The Invisible Battle for America's Construction Workers
In 2024 and 2025, America's infrastructure faced unexpected competition, not from poor policy or funding shortages, but from an unforeseen rival. While state and local governments celebrated record debt sales for infrastructure projects, private companies quietly invested over $41 billion annually in data center construction, matching government spending on roads, bridges, and transit systems. This competition for resources is highlighted by Bloomberg, which notes the significant impact on infrastructure timelines.
These projects aren't drawing from separate labor pools; they're competing for the same electricians, concrete specialists, and general laborers, straining the labor market. According to Amazon's recent investment in Mississippi, the demand for skilled labor is unprecedented. Autodesk CEO Andrew Anagnost emphasized to Bloomberg that data center construction is diverting resources from other projects, slowing infrastructure progress.
Understanding the Scale of Data Center Investment
Private spending on data center construction exceeded $41 billion annually by 2024, a figure that underscores the scale of this investment. Major tech companies like Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and Meta have announced substantial data center expansion plans. Microsoft alone plans to invest billions over the next few years, driven by the need for AI compute power. The urgency is real, as companies race to secure AI capabilities, with Google focusing on capturing AI infrastructure advantages.
These companies are offering premium wages to construction crews, paying contractors bonuses to accelerate timelines, and securing strategic real estate. The competition for skilled labor is fierce, as highlighted by Fortune, which reports on the six-figure salaries construction workers are earning due to the data center boom.
