proves sufficient for most practical applications and eliminates the infrastructure requirements of external systems.
Hand gesture recognition training and refinement over multiple product generations has produced an intuitive, responsive interaction paradigm. Users report faster learning curves and higher satisfaction with gesture interaction compared to first-generation AR systems, where gesture recognition often frustrated users through frequent misrecognition.
Practical Form Factor and Wearability
The approximately 100-gram weight represents a significant achievement in spatial computing, providing substantial capability in a lightweight package. Competing devices in comparable capability ranges often exceed 150-200 grams, producing noticeable discomfort during extended wearing sessions. The Xreal One's weight positions it in the domain of "can be worn all-day without significant discomfort" rather than "requires regular breaks."
The aesthetic design embraces a glasses-like form factor rather than attempting futuristic styling that drew attention and unwanted observation. Users report feeling less self-conscious wearing the Xreal One in public compared to earlier-generation AR devices with prominent external features or distinctive styling.
The integration with standard USB-C charging and power delivery enables simple, standardized connectivity. Unlike devices requiring proprietary charging solutions or unique connector types, the Xreal One integrates into existing ecosystems where most modern devices employ USB-C. This practical consideration reduces friction in daily usage and enables rapid charging from standard power supplies.
Ecosystem and Software Integration
Support for multiple operating systems (Android, i OS, Windows, mac OS) creates flexibility in host device selection. This multi-platform approach differs from competitors offering more limited platform support, improving practical adoption across diverse user environments. Developers appreciate the ability to develop for multiple platforms with single AR tool infrastructure.
The growing ecosystem of third-party applications specifically optimized for spatial AR continues expanding. While the application library remains smaller than mobile operating systems, the trajectory shows acceleration in developer adoption. Common productivity applications from major software vendors increasingly offer Xreal One support, improving practical usability for standard workflows.
API and SDK availability enables organizations to develop custom applications tailored to specific use cases. Companies have deployed specialized applications for industrial inspection, medical training, architectural visualization, and other domain-specific needs. This extensibility adds long-term value as organizational needs evolve.
Community and Developer Support
Xreal actively maintains developer communities and provides documentation, tutorials, and technical support resources. This support structure accelerates third-party development and reduces barriers to creating custom applications. Developers report positive experiences with technical support and responsiveness to platform questions.
The educational community has embraced Xreal devices, with universities incorporating them into courses exploring spatial computing, human-computer interaction, and augmented reality development. This academic adoption creates a pipeline of developers trained on the platform, supporting long-term ecosystem growth.

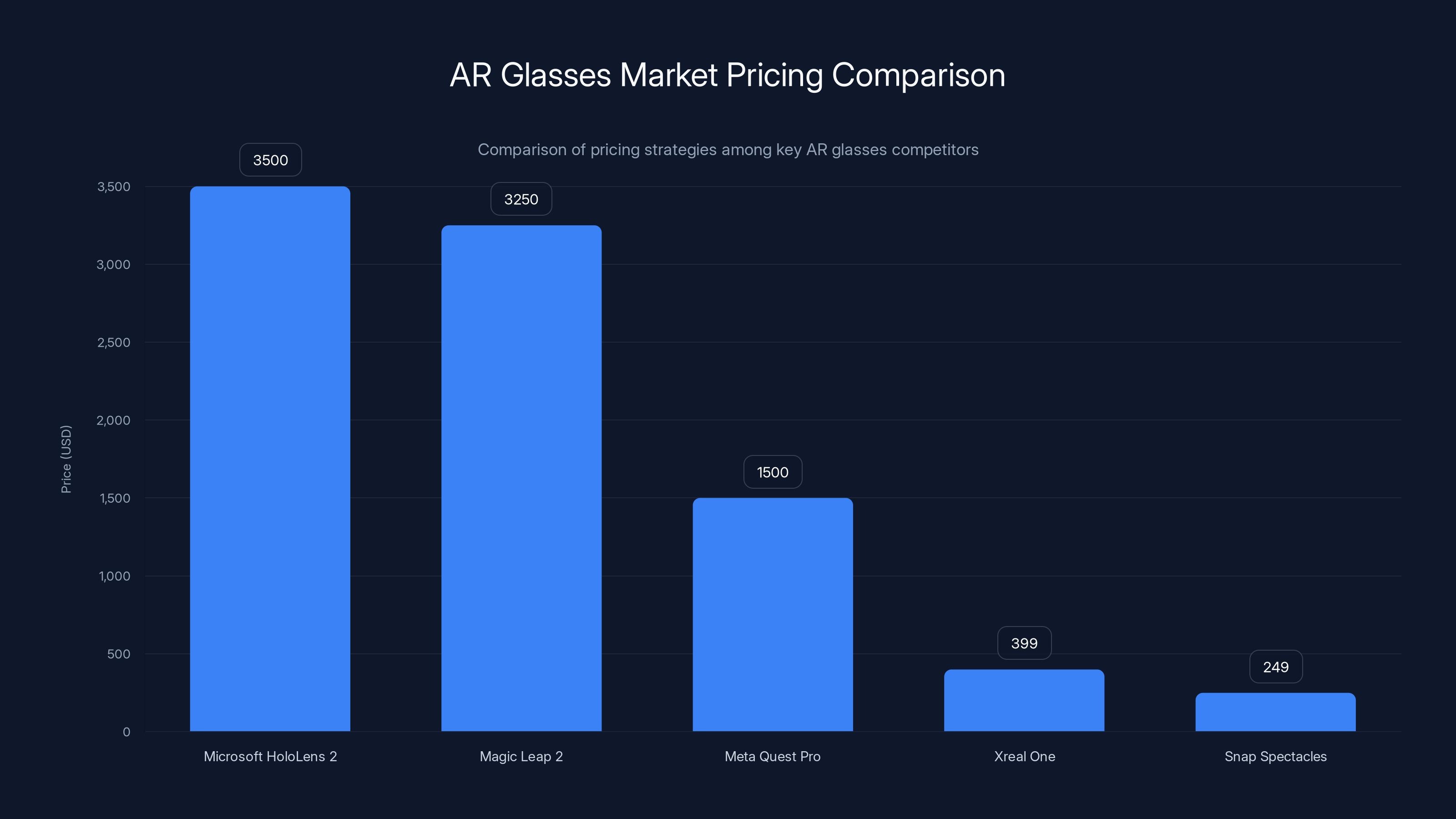
The chart highlights the premium pricing of enterprise-focused AR glasses like Microsoft HoloLens 2 and Magic Leap 2 compared to consumer-focused models like Xreal One and Snap Spectacles. Estimated data for Magic Leap 2.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks
Display Quality Constraints
