Introduction: The Vertical Video Revolution You've Been Waiting For
If you've spent the last five years watching creators squeeze their beautiful widescreen videos into vertical formats for Tik Tok and Instagram Reels, you know how painful that looks. Black bars. Cropped content. Lost visual impact. Google just fixed that problem.
In January 2025, Google unveiled a significant update to its Veo 3.1 AI video generation model. The headline feature sounds simple: native vertical video support with reference images. But what's actually happening under the hood is way more interesting. Google didn't just rotate the aspect ratio. They rebuilt how the AI understands and generates video when you give it a reference image to work from.
This matters because vertical video has become the primary format for how billions of people consume content. YouTube Shorts, Instagram Reels, Tik Tok, Snapchat, Be Real. If your content doesn't look native to these platforms, it looks amateur. And if you're creating videos with AI, you're now dealing with an additional constraint: the model needs to understand your visual intent from a reference image, then translate that into smooth, expressive motion within a completely different aspect ratio.
Veo 3.1 handles all of this. The model now generates videos that are natively 9:16 vertical format, works from your reference images to maintain visual consistency, produces more expressive character movements and emotions, and handles upscaling to 1080p and 4K without degradation. You can access these features directly in the Gemini app, YouTube Shorts, YouTube Create, Google's Flow video editor, or through the API if you're building something custom.
What's genuinely interesting about this update isn't just the feature set. It's what it signals about where AI video generation is heading. For the first time, we're seeing a major AI video model treat vertical video as a first-class citizen rather than an afterthought. Google isn't forcing creators to choose between creative control and platform compatibility anymore. You can have both.
Let's dig into what changed, how it works, why it matters for creators and businesses, and how this compares to what competitors are doing.
TL; DR
- Veo 3.1 now creates native 9:16 vertical videos eliminating cropping and black bars on social platforms
- Reference images generate more expressive videos with better character emotions and movements, even with shorter prompts
- Improved consistency features blend characters, objects, backgrounds, and textures for cohesive outputs across entire videos
- Upscaling reaches 1080p and 4K on professional tools like Flow and Vertex AI for broadcast-quality vertical content
- Multiple access points including Gemini app, YouTube Shorts, YouTube Create, and APIs make this accessible to creators and developers