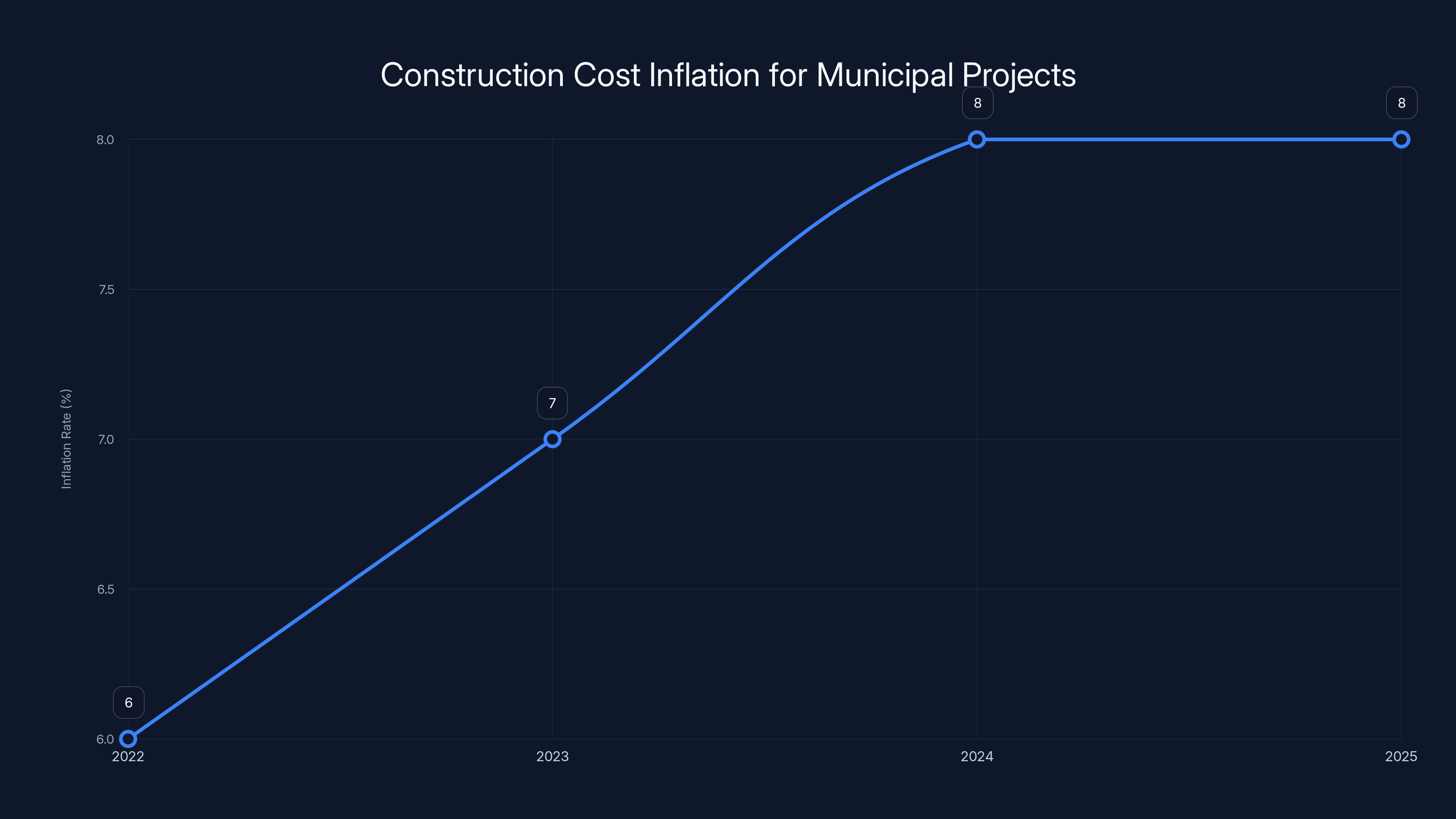
Construction cost inflation for municipal projects has averaged 6-8% annually since 2022, driven by competition from private sector projects. Estimated data.
The Infrastructure Funding Paradox
State and local governments sold record amounts of debt in 2024, planning to sell another $600 billion in municipal bonds next year, according to U.S. Census Bureau data. This funding is critical for addressing infrastructure backlogs, such as roads with potholes and aging water systems. However, the availability of skilled workers is a significant bottleneck, as highlighted by Long Island Business News, which reports on the strain in construction jobs due to zoning and labor issues.
Hyperscaler companies offer better pay and steadier work, drawing workers away from municipal projects. A concrete specialist earning
Immigration Policy and Labor Shortage Multiplication
The construction labor market is further strained by immigration restrictions. Aggressive enforcement and restrictive visa caps have reduced the availability of immigrant workers, who historically make up a significant portion of the construction workforce. According to ITEP, immigrants represent roughly 25-30% of the construction workforce nationally.
As skilled workers retire, the industry loses both labor capacity and institutional knowledge. The combination of declining immigration, retiring workers, and growing AI data center demand creates a perfect storm for labor shortages.
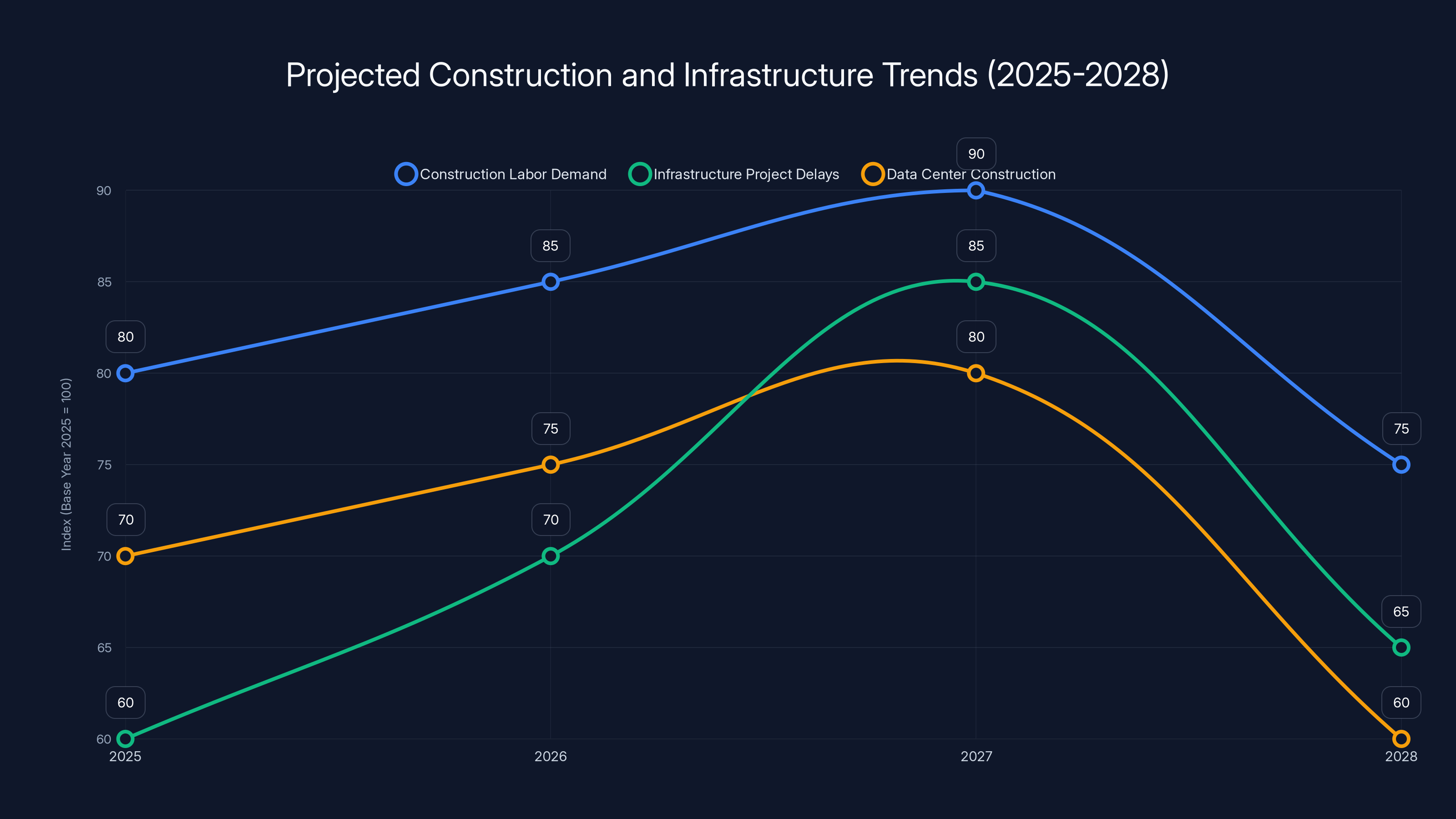
The chart illustrates projected trends in construction labor demand, infrastructure project delays, and data center construction from 2025 to 2028. Estimated data suggests a peak in 2027, followed by potential easing.
The Geography of Competition
