iPhone Fold 2025: The Complete Rumor Breakdown, Design Specs, and Everything We Know
For nearly a decade, tech enthusiasts and industry analysts have speculated about Apple's entry into the foldable smartphone market. While Samsung and Google have already established themselves with proven foldable devices, Apple's expected arrival into this category represents a watershed moment that could fundamentally reshape how consumers think about portable computing. The company's historical approach to emerging technologies—waiting for maturity, then executing with precision—suggests that when the iPhone Fold finally arrives, it will bring a level of refinement that could set new industry standards.
The momentum around Apple's foldable phone has accelerated dramatically in recent months. Supply chain analysts, renowned tech reporters, and multiple industry sources now converge on a remarkably consistent timeline: a launch window in the second half of 2026, likely coinciding with the iPhone 18 series announcement. This represents a significant shift from the vague "someday" speculation that dominated earlier years.
What makes this moment particularly interesting is the convergence of enabling technologies. Samsung Display has publicly demonstrated crease-less OLED panels specifically designed for foldable devices. Manufacturing processes have matured. Consumer acceptance of foldables has grown substantially, with Samsung shipping millions of units annually. The market conditions appear optimal for Apple's entrance.
This comprehensive guide synthesizes the most credible reporting, supply chain intelligence, and technical analysis to provide the clearest picture yet of what the iPhone Fold will likely offer. We've examined rumors from the most reliable sources in the industry, cross-referenced competing reports, and highlighted where consensus exists versus where disagreement persists. Whether you're an Apple devotee tracking every development, a tech journalist covering the foldable space, or simply curious about the future of mobile devices, this deep dive will bring you current on everything credible we know about Apple's foldable ambitions.
iPhone Fold Launch Timeline: When Apple's Foldable Will Arrive
The 2026 Target Window
After years of speculation extending back to 2017, industry sources now point to a remarkably consistent timeframe: fall 2026. Mark Gurman, Bloomberg's senior Apple reporter with an exceptional track record on Apple announcements, initially suggested the device could launch "as early as 2026" before refining his timeline to indicate a "end of 2026" shipment with 2027 as the primary sales year. Ming-Chi Kuo, the noted Apple supply chain analyst with decades of accuracy predicting component sourcing and production schedules, has repeatedly cited the second half of 2026 as Apple's target launch window.
This convergence on a specific timeframe differs markedly from earlier rumors that suggested anywhere from 2024 to 2028 as possible launch windows. The specificity of the current reporting, combined with the consistency across multiple independent sources with verified track records, suggests genuine momentum rather than speculation.
Manufacturing and Development Challenges
However, several analysts and supply chain sources caution that 2026 represents Apple's target, not a guaranteed date. Apple has a historical pattern of delaying products it deems insufficiently mature for market. The iPhone, for example, was delayed in its development. The first iPad was pushed back multiple times. The HomePod faced extended development challenges. This corporate culture of "releasing when ready, not when scheduled" means the iPhone Fold could feasibly slip into early 2027 if durability or manufacturing challenges emerge.
Specific technical challenges could trigger delays. The hinge mechanism—which must operate reliably through hundreds of thousands of open-close cycles while resisting dust and moisture intrusion—represents an engineering frontier Apple is still exploring. The display, despite Samsung's advances, must meet Apple's exacting standards for color accuracy, brightness, and crease invisibility. Battery placement within a foldable form factor requires novel thermal management solutions. Each of these systems could extend development timelines if integration proves more complex than current planning assumes.
Pre-Launch Competitive Context
By 2026, Samsung will have refined its Galaxy Z Fold lineup through at least six or seven generations, with the Z Fold 8 or Z Fold 9 already shipping. Google's Pixel Fold will be on its third or fourth iteration. This competitive maturity actually benefits Apple, as it establishes the foldable category's viability and allows consumers to recognize the value proposition. Apple essentially gets to learn from thousands of customer use cases before introducing its interpretation.
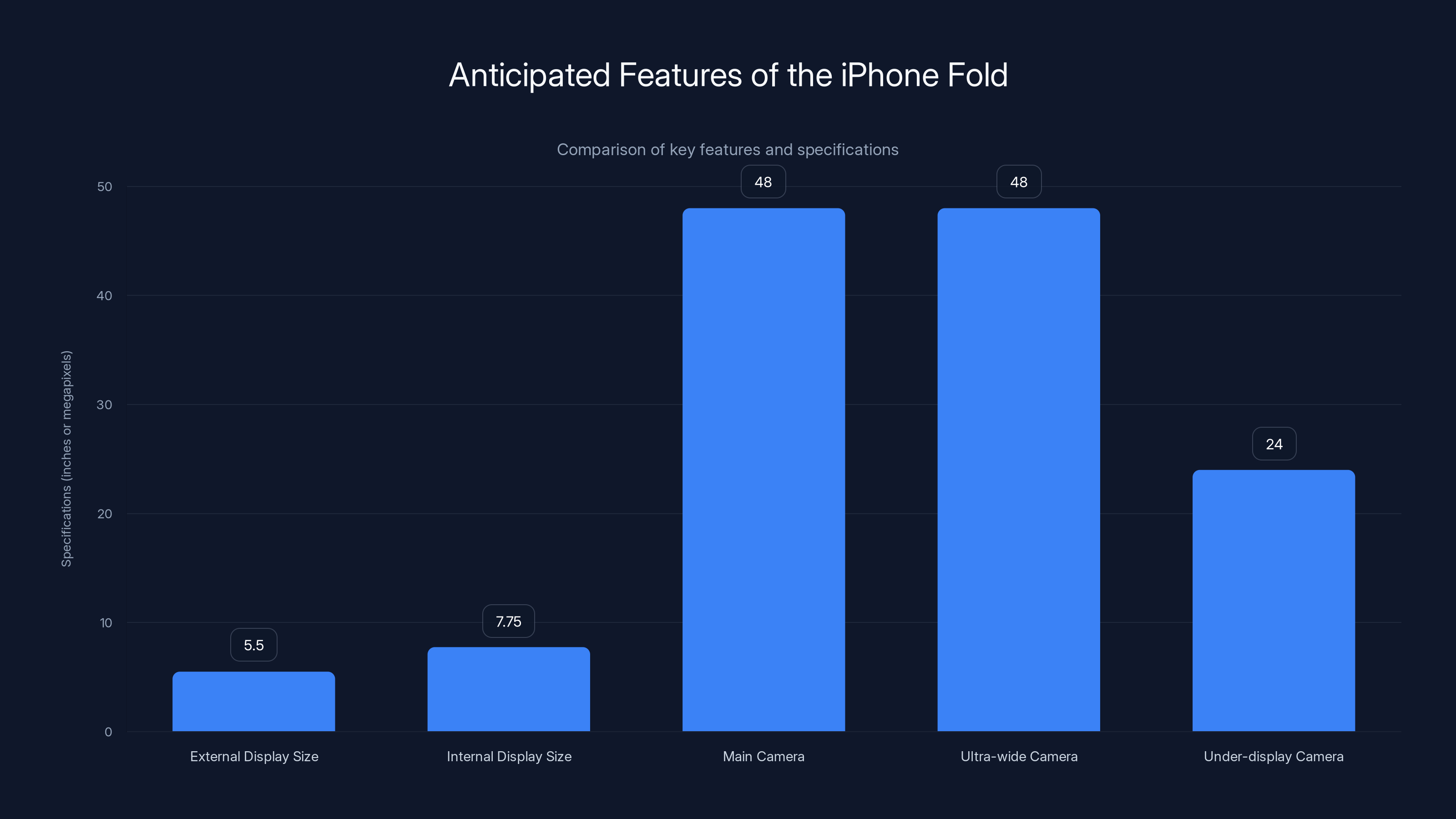
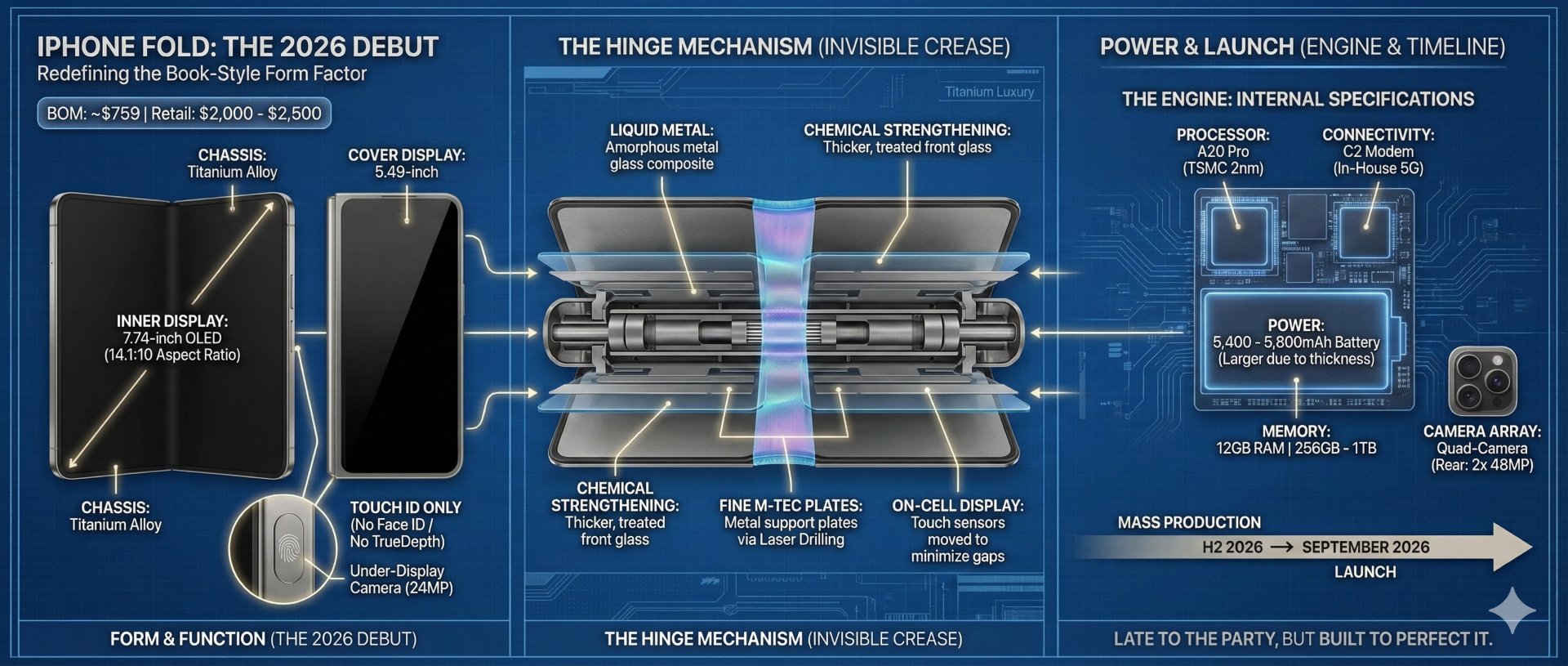
The iPhone Fold is expected to feature a 5.5-inch external and 7.75-inch internal display, with a robust camera system including a 48MP main and ultra-wide camera, and a 24MP under-display camera.
