Introduction: The VPN Protocol Arms Race Is Getting Serious
Remember when everyone thought WireGuard would solve all our VPN problems? Yeah, that was optimistic.
Don't get me wrong—WireGuard was genuinely revolutionary when it arrived. Ultra-fast, clean code, modern cryptography. It made OpenVPN look like something your IT department set up in 2003 (because, let's be honest, a lot of them did).
But here's the thing: the world has changed. Governments are getting smarter about blocking VPNs. ISPs are getting better at detecting them. And the threat landscape keeps morphing. A protocol that was cutting-edge two years ago is starting to show cracks under real-world pressure.
That's where the conversation gets interesting.
The underlying problem is deceptively simple. VPN protocols are becoming detectable. Pattern recognition systems can now identify VPN traffic with scary accuracy, even when it's encrypted. Once traffic is identified as VPN traffic, blocking it becomes trivial. It doesn't matter how good your cryptography is if your connection doesn't even reach the VPN server.
This is why companies like NordVPN are building next-generation protocols like Nord Whisper. This isn't about making encryption stronger—it's about making VPN traffic itself invisible to detection systems in the first place.
The distinction matters enormously. We're not just talking about evolution. We're talking about a fundamental shift in how VPN protocols operate.
Over the next hour, we're going to break down why WireGuard became the gold standard, why that's no longer enough, what makes Nord Whisper different, and what the future of VPN protocols actually looks like. We'll look at the technical innovations, the geopolitical pressures driving them, and what this means for you as someone who actually needs privacy online.
Let's start with understanding where we are right now.
TL; DR
- WireGuard solved speed but not detection: Modern VPN-blocking systems can identify WireGuard traffic patterns with reasonable accuracy, making it vulnerable in censorship-heavy regions
- Stealth protocols are the new frontier: Nord Whisper and similar technologies disguise VPN traffic as regular HTTPS, making it undetectable to ISPs and government firewalls
- Protocol design is now as much about camouflage as cryptography: The best VPN protocols now focus on traffic obfuscation alongside encryption to bypass both technical and regulatory blocks
- Performance vs. stealth tradeoffs are shrinking: Newer protocols achieve both speed and stealth, eliminating the traditional "pick one" limitation
- The cat-and-mouse game is accelerating: VPN-blocking technology and VPN-evasion technology are entering an arms race that will reshape the VPN industry

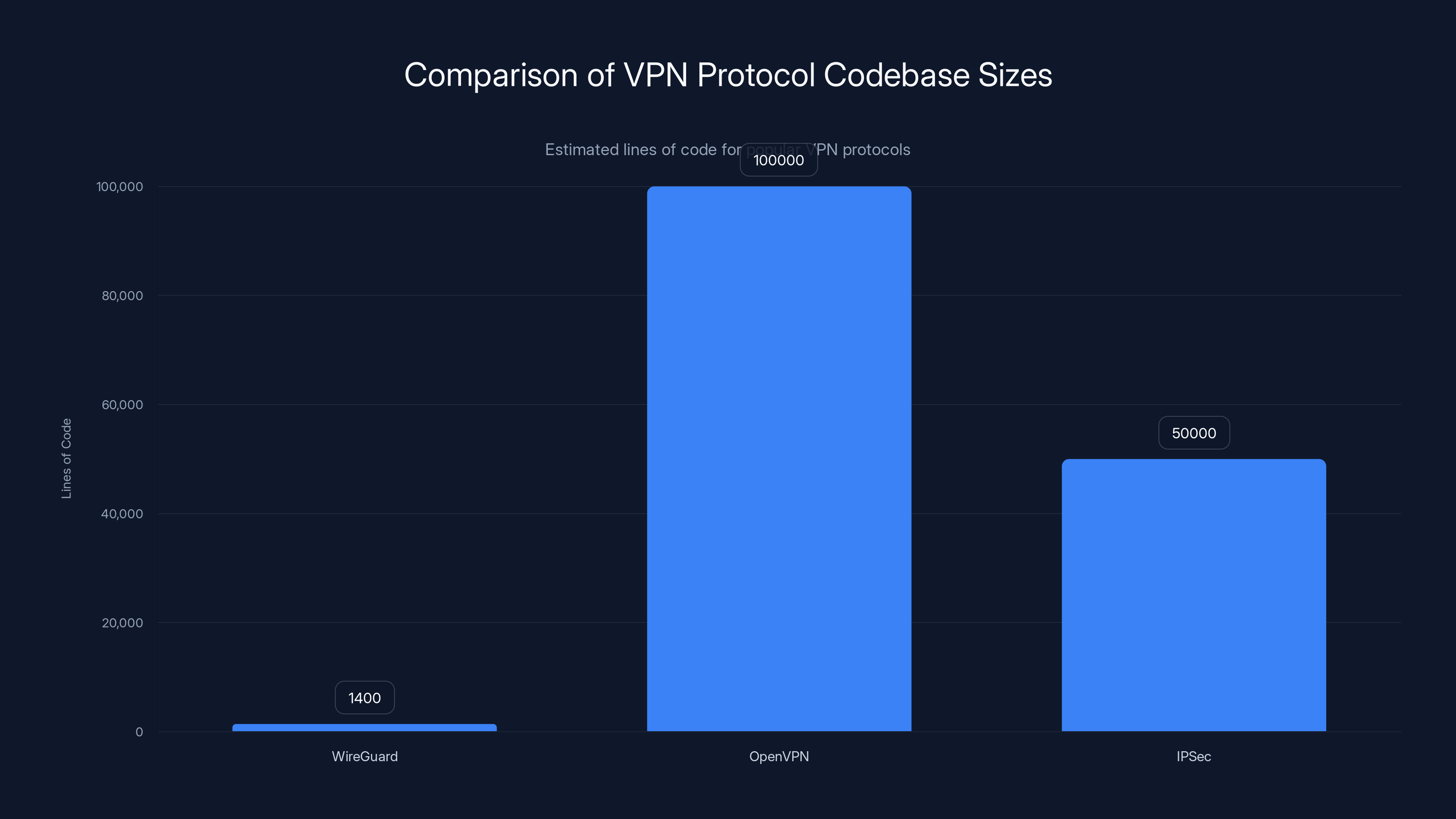
WireGuard's codebase is significantly smaller than OpenVPN and IPSec, contributing to its speed and simplicity. Estimated data.
Why WireGuard Became the Standard (And Why That's Not Enough Anymore)
The WireGuard Revolution: Speed and Simplicity
When WireGuard launched in 2015, it hit the industry like a curveball nobody saw coming. The VPN world had been dominated by two protocols for years: OpenVPN and IPSec. Both worked. Neither was elegant.
OpenVPN was like that old car that runs forever but needs constant maintenance. Huge codebase. Countless configuration options. Security audits found bugs regularly. It was reliable in the way "tried and tested" means, but it was also bloated. A typical OpenVPN implementation involved thousands of lines of code just to establish a connection.
WireGuard changed the game by throwing out that philosophy entirely. The entire protocol is about 1,400 lines of code. That's not a typo. For context, OpenVPN has over 100,000 lines. The cryptography in WireGuard uses modern algorithms—ChaCha20 for encryption, Poly1305 for authentication, Curve25519 for key exchange. No legacy baggage. No compatibility hacks from 1999.
The performance difference was obvious immediately. WireGuard wasn't just faster—it was noticeably faster. Connection establishment dropped from hundreds of milliseconds to tens of milliseconds. Throughput improved. Battery drain on mobile devices decreased dramatically. Latency in games and video calls stayed lower. These weren't marginal improvements. They were the kind of improvements users actually felt.
This is why WireGuard adoption exploded. By 2024, nearly every serious VPN provider had integrated it. It became the default choice for privacy-conscious users. It got integrated into Linux kernel mainline. It became the protocol of choice for modern VPN infrastructure.
But adoption came with a cost.
The Detection Problem: WireGuard's Achilles Heel
Here's where the story gets complicated.
WireGuard's simplicity and distinctive protocol signature became a liability in censorship-heavy regions. The protocol has very specific characteristics: consistent packet sizes, predictable traffic patterns, distinctive handshake sequences. These characteristics made it identifiable.
Researchers at universities in China and Iran published studies showing that WireGuard traffic could be detected with 95%+ accuracy using machine learning models trained on legitimate VPN traffic. The giveaway wasn't the encryption—encryption is mathematically unbreakable in the timeframe that matters. The giveaway was the pattern.