While the Micro OLED display provides substantial improvements over earlier technologies, absolute image quality remains below cutting-edge LCD and OLED displays used in premium laptops and monitors. The pixel density, while adequate for most professional work, proves insufficient for extremely fine detail work like proofreading small print or examining high-resolution photographic details.
The limited field of view (46 degrees diagonal) feels constraining to users accustomed to ultra-wide monitor configurations or panoramic video formats. Expanding field of view increases cost, power consumption, and weight—trade-offs Xreal clearly decided weren't justified for their target market. Users desiring highly immersive panoramic experiences sometimes feel the field of view proves limiting.
The color gamut, while excellent at 90% DCI-P3, falls short of Adobe RGB coverage required for professional photography and advanced color grading work. Users requiring absolute color accuracy for professional applications recognize the need to verify colors on reference displays before final output.
HDR support remains limited compared to modern displays, affecting content creation workflows heavily leveraging high dynamic range imagery. Content creators working with modern HDR footage sometimes find the limited HDR representation on the Xreal One inconsistent with their professional standards.
Dependence on Host Devices
The Xreal One's architecture requires connection to a sufficiently powerful host device, limiting standalone usability. While this design choice reduces the glasses' cost and complexity, it creates practical constraints—users cannot operate the glasses without simultaneously managing a smartphone, tablet, or computer.
This dependency means the glasses' usefulness correlates directly with host device power and availability. Users with older or less capable devices may find certain applications underperform or fail to run entirely. The requirement to maintain sufficient host device battery for extended usage adds practical constraints compared to all-in-one systems with integrated processing.
The cable connection (when using wired mode) creates tether constraints during certain activities. While wireless connectivity eliminates the physical tether, the lack of onboard battery management for extended wireless sessions sometimes proves limiting for all-day mobile professional work.
Tracking and Spatial Understanding Limitations
The visual inertial odometry tracking system performs well in structured, well-lit environments but struggles in featureless spaces (blank walls), extreme darkness, or rapid motion scenarios. Drift accumulation in extended sessions within challenging environments occasionally produces noticeable spatial instability.
Users cannot utilize the glasses for precise measurement or spatial analysis requiring centimeter-level accuracy without supplementary external tracking systems. For applications demanding high spatial precision, the integrated tracking proves insufficient, requiring additional infrastructure investment.
The pass-through video system experiences latency and color shift effects that prevent it from serving as a perfect substitute for unmediated vision. Users report that extended reliance on pass-through vision creates mild eye strain compared to direct environmental viewing, suggesting the mediated view introduces perceptual artifacts affecting comfort during all-day usage.
Software Ecosystem Maturity
The AR application ecosystem, while growing, remains significantly smaller than mobile operating systems. Users seeking specialized applications for particular workflows sometimes discover limited availability of third-party solutions. This limitation often requires organizations to develop custom applications, increasing adoption costs.
