AI in Sales 2026: The Complete Guide to the Revolution Happening Right Now
Introduction: The End of an Era
The sales profession stands at an unprecedented inflection point. For decades, the fundamental mechanics of go-to-market operations remained remarkably consistent—human salespeople prospecting, qualifying leads through email cadences, attending discovery calls, and managing deal pipelines. This playbook dominated from the early 2000s through 2024. But between early 2024 and early 2026, everything changed.
We're witnessing the transition from a human-led sales model to an AI-augmented ecosystem, and the transformation is happening faster than almost anyone predicted. The conversation has shifted from "Will AI transform sales?" to "How quickly will it displace human roles?" This shift isn't theoretical—it's happening in real production environments at actual companies, with measurable business outcomes.
The most compelling evidence comes from direct experimentation. When a founder deliberately replaced an entire sales organization with AI agents and achieved equivalent revenue with 1.2 humans instead of 10, the implications became undeniable. The math isn't aspirational; it's documented reality. A
These aren't edge cases or theoretical scenarios. They represent the baseline capabilities of current AI sales systems. The question founders and sales leaders now face isn't whether AI will change sales—it's whether they'll be ahead of or behind the curve as this transformation accelerates.
This comprehensive guide examines what's actually happening in AI-driven sales organizations, which roles are genuinely at risk, which are thriving, how to implement AI systems effectively, and what alternatives exist for teams seeking to modernize their go-to-market operations. We've moved beyond speculation into the era of practical, measurable results—and the strategic implications are profound.
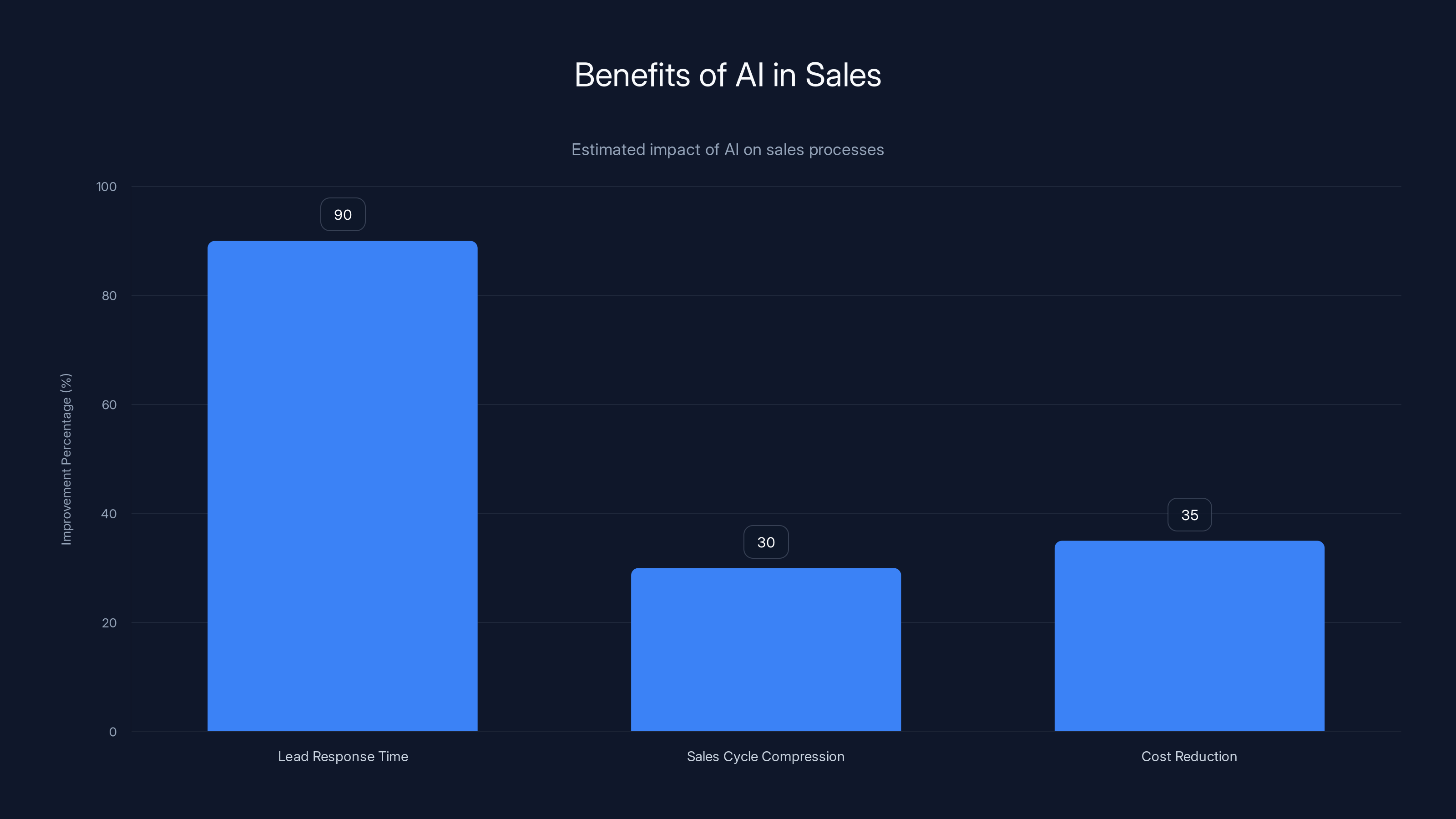
AI in sales drastically improves lead response times, compresses sales cycles by 20-40%, and reduces customer acquisition costs by 25-40%. Estimated data.
The Numbers Behind the Transformation: What Happened at SaaStr
Understanding the scale of AI's impact on sales organizations requires looking at specific case studies with actual metrics. The SaaStr experiment provides one of the clearest windows into this transformation.
The Catalyst: When Headcount Met AI
In May 2025, something entirely unremarkable happened at SaaStr—two salespeople quit. This is a normal business occurrence, not a strategic inflection point. Historically, this would trigger a standard hiring process: job description refinement, recruiter engagement, interview rounds, onboarding. Instead, a different decision was made. Rather than hiring replacements, the organization doubled down on AI agent experimentation that had already demonstrated promise in handling specific workflows.
The setup that emerged from this decision became the operational blueprint: 20 AI agents across different sales workflows, supported by one full-time human Account Executive and approximately 20% of a dedicated "Chief AI Officer's" time. The architecture itself reveals important principles about hybrid human-AI sales teams. Different agents handled different sales cycles—low-ticket sales (under $5,000) operated entirely through AI agents, mid-market deals received human involvement at negotiation stages, and enterprise sponsorships engaged human sellers at procurement phases.
The results defied conventional wisdom about automation. Not only did the organization maintain equivalent revenue with dramatically fewer humans, but several metrics actually improved. Response times to inbound opportunities compressed from hours to seconds. AI agents responded to inquiries at 11 PM on Saturday nights—windows where no human salesperson would be available. Lead qualification actually improved because AI agents never cherry-picked leads or showed favoritism. Every single opportunity received systematic follow-up without fatigue, bias, or variable quality.
The Math: From 8-9 Humans to 1.2 Humans Plus 20 Agents
The raw numbers tell the story:
- Traditional sales team size: 8-9 full-time employees
- New AI-augmented team: 1 full-time AE + 0.2 Chief AI Officer equivalent + 20 AI agents
- Business outcome: Equivalent revenue maintained
- Implicit efficiency gain: 625-750% increase in revenue per human employee
Breaking this down further reveals the economics driving the shift:
Traditional Team Economics:
- 8-9 salespeople at average loaded cost of 200,000 per person
- Annual expense: 1.8M
- Revenue generated (assuming 250K per person):2.25M
- Revenue-to-expense ratio: 1.3:1 to 1.4:1
AI-Augmented Team Economics:
- 1 full-time AE at $150,000
- 0.2 Chief AI Officer at $40,000 (annual cost)
- 20 AI agent subscriptions at approximately 2,000 per month each
- Estimated annual technology cost: 480,000
- Total annual expense: 670,000
- Same revenue maintained: 2.25M
- Revenue-to-expense ratio: 2.4:1 to 7.3:1
Even accounting for conservative estimates on AI pricing, the economic efficiency improvement is staggering. The organization isn't sacrificing revenue to achieve this—it's maintaining the same business results with a fraction of human resources and a different technology investment.
Autonomous Deal Closure: The 100K Examples
Most arguments about AI in sales eventually hit a credibility wall: "That's fine for supporting roles, but AI could never handle a real deal." The
The $70,000 deal that closed autonomously happened outside business hours—11 PM on a Saturday. No human salesperson was available. An AI agent managed the entire interaction: engaging the prospect, understanding their needs, presenting options, addressing objections, and closing the agreement. The arrangement only involved human review after the AI agent had already secured commitment. The prospect accepted the terms, the paperwork flowed to procurement without human sales involvement, and the deal was booked.
The $100,000 agreement closed on New Year's Eve—another scenario where human availability is minimal and sales velocity historically plummets. An AI system independently managed this engagement and secured closure before human team members could even review it.
These cases serve an important function in the AI sales narrative: they prove that the constraints on AI sales systems aren't inherent to the technology—they're often self-imposed through conservative deployment strategies. When organizations actually unleash AI agents on real deals rather than relegating them to lead qualification, the results challenge our assumptions about where human involvement is essential.
What's Going Extinct: The 12-Month Timeline
Predictions about technological disruption often suffer from vagueness—the "AI will transform sales" assertion that could mean anything from minor efficiency gains to total job displacement. More useful are specific role predictions with timelines. Several sales positions appear headed toward functional extinction within 12 months.
SDRs Sending Templated Emails: The Casualty of Scale
The Sales Development Representative role, in its current form, appears near extinction. This requires nuance—not all SDRs will disappear, but the function of sending templated email cadences to inbound leads and qualifying opportunities will become automated at most organizations.
The reason is structural rather than preferential. Email-based SDR work has several characteristics that make it particularly vulnerable to AI displacement:
1. High-Volume, Repetitive Nature: SDRs traditionally manage 100-200 inbound leads monthly, sending variations of similar messages with slight personalization. AI systems execute this workflow faster and more consistently than humans.