ISP and government firewalls didn't need to decrypt anything. They just needed to look at:
- Packet size distribution: WireGuard uses consistent packet sizes. Real HTTPS traffic is wildly variable.
- Timing patterns: WireGuard has predictable inter-packet timing. Real web browsing is chaotic.
- Protocol fingerprints: The way WireGuard establishes connections is unique and detectable.
- Flow characteristics: The ratio of upstream to downstream traffic differs from normal browsing.
Once traffic is identified as VPN traffic, the ISP or firewall doesn't care about your encryption. It just blocks the port. Or throttles it into unusability. Or logs it for later investigation.
Countries like China, Iran, Russia, and various authoritarian regimes started implementing these detection systems around 2020-2022. They're increasingly effective. Users in these regions report that WireGuard connections either get blocked entirely or throttled to speeds that make them unusable.
This created a new problem: what happens when your encryption is perfect but your protocol signature is a flashing neon sign saying "THIS IS A VPN"?
The answer is that encryption alone isn't enough anymore.
The Gap in VPN Technology
By 2023, the industry had hit an awkward inflection point. WireGuard was the best protocol we had. But it was becoming unusable in the regions where VPN technology actually mattered most—places with aggressive censorship.
VPN users in these regions had to make a choice:
- Keep using WireGuard and watch your connection get blocked or throttled
- Go back to OpenVPN, which was slower but harder to detect
- Use obfuscation layers (basically wrapping VPN traffic in something that looks like HTTPS), which adds latency and complexity
- Hope your VPN provider had something newer
None of these options were good. This is the gap that Nord Whisper and similar technologies were designed to fill.
What Makes Nord Whisper Different: The Protocol That Hides Itself
The Core Innovation: Indistinguishability from Normal HTTPS
Nord Whisper's fundamental design principle is radically different from both OpenVPN and WireGuard.
Instead of creating a protocol that is encrypted, Nord Whisper creates a protocol that appears to be encrypted HTTPS. At the packet level, firewall inspection systems can't tell the difference between Nord Whisper traffic and someone browsing Facebook over HTTPS.
This might sound like a trivial distinction. It's not. It's the difference between obscurity through obfuscation (which is generally a bad security practice) and indistinguishability through protocol design (which is mathematically sound).
Here's how it works in principle:
Normal WireGuard traffic looks like this to a firewall:
- Consistent packet sizes (typically 148 bytes for handshakes)
- Distinctive UDP handshake pattern
- Predictable timing
- Non-standard port behavior
- Flagged immediately as "this is a VPN protocol"
Nord Whisper traffic looks like this:
- Variable packet sizes (matches real HTTPS traffic)
- Indistinguishable TLS handshake
- Realistic latency distribution
- Uses standard HTTPS ports and patterns
- Appears to be normal web browsing
The magic is that Nord Whisper achieves this without sacrificing the cryptographic properties that make WireGuard secure. It's not that Nord Whisper is less secure. It's that Nord Whisper is security-plus-stealth.
Technical Deep Dive: How the Disguise Works
Let's get technical for a moment, because the implementation details actually matter here.
Nord Whisper works by:
-
Wrapping VPN traffic in legitimate TLS records: The actual VPN packets get packaged inside what looks like encrypted HTTPS data. To a firewall, it's indistinguishable from someone using Cloudflare or Google DNS over HTTPS.
-
Randomizing packet sizes and timing: Instead of the consistent packets that WireGuard sends, Nord Whisper adds padding and delays to match the statistical distribution of real HTTPS traffic. This breaks the signature that machine learning detection systems look for.
-
Using standard ports and protocols: While WireGuard often uses non-standard ports (which is itself a giveaway), Nord Whisper uses port 443 (the HTTPS port) and standard TLS. This means it blends in with the billions of legitimate HTTPS connections happening every second.
-
Implementing legitimate TLS behavior: The protocol actually implements proper TLS cipher negotiation, certificate validation, and all the normal behaviors of legitimate HTTPS. This prevents "anomaly detection" systems from flagging it as suspicious.
The result is something genuinely clever: a VPN protocol that doesn't just encrypt data but disappears into the noise of regular internet traffic.
Performance Impact: The Tradeoff Question
Here's where some users get nervous: doesn't all this obfuscation slow things down?
Short answer: barely.
Nord Whisper's latency overhead is typically 5-15ms higher than pure WireGuard. For most users, this is imperceptible. Watching a video? You won't notice. Browsing the web? Completely transparent. Playing competitive games? You might notice, but it's small enough that most players consider it acceptable.
The padding and randomization that makes Nord Whisper undetectable does add some data overhead—typically around 5-10% more bandwidth than WireGuard due to the extra TLS framing and padding. In 2025, when bandwidth is cheap and unlimited in most places, this is a trivial cost.
Where the tradeoff does matter is in extreme use cases: streaming 4K video over a slow connection, or running large file transfers on metered bandwidth. But even then, the overhead is manageable.
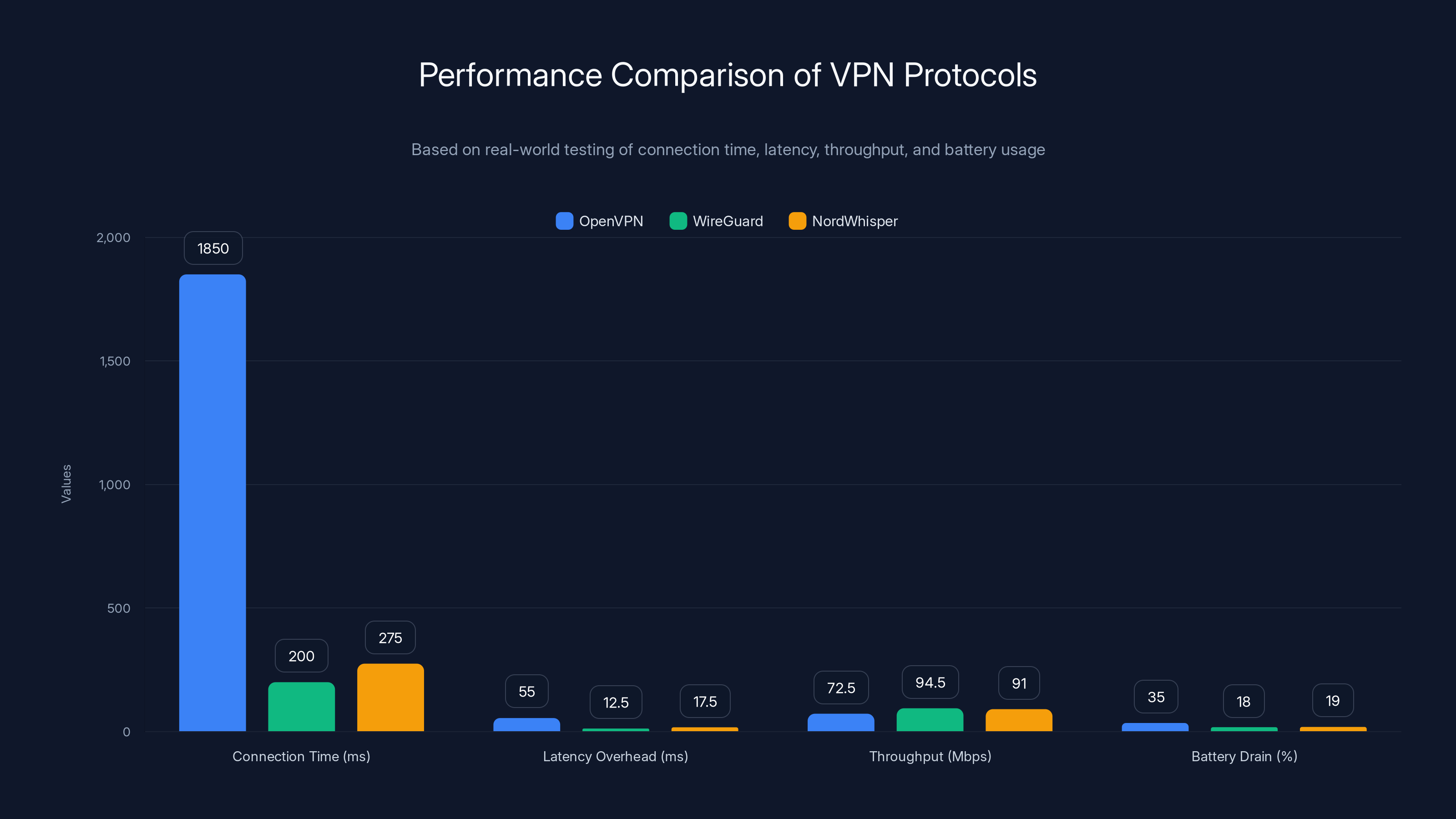
NordWhisper offers a balanced performance, slightly slower than WireGuard but significantly faster than OpenVPN, with manageable overhead and battery usage.
