How Password Security Actually Works in 2025
You probably think your biggest security threat is a hacker guessing your password. You're wrong. The real threat is much more mundane—it's you, reusing the same password across 47 different websites because remembering unique ones is exhausting.
That's the gap Bitwarden is trying to fix with its latest update. And honestly, the changes they're rolling out hit at exactly the right moment, because password fatigue is getting worse, not better.
Most people think cybersecurity is about complex technical barriers. But according to Verizon's 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, 74% of breaches involve human interaction, which means social engineering, phishing, and credential reuse are still the fastest routes into systems. Bitwarden's new features directly address these gaps.
The update covers five main areas: vault health monitoring, password strength coaching, expanded storage, enhanced 2FA capabilities, and a new phishing blocker. Each one solves a specific problem that password manager users face in the real world. Let's break down what's actually changing and whether the price increase is worth it.
TL; DR
- Vault Health Alerts: Bitwarden now flags reused, exposed, and weak passwords automatically
- Password Strength Coaching: Get real-time guidance when creating new passwords, not just after
- Storage Expansion: 5GB for attachments, up to 10 authentication methods per account
- Phishing Detection: New tool proactively blocks malicious sites before they can steal credentials
- Price Increase: Individual plans jump from 19.80, Family plans from47.88—but existing customers get 25% off their first renewal

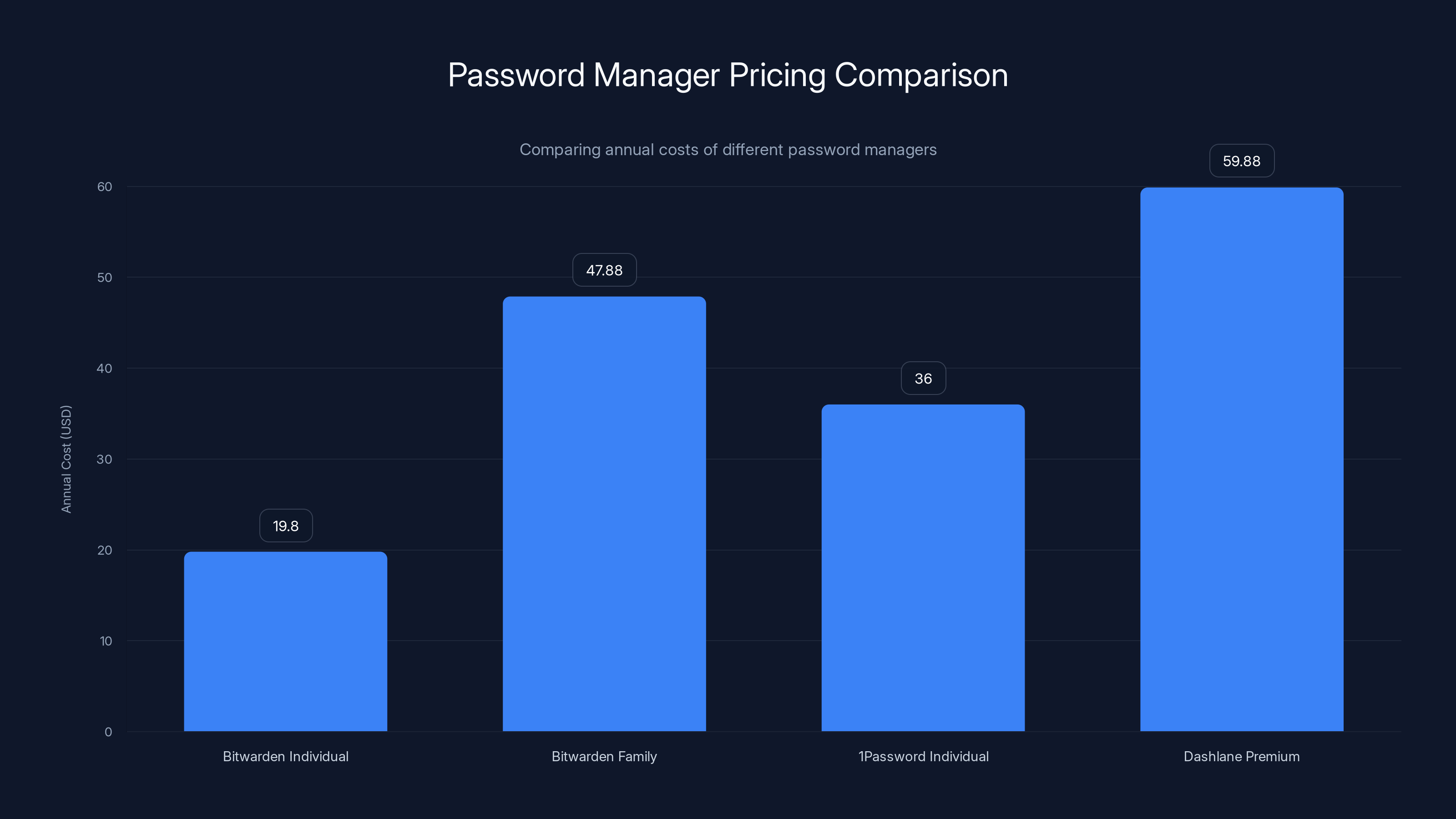
Despite the price increase, Bitwarden's Individual plan remains more affordable compared to 1Password and Dashlane. The Family plan also offers competitive pricing.
Understanding Vault Health Alerts and Why They Matter
Here's the thing about password reuse: it's incredibly common, incredibly dangerous, and almost impossible for users to track manually. You've got dozens or hundreds of passwords stored in your vault. How do you know which ones are weak? Which ones have been exposed in a breach? Which ones are used on multiple sites?
You don't. Not without help.
Bitwarden's vault health alert system automatically scans your stored passwords and flags problems. Reused passwords get tagged. Exposed passwords (ones that appeared in known data breaches) get flagged. Weak passwords—ones that don't meet modern security standards—get highlighted.
What makes this different from other password managers is the coaching aspect. When Bitwarden flags a problem, it doesn't just say "fix this." It actively guides you toward a better password.
The dashboard shows you at a glance how many passwords are weak, how many are exposed, how many are reused. Then it lets you sort by problem type so you can tackle the most critical issues first. This is genuinely useful for people who've been using the same password manager for years and accumulated password debt.
Most password managers give you a report. Bitwarden goes further—it tells you which passwords to fix first, shows you the relative risk of each one, and then coaches you through creating a replacement. It's the difference between a warning light on your dashboard and a mechanic who calls you with a repair plan.
For enterprises and families with shared vaults, this feature alone could prevent catastrophic breaches. If your family vault contains passwords for joint accounts and any of them are reused from public services, a breach at those public services instantly compromises your family's shared accounts. Vault health alerts catch this immediately.