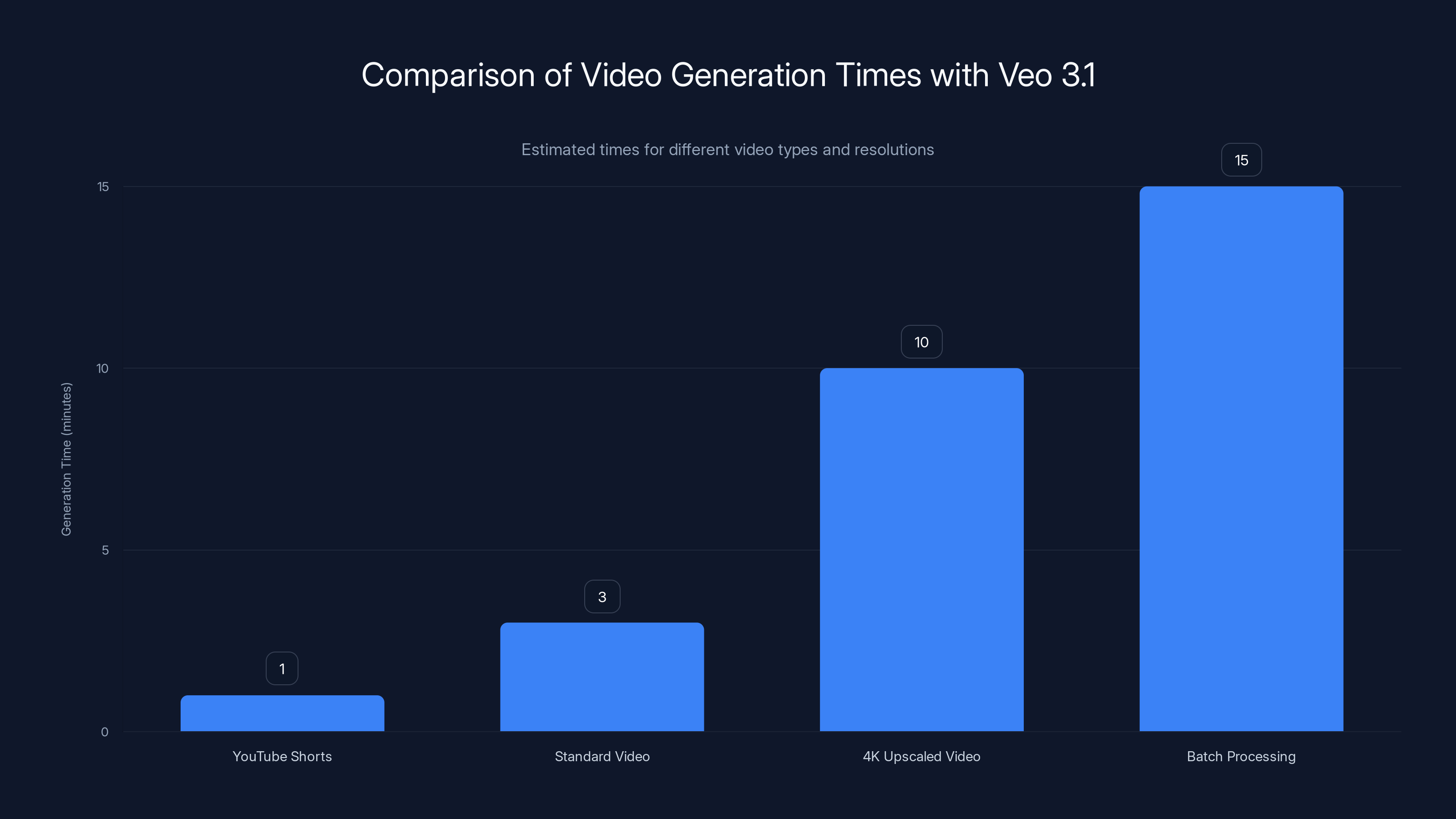
Veo 3.1 generates YouTube Shorts quickly, while 4K upscaling takes longer. Batch processing is efficient for multiple videos. Estimated data.
What Google Veo 3.1 Actually Is
Veo 3.1 is Google's text-to-video and image-to-video generation model. Let's be precise about what that means. You don't point a camera at real people and film them. Instead, you describe what you want to see (or show the model an image), and the AI generates a video from scratch.
Google released the original Veo model in 2024. Then, in October 2025, they shipped Veo 3.1 with better audio output and more granular editing controls. People could already make vertical videos with Veo 3.1, technically. But the update that landed in January 2025 changes the game because now the model is actually optimized for vertical format instead of just allowing it.
Here's what that distinction means in practice: When you're generating video from a reference image, the AI needs to understand the spatial relationships in your image and then extrapolate motion within those relationships. A wide, widescreen image has totally different compositional rules than a tall, narrow vertical image. Character positioning, background depth, where action happens in the frame—all of that changes.
Before this update, Veo 3.1 would generate video at whatever aspect ratio you requested, but it was always working from an underlying widescreen bias. The model trained on widescreen video, optimized for widescreen composition, defaulted to widescreen thinking. If you asked for vertical, you got a vertical crop of widescreen thinking. Sometimes that worked fine. Sometimes it looked awkward because the composition didn't actually make sense in vertical format.
Now Veo 3.1 thinks natively in vertical. It understands vertical composition as a first-class format, not a constraint to work around.
Google also added the reference image feature directly to YouTube Shorts and YouTube Create. That's significant because it means millions of creators who never touch the Gemini app or API documentation can now access this functionality. You upload a reference image, describe what you want, and Veo 3.1 generates video that looks like it actually evolved from your image. The character expressions are more believable. The movements feel more natural. Objects stay where you put them.
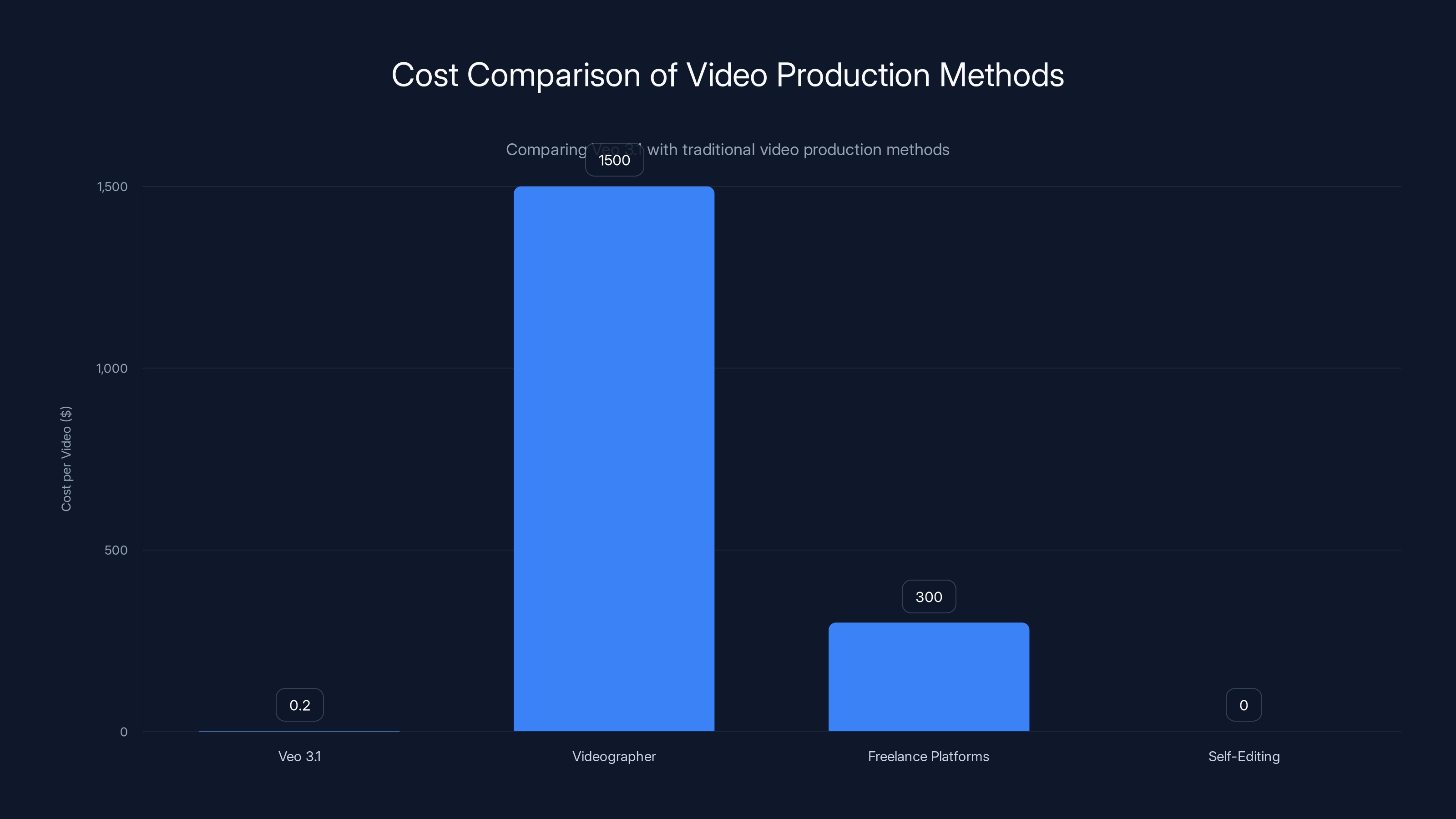
Veo 3.1 offers a cost-effective solution for video production, with costs as low as $0.20 per video, compared to traditional methods like hiring a videographer or using freelance platforms, which can cost hundreds to thousands of dollars per video.
The Reference Image Game-Changer: How It Actually Works
Let's talk about the reference image feature because this is where Veo 3.1 gets interesting.
With reference images, you're telling the AI: "Here's what I want the video to look like. Now make it move."
That's a completely different task than generating video from pure text. When you generate from text alone, the model has total creative freedom. You say "a woman running through a forest" and it invents the woman, the forest, the lighting, everything. Sometimes that looks great. Sometimes the woman's proportions are weird. Sometimes the trees phase in and out of existence. You're trusting the model's imagination to be accurate.
With reference images, the model has constraints. It sees the woman you want. It sees the forest you want. Now it needs to animate those specific things while maintaining visual consistency. The woman's face should look like the face in your image. The forest background should look like the background you showed it. The motion should make sense given what you're seeing.
Google claims that Veo 3.1's reference image capability now produces more expressive, dynamic video. That means better character expressions, more natural movements, and improved emotional communication. Even if your text prompt is vague ("she's reacting to something"), the reference image gives the model enough information to figure out what "something" should look like based on the context you've established visually.
The model also improved at blending multiple reference elements. Say you want a video with a specific character, a specific background, and specific objects in the scene. Veo 3.1 can now blend those elements together while maintaining consistency throughout the entire video. Your character doesn't suddenly change appearance halfway through. The background stays coherent. Objects don't teleport.
This matters for vertical video specifically because vertical composition is actually harder to get right. You have less horizontal space, so every element in the frame matters more. A poorly placed background in widescreen might not matter much. In vertical format, it dominates the screen. Veo 3.1 now understands this spatial relationship and adjusts accordingly.
Vertical Video Format: Why This Actually Matters
You might think aspect ratio is just a technical detail. It's not. Vertical video is a fundamental shift in how humans consume content, and trying to adapt horizontal video for vertical platforms is like trying to fit a billboard into a phone.
Consider the economics. YouTube Shorts creator fund pays creators based on views. Instagram Reels engagement drives algorithmic reach. Tik Tok's entire algorithm is built around vertical video. If you create horizontal video and then crop or pillarbox it for vertical platforms, you're leaving money and reach on the table.
But there's also a creative element. A well-composed vertical video looks and feels different from a horizontal video squeezed into vertical format. The pacing is different. Where you place subjects in the frame is different. The depth of field perception is different. Professional vertical video creators think differently about composition than widescreen creators.
Before Veo 3.1's vertical-first approach, AI video models essentially forced you to accept widescreen thinking. You could output vertical format, sure, but the creative thinking underneath was optimized for widescreen. That constraint cascaded through the entire generation process.
Now, with native vertical support, creators can think about vertical composition from the moment they write their prompt or choose their reference image. The AI's entire generation process is optimized for vertical. That means more natural use of negative space, better understanding of how subjects should be positioned in a tall frame, and motion that actually makes compositional sense in vertical format.
For creators, this is huge. It means you're not compromising creative quality to hit platform requirements. You're not choosing between "looks great on desktop" and "looks great on Tik Tok." You get both, because vertical is the native format.
For businesses, it's even bigger. Major brands now post Tik Toks and Reels alongside their YouTube content. The quality of that vertical content directly impacts brand perception. If your brand's vertical videos look like they were created for widescreen and then squeezed, that degrades your brand image. If they look native to the platform, it feels professional and intentional.
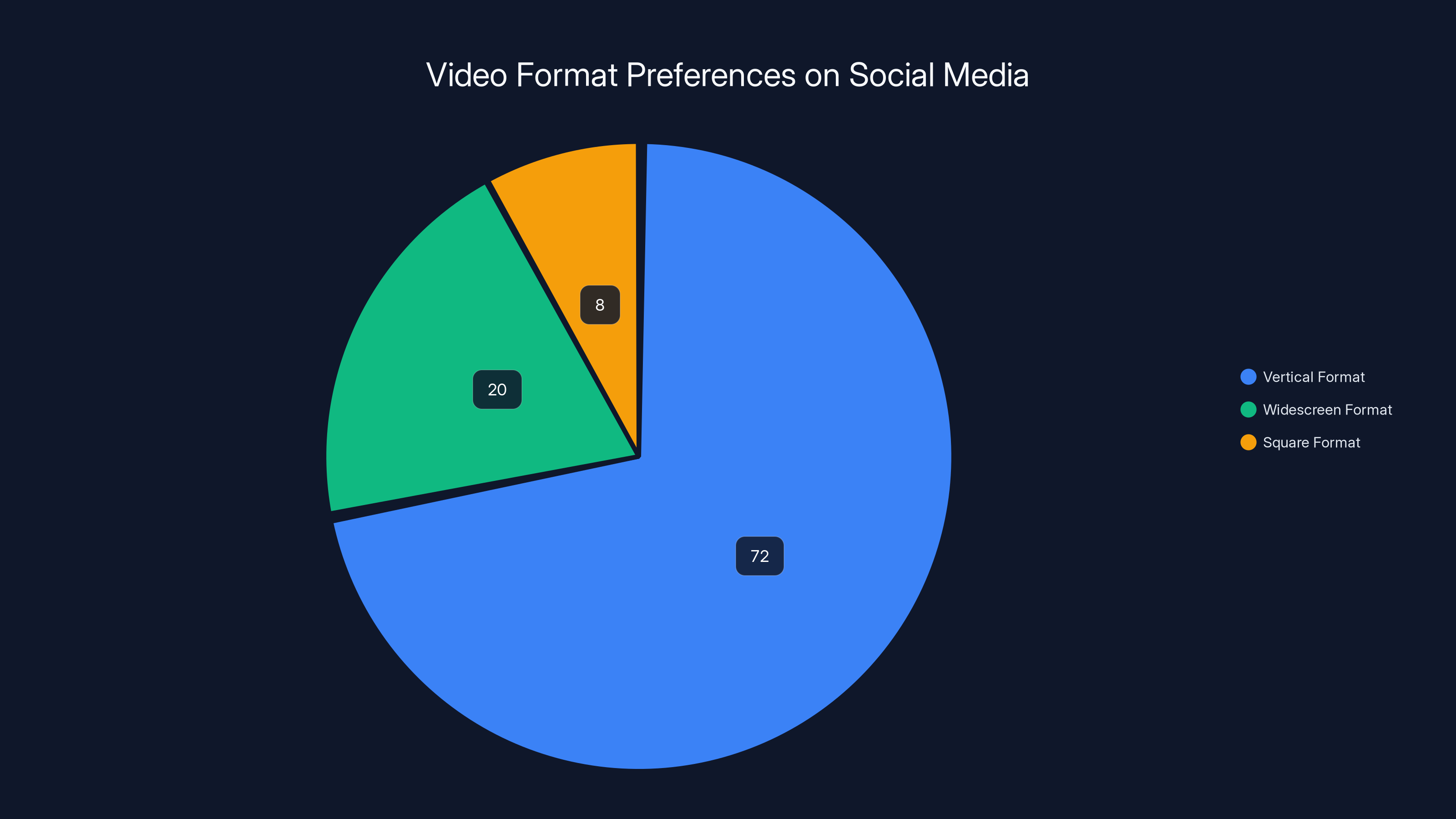
An estimated 72% of videos on platforms like TikTok are consumed in vertical format, highlighting the importance of optimizing content for this aspect ratio. Estimated data.
Character Expression and Movement: The AI Gets Better at Emotion
One of the most impressive improvements in this update is how Veo 3.1 now generates character expressions and movements when working from reference images.
This is actually a genuinely hard problem in AI video generation. When you're creating character animation from text alone, the model needs to:
- Imagine a character that fits your description
- Understand what emotions or actions you're describing
- Generate natural movement that communicates those emotions
- Do all of this while maintaining consistent appearance across multiple frames
That's a lot of cognitive load for a model. It's why early AI video often had weird, uncanny character movement. The model would nail the appearance in frame one, then struggle to maintain consistency. Or it would focus so hard on movement that facial expressions became blank and lifeless.
When you use a reference image, you're removing variables from that equation. The model no longer needs to imagine the character. It can see the character's face, posture, and appearance. Now it can focus entirely on generating natural movement and expressions that make sense given what you're seeing.
Google's update specifically improved this. The model is now better at reading facial expressions from reference images and translating those into video. If your reference image shows a character with raised eyebrows and a slight smile, Veo 3.1 will generate video that maintains that emotional state or evolves it naturally based on your prompt.
The practical impact: shorter prompts work better. You used to need detailed prompts like "woman with surprised expression turns to look left, eyes wide, eyebrows raised high." Now you can say "she reacts to something" and the model uses your reference image to infer the emotional baseline and generate appropriate movement from there.
This improvement to character expression is particularly important for vertical video because vertical format emphasizes faces. In a tall frame, faces take up more screen real estate. They're harder to ignore. They communicate more. If character expressions look off, the entire video feels wrong. Veo 3.1 now handles this better, which means vertical video feels more emotionally authentic.
Consistency and Coherence: Objects Stay Put
One of the most frustrating issues with AI video generation is when objects or characters randomly change appearance or position mid-video. You describe a character with a red shirt, and halfway through the video the shirt is blue. Or a background element that should be consistent suddenly looks completely different.
This happens because video generation is fundamentally frame-by-frame synthesis. The model generates frame one, then uses frame one to inform frame two, then uses frame two to inform frame three, and so on. If there's any divergence in how the model interprets visual information between frames, consistency breaks down.
Veo 3.1's consistency improvements address this through what Google calls "blending." When you're using reference images, the model can now blend:
- Character consistency: The same person maintains their appearance, proportions, and defining features throughout the video
- Object consistency: Props, clothing items, and background objects stay visually coherent
- Background consistency: Environmental elements maintain their appearance and spatial relationships
- Texture consistency: Material properties (wood, metal, fabric, skin) remain consistent
These aren't separate passes through the video. They're integrated into the generation process. The model is trained to understand that visual elements should remain consistent unless explicitly changed, and to maintain that consistency even as it generates new motion and changes in expression.
For vertical video, this matters because vertical format often has less negative space. Everything in the frame is important. If a background element flickers or changes appearance, it's way more noticeable in vertical format than in widescreen. A dancing character in front of a pillar in widescreen video? The pillar is background noise. In vertical format, that pillar dominates. If it changes appearance mid-video, it's immediately noticeable.
Veo 3.1's consistency improvements make vertical video more reliable and professional-looking.