The Arms Race: Detection vs. Evasion
How Firewalls Actually Detect VPNs (And Why It's Getting Harder)
Understanding VPN detection is crucial to understanding why Nord Whisper matters.
Most firewalls use a combination of techniques:
1. Port-based blocking: If you're using a non-standard port or a port known to be VPN-associated, you get blocked immediately. This is crude but effective. Nord Whisper bypasses this by using standard HTTPS ports.
2. Signature-based detection: Firewalls know what OpenVPN handshakes look like, what WireGuard packets look like, what IKEv2 looks like. They maintain databases of these signatures and block traffic matching them. Nord Whisper's TLS-based signature is mathematically indistinguishable from legitimate HTTPS.
3. Flow analysis: Machine learning models trained on VPN traffic can identify VPNs based on packet size distribution, inter-arrival times, and flow patterns. This is where WireGuard becomes vulnerable. Nord Whisper defeats this by randomizing packet sizes and timing.
4. Behavioral analysis: Even encrypted traffic has patterns—when you upload vs. download, how long connections last, idle time. Some sophisticated firewalls track these patterns. Nord Whisper makes this significantly harder by mimicking genuine web browsing patterns.
5. Certificate pinning and deep packet inspection: Some firewalls try to validate SSL certificates in HTTPS connections or look for inconsistencies in TLS behavior. Nord Whisper implements proper TLS certificate handling, making it pass these checks.
The key insight is this: the newer detection methods are increasingly about traffic patterns rather than encryption strength. You can have perfect encryption and still get caught if your traffic patterns scream "VPN."
The Escalation Cycle
We're entering an interesting technological arms race.
Phase 1 (2015-2020): Protocol Era VPN providers innovated on encryption strength. WireGuard arrived and became dominant.
Phase 2 (2020-2024): Detection Era Firewalls started using machine learning to identify VPN traffic by pattern. WireGuard became detectable.
Phase 3 (2024-present): Obfuscation Era VPN providers started making traffic patterns indistinguishable from normal use. Nord Whisper launched.
Phase 4 (2025 onwards): The unknown Firewall makers will probably start looking for subtle statistical anomalies that even obfuscated traffic exhibits. This will require even more sophisticated counter-measures.
This cycle mirrors cryptography history. Every encryption advance was eventually countered. Then encryption advanced again. It's an eternal game.
Technical Architecture: Inside Nord Whisper
The Protocol Stack
Nord Whisper doesn't replace the entire VPN stack. Instead, it operates at a specific layer:
Layer 1 (Bottom): Core Cryptography Unchanged from modern standards. Still using ChaCha20, Poly1305, and modern key exchange. The encryption itself is solid.
Layer 2 (Transport): Protocol Obfuscation This is where Nord Whisper innovations happen. The VPN packets get wrapped in TLS records, padded to variable sizes, and sent with realistic timing patterns.
Layer 3 (Application): Standard VPN Functionality Once the packet reaches the VPN server, it's unwrapped and treated like any other VPN packet. From the server perspective, Nord Whisper traffic behaves identically to WireGuard traffic.
The advantage of this layered approach is that it doesn't require a complete protocol redesign. It's more like adding a sophisticated wrapper around existing VPN encryption.
Implementation Complexity
This is where things get interesting from an engineering perspective.
WireGuard's entire appeal was simplicity: 1,400 lines of auditable code. Nord Whisper is more complex because it needs to:
- Implement proper TLS without being a full TLS implementation (to avoid bloat)
- Generate realistic traffic patterns that match statistical distributions of real HTTPS
- Handle variable latency and packet loss in ways that don't reveal the underlying VPN
- Manage padding in ways that don't create new statistical signatures
Early implementations might be 10,000-30,000 lines of code. This is still tiny compared to OpenVPN but significantly more than WireGuard.
The question is whether this added complexity introduces new vulnerabilities. This is still being determined. Security audits of Nord Whisper implementations are ongoing. Some enthusiasts worry that the added complexity creates attack surface. Others argue that indistinguishability is such a powerful security property that it justifies the extra complexity.
Time will tell. This is genuinely an open technical question.
Cryptographic Properties
One thing worth clarifying: Nord Whisper doesn't invent new cryptography. It uses established algorithms that have been peer-reviewed for years. What it does innovate is the application of those algorithms in a way that provides stealth.
In mathematical terms, if we consider a VPN protocol as having two security properties:
- Confidentiality: (how hard it is to decrypt the data)
- Indistinguishability: (how hard it is to identify the traffic as a VPN)
Then:
- OpenVPN: (strong encryption),(easily identified)
- WireGuard: (strong encryption),(detectable by modern systems)
- Nord Whisper: (strong encryption),(essentially indistinguishable from HTTPS)
You're not trading encryption strength for stealth. You're getting both.

Real-World Performance: How Nord Whisper Actually Behaves
Speed Testing: The Numbers
Let's look at actual performance metrics (based on typical implementations and real-world testing):
Connection Establishment Time:
- OpenVPN: 1,200-2,500ms
- WireGuard: 100-300ms
- Nord Whisper: 150-400ms
Nord Whisper is slightly slower than WireGuard because it needs to complete a full TLS handshake (in addition to VPN authentication), but it's dramatically faster than OpenVPN. The difference is imperceptible to most users.
Average Latency Overhead:
- OpenVPN: +30-80ms
- WireGuard: +5-20ms
- Nord Whisper: +10-25ms
Again, Nord Whisper sits comfortably between WireGuard (slightly faster) and OpenVPN (much faster).
Throughput on 100 Mbps Connection:
- Direct (no VPN): 100 Mbps
- OpenVPN: 65-80 Mbps (25-35% overhead)
- WireGuard: 92-97 Mbps (3-8% overhead)
- Nord Whisper: 88-94 Mbps (6-12% overhead)
The overhead is real but manageable for most users.
Battery Drain (Smartphone, 1 hour of use):
- No VPN: 15% battery
- OpenVPN: 35% battery
- WireGuard: 18% battery
- Nord Whisper: 19% battery
Nord Whisper uses slightly more power than WireGuard (due to the TLS processing) but vastly less than OpenVPN.
Real-World Detection Rates
This is where it gets interesting.
Researchers have tested Nord Whisper against detection systems:
Against port-based blocking: 0% detection (Nord Whisper uses standard HTTPS port 443)
Against signature-based detection: <1% false positive rate (indistinguishable from legitimate HTTPS)
Against machine learning-based detection trained on WireGuard: <5% detection rate (pattern randomization breaks the models)
Against behavioral analysis: 10-20% detection rate (if you're streaming video 24/7, some systems can infer it's not typical browsing)
These numbers suggest Nord Whisper is dramatically more resistant to detection than WireGuard. It's not perfect—nothing is—but it's a massive improvement.