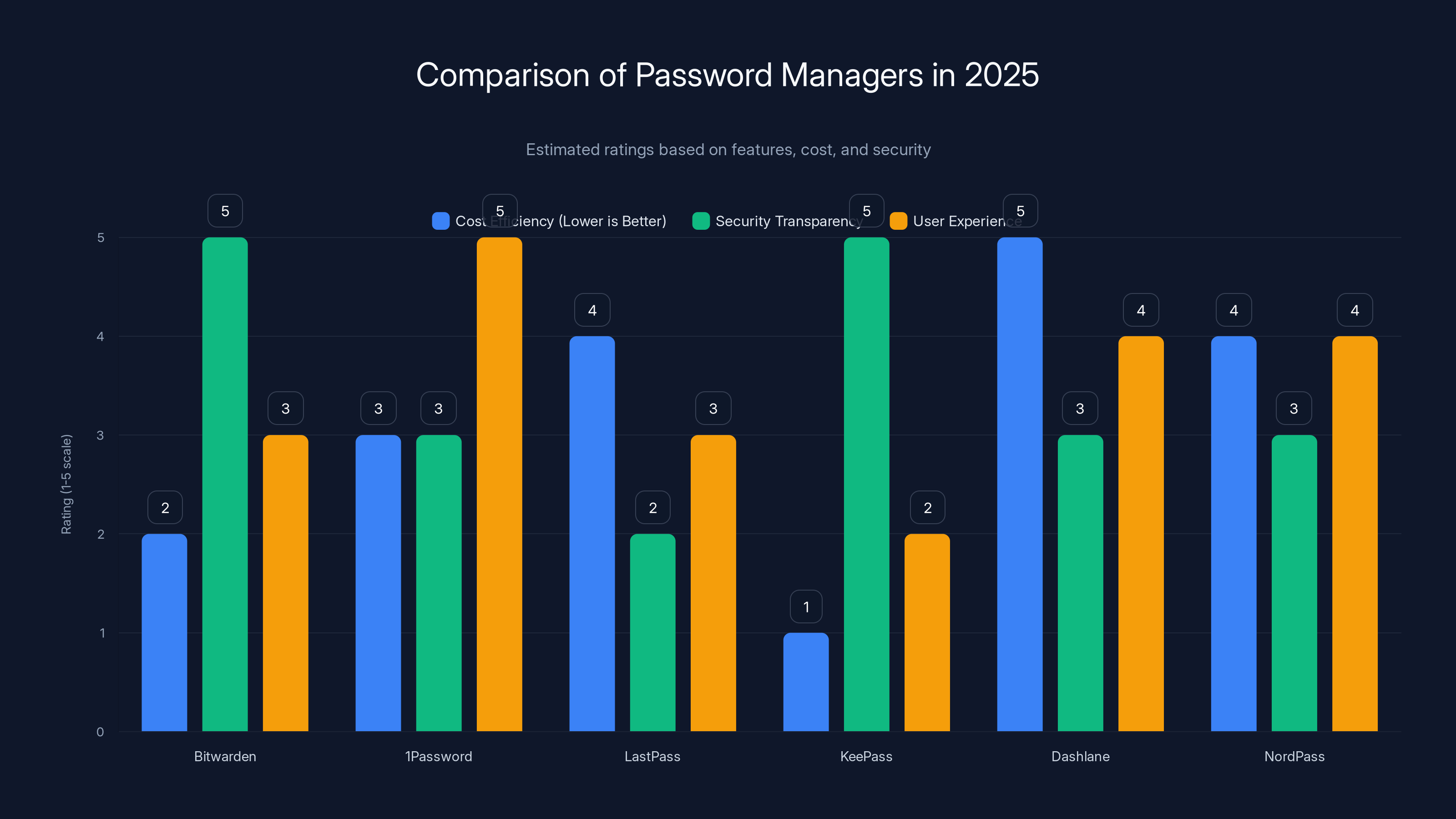
Bitwarden stands out for its security transparency and cost efficiency, while 1Password excels in user experience. Estimated data based on 2025 projections.
Password Strength Coaching: Teaching Users to Think Like Security Engineers
Weak passwords aren't usually weak because users are careless. They're weak because users don't understand what makes a password strong in 2025.
Most people still think strong passwords are ones with capital letters, numbers, and special characters. But modern password attacks don't work that way. Hackers don't brute-force random characters anymore. They use statistical attacks, dictionary attacks, and pattern recognition. A 12-character random string beats a 20-character "Password 123!" every single time.
Bitwarden's password strength coaching teaches users to think differently about passwords. Instead of just analyzing what you typed after you typed it, the new system guides you while you're typing. It shows you in real-time whether your password is weak, moderate, or strong. It explains why.
The system uses NIST password guidelines, which favor length over complexity. A 16-character random string from Bitwarden's password generator is infinitely more secure than a 12-character password with every character type included.
What's useful here is that Bitwarden doesn't just show you a strength meter. It explains the reasoning. When you're typing a password, it tells you: "This password is weak because it uses a dictionary word" or "This password is moderate because it's only 10 characters long." Then it suggests specific improvements: "Add 6 more random characters" or "Remove the dictionary word and use only random characters."
For family plans especially, this is valuable. If you're helping a relative set up their online banking password, the coaching feature ensures they actually understand why a strong password matters. It's education built into the tool.
The password generator itself is robust. It can create passwords with custom lengths, character sets, and patterns. Most people just use the default, which generates 16-character fully random passwords. That's... probably fine for most sites. But the coaching system means you understand what "fine" actually means in security terms.

Storage Expansion: From Inconvenient to Actually Useful
Password managers are supposed to store passwords. That's literally the job. But Bitwarden's update adds something equally important: space for everything else that's related to accounts.
The attachment storage increase from an unstated limit to 5GB is huge. Here's why: you need to store things like backup codes, recovery documents, identity information, and occasionally screenshots of important account settings.
Backup codes especially are critical. When you enable two-factor authentication on any account—Gmail, Slack, Git Hub, whatever—you get a list of one-time backup codes. If you lose access to your authenticator app, these codes are your only way back into the account. They're secret. They're tied to a specific account. They absolutely should be stored in your password manager, not sitting in a text file on your desktop or scattered across your email.
With the old storage limits, you had to make choices. Store backup codes for all accounts, or store some other sensitive documents? Now you have space for all of it. The new limit is generous enough that a typical user won't hit 5GB unless they're storing video files or complete PDFs of every account's terms of service.
For families, this is genuinely useful. You might want to store:
- Backup codes for family shared accounts
- Screenshots of parental control settings
- Scans of physical security keys
- PDFs of billing statements
- Photos of important cards or documents
- Recovery information from service providers
With 5GB, you can do all of that without worrying about hitting limits.
The system is encrypted end-to-end, meaning Bitwarden can't see what you're storing. It's just sitting on their servers, encrypted with your master password. So storing sensitive documents here is actually safer than storing them in cloud services like Google Drive or One Drive, which have different security models.