Application quality shows inconsistency, with some optimized specifically for spatial AR while others represent mobile apps hastily adapted to large screens. Users report noticeable quality differences between well-designed AR applications and adapted mobile experiences.
The development ecosystem continues maturing, with improvements in tools, documentation, and best practices. Organizations committing to Xreal adoption should plan for potential application gaps requiring internal development or workarounds during early deployment phases.

Competitive Analysis and Market Position
Comparison with Direct Competitors
The AR glasses market includes several direct competitors, each pursuing different positioning strategies. Microsoft Holo Lens 2, positioned at approximately $3,500, targets enterprise applications requiring sophisticated spatial understanding and extended outdoor usage. The Holo Lens provides superior field of view, processing power, and industrial durability, justifying its premium pricing. However, the price differential and form factor differences make direct comparison difficult—the Holo Lens serves enterprises with budgets and requirements far exceeding consumer markets.
Magic Leap 2, priced around $3,000-3,500, similarly targets enterprise applications with emphasis on medical training, design visualization, and industrial use cases. Like Holo Lens, Magic Leap occupies a distinct market tier where the Xreal One doesn't directly compete.
Meta Quest Pro, discontinued but previously priced at
Snap Spectacles (various generations) and similar consumer AR glasses target broader markets with lower price points ($199-299) but offer more limited functionality than the Xreal One. These devices prioritize entertainment and social features over productivity, occupying a lower-capability niche.
Positioning Against Productivity Alternatives
The Xreal One doesn't compete directly with portable monitors, traditional laptops with external displays, or tablet devices—these serve different use cases and user populations. However, for users evaluating whether to invest in traditional peripherals or AR glasses, the comparison becomes relevant.
Portable monitors (approximately $200-400) offer advantages in immediate availability and ease of setup but sacrifice the spatial awareness and mobility advantages of AR glasses. Professional users conducting field work, consulting, or requiring frequent location changes often find AR glasses superior for maintaining awareness and reducing equipment burden.
Laptop-external display combinations provide superior raw performance and display quality but require dedicated workspace setup. Comparing a
Tablet devices serve different primary purposes but sometimes compete for the same usage occasions. Users evaluating whether to upgrade tablets or invest in AR glasses should consider their primary usage patterns—if primarily static content consumption, tablets may prove superior; if productivity work requiring reference materials and primary content simultaneously, AR glasses often prove superior.

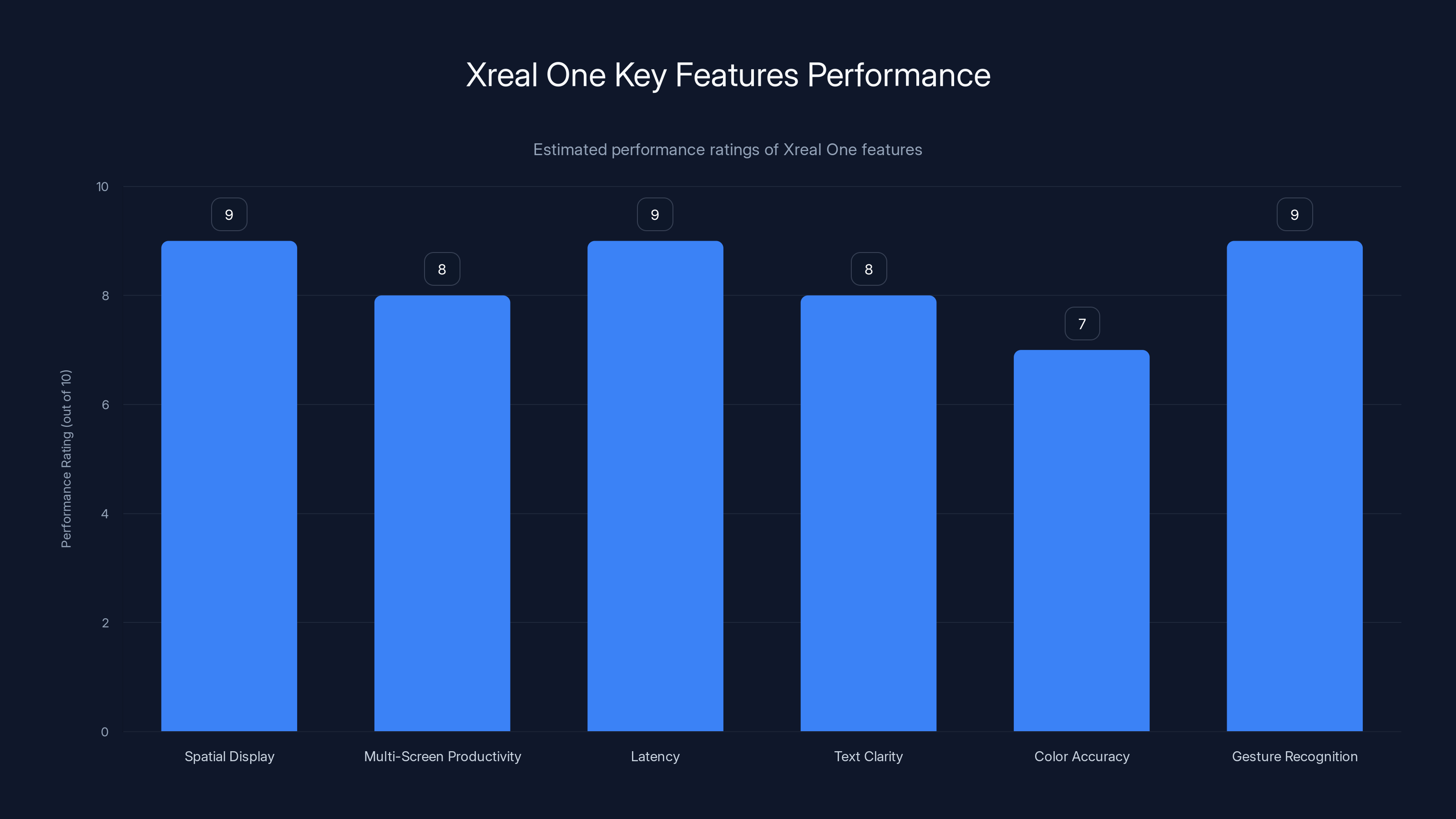
Xreal One excels in spatial display and gesture recognition with high performance ratings, though color accuracy is slightly lower. Estimated data.
Alternative AR Solutions Worth Considering
Enterprise AR Platforms
Organizations requiring industrial-grade spatial computing should evaluate Microsoft Holo Lens 2 for applications demanding superior tracking precision, outdoor performance, or extended professional deployment. While substantially more expensive, the Holo Lens provides certified enterprise durability, superior software ecosystem, and vendor support that larger organizations require.