Design and Form Factor: The Book-Style Approach
Book-Fold vs. Clamshell Configuration
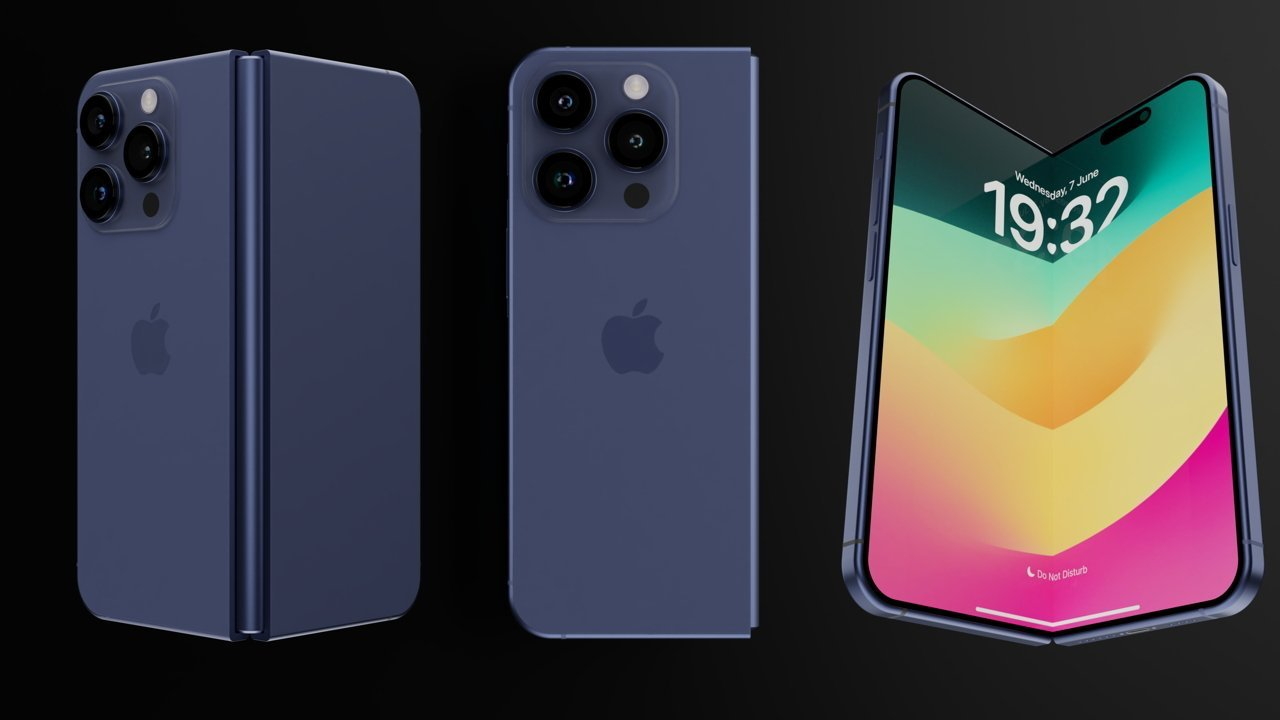
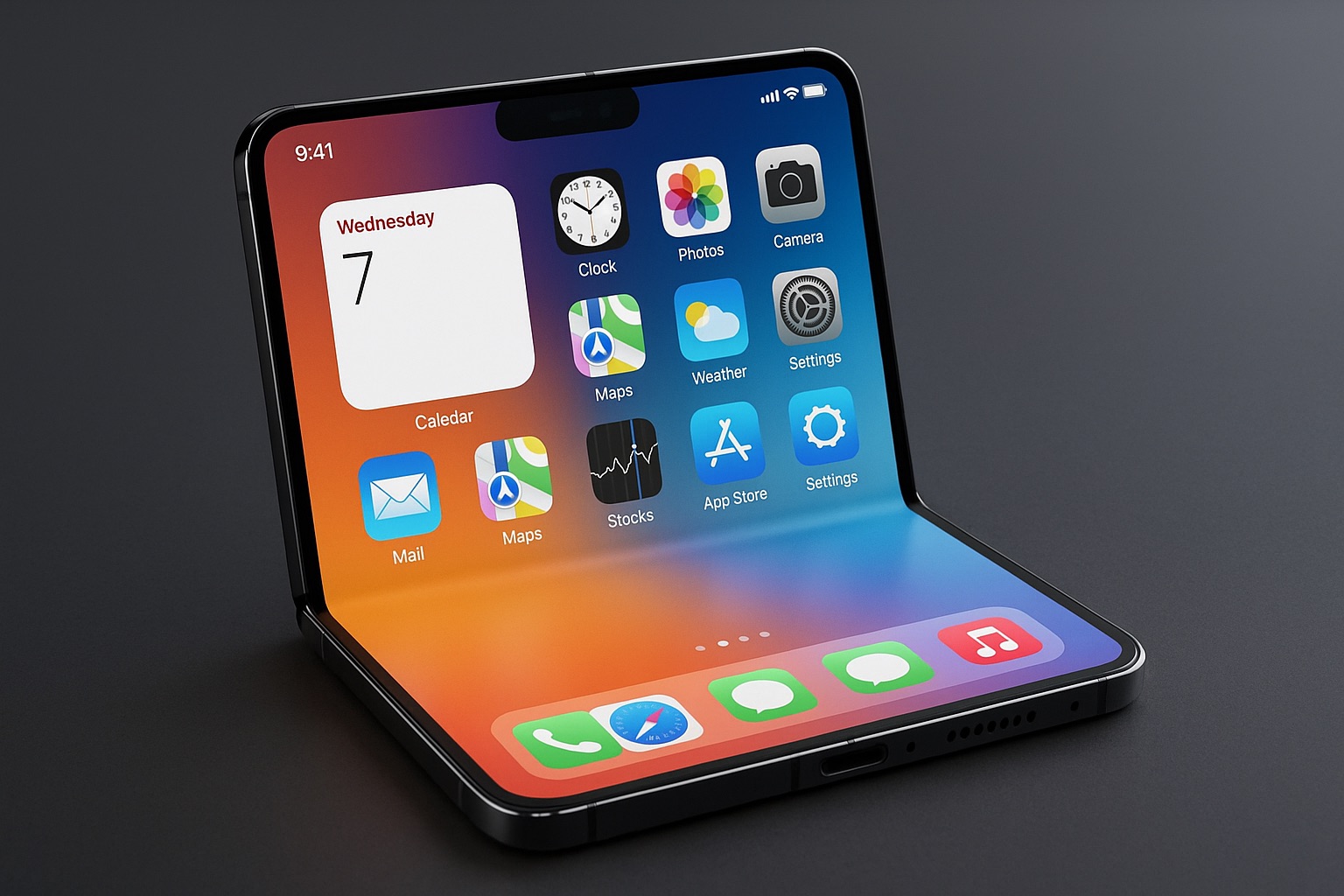
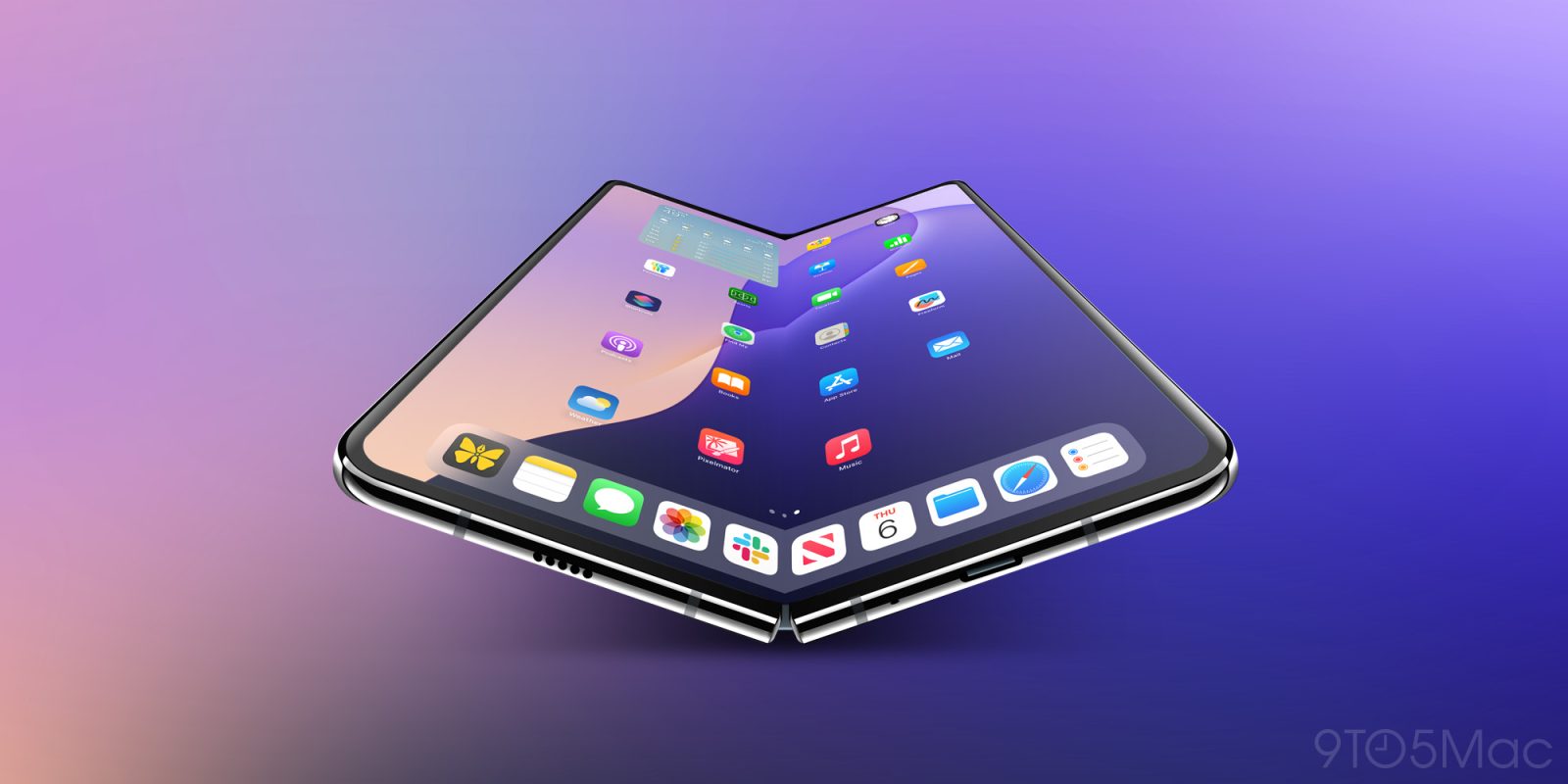
Consensus strongly indicates Apple has committed to a book-style foldable design, similar to Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold series, rather than a clamshell configuration like the Galaxy Z Flip or Motorola Razr. This means the iPhone Fold will unfold along a vertical seam to reveal a larger internal display, rather than folding horizontally to open like a traditional flip phone.