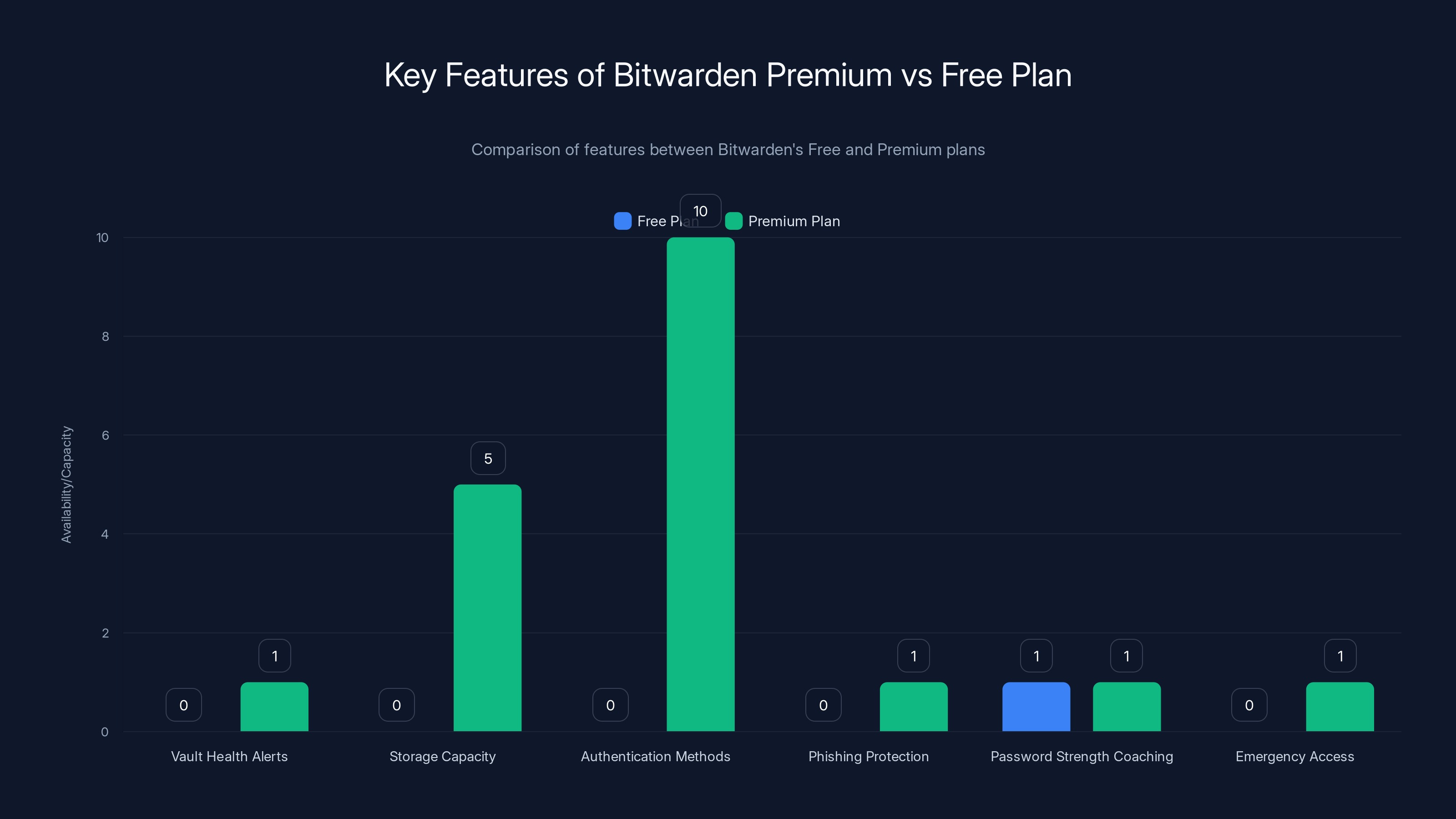
Bitwarden's Premium plan offers enhanced features such as vault health alerts, increased storage capacity, and phishing protection, which are not available in the Free plan. Estimated data based on feature descriptions.
Two-Factor Authentication Storage: Up to 10 Methods Per Account
Two-factor authentication is non-negotiable for any account that matters. But managing it is a pain, especially when you have multiple authenticator apps, physical keys, and recovery codes scattered across different devices and locations.
The old limit on 2FA storage methods in Bitwarden wasn't clearly stated, but the new limit of up to 10 authentication methods per account is basically unlimited for practical purposes. Most people use one or two per account. Having room for 10 means you can store:
- Your primary authenticator app (like Google Authenticator or Authy)
- A backup authenticator app on a different device
- Hardware security keys (Yubikey, etc.)
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint, face recognition)
- Passkeys (the new standard replacing passwords)
- SMS backup
- Email backup
- Recovery codes
- Trusted device tokens
- Phone number for emergency access
What's interesting here is that Bitwarden is positioning itself as a centralized hub for authentication methods, not just passwords. This makes sense because the future of authentication isn't passwords at all—it's passkeys.
Passkeys are cryptographic keys tied to your device, not text strings you type. They're more secure than passwords and 2FA combined. They're also becoming the standard—Microsoft, Google, Apple, and the W3C all support them.
Bitwarden's passkey support means you can store these cryptographic secrets in your vault, synced across devices, with full backup and recovery options. That's a big deal because losing a passkey usually means losing access to an account. If your passkey is stored in your Bitwarden vault with 5GB of backup space, you've got recovery options.
For family plans, having room for multiple authentication methods per account means every family member can have their own authenticator app set up while still being able to access shared accounts through Bitwarden. It's better security without losing convenience.
The New Phishing Blocker: How It Works and What It Actually Does
Bitwarden is being deliberately vague about the phishing blocker, which is either smart marketing or a sign that it's still being perfected. The official description: "Proactively identify and block malicious websites before they can steal credentials."
That's... vague. But here's what's likely happening under the hood.
Phishing works when you visit a fake website that looks exactly like the real thing. You log in with your credentials, and the attacker now has them. Traditional phishing protection works in two ways:
- URL checking: Before you visit a website, check if it's known to be malicious. Google Safe Browsing does this—it's the reason Chrome warns you about unsafe sites.
- Behavior detection: Watch for suspicious patterns. Did you click a link in an email from someone new? Are you visiting a URL that's similar to but slightly different from a legitimate site you use regularly?
Bitwarden's phishing blocker probably uses both. When you're about to enter your credentials into a login form, the blocker checks:
- Is this domain in any known phishing database?
- Does this domain match the domain your password is stored for?
- Is this domain similar to a domain where you have stored credentials?
- Does this page show typical phishing patterns?
The genius move is that Bitwarden is integrating this directly into the password autofill process. Most of the time when you use Bitwarden, you just click the extension, see your passwords, and click one to autofill. If Bitwarden detects you're on a phishing site, it could refuse to autofill or show a warning.
This is legitimately useful because you're protected at the moment of highest risk—when you're actually about to enter credentials.
The implementation details matter though. A poorly tuned phishing detector creates false positives and becomes noise that users ignore. A good one catches actual threats. We don't know yet which category Bitwarden's falls into, but given that they're being cautious about the rollout, they're probably testing carefully.