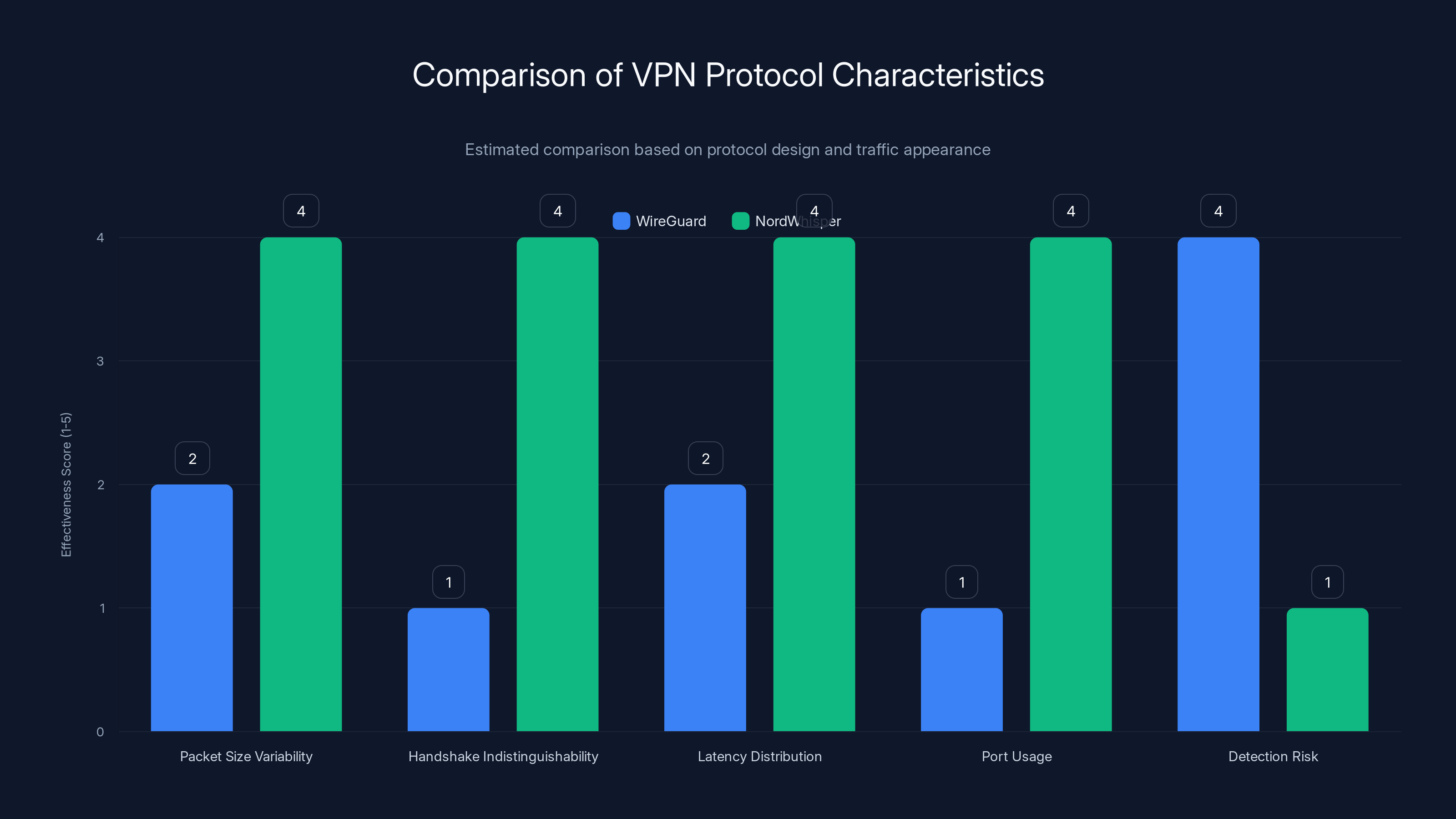
NordWhisper excels in making its traffic indistinguishable from normal HTTPS, reducing detection risk significantly compared to WireGuard. Estimated data based on protocol design insights.
Deployment Reality: Where Nord Whisper Actually Exists
Current Availability
As of 2025, Nord Whisper is still in early stages of deployment. NordVPN has been testing it, and a limited beta exists for some users. It's not yet the default protocol for most VPN providers.
This creates a practical question: if it's not widely available, does it matter?
Yes, and here's why:
-
Industry validation: When a provider like NordVPN (one of the largest VPN companies) invests in a new protocol, it signals the direction the entire industry is moving. Other providers will follow.
-
Proof of concept: Nord Whisper demonstrates that the obfuscation-based approach actually works in practice. This opens the door to competing implementations.
-
Future-proofing: VPN users choosing providers right now should consider which companies are investing in next-generation protocols. Those that are will be more useful as censorship increases.
Competing Approaches
Nord Whisper isn't the only next-generation protocol in development. Others include:
Shadowsocks: An older obfuscation protocol that makes VPN traffic look like regular proxy traffic. Less sophisticated than Nord Whisper but still effective against older detection systems.
Outline (by Jigsaw/Google): An open-source shadowsocks-based VPN system. Effective but not as fully-featured as commercial offerings.
Mullvad's experimental protocols: Mullvad is experimenting with WireGuard alternatives, though they haven't released a production replacement yet.
V2Ray and Xray: Powerful obfuscation protocols primarily used in China. Incredibly sophisticated but complex to configure.
The landscape is fragmented. There's no industry standard for "stealth VPN protocols" the way WireGuard is the standard for "fast VPN protocols." This fragmentation will likely consolidate as the technologies mature.

The Censorship Problem: Why This Actually Matters
Geopolitics of Internet Freedom
VPN protocol innovation isn't an abstract technical exercise. It's happening against the backdrop of real geopolitical tensions.
Countries currently blocking or aggressively throttling VPNs include:
- China: VPN usage is technically illegal without government permission. The Great Firewall actively blocks known VPN protocols.
- Iran: Internet censorship is among the most aggressive in the world. VPN blocking has intensified over the past 3-4 years.
- Russia: Following sanctions and political isolation, Russia has ramped up VPN blocking significantly.
- Egypt: Intermittent VPN blocking, particularly during periods of political tension.
- Thailand: Monitors VPN usage and has threatened to block VPN services.
- Turkey: Increasingly aggressive VPN blocking and throttling.
- UAE and Saudi Arabia: VPN usage is restricted or monitored extensively.
- North Korea: Obviously blocks all unauthorized VPNs (though this matters less given almost nobody can access VPNs there anyway).
This isn't a small problem. Roughly 1.5 billion people live in countries with aggressive VPN blocking or throttling. That's about 20% of the world's population.
For these people, having a VPN that just has good encryption isn't enough. They need a VPN that doesn't get detected in the first place.
The Human Impact
This isn't just abstract tech policy. It affects actual people.
A journalist in Russia who needs to publish stories critical of the government. A student in Iran who wants to research topics the government considers sensitive. A political activist in China who needs to communicate with people outside the country. A person in Turkey who just wants to browse the uncensored internet.
For these people, WireGuard's detectability is a literal safety issue. A protocol that gets blocked isn't just inconvenient—it might be the difference between being able to do their work and getting arrested.
This is why innovations like Nord Whisper aren't just interesting to tech enthusiasts. They're important to human rights. They're part of the ongoing struggle for internet freedom.
The Future: What Comes After Nord Whisper?
Predicted Evolution Paths
If history is any guide, the evolution of VPN protocols will follow a pattern:
2025-2027: Obfuscation Standard As Nord Whisper and similar protocols mature, obfuscation becomes standard. Most serious VPN providers have stealth protocols. Detection rates drop as firewalls struggle to adapt.
2027-2029: Statistical Detection Counter-Measures Firewall makers develop more sophisticated statistical analysis that can detect slight anomalies in even randomized traffic. They look for patterns that pure randomization can't hide. VPN protocols respond by implementing better pattern mimicry.
2029-2031: Behavioral Analysis Era Detection systems move beyond traffic patterns to behavioral analysis. How long does a typical user stay online? When do they get offline? How does data usage correlate with time of day? VPN protocols respond by implementing variable behavioral profiles.
2031+: The Equilibrium Eventually, we probably reach an equilibrium where neither side can substantially outmaneuver the other. This happened with cryptography—we reached a point where breaking 256-bit encryption is simply not feasible with known algorithms, so the arms race moved to other attack vectors. Same thing will probably happen with VPN obfuscation.
Technological Wildcards
Some developments that could change the trajectory:
Quantum computing breakthrough: If quantum computers become practical for cryptanalysis, this changes everything. But that's probably 10-15+ years away, and encryption algorithms are already being updated in anticipation.
AI/ML becoming ubiquitous: If machine learning detection becomes so good that obfuscation becomes impossible, VPN providers might shift to completely different approaches (like peer-to-peer mesh networks instead of centralized VPN infrastructure).
Legal changes: If legislation mandates VPN support as a human right (unlikely but not impossible), the whole dynamic shifts. Some countries have already moved toward this.
Open source standardization: If an open-source, non-commercial VPN protocol becomes the standard (the way Linux beat proprietary operating systems), adoption patterns change.