The impact of data center construction isn't uniform across the U.S. Virginia, for example, has become the data center capital of the United States, with significant investments from Google, Amazon, and Microsoft. This has led to tight labor markets and rising costs, as reported by Amazon.
Texas is experiencing similar pressures, with major buildouts planned in Austin, Dallas, and Houston. Meanwhile, California faces constraints from environmental regulations and power availability, affecting data center growth. Midwest states like Ohio and Indiana are emerging as secondary hubs due to less expensive land and better power infrastructure, according to Morgan Lewis.
Concrete vs. Silicon: Which Project Wins?
Data center projects often win the resource wars due to urgency, profitability, and political will. Municipal projects, while politically valuable, face delays without immediate catastrophic consequences. In contrast, data center delays impact quarterly earnings and competitive positioning, as noted by Mara.
The economics favor data centers, which offer premium wages and attract the best crews. Political asymmetry also plays a role, with Fortune 500 companies receiving tax incentives and streamlined permits, while municipal projects face traditional processes.
The Materials and Supply Chain Angle
Data center construction competes for materials and supply chain resources. High-density cables, specialized cooling systems, and redundant power infrastructure are in high demand. When hyperscalers book significant production capacity, other projects, like city transit stations, face delays, as highlighted by Planet Detroit.
Electrical infrastructure is a prime example. Data centers require specialized high-capacity systems, which manufacturers prioritize due to larger orders from companies like Google, as noted by Andreessen Horowitz.