For family plans, phishing protection is especially valuable. If you've got relatives who click every link in every email, this might be the thing that actually prevents them from getting compromised.

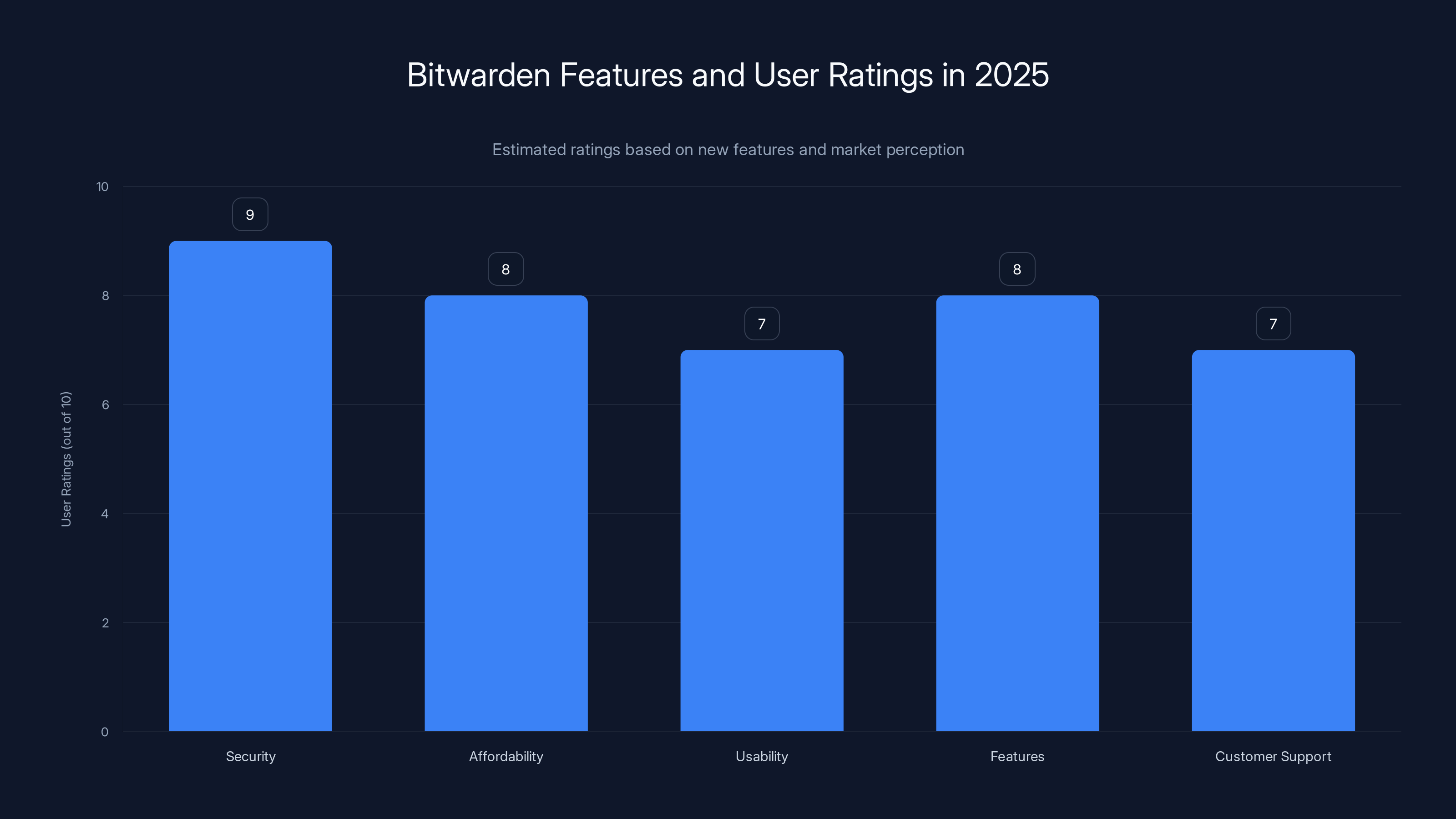
Bitwarden is rated highly for security and affordability, with strong features and usability. Estimated data based on 2025 projections.
The Pricing Change: What You're Actually Paying For
Let's talk money, because the price increase is real and it matters.
Individual Premium plan:
- Old price: 0.83/month)
- New price: 1.65/month)
- Increase: 98% price increase
Family Premium plan (up to 6 users):
- Old price: 3.33/month)
- New price: 3.99/month)
- Increase: 20% price increase
That's a dramatic increase for individuals, but less dramatic for families (which makes sense—families were underpriced before). To soften the blow, Bitwarden is giving existing customers a 25% discount on their first renewal year. That brings the individual price down to about
Here's the framework for deciding if it's worth it:
The Individual Plan is worth it if you:
- Use the same password manager across multiple devices
- Have more than 10 critical accounts you care about
- Want recovery from phishing attacks
- Need to store sensitive documents alongside passwords
- Value the open-source transparency (Bitwarden publishes its source code)
The Family Plan is worth it if you:
- Have 3+ family members who need password management
- Want shared accounts (streaming services, family email, etc.)
- Need to teach less tech-savvy family members about security
- Want password strength coaching for family members
- Need a way to store important family documents (tax records, insurance info, etc.)
For comparison, 1 Password Individual costs
The break-even point depends on how much you value the features. If you never use vault health alerts and you don't store attachments, the price increase is objectively worse. But if you have a reused password sitting in your vault right now that could compromise multiple accounts, vault health alerts alone justify the cost. One prevented breach pays for years of Bitwarden subscriptions.

