AI Trends in Data Analytics: 7 Game-Changing Use Cases for 2026
Here's the thing about AI and data analytics: they're not actually separate things anymore. And that's changing everything.
For years, analytics was the domain of specialized teams who could spend hours digging through dashboards, building reports, and trying to answer questions like "Why did conversion drop 2% last Tuesday?" That work was necessary. But it was also... slow. Expensive. And the insights? They often came too late to act on them.
AI changes that equation completely. Instead of waiting for a human analyst to finish their detective work, AI can scan massive datasets, spot patterns humans would miss, and hand you not just an answer but the next three steps you should take. That's not just faster. That's a fundamental shift in how we think about making decisions.
But here's what I want to be clear about upfront: AI in analytics isn't magic. It gets things wrong. It can be confidently incorrect in ways that are almost charming if they weren't so costly. And like any powerful tool, it works best when humans stay in the loop.
So what are the actual trends shaping analytics in 2026? Not the hype. Not the marketing speak. The real, tangible shifts that are changing how companies make decisions?
Let me walk you through seven of them. Some might surprise you. Some might already be in your toolkit. But all of them are worth understanding because they're either already affecting how data moves through your organization or they will be soon.
TL; DR
- AI is turning insights into actions in real time, moving beyond "what happened" to "what should we do next"
- Automated anomaly detection catches problems before they impact revenue, often flagging issues humans would miss entirely
- Predictive models are getting faster and more accessible to teams without machine learning expertise
- Natural language queries are making analytics accessible to non-technical team members, democratizing data access
- Integration across first-, second-, and third-party data is finally becoming seamless, creating a 360-degree view of customer behavior
- AI-powered data cleaning is taking hours of manual work and compressing it into minutes
- Privacy-first analytics is emerging as companies navigate regulations while maintaining data utility
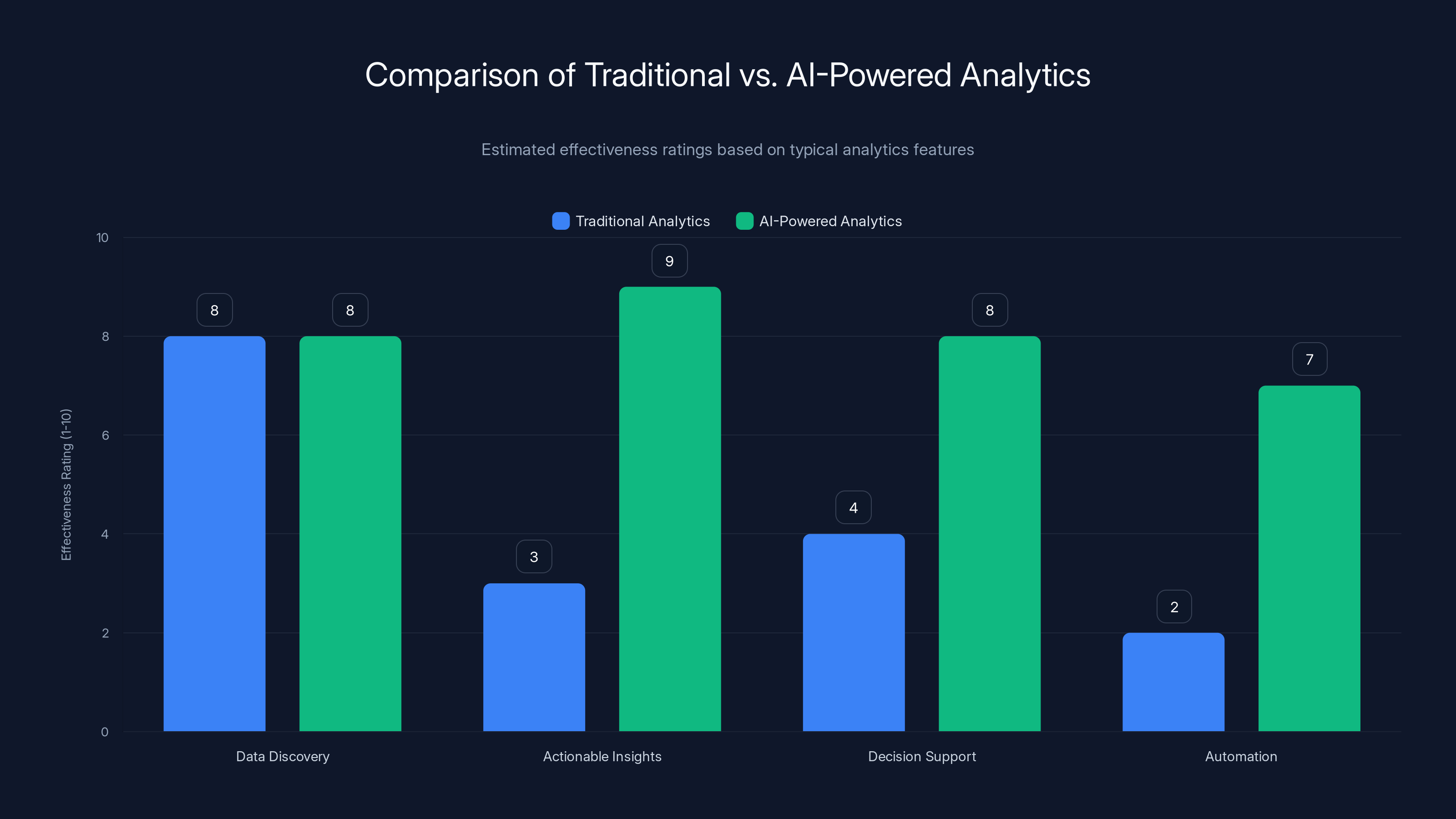
AI-powered analytics significantly enhance actionable insights, decision support, and automation compared to traditional analytics tools. Estimated data.
1. Actionable Insights Are Becoming Automated (Not Just Informational)
Let me tell you something that took me years to understand: most analytics don't actually change anything. A team runs a report. They present findings. Someone nods politely. Life goes on.
The insight gets lost somewhere between discovery and decision-making.
What's different now is that AI is being built specifically to bridge that gap. Instead of stopping at "here's what the data shows," modern analytics platforms are starting to say "here's what you should do about it."