2. Objective Qualification Criteria: Lead qualification typically follows Boolean logic—company size, industry, technical stack, budget signals. These rules translate cleanly into AI decision-making frameworks.
3. Standardized Process: The SDR playbook is typically documented, templated, and repeatable. Documented processes are easier for AI to learn and execute.
4. Measurable Output Metrics: SDR performance is usually measured through quantifiable metrics—response times, qualification rate, meeting volume. These same metrics demonstrate that AI improves on human baselines across nearly all dimensions.
Timeline Evidence: Organizations that have deployed AI for inbound lead qualification already report 80-95% automation of the qualification process, with humans reserved for exceptions, escalations, and complex negotiations. Given the 12-month technology acceleration cycle, this capability will propagate to most organizations using modern sales infrastructure by late 2026 or early 2027.
What won't disappear: The concept of an SDR role may persist, but the job description will transform entirely. Instead of sending emails, SDRs will manage, train, and optimize 5-10 AI agents each—more of a technical operations role than a sales execution role.
BDRs Running Classic Cadence Campaigns: Dinosaur Territory
Business Development Representatives relying on cadence-based outbound campaigns face similar structural displacement. Traditional outbound BDR work involves:
- Multi-touch campaigns (typically 7-9 touches over 21-30 days)
- Email, Linked In, phone, and occasional value adds (content, calendar links)
- Manual list building and CRM hygiene
- Tracking campaign metrics and adjusting based on performance
- Reporting on weekly/monthly outbound metrics
AI systems now handle most of these components better than humans. An AI agent can simultaneously manage outbound campaigns to 1,000+ prospects, personalizing each interaction with company research, industry context, and individualized messaging. The agent learns from responses, adjusts cadence timing, and escalates to humans when engagement reaches specific thresholds.
The survival scenario for BDRs requires transformation from "person who runs campaigns" to "person who builds and optimizes AI agent campaigns." This is a different job requiring different skills—data analysis, AI agent management, experimentation design. The traditional cadence BDR faces displacement in the 12-month window.
Sales Roles Based Primarily on Information Routing
A broader category of sales positions, particularly in larger organizations, exist primarily to route information between systems and people. These include:
- Sales operations professionals focused on data entry and CRM updates
- Lead qualification specialists who don't engage directly with prospects
- Sales assistants managing administrative workflows
- Territory managers whose primary function is assignment logic rather than selling
These roles are vulnerable because they don't require sales skill—they require process execution. If the process can be documented and the decision logic clarified, AI can execute it. Organizations that eliminate these roles entirely will replace them with better data infrastructure and more sophisticated AI systems, rather than with different humans.
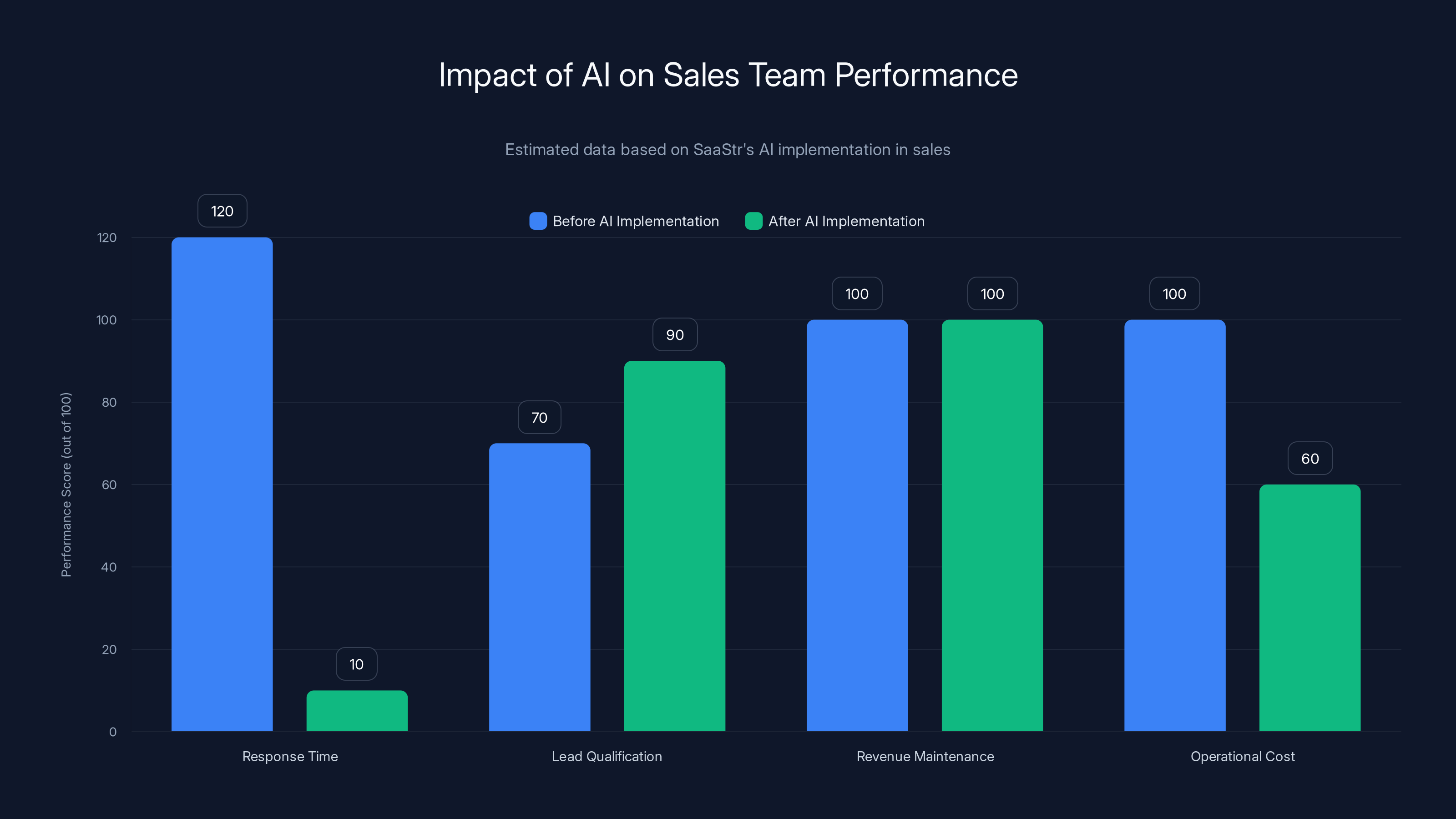
AI implementation significantly reduced response times and improved lead qualification, while maintaining revenue and reducing operational costs. Estimated data based on SaaStr's AI adoption.
What's Surviving: The Human Sales Roles That AI Reinforces
Not everything in sales is disappearing. Several role categories appear durable, at least in the medium term, because they require skills that current AI systems don't possess or because the value of human judgment in specific contexts remains irreplaceable.
Complex Enterprise Negotiations and Procurement
When a deal exceeds a certain complexity threshold—typically involving procurement committees, legal review, custom terms, or integration requirements—human sales leadership becomes valuable. An AI system can manage the initial engagement, discovery, and basic negotiation, but the senior Account Executive who understands the political dynamics of a Fortune 500 buying committee has genuine strategic value.
This isn't because the human is better at talking; it's because the human understands context, builds relationships, and navigates organizational dynamics that don't appear in emails or meeting transcripts. A CRO negotiating a $5 million deal with custom security requirements isn't being displaced by AI—they're being supported by AI agents handling the administrative burden.
High-Trust, Relationship-Based Enterprise Sales
Certain selling scenarios inherently depend on relationship. A VC partner selling their fund's value proposition, a strategic advisor selling transformation consulting, or an enterprise software sales leader selling a company-wide transformation—these conversations require genuine human trust-building.
AI can support these relationships (preparing research, managing logistics, qualifying prospects), but the core conversation benefits from human judgment, emotional intelligence, and the ability to respond to unexpected objections with genuine insight rather than trained responses.
Duration estimate for survival: Relationship-intensive sales roles appear durable for 3-5 years minimum, and possibly indefinitely if AI doesn't develop genuine reasoning and empathy capabilities.
Sales Leaders Who Understand AI Operations
A new category of durable sales role is emerging: sales professionals who manage AI agent systems. These require several specific capabilities:
1. Quantitative Literacy: Understanding metrics, A/B testing, statistical significance, and performance measurement. Not every salesperson has this foundation.
2. System Thinking: Seeing sales as a connected system where changes to one AI agent's messaging affect response rates, qualification rates, and downstream deal quality.
3. Patience with Iteration: Recognizing that AI agents require training, correction, and continuous optimization—not fire-and-forget deployment.
4. Technical Fluency: Understanding enough about AI systems to brief engineering teams, troubleshoot integrations, and make informed technology decisions.
Salespeople who develop these capabilities become increasingly valuable because they bridge technical infrastructure and business outcomes. This is where the $250K SDR concept emerges—an SDR who earns higher compensation because they're managing and optimizing 5-10 AI agents rather than sending individual emails.
The Jobs That Will Transform: The $250K SDR and AI Management
While some roles disappear and others survive unchanged, the most interesting category involves roles that fundamentally transform. The job title persists, but the job description becomes unrecognizable.
The Emergence of the $250K AI-Managed SDR
In organizations that fully adopt AI-driven sales models, a new SDR archetype will emerge. This SDR:
Primary Responsibility: Manages 5-10 AI agents across different workflows
Technical Skills:
- Prompt engineering and agent configuration
- Data analysis and reporting
- A/B testing and statistical analysis
- CRM administration and data quality management
- Basic Python or workflow scripting
Strategic Skills:
- Sales process optimization
- Message and positioning development
- Training materials and knowledge base creation
- Agent performance diagnostics
- Cross-functional alignment
Compensation Justification: If a single person manages AI agents that generate 5-10 times the pipeline of a traditional SDR, the total value creation justifies higher compensation. A SDR managing AI agents that generate
Timeline: This transformation is already underway at leading organizations. By 2027-2028, this will be the baseline SDR expectation at tech-forward companies.
Account Executives Who Manage AI Deal Support
Account Executives face a different transformation. The best AEs will become specialists in:
1. Complex Deal Architecture: Understanding what an AI agent can and can't do in their deals, designing workflows where AI handles routine elements while humans focus on strategic negotiation.