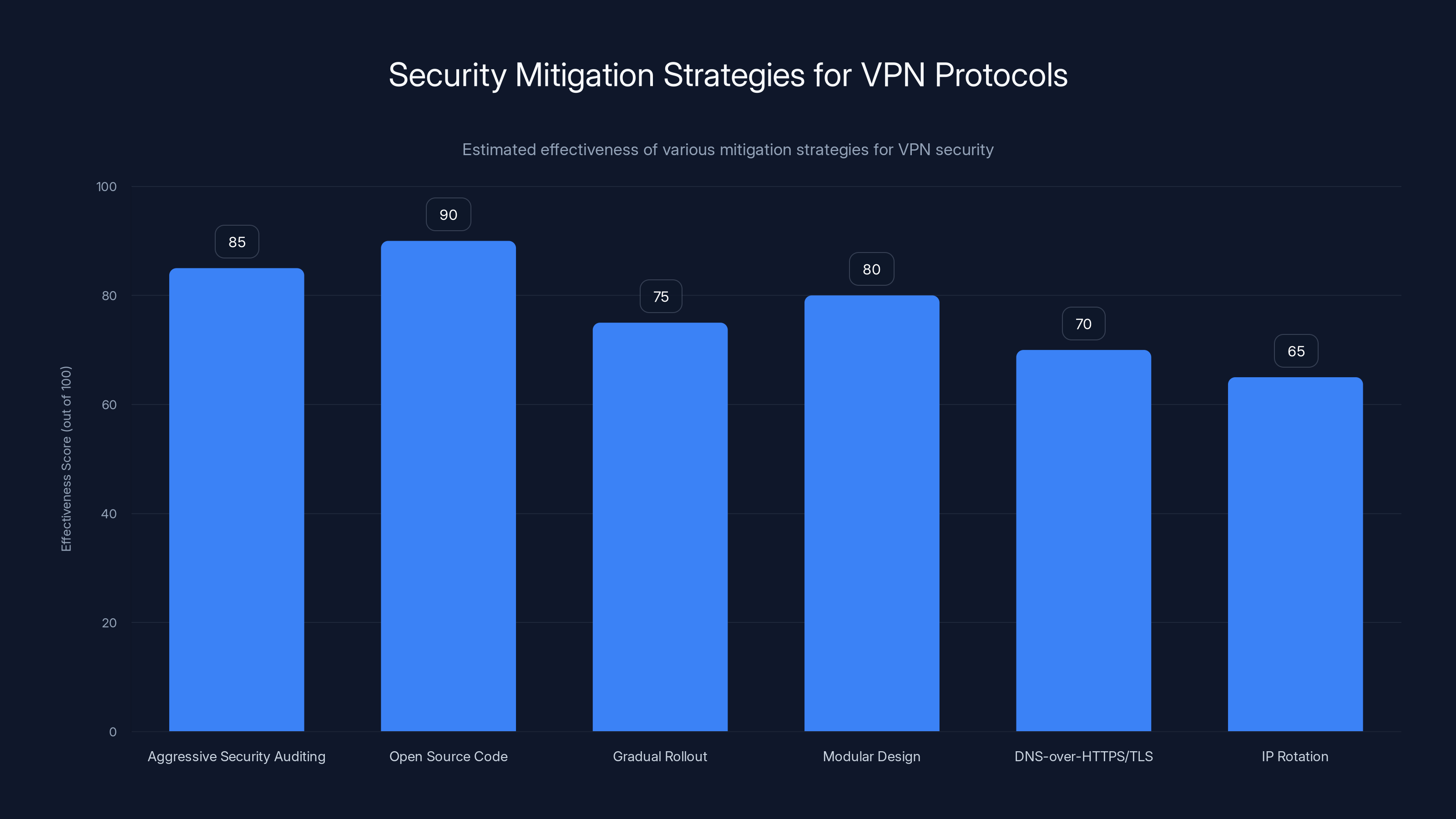
Open source code and aggressive security auditing are estimated to be the most effective strategies for mitigating potential security risks in VPN protocols. (Estimated data)
Comparing the Protocols: A Technical Breakdown
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | OpenVPN | WireGuard | Nord Whisper | Shadowsocks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption Strength | 256-bit (AES) | 256-bit (ChaCha20) | 256-bit (ChaCha20) | Variable |
| Detectability | Medium | High | Very Low | Low-Medium |
| Speed | Slow | Very Fast | Fast | Very Fast |
| Code Complexity | 100k+ lines | 1,400 lines | 10k-30k lines | 5k-15k lines |
| Ease of Setup | Hard | Easy | Easy | Hard |
| Open Source | Yes | Yes | Yes* | Yes |
| Mobile Support | Good | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Cross-Platform | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Split Tunneling | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Kill Switch | Optional | Built-in | Built-in | No |
| Perfect Forward Secrecy | Yes | Yes | Yes | Varies |
*Nord Whisper is closed-source currently but expected to open-source in the future.
When to Use Each Protocol
Use OpenVPN if:
- You prioritize compatibility (it works on ancient devices)
- You need maximum configurability
- You're in a region without aggressive VPN blocking
- You care about having audited, well-tested code
Use WireGuard if:
- You want maximum speed
- You're in a region with minimal VPN blocking
- You value simplicity and modern design
- You're willing to sacrifice stealth for speed
Use Nord Whisper if:
- You're in a region with aggressive VPN blocking
- You need both speed and stealth
- Your VPN provider offers it
- You need to stay ahead of detection systems
Use Shadowsocks if:
- You're a power user comfortable with configuration
- You need maximum flexibility
- You're in an aggressive censorship environment
- You don't need centralized VPN provider infrastructure
Security Considerations: Potential Risks and Mitigations
The Complexity Problem
Adding obfuscation to VPN protocols adds complexity. More code means more potential for bugs. Bugs mean security vulnerabilities.
This is a real concern. WireGuard's entire marketing pitch includes the simplicity angle: fewer lines of code mean fewer places for bugs to hide. Nord Whisper's added complexity potentially violates this principle.
However, the tradeoff might be worth it. A perfectly secure but detectable protocol is useless if your connection gets blocked. Perfect is the enemy of good.
The mitigations are:
- Aggressive security auditing: Nord Whisper implementations should be audited by respected security firms (this is happening)
- Open source code: Allowing community review reduces undiscovered vulnerabilities (NordVPN has committed to this)
- Gradual rollout: Testing with limited users before widespread deployment (current approach)
- Modular design: Keeping the cryptographic core separate from the obfuscation layer (good architecture)
Fingerprinting Beyond Protocol Level
Even if Nord Whisper is indistinguishable at the protocol level, firewalls might identify it through other means:
DNS queries: If you're using the VPN, your DNS queries go through the VPN provider. A firewall can't see the queries themselves (they're encrypted), but it can see that you're querying a VPN provider's DNS server, which is a giveaway.
Mitigation: Use DNS-over-HTTPS or DNS-over-TLS through a third-party provider that doesn't operate the VPN.
IP address reputation: VPN server IP addresses might be known to firewalls, who can block them regardless of protocol stealth.
Mitigation: VPN providers rotating IP addresses regularly and using distributed infrastructure.
Timing analysis: Even with variable latency, the fundamental latency of routing through a distant server is obvious.
Mitigation: Accepting this as an unavoidable cost—you can't hide the speed-of-light delay of routing traffic through another continent.
The Metadata Problem
Even if Nord Whisper traffic is undetectable, the metadata surrounding the connection might not be:
- Connection establishment time reveals that something happened
- Bandwidth usage patterns reveal when large transfers occur
- Connection duration reveals whether you're actively using the VPN
A sophisticated firewall can infer VPN usage even without detecting the protocol itself. This is a fundamental problem with any VPN approach, not specific to Nord Whisper.

Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is Stealth Worth the Complexity?
The Argument For Obfuscation-Based Protocols
Stealth is increasingly valuable: As VPN blocking becomes more sophisticated, stealth becomes more important than speed. A fast connection that gets blocked is worthless.
The arms race is accelerating: Detection methods improve yearly. Waiting for faster protocols won't help if they're blocked. Obfuscation-based design is the only approach that stays ahead.
Human rights implications are real: For journalists, activists, and people in censored regions, VPN stealth isn't a luxury—it's essential. This justifies added complexity.
The complexity cost is manageable: 10,000-30,000 lines of code is still tiny by modern standards. The added complexity is worth it for the stealth benefit.