Take this concrete example: you're running an e-commerce site, and your analytics tool notices that users from mobile devices visiting on Thursday evenings have a 34% higher cart abandonment rate than other segments. A traditional analytics approach would surface that data. You'd see the numbers. A smart analyst might flag it as notable.
But what happens next? Usually, nothing. Because translating "here's an interesting pattern" into "here's a concrete action" requires context, domain knowledge, and decision-making frameworks that aren't built into the tool.
AI-powered analytics change this. They can connect that pattern to your optimization goals, consider your current marketing budget, evaluate technical constraints, and then recommend something like: "Shift $8,000 of your Thursday evening ad spend to Wednesday and Friday. Test a mobile-specific checkout flow with a persistent chat feature. Measure impact over three weeks."
Notice what happened there. The AI didn't just point out a problem. It recommended a specific action, sized the investment, provided a timeline, and gave you a way to measure success.
This shift from informational to actionable represents the real innovation in AI analytics. It's the difference between having information and being able to act on it without additional research, discussion, or guesswork.
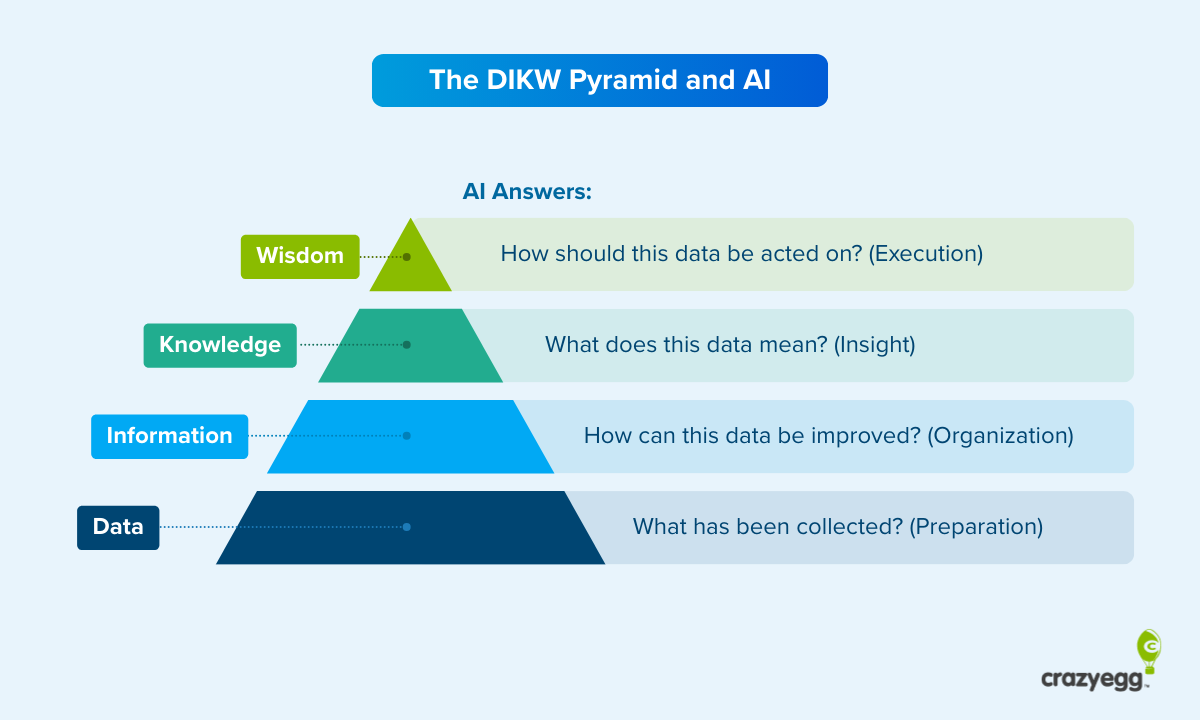
The DIKW pyramid is a useful framework for understanding this. Data at the base becomes Information through cleaning and context. Information becomes Knowledge through analysis and pattern recognition. Knowledge becomes Wisdom through the lens of decision-making and optimization frameworks.
AI is automating movement through all four layers. It connects disparate data sources (Data layer), cleans and enriches them (Information layer), identifies meaningful patterns using statistical models (Knowledge layer), and then applies decision-making frameworks to suggest actions (Wisdom layer).
What's fascinating is that this is still early. The AI advisor tools in platforms like Google Analytics are still relatively generic. They'll tell you your bounce rate on mobile is high and suggest you improve page speed. Which is true. But it's not personalized to your specific business model, your constraints, or your goals.
As this matures, expect to see AI that understands your specific business, your current initiatives, and your available budget. Instead of generic advice, you'll get personalized recommendations that account for everything unique about your situation.
The implications are significant. Decision latency (the time between identifying a problem and acting on it) collapses. Teams move faster. And critically, decisions are more informed, because the AI can bring to bear data patterns and optimization frameworks that would take humans hours to research.
But I'll be honest: this is where AI also struggles most. Recommendations are sometimes confidently wrong. They can miss context. They occasionally suggest actions that sound good on paper but don't account for organizational constraints or cultural realities that a human would immediately recognize.
This is why the best implementation pattern I'm seeing is human-in-the-loop: AI generates recommendations, but humans approve action and provide feedback that trains the AI's recommendations over time. You get the speed of automation plus the judgment of human decision-makers.