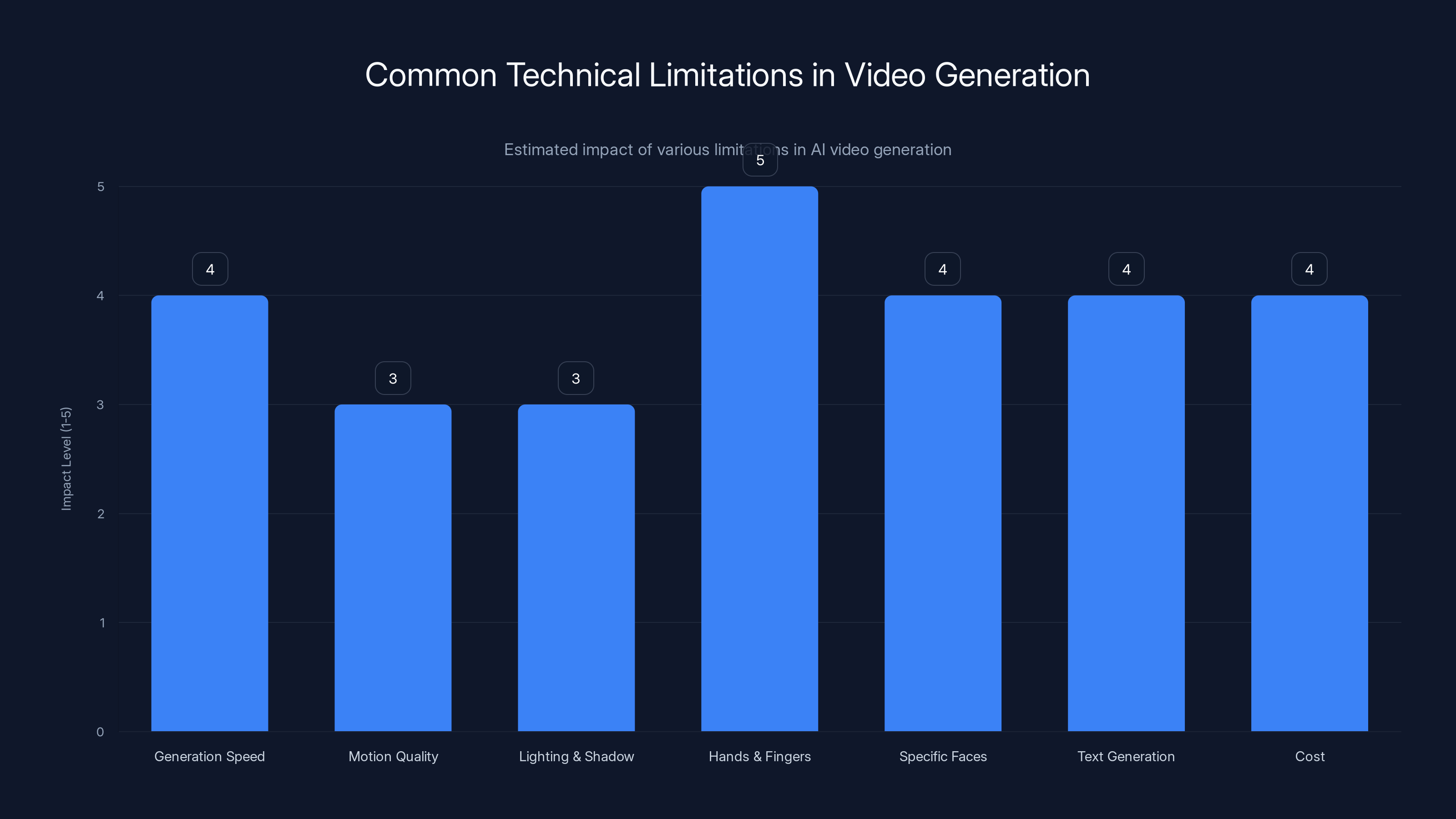
Hands and fingers present the highest challenge in AI video generation, often requiring manual editing. Estimated data.
Upscaling to 1080p and 4K: Broadcast Quality Vertical Video
Before this update, upscaling was available on Veo 3.1, but it's now improved and available on more platforms.
Upscaling matters because when you generate video with an AI model, you're not usually generating at full resolution. You generate at a lower resolution (maybe 480p), then use a separate upscaling model to enlarge it to 1080p, 1440p, or 4K. This saves computation and speeds up generation. The downside is that upscaling can introduce artifacts, blur, or weird visual glitches.
Google improved their upscaling approach. Now when you generate vertical video through Flow (their professional video editor), Gemini API, or Vertex AI, you can output at 1080p or 4K. The upscaling is more sophisticated. It preserves detail better. It doesn't introduce weird artifacts.
This is significant for professional use cases. If you're a creator or brand generating hundreds of videos with Veo 3.1, you probably need broadcast-quality output. A YouTube Shorts video that looks blurry or artifacted will get lower engagement. An Instagram Reel with visible upscaling artifacts looks cheap.
With improved upscaling, Veo 3.1 becomes viable for professional vertical video content. You're not generating low-res outputs and hoping upscaling doesn't destroy them. You're generating with the understanding that upscaling will preserve quality.
The math on this is worth understanding. Vertical video at 1080p means 1920x1080 resolution displayed as 1080x1920 (height by width for vertical format). That's actually lower total pixel count than horizontal 1080p (1920x1080 has the same 2,073,600 pixels, just arranged vertically). But the rendering challenge is different. Vertical video needs very high detail in certain areas (faces, text, foreground objects) because they take up proportionally more screen real estate.
Google's improved upscaling also means less trial-and-error. You can generate one video at 4K instead of generating at lower resolution, upscaling, checking quality, regenerating if needed. That saves time and computation cost.
Access Points: Gemini, YouTube, Flow, and Beyond
Google didn't just improve the model. They made it accessible in multiple ways.
The Gemini app gives you direct access. You can chat with Gemini, describe what you want, provide reference images, and generate video. It's the most conversational approach. You're having a dialogue with the AI.
YouTube Shorts and YouTube Create (Google's mobile app for creators) now have Veo 3.1 built in. You don't need to generate a video elsewhere and then upload. You generate inside the platform. That matters because it removes friction. A creator thinking about posting to Shorts doesn't need to open another app or website. They can generate and upload in the same workflow.
Flow is Google's professional video editor. If you're doing serious video work, Flow lets you generate, edit, refine, and upscale. It's more powerful than the simple Shorts interface because it gives you granular control over generation parameters, reference images, and output quality.
The Gemini API and Vertex AI are for developers and enterprises. If you're building an application that needs to generate vertical video, you can integrate Veo 3.1 directly. This enables use cases like automated marketing video generation, personalized video at scale, or AI-assisted content creation tools.
This multi-platform approach is smart. It means:
- Casual creators can generate video without learning anything new
- Professional creators get tools that match their workflow
- Developers can build custom applications
- Enterprises can integrate into existing systems
Nobody gets forced into a one-size-fits-all approach. That's actually unusual for AI video models, most of which live in their own dedicated interfaces.