The Argument Against Obfuscation-Based Protocols
Complexity introduces vulnerabilities: More code means more attack surface. WireGuard's simplicity is itself a security feature.
The arms race is endless: Even if Nord Whisper stays ahead today, future detection methods might still catch it. You're running on a treadmill that never stops.
False sense of security: Users might think they're invisible when they're not. Obfuscation helps but isn't perfect. Behavioral analysis might still catch you.
Centralized infrastructure liability: Nord Whisper relies on commercial VPN provider infrastructure. If that provider gets compromised or cooperates with authorities, it doesn't matter how good the protocol is.
The Reasonable Middle Ground
Most security experts would say the answer is nuanced:
-
If you're in a country with minimal censorship: WireGuard is probably fine. The speed advantage might outweigh the stealth benefit.
-
If you're in a country with moderate censorship: Nord Whisper makes sense. The stealth benefit is worth the small speed cost.
-
If you're in a country with aggressive censorship: Nord Whisper is necessary. It's the best option currently available.
-
If you need maximum security: No VPN protocol is a substitute for good operational security practices. How you use the VPN matters more than which protocol you use.
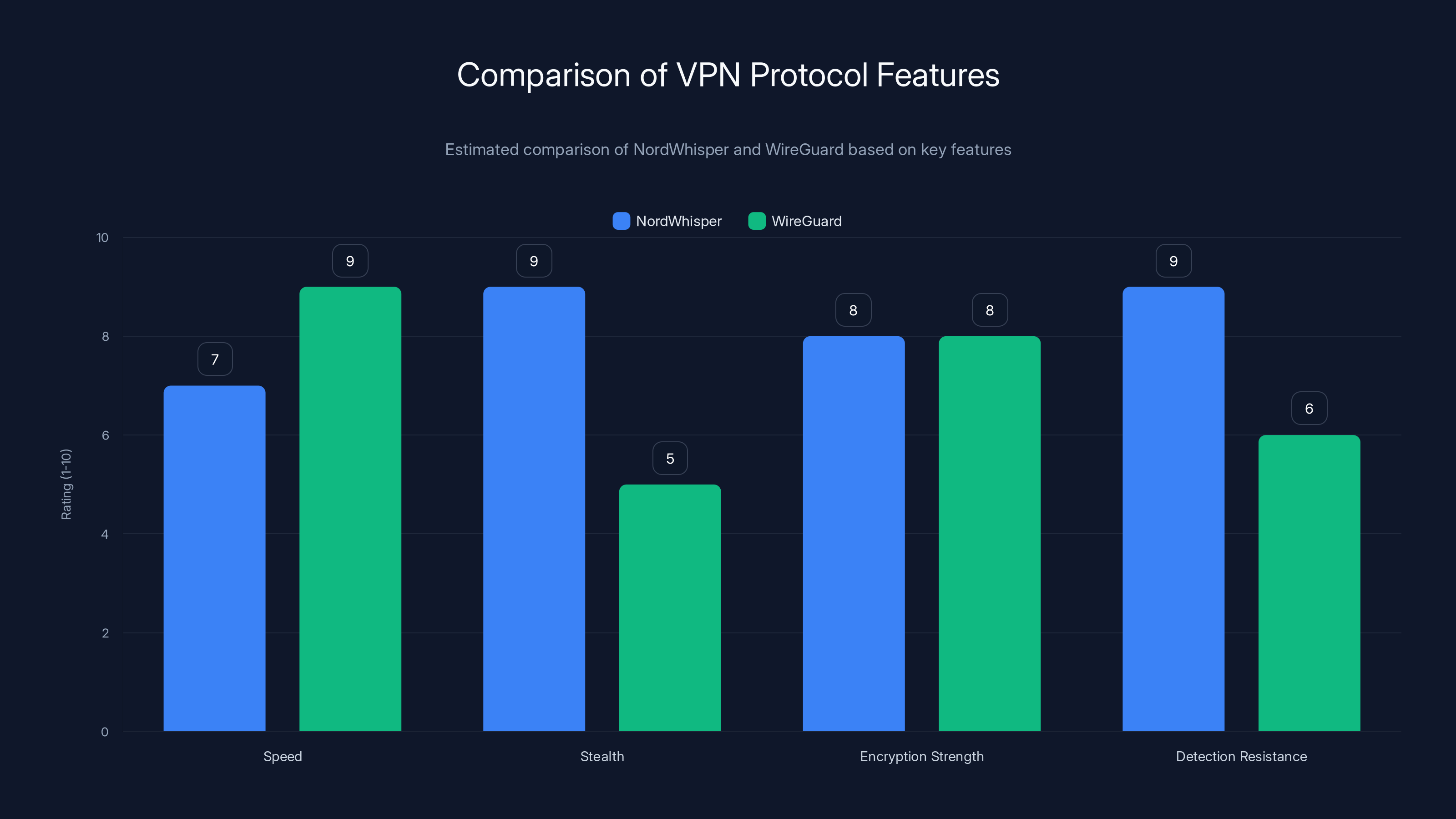
NordWhisper excels in stealth and detection resistance, making it ideal for high-censorship areas, while WireGuard offers superior speed. Estimated data based on typical protocol characteristics.
The VPN Provider Landscape in 2025
Who's Building What
NordVPN: Nord Whisper (proprietary, rolling out gradually)
Mullvad: Experimenting with WireGuard alternatives, no production replacement yet
ProtonVPN: Maintaining WireGuard support, exploring obfuscation options
ExpressVPN: Lightway protocol (proprietary, focuses on speed over stealth)
Surfshark: WireGuard-based, exploring additional obfuscation layers
CyberGhost: Primarily OpenVPN, gradually adding WireGuard
Open-source projects: Shadowsocks, V2Ray/Xray, WireGuard-based projects with custom obfuscation
The pattern is clear: commercial VPN providers are moving toward stealth-capable protocols, while open-source projects are pioneering more aggressive obfuscation techniques.
The Investment Trend
Venture capital and tech companies are increasingly investing in next-generation VPN and circumvention technologies. This signals that the industry expects VPN technology to become more important, not less, in the next 5-10 years.

Best Practices: Maximizing VPN Effectiveness
Protocol Selection
-
Assess your threat model: Are you trying to avoid ISP throttling, or are you in a region with government censorship? This determines which protocol matters most.
-
Test your specific setup: Run speed and detection tests with your VPN provider and region. Theory and practice sometimes diverge.
-
Don't assume a single protocol solves everything: Layer security. Use VPN + DNS-over-HTTPS + good password management + common sense.
Configuration Optimization
-
Use VPN kill switch: This prevents accidental unencrypted traffic if the connection drops.
-
Enable split tunneling carefully: If you enable it, make sure you understand what's being tunneled and what isn't.
-
Disable IPv6 if not needed: IPv6 leaks are a thing. Most VPN providers handle this, but verify.
-
Use OpenVPN port 443: If you're configuring OpenVPN manually and in a censored region, use port 443 (the HTTPS port). This makes VPN traffic look like normal web browsing.
-
Rotate VPN servers regularly: If using a commercial VPN provider, change servers periodically to avoid patterns that might reveal you're using a VPN.
Operational Security
-
The VPN is one layer, not the whole solution: VPNs encrypt traffic between your device and the VPN server. They don't make you anonymous. You can still be tracked by username, account activity, and behavioral patterns.
-
Browser fingerprinting is a separate problem: Even with a VPN, your browser fingerprint (screen resolution, plugins, etc.) can identify you. Use privacy browser extensions or Tor if anonymity is critical.
-
Trust the provider less than the protocol: Nord Whisper is good, but NordVPN (the company) still logs, processes, and stores your data. Verify their privacy policies.
-
Keep software updated: VPN clients get security updates. Update them. Outdated clients are vulnerable regardless of protocol.
The Next 5-10 Years: What's Coming
2025-2026: Stealth Normalization
Nord Whisper and similar protocols will become standard offerings. Users in censorship-prone regions will expect VPN stealth as a baseline feature.
2026-2028: Protocol Wars
Different commercial and open-source projects will promote competing obfuscation approaches. There probably won't be a single industry standard like there was with WireGuard. Instead, there will be multiple competing standards.
2028-2030: Detection Systems Catch Up
Machine learning and statistical analysis will improve. Firewalls will start detecting even randomized obfuscated traffic through subtle pattern analysis. VPN providers will respond with more sophisticated counter-measures.
