Introduction: The Future of Television Arrives at CES 2026
Every January, the Consumer Electronics Show delivers a glimpse into the technological future, and 2026 proved to be no exception for the television industry. The innovation landscape has fundamentally shifted at this year's event, with manufacturers pushing the boundaries of what's possible in display technology. Gone are the days of incremental improvements—this year's announcements represent genuine paradigm shifts in brightness, scale, and color reproduction that will reshape how we experience content at home.
The television market has been in a state of constant evolution over the past decade, moving from LCD dominance through the OLED revolution and into a period where multiple competing technologies coexist, each with distinct advantages. What we witnessed at CES 2026 suggests we're entering a new phase where the industry isn't choosing a single winner, but rather refining multiple pathways simultaneously. Manufacturers are pursuing increasingly aggressive brightness targets for OLED displays, expanding the maximum screen sizes to unprecedented levels, and perfecting mini-LED backlighting with unprecedented precision and color control.
This convergence of technologies matters profoundly for consumers because it means choice, competition, and genuine performance improvements across all price points. Whether you prioritize picture quality, screen size, gaming performance, or streaming quality, the 2026 television lineup offers solutions that would have seemed impossible just two years ago. The innovations aren't merely marketing fodder—they represent years of research, billions in manufacturing retooling, and fundamental advances in materials science and optical engineering.
Understanding these new technologies requires more than just reading spec sheets. It demands comprehension of what brightness means in different contexts, why screen size scaling presents unique engineering challenges, and how different backlighting technologies achieve their visual effects. Throughout this article, we'll explore not just what's new at CES 2026, but why it matters, how it works, and what you should consider when evaluating these next-generation displays for your home.
The television industry's evolution reflects broader trends in consumer technology: a relentless push toward more immersive experiences, increased power efficiency despite higher performance targets, and growing differentiation between premium and budget segments. The innovations we're discussing today won't be confined to high-end models for long; they'll cascade down the market in the coming years, eventually reaching mainstream price points. Understanding them now positions you to make informed decisions about television investments over the next decade.
The Brightness Revolution: Next-Generation OLED Technology Explained
Understanding Peak Brightness in OLED Displays
Traditional OLED technology has always carried one significant limitation: achieving high brightness on large screen areas simultaneously. While OLED displays can produce extraordinarily bright individual pixels, they've historically struggled to maintain those brightness levels across entire scenes without risking pixel degradation or reducing display lifespan. CES 2026 revealed breakthrough solutions that fundamentally address this challenge through advanced thermal management, improved phosphorescent materials, and intelligent brightness distribution algorithms.
Brightness, measured in nits, represents the amount of light the display produces. A typical high-quality standard dynamic range (SDR) film or television show requires around 100 nits to display properly. However, high dynamic range (HDR) content, which is increasingly common in streaming services and physical media, requires peak brightness levels of 1,000 nits or higher for small portions of the image. OLED displays have traditionally managed 800-1,200 nits in small areas, but maintaining these levels across 30-40% of the screen presented serious challenges. The new OLED panels revealed at CES 2026 demonstrate the ability to sustain 2,000-3,000 nits peak brightness on larger portions of the image without significant degradation.
The breakthrough involves several converging technologies. First, manufacturers have developed new phosphorescent materials that emit more efficiently, requiring less electrical current to produce the same light output. Second, advanced heat dissipation systems using copper vapor chambers and innovative substrate designs have enabled better thermal distribution. Third, processors employing machine learning algorithms intelligently manage brightness distribution, preventing any single pixel or region from remaining at maximum brightness for extended periods. This combination allows for sustained peak brightness that was previously impossible in OLED technology.
The practical implications are substantial. Bright scenes in action movies—explosions, sunlight, bright white text on dark backgrounds—now display with the intensity and clarity they deserve. For people who watch in bright living rooms rather than darkened home theaters, this brightness improvement closes a significant gap with competing technologies. The color accuracy maintains OLED's traditional advantage while adding brightness previously associated with LCD and mini-LED alternatives.
QD-OLED vs. WOLED vs. MLA Technology
CES 2026 showcased competing OLED architectures, each claiming advantages in specific performance domains. Understanding these technologies requires examining the fundamental differences in how they generate light and manage color. Quantum Dot OLED (QD-OLED), developed primarily by Samsung Display, represents one approach where quantum dot layers convert OLED light into precise color outputs. White OLED (WOLED), pioneered by LG Display, uses white light generation followed by color filters. Micro Lens Array (MLA) technology, incorporating sophisticated optical elements, enhances light extraction efficiency across both approaches.
QD-OLED technology excels at color vibrancy and brightness efficiency. The quantum dot layer absorbs blue OLED light and re-emits it as red or green through the photoluminescence process. This approach theoretically allows for brighter colors with less electrical input because quantum dots convert blue photons into longer wavelengths more efficiently. At CES 2026, Samsung Display demonstrated QD-OLED panels achieving a claimed 3,000+ nits peak brightness with exceptional color saturation. The color gamut reaches 99% of the DCI-P3 cinema color space, meaning virtually all colors in professional cinema are accurately reproducible.
WOLED technology takes a different approach, generating white light across the entire panel and then using color filters to create the final image. While seemingly less efficient, LG has made remarkable progress with their white OLED process, particularly regarding longevity. The tungsten oxide materials used in WOLED displays have demonstrated superior degradation resistance over extended operating periods. LG's announcements at CES 2026 emphasized improvements in contrast ratio and black level uniformity, with particular focus on near-black detail in dark scenes.
MLA technology, applicable to both architectures, uses microscopic lens structures to redirect light more efficiently toward the viewer. These lenses, some only a few micrometers in size, act like tiny magnifying glasses that enhance light extraction efficiency by 20-40% depending on implementation. Several manufacturers displayed MLA-equipped OLED panels at the show, claiming improved brightness without proportional increases in power consumption. The technology represents a relatively mature innovation that multiple manufacturers have begun implementing, suggesting it will become increasingly common in 2026 and 2027 television models.
Power Consumption and Heat Management Innovations
Increased brightness historically came with proportionally increased power consumption and heat output, creating a challenging trade-off. Display brightness improving 50% usually meant power consumption increasing 50% as well. CES 2026 revealed technologies that decouple this relationship, delivering the brightness gains while maintaining or even reducing overall power consumption. These advances matter for both environmental responsibility and practical home operation, where excessive heat generation can affect room comfort and display longevity.
Advanced thermal management systems represent one major innovation category. Copper vapor chambers embedded in the display substrate actively redistribute heat away from high-usage areas. These chambers, typically 1-2 millimeters thick, contain a small amount of purified water that continuously circulates based on temperature gradients. As localized areas heat up, water evaporates from those regions, carries heat across the chamber, and condenses elsewhere, creating a continuous cooling cycle. Multiple manufacturers demonstrated these systems at CES, with some claiming 30-40% improvements in thermal efficiency compared to previous generation displays.
Power distribution optimization represents another crucial innovation. Modern television processors now employ predictive algorithms that analyze upcoming content frames and distribute brightness requirements across time and space more efficiently. If a scene contains one very bright element against a dark background, the processor can schedule pixel activation patterns to keep any individual area from sustaining maximum brightness too long. This algorithmic approach, powered by dedicated AI processors, reduces sustained power draw while maintaining the subjective brightness perception.
Some manufacturers also demonstrated hybrid approaches combining OLED with targeted mini-LED backlighting zones for specific brightness boosts in specific areas. While technically not pure OLED, these hybrid displays represent pragmatic solutions to brightness demands. The small mini-LED zones provide additional brightness for highlights without requiring the entire OLED layer to operate at unsustainable levels. This hybrid approach appeared on several premium models at CES 2026, suggesting it represents a viable path forward for manufacturers seeking maximum brightness with minimum complexity.
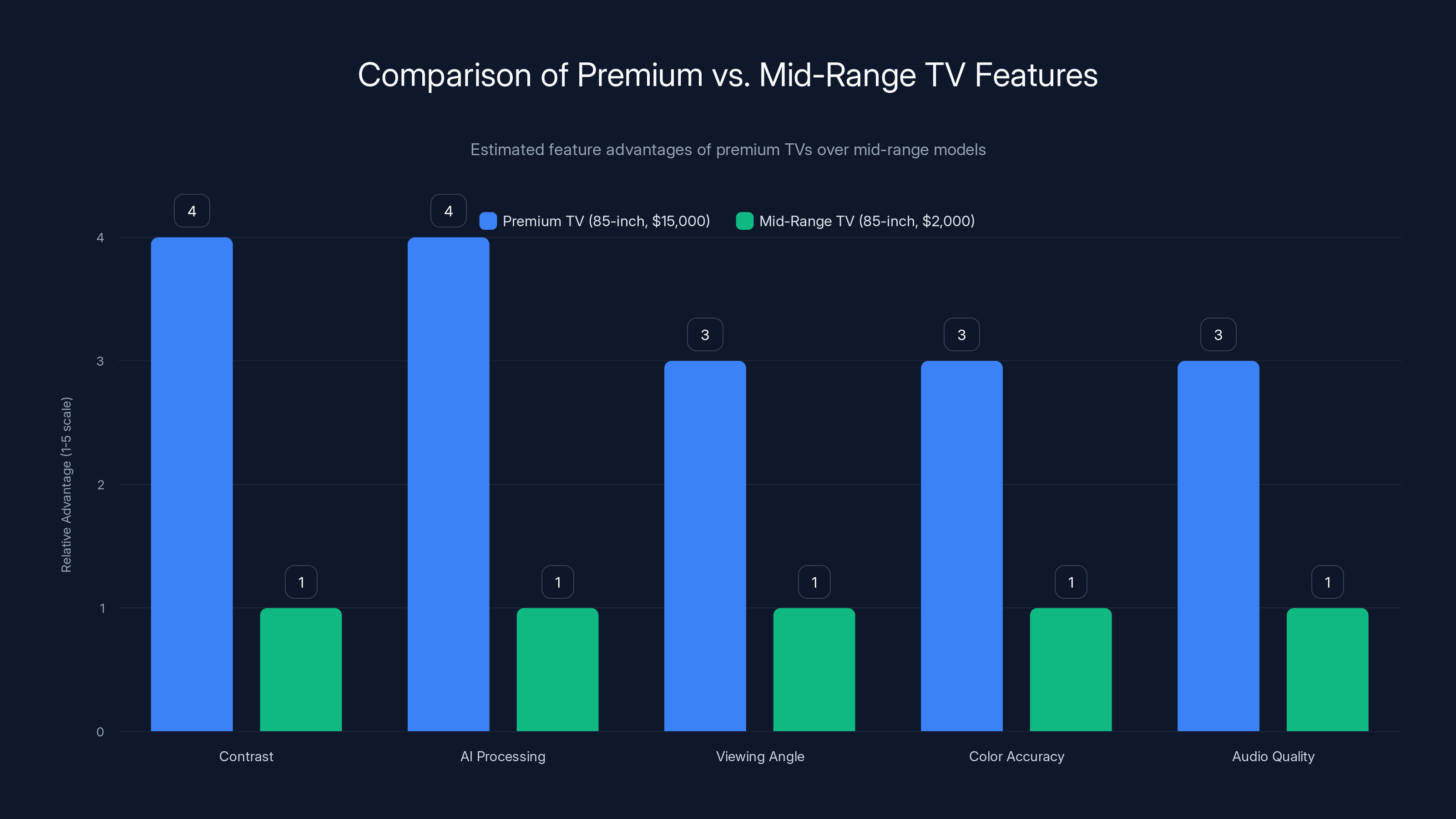
Premium TVs offer significantly better contrast and AI processing, with notable improvements in viewing angle, color accuracy, and audio quality compared to mid-range models. Estimated data.