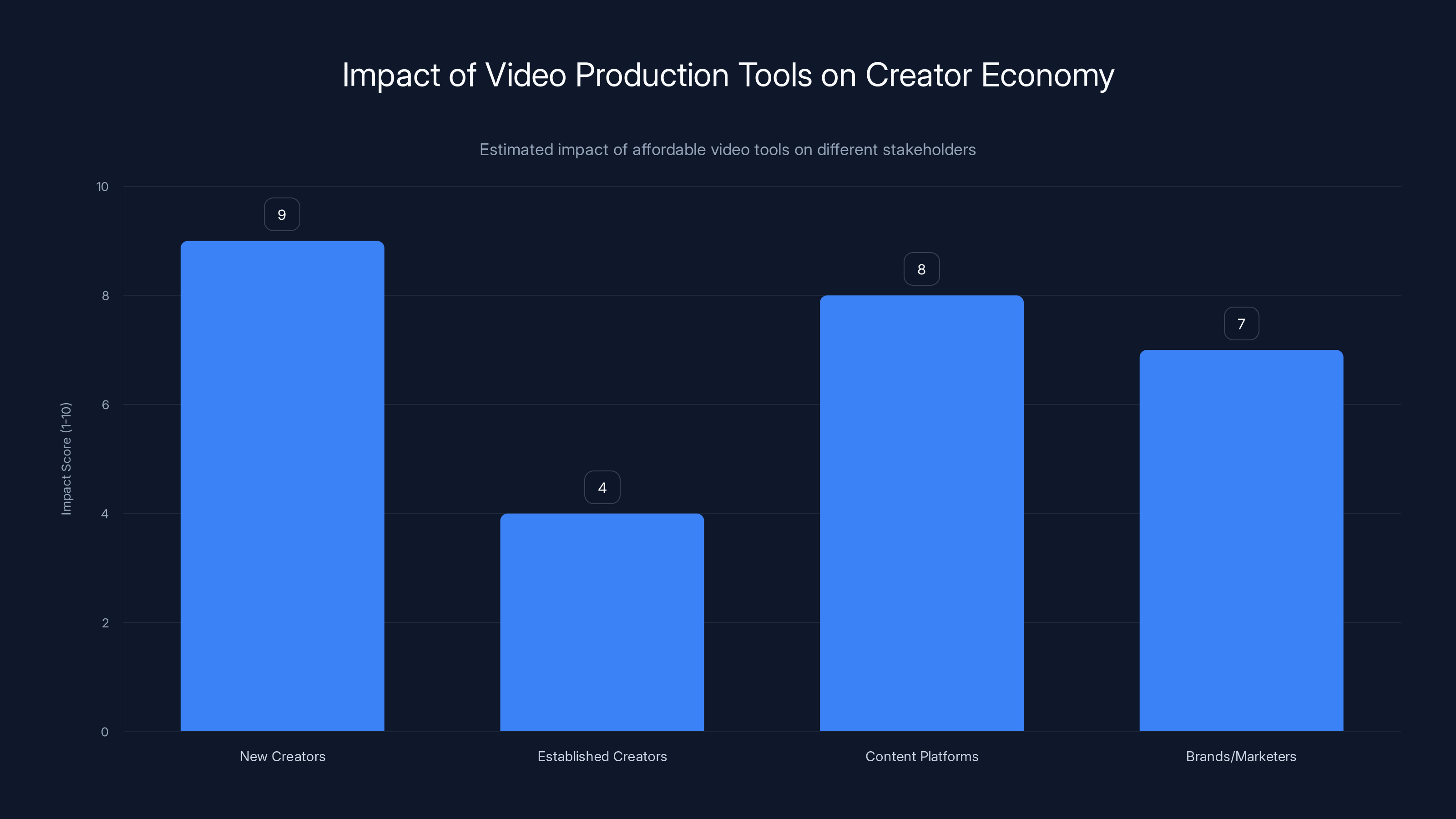
Affordable video production tools significantly empower new creators and content platforms, while posing challenges for established creators. Estimated data.
Comparison to Competitors: Where Veo 3.1 Stands
Veo 3.1 isn't the only AI video generation model. There's Open AI's Sora, Runway's Gen-3, Synthesia, and others. How does Veo 3.1 compare?
Sora (Open AI's model) generates longer videos and handles complex motion well, but it's currently limited access and doesn't have as strong reference image capabilities or vertical video optimization. Sora excels at cinematic, widescreen video generation.
Runway Gen-3 focuses on photo-realistic quality and handles physical simulation well. Its motion matching (similar to reference images) works, but Runway hasn't optimized specifically for vertical format the way Veo 3.1 has.
Synthesia generates talking-head videos with presenters. It's optimized for vertical video by design (because business video and marketing often goes vertical), but it doesn't handle general video generation the way Veo 3.1 does.
Veo 3.1's specific advantage is the combination of:
- Native vertical format optimization (most competitors treat vertical as secondary)
- Strong reference image capabilities with improved expression and movement
- Built-in access through YouTube and other Google products
- Improved consistency and coherence
- Better upscaling to 1080p/4K
The specific angle where Veo 3.1 wins is: if you're a creator who needs native vertical video with visual consistency and professional quality, Veo 3.1 is now the best option. Sora might generate more impressive widescreen video, but if you need vertical, Veo 3.1 is built for that.
For competitors, this update signals that vertical video is serious business. The creator economy is huge, most creator video is vertical, and models that ignore that are going to lose market share to models that embrace it. Expect Sora, Runway, and others to follow with their own vertical-first improvements.