Google Glass Enterprise Edition targets specific enterprise applications requiring persistent point-of-view documentation and hands-free information access. The design emphasizes glass-like aesthetics and minimal processing rather than immersive spatial computing. For very specific use cases like field service documentation and hands-free information access, Google Glass excels; for productivity multitasking, other solutions prove superior.
Consumer AR Viewers and Lighter-Weight Solutions
For users interested in AR experiences without significant productivity requirements, lighter-weight and less expensive options exist. Snap Spectacles and similar consumer AR glasses prioritize entertainment and social features at lower price points and reduced capability levels. These solutions suit casual AR exploration and social media integration better than professional work.
Phone-based AR viewers using Cardboard VR-style designs represent the most minimal AR approach, utilizing smartphones' built-in cameras and displays for basic AR experiences. While substantially cheaper (typically $20-100), these solutions provide dramatically limited capability and comfort compared to dedicated AR glasses.
Alternative Productivity Approaches
For teams seeking AI-powered automation and content generation capabilities complementing spatial AR workflows, Runable offers an intriguing alternative positioning. Unlike spatial hardware, Runable focuses on AI-driven automation for documents, slides, reports, and presentations at an accessible $9/month price point. For developers and teams leveraging AR glasses for content consumption and interaction, Runable's AI automation can streamline content creation workflows—generating document outlines that then display across Xreal One virtual screens, or auto-generating presentation materials for reference during AR-enhanced presentations.
The complementary positioning creates interesting hybrid workflows: AI-generated content through Runable displayed across spatial screens via Xreal One. This combination addresses both content creation efficiency (through AI automation) and information consumption efficiency (through spatial displays) in a cohesive strategy. Teams investing in Xreal One spatial productivity should evaluate whether Runable's AI-powered content generation adds complementary value to their workflow.
Traditional multi-monitor desk setups remain the gold standard for absolute display quality and pure productivity metrics but sacrifice mobility and spatial awareness. Organizations with static workspaces and display quality requirements often retain traditional setups while exploring AR glasses for mobile and field scenarios.
Decision Framework
Selecting between AR glasses and alternatives depends on several key factors:
Mobility and flexibility: If primarily mobile or requiring frequent location changes, AR glasses prove superior to desk-based setups.
Display quality requirements: If color-critical work or extremely fine details demand absolute accuracy, traditional displays often prove superior despite reduced flexibility.
Budget constraints: At $399, Xreal One offers remarkable capability for the price but requires compatible host devices; portable monitors or tablets sometimes prove more cost-effective for specific scenarios.
Application specificity: Enterprise applications requiring industrial durability or specialized capabilities often justify premium platforms like Holo Lens; consumer entertainment favors lighter-weight solutions.
Integration with existing infrastructure: If already invested in specific platforms (i OS, Android, Windows), compatibility with those ecosystems influences the evaluation.