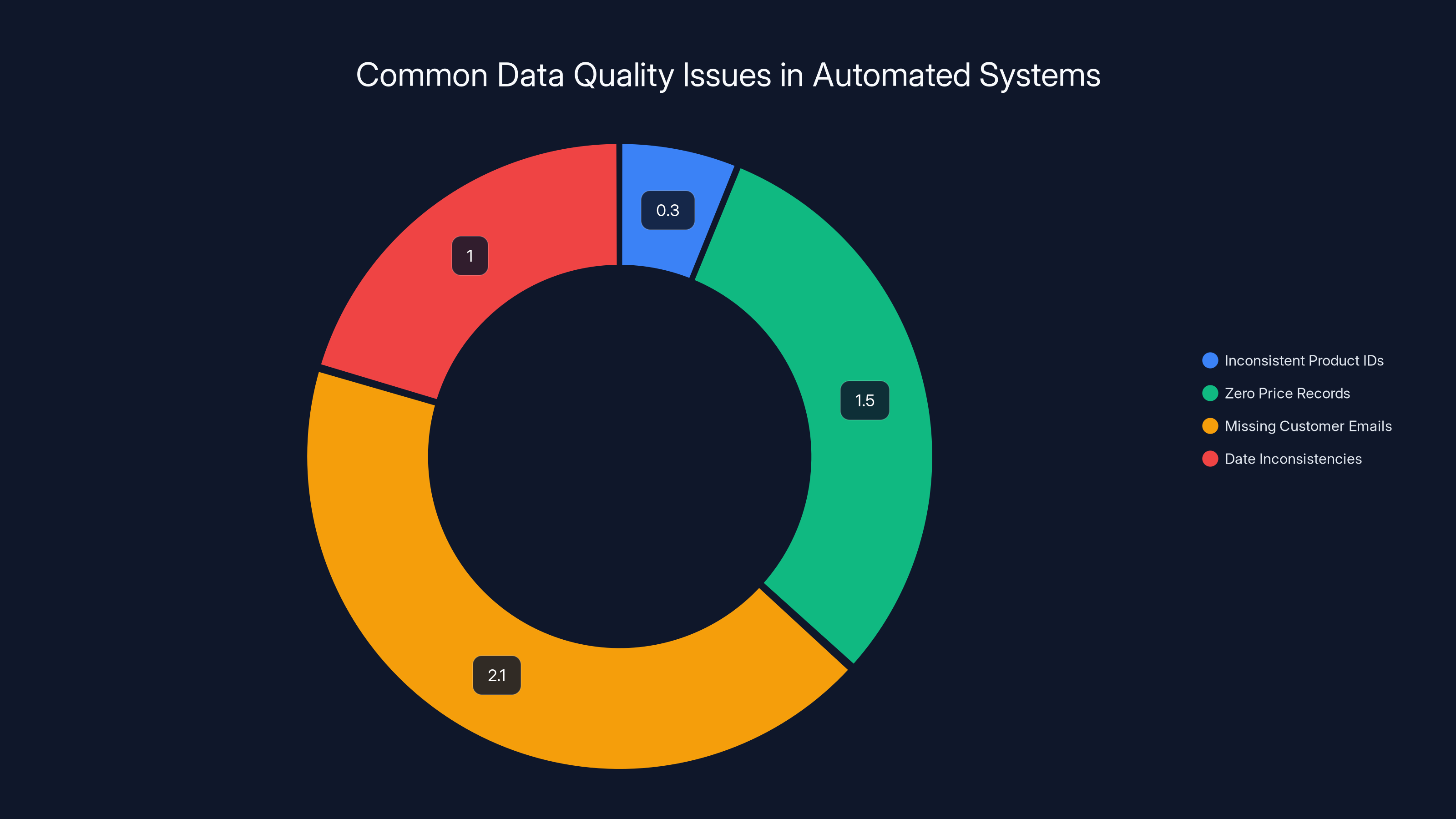
Estimated data shows that missing customer emails and zero price records are among the most common issues flagged by automated data cleaning systems.
2. Anomaly Detection Now Catches Problems Before They Become Crises
One of my favorite uses of AI in analytics is something most people never see: anomaly detection running silently in the background, catching weird stuff automatically.
Here's why this matters. Your website gets 10,000 visitors a day. Your conversion rate is usually 3.2%. Today it's 2.8%. Is that a problem? Could be normal variance. Could be a JavaScript error breaking checkout. Could be that your competitor's ad is running in a premium position. Could be the weather.
A human checking dashboards once a day might not notice. Might notice and assume it's just normal fluctuation. Might notice, worry, spend an hour investigating, and discover it was nothing.
AI-powered anomaly detection is watching in real time. It knows your baseline. It knows your normal variance. It understands seasonality, day-of-week effects, and campaign impacts. So when something genuinely unusual happens, it flags it. Not as "something happened" but as "this is unusual given everything we know about how your site normally performs, here's the magnitude of the deviation, and here's what we think might have caused it."
I watched a team catch a revenue-crushing bug using this that manual processes missed for 4 hours. A form submission was failing silently for one mobile browser version. Users weren't being told. The revenue impact was modest (about $2,000 per hour) but would have continued until someone manually investigated. The AI caught it because conversion rates for that traffic segment suddenly dropped 67% over a 10-minute period.
That's not just useful. That's worth money.
What's particularly interesting about modern anomaly detection is that it's moving beyond simple statistical flagging. It's starting to incorporate causal reasoning. Instead of just saying "this metric is weird," it's starting to say "this metric is weird AND here are the other metrics that changed in a correlated way, which suggests the cause might be X, Y, or Z."
The implementation challenge is setting sensitivity properly. Too sensitive and you get false alarms constantly. Too insensitive and you miss real problems. This is where AI learning comes in. The system learns from which anomalies you actually care about versus which ones you ignore. Over time, it gets better at flagging what matters to your business.
I expect anomaly detection to be table stakes for any serious analytics platform by the end of 2026. It's moved from "nice to have" to "why isn't this already in every platform?"

3. Predictive Analytics Is Becoming Accessible to Non-Data Scientists
Predictive modeling used to require a specific skillset. You needed to understand statistical methods, be comfortable with programming, and have the patience to spend weeks building, testing, and validating models.
That barrier is collapsing.
Modern AI is making it possible for analysts who've never written a line of code to build predictive models. You point the system at historical data, tell it what outcome you're trying to predict, and it goes to work. It tests different algorithms, handles feature engineering, checks for bias, and surfaces a model that works.
Let me give you a practical example. An e-commerce company wants to know which customers are likely to churn in the next 90 days. Three years ago, that project required hiring a data scientist. Now? An analyst can load historical customer data (purchase history, support tickets, email engagement, time since last order) into a platform like Runable (which offers AI-powered automation and predictive modeling capabilities) or similar tools, describe what they're predicting, and get a usable model in hours instead of weeks.