The Scale Revolution: 130-Inch Televisions and Beyond
Engineering Challenges of Ultra-Large Displays
Displaying content on a 130-inch television screen presents engineering challenges that seem almost insurmountable on first consideration. A 130-inch TV, measured diagonally, creates a viewing surface roughly 113 inches wide and 63 inches tall—dimensions exceeding the width of most living rooms and approaching the height of standard room ceilings. Manufacturing, transporting, and supporting such massive displays requires solving problems in materials science, mechanical engineering, thermal management, and optical physics that have no precedent in consumer electronics.
The fundamental challenge involves maintaining pixel uniformity across a display large enough to cover an entire wall. As display dimensions increase, maintaining consistent brightness and color across the entire surface becomes exponentially more difficult. Light generated in one region of the display may propagate unevenly to adjacent regions due to fundamental optical properties. Thermal gradients become more pronounced over longer distances, causing different regions to maintain different temperatures and therefore different brightness and color characteristics. Manufacturing becomes statistically harder because any defect that would go unnoticed on a 65-inch display becomes glaringly obvious on a 130-inch version covering fifteen times the surface area.
Mechanical support structures for ultra-large displays must withstand significant weight while remaining flexible enough to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. A modern OLED panel of this size can weigh 200+ pounds without any bezel or stand structure. Adding the support structure, electronics, and speakers can push total weight to 400+ pounds. The stand structure must distribute this weight across a floor footprint that doesn't consume the entire living room, creating complex stress-distribution problems. Some manufacturers at CES 2026 revealed wall-mount bracket systems rated for 500+ pounds, designed specifically for ultra-large television installation.
Transportation and installation present practical challenges manufacturers have addressed through innovative design. Several companies demonstrated modular 130-inch displays that ship in two or more sections, then bolt together during installation. This approach reduces the largest individual shipment to manageable dimensions while maintaining full functionality once assembled. The bolted joints must be perfectly rigid and essentially invisible to viewers—a significant engineering achievement requiring precision manufacturing of interfacing surfaces and alignment systems.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Implications
Scaling manufacturing to produce large quantities of 130-inch displays requires investment in new fabrication facilities and processes. Display manufacturing typically occurs on large glass substrates called "mother glass," from which multiple smaller displays are cut. Larger displays consume more area per unit, reducing the number of finished products per mother glass sheet. Some manufacturers have built entirely new production lines optimized for large display production, while others have retrofitted existing facilities. This explains why 130-inch televisions remained rare at CES 2025 but appeared as multiple production models at CES 2026—the manufacturing infrastructure had finally matured.
Yield rates, the percentage of successfully manufactured displays per production run, present another challenge. Larger displays statistically encounter more manufacturing defects simply because they contain more pixels and more complex circuitry. A defect in a single pixel might be invisible on a 55-inch display but catastrophic on a 130-inch version. Manufacturers revealed at CES 2026 that they've achieved yield rates of 75-85% on 130-inch panels, meaning 15-25% of production becomes scrap. This low yield rate partly explains the premium pricing for ultra-large displays—the manufacturing cost per unit produced is extraordinarily high when a quarter of attempts fail.
Supply chain complexity increases dramatically at this scale. Instead of sourcing standard components in volume, manufacturers must commission custom components for ultra-large displays. Custom circuit boards, unique cooling systems, specialized panel adhesives, and bespoke mechanical components all require dedicated supplier relationships and longer lead times. Several companies displayed at CES 2026 have vertically integrated significant portions of their 130-inch television manufacturing, preferring to control production of critical components rather than relying on external suppliers.
Viewing Experience and Room Integration Considerations
Owning a 130-inch television fundamentally changes the living room experience in ways both obvious and subtle. The sheer screen size creates an immersive experience that smaller displays cannot match, surrounding the viewer's peripheral vision with content. For home theater enthusiasts, this represents the pinnacle of consumer display technology. However, this immersive quality requires careful consideration of viewing distance, room lighting, and content selection to achieve its potential.
Viewers sitting too close to a 130-inch display will begin seeing individual pixels, a phenomenon called the "screen door effect," where gaps between pixels become perceptible as a subtle grid pattern overlaid on the image. Manufacturers recommend sitting at least 10-12 feet from the display to avoid this effect. For viewers in smaller rooms, the optimal viewing distance for a 130-inch television exceeds the available space, creating a mismatch between the display size and room dimensions. This represents a genuine practical limitation that affects many potential buyers.
Room integration presents aesthetic challenges for permanent installation. A 130-inch television cannot be hidden away or disguised; it becomes the dominant visual element in any space. Successful integration requires thoughtful room design with coordinated colors, minimalist furnishings that don't compete for visual attention, and often professional installation by home theater specialists. The television essentially becomes interior design, not merely a device within a room. Several manufacturers showcased integration concepts at CES 2026, including frame-mounted displays that resemble artwork and room-dividing implementations that serve dual purposes.
Content quality becomes critically important at 130-inch scale. Standard definition or poorly compressed streaming content becomes noticeably degraded when displayed on such a large surface. Viewers must maintain access to high-quality source material: 4K streaming services, Blu-ray discs, or high-quality streaming at maximum bitrate. Some users have reported dissatisfaction with large displays when primarily watching compressed streaming services at lower quality tiers, as imperfections become apparent. This suggests 130-inch televisions represent best-suited solutions for dedicated home theater rooms rather than general living room television.

OLED displays excel in black levels and contrast ratio, while Mini-LEDs offer higher peak brightness. Estimated data based on typical characteristics.
The RGB Mini-LED Revolution: Superior Backlighting Architecture
Traditional Mini-LED Limitations and RGB Innovations
Mini-LED backlighting represents a mature technology that's been used in televisions since approximately 2019, but the implementation at CES 2026 reveals significant architectural improvements. Traditional mini-LED displays use thousands of tiny LEDs arranged in a grid behind an LCD panel, with each LED emitting white light. These white LEDs are then filtered through the LCD layer to produce colored pixels. This architecture enables exceptional contrast ratios because the backlight can dim to near-zero levels in dark regions while maintaining bright regions in other areas. However, white LEDs inherently create color limitations because all colors are produced by filtering white light, similar to traditional LCD technology but with far superior dimming capabilities.
RGB mini-LED technology represents a fundamental departure from this architecture. Instead of white LEDs, manufacturers use red, green, and blue micro-LEDs arranged in clusters, producing color directly from the light source rather than filtering white light. This approach, demonstrated extensively at CES 2026, offers several advantages: increased color volume (the ability to display colors at high brightness and high saturation simultaneously), reduced power consumption because light isn't wasted through filters, and more direct color control because each color channel operates independently.
The engineering challenge involves arranging millions of individual RGB mini-LEDs in precise patterns while maintaining uniformity in brightness and color. A 65-inch television display might contain over 5 million individual RGB micro-LEDs, each requiring precise positioning and reliable electrical connection. Spacing must be consistent to avoid visible patterns or brightness variations. LEDs must be thermally isolated from each other to prevent heat cross-talk where one LED's heat affects adjacent LEDs' color output. Several manufacturers revealed innovative assembly techniques at CES 2026 that use automated systems with sub-millimeter precision to position LEDs in their correct locations.
Dimming Zones and Dynamic Contrast Performance
Traditional mini-LED displays typically include 100-600 dimming zones—independent regions of the backlight that can be dimmed or brightened individually. This creates the possibility of very bright regions with very dark regions on the same screen, since the backlight can adjust brightness per zone rather than across the entire display. However, this creates a trade-off: using too few zones creates visible blooming where bright objects have halos of increased brightness in neighboring zones. Using too many zones requires exponentially more processing power and cooling capacity.
RGB mini-LED systems revealed at CES 2026 include 1,000+ dimming zones, approaching the theoretical limit where each zone comprises only a few pixels. With this many independent dimming zones, visual artifacts essentially disappear and contrast ratios reach levels previously achievable only with OLED technology. A bright white object can sit directly adjacent to pure black with minimal blooming or halo effects. Multiple manufacturers demonstrated this capability with dramatic side-by-side comparisons showing previous-generation displays with visible blooming and new displays with nearly perfect contrast isolation.