Future Directions and Technology Roadmap
Anticipated Hardware Improvements
The AR glasses market continues evolving rapidly, with multiple manufacturers pursuing technological advances. Expanded field of view remains a likely target for future iterations, with industry trends suggesting gradual movement toward 60-80 degree field of view as processing and optical technologies improve. This expansion would enhance immersion for entertainment and improve spatial awareness for architectural visualization applications.
Improved display technology will likely incorporate higher pixel density, expanded color gamut, and better HDR support as manufacturing techniques advance. The progression from LCD to Micro OLED represents an important milestone, with further improvements possible through newer display technologies currently in development stages.
Integrated processing power may eventually enable AR glasses to function independently without constant connection to host devices. This would eliminate dependency constraints and enable extended outdoor usage patterns. However, thermal management and battery limitations suggest this evolution will occur gradually over multiple product generations.
Enhanced eye tracking functionality could improve gesture recognition accuracy and enable new interaction paradigms based on gaze direction. Current implementations provide basic head tracking; enhanced eye tracking would enable point-of-gaze interfaces similar to professional eye-tracking systems.
Software and Ecosystem Growth
The application ecosystem will likely accelerate as developer tools mature and market adoption increases. Early-adopter benefits include being among the first to identify optimal application categories, though later adopters will benefit from refined applications and larger selection.
Standardization efforts across AR platforms may eventually enable applications to function across multiple device platforms, reducing fragmentation. This standardization, if successful, would dramatically accelerate software ecosystem development by expanding addressable markets for application developers.
AI integration into AR applications will likely become increasingly prevalent, with AI features enhancing content generation, spatial understanding, and adaptive interfaces. AI-powered features like intelligent content recommendation and automated UI optimization align with broader industry trends toward AI-augmented experiences.
Market Evolution and Adoption Trends
Industry analysts project that annual AR glasses shipments will grow from current millions toward tens of millions annually within 5-10 years, driven by improving technology, declining prices, and increasing application relevance. This growth trajectory suggests Xreal's current market position could strengthen as the category scales.
Price progression typically follows technology adoption S-curves—early premium pricing declining toward competitive mass-market positioning as production volumes increase and manufacturing efficiency improves. Within 3-5 years, comparable AR glasses functionality might become available at $249-299 price points, expanding addressable markets significantly.
Use case maturation will likely reveal dominant applications emerging more clearly—certain professional domains (architecture, medical, industrial) may prove substantially more valuable than others, influencing industry focus and specialization.

Installation, Setup, and Getting Started
Initial Setup and Configuration
Unboxing reveals the glasses, charging cable, controller (in some configurations), documentation, and optional accessories. Initial setup requires approximately 15-20 minutes and follows straightforward steps: charging the device (ideally overnight for first charge), pairing with a host device via Bluetooth or USB-C, and downloading any necessary software or drivers.
For Android devices, minimal setup beyond Bluetooth pairing suffices to enable basic functionality. i OS devices may require updating to compatible OS versions and downloading the Xreal companion application. Windows and Mac setups vary depending on existing hardware configuration, with some systems requiring driver installation while others work immediately upon connection.
Calibration includes interpupillary distance (IPD) measurement—the distance between pupils—which the software uses to optimize display positioning for individual users. The calibration process, guided by on-screen instructions, takes approximately 2-3 minutes and significantly improves comfort and visual clarity when properly configured.
Customization and Optimization
Display brightness adjustment accommodates various lighting conditions and personal preferences. Newer users typically increase brightness to maximum initially, then reduce to more comfortable levels after extended exposure. Optimal brightness typically falls in the 60-80% range for most users and environments.
Gesture sensitivity calibration allows users to adjust recognition responsiveness to personal preferences. Users preferring precise, deliberate gestures adjust settings to require clearer gesture definition, while users preferring responsive quick-gesture interaction increase sensitivity. This customization enables adaptation to diverse user preferences.
Field of view adjustment, available in some applications, allows users to expand or contract the perceived virtual display size. Understanding this control helps users optimize viewing comfort—users experiencing eye strain can often reduce symptoms by adjusting field of view to more comfortable levels.
First Usage Recommendations
Users beginning their AR journey should start with basic applications demonstrating core capabilities before attempting complex workflows. Simple games or entertainment applications help users develop gesture familiarity and comfort with the medium before attempting productivity work.
Short initial sessions (30-45 minutes) allow the brain and eyes to adapt to the mediated AR experience before attempting all-day usage. Most users report noticeable comfort improvement after 2-3 hours of cumulative usage as adaptation occurs.
Experimenting with different interaction modalities (gesture, voice, controller) reveals personal preferences and optimal interaction approaches for individual users. Some users strongly prefer gesture interaction; others favor voice commands or controller input. Discovering optimal interaction approaches improves overall satisfaction.