More importantly, they get explanations. Not just "this customer has an 68% churn probability" but "this customer's churn risk is elevated primarily because their purchase frequency has dropped 40% in the last 60 days, and their support ticket average response time is 2.3x higher than their cohort average."
That's actionable. You know what to investigate. You can prioritize intervention.
What's enabling this is a combination of advances: better algorithms, more computational power, and AI systems that handle the tedious parts of model building automatically. The human still provides domain expertise and decides what to build. But the AI handles the heavy lifting.
The limitation here is still data quality. Garbage in, garbage out. If your historical data is incomplete, inconsistent, or biased, the model will reflect those problems. So companies investing in predictive analytics are simultaneously investing in data quality and governance.
But the trajectory is clear: predictive analytics, which was accessible only to specialists three years ago, will be a routine capability for any analyst by 2026. That's a fundamental shift in how organizations make decisions.
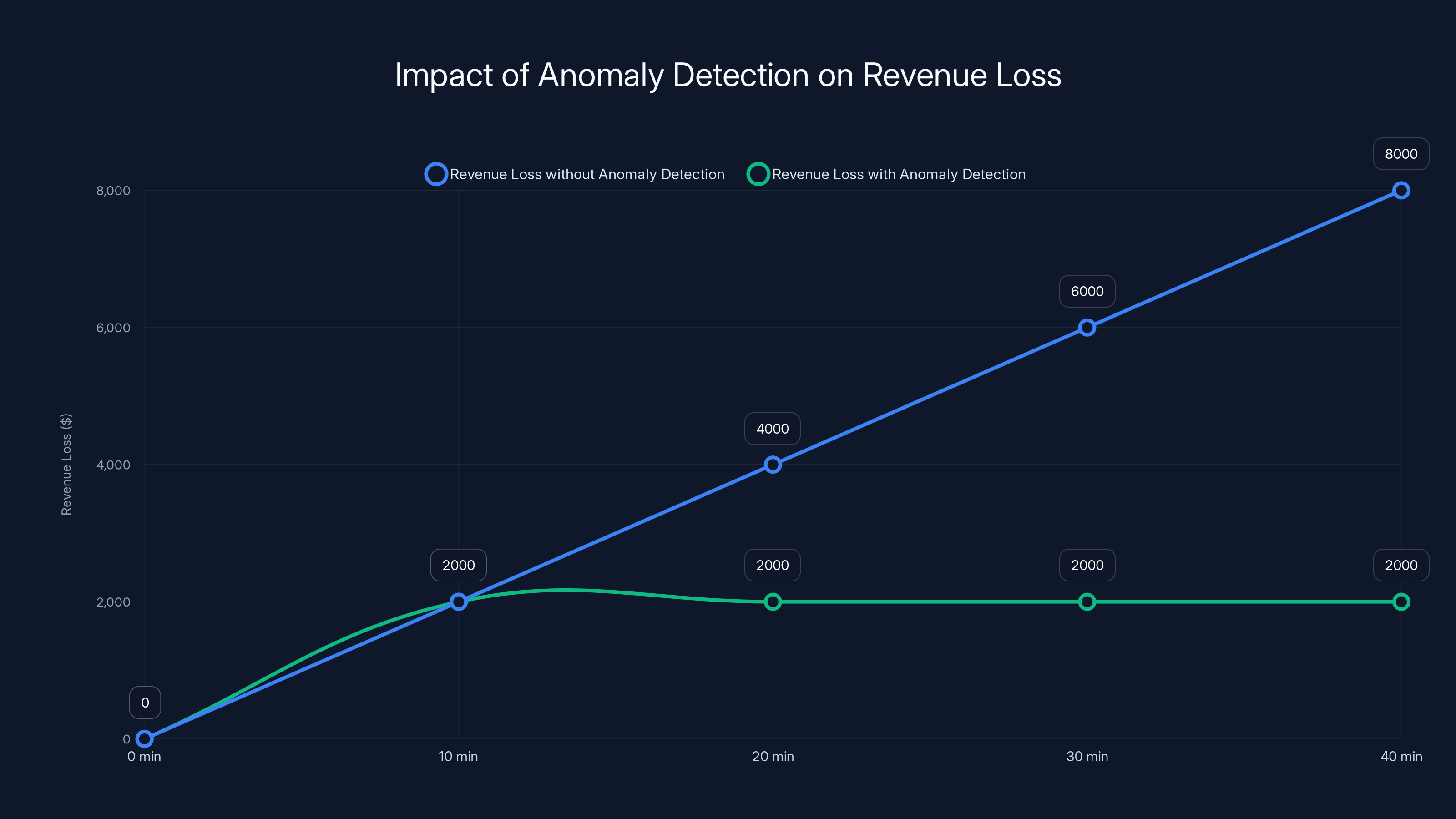
AI-powered anomaly detection can significantly reduce revenue loss by identifying issues early. Estimated data shows that without detection, losses could escalate quickly, while detection stabilizes impact.
4. Natural Language Queries Are Making Analytics Accessible to Everyone
Imagine you're in a meeting. Someone asks, "How many users from California visited the pricing page last Tuesday after clicking an ad from our Google Ads Summer campaign?"
Traditionally, someone would say, "Let me check," then spend 10 minutes building a query in SQL or your analytics tool, come back with an answer (or realize they need to clarify which campaign variant they meant), and everyone's moved on to another topic.
Now imagine asking that same question in plain English and getting an answer in 3 seconds.
That's what natural language query capability in analytics is doing. You describe what you want to know in human language. The system translates it into a query against your data. You get an answer.
What's remarkable is how well this actually works. For straightforward questions—"what's our bounce rate this week," "how many users converted yesterday," "what was our top traffic source last month"—modern natural language systems get it right consistently.
For more complex questions, it gets trickier. "What percentage of users who clicked our email campaign and then visited the pricing page but didn't convert are likely to return in the next 30 days?" That requires understanding multiple relationships in your data and making assumptions about time windows that might be ambiguous.
But even for complex questions, natural language is faster than forcing people to learn query languages or navigate complicated UI systems.
The real impact is democratization. Right now, analytics is often a bottleneck. You have a few people who understand your data deeply, and everyone else has to ask them questions. Natural language analytics lets more people ask their own questions and get their own answers.