2. AI Agent Supervision: Training, monitoring, and correcting AI agents that participate in deal processes. This requires understanding the agent's decision-making and adjusting accordingly.
3. Value Engineering: Working with AI-generated data to architect customer solutions, rather than just communicating pre-designed offerings.
4. Relationship Leverage: Using human relationship skills to convert AI-managed initial engagement into strategic partnerships.
AEs who resist this transformation—who want to do sales exactly as they did in 2023—will find themselves in the 40-50% of AE jobs that face displacement risk. AEs who embrace AI as a tool amplifying their capabilities will become more valuable, not less.
The Training Reality: 30 Days, Not 30 Minutes
A critical misconception haunts AI sales deployment: that standing up an AI sales system is quick and straightforward. The reality is messier and requires significant upfront investment.
The 50-60 Hour Training Requirement
Deploy an AI agent to replace your SDR team and within 30 days, you'll likely be frustrated if you haven't invested properly in training. The problem isn't the AI system—it's incomplete training.
Week 1: Data Foundation
- Compile 100-200 examples of your best historical email copy
- Extract customer research, company research, and personalization data
- Load historical conversation data so the AI understands your typical prospect interactions
- Document your qualification framework—what makes a "qualified" lead
- Time required: 12-15 hours
Week 2: Configuration and Iteration
- Set up the AI agent with your email copy as baseline templates
- Test initial message generation against different prospect profiles
- Compare AI-generated messages to your best historical messages
- Identify patterns in where the AI underperforms
- Correct specific failures and re-run tests
- Time required: 15-18 hours
Week 3: Refinement and Personalization
- Introduce more nuanced personalization (industry signals, recent news, competitive context)
- Set up A/B testing frameworks to compare message variants
- Train the agent on your follow-up cadence preferences
- Connect the agent to your CRM and data sources for real-time information
- Review outputs obsessively—every single message for this week
- Time required: 12-15 hours
Week 4: Live Testing and Adjustment
- Deploy the agent to a controlled segment (perhaps 5-10% of inbound leads)
- Monitor response rates, qualification accuracy, and prospect feedback
- Make final adjustments based on live data
- Prepare team training materials for operators
- Document edge cases and escalation procedures
- Time required: 12-15 hours
Total investment: 50-60 hours of skilled work
This is concentrated effort from someone who deeply understands your sales process, your best practices, and your customer landscape. If you delegate this training to someone unfamiliar with your sales execution, you'll get mediocre results and blame the AI system.
The Hidden Cost: Operational Friction
Beyond training time, implementing AI sales systems creates unexpected operational challenges:
CRM Integration Complexity: Your CRM probably has years of accumulated configuration quirks, custom fields, and workflows that don't cleanly integrate with AI systems. Budget additional hours for API work, field mapping, and data normalization.
Data Quality Issues: Most organizations discover that their "clean" CRM data is actually quite messy—duplicate records, incomplete fields, outdated information. AI agents exposed to bad data produce bad outputs. Expect 10-20 hours of data cleanup before going live.
Sales Process Documentation: You'll discover that your actual sales process differs from your documented process. Mapping this clearly so AI can execute it requires interviews with top performers and process documentation that may not exist.
Prospect Communication Resistance: Some prospects will object to AI engagement or respond negatively to initial contact from an AI agent. Developing protocols for handling these scenarios adds complexity.
The Real Timeline: Expect 60-90 days from decision to functional AI sales system, not the "30 minutes" of initial setup time.
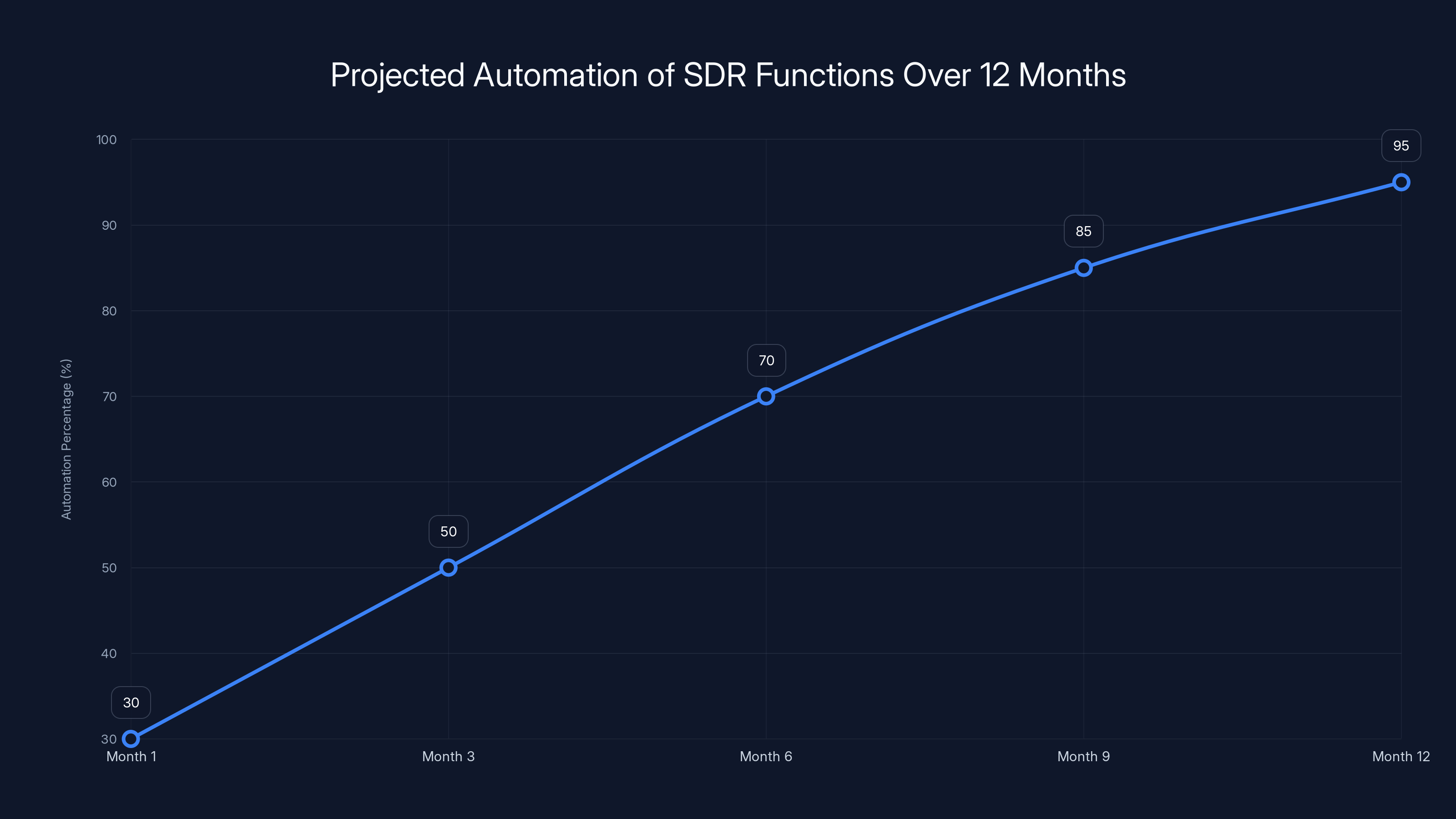
Within 12 months, AI is projected to automate 95% of SDR functions, primarily focusing on templated email tasks and lead qualification. Estimated data based on current trends.
The Chief AI Officer: Why You Need a Dedicated Role
Organizations that successfully deploy AI sales systems universally report the same finding: dedicated oversight of AI operations isn't optional. The most successful implementations include someone fulfilling a "Chief AI Officer" function—not necessarily full-time initially, but with dedicated focus and specific qualifications.
Required Characteristics
1. Quantitative Mindset: This person must be genuinely comfortable with data, metrics, and statistical analysis. They need to spend hours analyzing agent performance, identifying patterns in where AI succeeds and fails, and making data-driven adjustments.
2. Obsessive Attention to Detail: AI systems compound mistakes. If an agent has a subtle messaging problem, it compounds across thousands of outreach attempts. The Chief AI Officer catches these before they become expensive mistakes.
3. Comfort with Ambiguity: AI behavior isn't perfectly predictable. The Chief AI Officer must be comfortable with iteration, experimentation, and learning from failures rather than needing crystal-clear process documentation.
4. Cross-Functional Communication: This person translates between technical AI teams (who build the systems) and business teams (who use them). They need fluency in both domains.
5. Genuine Interest in AI: This isn't a role for someone who "has to do AI as part of their job." The Chief AI Officer must be intrinsically interested in how AI systems work, why they fail, and how to improve them.
Why This Role Exists
Without dedicated oversight, AI systems drift. The agent's performance gradually degrades because the data it's working with becomes stale. Messaging that resonated in January doesn't resonate in March. New competitor messaging renders existing AI templates outdated. Prospect preferences shift seasonally.
The Chief AI Officer catches these drift patterns through systematic monitoring and orchestrates corrections. This prevents the "AI system we trained and deployed is now underperforming" scenario that derails many implementations.
Time Commitment Reality
Initially, this role might be 50-100% of someone's time (maybe a sales leader taking on expanded responsibilities). As the system matures and automation increases, it might drop to 20-30% of one person's time. But it never becomes zero—systems require ongoing monitoring and management.

What Actually Works: The Playbooks That Evolved from 2019
A crucial distinction separates what's changing from what's not: go-to-market fundamentals haven't changed. What changed are execution playbooks.
Enduring Principles
These GTM principles proved durable through multiple technology cycles:
1. Understanding Your Customer: The more specifically you understand your ideal customer profile—their challenges, decision process, and key stakeholders—the better your sales execution. This principle held true with manual sales, with sales automation platforms, and with AI systems.
2. Value-Based Positioning: Leads respond to messaging about their problems and outcomes, not about features. This psychological principle doesn't change because the messenger is AI rather than human.
3. Process Consistency: Having a defined sales process—discovery, qualification, demonstration, negotiation, close—that everyone follows improves predictability. This applies equally whether humans or AI agents execute the process.