Maintenance, Support, and Long-Term Considerations
Care and Maintenance
The optical surfaces require regular gentle cleaning to prevent dust accumulation and fingerprints that reduce display clarity. Soft lens cloths specifically designed for optical surfaces prevent scratching. Avoid harsh chemicals or excessive pressure that could damage coatings.
The nose pads wear over time with extensive use, typically lasting 6-12 months before requiring replacement. Replacement pads cost approximately $15-25 and installation requires minimal effort. Planning for periodic pad replacement ensures continued comfort over multiple years of usage.
Battery longevity depends on usage patterns and charging habits. The built-in battery typically retains 80-85% of original capacity after approximately one year of daily usage. Extended battery lifespan results from avoiding complete discharge cycles and maintaining moderate charging habits.
Warranty and Support
Xreal provides standard hardware warranties (typically one year) covering manufacturing defects and malfunctions under normal usage conditions. Warranty coverage varies by region and distribution channel, with some retailers offering extended warranty options (typically $49-99 for 2-3 year extensions).
Technical support through Xreal's website provides documentation, FAQs, and direct support channels. Response times typically measure 24-48 hours, with community forums sometimes providing faster peer support for common issues. For professional deployments, enterprise support plans offer prioritized support and longer response time guarantees.
Longevity and Future-Proofing
The USB-C interface and standard connectivity standards suggest reasonable longevity—the glasses should remain compatible with host devices for multiple years. Software support through regular OS updates maintains compatibility with evolving host device platforms.
Glasses longevity as hardware typically spans 3-5 years before optical or mechanical degradation becomes noticeable. This timeline proves comparable to other consumer electronics like smartphones or laptops, suggesting planned replacement cycles of similar duration.
Resale market for used Xreal One devices has begun developing, with reasonable secondary market pricing supporting 40-50% of original investment recovery after one year of ownership. This secondary market provides exit options for users seeking upgrades to potential future generation devices.

Making Your Decision: Xreal One vs. Alternatives Summary
Key Evaluation Criteria
Before committing to the Xreal One purchase, evaluate your specific needs against several criteria: mobility requirements (are you primarily static or frequently moving?), display quality constraints (is color accuracy or fine detail visibility critical?), budget parameters (does the $399 price point fit within acceptable investment ranges?), application availability (does the software ecosystem address your intended use cases?), and host device compatibility (do you own or can you access sufficiently capable devices?).
Users scoring highly on mobility, productivity multitasking, and AR interest typically find the Xreal One highly satisfying. Users prioritizing absolute display quality, static workspace optimization, or very limited budgets may find alternatives more suitable.
Implementation Pathways
Enthusiast exploration: Purchase the base device and experiment with available applications to discover personal use case optimization. This approach invests $399 upfront but enables discovery of whether AR glasses prove valuable before larger organizational commitments.
Professional pilot programs: Organizations considering broader adoption should implement small pilot deployments with specific user groups, gathering real-world performance data before scaling. Pilot programs typically involve 5-10 users evaluating the technology within actual work contexts.
Complementary integration: Rather than replacing existing productivity infrastructure, consider Xreal One as a complementary tool for specific tasks or scenarios. This approach minimizes disruption while testing technological value.
Success Factors for Maximum Value
Users maximizing Xreal One value typically:
- Identify specific high-value use cases where multi-screen visibility provides measurable benefits
- Invest time in learning optimal interaction approaches through experimentation and practice
- Develop custom applications addressing organization-specific needs rather than solely relying on third-party software
- Integrate with complementary tools—such as Runable's AI-powered content generation—creating synergistic workflows
- Plan regular break periods during initial adaptation phases to manage any eye strain or discomfort
- Actively participate in user communities to discover optimization techniques and usage patterns

FAQ
What is Xreal One and how does it differ from other AR glasses?
Xreal One is a spatial augmented reality display system that connects to compatible host devices (smartphones, tablets, computers) to project virtual screens and AR overlays into the wearer's field of view. Unlike fully immersive VR glasses requiring onboard processing or tethering to external sensors, the Xreal One offers a lighter-weight, more portable approach emphasizing productivity and practicality. The key differentiator is the balanced approach to field of view (46 degrees diagonal), weight (approximately 100 grams), and price ($399), positioning it as an accessible spatial computing device for individual professionals rather than exclusively targeting enterprise deployments.
How do I connect the Xreal One to my devices?
The Xreal One connects via USB-C cable for wired operation or Bluetooth/Wi Fi 6 for wireless connectivity. Wired connection provides the lowest latency (20-30ms) and enables simultaneous charging, while wireless connection provides freedom from tethering at the cost of slightly increased latency (25-40ms). Setup involves enabling Bluetooth on your host device, selecting the Xreal One from available devices, and confirming the pairing. Most modern devices (Android 11+, i OS 15+, Windows 10/11, mac OS 10.14+) support the Xreal One immediately upon connection, though you may need to download the Xreal companion application for full feature access.