There's also a productivity angle. A typical analyst probably spends 30-40% of their time answering routine questions that could be answered by someone with access to natural language analytics. Free those analysts from that work, and they can focus on deeper analysis, strategic research, and building frameworks.
The limitation is still accuracy. Natural language systems sometimes misinterpret questions. "Users from California" could mean "users located in California," "users who downloaded our California guide," or "users whose IP address shows California." The system has to make assumptions.
This is why good implementations include a feedback loop. If the AI got something wrong, you correct it, and the system learns. Over time, it understands your data better.
5. Cross-Platform Data Integration Is Finally Seamless
Most organizations have data scattered across multiple systems. Google Analytics 4 tracks web behavior. Shopify or your e-commerce platform tracks transactions. HubSpot or Salesforce tracks customer interactions. Email platforms track engagement. Ad platforms track campaign performance. Customer support systems track tickets and chats.
Connecting all of this is where things get messy.
Problem one: all these systems use different data models and identifiers. HubSpot might identify customers by email. Your e-commerce platform by user ID. Your email system by subscriber ID. They're the same person, but the systems don't know that.
Problem two: data moves at different speeds. Some platforms update in real time. Others batch overnight. Reconciling a question that spans multiple platforms means dealing with timing mismatches.
Problem three: the integrations often break. An API changes. A permission gets revoked. Suddenly data stops flowing and nobody notices until it's been broken for days.
What's changing is that AI is increasingly handling the glue code. Instead of analysts manually creating lookup tables and reconciliation logic, AI can infer relationships between datasets, match records across systems, and handle timing differences automatically.
I watched a team use this recently to create a truly unified view of customer behavior. They had web analytics, email engagement, purchase history, and support ticket data. Building that unified view manually would have taken weeks and required constant maintenance.
Using AI-powered integration, they had a workable unified customer profile in days. Not perfect initially, but functional. And it updated automatically.
The implication is that analysts spend less time doing data plumbing and more time doing analysis. That time investment is redirected toward valuable work.
There's also a freshness dimension. Real-time integration means decisions can be based on fresher data. You're not analyzing reports from yesterday. You're working with data from hours or minutes ago.

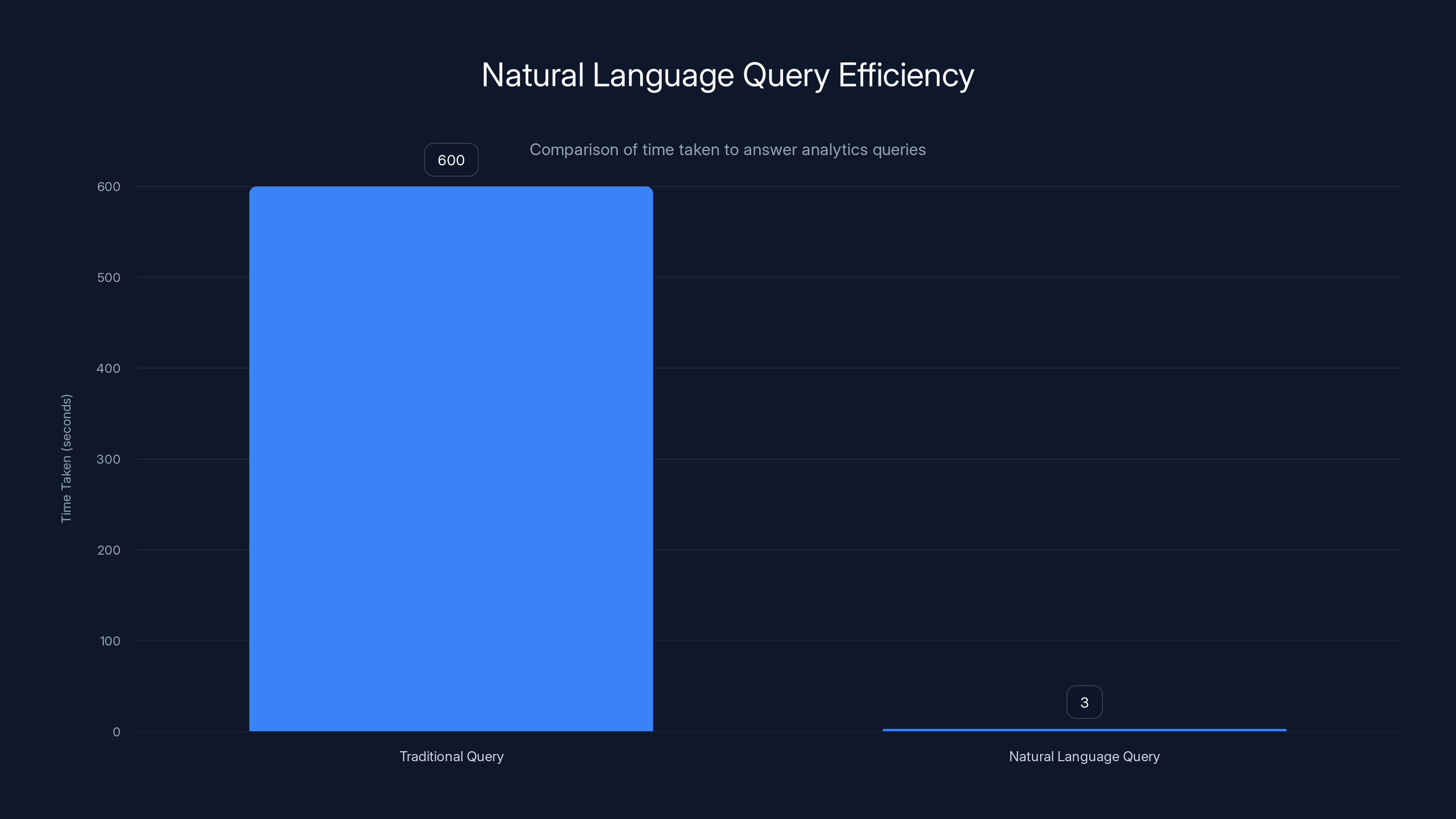
Natural language queries significantly reduce the time to get answers from analytics, dropping from 600 seconds to just 3 seconds. Estimated data.