Bitwarden's Pricing Structure and the Tier System Explained
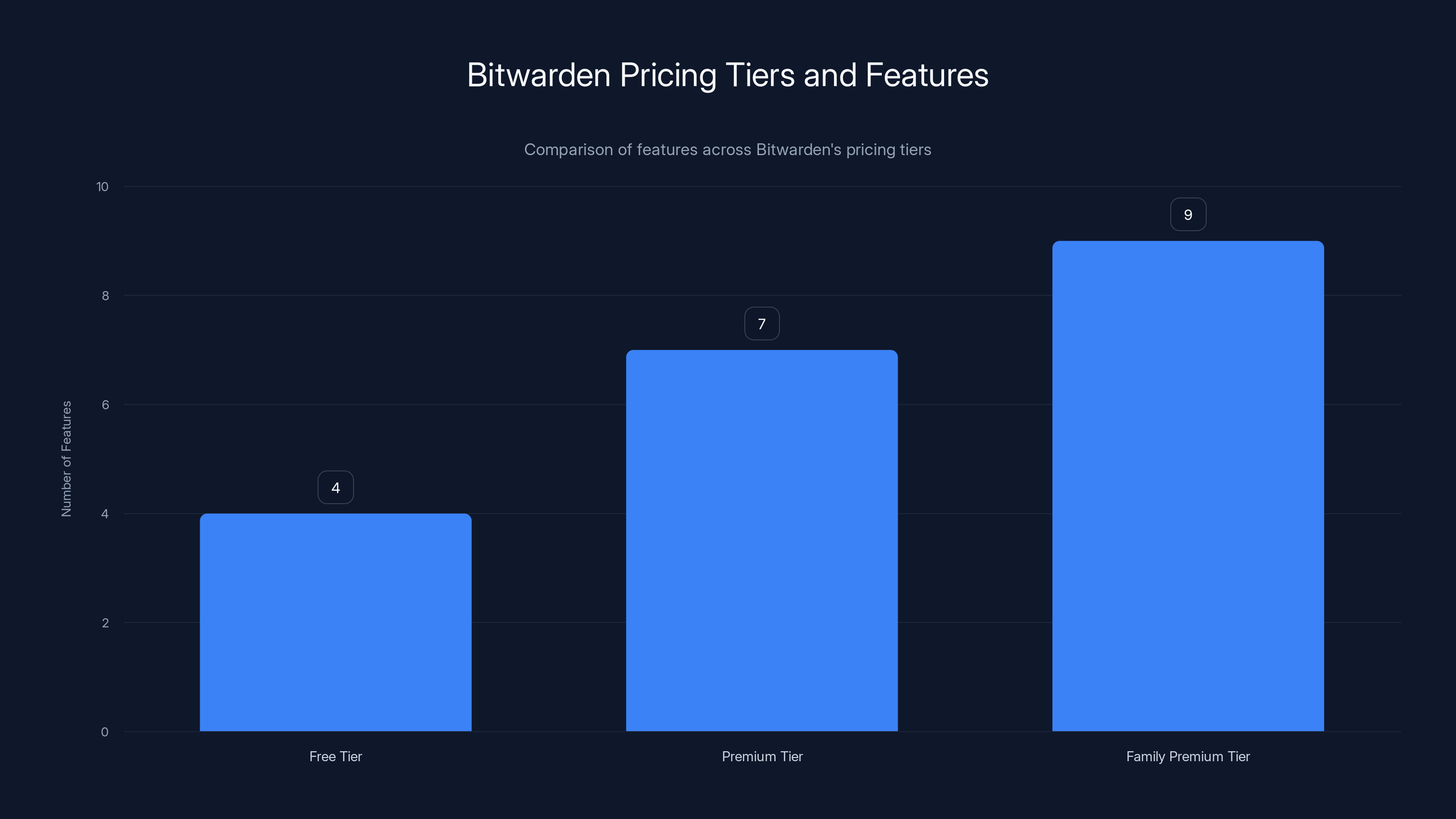
Bitwarden actually has a pretty interesting pricing structure that most users don't fully understand. There's a free tier, a Premium tier, and an Organizations tier (for teams).
The free tier gives you:
- Unlimited passwords and notes
- Apps for every device
- Desktop app, browser extensions, mobile apps
- Full encryption
That's... basically everything you need. Most people can use Bitwarden's free tier forever and be perfectly secure. The paid tier adds convenience and advanced security features, not core functionality.
The Premium tier adds:
- Vault health reports and alerts
- Password strength coaching
- Attachment storage (now 5GB)
- Emergency access (let someone retrieve your vault if you become incapacitated)
- Priority support
- Two-factor authentication method storage
- Phishing detection
The Family Premium tier adds:
- All of the above
- For up to 6 family members
- Shared vault functionality
- Individual and shared items
There's also an Organizations tier for businesses, but that's a different pricing model based on number of users.
What's smart about this structure is that Bitwarden is charging for features most users actually want, not for core security. You can have military-grade encryption for free. You only pay if you want vault management features and better organization.
This is very different from, say, 1 Password, which charges for almost everything. It's also different from Last Pass, which has a confusing tier system that's changed multiple times.
Bitwarden's approach is transparent: here's what's free, here's what costs money, here's why. You decide if it's worth it.
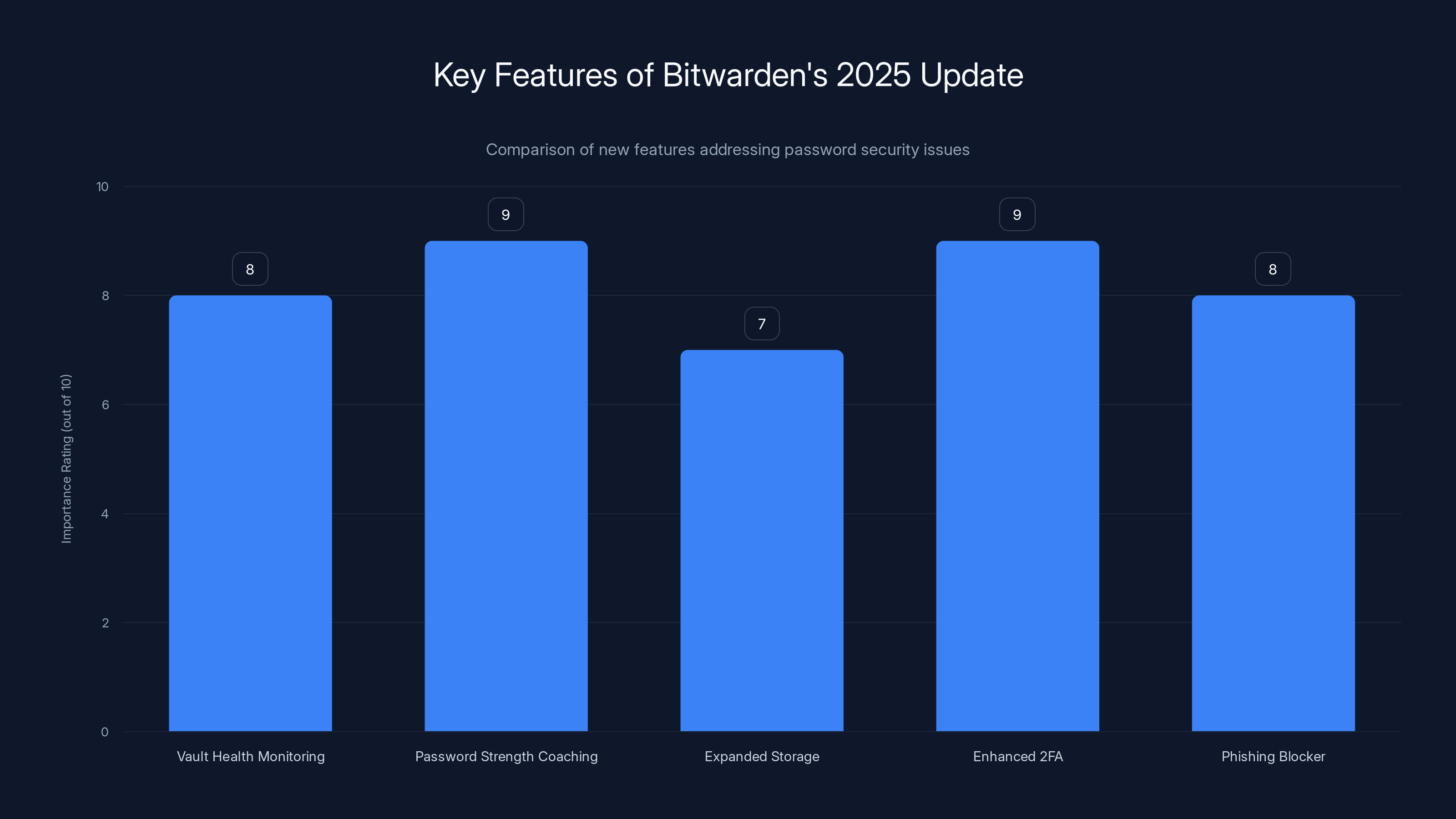
Bitwarden's 2025 update focuses on critical areas like password strength and phishing protection, with high importance ratings for each feature. Estimated data based on feature descriptions.