The processing requirements for managing 1,000+ dimming zones simultaneously are substantial. A dedicated processor must analyze incoming video frame by frame, determine optimal brightness levels for each zone based on upcoming content, and execute dimming commands faster than human perception can detect. Several manufacturers at CES 2026 revealed AI-accelerated processors specifically designed for this function, using machine learning trained on millions of video frames to predict optimal zone brightness values. These processors can also extrapolate brightness patterns for upcoming frames based on analysis of current and previous frames, enabling predictive dimming that further reduces visible artifacts.
Color Accuracy and Peak Brightness Combination
One of the most impressive achievements demonstrated at CES 2026 involved combining RGB mini-LED technology with advanced color management to achieve previously impossible simultaneous characteristics: extraordinary peak brightness while maintaining accurate color across the entire brightness range. Traditional displays must compromise between brightness and accuracy—bright colors often become oversaturated or shift toward the peak color (typically red), while dimming improves accuracy at the cost of brightness. RGB mini-LED systems overcome this limitation through direct color control.
When displaying bright white content, an RGB mini-LED zone simply operates all three colors at full brightness, producing maximum brightness with perfect neutral white color. When displaying a bright saturated red, only the red subunits operate at full brightness while green and blue operate at reduced levels. This allows for both high absolute brightness and accurate color because the individual color channels modulate independently. Traditional designs using white LEDs with filters cannot achieve this flexibility because the filter strength is fixed—you cannot produce bright saturated colors without either reducing overall brightness or increasing white-light brightness, creating blooming in other areas.
Manufacturers demonstrated this capability with side-by-side comparisons showing traditional mini-LED TVs with noticeable color shift in bright scenes compared to RGB mini-LED versions maintaining perfect color accuracy even at peak brightness. This represents a genuine technical advantage that translates to improved viewing experience, particularly for content with bright but color-accurate scenes—sports broadcasts with bright stadium lighting, daylight exterior scenes, or artwork with bright vibrant colors.
HDR Performance Standards and Industry Standardization
Understanding Modern HDR Content Specifications
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content has become increasingly common in streaming services, physical media, and gaming, yet many consumers remain confused about what HDR means and whether their displays truly support it. CES 2026 revealed increased industry standardization around HDR specifications, with manufacturers committing to clearer labeling and more rigorous conformance testing. Understanding these standards helps evaluate whether new televisions genuinely deliver the HDR experience they claim.
HDR specifications typically include four key parameters: peak brightness, color volume, dynamic range, and technical format support. Peak brightness specifies the maximum brightness the display can produce for small portions of the image, typically measured in nits. The critical distinction, which confused many consumers in previous years, involves "peak brightness for small areas" versus "average brightness across the entire screen." A display might achieve 1,000 nits for a small highlight while maintaining only 300 nits average across a full-white screen. The CES 2026 manufacturers increasingly distinguish between these measurements, improving transparency.
Color volume describes the intersection of brightness and color saturation—essentially, the maximum saturation achievable at different brightness levels. A display might produce highly saturated colors at medium brightness but lose saturation when brightness approaches maximum. Professional color standards like DCI-P3 define specific colors that displays must reproduce accurately. Modern HDR displays at CES 2026 claim to cover 95-99% of DCI-P3, meaning nearly all professional cinema colors are accurately producible. This represents a substantial improvement over previous years when 90% coverage was considered excellent.
Dynamic range, measured in stops, represents the brightness ratio between the brightest and darkest reproducible tones. A ratio of 1,000,000:1 represents a range of approximately 20 stops, approaching the dynamic range of human eye vision. While consumers don't need to understand stops, understanding that larger dynamic range numbers indicate superior picture quality remains important. Displays at CES 2026 boasted ranges from 100,000:1 (entry-level) to 10,000,000:1 (premium models), representing genuine technical improvements.
Dolby Vision, HDR10, and Advanced Format Support
Multiple HDR formats compete in the consumer market, each with different technical specifications and content availability. Dolby Vision, developed and licensed by Dolby Laboratories, represents a proprietary format with dynamic metadata that allows for frame-by-frame brightness optimization. Content creators include specific brightness instructions for each frame, enabling displays to maximize visual impact for that specific frame. This represents a significant advantage over static HDR formats where the same brightness parameters apply to entire scenes.
HDR10, developed through collaboration between multiple manufacturers, represents an open standard with wide industry support and content availability. HDR10 uses static metadata, meaning the same brightness information applies to entire scenes rather than individual frames. While less flexible than Dolby Vision, HDR10's open nature has enabled rapid adoption across streaming services, gaming platforms, and disc formats. Virtually every HDR television supports HDR10, making it the practical baseline standard.
At CES 2026, manufacturers emphasized support for both formats plus emerging standards like HDR10+ and HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma). Supporting multiple standards ensures maximum content compatibility and future-proofs displays against evolving industry standards. Premium displays increasingly include support for five or more HDR formats, providing assurance that nearly all existing and emerging content will display correctly. This represents a maturation of the industry away from proprietary lock-in toward inclusive standards support.
Gaming HDR and Variable Refresh Rate Optimization
Gaming represents an increasingly important use case for television displays, with next-generation gaming consoles (PS6, Xbox Series X+, successor devices) emphasizing HDR gaming experiences. Gaming HDR presents unique technical challenges compared to filmed content because games render in real-time rather than from pre-created source material, and games require responsiveness that film content doesn't. Several manufacturers at CES 2026 revealed gaming-optimized HDR implementations addressing these unique requirements.
Variable refresh rate (VRR) technology allows displays to synchronize their refresh rate with the output of gaming consoles, eliminating tearing artifacts and smoothing motion. Both HDMI 2.1 and proprietary gaming technologies like NVIDIA G-SYNC and AMD Free Sync enable VRR on television displays. At CES 2026, manufacturers demonstrated VRR at increasingly high refresh rates: 120 Hz for standard content and up to 240 Hz for gaming scenarios. HDMI 2.1 theoretically supports up to 480 Hz refresh rate, though currently, gaming devices only support up to 240 Hz.
Gaming HDR requires displays to process and display dynamic content with minimal latency while maintaining color accuracy and brightness consistency. Game developers expect consistent behavior across different displays, creating a challenge for television manufacturers seeking to apply aggressive image processing that might optimize for film content but degrade gaming quality. At CES 2026, manufacturers introduced gaming modes that disable image processing and prioritize color accuracy and low latency. These modes represent a significant improvement over previous years when gaming performance on television displays remained significantly inferior to dedicated gaming monitors.
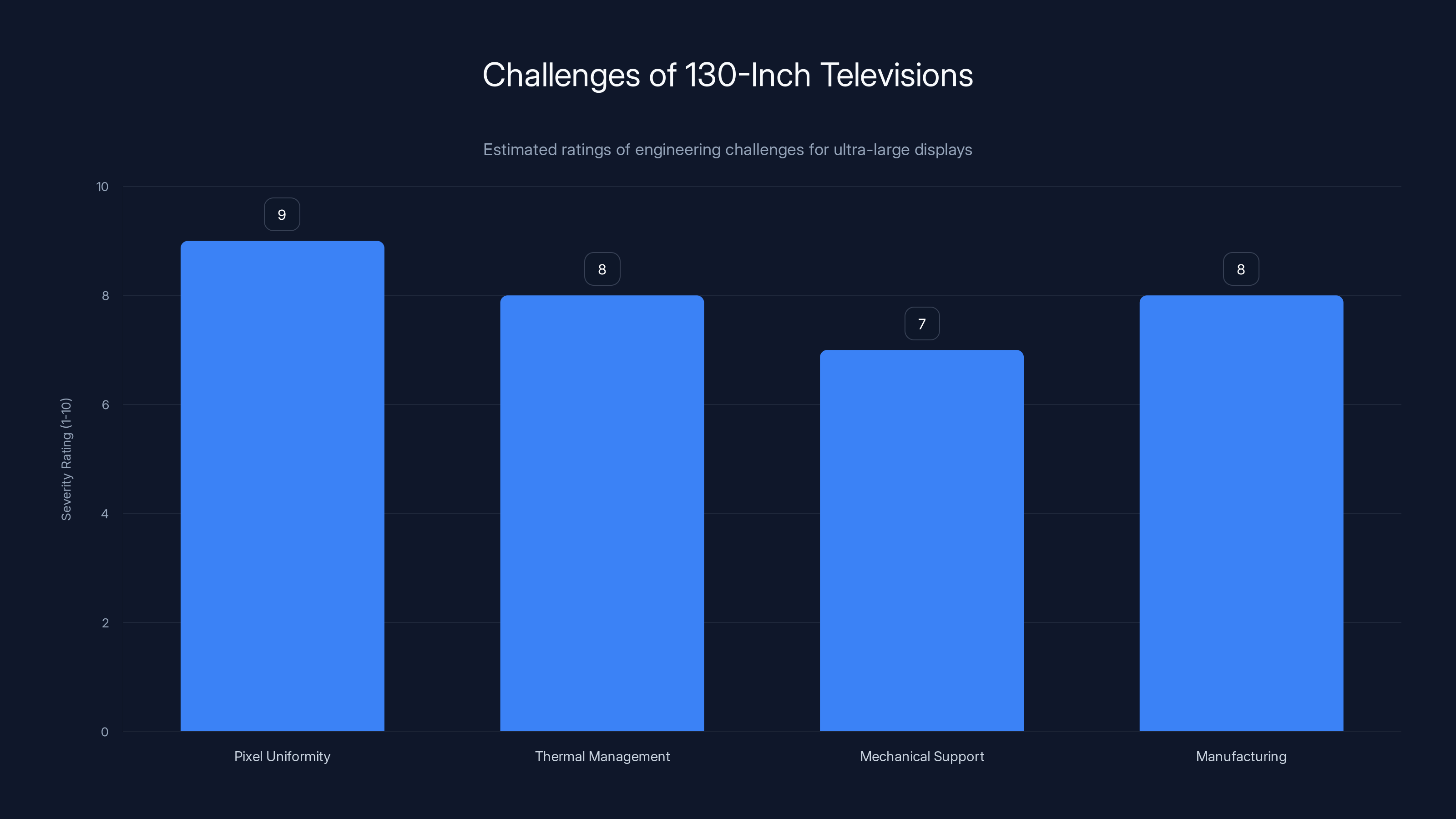
Pixel uniformity is the most severe challenge in creating 130-inch TVs, followed closely by thermal management and manufacturing issues. (Estimated data)
Processing Power and AI-Driven Picture Optimization
Real-Time Image Enhancement Algorithms
Modern televisions contain processors comparable in power to smartphones from a few years ago, enabling real-time image analysis and enhancement never previously possible. These processors analyze incoming video frame by frame—up to 120 frames per second for some models—and apply optimizations that improve perceived quality beyond the capabilities of the source material. The algorithms represent the intersection of advanced mathematics, computer vision, and machine learning, developed through years of research at major display manufacturers.