The book-style approach offers several advantages that align with Apple's design philosophy. First, it provides a tablet-like experience when unfolded, offering meaningful productivity upgrades for document editing, creative work, and media consumption. Second, it maintains the familiar smartphone form factor when folded, preserving the one-handed usability that remains central to iPhone design. Third, it allows for a more balanced device that doesn't feel awkwardly elongated in either orientation.
Given Apple's iPad ecosystem, the book-style design creates natural workflow bridges. Users could draft a document on the iPhone Fold's unfolded display, then seamlessly transition to an iPad or Mac for final production. This integration approach characterizes Apple's best design decisions.
Display Dimensions and Aspect Ratios
When unfolded, the iPhone Fold's internal display is expected to measure between 7.7 and 7.8 inches diagonally. To provide perspective, the current iPad mini has an 8.3-inch display, meaning the unfolded iPhone Fold will deliver a meaningful step up from a standard iPhone's 6.1-inch screen while remaining noticeably more compact than an iPad.
When folded, the external display should measure approximately 5.5 inches, positioning it between the standard iPhone 16 (6.1 inches) and the iPhone 16 Plus (6.7 inches). This external display must provide a fully functional smartphone experience, supporting all standard applications without degradation.
CAD leaks and alleged case-maker molds reveal something unexpected about the folded proportions: the device will reportedly be noticeably shorter and wider than a conventional iPhone, creating a squarer aspect ratio. This square footprint when folded actually matches the aspect ratio of the unfolded internal display more closely, which makes geometric sense for the hinge arrangement and display symmetry. A device that's roughly square when closed will unfold to reveal a display with proportions closer to 4:3 rather than the typical smartphone 20:9 aspect ratio.
Thickness and Material Construction
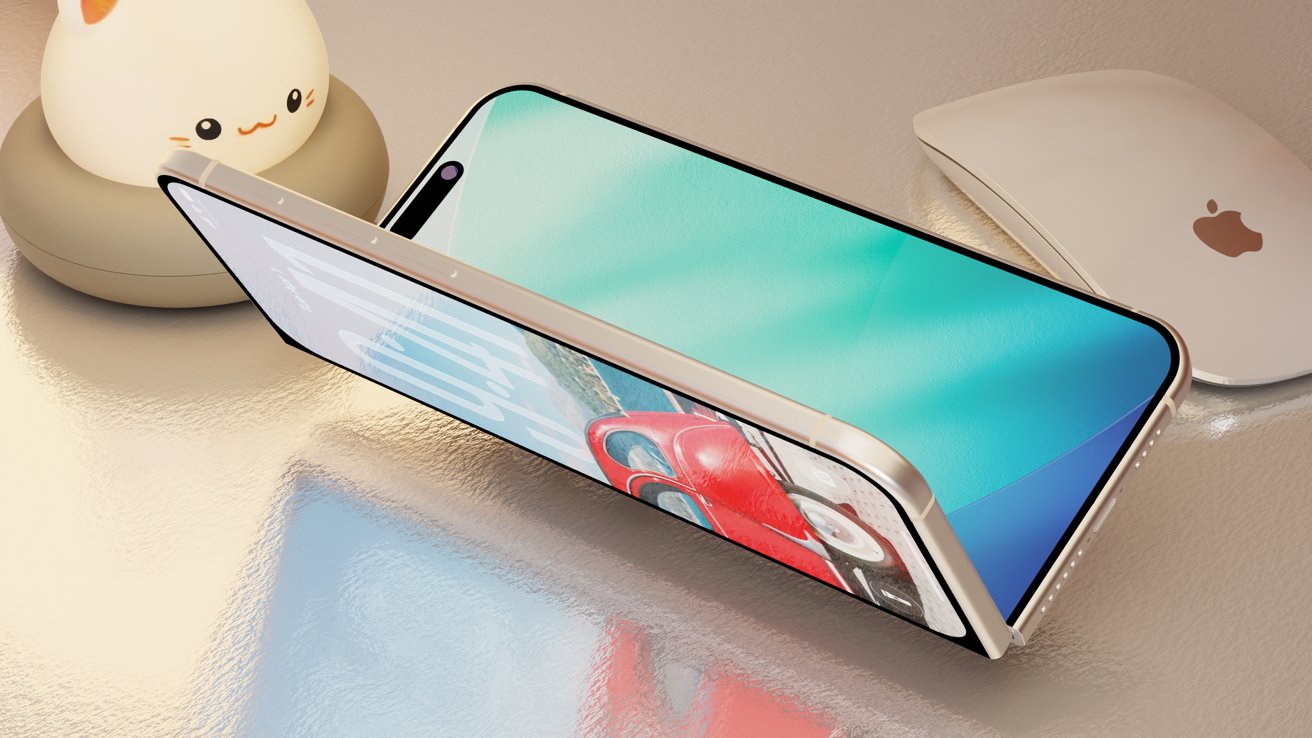
Thickness represents one of the most challenging engineering parameters for foldable devices. When unfolded, the iPhone Fold is expected to measure between 4.5 and 5.6mm thick, positioning it in a similar thickness range to the iPhone Air—which has been widely interpreted by analysts as a preview of one half of the foldable's thickness profile. This ultra-thin unfolded profile represents a significant engineering achievement, as it must accommodate dual display layers, flexible circuitry, battery components, and thermal management systems.
When folded, the device will be substantially thicker, likely between 9 and 11mm, depending on final hinge design and internal component layering. This thickness range, while noticeable, remains manageable and comparable to multiple standard iPhones stacked together.
Apple has explored various materials for the foldable's chassis, including titanium, aluminum alloys, and proprietary compositions. The use of sapphire crystal for protective layers over the crease region has been suggested in some reports, though confirmation remains absent.
Size Comparison to Existing Products
To contextualize the expected dimensions: when folded, the iPhone Fold will likely be slightly taller than an iPhone 16 Plus, but considerably shorter than a standard iPad mini. When unfolded, it will provide roughly 65-70% of the screen real estate of an iPad mini, creating a compelling middle ground between current iPhones and iPads.
This positioning allows Apple to offer users a device that captures legitimate foldable benefits—productivity gains, media consumption enhancement, creative tool versatility—without replacing their iPad purchases. The iPhone Fold becomes complementary rather than cannibalistic to the broader product lineup.
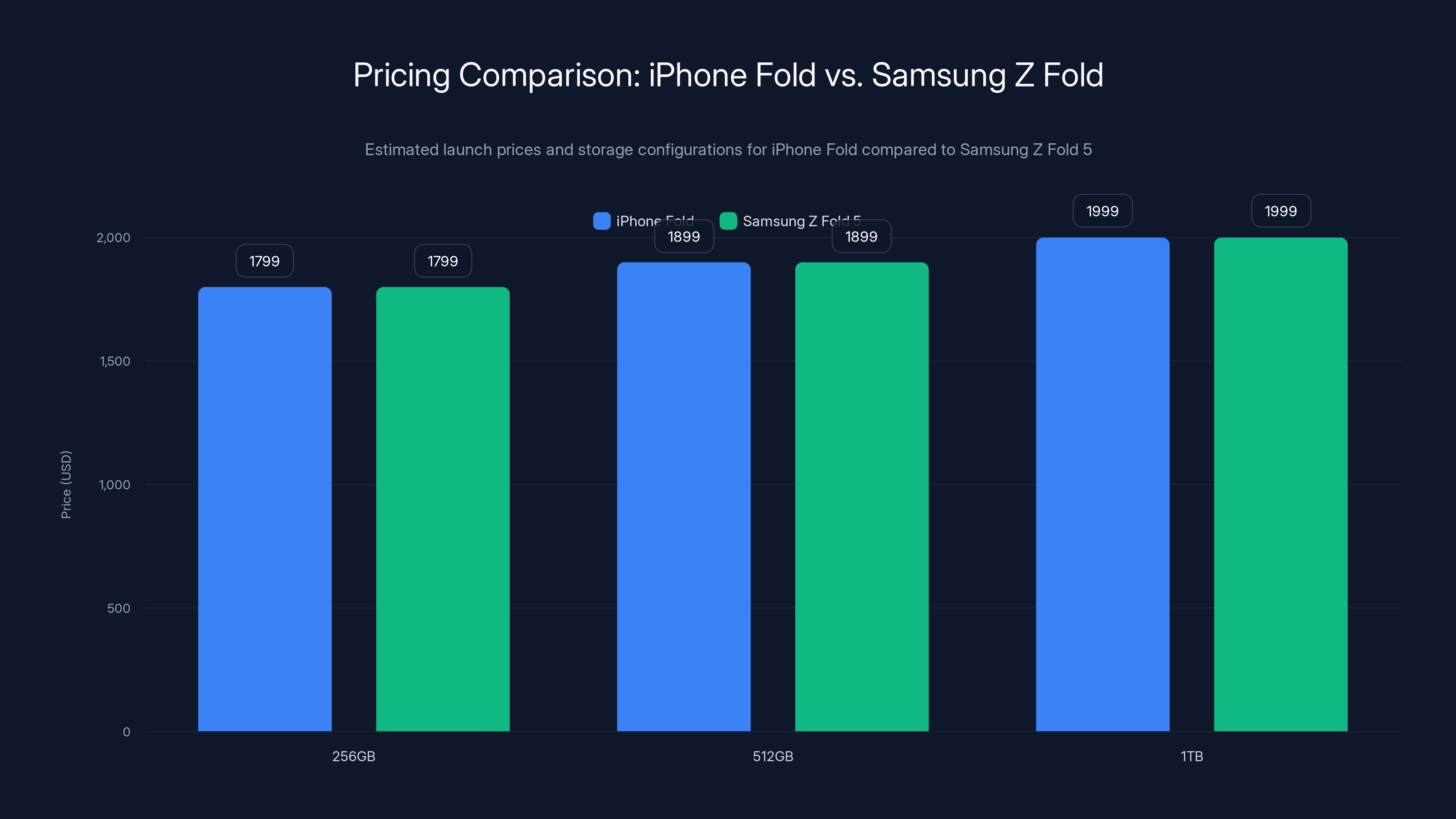
The iPhone Fold is expected to launch with prices ranging from
Display Technology: The Crease-Less Innovation
Samsung Display Partnership and OLED Advancement
Multiple credible sources confirm that Apple will rely on Samsung Display as its primary OLED panel supplier for the iPhone Fold. This partnership represents a fascinating reversal of typical tech industry dynamics: Apple, known for vertical integration and component control, will depend on its primary smartphone competitor for a critical component.