Use Cases: Who Should Actually Use This
Let's talk about real-world applications.
Social Media Creators gain the most immediately. If you create Tik Toks, Instagram Reels, or YouTube Shorts, Veo 3.1 lets you generate native vertical video without composition compromises. You can post directly from YouTube Shorts or YouTube Create without additional tools. The reference image feature means you can establish a visual style (through a reference image) and maintain it across videos.
E-commerce and Product Marketing is a strong use case. Imagine you're selling a product on Tik Tok Shop. You could create reference images showing the product in different contexts, then generate 6-10 videos with different scenarios. All would maintain visual consistency (same product appearance) while showing different use cases. You could generate these at scale.
Educational Content benefits from improved character expression. If you're creating explainer videos with animated characters, better character expression and movement means more engaging education. Students understand and retain information better when presented through emotionally expressive characters.
Small Businesses without video budgets can now create professional vertical video content. The cost is low (you just need API access or Gemini subscription), and you don't need to hire a videographer or learn video editing. You describe what you want, upload a reference image, and the model generates.
Marketing Agencies can offer video generation as a service. They can create style guides (reference images that establish brand visual language), then generate variations quickly. This is more efficient than hiring videographers for every project.
Live Shopping and Streaming could use this to generate promotional videos or product showcases on demand. During a live shopping event, you could generate promotional video in minutes instead of hours.
The common thread: anytime you need vertical video at scale, with visual consistency, and without a huge budget or production timeline, Veo 3.1 becomes valuable.