How Bitwarden Compares to Other Password Managers in 2025
The password manager market is actually pretty competitive right now. Bitwarden isn't the only option, and it's definitely not the fanciest. But it's got some real advantages and some real disadvantages.
Bitwarden vs. 1 Password: 1 Password has a slicker interface and better design. Bitwarden is more transparent about security (open source). 1 Password costs more (
Bitwarden vs. Last Pass: Last Pass had a major breach in 2022 that compromised customer vaults. They've since recovered, but trust was damaged. Bitwarden has had no major breaches. Last Pass has a confusing pricing structure. Bitwarden's is straightforward. For security-conscious users, Bitwarden wins decisively.
Bitwarden vs. Kee Pass: Kee Pass is free, open source, and completely local (no cloud sync). Bitwarden is also open source but has cloud sync, which is more convenient. Kee Pass never had a breach because there's nothing to breach (no servers). Bitwarden had no breaches despite having servers. For most people, Bitwarden's convenience and better UX wins. For paranoia enthusiasts, Kee Pass wins.
Bitwarden vs. Dashlane: Dashlane costs more ($59.88/year). Dashlane focuses more on ease of use and less on transparency. Bitwarden is more transparent about security. Dashlane has some nice UX touches that Bitwarden lacks. For most users, Bitwarden's lower cost and better security transparency wins.
Bitwarden vs. Nord Pass: Nord Pass is owned by Nord Security, the VPN company. It's integrated with their VPN. For users already in the Nord ecosystem, it makes sense. For everyone else, Bitwarden's independence is actually an advantage. Pricing is similar ($19/year for Nord Pass).
The theme here is that Bitwarden sits in a sweet spot. It's not the most user-friendly (1 Password), not the fanciest (Dashlane), not the cheapest (it's free, technically), but it's the best balance of security, transparency, cost, and functionality.

Migration: Moving from Another Password Manager to Bitwarden
If you're currently using another password manager, switching to Bitwarden isn't painful. Most password managers can export their data in a standard format, and Bitwarden can import it.
The process goes like this:
-
Export from your current manager: Go into settings, find "export" or "backup," and download a CSV or JSON file of your passwords. This file will contain all your credentials in plain text (locally), so handle it carefully.
-
Import into Bitwarden: Log into your Bitwarden account, go to Tools > Import Data, select the file you exported, and run the import. Bitwarden will handle the mapping automatically.
-
Verify the import: Check a few entries to make sure everything imported correctly. Sometimes formatting differences between password managers cause issues.
-
Delete the export file: That CSV file sitting on your computer contains your passwords in plain text. Delete it securely (not just to trash, actually permanently delete it).
-
Update your master password: If you want to be extra careful, change your Bitwarden master password after importing. This ensures that if your old password manager was ever compromised, the new one is secure.
The whole process takes maybe 10 minutes. The hardest part is deciding whether to delete your old password manager account immediately or keep it around as a backup for a month.
One thing to be aware of: some password managers don't export perfectly. Last Pass, for example, sometimes loses folder organization during export. Bitwarden will import everything, but you might need to reorganize it into folders afterward. It's not hard, just tedious.
The vault health alerts actually make this a great time to switch. When you import your old passwords into Bitwarden, the vault health scan will immediately flag any passwords that are reused, exposed, or weak. That gives you a clear to-do list of accounts to secure first.
Bitwarden's free tier offers essential security features, while the Premium and Family Premium tiers add advanced management and sharing capabilities. Estimated data based on feature descriptions.
Setting Up Two-Factor Authentication Within Bitwarden
Once you're using Bitwarden, the next step is enabling 2FA on your Bitwarden account itself. This is critical—your Bitwarden account is the master key to all your passwords. If someone compromises it, they compromise everything.
Bitwarden supports multiple 2FA methods:
Authenticator app (recommended) Use Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Authy, or any TOTP-compatible app. This generates a six-digit code that changes every 30 seconds. It's secure, convenient, and works even if your phone doesn't have internet.
Email Bitwarden sends a code to your email after you log in. This is convenient but less secure (if your email is compromised, this is compromised).
Hardware security key A physical device like a Yubikey. This is the most secure option but requires carrying an extra device. Very few people use this for password managers, but it's available.
Duo Duo Security is a service that sends push notifications to your phone for approval. It's convenient and secure, but requires an additional account.
Remember this device Bitwarden can remember your device for 30 days, so you don't have to enter a 2FA code every single time you log in.
The best practice is to use an authenticator app (so it works even if your phone has no service) and enable "remember this device" on your home computer. This balances security with convenience.
When you set up 2FA on Bitwarden, you'll get backup codes. Store these in a safe place. Ironically, the safest place to store them is... in a different Bitwarden account, or written down on paper, or stored in a different secure system. You don't want your 2FA backup codes in the same vault as everything else, because if someone compromises your Bitwarden account, they've got everything.

Best Practices for Using Bitwarden Securely
Bitwarden is secure by default, but you can make it even more secure with a few practices.
Use a strong master password Your master password is the only key to your vault. If it's weak, everything is weak. Use the password generator to create a 20+ character random password, or use a passphrase of random words. Write it down (yes, physically, on paper) and store it somewhere safe. You won't need to type it often, so having it written down is acceptable.
Enable 2FA We covered this above, but it's critical. Don't skip this step.
Use biometric unlock On mobile devices, enable fingerprint or face unlock. This means you don't have to type your master password every time, but someone can't just unlock your phone and access Bitwarden without your fingerprint or face.
Lock your vault on app close Bitwarden can auto-lock your vault when you close the app or after a period of inactivity. This means if someone grabs your device while you're away, they can't access your vault.
Review vault permissions If you're sharing a vault with family members, review who has access to what. Shared items should only be shared with people who actually need them.
Don't share your master password Your master password is yours alone. Bitwarden doesn't need it, your family doesn't need it, nobody needs it but you. If you need to give someone access to specific passwords (like family bank account access), use Bitwarden's sharing features instead of giving them your master password.
Keep Bitwarden updated New security features and patches are released regularly. Keep your app updated. Bitwarden auto-updates on most platforms, but check occasionally to make sure you're current.