The specific Samsung panel technology is expected to be the crease-less OLED innovation that Samsung publicly showcased at CES 2026. This technology combines a flexible OLED layer with an innovative laser-drilled metal support plate designed specifically to distribute and manage stress during the folding motion. The laser-drilled structure creates thousands of microscopic channels that allow the substrate to flex without visible creasing at the fold line.
This represents a genuine engineering breakthrough. Current foldable displays, including Samsung's own Galaxy Z Fold series, still display visible creases under certain lighting conditions, particularly oblique angles in bright environments. Users frequently notice and comment on this creasing as a notable limitation of the foldable experience. Apple's historical insistence on display quality—the company's original innovation with Retina displays fundamentally raised industry expectations—suggests the company would refuse to launch a foldable with visible creasing.
Crease Reduction and Visual Imperceptibility
The crease-elimination goal represents Apple's primary technical focus. Sources indicate the company views a nearly invisible crease as essential before market entry. This isn't merely aesthetic preference; a visible crease impacts the user experience substantially. Reading text across the crease, viewing images that span the fold line, or watching video content becomes noticeably compromised when a visible discontinuity interrupts the display.
Samsung's CES 2026 demonstration showed significant progress, with observers noting that the crease became nearly imperceptible under normal viewing angles with standard lighting. The laser-drilling technique works by creating micro-scale discontinuities that prevent the formation of macro-scale visible creasing, essentially distributing stress so evenly that no single point of maximum curvature emerges.
Brightness, Color Accuracy, and Display Specifications
Beyond crease elimination, the internal display must meet Apple's exacting standards for color accuracy and brightness. Current Apple displays achieve peak brightness exceeding 2,000 nits in HDR modes, setting industry benchmarks that competitors struggle to match. The iPhone Fold's internal OLED will likely target similar brightness levels, ensuring that unfolded usage remains visually comparable to standard iPhone experiences.
Color accuracy will need to meet Display Mate standards that Apple typically enforces, ensuring that creative professionals using the device for photo editing or video grading can trust the on-screen representation. The display will likely feature the wide color gamut (DCI-P3 or better) and gamma-curve accuracy that characterize current iPad displays.
Refresh rate is expected to match current iPhone standards at 120 Hz, providing smooth scrolling and responsive interface interactions. Some reports suggest potential for 144 Hz refresh rate support for gaming and high-motion content, though confirmation remains unclear.
External Display Technology
The external folded display faces different technical requirements. It must be durable enough to resist scratches and impacts during daily use when the device is folded. It must provide full smartphone functionality, supporting every iOS application without limitation. It should maintain adequate brightness for outdoor use while managing power consumption appropriately.
The external display will likely be a conventional OLED, not the flexible substrate of the internal display, as it experiences less stress during the folding motion. This allows Apple to source a more traditional panel, reducing complexity and cost for that component.
Camera System Architecture
Four-Camera Setup and Sensor Specifications
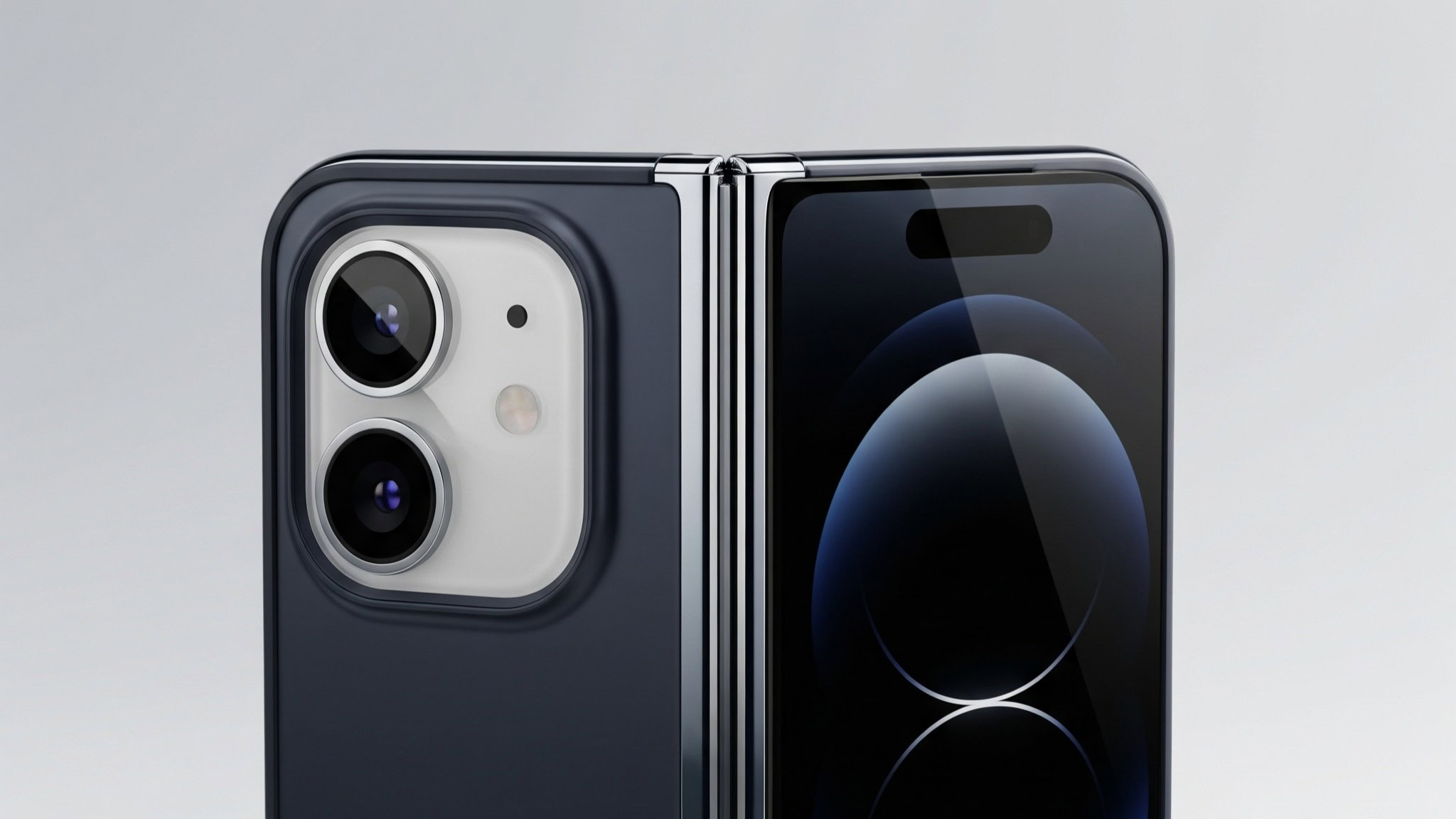
Reports consistently indicate a four-camera system across both displays. The configuration is expected to include two rear cameras (main and ultra-wide, both likely featuring 48MP sensors), one punch-hole camera positioned on the outer folded display, and one under-display camera integrated into the larger internal screen.
The dual rear cameras, positioned along the device's spine when unfolded, will provide the standard focal lengths that characterize modern iPhones. The 48MP main sensor represents a continuation of current iPhone specifications, suggesting that Apple will prioritize image quality and dynamic range rather than pure megapixel counts. The ultra-wide camera at 48MP would be an increase from current iPhone specifications, potentially enabling improved crop flexibility and lower-light performance in wide-angle capture.
Under-Display Camera Technology and Innovation
The under-display camera on the inner screen represents the most technically ambitious camera component. Under-display camera technology, where the sensor sits beneath transparent OLED pixels, historically produced noticeably inferior image quality compared to traditional punch-hole or notch-based designs. The transparent pixels required to allow light through to the sensor below create diffusion effects that reduce sharpness, color accuracy, and low-light performance.
Apple's rumored 24MP under-display sensor represents a significant step forward from existing implementations. Current foldable devices typically employ 10MP or lower-resolution under-display cameras, accepting the technology's limitations for design purity. A 24MP sensor suggests Apple has developed either superior transparent pixel design or computational photography techniques that compensate for the physical limitations.
The under-display camera implementation serves essential functions. It enables video calling and face recognition usage when the device is unfolded in tent mode. It allows for uninterrupted user-facing video capture and live streaming without a visible cutout interrupting the display experience. For creative professionals using the device for content creation, the seamless display becomes increasingly valuable.