Upscaling algorithms represent one important application, using AI to reconstruct higher-resolution images from lower-resolution source material. When watching a standard-definition broadcast or legacy film content through a 4K display, native resolution is 1,920x 1,080 or lower, while the display has 4K resolution (3,840x 2,160). Older upscaling simply interpolated pixels, creating soft or blurry results. Modern AI upscaling analyzes the image content, identifies recognizable objects and patterns, and reconstructs plausible high-resolution versions maintaining important details. At CES 2026, manufacturers demonstrated upscaling comparisons where content displayed through AI upscaling appeared noticeably sharper than upscaling from previous generations, with preserved detail rather than softness.
Motion enhancement algorithms use similar techniques to interpolate intermediate frames between actual video frames. Source content typically operates at 24fps (film) or 60fps (television), but displays refresh at 120 Hz or higher. Rather than simply repeating frames, motion enhancement analyzes motion vectors and creates plausible intermediate frames. This creates the controversial "soap opera effect" where motion appears unnaturally smooth to viewers accustomed to traditional frame rates. Most manufacturers now allow viewers to disable this feature, or offer user-adjustable intensity levels, recognizing that personal preferences differ significantly.
Machine Learning for Content-Specific Optimization
Advanced processors at CES 2026 employ machine learning models trained on thousands of hours of film, television, sports, gaming, and other content types to optimize display characteristics automatically based on content type detection. The processor identifies content characteristics, determines likely content type, and applies genre-specific optimization profiles. A sports broadcast might trigger algorithms emphasizing motion clarity and color saturation in skin tones and grass, while a film movie triggers algorithms optimizing for natural color reproduction and minimizing processing artifacts that might degrade cinematic intent.
These machine learning models require substantial processing power to execute in real-time. Manufacturers revealed specialized AI accelerators within television processors, components optimized specifically for neural network processing. Similar to GPUs in computers, these AI accelerators perform the mathematical operations underlying machine learning orders of magnitude faster than general-purpose processors. This enables increasingly sophisticated models operating on every frame of video, something completely impractical without specialized hardware.
Content detection itself relies on machine learning, analyzing image characteristics to determine whether content is sports, film, television, gaming, or other categories. Different sports trigger different optimizations—basketball might emphasize detail and orange/brown tones, while soccer emphasizes green saturation and motion clarity. Manufacturers demonstrated remarkable accuracy in automatic content detection, with system behavior adapting visibly as content changed. Viewers can also manually select content types if automatic detection fails, overriding the automatic selection.
Thermal Management and Processor Optimization
Increased processor power generates increased heat, requiring sophisticated cooling systems to maintain device reliability and longevity. Modern televisions employ aluminum heat pipes, copper vapor chambers, and in some cases active cooling fans, distributing heat from the processor to heat sinks or the television cabinet itself. At CES 2026, manufacturers revealed increasingly sophisticated thermal management systems that maintain optimal processor operating temperature while minimizing fan noise—a critical consideration since television viewers tolerate less fan noise than computer users.
Processor power consumption has become a significant environmental and utility cost consideration. A television running 24/7 might consume 150-300W depending on technology and optimization. Over a decade, this might add hundreds of dollars to electricity costs. Manufacturers at CES 2026 emphasized power efficiency improvements, with some claiming 20-30% reductions in power consumption compared to previous generations despite increased processing capability. These improvements result from more efficient processor designs, better power delivery systems, and intelligent load management that keeps processors in lower-power states when full processing capability isn't required.
Connectivity and Smart Television Capabilities
HDMI 2.1 and Emerging Connection Standards
HDMI 2.1 represents the current standard for connecting high-quality video sources to televisions, supporting up to 10K resolution, higher frame rates, enhanced audio formats, and reduced latency. At CES 2026, nearly all premium televisions featured multiple HDMI 2.1 ports, enabling simultaneous connection of multiple high-bandwidth sources. However, HDMI 2.1 implementation varies significantly between manufacturers—some provide full-featured HDMI 2.1 implementation while others include reduced-capability versions labeled HDMI 2.0b or HDMI 2.1 with limited bandwidth.
Manufacturers revealed emerging connection standards at CES 2026, including USB-C video output becoming increasingly common as a future replacement for HDMI. USB-C can transmit video at high resolution and refresh rate while simultaneously delivering power and data, reducing the number of cables required. However, adoption remains limited due to compatibility concerns and the established HDMI infrastructure. Progressive migration toward USB-C seems inevitable, but HDMI will likely remain the standard for consumer televisions throughout 2026 and 2027.
Wireless video transmission standards like Wi-Fi Direct and emerging standards enabling low-latency wireless video remain in development. Several manufacturers demonstrated wireless video capabilities at CES 2026, though with important caveats: latency ranges from 5-50 milliseconds depending on implementation, making them suitable for most content but potentially problematic for gaming. As wireless technology matures, these standards may eventually reduce dependency on wired connections, but currently, wired connections remain necessary for maximum quality and performance.
Smart TV Operating Systems and Content Access
Almost all televisions sold today include built-in smart television capabilities, typically based on Android TV, web OS, Roku, Tizen, or proprietary operating systems. CES 2026 revealed increasingly sophisticated smart TV interfaces that anticipate user preferences and provide personalized content recommendations. Machine learning algorithms analyze viewing history and patterns to suggest likely content preferences, adapting recommendations based on time of day, viewing context, and seasonal factors.
Manufacturers increasingly emphasized interoperability between their smart TV platforms and multi-device ecosystems. Televisions can serve as hubs for smart home devices, connect seamlessly with smartphones and tablets, and participate in broader smart home networks. Several manufacturers demonstrated voice control capabilities that understand natural language and context, enabling commands like "show me the weather and my calendar while I eat breakfast," with displays automatically organizing multiple information sources on the television screen.
Content fragmentation remains a challenge, with different streaming services available on different platforms. CES 2026 showed manufacturers attempting to unify access through aggregation apps that compile content recommendations across services. Rather than navigating separately through Netflix, Prime Video, Disney+, and other services, unified interfaces provide recommendations combining all available content. While not perfect, these aggregation approaches reduce friction in finding content to watch.

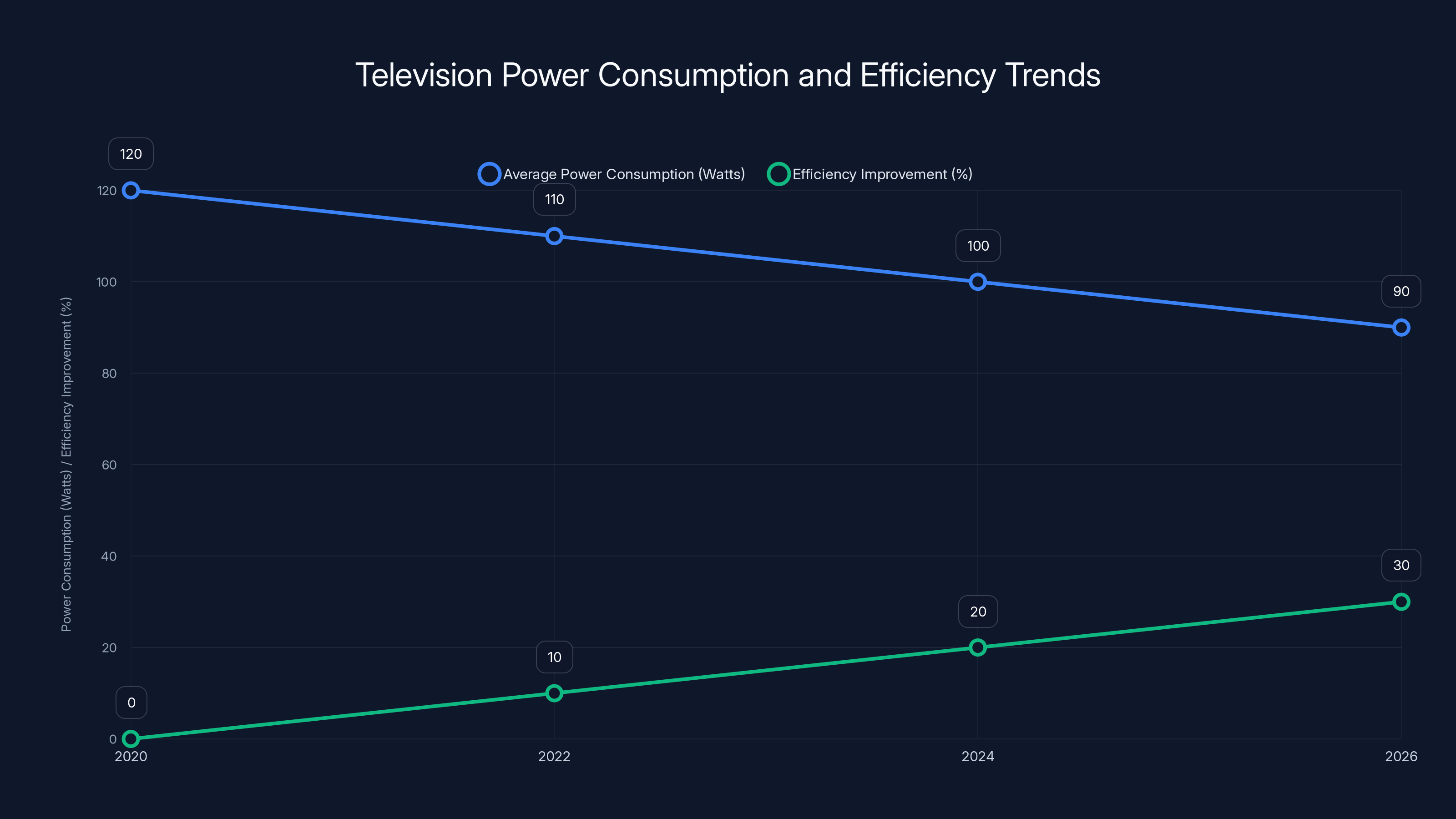
Television power consumption has decreased significantly from 2020 to 2026, with efficiency improvements reaching up to 30%. Estimated data highlights the impact of technological advancements and efficiency standards.