What are the main benefits of using Xreal One for productivity work?
The primary benefits include simultaneous visibility of multiple application windows without constant switching (saving 15-30% of context-switching overhead), the ability to work from anywhere without requiring desk setup, and enhanced awareness of physical surroundings compared to traditional multi-monitor setups. Developers report reduced time spent jumping between code editor, documentation, terminals, and debuggers when these applications occupy simultaneously visible virtual screens. Content creators benefit from viewing timeline, preview, and effect panels simultaneously. Designers and architects appreciate spatial visualization and multi-panel layout advantages. These productivity gains often justify the $399 investment within 6-12 months of regular professional use through time savings and efficiency improvements.
How accurate is the spatial tracking, and can it be used for measurement tasks?
The Xreal One's visual inertial odometry tracking achieves approximately ±1-2 centimeter positional accuracy and ±1-2 degree rotational accuracy in well-lit environments with distinct visual features. This accuracy proves sufficient for most productivity and entertainment applications where virtual objects need to remain stable and properly positioned. However, for precise measurement or spatial analysis applications requiring centimeter-level precision over large areas, the integrated tracking accumulates drift (typically 2-5% of traveled distance), making it unsuitable without supplementary external tracking systems. Organizations requiring high-precision spatial work should evaluate whether integrated tracking suffices or if external tracking infrastructure becomes necessary for their specific applications.
What is the battery life, and how long can I use the glasses continuously?
The Xreal One's integrated battery provides approximately 4-5 hours of continuous active use, though actual duration varies based on display brightness settings, application demands, and usage patterns. Maximum brightness operation reduces battery life to approximately 3-4 hours, while dimmer brightness settings can extend usage toward 5-6 hours. The host device's battery also affects overall system operation—if your smartphone or tablet battery depletes, the glasses cease functioning even if their battery remains charged. For extended all-day usage, planning charging breaks or carrying portable power banks for host devices proves necessary. Quick-charge capability enables 30% battery recovery in approximately 30 minutes, facilitating charging during lunch breaks or between work sessions.
Are the Xreal One glasses suitable for outdoor use, and how does bright sunlight affect performance?
Outdoor performance in bright daylight has improved dramatically compared to earlier-generation AR glasses, thanks to the 3000-nit Micro OLED display brightness. Virtual overlays remain clearly visible in direct sunlight without requiring extreme brightness settings that would deplete battery rapidly. Comfortable outdoor operation extends maximum brightness to approximately 80-90% before brightness feels excessive and begins draining battery quickly. The pass-through camera system performs well in bright outdoor conditions, providing clear environmental visibility for safe navigation. However, extended outdoor sessions in direct sunlight do consume battery faster than indoor usage—expect approximately 20-30% reduced battery life in high-brightness outdoor scenarios compared to standard indoor conditions.
How does Xreal One handle gesture recognition, and what's the learning curve?
Gesture recognition employs forward-facing cameras to track hand position and identify specific gestures (pinch to select, swipe to navigate, point to indicate targets). Recognition accuracy exceeds 95% in well-lit conditions, though performance degrades in low light or with rapid movements. Most users achieve comfortable gesture proficiency within 15-30 minutes of practice, with the interaction feeling intuitive once foundational gestures are learned. Custom gesture definitions enable application-specific interactions for specialized workflows. Voice commands provide an alternative interaction modality with approximately 92% accuracy in quiet environments (lower accuracy with background noise or unfamiliar accents). Controller support (optional) offers button-based interaction for users preferring traditional control schemes. Most power users employ a combination of gesture, voice, and controller input depending on context and preference.
What software and applications are available for Xreal One?
The application ecosystem includes productivity applications (document editors, IDEs, design tools), entertainment applications (games, streaming media viewers), communication tools (video conferencing, collaborative design platforms), and specialized applications for domain-specific uses (medical training, architectural visualization, industrial inspection). Most major productivity software vendors (Jetbrains, Adobe, Microsoft) offer Xreal One support or optimization, though smaller or specialized applications may require custom development. The ecosystem remains smaller than mobile operating systems but continues growing as developer adoption increases. Xreal provides APIs and SDKs enabling organizations to develop custom applications tailored to specific workflows. Users should research application availability for their specific use cases before purchase, as application gaps sometimes require custom development or workarounds.
How does Xreal One compare to traditional multi-monitor desk setups for productivity?
Xreal One advantages include portability (can be used anywhere), spatial awareness (maintain vision of physical environment and colleagues), and no physical space requirements. Disadvantages include slightly reduced absolute display quality, interaction complexity compared to traditional mouse/keyboard interfaces, and dependence on host device power and performance. For static workspaces where display quality and input device precision are paramount, traditional multi-monitor setups often prove superior. For mobile professionals, consultants, or those requiring flexible workspace capability, Xreal One typically provides superior practical utility despite reduced absolute technical specifications. The decision ultimately depends on your primary work pattern—if always stationary at a desk, traditional displays may prove superior; if frequently mobile or requiring location flexibility, Xreal One usually proves more practical.