Punch-Hole Camera on External Display
The punch-hole camera positioned on the outer display serves the standard smartphone use cases when the device is folded. This camera likely delivers specifications comparable to current iPhone 16 front cameras, around 12MP resolution with advanced facial recognition and computational photography processing.
The punch-hole design, while creating a small display interruption, represents a practical compromise that maintains image quality while allowing the external display to function as a complete smartphone. Apple has long rejected notch designs for aesthetic reasons, so a punch-hole that minimizes the visual impact represents progress the company would likely accept.
Absence of Face ID in Favor of Touch ID
Multiple sources claim Apple will abandon Face ID entirely on the iPhone Fold in favor of Touch ID integrated into the power button. This represents a notable departure from iPhone design language, where Face ID has been central since the iPhone X in 2017.
The rationale makes technical sense: Face ID requires either a notch or a Dynamic Island to accommodate the True Depth camera array containing multiple sensors. Both options would compromise either the external or internal display. Touch ID in the power button, proven reliable on recent iPad models, allows both displays to remain uninterrupted by camera or sensor cutouts.
This decision prioritizes display purity and functionality over the facial recognition convenience that iPhone users have grown accustomed to. It represents a trade-off Apple is willing to make specifically for the foldable form factor, but it also signals that Face ID may not be technically feasible within the foldable's constraints.
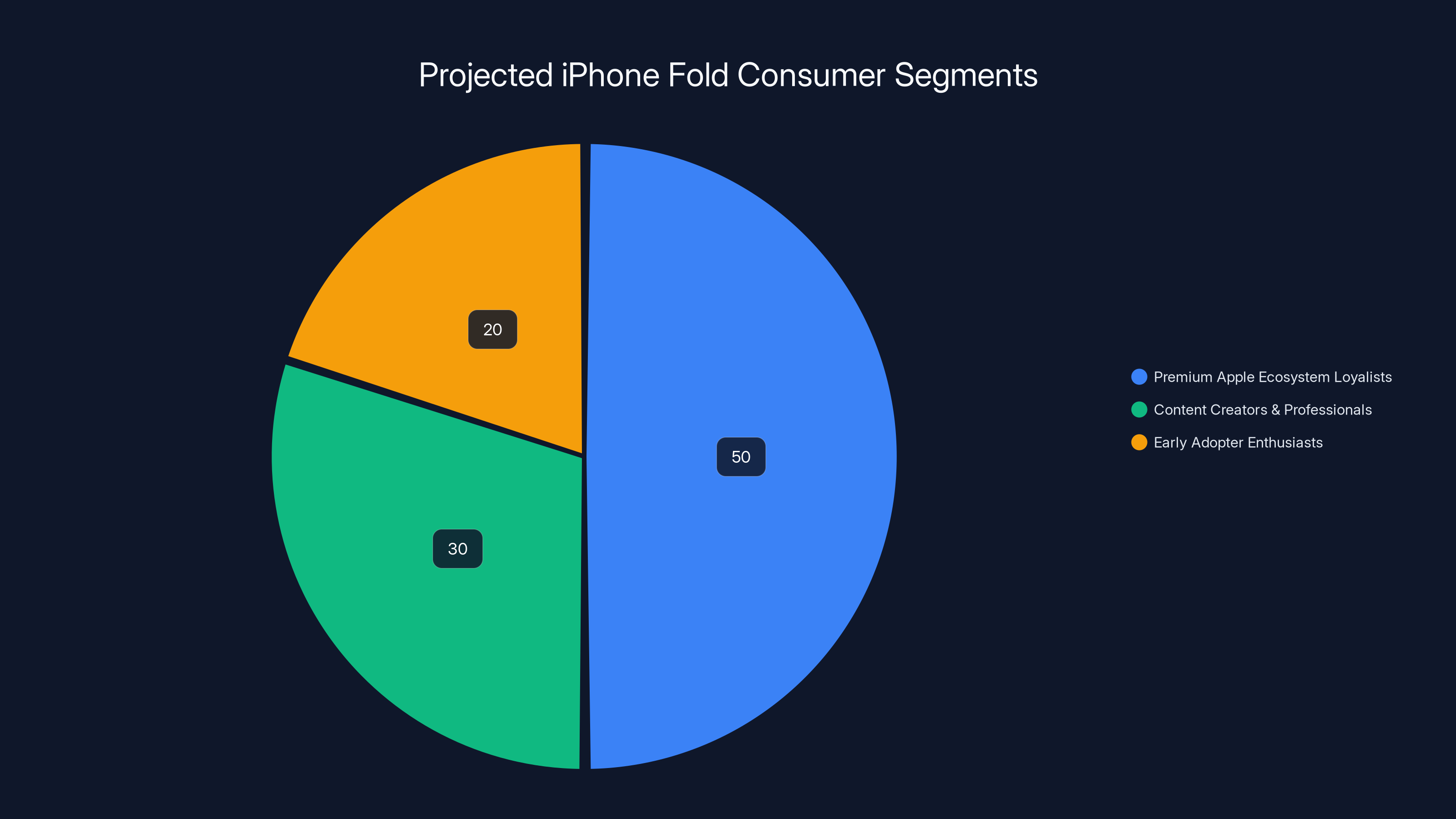
Estimated data suggests that Premium Apple Ecosystem Loyalists will make up the largest segment of initial iPhone Fold adopters, followed by Content Creators and Early Adopter Enthusiasts.
Hinge Design and Liquidmetal Innovation
Liquidmetal: The Proprietary Material
Multiple credible sources claim Apple will utilize Liquidmetal—a trade name for metallic glass alloy—in the hinge mechanism. Apple has explored Liquidmetal in various small components for years, filing patents and maintaining a licensing relationship with Liquidmetal Technologies. The material's properties make it particularly suitable for the foldable hinge application.
Liquidmetal exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, comparing favorably to titanium while remaining relatively lightweight. More importantly, it demonstrates superior resistance to deformation and plastic flow—the permanent bending that occurs when materials experience repeated stress cycles. A smartphone hinge undergoes hundreds of thousands of open-close cycles throughout its operational lifetime, making resistance to fatigue and deformation absolutely critical.
The metallic glass structure provides exceptional hardness comparable to ceramics, enabling the hinge to resist damage from dust intrusion or edge impacts. Unlike titanium, which can permanently deform if bent beyond certain stress thresholds, Liquidmetal better resists plastic deformation, theoretically allowing it to recover from minor overstress events.
Hinge Stress Distribution and Durability
The hinge design must accomplish multiple objectives simultaneously. It must fold and unfold smoothly through hundreds of thousands of cycles without developing play or looseness. It must seal out dust and moisture, protecting internal components from environmental contamination. It must maintain consistent tension throughout the device's operational life, preventing the foldable action from becoming too loose or too tight.
Apple's engineering approach likely incorporates sophisticated stress distribution mechanisms, possibly including spring elements, dampening systems, and multi-material construction that coordinates rigid and flexible components. The Liquidmetal component probably serves as the structural spine, providing the strength necessary to manage the enormous stresses generated during folding.
Testing foldable hinges requires accelerated life cycle testing involving tens of thousands of automated open-close cycles, often coupled with environmental stress testing including temperature cycling, humidity exposure, and salt-fog corrosion testing. Apple's testing standards are known to exceed industry requirements, suggesting the iPhone Fold's hinge will undergo more rigorous validation than competitors' implementations.
Sealing and Dust/Water Resistance
The hinge represents the greatest design challenge for water and dust resistance. While most iPhones achieve IPX8 water resistance rating, foldables present additional complexity due to the gap created by the hinge mechanism. This gap must remain sealed when closed, yet allow for the folding motion, creating a seemingly contradictory requirement.
Apple likely approaches this through multiple sealing layers, possibly including gasket materials, brush seals, or innovative labyrinth designs that prevent dust ingress while permitting the necessary mechanical articulation. The Liquidmetal hinge, with its smooth surfaces and superior sealing potential compared to titanium, may contribute meaningfully to dust resistance.
A full IP rating (both dust and water) on a foldable device would represent a significant achievement, though some reports suggest the iPhone Fold may receive only an IPX rating (water resistant but not dust resistant) similar to certain Apple Watch models. However, Apple's track record with durability innovations suggests aggressive pursuit of full IP resistance.
Hinge Tension and Feel
The subjective experience of opening and closing the foldable—how much resistance the hinge provides, whether it snaps into fully open or closed positions, or maintains any angle in between—significantly impacts user satisfaction. Samsung's hinges improved dramatically across generation, with the Galaxy Z Fold 5 and later models providing significantly better tactile feedback than earlier versions.
Apple's engineering, historically obsessive about tactile feedback in mechanical design (the click of a trackpad button, the feel of a scroll wheel, the resistance of a power button), will likely prioritize hinge feel extensively. The ideal hinge provides sufficient resistance to prevent accidental opening, snaps positively into fully opened and fully closed positions for intent clarity, and could potentially maintain intermediate angles for tent-mode positioning.
Battery and Power Management Architecture
Battery Capacity and Cell Configuration
Fitting a capable battery into a foldable form factor presents substantial engineering challenges. The battery cannot occupy the hinge area, limiting available space. The battery must be split across multiple cells positioned on either side of the device or stacked in layers, complicating management and manufacturing.
Estimates suggest the iPhone Fold will incorporate a total battery capacity in the 4,500-5,500mAh range, comparable to current iPhone Plus models. This assumes Apple splits the battery across two or more cells, positioning them away from the hinge zone. Such a configuration requires specialized battery management electronics capable of monitoring and balancing charge across multiple cell groups, adding marginal complexity and cost.
The positioning of separate battery cells affects thermal distribution and overall device balance when unfolded. Apple's engineering likely dedicates significant effort to ensuring even weight distribution, preventing one half of the unfolded device from feeling noticeably heavier than the other.
Thermal Management in a Compact Form Factor
Compressing all of an iPhone's components into a foldable form factor while maintaining thermal performance represents a significant engineering challenge. Heat dissipation pathways become constrained, and the thin profile (4.5-5.6mm unfolded) limits the thermal mass available for heat absorption.
Apple likely employs graphite sheets or other phase-change materials to manage heat flow away from processing components toward the device perimeter. Vapor chamber technology, sometimes employed in premium tablets and laptops, might facilitate heat distribution across larger surface areas. The hinge region, despite being functionally critical, may also serve as a thermal conduit, channeling heat away from interior components.