Audio Technologies and Integrated Sound Systems
Television Audio Evolution and Surround Sound Integration
Modern television speakers have improved substantially from the tinny, inadequate audio of older displays, but they remain fundamentally limited by physical constraints. Ultra-thin television designs leave minimal space for substantial speaker systems, and sound production requires physical displacement of air, which thin bezels cannot accommodate. At CES 2026, manufacturers revealed several approaches to improving television audio despite these constraints, ranging from improved speaker placement to external sound system integration.
Object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos enable precise spatial audio, with sounds appearing to emanate from specific points in three-dimensional space. Premium television displays at CES 2026 included built-in Atmos support through clever speaker arrangements positioning drivers at different angles and using audio processing to create directional effects. While not equivalent to dedicated Atmos speaker systems, built-in Atmos creates noticeable spatial effects that improve audio immersion compared to traditional stereo sound.
Several manufacturers demonstrated wireless speaker integration, where televisions automatically detect compatible speakers and enable surround sound through wireless connection. The television handles audio processing internally, then distributes processed surround and center channel audio to wireless speakers. While introducing latency concerns, carefully optimized wireless systems can minimize perceptible delay. This approach simplifies home theater setup compared to running speaker cables through walls and ceilings.
Wireless Audio Transmission and Latency Reduction
Wireless audio transmission has advanced significantly, with modern standards like Wi SA (Wireless Speaker Association) and Bluetooth enabling increasingly high-quality transmission. However, wireless transmission inherently introduces latency—the slight delay between when audio is generated and when it's reproduced from speakers. For music or dialogue, latency below 100 milliseconds is generally imperceptible. For gaming, latency below 20 milliseconds is required to avoid obvious out-of-sync sensations. At CES 2026, manufacturers demonstrated wireless audio systems with latency measurements of 15-30 milliseconds, approaching gaming-acceptable performance levels.
The challenge involves maintaining low latency while transmitting high-quality audio across multiple speakers in complex wireless environments. Radio frequency interference from Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and other wireless devices can disrupt audio transmission or increase latency. CES 2026 displays revealed adaptive protocols that detect interference and either switch channels or increase transmission robustness, maintaining connection quality despite challenging environments. Some systems employ dedicated wireless protocols optimized for video and audio transmission rather than relying on standard Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.

Design Philosophy and Industrial Design Innovation
Bezel Design and Screen-to-Body Ratio Trends
Display bezels—the non-display areas surrounding the screen—represent a design challenge and opportunity. Thinner bezels provide more screen in the same physical footprint and create a more premium visual appearance. However, bezels serve important functions: containing the display's internal electronics, providing structural support, and hiding dead pixel areas. CES 2026 showed manufacturers reaching practical limits in bezel reduction, with some displays featuring bezels as thin as 3-5 millimeters on the sides and top, though bottom bezels typically remain thicker to accommodate speaker and control placement.
Several manufacturers revealed innovative bezel integration concepts, including transparent bezels using see-through acrylic materials, though transparency trades brightness and contrast for this visual effect. Others demonstrated minimal bezels achieved through relocating internal electronics to different display layer locations. The practical reality is that ultra-thin bezels require either accepting compromised image quality at bezel edges or accepting higher manufacturing costs and design constraints.
Stand design and wall-mount optimization received significant attention at CES 2026. Manufacturers recognized that televisions increasingly hang on walls rather than sitting on stands, shifting design priorities toward cable management integration and minimal stand footprints for those who prefer stand placement. Some models featured cable channels built into the stand and back panel that allow careful wire routing with minimal visible cables. This represents a design-focused improvement that doesn't affect image quality but improves overall aesthetic impact.
Material Innovation and Sustainability Considerations
Display manufacturers increasingly prioritized sustainable materials and manufacturing practices, recognizing that consumers increasingly consider environmental impact when making purchasing decisions. CES 2026 revealed manufacturing commitments toward recycled plastics, reduced manufacturing waste, and improved product recyclability. Some manufacturers achieved 50%+ recycled content in plastic components, while maintaining necessary performance characteristics.
Refurbishment and component upgrade capabilities represent another sustainability innovation revealed at CES. Some manufacturers designed displays modularly, enabling replacement of aging components rather than requiring complete device replacement. For example, power supplies or LED backlights could theoretically be replaced, extending display lifespan to 15-20 years rather than the typical 8-10 year expected lifespan. While not widely implemented yet, this represents a long-term trend recognizing that reducing manufacturing overall is more environmentally responsible than manufacturing for short lifespans.

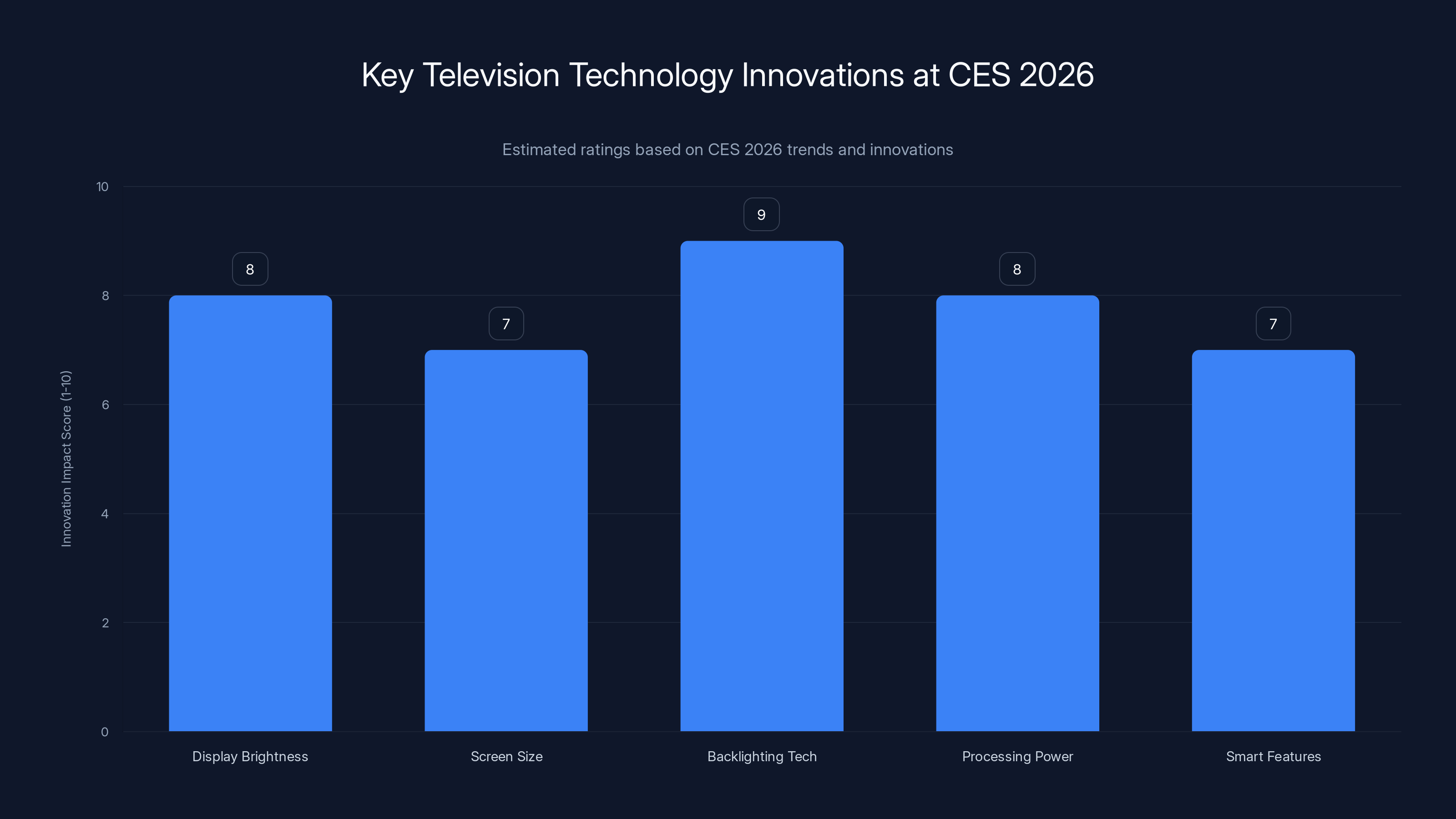
CES 2026 highlighted significant innovations across various television technologies, with backlighting technology and display brightness showing the highest impact. Estimated data.
Pricing and Market Segmentation Strategy
Premium Segment Pricing and Technology Justification
Premium television displays at CES 2026 reached prices exceeding
A
Manufacturers use premium segments to establish brand prestige and justify margins that fund R&D for technologies that eventually reach mid-range and budget segments. A technology costing
Mid-Range Segment Value Propositions
Mid-range televisions at
Value in mid-range displays comes from selective feature implementation: mini-LED with fewer dimming zones than premium models, competent but not cutting-edge AI processing, and adequate but not premium audio systems. These trade-offs reduce cost while maintaining the most important performance characteristics. For viewers prioritizing overall quality while managing budgets, mid-range displays typically offer optimal value. The performance gains stepping up from budget to mid-range are substantial—typically 30-50% improvement in contrast and picture quality. Stepping from mid-range to premium provides improvements that may not justify the expense for typical viewers.