Back up your master password recovery code When you create your Bitwarden account, you get a recovery code. This code can be used to reset your master password if you forget it. Store it somewhere safe and offline (not in Bitwarden).

The Security Architecture Behind Bitwarden's Encryption
Bitwarden's architecture is interesting because it's built on a principle that sounds simple but is hard to execute: the company can't decrypt your passwords even if they wanted to.
Here's how it works:
-
Client-side encryption: Everything is encrypted on your device before it's sent to Bitwarden's servers. Your passwords never exist in unencrypted form on Bitwarden's servers.
-
Master password derivation: Your master password isn't stored anywhere. Instead, it's used to derive encryption keys through a process called PBKDF2. The math:
iterations = 600,000,hash function = SHA-256. This means that brute-forcing your master password would take an absurdly long time, even with powerful computers. -
Vault encryption: Your vault is encrypted with a randomly generated key. That key itself is encrypted with your master password. So the data flow is: Password → Key → Encrypted Vault.
-
End-to-end encryption: When you share passwords with family members, the sharing happens with additional encryption layers. The shared password is encrypted for the recipient using their encryption key.
The beauty of this architecture is that Bitwarden's servers hold nothing useful. A hacker who compromises Bitwarden's servers gets encrypted data that's worthless without the master passwords. Bitwarden employees can't read your passwords even if a court subpoenas them.
This is provable because Bitwarden is open source. You can audit the code yourself. Security researchers have audited it. Third parties have verified it. It's not a black box.
Compare this to Last Pass, which isn't open source. Nobody can verify their encryption claims. That asymmetry of trust is why Bitwarden feels safer to a lot of people.
The encryption strength comes down to the master password. If your master password is weak, a hacker with a captured encrypted vault could potentially crack it using a dictionary attack or rainbow tables. But if your master password is truly random and 20+ characters, the computational cost of cracking it is absurd. We're talking about "more expensive than the value gained" level of absurd.
Zero-Knowledge Proof and Why It Matters
Zero-knowledge proof is a concept that sounds complicated but isn't. It means: proving that something is true without revealing any information beyond that fact.
In Bitwarden's context, it means: Bitwarden can verify your identity (know that you're who you claim to be) without ever knowing your master password.
Here's a simplified version of how it works:
- You set a master password: "My Secure Password 123!"
- You derive an encryption key from it using math: Key = f(Password)
- You send the server only a hash of the key, not the key itself
- Every time you log in, you send the server: "Here's my password hash. Does it match what you have?"
- The server says yes or no without ever knowing your actual password
This is why Bitwarden can't reset your password. If you forget your master password, they can't recover it because they never had it. They can only let you create a new vault with a new master password (losing everything in your old vault).
This is annoying if you forget your password, but it's brilliant for security. It means even if someone compromises Bitwarden's database of password hashes, they can't do anything with them. The hashes are derived from your master password, not your actual password.
OWASP recommends never storing passwords in ways that let you recover them. Bitwarden follows this principle religiously.
When to Use Premium vs. Free Bitwarden
Let's be practical about this. The free tier of Bitwarden is genuinely comprehensive. You get:
- Unlimited password storage
- Unlimited secure notes
- Apps for every platform
- Full encryption
- All the core security features
If all you need is a secure place to store passwords, free Bitwarden is all you need. You'll never hit a limit.
You should upgrade to Premium if:
- You want vault health alerts that identify weak, reused, or exposed passwords
- You store sensitive documents (tax returns, insurance cards, medical records) alongside passwords
- You want password strength coaching to understand what makes a strong password
- You need to store multiple 2FA methods per account
- You want priority support and emergency access (recovery of your vault if you can't access it)
- You want the phishing protection feature
- You want to feel like you're supporting an independent security company
You should use Family Premium if:
- You have 3+ family members who need password management
- You want to set up shared accounts (Netflix, Amazon, etc.) that multiple family members access
- You want to teach family members about password security with built-in coaching
- You want parental controls for younger users' vaults
- You want a centralized way to manage family emergency access
The break-even math: if even one vault health alert prevents you from getting compromised once in the next decade, Premium pays for itself many times over. If nothing else, it's cheaper than dealing with identity theft.
Common Mistakes People Make with Password Managers
People are surprisingly bad at using password managers, even though the concept is simple.
Mistake #1: Using a weak master password because they think Bitwarden will remember it Bitwarden won't. If your master password is "password 123," your vault is effectively worthless. Use a strong one.
Mistake #2: Not enabling 2FA on the password manager itself Your password manager is the crown jewel. Protect it like Fort Knox. Enable 2FA.
Mistake #3: Not using the password generator Most people create passwords by hand. Most hand-created passwords are weaker than they think. Use the generator. Let it create 20-character random passwords. Your brain is bad at randomness.
Mistake #4: Storing the master password in the password manager This defeats the entire purpose. The master password should be in your head or written down and stored somewhere safe. Not in the vault.
Mistake #5: Not storing backup codes for 2FA in the password manager Here's where it gets funny: you should store your 2FA backup codes in your password manager. But not on the same account that has the master password. Have a backup account, or store them in another secure location.
Mistake #6: Not reviewing vault health alerts Bitwarden will tell you which passwords are weak or reused. If you ignore those warnings, you're missing the entire point.
Mistake #7: Trusting a "memorable" password you created yourself Your personal "memorable" password is probably weaker than you think and easier to guess than Bitwarden's generated password. Trust the generator.
Mistake #8: Not keeping Bitwarden updated Updates include security patches. Use them.
The Future of Password Management and Where Bitwarden Fits In
Passwords are dying. That's not new news—security experts have been saying "passwords are dead" for about 15 years. But they're actually dead now.
The replacement is passkeys. Passkeys use cryptographic keys instead of text strings. They're faster, more secure, and impossible to phish. Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Amazon all support them. Git Hub, Slack, Discord, and hundreds of other services now support them.
Bitwarden is betting on passkeys being the future, which is why they added passkey storage to the new update. You can store your passkey in your Bitwarden vault, and it syncs across all your devices. When you need to log into a service, you authenticate with your biometric (fingerprint, face) and the passkey is used under the hood.
This solves a major problem with passkeys: they're stored on your device by default, which means losing your device means losing your passkeys. But Bitwarden can back them up to the cloud (encrypted, of course), so if you switch phones, you still have your passkeys.
In 5-10 years, passwords might be genuinely uncommon. Most login systems will use passkeys. But we're not there yet. Right now, you need both a password manager for the thousands of websites that still use passwords, and passkey support for the growing number of sites that support them.
Bitwarden is positioned well for this transition. They're adding passkey support, cloud backup for passkeys, and support for emerging authentication standards. If you're choosing a password manager today, choosing one that supports passkeys tomorrow is smart.
FAQ
What is Bitwarden's vault health alert feature?
Vault health alerts automatically scan your stored passwords for three types of security problems: reused passwords (the same password used on multiple sites), exposed passwords (passwords that appeared in known data breaches), and weak passwords (ones that don't meet modern security standards). When Bitwarden finds problems, it flags them and provides guidance on which accounts to fix first. This is valuable because most people have dozens or hundreds of passwords and can't manually track which ones are weak or reused.