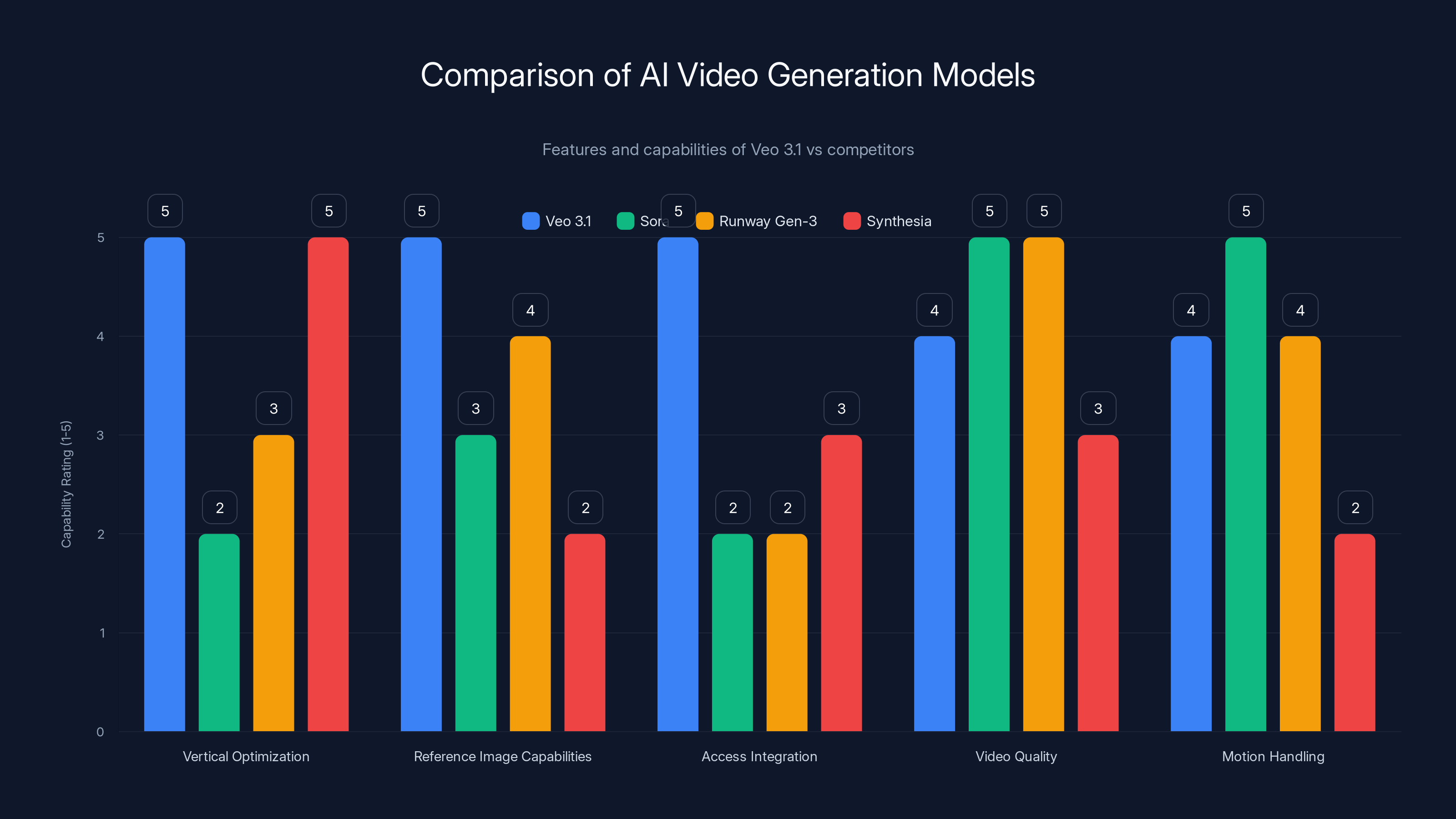
Veo 3.1 excels in vertical optimization and reference image capabilities, making it ideal for creators focused on vertical video content. Estimated data based on feature descriptions.
Technical Limitations and Gotchas
Before you dive in, understand the limitations.
Generation speed is still slower than you might want if you're generating lots of video. A single video might take 30 seconds to several minutes. If you're generating 100 videos, you're looking at 50+ minutes of generation time (not including upscaling).
Motion quality is good but not perfect. Veo 3.1 handles human motion better than object motion. Physics-based motion (objects falling, rolling, etc.) sometimes looks off. If you're generating videos with complex physical interactions, manual editing might be needed.
Lighting and shadow consistency can be weak. If a character moves between different lighting conditions (sunlit to shadowed), the model might not adjust shadows realistically. You might need to edit.
Hands and fingers still sometimes look weird. This is a known issue across most generative models. If your video requires detailed hand animation, manual fixes might be necessary.
Specific faces are hard to maintain. If you want a specific real person (like your brand's CEO) in the video, reference images help but exact facial reproduction is difficult. The model might generate someone who looks similar but not identical.
Text generation is still unreliable. If you need readable text in your video, don't rely on Veo 3.1 to generate it. Use reference images with text already present, or add text in post-production.
Cost is significant if you're generating massive volume. Exact pricing depends on your access level, but generating 100 videos per day gets expensive quickly.
These aren't deal-breakers for most use cases. They're just reality checks. Veo 3.1 generates impressive video, but it's not magic. It's best when you understand its strengths and work within them.