Budget Segment Innovations and Accessibility
Budget televisions at
The trade-off in budget displays primarily involves brightness, contrast ratio, and color accuracy. A budget display might achieve 500 nits peak brightness while premium displays reach 3,000+ nits, making a substantial difference in bright room viewing. Contrast ratios might measure 1,000:1 compared to 100,000:1 in premium models, meaning less separation between bright and dark content. Color accuracy might cover 85% of DCI-P3 instead of 99%, meaning some colors display with slight inaccuracy. These differences might prove barely perceptible in casual viewing but become glaring in side-by-side comparisons or dedicated home theater environments.

Gaming Performance and Next-Generation Console Optimization
120fps Gaming and Ultra-Low Latency Support
Next-generation gaming consoles and gaming PCs increasingly target 120 frames per second (fps) at 4K resolution, demanding display support for these specifications. Televisions supporting 120fps gaming require HDMI 2.1 bandwidth, variable refresh rate support, and specialized processing to minimize latency. Input lag—the delay between controller input and on-screen response—must measure under 20 milliseconds for responsive gameplay feeling, creating a technical challenge for television displays traditionally designed for content consumption with more lenient timing requirements.
Manufacturers at CES 2026 emphasized gaming mode optimizations that disable image processing that might introduce latency, enabling direct video pass-through to the display with minimal processing. Frame interpolation, motion enhancement, and other processing features that improve film viewing actually degrade gaming experience by introducing latency. Gaming modes keep this processing disabled, prioritizing responsiveness over image enhancement. Some premium displays measured input latency below 4 milliseconds, competitive with dedicated gaming monitors.
Variablе refresh rate technology enables the display refresh rate to match the game's frame rate dynamically, eliminating tearing (horizontal lines where the display refreshes while drawing a frame) and stuttering (inconsistent frame rate creating jerky motion). Both NVIDIA G-SYNC and AMD Free Sync work on 2026 displays, with HDMI 2.1 including VRR support enabling these technologies across different gaming platforms. Multiple manufacturers demonstrated gaming scenarios running at variable frame rates that previously would have displayed visual artifacts, now appearing smooth and artifact-free.
VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) Implementation and Standard Support
VRR implementation varies between manufacturers and between different VRR standards (G-SYNC, Free Sync, HDMI VRR), creating complexity for consumers unsure which displays support their specific gaming devices. At CES 2026, manufacturers increasingly supported multiple VRR standards simultaneously, ensuring compatibility with virtually any gaming device. This represents a maturation toward interoperability from earlier fragmentation where different standards competed without mutual support.
Refresh rate ranges supported by VRR also expanded significantly. Earlier implementations supported VRR between 40-120 Hz, meaning frame rates outside this range would disable VRR and introduce tearing. CES 2026 displays support broader ranges, typically 24-120 Hz, covering virtually all gaming scenarios. Some displays support up to 240 Hz refresh rate for gaming hardware capable of 240fps output, though current gaming consoles max out at 120fps.
Ray Tracing and Advanced Graphics Support
Next-generation gaming embraces ray tracing—realistic lighting simulation that calculates light paths through virtual scenes rather than using simplified approximation—creating extraordinarily realistic lighting and shadows. Ray-traced gaming requires displays capable of reproducing subtle lighting variations, high contrast ratios for realistic shadows, and low input latency since ray tracing computationally demands high frame rates. Displays optimized for ray-traced gaming emphasize these characteristics.
Manufacturers revealed display technologies optimized specifically for ray-traced content, using advanced contrast enhancement and color mapping to maximize visual impact of detailed ray-traced scenes. However, the fundamental requirement is simply a high-quality display with excellent contrast and color accuracy—no special display technology is required specifically for ray tracing. Marketing sometimes creates confusion by claiming ray tracing optimization, when really the displays are simply very good overall quality displays.

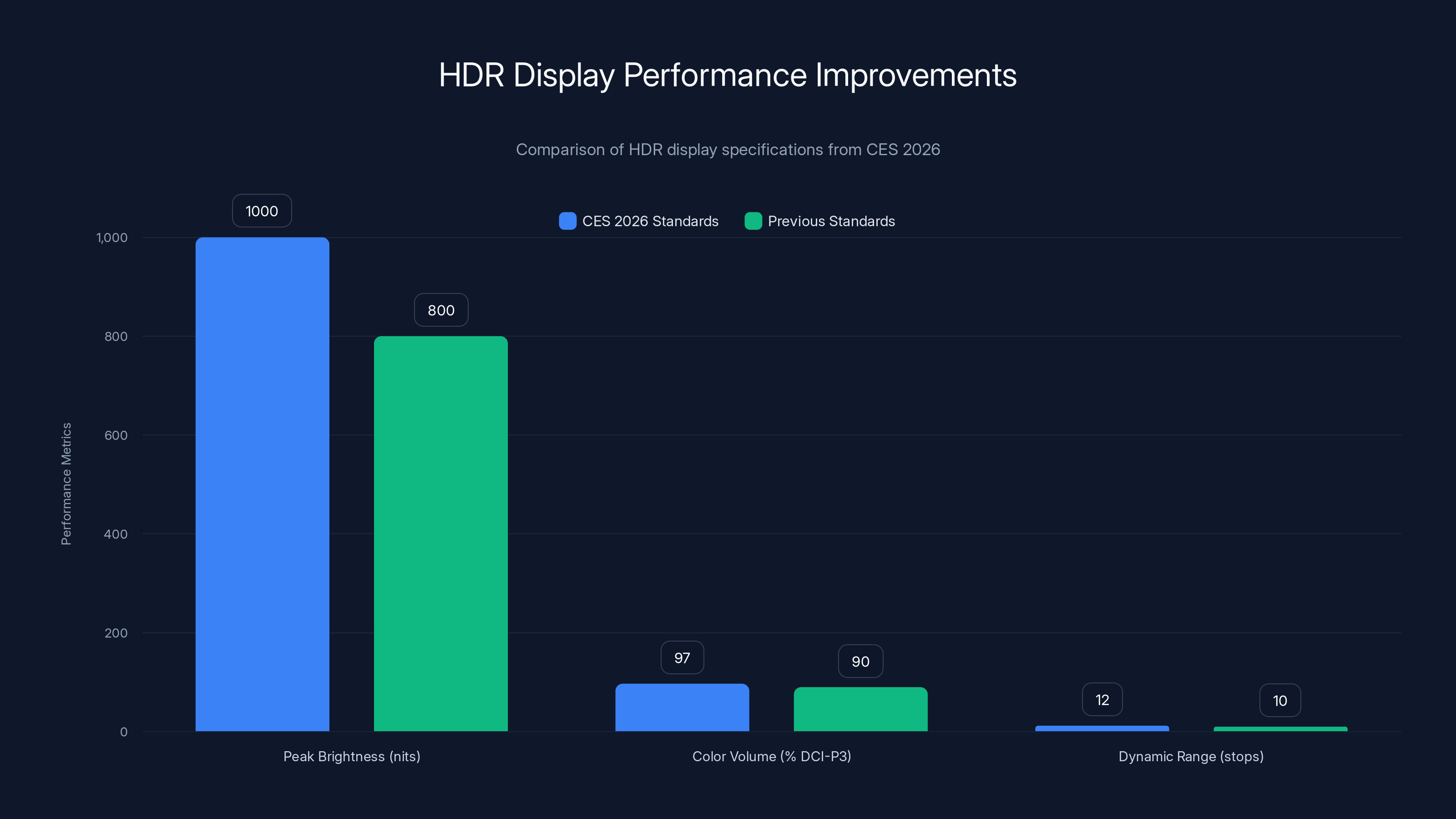
CES 2026 revealed improved HDR standards with higher peak brightness, better color volume coverage, and enhanced dynamic range compared to previous years. Estimated data.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Power Consumption Trends and Efficiency Standards
Television power consumption has become increasingly important as environmental consciousness grows and electricity costs accumulate over product lifespans. A 100-watt television running 24/7 for 10 years consumes approximately 8,760 kilowatt-hours, costing $1,000-2,000 depending on local electricity rates and representing significant environmental impact. Manufacturers at CES 2026 increasingly prioritized power efficiency improvements, with some achieving 30-40% reductions compared to previous generations despite increased processing power and display brightness.
Energy Star certification has become increasingly meaningful, with certified displays meeting rigorous efficiency standards. The program focuses on off-mode power consumption (standby), on-mode consumption, and overall energy per brightness unit, encouraging manufacturers to optimize across all operating states. At CES 2026, manufacturers showcased Energy Star certified displays, some achieving efficiency levels that would have seemed impossible just years earlier.
Ambient light sensors represent another efficiency innovation, where televisions automatically adjust brightness based on room lighting conditions. Bright room environments automatically receive increased display brightness for adequate visibility, while dark rooms automatically reduce brightness to comfortable levels. This not only improves viewing comfort but reduces power consumption significantly—a television that might consume 150W at maximum brightness uses substantially less power at automatically reduced brightness. However, viewers must trust the automatic adjustment and resist overriding settings, sometimes challenging for those preferring manual control.
Manufacturing Footprint and Supply Chain Sustainability
Manufacturers increasingly published environmental impact data, including carbon emissions from manufacturing, transportation, and recycling. Companies like LG and Samsung highlighted their renewable energy usage in manufacturing facilities and carbon-neutral commitments by specific future dates. While some skepticism is warranted regarding sustainability claims that sometimes involve offset purchasing rather than actual emission reduction, the trend toward transparency and accountability improves accountability compared to previous industry silence on environmental issues.
Recycling programs at CES 2026 received increased emphasis, with manufacturers implementing take-back programs for old displays. Some programs guarantee display recycling at end-of-life with recovery of valuable materials like rare earth elements from LED backlighting and glass from display panels. While participation remains modest, these programs represent important infrastructure for managing the eventual obsolescence of billions of television displays from previous years.