6. Automated Data Cleaning and Quality Checks Are Becoming Standard
Every analyst has experienced this: you're excited about an insight you found, you dig deeper, and you discover the data is bad. A field has weird values. Records are duplicated. Timestamps are inconsistent. Time spent: hours that could have been spent on actual analysis.
Data quality is still the bottleneck for most analytics teams. Studies suggest analysts spend 30-40% of their time preparing and cleaning data rather than analyzing it.
AI is starting to automate this. Systems can now scan your data and identify quality issues automatically. Missing values. Duplicates. Inconsistent formats. Outliers that might indicate errors. The system flags all of this and can often fix it automatically.
Here's a concrete example. You're loading transaction data from your e-commerce platform. A system might automatically identify that:
- Product IDs are inconsistent in 0.3% of records (sometimes "PROD-001," sometimes "prod-001," sometimes "001")
- 47 records have prices of $0 (likely test transactions)
- Customer email addresses are missing for 2.1% of transactions
- Ship dates are sometimes after delivery dates
A good data quality system doesn't just flag these. It applies heuristics to fix what it can and quarantines what it can't. The data you use for analysis is automatically cleaned.
I should note: this requires validation. You want to understand what the system changed and why. It's possible the automated logic is wrong for your specific business context. But even requiring that validation, this saves massive amounts of time versus manual cleaning.
What's emerging is a practice called "data observability," which treats your data systems like you'd treat your application systems. You monitor for anomalies, track quality metrics, and alert when things break. AI is core to making this practical at scale.

7. Privacy-First Analytics Are Becoming Competitive Requirements
Here's a tension: customers want personalized experiences. That requires understanding their behavior. But customers also want their data protected. And regulators are increasingly mandating data protection through regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and dozens of others.
You can't just collect everything and analyze everything. You need to make smart choices about what data you collect and how you analyze it.
What's emerging is privacy-first analytics architecture, where you design for privacy from the beginning rather than treating privacy as a constraint added later.
This is where AI comes in. AI can help you accomplish several things simultaneously:
First, it can identify what data you actually need to answer important questions. You might think you need full granular user behavior data. AI analysis might show you can answer 80% of your important questions with aggregated, anonymized data.
Second, it can synthesize insights while preserving privacy. Instead of analyzing raw customer data, you analyze statistical models built from that data. You can understand patterns without exposing individual records.
Third, it can help you comply with data subject rights. When someone requests "all my data," AI can extract and format that data automatically. When someone requests deletion, AI can help identify and remove related records across your systems.
Fourth, it can help you assess privacy risk. Given your data collection practices and your analytics needs, what's your exposure? What regulations apply? What should you change?
What's fascinating is that privacy-first approaches often improve data quality. When you're collecting less data and being more intentional about its use, you collect better data.
I expect privacy-first analytics to become a competitive advantage by 2026. Companies that can answer important business questions while respecting customer privacy and complying with regulations will win both customer trust and regulatory favor.

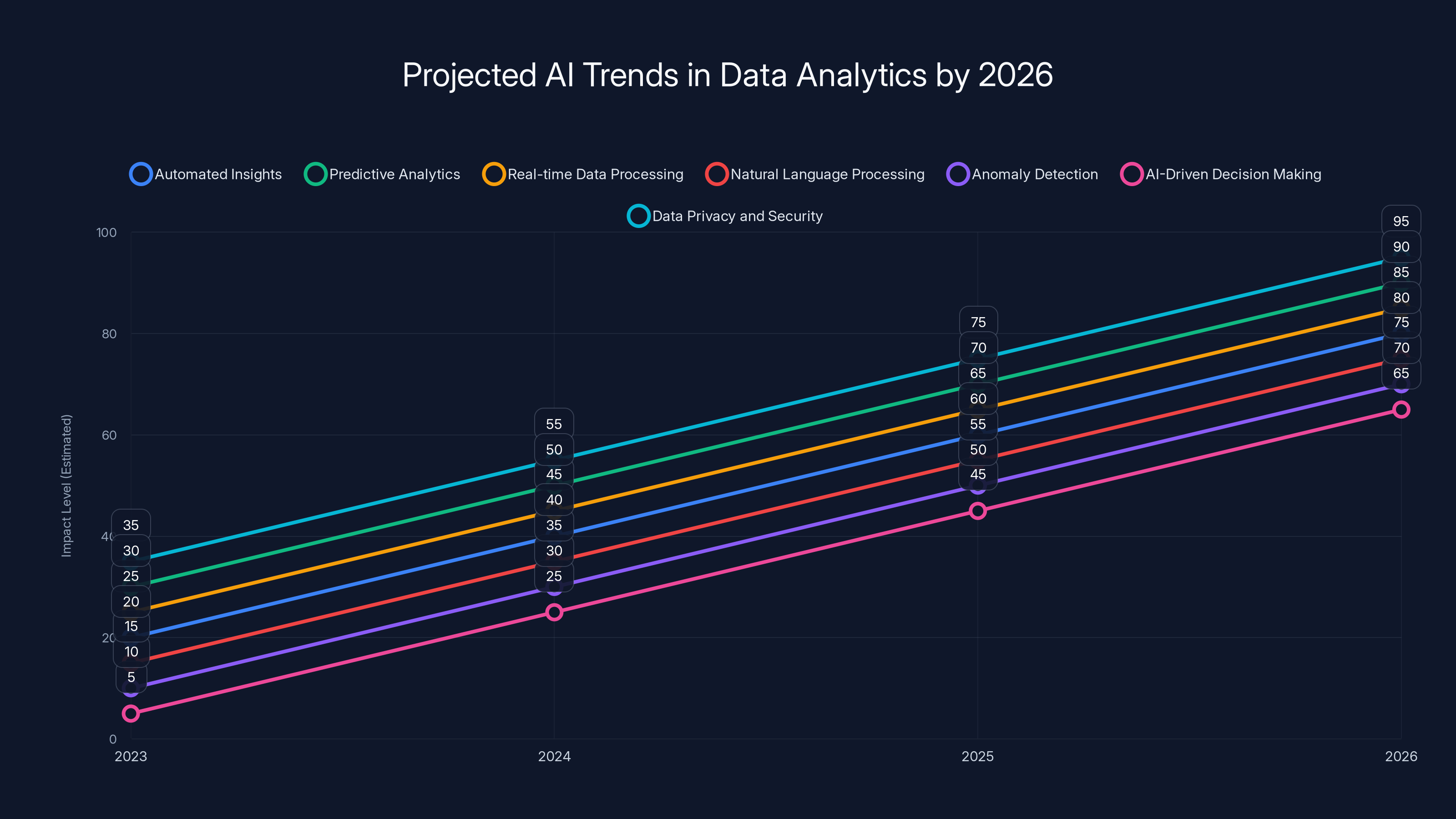
Estimated data shows increasing impact of AI use cases in data analytics by 2026, with predictive analytics and data privacy/security leading the way.