Workflow Integration: How to Actually Use This
Let's say you're a creator who wants to use Veo 3.1. What's the actual workflow?
Option 1: YouTube Shorts Direct
If you're posting to YouTube Shorts, the simplest workflow is:
- Upload a reference image (or take a screenshot from a video you like)
- Describe what you want to happen in the video
- Generate through YouTube Create
- Review and post
Total time: 10-15 minutes including generation. No other tools needed.
Option 2: Professional Editing with Flow
If you want more control:
- Create reference images in your preferred tool (Figma, Photoshop, Canva)
- Log into Flow
- Upload reference images and describe variations
- Generate multiple versions
- Edit and refine (trim, add music, adjust colors)
- Upscale to 1080p or 4K
- Export and distribute to platforms
Total time: 30-60 minutes depending on complexity.
Option 3: API Integration (Developers)
If you're building an application:
- Integrate Gemini API or Vertex AI into your application
- Send reference images and prompts programmatically
- Handle generation asynchronously (it takes time)
- Store and serve generated videos
- Implement UI for users to request videos
Total time: depends on your application complexity, but core integration might be a few hours.
The key insight: there's no single "right" workflow. Different use cases benefit from different approaches.

Cost Considerations and Value Calculation
Veo 3.1 isn't free. How much does it cost? That depends on how you access it.
Gemini app (free tier) gives you limited generations per day (the limit is unspecified but exists). Pay for Gemini Advanced (if offered in your region) for higher limits.
YouTube Shorts/YouTube Create probably uses free tier or Creator-specific pricing.
Flow, Gemini API, and Vertex AI have per-generation pricing. Exact rates change, but it's roughly in the range of
For a creator generating 5-10 videos per week, monthly cost might be
Is it worth it? Calculate the alternative cost:
- Hiring a videographer: $500-2000 per video
- Using freelance platforms: $100-500 per video
- Learning video editing yourself: 50+ hours of learning, plus 5-10 hours per video
Compared to those alternatives, Veo 3.1's cost is negligible. Even at $0.20 per video, you're saving massive money and time compared to hiring.
The value calculation changes at scale. If you're generating 1000 videos per month, cost matters more. But for most creators and small businesses, Veo 3.1 is one of the cheapest ways to produce video at scale.

Future Roadmap: What's Coming Next
Google hasn't announced specific upcoming features, but based on the trajectory, expect:
Longer video generation: Sora can generate up to 60 seconds. Veo 3.1 currently has limits. Expect these to extend.
3D-aware generation: The next frontier is models that understand 3D space, camera movement, and allow you to control camera path. This would enable cinematic vertical video with camera movement.
Audio sync: Better automatic audio generation and sync to video movement. Imagine describing the audio and having it automatically sync to character mouth movements.
Style transfer and consistency packs: Pre-built visual styles that you can apply to any video. This would help creators maintain brand consistency without manually creating reference images.
Real-time generation: Currently generation takes 30 seconds to several minutes. Real-time or near-real-time generation would enable live interactions.
Multi-shot scenes: The ability to generate complex scenes with multiple characters interacting, rather than single-subject videos.
These are educated guesses based on where the field is heading. But it's clear that vertical video generation will become increasingly sophisticated, and Veo 3.1 is just the beginning of that trajectory.

How This Compares to Traditional Video Production
Let's get real about the elephant in the room: Can AI video actually replace human videographers?
For certain use cases, yes. If you're creating repetitive, variation-based content (product showcase, explainer, educational), Veo 3.1 is faster and cheaper than hiring a videographer.
For other use cases, absolutely not. If you need:
- Actual real people (not AI-generated)
- Specific real locations
- Complex logistics or stunts
- Emotional authenticity that requires real human performance
- Legal/liability reasons to use real footage
Then you're hiring a videographer. That's not changing.
But in the middle ground—where many creators and businesses live—AI video becomes a serious alternative. It's not about replacing videographers entirely. It's about offloading the repetitive, time-consuming parts so videographers can focus on creative work.
Think of it like photography. Digital cameras didn't replace professional photographers. They just meant that every business could take decent photos without hiring a photographer for every shot. Professional photographers still exist, but now they do higher-end work.
Veo 3.1 is following that trajectory with video.

Practical Tips for Getting Great Results
Based on how Veo 3.1 works, here's what actually produces good output:
Reference images matter most: The single biggest factor in output quality is reference image quality. Spend time finding or creating good reference images. Well-composed, well-lit reference images produce better video.
Specific prompts work better than vague ones: "She reacts" produces better video than "she moves." Give the model something to work with.
Short prompts work well with reference images: You don't need long, complex prompts. The reference image provides context. Keep prompts short and specific.
Consistency over creativity: If you're generating multiple videos in a series, using the same reference images creates consistency. Variation in prompts, consistency in reference images.
Edit in post: Don't expect perfect output. Plan to spend 5-10 minutes per video editing (trimming, audio, color correction). Veo 3.1 is a tool that creates the raw material. Editing makes it polished.
Batch generation: Generate multiple variations. Generate 5 versions with slight prompt variations, pick the best one. The extra generation time is worth it.
Start simple: Don't try to generate complex scenes with multiple characters and objects first. Generate simple scenes, understand what works and what doesn't, then scale complexity.

The Creator Economy Implications
This update signals something bigger: the creator economy is shifting in real time.
Professional video production used to require equipment, training, and significant time investment. That meant video content was limited to people who could afford that investment. Everyone else created written content, images, or audio.
Now, Veo 3.1 and similar tools are commodifying video production. A creator with a $0 video budget can now generate professional-quality vertical video. That changes the competitive landscape. Creators compete on ideas and creativity, not on who has the best camera equipment or can afford the best videographer.
For established creators with production budgets, this is a threat. For new creators with ideas but no budget, this is liberating.
For platforms like YouTube and Tik Tok, this changes content availability. There's a potential explosion in video content volume, which means more competition for attention but also more diverse voices and ideas.
For brands and marketers, this means video is now a viable channel even for small budgets. A brand with no marketing budget can now create video content cheaply and test ideas before investing in professional production.
The long-term implication: video becomes as common as written content is today. Everyone has video, which means quality and creativity become the differentiators, not access to production tools.

Integrating Veo 3.1 Into Your Content Strategy
If you're thinking about using this, where does it fit in your overall strategy?
For content volume: Use Veo 3.1 to increase content output without proportional increase in time or cost. Generate 3 videos per week instead of 1.
For A/B testing: Quickly generate variations to test which creative direction resonates. Use API to generate 10 variations, see which performs best, then invest in professional production for winners.
For evergreen content: Generate foundational videos, then edit and repurpose across platforms. A single vertical video can become a Tik Tok, Instagram Reel, YouTube Short, and Twitter video with minimal editing.
For trending content: When trends move fast (trend formats, sounds, topics), Veo 3.1 lets you generate relevant content quickly. By the time a trend peaks, you've already created 5 variations.
For personalization: Build customer-specific video content. E-commerce stores could generate product videos personalized to customer preferences.
For visual storytelling: Create animations and visual explainers that would be expensive to produce manually.
The strategic question: How does video generation fit your existing workflow? For most creators, it's not a complete replacement for human-made content. It's a tool that amplifies production capacity and enables experimentation.