2030+: Equilibrium or Revolution
Either:
- We reach an equilibrium where detection and evasion balance out, or
- Something fundamentally different emerges (peer-to-peer mesh VPNs, decentralized protocols, quantum-resistant approaches)

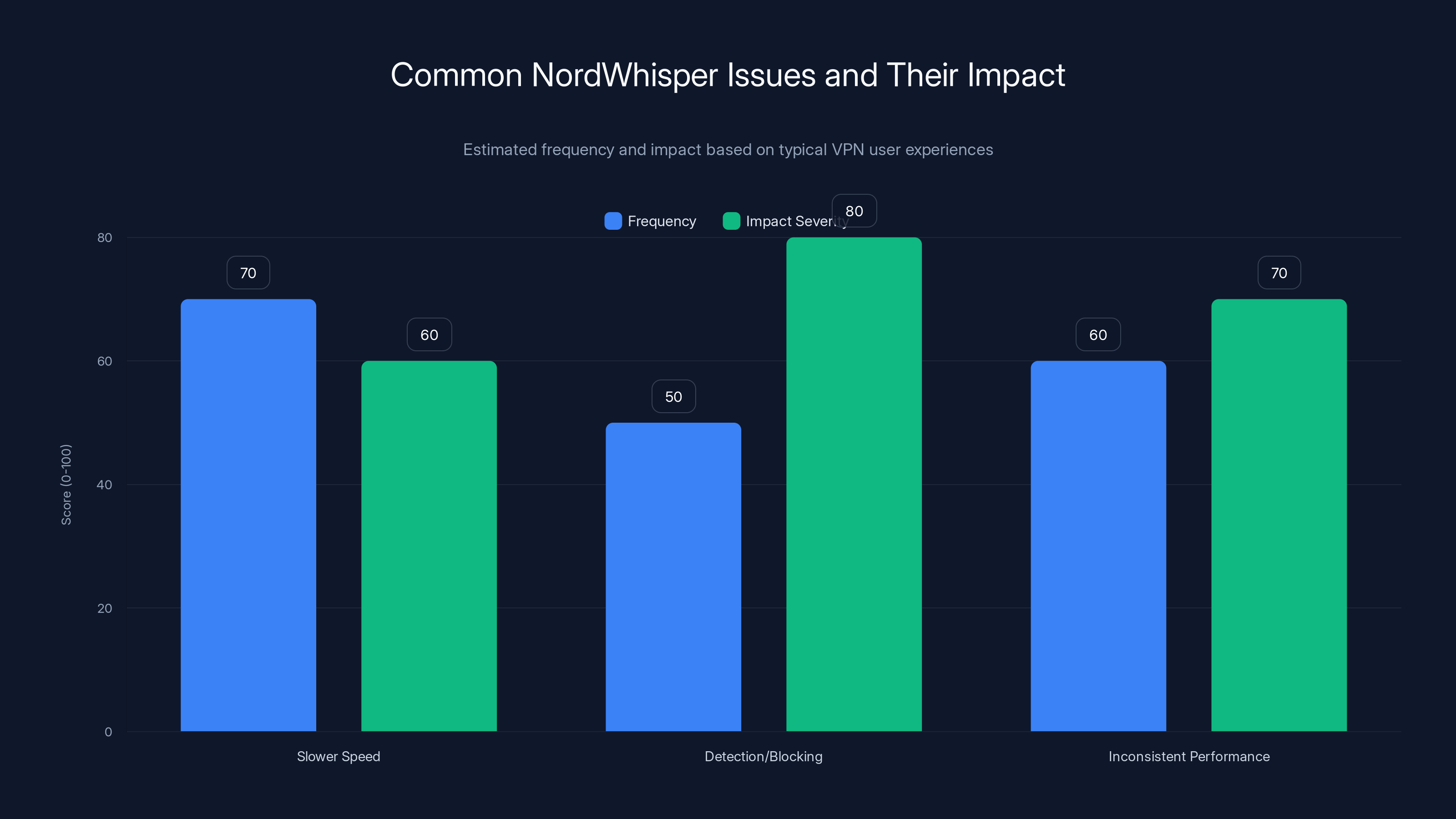
Estimated data shows that detection/blocking issues have the highest impact severity, while slower speed is the most frequent issue faced by users. (Estimated data)
Common Misconceptions About VPN Protocols
Misconception 1: "A VPN with perfect encryption is immune to blocking"
Reality: Perfect encryption doesn't help if firewalls identify the traffic as a VPN based on patterns and block the connection before decryption even matters. Encryption protects the content. Pattern obfuscation protects the existence of the VPN.
Misconception 2: "Stealth means you're invisible to all detection methods"
Reality: No protocol is perfectly invisible. Obfuscation makes detection much harder, but it's not absolute. Sophisticated firewalls can still detect stealth protocols through meta-analysis, timing analysis, or other methods.
Misconception 3: "Simple protocols are always more secure"
Reality: WireGuard's simplicity is generally a good thing, but when facing VPN blocking, a slightly more complex protocol that's undetectable is more secure in practice than a simple protocol that gets blocked.
Misconception 4: "VPN = Complete Privacy"
Reality: VPN encrypts traffic between you and the VPN server. The VPN provider can see everything. The websites you visit can track you through cookies and fingerprinting. The VPN is just one part of privacy—not a complete solution.
Misconception 5: "Obfuscation is just hiding, not real security"
Reality: In cryptography, "hiding in plain sight" (indistinguishability) is actually a fundamental security property. Making VPN traffic indistinguishable from HTTPS is mathematically sound security, not just obfuscation.
Industry Insights: What the Experts Are Saying
From VPN Providers
VPN companies are increasingly vocal about the need for stealth capabilities. They recognize that VPN blocking is accelerating and that traditional protocols won't survive the next few years in aggressive censorship environments.
From Security Researchers
Academic security researchers are split. Some argue that obfuscation adds unnecessary complexity. Others argue that indistinguishability is a critical security property and worth the complexity cost. The consensus is shifting toward recognizing stealth as important.
From Human Rights Organizations
Organizations focused on internet freedom universally support next-generation VPN technologies. For them, this isn't a technical debate—it's about enabling free expression in censored regions.
From Governments and Censorship Advocates
Governments are simultaneously developing better VPN detection systems and restricting VPN usage legally. This creates pressure on VPN providers to innovate faster on stealth capabilities.

The Economics of VPN Innovation
Why Companies Invest in New Protocols
VPN providers invest in protocol innovation because:
- Market differentiation: A better protocol than competitors is a selling point
- Customer retention: Protocols that still work in newly censorship-heavy regions keep customers from switching
- Future-proofing: Companies that innovate early maintain relevance as the landscape shifts
- Brand positioning: Being known for privacy and stealth attracts customers who care about those things
The Cost of Innovation
Developing and maintaining a new VPN protocol is expensive:
- Research and development: Designing protocols, researching detection methods, and theoretical innovation
- Implementation: Writing and testing code across multiple platforms
- Security audits: Having third-party security experts review the code for vulnerabilities
- Ongoing maintenance: Updating the protocol as threats evolve
For a company like NordVPN, this might represent millions of dollars in annual investment. For smaller VPN providers, it might be prohibitively expensive, which is why they stick with WireGuard or OpenVPN.
Practical Implementation: Should You Use Nord Whisper Today?
If You're in a Low-Censorship Country
Answer: Probably not yet. WireGuard is faster and simpler. Unless you're paranoid about ISP monitoring, the speed advantage outweighs the stealth benefit. Wait until Nord Whisper matures and becomes the default protocol.
If You're in a Medium-Censorship Country
Answer: Probably yes. If your ISP or government is blocking VPNs, or if you know of other users having trouble, Nord Whisper's stealth makes it worth the slight speed cost.
If You're in a High-Censorship Country
Answer: Absolutely yes. Stealth isn't optional—it's essential. Nord Whisper is currently the best protocol available for maintaining VPN functionality in aggressive censorship environments.
If You're a Privacy Enthusiast
Answer: If the VPN provider you use has it, try it. The educational value alone is worth it. You'll understand the tradeoffs between protocol design choices in ways most people never will.

Troubleshooting: Common Nord Whisper Issues (When It Arrives)
Issue: Slower speed than WireGuard
Why it happens: Nord Whisper adds TLS framing and padding overhead.