4. Measurement and Optimization: The best sales organizations measure what's working and continuously optimize. This is actually easier with AI because the volume of data is larger and the measurement is more precise.
5. Clear Decision Rights: Knowing who makes which decision at each stage reduces friction. This applies equally to AI and human sales processes.
What Became Obsolete
Conversely, several tactics that dominated 2019-era GTM playbooks are becoming obsolete:
Email Cadence as a Competitive Advantage: In 2019, the companies with the most aggressive email cadences (sometimes 8-10 touches over 30 days) outperformed competitors with lighter touch. This advantage evaporated when AI systems can manage aggressive cadences without team fatigue or quality degradation. The competitive advantage shifted from "can our team send more emails" to "how effective is each email."
Sales Heroics and Personal Relationships at Scale: In earlier eras, star salespeople who built deep relationships with individual prospects were crucial competitive advantages. AI systems don't have personal relationships, but they also don't have personalities—they follow consistent, optimized processes. This levels the playing field against sales teams built on hero salespeople.
Long Sales Cycles as Inevitable: Many organizations accepted 6-12 month sales cycles as inherent to their market. AI engagement starting earlier and happening 24/7 can compress sales cycles by 20-40% simply through velocity improvement.
Sales Intuition Over Data: In 2019, "gut feel" about deals still influenced decision-making. Modern systems are quantitative and data-driven. Organizations that embrace this thrive; those that resist underperform.
Implementation Strategy: The Proven Path
Organizations that successfully implement AI sales systems follow a distinct implementation sequence rather than attempting big-bang replacement of their entire sales function.
Phase 1: Start With Support (Weeks 1-8)
Most companies can't provide 24/7 customer support at scale, but AI can. This is the lowest-risk, highest-impact entry point for AI system implementation.
Why Support First:
- Support interactions follow defined processes and FAQs that structure well for AI
- Failures in support have lower cost than failures in sales—a slow response in support is disappointing; an incorrect sales statement loses deals
- Support teams typically welcome automation to handle volume they can't manage
- Success in support builds internal confidence in AI systems
- Customer sentiment about AI support is typically positive—they appreciate 24/7 availability
Implementation Details:
- Start with FAQ automation and simple routing
- Expand to complex troubleshooting queries
- Measure first-contact resolution rate (target: 70-80% improvement)
- Gather customer feedback on AI helpfulness
Typical Metrics: Organizations implementing AI support typically see first-contact resolution improve by 40-60%, average resolution time decrease by 30-50%, and support cost-per-ticket decline by 25-35%.
Phase 2: Inbound Lead Qualification (Weeks 8-16)
Once support systems are running smoothly, deploy AI to inbound lead qualification.
Implementation Details:
- Use historical inbound leads to train your qualification model
- Start with lead routing (which leads go to which sales rep)
- Expand to qualification (which leads are ready for sales engagement)
- Measure accuracy against your historical qualification standards
Key Success Factor: Make sure your historical qualification decisions are actually good. If your SDRs have been doing suboptimal qualification, the AI will learn suboptimal patterns. Review 20-30 of your best-qualified leads and 20-30 of your worst to establish clear decision criteria.
Phase 3: Outbound Initial Engagement (Weeks 16-24)
Once inbound systems are working, deploy outbound AI to initial prospect engagement.
Implementation Details:
- Use your best historical outbound email copy as templates
- Start with a pilot segment (10-20% of your regular outbound volume)
- Measure response rates, scheduling rates, and sales quality against your SDR baseline
- Expand gradually as metrics prove comparable or superior
Typical Progression:
- Week 1-2: Pilot shows 15-20% improvement in response rates due to AI's ability to optimize message timing and personalization
- Week 3-4: Accuracy concerns emerge—the AI is over-promising or misrepresenting capabilities
- Week 5-6: After corrections, response rates stabilize at 20-30% improvement
- Week 7-8: Expansion to 100% of outbound volume
Phase 4: Sales Process Integration (Weeks 24-36)
Final phase involves weaving AI into the complete sales process.
Implementation Details:
- AI manages initial qualification, scheduling, and information gathering
- AI prepares pre-call briefs for account executives
- AI handles post-call follow-up and next-step scheduling
- Humans focus on discovery conversation and negotiation
Expected Outcome: AEs spend 40-50% less time on administrative sales work and 40-50% more time on strategic conversation.
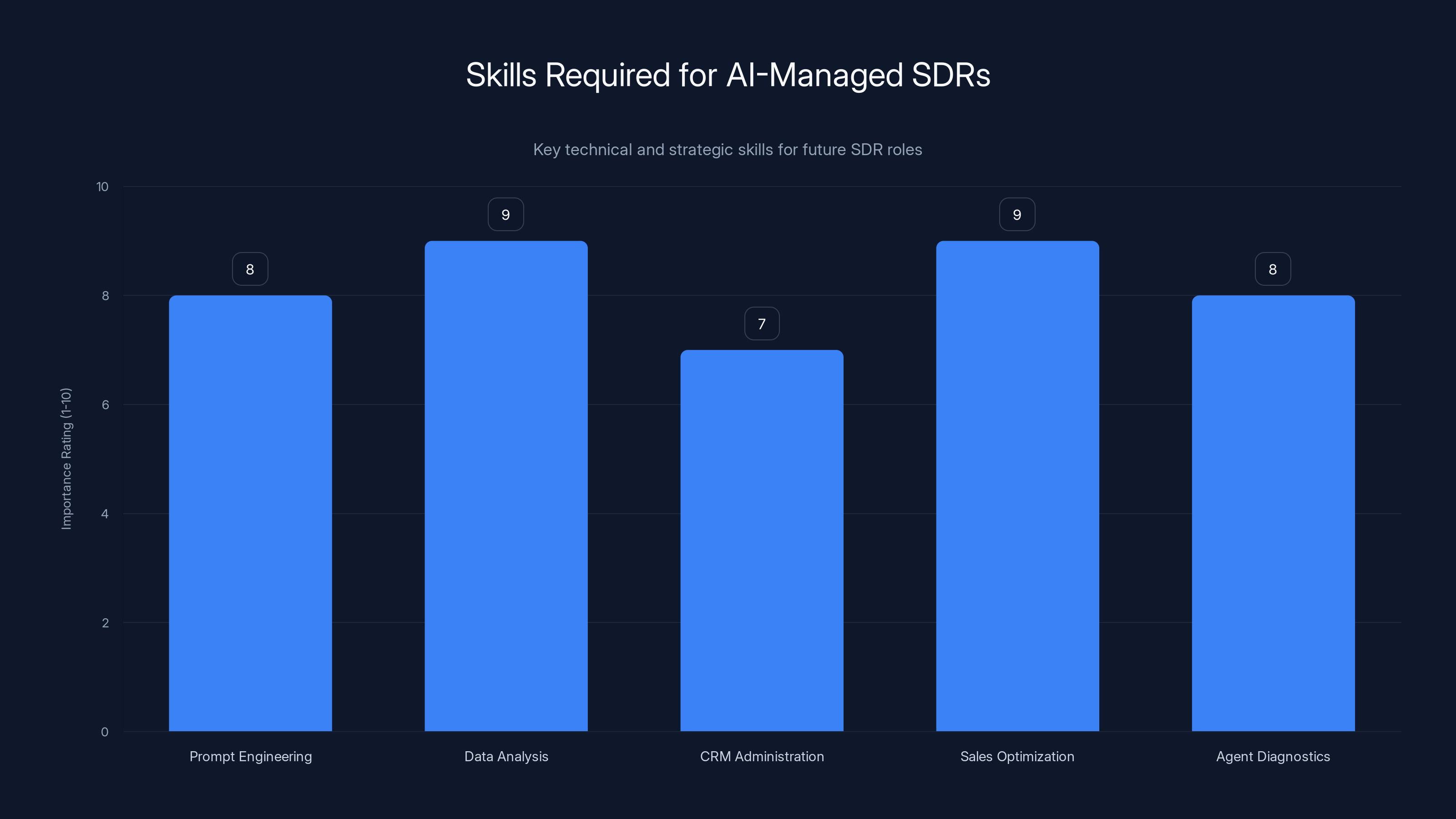
Future SDR roles will require a blend of technical and strategic skills, with data analysis and sales optimization being highly important. Estimated data based on role transformation.
The Uncomfortable Truth: AI Is Displacing Mediocre Sales Talent
Media narratives about technology and job displacement often exaggerate or minimize impact. The truth about AI and sales talent is more nuanced but also more harsh.
The Three Tiers of Sales Impact
Tier 1: Top Sales Talent (Top 10-15%)
- Impact: Minimal displacement risk
- Reason: Top performers combine skills that AI doesn't replicate—strategic thinking, executive presence, relationship building, complex problem-solving
- Opportunity: These professionals become more valuable by leveraging AI to amplify their impact
- Typical trajectory: Earn higher compensation for managing AI-augmented teams or focus on strategic relationship roles
Tier 2: Solid Professional Sales Talent (Middle 60-75%)
- Impact: Significant pressure but not displacement
- Reason: This cohort can execute well-defined processes but lacks the strategic differentiation of top performers. AI can execute their playbook as well as they can.
- Requirement for Survival: Transition to AI management, process optimization, or relationship focus
- Typical trajectory: Those who adapt move to managing AI agents; those who resist face stagnant compensation and limited advancement
Tier 3: Below-Average Sales Talent (Bottom 10-25%)
- Impact: High displacement risk
- Reason: Below-average performers are, by definition, worse at executing defined sales processes than both their peers and AI systems optimized for those processes
- Adaptation: Difficult—job displacement or significant retraining required
- Typical trajectory: Displaced or moved to non-sales roles
The Headcount Reality vs. The Narrative
Media coverage often emphasizes "AI will eliminate millions of sales jobs." This framing isn't wrong but is incomplete. The actual mechanism is more subtle:
What's Not Happening: Companies aren't mass-laying off their existing sales teams and replacing them with AI. Sales is often the most visible P&L metric, and boards aren't comfortable with dramatic headcount cuts in that function.
What's Actually Happening: Companies are backfilling open sales roles with AI instead of hiring humans. When an SDR quits, you don't necessarily replace them with a new hire; you invest in AI agents instead. The headcount never gets added, but the disruption is invisible to media coverage that only notices actual layoffs.