Charging Speed and Wireless Capability
MagSafe charging, Apple's proprietary magnetic charging system introduced with the iPhone 12, will likely feature on the iPhone Fold. MagSafe provides convenient wireless charging while enabling a rich accessory ecosystem of magnetic attachments. The larger surface area of the foldable device allows for larger MagSafe magnets and improved charging coil efficiency compared to standard iPhones.
Charging speed expectations should align with current iPhone standards, likely supporting 25-30W wired charging and potentially higher MagSafe wireless charging speeds (possibly 15-20W) compared to standard iPhones. The larger physical form factor permits more efficient wireless charging coil designs capable of accepting higher power levels without overheating.

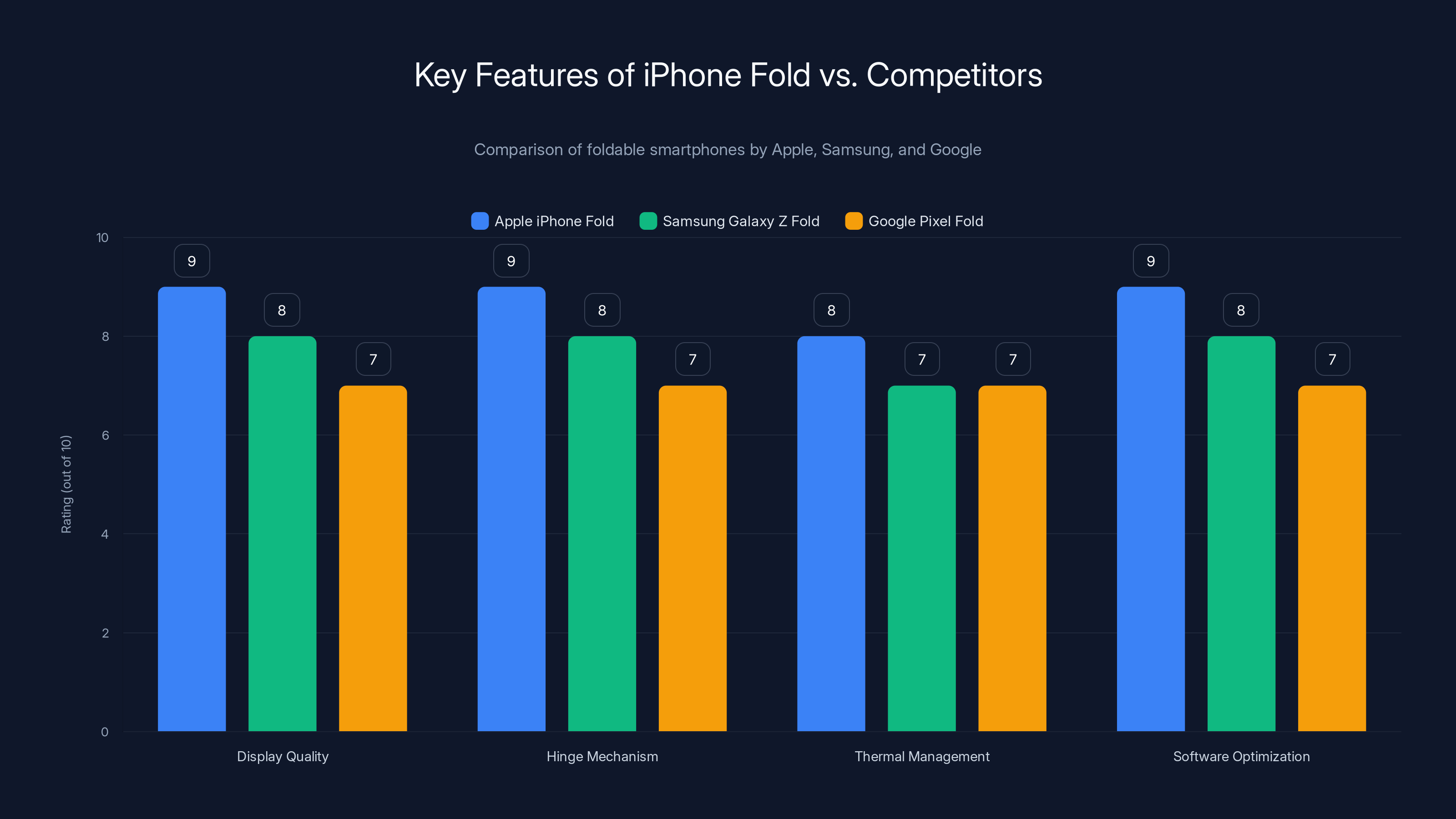
The iPhone Fold is expected to lead in display quality and software optimization, setting a new benchmark for foldable smartphones. Estimated data based on industry trends.
Software Experience and iOS Optimization
Multi-Window Multitasking and Split-View
iPadOS already supports sophisticated multitasking with multiple apps running simultaneously in split-view and slide-over configurations. The iPhone Fold's large unfolded display will demand native support for similar multitasking paradigms, likely requiring substantial iOS software development to enable experiences previously limited to iPad.
Apple will almost certainly develop dedicated split-screen capabilities optimized for the Fold's unfolded aspect ratio and dimensions. Standard apps should adapt intelligently to the larger screen, potentially providing expanded interfaces that leverage the additional real estate. The software must handle the transition seamlessly when the device moves between folded and unfolded states, preserving app state and context.
Responsive Design and Dynamic Layout Adaptation
App developers will need powerful responsive design frameworks to create layouts that intelligently adapt to both the 5.5-inch folded external display and the 7.7-7.8-inch unfolded internal display. Apple will likely provide comprehensive frameworks and guidelines ensuring third-party apps automatically adapt without explicit developer effort.
The crease zone presents unique software challenges. App interfaces must avoid placing critical interactive elements directly over the crease, where they'd be partially obscured. Content flowing across the crease must handle the temporary interruption gracefully. Apple's system frameworks will likely automatically adapt layout algorithms to account for crease positioning.
Tent Mode and Productivity Scenarios
The foldable form factor enables a "tent mode" where the device stands at an angle, balancing on the hinge with screens facing different directions. This positioning suits video calling, content watching, and hands-free usage scenarios that benefit from an upright screen orientation.
iOS will need to intelligently detect tent-mode positioning through accelerometer data and potentially provide mode-specific interface optimizations. Video calling apps might automatically adjust camera positioning and UI layout for tent-mode usage. Content consumption apps might expand UI elements to fill the unfolded screen more effectively. The system framework should allow apps to query device orientation and adjust accordingly.

Comparison to Competitor Foldables
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold Series Positioning
By 2026, Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold lineup will have established itself through seven or eight generations, with millions of units sold and refined through continuous improvement. The Z Fold series has proven the viability of the book-style foldable form factor, established consumer expectations, and identified the core use cases that drive adoption.
Apple's entry differs in several key aspects. Apple's ecosystem integration, connecting seamlessly with iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch, provides experiences Samsung cannot match. The expected crease-less display technology, if realized, addresses the single most frequently cited foldable limitation. Touch ID instead of Face ID represents a different security paradigm, acceptable to consumers familiar with iPad authentication methods.
Apple will likely price the iPhone Fold at a premium to Samsung's offerings, following Apple's historical strategy. A
Google Pixel Fold and Competitive Differentiation
Google's Pixel Fold, launched after Samsung had already established the category, positioned itself as a software-first interpretation of the foldable concept. Google's computational photography capabilities and deep Android customization allowed for innovative software experiences not possible on competing devices.
Apple's competitive advantages—vertical integration, ecosystem cohesion, display technology partnerships, manufacturing precision—differ substantially from Google's strengths. Where Google emphasizes computational intelligence and software, Apple emphasizes hardware refinement and ecosystem coherence. These different philosophies will likely result in distinctly different user experiences despite similar hardware categories.
Motorola Razr and Clamshell Alternatives
Motorola's Razr reboot, utilizing clamshell design, has captured meaningful market share among users preferring more compact folded dimensions. The Razr folds to approximately 4 inches thick, substantially more pocketable than book-style foldables that exceed 9mm when closed.
Apple's commitment to book-style design represents a deliberate choice prioritizing unfolded functionality over folded compactness. Apple has never positioned itself as the "smallest" manufacturer—rather, Apple focuses on the experiences enabled by specific form factors. The book-style fold enables iPad-class productivity on a portable device, a value proposition Apple clearly prefers to the ultra-compact Razr approach.