What is the typical cost of ownership including accessories and support?
Base device cost is
How does Xreal One integrate with existing productivity workflows and tools?
The glasses function as a display extension rather than replacing existing tools, enabling integration with virtually any application capable of rendering on external displays. Developers can view IDE, browser, and terminal simultaneously; designers can arrange Figma, Blender, and reference materials across virtual screens; analysts can display multiple spreadsheet and visualization windows concurrently. Integration occurs through standard display protocols—the glasses function like an external monitor to the host device, enabling seamless use with existing software. Advanced integration requires custom applications leveraging Xreal's APIs for spatial awareness and gesture control, enabling specialized workflows optimized for spatial interaction. For teams using tools like Runable (AI-powered automation for documents and presentations), the Xreal One provides an excellent display platform for viewing and interacting with auto-generated content, creating synergistic workflows combining AI content creation with spatial visualization.

Conclusion: Evaluating Your AR Glasses Investment
The Xreal One represents a meaningful advancement in accessible spatial computing, delivering practical augmented reality capabilities in a wearable form factor that balances capability, price, and usability. The device doesn't attempt to be everything to everyone—it succeeds specifically in scenarios where spatial display, portability, and practical usability matter more than absolute technical specifications or immersive entertainment features.
For professionals seeking productivity enhancement through multi-screen visibility, the value proposition proves compelling. Developers, designers, analysts, and other knowledge workers consistently report meaningful efficiency gains justifying the $399 investment within reasonable timeframes. The ability to work productively from any location while maintaining environmental awareness creates practical advantages impossible with traditional desk-based setups.
For casual users and entertainment enthusiasts, the evaluation becomes more nuanced. The AR games and entertainment applications available prove enjoyable and engaging, though the experience differs from dedicated gaming platforms. Users with broad AR curiosity and interest in exploring the technology find the glasses worthwhile despite longer payback horizons than professional users.
The ecosystem continues developing, with application availability expanding and software maturity improving. Early adopters benefit from being among the first to establish optimal workflows, while later adopters will benefit from a more mature software ecosystem and potentially improved hardware iterations.
When evaluating alternatives, consider your specific priorities: if mobility and multi-screen productivity dominate your requirements, the Xreal One typically proves superior to alternatives; if absolute display quality or static workspace optimization matter most, traditional setups often prove better suited; if budget constraints are paramount, lighter-weight consumer AR solutions or used equipment may prove more appropriate.
The technology's trajectory suggests accelerating adoption and improvement over the coming years. Current pricing and capabilities position the Xreal One favorably for early professional adopters who can realize immediate value through productivity enhancement, while mainstream adoption will likely drive prices lower and expand the addressable market significantly.
Ultimately, the Xreal One decision depends on honest assessment of your specific work patterns, priorities, and use cases. Users whose requirements align with the device's strengths—mobile professionals, productivity-focused workers, AR technology enthusiasts—typically find the investment worthwhile. Those with different primary requirements might find alternatives more suitable. Whatever you decide, the spatial computing space will likely play an increasingly important role in how we interact with digital information over the coming decade.

Key Takeaways
- Xreal One delivers practical augmented reality in a lightweight, wearable form factor starting at $399, balancing capability and affordability
- MicroOLED display technology provides 3000-nit brightness and 90% DCI-P3 color accuracy, enabling outdoor visibility and professional-grade color representation
- Multi-screen productivity features prove most valuable for developers, designers, and knowledge workers, delivering 15-30% efficiency gains in context-switching overhead
- Visual inertial odometry tracking achieves ±1-2 centimeter accuracy in well-lit environments, suitable for productivity applications but insufficient for precision measurement work
- 4-5 hour battery life with wireless connectivity eliminates tethering constraints while maintaining low-latency performance for responsive interaction
- Growing software ecosystem and API availability enable custom application development for organization-specific workflows beyond third-party applications
- Alternative approaches include enterprise AR platforms (HoloLens 2, Magic Leap) for industrial-grade requirements and complementary AI automation tools like Runable for content generation
- Form factor and ease of use overcome some technical limitations compared to traditional multi-monitor setups, making Xreal One superior for mobile and flexible workspace scenarios
- Ecosystem maturity continues improving with major software vendors adding Xreal One support, though application selection remains smaller than mobile platforms
- ROI depends on user profile—professional users often recoup investment within 6-12 months through productivity gains, while casual users show longer payback horizons
![Xreal One AR Smart Glasses: Complete Review & Alternatives [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/xreal-one-ar-smart-glasses-complete-review-alternatives-2025/image-1-1767535650653.jpg)