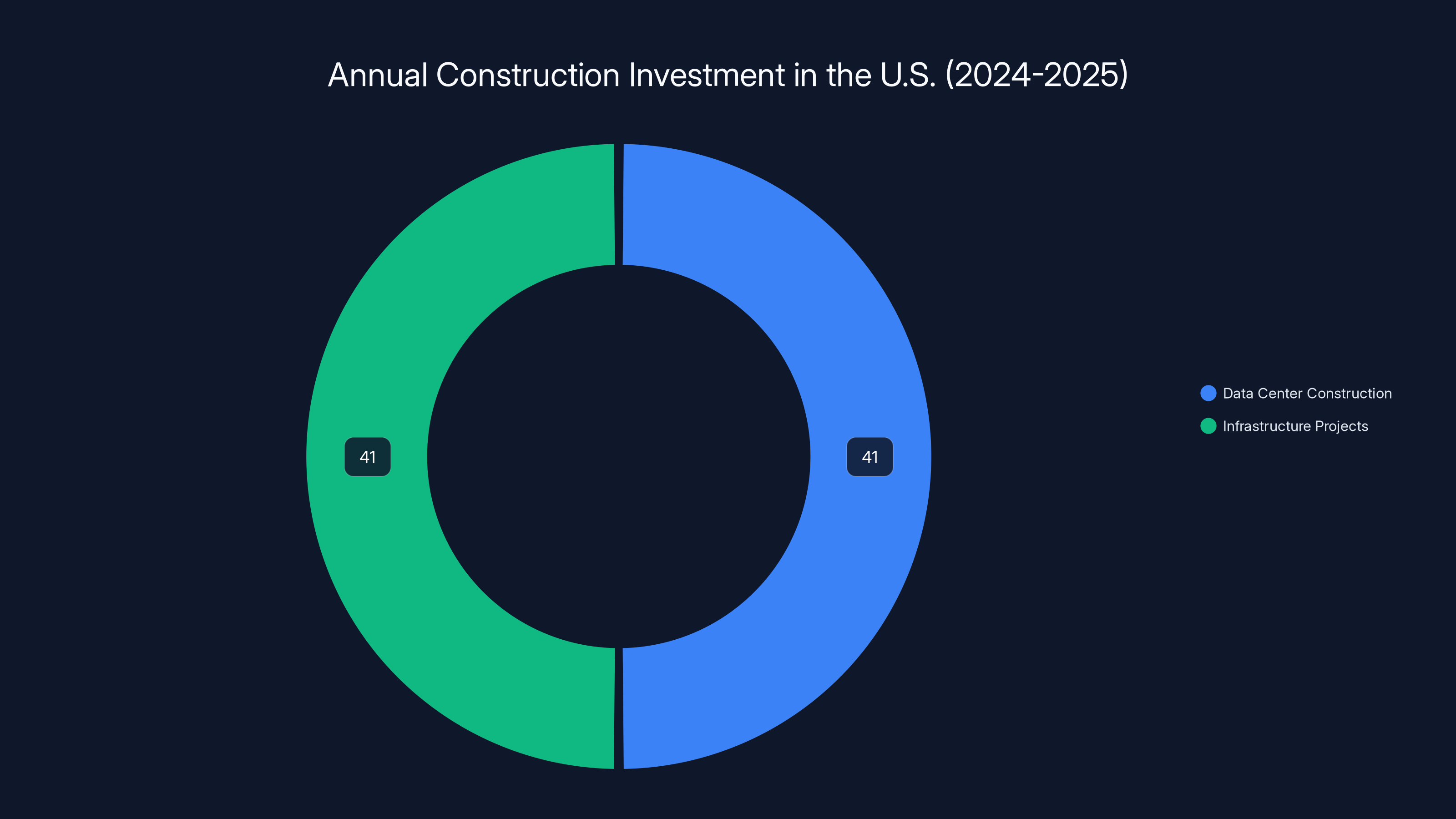
Estimated data shows equal investment in data centers and infrastructure projects, highlighting competition for construction workers.