Understanding Current Limitations and When AI Gets It Wrong
I want to be direct about something: AI in analytics isn't perfect, and it's important to understand where it struggles.
Reliability issues: AI systems make confident recommendations that are sometimes confidently wrong. A model might identify a pattern that looks statistically significant but is actually just noise or reflects bias in historical data. An insight that seems obvious to the system might miss important context a human would immediately recognize.
Context blindness: AI can identify patterns but might not understand the business context that makes an insight relevant or irrelevant. "Users from this demographic have lower conversion rates" is a pattern. But if that demographic only represents 0.2% of your traffic, is it worth optimizing for? The AI might flag it. A human should judge whether it matters.
Bias amplification: If your historical data has biases (you marketed more heavily to certain demographics, your product served some geographies better), AI models trained on that data will amplify those biases. You might get insights that seem valid but actually reflect past choices rather than future opportunity.
Data dependency: AI can only work with the data you give it. If important data is missing or if the data you have doesn't actually predict what you're trying to predict, the AI will struggle. This is why data quality is so critical.
Explainability: Some AI models are black boxes. They make predictions but can't explain why. That's fine for certain use cases but problematic for decisions that need human understanding and judgment.
The trajectory here is toward improvement. Systems are getting better at explaining themselves. Methods for detecting bias are improving. Techniques for handling missing data and context are advancing. But right now, the best approach is human-in-the-loop: let AI do what it's good at (pattern recognition, processing scale, tireless consistency), but keep humans in place for judgment, context, and ultimate decision-making.

Building an AI-Ready Analytics Strategy
So how do you actually implement these trends? How do you move from current-state analytics to AI-powered analytics?
Here's what I'm seeing work:
Start with a specific problem. Don't implement AI because it's trendy. Pick something that's currently painful. Maybe it's "our analysts spend too much time answering routine questions." Or "we're missing operational issues until they become crises." Or "we can't predict which leads will convert." Pick one.
Invest in data quality first. Before implementing predictive models or AI-powered anomaly detection, make sure your data is clean and comprehensive. This is the foundation everything else builds on.
Pick the right tools. Not every analytics platform is equal. Some have sophisticated AI. Others offer basic AI features as a nice-to-have. Evaluate based on your specific needs.
Start small and measure impact. Implement one AI capability, measure the business impact, and iterate. Did anomaly detection actually reduce the time it takes to catch problems? Does natural language query capability actually reduce the load on your analytics team? Use these outcomes to inform the next investment.
Build feedback loops. AI learns from feedback. When your system makes a recommendation, track whether that recommendation led to positive outcomes. Use that feedback to train and improve the AI.
Stay human-centric. The goal isn't to replace analysts. It's to multiply their effectiveness. Use AI to automate the tedious work so analysts can focus on strategic research and high-value thinking.
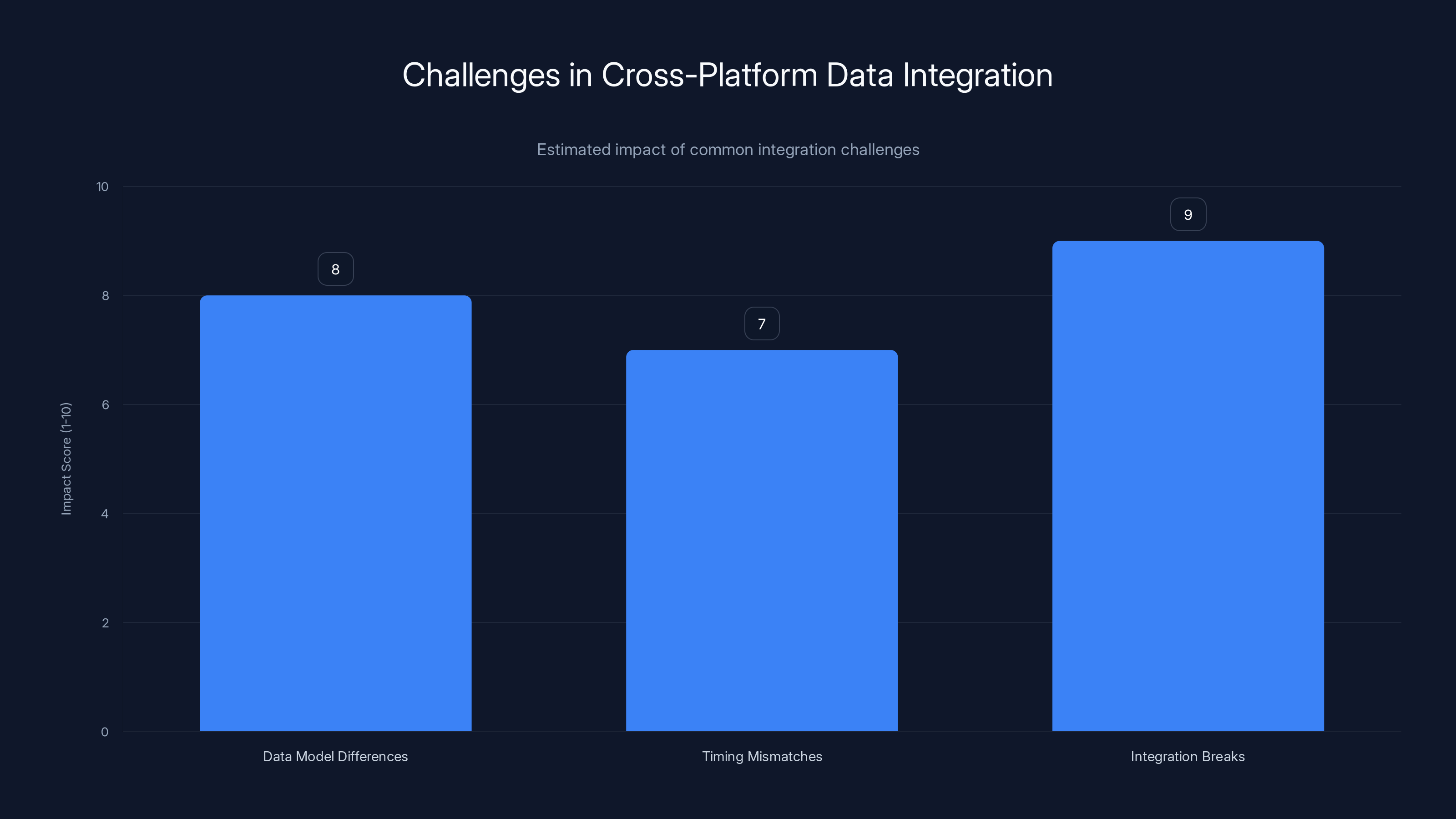
Integration breaks have the highest impact on cross-platform data integration, followed by data model differences and timing mismatches. (Estimated data)
The Future: Where Analytics Is Heading
Looking forward to late 2026 and beyond, I expect to see several things:
Analytics platforms will become more opinionated. Instead of just showing you data, they'll make explicit recommendations based on your industry, your goals, and your constraints. This will require building out more domain knowledge into analytics platforms.