The Cascading Effect: Over a 3-5 year period, this differential hiring approach produces the same outcome as layoffs—dramatically fewer humans in sales roles—but through attrition rather than reduction.
Timeline: By 2028-2030, sales teams at forward-thinking companies will be 40-60% smaller than 2024 equivalents while maintaining or exceeding revenue, but this will have happened incrementally rather than through dramatic restructuring.
For Sales Professionals: The Timing Question
For individual salespeople, the key question is timing: Do I adapt now or wait until I'm forced to?
The Case for Adaptation Now:
- First movers who become expert at AI-augmented sales have years of experience by the time this becomes standard
- The knowledge and skill of managing AI agents will become valuable and differentiated
- Learning happens faster when not under pressure of job replacement
- Companies value salespeople who can bridge AI systems and human judgment
The Case for Waiting:
- AI capabilities might hit plateaus; current trends aren't guaranteed to continue indefinitely
- The best learning happens when tools are mature, not during the chaos of rapid change
- Your existing sales skills remain valuable and probably will for 3-5+ years
Most experts believe the risk of waiting exceeds the risk of adapting early, particularly for professionals in roles that seem most vulnerable to AI replacement.
The Vendor Selection Complexity: Build vs. Buy
Founding teams often face the "build vs. buy" decision: should we develop custom AI sales tools or purchase existing platforms?
When to Build
Building custom AI sales systems makes sense when:
1. You Have Specialized Technical Talent: Someone on your team is genuinely skilled at AI development and genuinely wants to build this. Not "can probably do it" or "has engineering on staff." Someone who's excited about this problem.
2. Your Sales Process is Genuinely Unique: Most sales processes are actually quite standard. If yours is truly different—unusual workflow, specialized vocabulary, unique decision process—custom tooling might be justified.
3. You Have the Time Horizon: Building takes 6-12 months minimum before you have something production-ready. If you need AI sales systems in 8 weeks, building isn't realistic.
4. You Understand the Maintenance Burden: Custom systems require ongoing maintenance, updates, and optimization. You're committing to this indefinitely, not just one-time development.
Realistic Assessment: Fewer than 10% of companies actually meet these criteria. Most overestimate their need for customization and underestimate the maintenance burden.
Why Buying Usually Wins
Existing AI sales platforms are evolving faster than any custom development team can keep pace.
January 2025 Capabilities: Your vendor updates their platform with new AI models, improved personalization algorithms, better integration options.
March 2025 Capabilities: You implement new features that took your vendor's team 10 engineers three months to build.
May 2025 Capabilities: The vendor releases major architectural improvements based on learning from thousands of implementations.
If you built custom, you're now months behind, and dedicating engineering resources to catch up is expensive and inefficient.
Vendor Selection Criteria
When evaluating AI sales platform vendors, look for:
1. Implementation Support: Vendors who help you train your AI agents, not just give you access to the platform. Implementation is where success is won or lost.
2. Transparent ROI Metrics: Reputable vendors help you measure specific, quantifiable outcomes. Be suspicious of vendors who can't articulate what success looks like.
3. Flexibility Without Chaos: You need ability to customize behavior for your specific sales process, but you also need baseline structure so you're not starting from zero.
4. Honest About Limitations: Any vendor claiming their system works perfectly in all scenarios is overselling. Reputable vendors acknowledge limitations and describe failure modes.
5. Active Development: Check their product roadmap. Are they actively improving capabilities? Or has development stalled?
The Separating Factor: Implementation support is often the difference between success and failure. The best platform in the world fails if you don't know how to train it. The middle-tier platform succeeds if the vendor helps you train it properly.

The Easy Starting Point: AI in Customer Support
While sales implementation is complex, customer support is remarkably receptive to AI automation.
Why Support Is Lower Risk
1. Defined Scope: Support interactions typically follow established protocols and FAQs. Structure makes AI work better.
2. Objective Success Metrics: You can measure first-contact resolution, resolution time, customer satisfaction—all with clear numerical targets.
3. Asymmetric Upside: Success means faster resolution and happier customers. Failure means slower resolution—inconvenient but not relationship-destroying.
4. 24/7 Coverage: Your support team probably has coverage gaps. AI can provide continuous availability.
5. Easy Expansion: Start with FAQ automation, expand to complex troubleshooting, eventually reach 50-80% automation.
Implementation Path
Week 1-2: Deploy AI to FAQ-type questions ("How do I reset my password?", "What's your refund policy?")
Week 3-4: Expand to multi-step troubleshooting workflows
Week 5-8: Introduce escalation paths for questions the AI isn't confident answering
Outcome: Most leading companies report 50-80% of support volume is now handled entirely by AI, with humans focused on complex, escalated, or relationship-critical interactions.
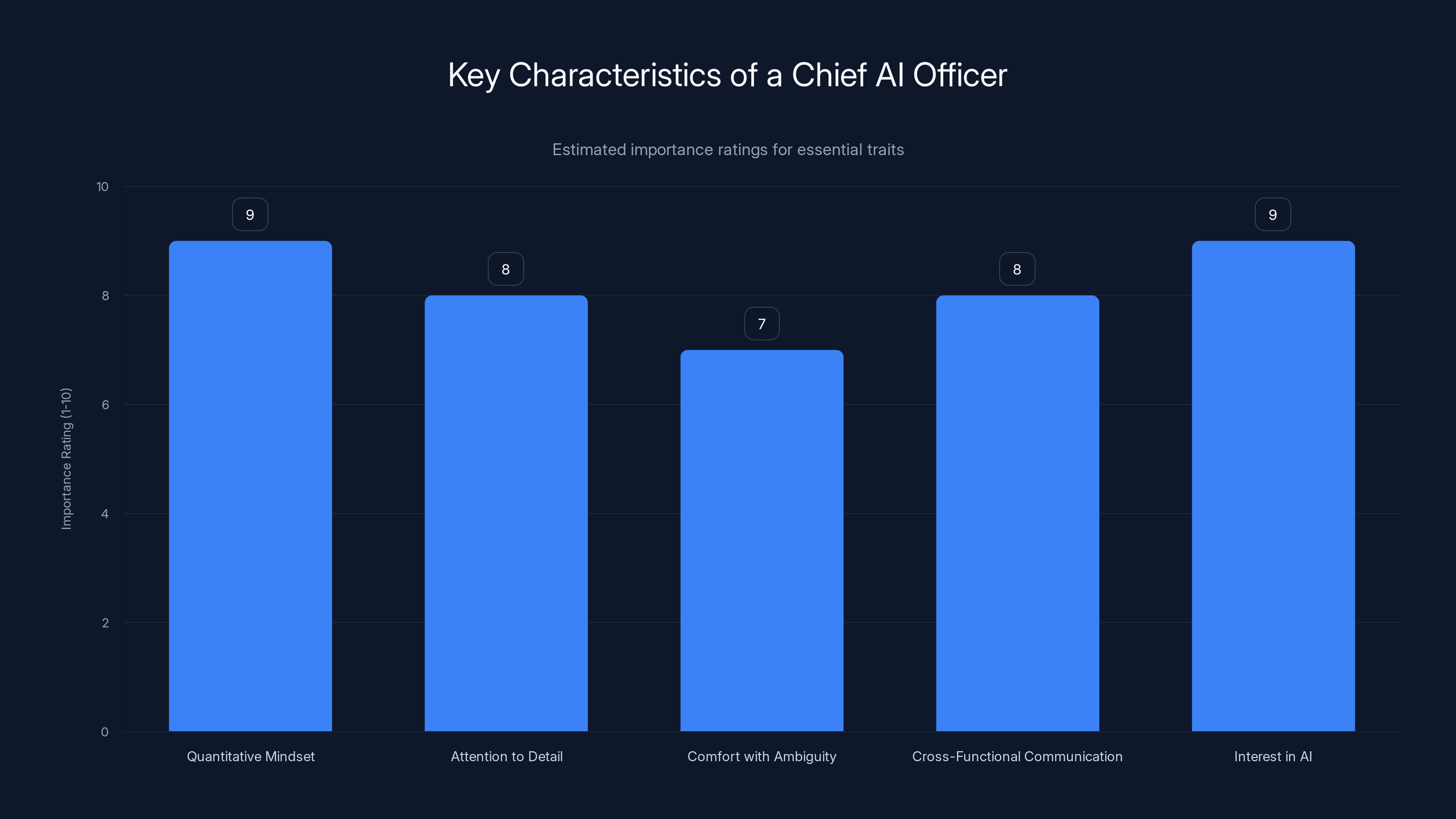
The Chief AI Officer role requires a strong quantitative mindset and genuine interest in AI, rated highest in importance. Estimated data.
Safe Predictions and Genuine Uncertainty
Predicting technology impact is inherently risky, but some predictions are more grounded than others.
Safe Prediction: 70% of AE Jobs Are Safe for Now
Account Executives handling complex deals, relationship building, and strategic negotiation aren't going to be replaced by AI in the 2-3 year window. The probability this is wrong is low.
But note the qualifier: "For now" and the time horizon matter. This prediction covers 2026-2028. After that, if AI capabilities advance as aggressively as the 2024-2026 trajectory suggests, the 70% figure drops to 50-60% by 2028-2030 and possibly lower by the 2030s.
Real Uncertainty: Will AI Plateau or Accelerate?
The biggest unknown is whether AI capability growth will continue at the accelerating rate of 2024-2026, plateau at a high level of capability, or face unexpected barriers.
Scenario A (Acceleration): AI capabilities double every 18 months for the next 5 years. Under this scenario, roles that seem safe today become vulnerable in 3-4 years.
Scenario B (Plateau): AI capabilities reach a plateau by 2027-2028 where further improvements are incremental rather than transformational. Under this scenario, job displacement levels off at 30-40% rather than accelerating to 50%+.
Scenario C (Breakthrough): AI develops genuine reasoning, intuition, and understanding capabilities—not just pattern matching on data. This would accelerate displacement across nearly all sales roles.
Honest assessment: We don't know which scenario will occur. Betting your career on any single scenario is risky.