Power Infrastructure: The Ultimate Constraint
Data centers require enormous amounts of reliable electrical power, competing with municipal infrastructure for electrical capacity. A large data center consumes 100-200 megawatts continuously, equivalent to a city's electricity demand. Power companies prioritize upgrades for hyperscalers due to long-term power purchase agreements, as reported by World Economic Forum.
Water is another critical factor. Cooling data centers requires significant water resources, creating conflicts in water-stressed regions. Some areas have restricted data center expansion due to water constraints, as noted by ITIF.
Cost Escalation: The Municipal Project Impact
Private construction spending drives up costs for everyone. Municipalities face higher costs for the same projects due to wage inflation and premium rates charged by specialized contractors. A city that budgeted
This creates a cycle where projects cost more, cities do fewer projects, and infrastructure backlogs grow. Over time, this leads to a visible divide between regions with hyperscaler data centers and those without, as noted by Financial Content.
Timeline Slippage: How Long Will Infrastructure Projects Actually Take?
Infrastructure project delays compound over time. A bridge replacement project budgeted for 24 months might extend to 36 months due to staffing issues, supply chain delays, and weather impacts. Projection models built in 2024 didn't account for massive data center construction pulling workers away, as highlighted by Connected World.
The result is significant timeline slippage through 2026-2028, with impacts on public health and safety due to deferred maintenance.
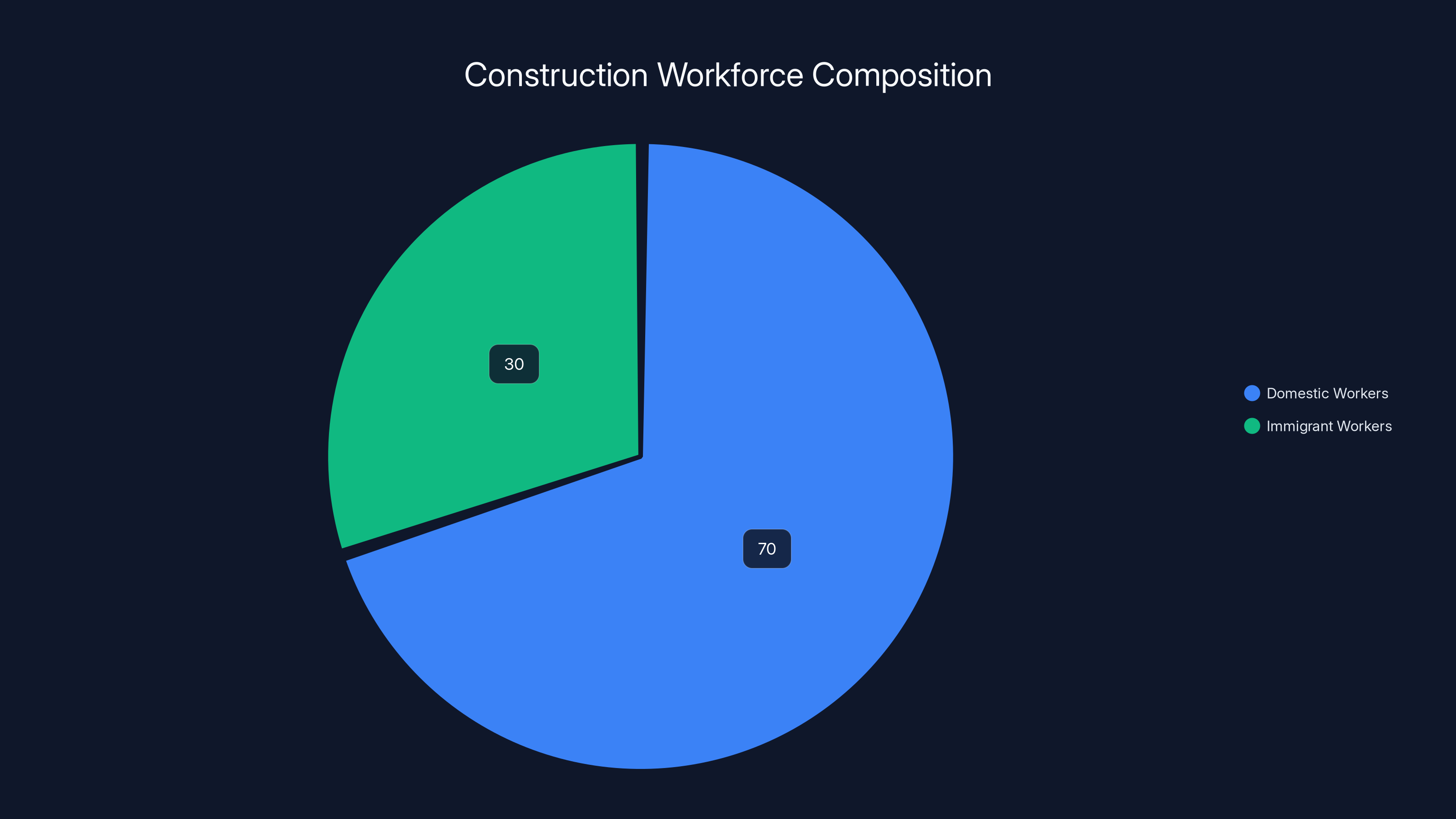
Immigrants make up approximately 30% of the U.S. construction workforce, highlighting their critical role in the industry. Estimated data based on national averages.