FAQ
What exactly is Veo 3.1's reference image feature?
Veo 3.1's reference image feature lets you upload an image and have the AI generate video that animates based on that image. The model uses the reference image to understand visual style, composition, character appearance, and background. You provide a text prompt describing what should happen, and the model generates video that evolves from the reference image while following your prompt. This is different from generating video purely from text description.
How does vertical video generation differ from horizontal video generation?
Vertical video (9:16 aspect ratio) requires different compositional thinking than horizontal video (16:9). In vertical format, subjects take up more of the frame, negative space is used differently, and camera movement has different impact. Veo 3.1's update means the model now generates with vertical composition in mind, rather than generating horizontal video and then cropping it to vertical. This produces better results that actually look native to vertical platforms like Tik Tok and Instagram Reels.
Can I use Veo 3.1 to generate videos of real people I know?
Technically you could use reference images of real people, but the model won't generate exact reproductions. It will generate someone who looks similar to the reference image, but likely not identical. If you need specific real people, you're better off filming them with a camera. However, for stylized or animated representations of people, reference images work well.
How long does it take to generate a video with Veo 3.1?
Generation time varies based on video length and whether you're upscaling, but generally expect 30 seconds to several minutes for a single video. YouTube Shorts might be on the faster end, while professional upscaling to 4K takes longer. If you're generating many videos, you'll want to batch them and let them run, rather than waiting for each one individually.
What's the cost of using Veo 3.1 at scale?
Exact pricing varies by access method, but API-based generation typically costs
Can Veo 3.1 generate videos with specific real-world locations?
Not directly. You can't say "generate a video at the Eiffel Tower" and expect photorealistic footage from that location. You'd need to provide a reference image of that location, and the model would generate video using that reference. The output would be AI-generated (not real footage), but it would use the location in your reference image as context.
How does Veo 3.1 handle consistency across multiple videos in a series?
If you use the same reference images across multiple videos with different prompts, the model will maintain visual consistency. The character will look the same, the background will look the same, and the overall style will remain consistent. This is ideal for creating series where you want visual cohesion while varying the action or narrative.
What are the main limitations of AI-generated video compared to human-filmed video?
AI-generated video currently struggles with: exact reproduction of real people, physically accurate motion (especially hands and complex interactions), realistic lighting and shadows, specific real-world locations, and emotional authenticity that comes from real human performance. It excels at: stylized video, variation generation, content at scale, and cost efficiency. Most limitations can be partially addressed through editing, but some use cases still require human-filmed video.
Can I use Veo 3.1 for commercial purposes and monetization?
Yes, content generated with Veo 3.1 can be monetized. You can post it to YouTube Shorts for monetization, use it for commercial products, or sell videos generated with the tool (as long as you follow Google's terms of service). There's no inherent copyright restriction on commercially using Veo 3.1-generated content, though you should review the specific terms for your access method.
How does Veo 3.1 compare to other AI video models like Sora or Runway?
Veo 3.1's specific strength is native vertical video optimization and strong reference image capabilities. Sora (Open AI) generates longer, more cinematic horizontal video but less optimized for vertical. Runway Gen-3 focuses on photorealistic quality. Synthesia specializes in talking-head videos. For vertical social media content creation, Veo 3.1 is currently the best choice. For other use cases, other models might be better depending on your needs.

Conclusion: The Vertical Video Era Has Arrived
Google's Veo 3.1 update isn't revolutionary in the sense of introducing entirely new technology. The model existed. Video generation existed. Vertical format existed. What's revolutionary is bringing these together as a cohesive, optimized whole.
For years, AI video models treated vertical format as an afterthought. You could generate vertical video, but the models weren't built for it. They were built for widescreen, then adapted. Veo 3.1 flips that script. Vertical video is now a first-class citizen.
This matters because vertical video is where content happens now. Not eventually. Not soon. Right now. The top social platforms are vertical-first. Creators post vertical. Audiences consume vertical. Brands need vertical content. For the first time, an AI video model is actually optimized for how content is created and consumed in 2025.
The reference image improvements and better character expression and movement mean the output is more usable. You're not generating raw material that needs extensive post-production. You're generating content that's closer to publication-ready.
The multiple access points (Gemini, YouTube, Flow, API) mean different users can access this at different levels of sophistication. Casual creators don't need to know anything about APIs. Professionals get tools that match their workflow. Developers can integrate into custom applications. Nobody gets forced into a one-size-fits-all approach.
What does this mean for you?
If you're a creator, you can now generate more content faster and cheaper. That means more experimentation, more ideas tested, more chances to find what resonates with your audience.
If you're a business, you can generate video content for your marketing, products, and customer education without hiring a production team.
If you're a developer, you can build applications that generate video on behalf of your users.
If you're in the video production industry, you're watching an era end and a new one begin. AI won't replace human videographers for premium, creative work. But it will take over the repetitive, variation-based work. The competitive advantage shifts to creativity and ideas, not to equipment and production logistics.
The vertical video era has arrived. Veo 3.1 is Google's bet that they're going to own this era. Whether they succeed depends partly on the model quality (which is good), but mostly on adoption. Creators need to actually use this instead of using competitors. That battle is just beginning.
The tools exist. The capability exists. The platform support exists. Now it comes down to execution. Can you use Veo 3.1 to create better, more engaging vertical video faster than you could create it manually? For most creators and businesses, the answer is yes. The question is whether you'll actually try it.

Key Takeaways
- Veo 3.1 generates native 9:16 vertical video optimized for TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts instead of forcing horizontal video into vertical format
- Reference image feature now produces more expressive character emotions and natural movements while maintaining visual consistency throughout videos
- Integration with YouTube Shorts, YouTube Create, Google Flow, and APIs makes this accessible to casual creators, professionals, and developers
- Improved upscaling to 1080p and 4K means broadcast-quality vertical video output suitable for professional use
- At 500-2000 per video) making it viable for creators and small businesses
Related Articles
- 8 Game-Changing Creative Software Updates That Transformed Content Creation in 2025
- Apple Creator Studio: The Ultimate Creative App Subscription Bundle [2025]
- Porn Taxes and Age Verification Laws: The Constitutional Crisis [2025]
- YouTube Shorts Filter: Complete Guide to Excluding Shorts from Search [2025]
- TikTok's 2026 World Cup Live Deal: What It Means for Sports Broadcasting [2025]
- 2025 Social Media Predictions Reviewed: What Actually Happened [2026]
![Google Veo 3.1 Vertical Videos: Reference Images Game-Changer [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/google-veo-3-1-vertical-videos-reference-images-game-changer/image-1-1768326115345.jpg)