Installation and Setup Considerations
Professional Installation Services and Home Integration
Ultra-large displays and advanced televisions with extensive connectivity requirements increasingly benefit from professional installation. Many manufacturers partnered with installation services to offer white-glove delivery, wall mounting, cable management, and setup services. For 130-inch displays requiring complex wall mounting and extensive calibration, professional installation becomes practically necessary for most consumers lacking home theater expertise.
Professional installers calibrate displays for optimal performance using specialized equipment that measures brightness, color accuracy, and other parameters, then adjusts display settings for maximum performance in specific room environments. A properly calibrated display can appear noticeably better than the same display using default settings, particularly for color-critical applications like film viewing. Calibration services range from $500-2,000 depending on display size and room complexity.
Integration with existing home theater systems, smart home networks, and other devices requires careful planning during installation. Installers coordinate networking setup, speaker system integration, and overall room design to maximize visual and audio quality. For consumers investing in expensive displays, professional installation services often prove worthwhile despite additional costs.
Wall Mounting and Structural Requirements
Wall mounting introduces considerations around structural capacity of typical residential walls. Most interior drywall walls supported by wooden studs cannot safely support 130-inch television weight without reinforcement. Professional installers verify wall structure and potentially install additional support behind the wall before mounting displays. For brick or concrete walls, installation becomes simpler but requires appropriate hardware rated for masonry.
Cable routing behind mounted displays requires careful planning. Running cables through walls works for some installations but creates maintenance challenges if equipment requires replacement. Visible cable management represents an alternative in some room configurations, using cable covers or routing cables along baseboards and edges to minimize appearance. At CES 2026, manufacturers increasingly provided cable routing guides and organization systems simplifying installation.

Comparison of Major Manufacturer Approaches
Samsung, LG, Sony, TCL, and Hisense Market Positioning
Different manufacturers took notably different approaches at CES 2026, reflecting different strategic priorities and technological strengths. Samsung emphasized QD-OLED technology with brightness achievements exceeding competitors, positioning themselves as brightness leaders. LG continued emphasizing WOLED advantages in color accuracy and longevity, with particular focus on premium WOLED models. Sony positioned themselves as the brand for professional-grade picture quality, emphasizing color science and detailed image processing. TCL and Hisense emphasized value propositions, delivering capable displays at aggressive pricing for budget and mid-range segments.
These positioning strategies create different trade-offs worth understanding. Samsung's brightness focus suits bright room viewing and gaming applications where brightness improves responsiveness perception. LG's WOLED focus suits dedicated home theater environments where peak brightness matters less than sustained color accuracy. Sony's professional positioning commands premium prices reflecting superior color science and detailed calibration. Budget brands provide competent performance at prices palatable to cost-conscious consumers willing to accept some performance compromises.
Mini-LED vs. OLED Strategic Positioning
Mini-LED and OLED represent different technological approaches to high-quality television displays, and manufacturers increasingly aligned with specific technologies. Samsung and LG leveraged OLED expertise to dominate the OLED market, while TCL, Hisense, and emerging brands invested heavily in mini-LED technology. The distinction reflects different manufacturing expertise: OLED requires mastery of organic electronics and vacuum deposition, while mini-LED demands expertise in precision LED assembly and millions of individual light sources.
Each technology excels in specific applications. OLED's perfect black levels and superior contrast make it ideal for dark room home theater. Mini-LED's brightness and power efficiency make it better suited to bright rooms and extended gaming sessions. As both technologies mature and approach theoretical limits, the distinction between them becomes narrower, with both capable of excellent performance at equivalent price points. The CES 2026 marketplace demonstrates both technologies have viable futures rather than one supplanting the other.

Future Technology Roadmap and Emerging Innovations
Micro-Display Technology and Virtual Reality Integration
Micro-display technology, potentially enabling glasses-based displays worn by viewers rather than traditional wall-mounted televisions, represents a long-term future direction shown in concept form at CES 2026. These theoretical displays would project high-resolution images directly onto viewers' eyes, eliminating the need for physical television sets. While current technology remains primitive and consumer adoption likely decades away, prototypes demonstrated at CES suggest active development of this technology by major manufacturers.
Implementing micro-display technology requires solving numerous challenges: power efficiency to enable multi-hour use without draining batteries, focus mechanisms allowing individual eye adjustment, eye-tracking for gaze-directed rendering, and visual system designs minimizing cybersickness from sustained micro-display viewing. Several patents filed by manufacturers suggest serious research efforts in these areas, though consumer products remain years away.
Stretchable and Flexible Display Prototypes
Flexible display technology enabling curved or stretchable viewing surfaces represents another emerging direction shown in limited prototypes at CES 2026. Imagine a television that rolls into a compact tube for storage, then unfolds into a large flat display. Or a curved display that stretches to different proportions for different content. While truly practical implementations remain years away, prototype demonstrations showed the concept as potentially viable long-term technology.
The manufacturing and practical challenges are substantial: creating flexible substrates maintaining electrical integrity under physical deformation, developing deformable backlighting systems, and designing cooling systems that work with irregular shapes. Current prototypes exist primarily as research demonstrations rather than products approaching commercialization, but their presence at CES 2026 indicates serious manufacturer investment in long-term display technology evolution.
Holographic and 3D Display Advances
Holographic displays capable of producing true three-dimensional images without requiring special glasses remain a long-sought goal demonstrated in various prototype forms at CES 2026. Current implementations struggle with limited brightness, narrow viewing angles, and computational requirements approaching real-time processing limitations. However, steady progress suggests that viable consumer holographic displays might become feasible within 10-15 years, though substantial technical challenges remain.
Three-dimensional displays using glasses or autostereoscopic (glasses-free) approaches have been attempted repeatedly without achieving significant commercial success, primarily because viewers tolerate the slight discomfort and image quality reduction of 3D viewing for limited time periods. Without special glasses, autostereoscopic displays require viewers to remain within narrow head positions, limiting practical use. Holographic displays overcome these limitations but require solving other substantial challenges in power consumption and processing capability.
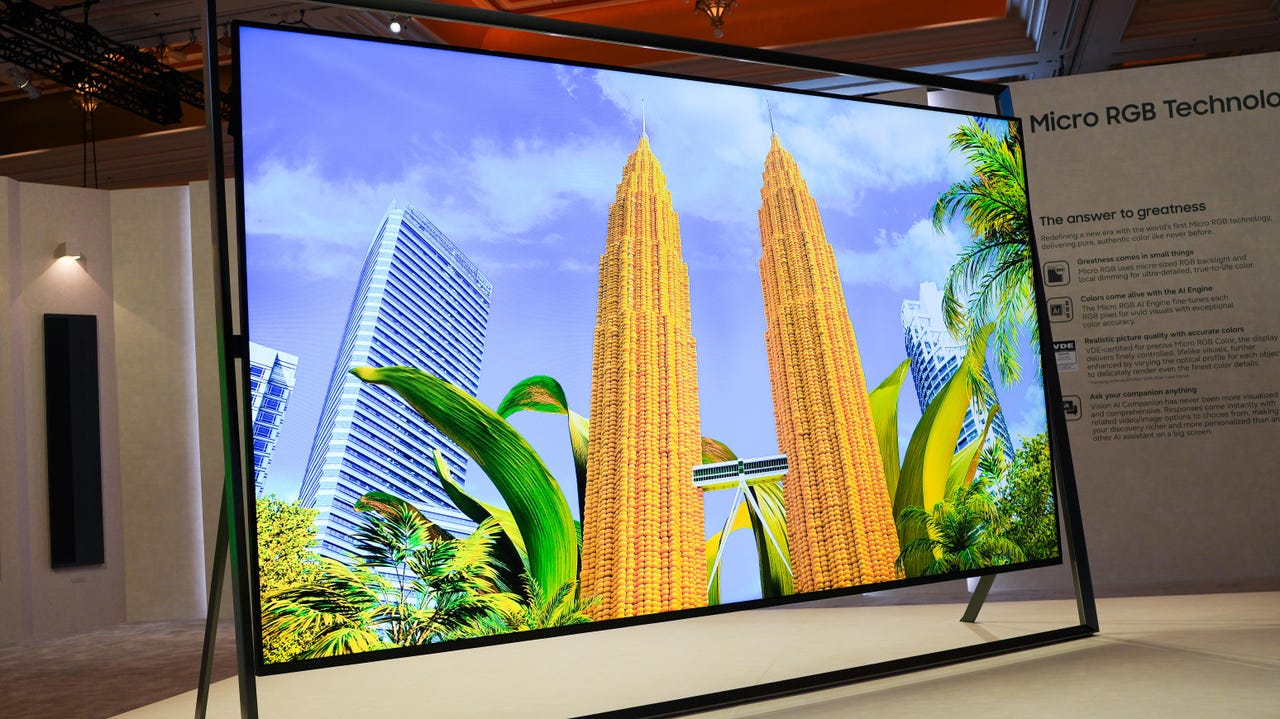

Purchasing Guide and Decision Framework
Determining Your Needs and Priority Characteristics
Purchasing a television requires identifying your specific needs and priorities before evaluating specific models. Start by considering viewing environment: bright rooms benefit from high brightness; dark dedicated home theaters prioritize contrast and color accuracy. Viewing distance matters—larger displays suit longer viewing distances; viewing from 6-8 feet away might benefit more from a mid-size display than a massive 130-inch television. Content preferences influence priorities: gamers prioritize low latency and refresh rate support; film enthusiasts prioritize color accuracy; casual viewers might prioritize value and features.
Room integration and space constraints significantly impact purchasing decisions. A 130-inch television requires specific room dimensions and wall preparation. A high-brightness premium display needs appropriate room lighting for visibility. Smart TV features require home network availability. Connectivity requirements depend on external device specifications. Creating a comprehensive list of your specific requirements helps narrow the overwhelming array of choices.