Regional Winners and Losers
Geographic variation is significant. Regions with hyperscaler data center investments, like Northern Virginia and parts of Texas, will see economic activity and wage growth but struggle with public infrastructure. Regions without major data center investment will have stable labor availability but slower economic growth, as reported by KULR8.
The Automation Factor: Will Robots Save Infrastructure?
Automation is slowly entering construction, with companies developing autonomous equipment and robotic systems. However, widespread deployment is likely years away, and much infrastructure work remains difficult to automate, as noted by Runable.
Equipment Manufacturing: The Unseen Bottleneck
Data center construction requires specialized equipment, and manufacturers are ramping up production to meet demand. However, lead times stretch, and prices rise, affecting infrastructure projects that need custom manufacturing, as highlighted by Andreessen Horowitz.
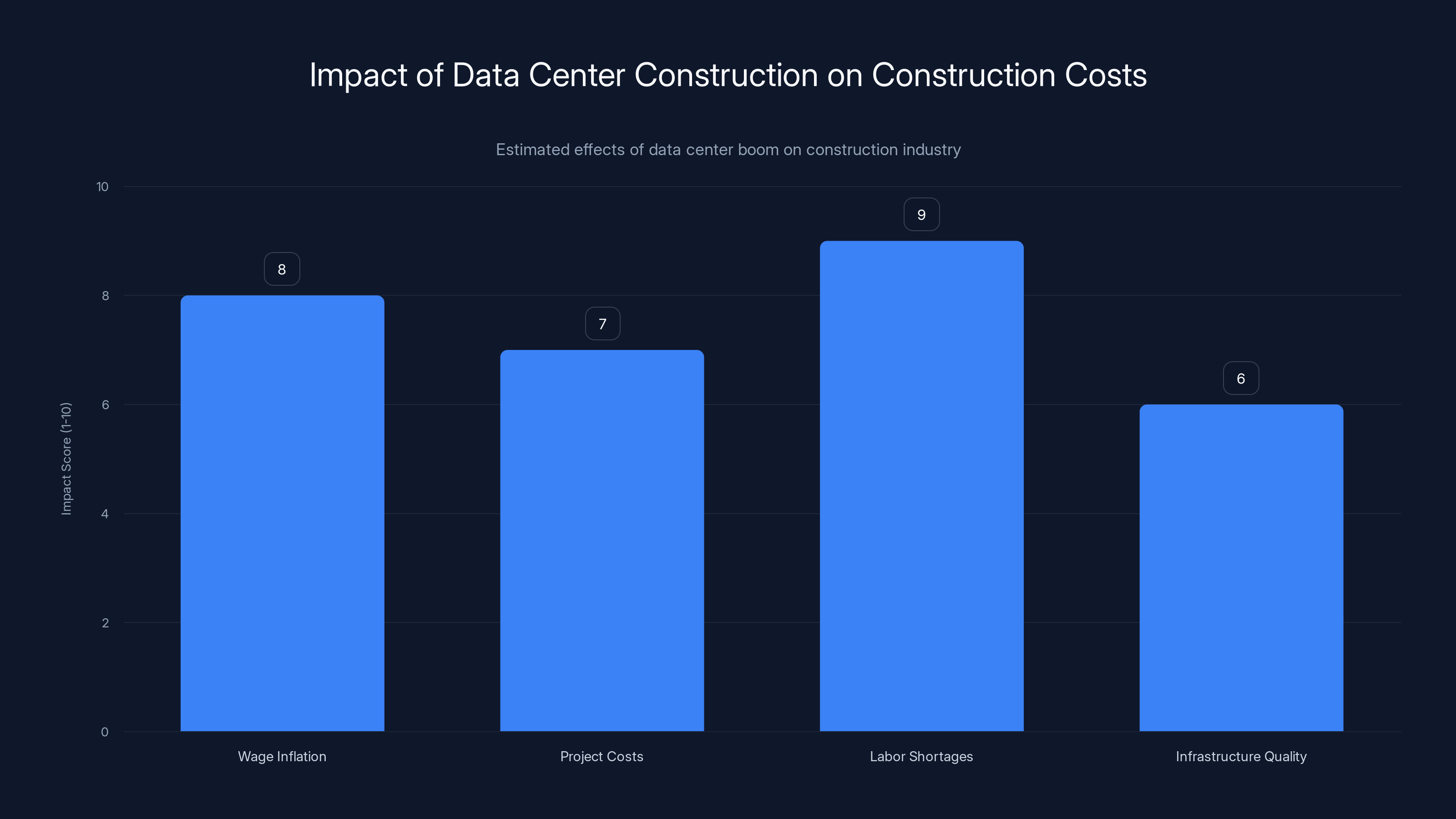
The data center boom significantly impacts construction costs, with labor shortages and wage inflation being the most affected areas. (Estimated data)
The Political Response: Are Governments Doing Anything?
Local and state governments are beginning to recognize the competition for construction resources. Some jurisdictions are incentivizing local workers to stay in municipal projects, while others negotiate with hyperscalers for coordinated construction timelines, as reported by Dallas News.
However, comprehensive national policy responses are lacking, and immigration policy remains unchanged, despite calls for reform.
Sustainability and Environmental Implications
Deferred infrastructure projects have environmental implications. Older systems are less efficient, leading to increased energy consumption and emissions. Data centers consume significant power, but they enable AI capabilities that might improve efficiency elsewhere, as noted by ITIF.
Corporate Responsibility and Industry Awareness