How does password strength coaching work in Bitwarden?
When you create or update a password in Bitwarden, the strength coaching feature provides real-time feedback about whether your password is weak, moderate, or strong. It explains the reasoning behind its assessment (e.g., "too short," "uses dictionary words") and suggests specific improvements. The system prioritizes length over complexity, following modern security standards that favor a 20-character lowercase password over a 12-character password with mixed characters. This helps users understand that strength comes from randomness and length, not from inserting capital letters and numbers into readable words.
Why should I upgrade from Bitwarden's free plan to Premium?
Bitwarden's free plan handles unlimited passwords and notes with full encryption, so it covers basic password management. However, Premium adds valuable features: vault health alerts to identify security risks, 5GB storage for sensitive documents like backup codes and recovery information, capacity to store up to 10 authentication methods per account, phishing protection to prevent credential theft on fake websites, password strength coaching, and emergency access (letting designated people access your vault if something happens to you). For most users, the phishing protection and vault health alerts alone justify the $19.80 annual cost by preventing potential breaches.
What is passkey support and why does Bitwarden emphasize it?
Passkeys are cryptographic keys that replace passwords for authentication. Instead of typing a password, you authenticate using your fingerprint, face, or a hardware key. Passkeys eliminate phishing because they're cryptographically tied to the specific website (you can't accidentally use a passkey on a fake website), and they're faster and more secure than passwords with two-factor authentication. Bitwarden emphasizes passkeys because the authentication industry is moving toward them as the standard. Bitwarden can store your passkeys in your vault, synced across devices with cloud backup, solving the major problem with device-local passkey storage.
How secure is Bitwarden compared to other password managers?
Bitwarden's security comes from three factors: end-to-end encryption (your passwords are encrypted on your device before reaching Bitwarden's servers), open-source code (anyone can audit it for security flaws), and zero-knowledge architecture (Bitwarden can't read your passwords even if they wanted to). The code is publicly auditable, and third-party security researchers have reviewed it. Compared to password managers like 1 Password (which is closed-source), Bitwarden offers more transparency. Compared to Last Pass (which had a major breach in 2022), Bitwarden has had no major security incidents. The main security weaknesses depend on user behavior: a weak master password undermines everything, and reusing the master password elsewhere defeats the entire system.
Is the price increase worth it for existing Bitwarden users?
The Individual plan price increase from
How do I switch from another password manager to Bitwarden?
Export your passwords from your current password manager (usually in Settings, look for "Export" or "Backup") as a CSV or JSON file, then import that file into Bitwarden through Tools > Import Data. Bitwarden will handle the mapping. Verify that a few entries imported correctly, then securely delete the export file (it contains your passwords in plain text). Wait a week before deleting your old password manager account, in case something didn't import correctly. When you import, Bitwarden's vault health scan will immediately flag any reused, weak, or exposed passwords, giving you a to-do list of accounts to secure first.
What should I do if I forget my Bitwarden master password?
Bitwarden can't recover your master password because they don't store it. This is a security feature—your master password is never known by Bitwarden. If you forget it, you have one option: use your master password recovery code (which you were given when you created your account) to reset your password and regain access to your vault. If you don't have the recovery code, you've permanently lost access to your vault. This is why storing your recovery code somewhere safe (written down, in a secure location) is critical. It's the only backstop if you lose your master password.
Can I share passwords with family members without sharing my master password?
Yes, and this is important: never share your master password. Instead, use Bitwarden's sharing features. In the Family Premium plan, you can create shared vaults that multiple family members can access. You can also share individual passwords with family members without giving them access to your entire vault. This ensures that family members can access shared accounts (like Netflix or Amazon) without knowing your master password. If a family member's device is compromised, the attacker can't access your entire vault because they don't have your master password.
What is the difference between Bitwarden's Individual and Family plans?
The Individual plan (

Conclusion: Is Bitwarden Right for You in 2025?
Password management isn't sexy. It's not exciting. But it's the foundation of your digital security, and getting it right prevents the vast majority of account compromises.
Bitwarden has positioned itself as the "boring but reliable" option in the password manager market. It's not the fanciest interface. It's not owned by a venture mega-corporation with unlimited marketing budgets. But it's secure, transparent, affordable, and it genuinely works.
The new update adds features that address real problems: vault health alerts catch the passwords you've forgotten about. Password strength coaching teaches users to think differently about security. The phishing blocker prevents the most common attack vector. The expanded storage and 2FA capacity make Bitwarden more useful for people with complex security needs.
The price increase is real, and it stings for individual users. But even at $19.80/year, Bitwarden is cheaper than most competitors, and the new features provide genuine value. For families, the upgrade is actually more attractive now because vault health alerts and password coaching become useful for multiple people.
If you're using a free password manager (or worse, no password manager), Bitwarden's free tier is a significant security upgrade. If you're using another paid password manager, Bitwarden's combination of transparency, affordability, and new features makes it worth considering a switch.
The real test is whether the update actually prevents breaches and whether users actually use the new features. Vault health alerts are only valuable if people act on them. Password strength coaching is only useful if people trust it. Phishing detection is only effective if it catches real phishing attempts without creating false alarms.
Based on how Bitwarden has handled security in the past, they're likely to get these features right. They're not trying to be fancy, they're trying to be practical. In 2025, when security threats are more sophisticated than ever, practical might be exactly what you need.
Start with the free tier if you're undecided. Try it for a month. If you find yourself wanting vault health alerts or better organization tools, the Premium upgrade is straightforward. If you're happy with the free tier, you've still got military-grade encryption for zero dollars.
Either way, the important thing is that you're using some form of password management instead of reusing the same password across 50 websites. That single change—moving from password reuse to unique passwords managed by Bitwarden—eliminates the attack vector that compromises most people.
Do that, and you're already ahead of 90% of internet users.
Key Takeaways
- The update covers five main areas: vault health monitoring, password strength coaching, expanded storage, enhanced 2FA capabilities, and a new phishing blocker
- Png)
*Despite the price increase, Bitwarden's Individual plan remains more affordable compared to 1Password and Dashlane
- Then it lets you sort by problem type so you can tackle the most critical issues first
- But Bitwarden's update adds something equally important: space for everything else that's related to accounts
- Here's why: you need to store things like backup codes, recovery documents, identity information, and occasionally screenshots of important account settings
Related Articles
- Driving Theory Test Cheating: How Technology is Breaking the System [2025]
- SSD Prices Are Rising: The Best Drives to Buy Before 2025 [2025]
- Best Time to Post on Instagram in 2026: Data-Backed Strategy [2026]
- Tottenham vs Borussia Dortmund Free Streams: How to watch Champions League 2025/26 | TechRadar
- Why Netflix Ditched Wireless Casting (But Google Won't) [2025]
- Quordle Hints & Answers: Daily Game Guide & Strategy [2025]