Alternative Platforms and Tools: Beyond the Obvious Choices
When organizations decide to implement AI-driven sales systems, they face numerous platform options beyond the obvious enterprise providers.
The Platform Spectrum
Enterprise AI Sales Platforms (
Mid-Market Solutions (
Developer-Friendly Automation Platforms (
Emerging Category: Custom Integration Layers
A growing number of organizations use general-purpose AI development platforms (like OpenAI, Anthropic, or open-source models) combined with custom wrapper layers to build sales AI systems. This approach offers maximum flexibility but requires significant technical investment.
Selection Matrix: How to Choose
For Enterprise (500+ employees): Enterprise platforms make sense. The integration complexity and customization needs typically justify the cost.
For Mid-Market (50-500 employees): Mid-market solutions often deliver the best value-to-functionality ratio. Strong out-of-the-box templates accelerate time to value.
For Early-Stage/Technical Teams (under 50 employees with engineering): Developer-friendly automation platforms or custom layers make sense if you have engineering resources. The control and cost efficiency often outweigh the implementation complexity.
For Early-Stage/Non-Technical Teams: Mid-market solutions with strong implementation support are the safest bet.
The Future of Sales Leadership: New Skills Required
Sales leaders managing AI-augmented teams need fundamentally different capabilities than pre-AI sales leaders.
Technical Literacy (Non-Negotiable)
Sales leaders in 2026+ need baseline understanding of:
1. How AI Systems Make Decisions: What data do they use? What biases might be embedded? When might they fail?
2. Data Quality Requirements: Most AI failures trace back to bad data. Leaders need to understand data requirements and quality implications.
3. Integration Complexity: How does the AI system connect to your CRM, email, prospecting tools, and pipeline reporting? What breaks when systems don't integrate cleanly?
4. Measurement Frameworks: What metrics matter? How do you know if your AI system is working? How do you distinguish AI-driven improvements from other factors?
This doesn't mean sales leaders need to be data scientists or engineers. But they need enough fluency to have meaningful conversations about capabilities and limitations.
Process Thinking
Leaders who succeeded through force of personality or sales heroics may struggle. Successful AI-augmented sales teams require:
1. Documented Processes: "The way we do things here" needs to be explicit and documented. Undocumented intuition doesn't translate into AI training.
2. Continuous Optimization: AI systems reveal where your process works and where it doesn't through performance data. Leaders need comfort with constant iteration.
3. A/B Testing Mindset: Is message A or message B more effective? Should we schedule follow-ups at 9 AM or 2 PM? These questions require experimentation, not intuition.
4. Scaling Thinking: If one AI agent can do the work of 5 human SDRs, how do you scale management? You can't use the same 1:5 manager-to-employee ratios. You need leverage.
Talent Management Evolution
Managing AI-augmented teams requires different talent strategies:
Retention: Your best sales talent is now your most vulnerable—they're likely to be recruited for AI management roles by other companies. Retention becomes mission-critical.
Development: Training shifted from "here's the new sales technique" to "here's how to work alongside AI systems and manage AI agents."
Hiring: When recruiting salespeople, you're increasingly looking for people who can optimize AI systems, not just execute sales conversations.

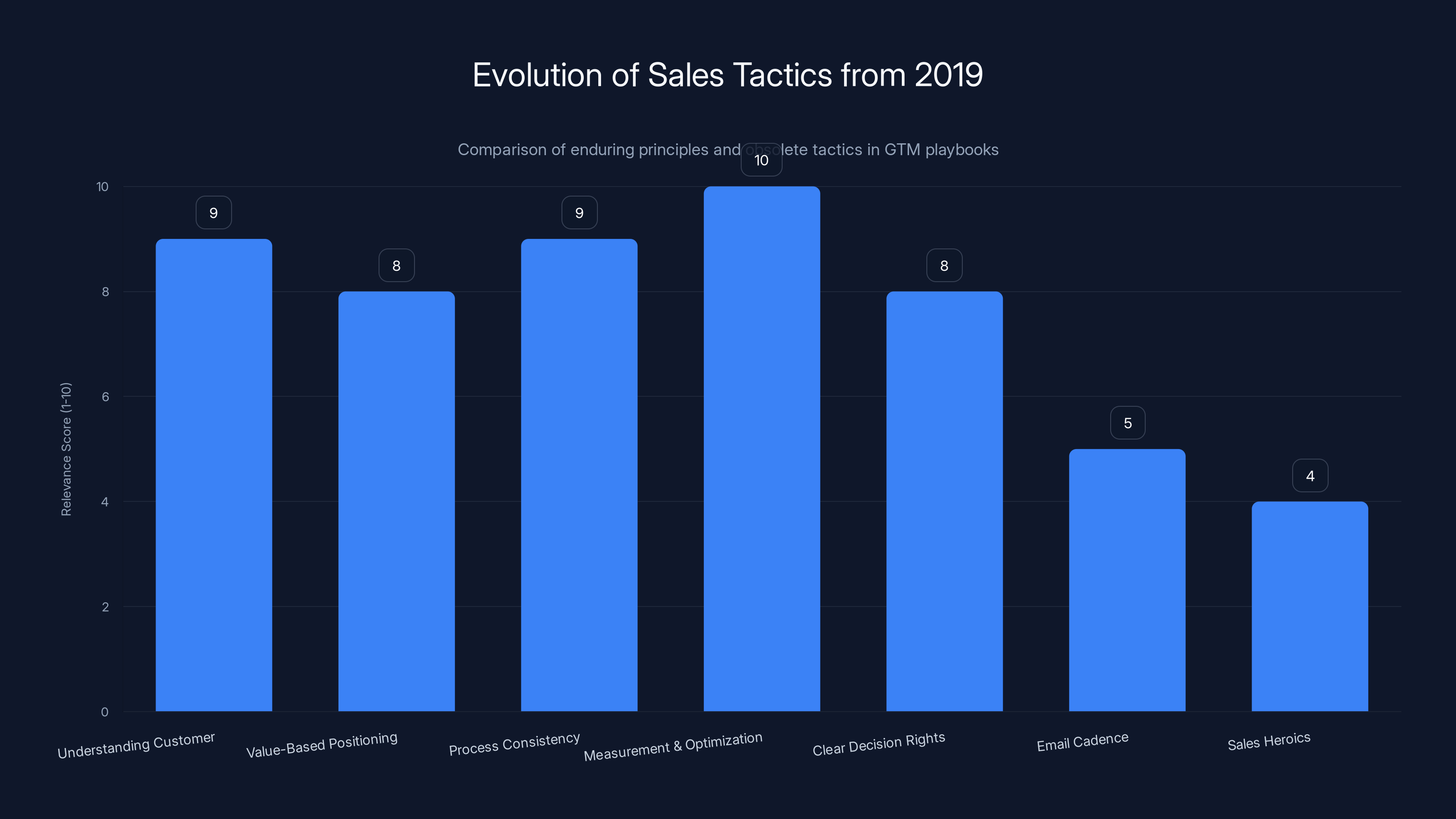
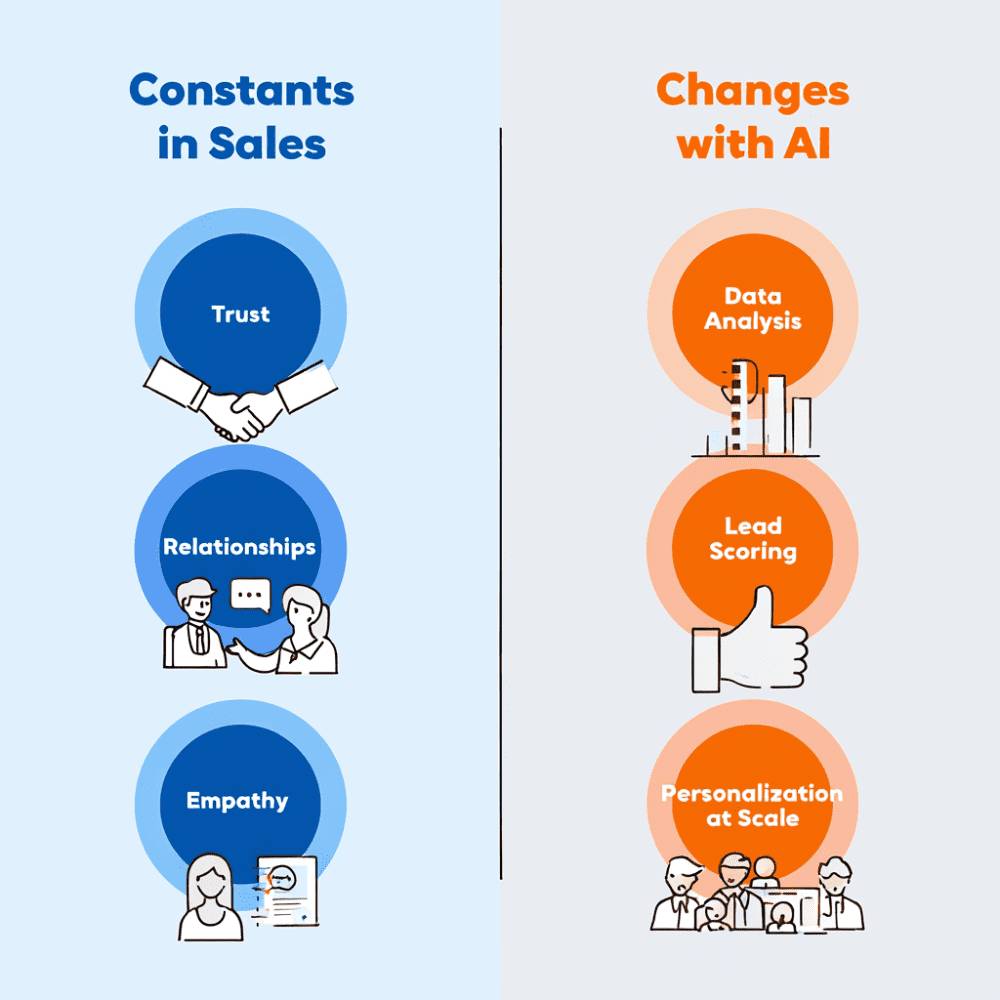
The chart highlights that while core principles like understanding customers and process consistency remain highly relevant, tactics such as aggressive email cadences and sales heroics have become less effective due to advancements in AI. Estimated data.