Some hyperscalers are aware of their impact on local labor markets and are taking steps to address it. Microsoft and Google have made statements about local workforce development, but meaningful action remains limited, as reported by Morgan Lewis.
The Next 18-24 Months: What to Expect
If current trends continue, construction labor will remain tight through 2027. Data center projects will accelerate, and municipal infrastructure projects will face delays and cost inflation. Public frustration with infrastructure delays will increase, as noted by Statista.
Strategies for Coping with Infrastructure Delays
Cities and regions can adopt several strategies to cope with infrastructure delays, including prioritizing critical projects, engaging in public-private partnerships, and investing in workforce development. These approaches can help mitigate the impact of labor shortages and maintain momentum on essential infrastructure projects.
The Bigger Picture: Economic Distortions and Long-Term Implications
The AI data center boom is creating structural imbalances in infrastructure investment. Private capital is directed toward AI infrastructure, while public infrastructure remains underfunded. Over time, this creates divergence in infrastructure quality across regions, as noted by Planet Detroit.
Looking Forward: The Automation Wildcard
Construction automation could significantly ease labor shortages if deployed at scale. Companies like Built Robotics are developing autonomous equipment, but widespread adoption is still years away. Automation could increase effective construction capacity, easing the infrastructure squeeze, as noted by Runable.
International Context: Are Other Countries Facing This Too?
The competition for construction resources is a global phenomenon. Europe, China, Japan, and South Korea are all investing in data centers and facing similar labor constraints. However, different labor laws and construction models affect how these dynamics play out, as reported by World Economic Forum.