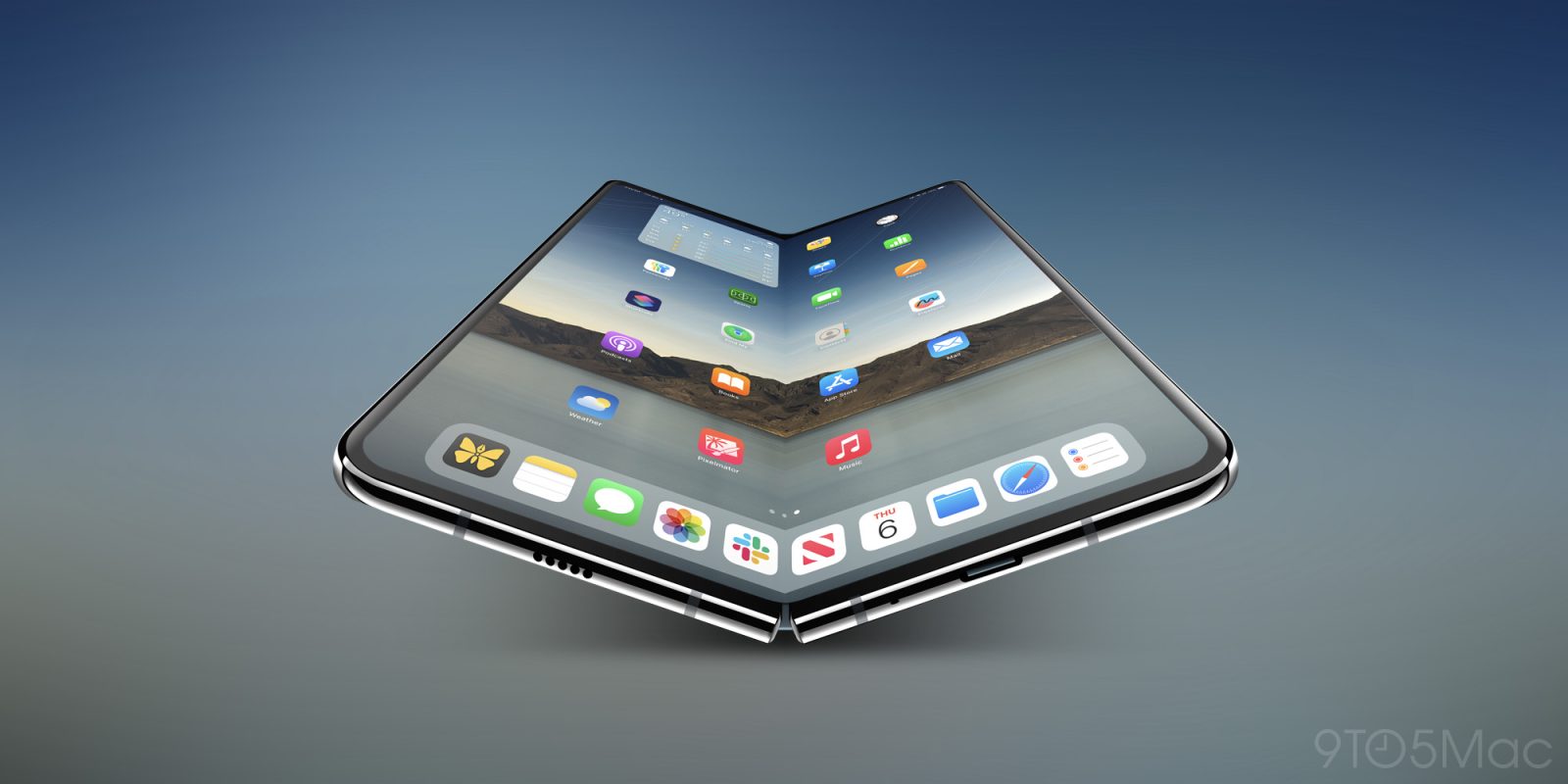

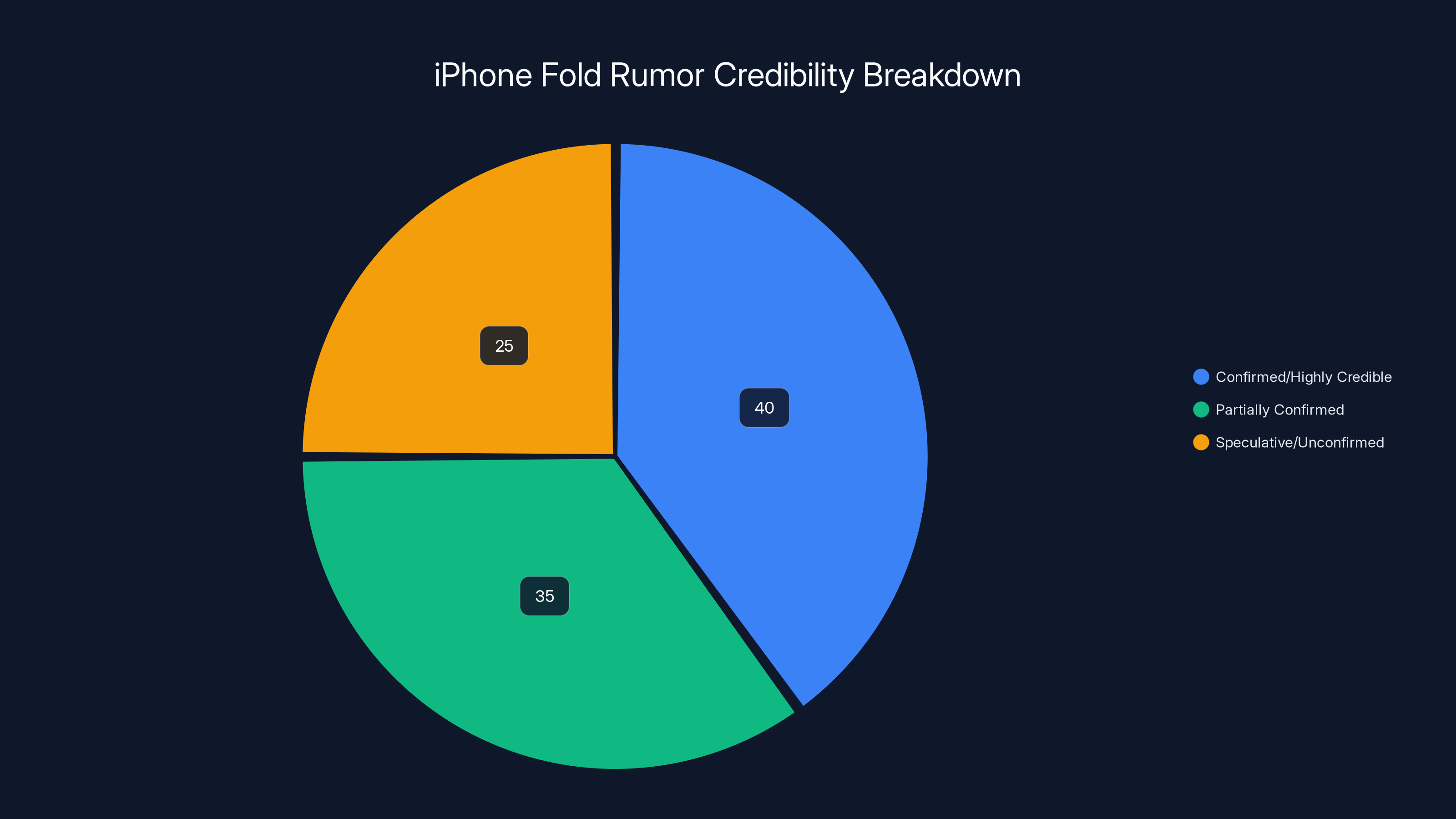
The majority of iPhone Fold rumors are either confirmed or highly credible, with 40% of the rumors fitting this category. Partially confirmed rumors account for 35%, while speculative or unconfirmed rumors make up 25%. Estimated data.
Pricing Strategy and Market Positioning
Expected Price Range and Tier Structure
Industry analysts expect the iPhone Fold to price between
Apple historically structures pricing around storage configurations. A probable structure might position the 256GB model at
The pricing logic assumes manufacturing costs around
Comparison to Samsung Z Fold Pricing
Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold 5 launched at $1,799, with the Z Fold 6 maintaining similar positioning. By 2026, Samsung will likely have adjusted pricing based on manufacturing cost reduction and competitive dynamics. Apple entering at comparable or slightly higher pricing reflects confidence in perceived quality advantages and ecosystem benefits.
An interesting dynamic emerges: Samsung typically offers substantial carrier discounts and trade-in promotions for Z Fold devices, effectively reducing net customer cost to
Carrier Positioning and Subsidy Strategy
Carriers including Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile will likely offer aggressive subsidies and financing options for the iPhone Fold, recognizing the device's appeal to premium-tier customers. Subsidized pricing of
Apple's historical carrier relationships ensure premium positioning and placement priority. The iPhone Fold will likely be featured heavily in carrier marketing, supported by sales incentive structures. Carriers recognize high-value customers attracted to premium foldable devices as ideal targets for enhanced service plans and premium data tiers.

Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and Availability
Production Volume Constraints and Gradual Ramp
Foldable device manufacturing, while matured compared to 2019-2020 when Samsung faced significant production challenges, remains more constrained than standard smartphone manufacturing. Yield rates (the percentage of successfully manufactured units meeting quality standards) for foldable displays and complex hinges remain lower than conventional components.
Apple likely plans conservative initial production volumes, potentially 2-3 million units in the first quarter, ramping to 5-7 million annually once manufacturing processes stabilize. This conservative approach protects brand reputation by avoiding launching with widespread defect rates, prioritizes quality over volume, and allows for refinement before scaling to mainstream volumes.
Component Sourcing and Strategic Partnerships
Beyond Samsung Display, Apple will depend on specialized suppliers for foldable-specific components. The Liquidmetal hinge requires proprietary manufacturing, likely concentrated with a single or limited set of suppliers. Under-display camera sensors will demand customized specifications from sensor manufacturers. Flexible circuit boards must be sourced from advanced manufacturers capable of routing electrical connections through the flexible hinge region.
Apple's notorious supplier management approach—developing long-term relationships, providing technical resources, investing in supplier capability development—will accelerate production ramp. Unlike competitors who might accept higher initial defect rates, Apple's supplier partnerships emphasize continuous improvement and quality advancement.
Geographic Manufacturing and Geopolitical Considerations
The iPhone Fold's complexity and Apple's manufacturing diversity suggests production across multiple geographic regions. Assembly might occur in China (primary), India (secondary), and potentially Vietnam or other Southeast Asian locations. The geographic distribution reduces dependence on any single region and provides supply chain resilience.
Geopolitical considerations around semiconductor access and manufacturing capacity in different regions will influence final production location decisions. Apple's historical hedging strategy, maintaining diversified manufacturing despite economic incentives toward concentration, positions the iPhone Fold to navigate geopolitical uncertainty.