Data integration will become even more seamless. You'll be able to connect new data sources and have them automatically integrated into your analytical view within minutes, not days or weeks.
Predictive capabilities will become more sophisticated. You won't just predict binary outcomes (will they churn? will they convert?). You'll predict multi-step sequences (will they buy, then upgrade, then renew?) and optimize for complex outcomes.
Privacy will become a core selling point. Companies will market their ability to answer important questions while respecting privacy. Regulations will continue tightening, and platforms that handle this naturally will have competitive advantage.
Collaboration will improve. Multiple people will be able to ask questions and iterate on insights together, with AI handling the technical complexity of turning natural language into data queries.
Most significantly, the latency between insight and action will shrink to near-zero. Instead of daily or weekly reports, you'll have continuous feedback. Instead of quarterly strategy decisions, you'll have real-time decision support. The business moves faster because the information system moves faster.
But I want to close with something important: technology is just the foundation. The real competitive advantage will come from organizations that build analytical thinking into their culture. Companies that ask better questions. That evaluate evidence rigorously. That combine AI insights with human judgment thoughtfully.
The tools are getting better. But the human skill of turning information into wisdom? That's still as important as it's ever been.
FAQ
What is AI in data analytics?
AI in data analytics refers to machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence systems that automate the process of finding patterns, making predictions, and generating actionable insights from large datasets. This includes capabilities like anomaly detection, predictive modeling, natural language query processing, and automated recommendations for optimization.
How does AI improve decision-making in analytics?
AI accelerates decision-making by moving beyond answering "what happened" to directly answering "what should we do next." It connects data analysis with optimization frameworks to surface prioritized, specific recommendations with context and reasoning. This compresses the time between identifying an opportunity and taking action, while also reducing the need for specialized expertise to interpret findings.
What are the main limitations of AI in analytics?
AI systems can make confidently incorrect predictions, may amplify biases present in historical data, sometimes lack important business context for judgment calls, depend heavily on data quality, and can create black-box models that are difficult to explain. The best implementations keep humans in the loop for final decision-making while using AI for pattern recognition and efficiency.
How does anomaly detection work in AI analytics?
Anomalous detection systems learn the normal patterns and variance in your metrics, then flag significant deviations from those patterns. Modern systems go beyond statistical flagging to incorporate causal reasoning, identifying not just that something is unusual but suggesting what might have caused the anomaly based on correlated changes in other metrics.
Can non-technical people use AI-powered predictive analytics?
Yes. Modern AI-powered analytics platforms now democratize predictive modeling by handling complex technical tasks automatically. An analyst without machine learning expertise can point the system at historical data, specify what outcome they want to predict, and the AI will test different algorithms, handle feature engineering, and surface a workable model with explanations.
How do you ensure privacy when using AI analytics?
Privacy-first analytics design involves collecting intentionally (only data you truly need), analyzing aggregated and anonymized data rather than raw records, synthesizing insights through statistical models, automating compliance with data subject rights like deletion requests, and continuously assessing privacy risk. Privacy requirements often improve data quality as a side benefit.
What should be the first step in implementing AI analytics?
Start with a specific, painful problem that AI can actually solve. This might be reducing analyst time on routine questions, catching operational issues faster, or building predictive models for churn. Then invest in data quality as the foundation, pick appropriate tools for your needs, implement one capability, measure impact rigorously, and iterate from there.
How does natural language query improve analytics adoption?
Natural language queries remove the barrier to entry for people who don't know SQL or analytics tools. Team members can ask questions in plain English and get answers in seconds, democratizing access to data. This frees specialized analysts from answering routine questions so they can focus on deeper strategic analysis.

Key Takeaways for Your Organization
If you're considering how AI impacts your analytics strategy in 2026, remember these essentials:
First: AI is not a replacement for good analytics thinking. It's a multiplier for human expertise. Use it to automate routine work and free analysts for strategic thinking.
Second: Data quality is the foundation. Invest in clean, integrated, well-documented data before investing in sophisticated AI capabilities.
Third: Start specific, not broad. Pick one problem to solve, measure the impact, and expand from there.
Fourth: Keep humans in the loop. Let AI make recommendations, but have humans validate, provide feedback, and make final decisions.
Fifth: Privacy is increasingly a business requirement, not a constraint. Design your analytics to respect privacy from the beginning.
The analytics world is transforming. Organizations that embrace these trends thoughtfully will move faster, make better decisions, and compete more effectively. The key is approaching it strategically rather than simply implementing the latest tools.