Measuring Success: The Metrics That Matter
Organizations often measure AI sales system success through the wrong metrics, leading to incorrect conclusions about whether implementation is working.
Vanity Metrics vs. Real Metrics
Vanity Metrics (Misleading):
- Number of AI agents deployed
- Percentage of outreach handled by AI
- Reduction in sales team headcount
These metrics can look good while hiding poor business outcomes.
Real Metrics (Informative):
- Cost per qualified lead (pre-AI vs. post-AI)
- Cost per sales-accepted opportunity
- Sales cycle length
- Win rate and average deal size
- Revenue per sales employee
- Customer acquisition cost by channel
The question isn't "Are we using AI?" but "Is using AI making our business metrics better?"
The Baseline Measurement Problem
Most companies can't properly measure AI impact because they lack clean pre-AI baselines.
Best Practice: Before implementing AI, run a clean measurement period (30-60 days) of your current state metrics. Establish precise baselines across:
- Lead volume by source
- Lead quality and qualification accuracy
- Time to response for inbound inquiries
- Sales cycle length
- Deal velocity by sales stage
- Win/loss rates
- Revenue generated per team member
After 90-180 days of AI implementation, remeasure against the same metrics. The difference is your AI impact.
The Confounding Variables Problem
Sales performance depends on dozens of variables: market conditions, product changes, team composition, compensation changes, process changes. AI is just one variable.
Rigorous Approach: Use A/B test design. Run AI agents against a control group of traditional sales processes for a period. Measure both groups against the same metrics. The difference between groups is AI impact.
The Timeline Acceleration Insight
One of the most important insights from tracking AI's evolution is how compressed the timeline has become.
The 6-Month Rule
Capabilities that seemed science fiction 6 months ago are becoming standard today. This acceleration affects predictions:
January 2024: AI sales agents could qualify some inbound leads July 2024: AI agents closing $50K+ deals autonomously January 2025: AI agents managing complex multi-touch outbound campaigns July 2025: AI agents handling procurement negotiations
Each 6-month cycle sees capabilities expand 40-60% beyond the previous cycle. If this trend continues:
By July 2026: AI agents might handle complex sales conversations humans currently consider non-delegable By January 2027: AI agents might manage account relationships and strategic customer communication
This acceleration is why the "70% of AE jobs are safe" prediction includes the qualifier "for now." In 36 months, the assessment might be very different.

The Biggest Mistake: Premature Scaling
Organizations implementing AI sales systems universally report the same mistake: attempting to automate too much too quickly.
The Failure Pattern
Month 1: Excitement about AI leads to ambitious goals. "Let's have AI handle 80% of our sales process."
Month 2: Deploy AI broadly without proper training or oversight. Results are mediocre because the AI isn't properly calibrated to your specific sales context.
Month 3: Team frustration with poor AI outputs. Sales team reverts to handling things themselves. Perception: "AI doesn't work for our business."
Month 4: Conclusion: AI is overhyped; we're sticking with human salespeople. Vendor contract is canceled.
The Correct Pattern
Phase 1 (Weeks 1-4): Pick one narrow workflow. Train the AI properly. Measure success.
Phase 2 (Weeks 5-12): Expand slightly to a second workflow only after phase 1 is stable and delivering results.
Phase 3 (Weeks 13+): Gradual scaling, each time ensuring proper training and oversight.
Timeline: 18-24 months to reach the state of 20 AI agents working effectively. Not 6 months, not 12 months. 18-24 months of careful, methodical implementation.
Organizations that accept this timeline typically succeed. Organizations seeking quick wins typically fail.
The Competitive Advantage Window
There's a finite window where implementing AI sales systems is a competitive advantage rather than table stakes.
Current Status (2026): Competitive Advantage
Organizations that have effectively implemented AI-driven sales processes currently have measurable advantages over competitors:
- 20-40% improvement in sales team productivity
- 30-50% reduction in sales cycle length
- 40-60% improvement in lead quality detection
- 25-35% reduction in customer acquisition cost
- Ability to operate 24/7 vs. business hours
These advantages compound—better lead quality leads to higher close rates, which improves unit economics, which allows increased marketing investment, which compounds the advantage.
Medium Term (2027-2028): Table Stakes
Within 18-24 months, AI sales capabilities will be table stakes in most industries. The companies that don't have AI-augmented sales will find themselves outcompeted by those that do.
The Implication
If your organization hasn't started seriously experimenting with AI sales systems, you're now behind the curve. Not catastrophically behind—there's still time to catch up—but behind.
The companies making decisions now to invest in AI sales system implementation will be years ahead of companies that make the same decision in 2028-2029.

Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Compilation of the most common errors organizations make when implementing AI sales systems:
Mistake 1: Insufficient Training Data
Providing limited training examples to your AI agent. "We'll just upload 20 emails and see what happens."
Why This Fails: AI learns patterns from large datasets. With only 20 examples, the AI lacks sufficient context and generates inconsistent outputs.
Correct Approach: Compile 100-200 of your best historical examples across different prospect types, industries, and deal stages. Feed all of this into the training.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Human Oversight
Deploying AI agents to production and checking back in after 30 days.
Why This Fails: AI systems produce bad outputs when they lack proper supervision. Early detection and correction is critical.
Correct Approach: Obsessive review of AI outputs for the first 30-60 days. Every message, every decision, every qualification should be reviewed and corrected if needed. This front-loads the training burden and prevents compounding errors.
Mistake 3: Misaligned Success Metrics
Measuring success by "percentage of leads handled by AI" instead of "revenue generated" or "cost per opportunity."
Why This Fails: An AI system could handle 100% of leads but generate poor quality, hurting overall results. You're optimizing for the wrong metric.
Correct Approach: Measure business outcomes, not AI usage. Does AI increase revenue per sales employee? Does it reduce cost per customer? Does it improve win rates? These are the metrics that matter.
Mistake 4: Insufficient Change Management
Deploying AI to a sales team that hasn't been prepared for how their job will change.
Why This Fails: Salespeople feel threatened by automation. Without clear communication about how AI changes their role (likely for the better), they sabotage implementation.
Correct Approach: Transparent communication from leadership about why AI is being implemented, how it changes roles, how compensation might change, and how salespeople can benefit from AI. Salespeople who understand they're becoming AI managers, not being replaced, are more cooperative.
Mistake 5: Over-Customization Without Standardization
Letting each salesperson customize their AI agent differently, leading to chaos and inability to manage systematically.
Why This Fails: You end up with 10 different AI systems with different behaviors, each with different training, each requiring different oversight. Management becomes impossible.
Correct Approach: Establish a standard framework all agents follow, with limited customization for specific use cases. This keeps complexity manageable.
The Return on Investment Calculation
How do you calculate actual ROI from AI sales implementation? Real formula for real organizations:
The Basic Formula
Cost of AI Implementation:
- Platform cost: 5,000/month depending on vendor and usage
- Training cost: 50-60 hours at 10,000-$12,000 (one-time)
- Annual operational cost: 60,000
- Ongoing training and optimization: 10-20 hours/month = 4,000/month
- Total Year 1 Cost: 100,000 depending on scale
Benefit of AI Implementation:
- Sales team productivity increase: 30-50%
- Sales cycle compression: 20-40% shorter
- Cost per acquisition improvement: 25-40% reduction
- Revenue increase per salesperson: 200,000 depending on baseline
If your sales team generates $10M annually:
- Current sales team: 10 people at $1M per person
- With 40% productivity improvement: Same revenue with 6 people
- Or: $14M revenue with same 10 people
ROI Calculation for 40% productivity improvement scenario:
- Year 1 Cost: $50,000 (average)
- Year 1 Benefit: 2M freed-up capacity)
- Year 1 Net: $50,000 positive
- Payoff period: ~3 months
For most organizations, AI sales implementation pays for itself in 3-6 months through efficiency gains, with the remainder of the year driving profit improvement.

Conclusion: The Time for Decision Is Now
The transformation of sales through AI isn't a future scenario—it's happening today. Organizations are not speculating about whether AI will change sales; they're actively implementing systems that are already changing sales, with measurable business results proving the impact.
The critical business question for founders and sales leaders isn't "Should we implement AI in sales?" That's already answered by the competitive dynamics. Companies that implement AI will have sustainable advantages over companies that don't. The question is "When will we implement AI in sales?" And more specifically: "Will we be ahead of or behind the curve when we do?"
The evidence is compelling:
-
Real Results: Organizations have replaced entire sales teams with AI agents while maintaining equivalent revenue with dramatically fewer humans. These aren't aspirational case studies; they're happening with quantifiable metrics.
-
Timeline Acceleration: The capabilities available today are 6-12 months ahead of capabilities from 6-12 months ago. This acceleration suggests that capabilities from 12-18 months ago will be baseline by late 2026.
-
Job Displacement Asymmetry: The impact on midpack and below-average salespeople will be severe. Top performers will remain valuable, but the median salesperson faces real career pressure.
-
Competitive Consolidation: Early implementers will have compounding advantages that become harder for late entrants to overcome. The 2026-2027 period is likely to be the window where implementation differences create lasting competitive gaps.
-
Skill Translation: The future of sales careers isn't "no jobs"—it's different jobs requiring different skills. Salespeople who proactively learn to work alongside AI systems will be more valuable, not less.
For sales leaders, the calculus is straightforward: investing 50-60 hours in training and 3-6 months of implementation work to transform your sales operation, improving productivity by 30-50% and reducing customer acquisition cost by 25-40%, is a high-ROI decision with measurable payoff within 90 days.
For salespeople, the career decision is similarly clear: beginning to learn how to work alongside AI systems now, when learning isn't under pressure of job replacement, is better than waiting until competency is forced.
For founders and investors, the strategic implication is that sales efficiency—currently one of the largest expense categories for SaaS companies—is about to undergo a structural shift. Companies that leverage this shift will have materially better unit economics than those that don't.
The real future of AI in sales isn't speculative. It's unfolding today. The companies deciding right now to invest in this transformation will be the winners in the next 5-year competitive cycle. Those waiting for more certainty, or for AI capabilities to mature further, will find themselves struggling to catch up after other players have already scaled their AI operations.