Technology Selection and Performance Trade-offs
Deciding between OLED and mini-LED involves understanding trade-offs: OLED offers superior contrast and color accuracy for dark room viewing, while mini-LED offers superior brightness and efficiency for bright rooms and gaming. QD-OLED offers better brightness than traditional WOLED but potentially worse longevity. RGB mini-LED offers better color than white mini-LED but increased complexity and cost. Understanding these trade-offs helps select technology matching your specific use case.
Screen size selection involves balancing immersion with practical constraints. Determining optimal viewing distance using the formula (display diagonal / 1.5 = recommended minimum viewing distance in feet) helps ensure appropriate size selection. A 75-inch display with 2.5-foot viewing distance creates uncomfortable pixel visibility; a 55-inch display viewed from 10 feet away appears too small. Getting the size-distance relationship right maximizes viewing satisfaction.
Brand Reliability and Long-term Support Considerations
Brand selection influences long-term satisfaction through warranty support, software update availability, and overall reliability. Major brands like Samsung, LG, and Sony offer comprehensive warranty programs and extended support options. Budget brands provide minimal support, which may not matter if displays prove reliable, but creates risk if failures occur beyond warranty periods. Evaluating brand track records through user reviews and warranty terms helps predict long-term satisfaction.
Software support longevity affects smart TV usability over extended lifespans. Some brands commit to supporting displays with software updates for 5+ years after purchase; others abandon support within 2-3 years. For buyers planning extended ownership, long-term software support becomes increasingly important as security vulnerabilities and operating system obsolescence become concerns. Checking manufacturer commitments before purchasing helps inform long-term value assessment.

Conclusion: The Television Evolution Continues
CES 2026 demonstrated that television technology remains far from mature, with substantial innovation continuing across multiple dimensions: display brightness, screen size, backlighting technology, processing power, and smart features. The convergence of multiple technological approaches—OLED, mini-LED, advanced processing—creates a rich ecosystem where different solutions excel for different use cases rather than a single superior technology dominating all applications.
The brightness breakthroughs demonstrated at CES 2026 address long-standing OLED limitations while mini-LED continues advancing in precision and color control. Ultra-large 130-inch displays, while remaining niche products, represent the culmination of decades of display technology advancement enabling unprecedented scale. RGB mini-LED technology provides mini-LED advantages previously achievable only with OLED, demonstrating convergence between competing approaches toward unified performance levels.
For consumers considering television purchases in the coming months and years, the CES 2026 innovations provide clarity about which technologies represent genuine advancement versus marketing hype. Understanding peak brightness versus average brightness, dimming zone counts, color volume, and contrast ratios enables informed comparison between competing displays and manufacturers. The breadth of choice—from budget displays delivering surprising capability to ultra-premium displays pushing technical boundaries—means displays exist for virtually every budget and requirement.
The television market evolution also reflects broader technology industry patterns: increasing AI integration, enhanced energy efficiency despite greater capability, improved connectivity and integration with smart home ecosystems, and continued optimization toward immersive experiences. These trends will continue accelerating through 2027 and beyond, with technologies shown as prototypes at CES 2026 becoming standard features in 2027-2028 models.
For those investing in television purchases, the CES 2026 announcements suggest waiting slightly for 2026 model availability allows access to revolutionary technologies like RGB mini-LED and next-generation OLED at prices approaching previous-generation levels. Those needing televisions immediately can confidently select from current models that remain highly competitive, knowing that feature gaps will eventually close through typical technology progression patterns. The television market has never been stronger, with genuine innovation and strong competition between manufacturers driving continued improvement and value expansion for consumers.

FAQ
What does "peak brightness" mean in television specifications?
Peak brightness, measured in nits, represents the maximum light a display can produce for small portions of the image, typically 3-10% of the screen. This differs from average brightness, which measures the overall light across a full-white screen and is typically 1/3 to 1/5 of peak brightness. Understanding the distinction helps accurately compare displays, since marketing sometimes emphasizes peak brightness while average brightness better reflects real-world viewing brightness.
How do mini-LED displays differ from OLED displays?
Mini-LED displays use thousands of tiny LEDs arranged in zones behind an LCD panel to provide dynamic backlighting with independent dimming control per zone. OLED displays have each pixel produce its own light independently, enabling perfect blacks and superior contrast but historically producing less peak brightness. Modern implementations increasingly blur the distinction, with mini-LED achieving OLED-like contrast through thousands of dimming zones and OLED achieving mini-LED-like brightness through new materials and thermal management innovations.
What is variable refresh rate (VRR) and why does it matter for gaming?
Variable refresh rate technology allows a display's refresh rate to adjust dynamically based on the gaming device's output, synchronizing them perfectly. This eliminates tearing (horizontal lines visible when refresh rate mismatches frame output) and stuttering (inconsistent frame rate creating jerky motion). For gaming, VRR creates dramatically smoother motion and more responsive gameplay, particularly at variable frame rates where traditional fixed-refresh displays struggle. VRR support is particularly important for next-generation gaming consoles targeting 120fps gaming.
How many dimming zones do I need in a mini-LED television?
More dimming zones generally mean better contrast performance, but with diminishing returns beyond certain thresholds. Televisions with 500+ zones provide excellent contrast for most viewers, essentially matching OLED performance in many scenarios. Displays with 100-300 zones offer acceptable performance for typical viewing but visible blooming (halos around bright objects) may appear in specific content. Fewer than 100 zones produce noticeable visual artifacts. For premium picture quality, 1,000+ zones represent the current state-of-the-art, providing essentially perfect contrast control.
What is RGB mini-LED and how does it improve on traditional mini-LED?
RGB mini-LED uses red, green, and blue micro-LEDs arranged in clusters instead of white LEDs with filters, enabling direct color generation from the light source. This approach increases color volume (ability to display colors at high brightness and saturation simultaneously), reduces power consumption by eliminating filter losses, and provides more precise color control. RGB mini-LED essentially combines mini-LED's brightness and zoning advantages with color control previously achievable only with OLED, representing a significant advancement in backlighting technology.
Are 130-inch televisions practical for typical living rooms?
No, 130-inch displays represent specialized installations requiring room dimensions beyond typical residential environments. The display itself, without bezels, measures approximately 113 inches wide and 63 inches tall. Proper viewing distance recommendations suggest sitting 10-15 feet away for comfortable viewing without visible pixels. If your viewing distance is less than 10 feet or your living room width is less than 120 inches, consider smaller displays. 130-inch televisions suit dedicated home theater rooms or large commercial installations rather than typical living rooms.
How important is HDR support when choosing a television?
HDR support has become essential for modern televisions since HDR content is increasingly available through streaming services, gaming consoles, and physical media. Without HDR support, you cannot access this content's enhanced brightness and color advantages. However, HDR capability varies substantially between displays—true HDR performance requires adequate brightness and color volume, not merely HDR format support. A display supporting HDR technically but lacking sufficient brightness provides minimal HDR benefit compared to non-HDR alternatives.
What's the difference between Dolby Vision and HDR10?
Dolby Vision uses dynamic metadata that provides frame-by-frame brightness optimization instructions, allowing every frame to achieve maximum visual impact for that specific frame. HDR10 uses static metadata applying the same brightness information to entire scenes. Dolby Vision offers superior optimization for carefully mastered content but requires licensing and manufacturers to implement support. HDR10's open standard ensures universal compatibility. Most streaming services support both formats, allowing displays supporting both to provide optimal experiences across content types. For practical viewing, either format provides substantial improvements over SDR content.
How much power does a modern television consume?
Modern 55-75 inch televisions typically consume 80-150 watts during normal viewing, with consumption varying based on brightness settings, content type, and technology. Minimum power consumption (standby) should measure under 1 watt. Maximum power consumption during peak brightness scenes might reach 200+ watts on premium models. Over a 10-year lifespan with 6 hours daily viewing, a 100-watt television consumes approximately 2,190 kilowatt-hours, costing roughly
What does "color volume" mean and why is it important?
Color volume describes the range of colors displayable at different brightness levels, essentially measuring how saturated colors can be at bright, medium, and dark brightness levels. A display with poor color volume might display highly saturated colors only at medium brightness, with colors becoming desaturated (less vivid) at high brightness or shifted toward white at dark brightness. Superior color volume means colors remain accurate and vibrant across the entire brightness range, which is particularly important for HDR content where highlights and shadows contain saturated colors requiring accurate reproduction.

Key Takeaways
- Brightness breakthroughs in 2026 OLED displays address previous limitations, with peak brightness reaching 2,000-3,000 nits through improved materials and thermal management
- 130-inch displays represent manufacturing achievements but practical limitations for typical living rooms; optimal for dedicated home theater installations only
- RGB mini-LED technology combines mini-LED brightness and zoning with superior color control previously exclusive to OLED, representing meaningful advancement
- Gaming optimization including 120fps support, VRR, and sub-20ms latency is increasingly standard in 2026 models, making televisions viable gaming displays
- Dimming zones matter significantly for mini-LED performance, with 500+ zones providing excellent contrast and 1,000+ zones approaching OLED capabilities
- Technology selection should reflect viewing environment and content priorities rather than assuming premium is universally best
- Price-to-performance sweet spots exist in mid-range displays ($2,000-4,000) delivering meaningful improvements over budget displays without premium pricing
- HDR support requires adequate brightness and color volume, not merely format support—true capability varies significantly between displays claiming HDR
- Professional installation becomes increasingly valuable for ultra-large displays and complex home theater integration scenarios
- Sustainability considerations including energy efficiency and recycling programs increasingly differentiate manufacturers and influence long-term cost of ownership

Related Articles
- Best 75-Inch TVs for Movies & Sports [2025]
- Why Samsung's Ballie Robot is Probably Never Coming Out [2026]
- Brunswick Boats at CES 2026: AI, Self-Docking & Solar [2026]
- LG's CLOiD Robot: Why Home Automation Still Isn't Ready [2025]
- The 7 Weirdest Gadgets at CES 2026: Musical Popsicles to AI Headphones [2025]
- Best Hi-Fi Audio Gear at CES 2026: Turntables, Speakers & More [2025]