The Verdict: What Actually Happens
Infrastructure projects in regions with significant data center construction will face delays and cost increases. Municipal budgets will be strained, and some maintenance will be deferred. This is a result of straightforward economics, with scarce labor going to the highest bidder. However, the situation is not permanent, and solutions are possible through policy changes, automation, and normalization of data center construction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the data center boom and why is it happening?
The data center boom refers to massive private investment in building new computing infrastructure facilities to support AI, machine learning, and cloud services. Companies like Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and Meta are racing to build the computational capacity needed for AI model training and deployment, driven by fierce competition and significant market opportunities.
How does data center construction compete with infrastructure projects?
Data center construction competes with infrastructure projects for skilled labor, materials, and supply chain resources. Private companies offer higher wages and better terms, attracting workers away from municipal projects and creating labor shortages that extend timelines and increase costs.
What are the economic impacts of this competition?
The economic impacts include wage inflation, rising construction costs, labor shortages, and diverging infrastructure quality. Municipal budgets face higher costs, forcing cities to choose between increasing budgets, reducing scope, or delaying projects, leading to infrastructure backlogs and deferred maintenance.
Which regions are most affected by data center construction competition?
Northern Virginia, Texas, and parts of the Midwest are most affected by data center construction competition. These regions experience tight labor markets and rising costs due to significant investments from major tech companies. Regions without major hyperscaler presence face less direct pressure but still experience indirect cost increases.
Why can't municipal projects just pay more to compete for workers?
Municipal budgets are constrained by taxpayer limitations and political processes, preventing rapid wage increases. Unlike private companies, municipalities must follow slow-moving budgetary processes, making them less attractive to workers even at comparable wages.
When will this construction labor shortage improve?
The shortage is expected to improve around 2027-2028, as data center construction normalizes, automation contributes to productivity, or immigration policy expands the labor pool. Until then, expect tight labor markets and extended timelines in regions with major data center activity.
What role can automation play in solving construction labor shortage?
Automation can increase effective labor capacity, easing shortages. However, widespread deployment is still years away, and much infrastructure work remains difficult to automate. Automation will help with certain tasks but won't eliminate the need for skilled human labor.
How does water and power infrastructure compete with data centers?
Data centers consume significant power and water for cooling, requiring infrastructure upgrades that compete with municipal projects for resources. Power utilities prioritize hyperscaler agreements over general municipal upgrades, creating indirect competition.
What policies could help address this competition?
Effective policies could include increased federal funding for municipal infrastructure, immigration reforms, workforce development programs, public-private partnerships, and timeline coordination regulations. However, these require legislative action and political coordination.
Will data centers move to other countries to avoid these constraints?
Some data centers may expand internationally, but companies prefer to locate near users for latency reasons and access developed infrastructure. While some international expansion is likely, significant capacity expansion will remain in the U.S., maintaining domestic competition for resources.
Key Takeaways for Infrastructure Planning
If you're responsible for municipal infrastructure planning, consider these practical implications:
-
Assume longer timelines: Budget for 15-25% schedule extensions for major projects in regions with significant data center activity.
-
Front-load critical work: Prioritize infrastructure with immediate safety or operational impact.
-
Engage private sector partners: Negotiate for hyperscalers to fund related municipal infrastructure upgrades.
-
Invest in workforce development: Start training programs now to expand labor capacity by 2027-2028.
-
Monitor cost escalation: Budget conservatively and plan for construction cost overruns.
-
Coordinate regionally: Share labor market intelligence and coordinate project timelines with neighboring municipalities.
-
Explore automation: Adopt construction automation where available to reduce long-term labor dependencies.
The data center boom is real, and its impact on infrastructure is significant. However, with proactive planning and realistic assumptions, the challenges are manageable.
![AI Data Center Boom vs Infrastructure Projects: The Resource War [2025]](https://runable.blog/blog/ai-data-center-boom-vs-infrastructure-projects-the-resource-/image-1-1765663686642.jpg)