The time for decision isn't 2027 or 2028. It's now.
FAQ
What is AI in Sales?
AI in sales refers to using artificial intelligence systems—typically large language models, machine learning algorithms, and autonomous agents—to automate parts of the sales process. This includes lead qualification, initial prospect outreach, follow-up cadences, information gathering, and even negotiation support. Rather than replacing salespeople entirely, AI systems typically augment human sales effort by handling repetitive tasks, analyzing data faster than humans could manually, and improving decision-making through data-driven insights. Modern AI sales systems can operate 24/7, process hundreds of conversations simultaneously, and learn from outcomes to continuously improve performance.
How does AI transform sales team structure?
Traditional sales teams with multiple SDRs, BDRs, and AEs are shifting to fewer humans managing multiple AI agents. For example, instead of 10 SDRs sending email cadences, organizations might employ 1 full-time AE and 20 AI agents handling different workflows, with a dedicated "Chief AI Officer" (sometimes part-time) overseeing optimization. This fundamentally changes the work—from "I send emails to prospects" to "I train and optimize the AI agents that engage prospects." The best salespeople transition to managing these AI systems rather than being replaced by them, effectively becoming more productive and earning higher compensation. This structure typically requires 50-60 hours of upfront training to properly configure AI agents for your specific sales process and customer base.
What are the benefits of AI in sales?
The quantifiable benefits include improved lead response times (from hours to seconds), eliminated SDR fatigue (AI agents work 24/7), improved qualification consistency (AI follows defined rules rather than showing human biases), faster sales cycles (typically 20-40% compression), and dramatically improved cost per customer acquisition (typically 25-40% reduction). Organizations have documented productivity improvements of 30-50% while maintaining equivalent revenue with significantly fewer salespeople. As stated in practical implementations, cost per opportunity and cost per qualified lead both improve substantially when AI agents handle initial engagement. Beyond metrics, AI enables support for multiple time zones and markets simultaneously, something humanly impossible to scale. Teams also report that salespeople appreciate AI handling administrative tasks, allowing humans to focus on higher-value negotiation and relationship work where human judgment adds clear value.
Which sales roles will be displaced by AI first?
SDRs sending templated email cadences and qualifying inbound leads face the highest risk of displacement in the 12-month window. These roles involve executing standardized processes with objective qualification criteria, which translate cleanly to AI automation. BDRs running classic cadence-based outbound campaigns face similar pressure. Sales operations and administrative roles focused on information routing are also vulnerable. However, Account Executives handling complex negotiations, Enterprise account managers building relationships, and sales leaders who adapt to managing AI agents typically remain safe (at least in the 2-3 year timeframe). The common pattern: roles that execute well-defined processes consistently are most vulnerable; roles that require strategic judgment, relationship building, and complex problem-solving are more durable. For professional development, focus on building skills that AI can't replicate—strategic thinking, executive presence, complex negotiation, and AI system optimization.
How long does it take to implement AI sales systems?
The implementation timeline is typically 18-24 months for full maturity, not the 30 minutes of initial setup. Initial setup takes 50-60 hours of concentrated work to properly train your AI agents with historical email examples, customer data, qualification criteria, and your specific sales terminology. Weeks 1-4 focus on data foundation and configuration. Weeks 5-8 involve testing and iteration. By week 8-12, you have a functional system but still requiring obsessive human review. Expect 30-90 days before the AI system reaches productivity parity with human salespeople doing the same work. Organizations that attempt faster timelines (90 days to full deployment) typically fail because insufficient training leads to poor AI outputs that damage team confidence. The approach that works: start with low-risk areas (support, simple qualification), expand gradually, and accept that proper training and iteration require sustained effort. Rushing the process is the most common cause of implementation failure.
What is a Chief AI Officer and do we need one?
A Chief AI Officer is a dedicated role responsible for overseeing, optimizing, and managing AI agent performance in the sales organization. This person is typically someone who is quantitatively minded, comfortable spending hours analyzing data and performance metrics, genuinely interested in how AI systems work, and able to communicate between technical teams and business stakeholders. They don't need to be a data scientist or AI engineer—they need to be obsessive about performance, comfortable with iteration and experimentation, and capable of diagnosing why an AI agent's performance degraded from 70% accuracy to 60% accuracy and implementing corrections. This role starts as 50-100% of someone's time but can eventually drop to 20-30% as systems mature. Without this oversight, AI systems drift—messaging becomes stale, data sources go out of date, agent performance gradually declines. The dedicated monitoring and correction from a Chief AI Officer prevents this drift and maintains performance. Most organizations that skip this role (believing AI is "set and forget") experience declining performance and eventually conclude AI "doesn't work." Those that invest in dedicated oversight see sustained improvements.
What are the key metrics for measuring AI sales system success?
Avoid vanity metrics like "percentage of leads handled by AI" or "number of agents deployed." Instead, measure business outcomes: cost per qualified lead (pre-implementation vs. post-implementation), cost per sales-accepted opportunity, sales cycle length (target: 20-40% improvement), win rate by sales stage, revenue per sales employee (target: 30-50% improvement), and customer acquisition cost by channel. Establish clean baselines before implementation (30-60 days of measurement) so you can accurately compare pre-AI to post-AI performance. The most telling metric: does your sales team generate more revenue per human employee after AI implementation? This captures the complete efficiency improvement. Most organizations see payback on their AI investment within 90 days through improved efficiency, with the remainder of year one driving margin expansion. If you're not seeing clear improvement in these business metrics by month 6 of implementation, troubleshoot your training, oversight, and agent configuration—the issue is rarely with the AI technology itself.
Should we build custom AI sales tools or buy existing platforms?
Buy existing platforms unless you have two specific conditions: (1) genuine expert technical talent who wants to build this, and (2) a sales process so unique that commercial platforms don't fit. Commercial platforms are evolving at a pace that custom teams cannot keep up with—vendors release major feature improvements every 4-8 weeks. Building custom tools means your system will be outdated in 6-12 months. Further, custom tools require permanent maintenance investment while vendor platforms have this maintenance built into subscriptions. The exception is teams with strong engineering that use general-purpose AI platforms (OpenAI, Anthropic) plus custom wrapper layers, but even these require significant ongoing investment. For most organizations, picking a reputable vendor and investing in proper implementation and training delivers better results than DIY development. When evaluating vendors, prioritize implementation support—this is often the difference between success and failure. The vendor who spends time helping you train your agents properly outweighs vendors with more features but less guidance.
What's the biggest mistake organizations make implementing AI sales systems?
Attempting to automate too much too quickly is the most common failure. Month 1 enthusiasm leads to ambitions like "AI will handle 80% of our sales process." Organizations deploy broadly without proper training. Month 2-3 results are mediocre because the AI isn't properly calibrated. Sales team reverts to manual handling. Month 4 conclusion: "AI doesn't work for our business." The correct approach is narrow, methodical scaling: pick one workflow, train it properly, measure success, then expand to a second workflow only after the first is stable. Expect 18-24 months to reach full maturity, not 3-6 months. Organizations willing to accept this timeline typically succeed; those seeking quick wins typically fail. Additional common mistakes include insufficient training data (uploading only 20 email examples), inadequate human oversight, and measuring success by "percentage automated" instead of "business results."
How will AI affect my sales career?
For top-tier salespeople (top 10-15% of performers): minimal displacement risk, opportunity to become more valuable by managing AI agents and focusing on high-complexity deals. For solid professional salespeople (middle 60-75%): significant career transition required but not displacement—those who adapt to AI management and optimization become more valuable and earn more; those who resist face stagnant compensation and limited advancement. For below-average salespeople (bottom 10-25%): high displacement risk—AI executes standard processes better than below-average performers, reducing job opportunities. The proactive career move is learning to work alongside AI now, when learning happens through curiosity rather than desperation. Salespeople developing expertise in AI agent management, optimization, and training will be increasingly valuable. Those waiting to be forced to adapt will find adaptation more difficult. The sales profession isn't disappearing; it's transforming. Career security comes from leading that transformation rather than resisting it.
What's the timeline for AI displacement in sales?
The immediate timeline (2026-2027): SDRs sending templated emails and BDRs running traditional cadence campaigns face highest displacement risk in this 12-month window, as commercial systems already handle these functions effectively. Mid-term (2027-2029): organizational backfilling of open sales roles with AI instead of human hires means sales team headcount shrinks 40-60% over this period, though through attrition rather than layoffs. Longer-term (2029+): if AI capabilities continue accelerating at current rates, the 70% of AE jobs currently considered safe may face pressure, though genuine uncertainty exists about whether AI will develop the reasoning and relationship-building capabilities required for all enterprise sales work. The key timing insight: there's a window where implementing AI is a competitive advantage (now through late 2026). In 2027-2028, it becomes table stakes—companies without AI-augmented sales will be outcompeted. By 2029-2030, AI-driven sales will be universal among competitive companies.
Key Takeaways
- AI has transformed SaaStr's sales operations from 8-9 humans to 1.2 humans plus 20 AI agents while maintaining equivalent revenue—proving AI viability at scale
- Email-based SDR roles sending templated cadences will be 90% displaced within 12 months as AI automates these functions better and faster than humans
- Top 10-15% of salespeople remain safe from displacement; middle-60% must adapt to AI management roles; bottom-25% face high displacement risk
- Implementing AI sales systems requires 50-60 hours of proper training over 18-24 months, not 30 minutes; organizations rushing this timeline typically fail
- AI has autonomously closed deals worth 100K without human intervention, proving capability extends beyond lead qualification to complex negotiation
- Organizations need a dedicated 'Chief AI Officer' to oversee AI agent performance and prevent system drift; without oversight, AI effectiveness degrades
- Customer support is the lowest-risk entry point for AI implementation, with 50-80% of support volume automatable at leading companies
- The competitive advantage window for AI implementation is 2026-2027; by 2028, AI-driven sales will be table stakes rather than competitive differentiator
- Account Executives focused on complex deals and relationship building remain durable for 3-5+ years as AI cannot replicate genuine human trust-building
- Proper measurement focuses on business outcomes (revenue per employee, cost per opportunity) not vanity metrics (percentage automated)