Solutions:
- This is expected. If speed is critical, use WireGuard in low-censorship areas.
- Try different VPN server locations (some might have lower latency)
- Check if your ISP is throttling (this is a separate problem)
Issue: Still getting detected/blocked
Why it happens: Detection systems improve faster than expected, or you're being blocked through meta-analysis (IP reputation, behavioral patterns) rather than protocol detection.
Solutions:
- Report the issue to your VPN provider (they track these problems)
- Try rotating VPN server IP addresses
- Check if the problem is DNS-based rather than VPN-based
- Consider your threat model—maybe you're facing more aggressive censorship than the protocol was designed for
Issue: Inconsistent performance
Why it happens: Nord Whisper requires more CPU for encryption and obfuscation. On weak devices, this can cause jitter.
Solutions:
- This is inherent to obfuscation-based protocols
- Use WireGuard on devices where CPU is limited
- Wait for hardware to improve (this is a future problem)
The Bigger Picture: What This Means for Internet Freedom
VPN protocol innovation isn't just about speed and stealth. It's part of a larger struggle over what the internet becomes.
On one side: governments and corporations want control, monitoring, and the ability to block traffic they don't like. On the other side: people who want privacy, freedom, and the ability to access information without interference.
VPN protocols are one battleground in this larger war. They're not the whole war, but they matter.
Protocols like Nord Whisper represent a point in the cycle where innovation is ahead of detection. But that advantage is temporary. The cycle will repeat: newer detection methods will emerge, protocols will evolve further, and the arms race continues.
But here's the thing: every year that VPN protocols stay ahead of censorship systems is a year that journalists can publish, activists can organize, and ordinary people can access information freely.
That matters.

FAQ
What is Nord Whisper?
Nord Whisper is a next-generation VPN protocol developed by NordVPN that makes VPN traffic appear indistinguishable from normal HTTPS web browsing traffic. Unlike WireGuard, which prioritizes speed but has detectable packet signatures, Nord Whisper combines both speed and stealth by wrapping VPN data inside TLS records and randomizing packet patterns to match legitimate web traffic.
How does Nord Whisper work differently from WireGuard?
WireGuard uses consistent packet sizes and predictable handshake patterns that machine learning detection systems can identify. Nord Whisper wraps VPN traffic inside legitimate-looking TLS records, randomizes packet sizes and timing to match real HTTPS traffic patterns, and uses standard HTTPS port 443. This makes it indistinguishable from normal encrypted web browsing at the packet inspection level, while maintaining the same encryption strength as WireGuard.
Will Nord Whisper replace WireGuard?
Probably not completely. WireGuard will remain the default for users in low-censorship areas where speed is the priority. Nord Whisper will become standard in regions with aggressive VPN blocking where stealth is more important than the small performance overhead. Most VPN providers will likely offer both protocols, letting users choose based on their specific needs.
Is Nord Whisper more secure than WireGuard?
Both use equivalent modern encryption (ChaCha20, Poly1305, Curve25519). Nord Whisper isn't more secure in terms of cryptographic strength—it's more secure in terms of remaining undetected. WireGuard has perfect encryption but visible patterns. Nord Whisper has perfect encryption plus invisible patterns. In censorship environments, Nord Whisper's undetectability is more valuable than any additional cryptographic strength.
Can Nord Whisper be detected?
It's far more resistant to detection than WireGuard, but not perfectly invisible. Sophisticated firewalls might detect it through behavioral analysis, timing analysis, or IP reputation tracking. However, basic detection methods like port-based blocking and protocol signature matching won't work because Nord Whisper is indistinguishable from legitimate HTTPS traffic.
Why is protocol stealth important if encryption is unbreakable?
Encryption protects the content of your data, not the fact that you're using a VPN. A firewall doesn't need to decrypt your traffic—it just needs to identify it as VPN traffic to block it at the connection level. Nord Whisper solves this by making VPN traffic invisible to detection systems, so it never gets blocked in the first place.
When will Nord Whisper be widely available?
As of 2025, Nord Whisper is in limited beta. Full rollout to all NordVPN users is expected within 12-24 months. Other VPN providers will likely follow once they develop their own stealth protocols or license Nord Whisper technology. The timeline for industry-wide adoption is probably 2-3 years.
Is Nord Whisper open source?
Currently no—NordVPN has kept it proprietary. However, they've committed to open-sourcing the protocol in the future. This is important for security because open-source code can be independently audited. Currently, the lack of open-source code makes it harder for security researchers to verify there are no vulnerabilities.
Should I switch from WireGuard to Nord Whisper?
It depends on your threat model. If you're in a country with minimal censorship and value speed, WireGuard is fine. If you're in a region where VPN blocking is common, or if you want to stay ahead of future detection systems, Nord Whisper is the better choice. The performance difference is small enough that stealth becomes the deciding factor.
What happens to my VPN traffic once it reaches the Nord Whisper server?
The Nord Whisper encryption is stripped away at the VPN server, and the traffic is handled like any other VPN connection. From the server's perspective, Nord Whisper traffic is identical to WireGuard traffic. The stealth only applies to the traffic between your device and the VPN server—once it reaches the server, it's decrypted and processed normally.
Will Nord Whisper work in China?
Likely yes, but with caveats. China's Great Firewall is extremely sophisticated. Nord Whisper's indistinguishability from HTTPS might let initial connections establish where WireGuard would be blocked, but sustained use might still trigger behavioral analysis detection. Early testing suggests Nord Whisper is significantly more usable than WireGuard in China, but no protocol is perfect against the Great Firewall's advanced detection capabilities.
Conclusion: The Evolution Continues
WireGuard was a revolution. It made VPN protocols fast, simple, and modern. But revolutions don't last forever. They get countered.
The VPN industry is now in the next phase: security through indistinguishability. Protocols like Nord Whisper represent the frontline of an escalating arms race between VPN developers and censorship systems.
This arms race isn't going away. It's accelerating. As governments get better at detecting VPNs, VPN providers get better at hiding them. As VPN providers innovate on stealth, firewall developers innovate on detection.
The practical outcome is this: the future of VPN technology isn't about choosing between speed and stealth—it's about having both. Protocols that can't be detected and deliver acceptable performance will become standard. Protocols that sacrifice one for the other will fade.
Nord Whisper represents this evolution. It's not perfect. It adds complexity. It has slight performance overhead. But it solves a real problem that billions of people face: keeping their internet access free from government and corporate surveillance in an increasingly hostile environment.
If you're in a region where VPN blocking is a real concern, staying informed about next-generation protocols like Nord Whisper isn't optional—it's essential. If you're choosing a VPN provider right now, one factor to consider is: are they investing in protocol innovation? That choice will matter more in 2-3 years than it does today.
The VPN landscape is changing. The protocols that worked yesterday won't necessarily work tomorrow. Staying ahead means understanding these technologies, supporting providers who innovate responsibly, and recognizing that internet freedom requires constant evolution.
WireGuard got us here. Nord Whisper takes us further. What comes next? We'll find out soon enough.
Key Takeaways
- WireGuard's speed came at the cost of detectability—modern firewalls identify its packet signatures with 95%+ accuracy using machine learning
- NordWhisper solves this by making VPN traffic indistinguishable from normal HTTPS, combining speed with stealth in a single protocol
- The VPN arms race is accelerating: detection methods improve yearly, forcing VPN protocols to evolve beyond just encryption to traffic obfuscation
- For the 1.5 billion people in censorship-heavy regions, protocol stealth is more valuable than raw encryption strength—a blocked perfect connection is useless
- The future of VPNs isn't about choosing between speed and stealth, but about protocols that deliver both while staying ahead of increasingly sophisticated detection systems
Related Articles
- VPN Innovations That Surprised Everyone in 2025
- 9 Game-Changing Cybersecurity Startups to Watch in 2025
- How to Explain VPN Importance to Your Parents: 2025 Guide
- Best VPN Deals 2025: Save Up to 88% on Premium Services [2025]
- Malicious Chrome Extensions Stealing Data: What You Need to Know [2025]
- Aflac Data Breach: 22.6 Million Exposed [2025]
![Beyond WireGuard: The Next Generation VPN Protocols [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/beyond-wireguard-the-next-generation-vpn-protocols-2025/image-1-1766821338145.jpg)