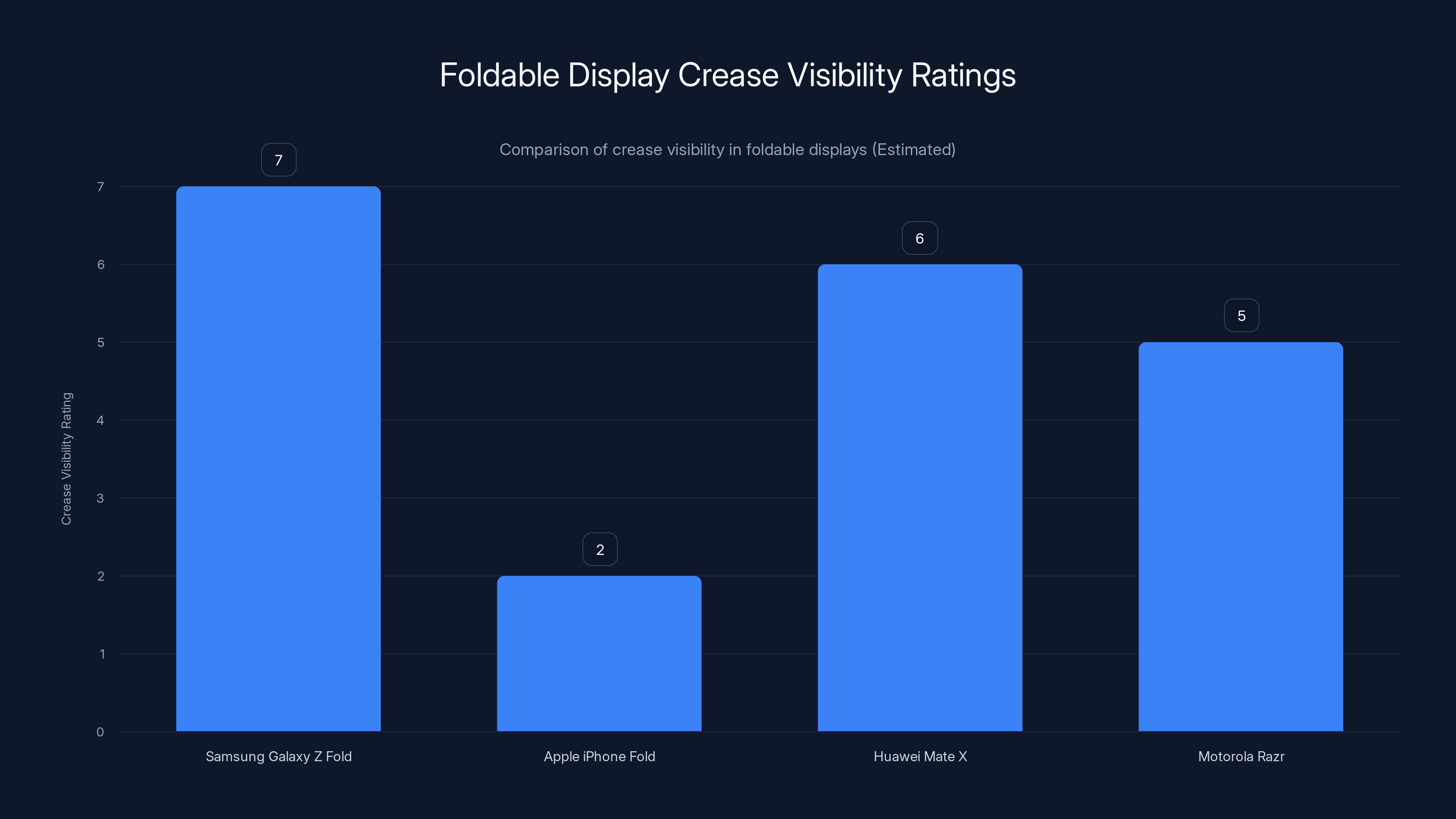
Estimated data suggests that Apple's iPhone Fold aims for significantly reduced crease visibility compared to existing models, enhancing user experience.
Key Rumors: What We Know vs. Speculation
Confirmed or Highly Credible
Several elements of the iPhone Fold narrative benefit from consistent reporting across multiple credible sources:
- Fall 2026 launch window: Repeatedly cited by Gurman, Kuo, and multiple supply chain sources with strong historical accuracy.
- Book-style foldable design: Virtually all reputable sources align on this configuration over clamshell alternatives.
- Samsung Display OLED partnership: Confirmed through supply chain reporting and strategic logic.
- Crease-less or crease-reduced display technology: CES 2026 Samsung demonstrations provide concrete evidence.
- Liquidmetal hinge material: Multiple independent sources cite this specific material.
- Touch ID authentication: Consistent across most credible reports.
- 7.7-7.8 inch internal display, 5.5-inch external display: Multiple source consistency on these measurements.
Partially Confirmed or Likely but Not Certain
Other elements have reasonable support but lack the consistency of the above categories:
- Specific camera specifications (48MP main/ultra-wide, 24MP under-display): Multiple sources cite these specs, but manufacturers adjust specifications regularly during development.
- Pricing at 1,999: Industry analyst consensus and typical Apple positioning, but not confirmed.
- 2027 as the primary sales year: Gurman's refined reporting suggests this, but demand could accelerate timelines.
- Absence of Face ID in favor of Touch ID: Consistent reporting, but Face ID integration hasn't been definitively ruled out by Apple.
Speculative or Unconfirmed
These elements appear in some reports but lack sufficient corroboration to consider likely:
- Specific thermal management technologies: Vapor chamber or other specific solutions remain unconfirmed.
- Battery capacity specifics: Estimates range widely from 4,500mAh to 5,500mAh without definitive sourcing.
- Wireless charging speeds: Specific wattage figures lack verification.
- Intermediate angle support in tent mode: Desirable but requires specific engineering not yet confirmed.

Development Challenges and Technical Hurdles
Thermal Dissipation in Constrained Space
The iPhone Fold's thin unfolded profile (4.5-5.6mm) constrains thermal dissipation pathways significantly. When running demanding applications—video editing, gaming, or 8K video recording—Apple processors generate substantial heat. This heat must dissipate through limited surface area without creating hot spots that damage components or trigger thermal throttling.
Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold devices have historically experienced minor thermal performance degradation compared to standard phones, with sustained high-performance applications sometimes triggering thermal throttling. Apple's fastidious approach to performance consistency will demand solutions ensuring thermal performance competitive with standard iPhones despite greater constraints.
Dust Resistance at the Hinge
While not explicitly confirmed as a requirement, Apple's historical commitment to durability and water resistance suggests aggressive pursuit of dust resistance despite the hinge design challenges. Dust particles, if allowed to infiltrate the hinge, could cause friction increases, sticking sensations, or eventual mechanical failure.
Apple likely employs multiple defense strategies: brush seals that redirect dust away from the hinge articulation, labyrinth designs that force dust particles to settle before reaching critical mechanisms, and surface coatings that discourage particle accumulation. The Liquidmetal hinge, with its smooth surfaces and potentially superior surface treatments, contributes to this objective.
Display Longevity and Degradation Rates
Flexible OLED displays, being bent thousands of times throughout their operational life, experience accelerated degradation compared to rigid displays. Organic compounds in the OLED structure experience stress-induced defects, potentially leading to color shifts, brightness decrease, or pixel failures over years of use.
Apple's testing will need to establish that the iPhone Fold's display maintains acceptable performance for 4-5 year ownership timespans typical for iPhone users. Accelerated aging tests, combined with consumer data from hundreds of thousands of test units, will validate longevity before commercial launch.
Software Optimization for Multifold States
Apps must function smoothly as the device transitions between folded and unfolded states. This requires intelligent software that preserves application state, adjusts layout dynamically, and maintains user context seamlessly. No existing iOS app was designed for this functionality—all existing apps assume fixed display dimensions.
Apple's framework developers will need to provide abstractions that allow existing apps to adapt without explicit redesign, while simultaneously enabling sophisticated new experiences for apps specifically optimized for the foldable. The operating system must also handle crease-aware layout, ensuring critical interface elements and important content avoids the crease zone.

Market Reception and Consumer Adoption Predictions
Target Consumer Segments
Initial iPhone Fold adopters will likely come from three primary segments:
-
Premium Apple Ecosystem Loyalists: Users invested in iCloud, Apple Care+, and multiple Apple devices who view the Fold as the natural evolution of their ecosystem. These users have demonstrated willingness to pay premium prices for Apple products and will likely adopt early regardless of specific feature comparisons.
-
Content Creators and Productivity Professionals: Video editors, photographers, designers, and business professionals who value the productivity gains from a larger portable screen. These users benefit substantially from the iPad-like capabilities when unfolded, justifying the premium price for professional tool purposes.
-
Early Adopter Enthusiasts: Technology enthusiasts and media observers who view foldable devices as the inevitable future of mobile computing and want to participate in this transformation. This segment, while relatively small, drives cultural conversation and media visibility.
Secondary adoption waves would include general premium iPhone purchasers once manufacturing scales and pricing becomes competitive with current flagship models.
Adoption Velocity and Market Penetration
Industry analysts predict iPhone Fold would capture 2-5% of Apple's total iPhone sales volume in its first full year, gradually increasing to 8-15% over subsequent years as manufacturing scales and consumer familiarity increases. This penetration rate suggests 15-30 million annual iPhone Fold units at mature adoption levels—a substantial market but representing the premium tier of the smartphone market.
Comparison points: Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold models have gradually increased from initial 1-2 million annual units to approximately 5-7 million units annually in recent years, representing roughly 5-8% of Samsung's smartphone sales. Apple's larger overall smartphone volume and stronger premium positioning suggest the iPhone Fold could achieve greater penetration if market conditions support it.
Competitive Implications and Market Dynamics
Apple's entry would likely accelerate foldable adoption across the broader market, much as iPhone itself accelerated smartphone adoption in 2007. When Apple validates a technology category through mainstream adoption, competitor products benefit from the rising tide, though Apple typically captures disproportionate profit despite not necessarily capturing the largest volume.
Samsung would likely see Galaxy Z Fold pricing pressure, though Samsung's marketing emphasis on innovation and early-adopter positioning could allow premium pricing to persist. Google might struggle to differentiate versus Apple's ecosystem advantages, potentially repositioning Pixel Fold toward different market segments. Emerging competitors from Chinese manufacturers might face increased competitive pressure as Apple's validation drives mainstream adoption.

How iPhone Fold Compares to Productivity Alternatives
iPad Mini as Direct Competitor
The iPad mini (8.3 inches) represents the closest current product that serves similar productivity functions as the unfolded iPhone Fold (7.7-7.8 inches). Users choosing between an iPhone Fold and an iPad mini face a critical trade-off: the Fold provides a device that transitions between portable phone and productivity tablet in a single unit, while the iPad mini remains a dedicated productivity device without phone functionality.
For users who prefer carrying a single device, the iPhone Fold becomes substantially more appealing. For users who already own an iPad and iPhone, the iPad mini provides a proven ecosystem product with five years of refinement and optimization. The iPhone Fold's appeal thus depends substantially on user philosophy: integrated devices versus focused-purpose products.
Integration with Existing Apple Ecosystem
The iPhone Fold's greatest competitive advantage over iPad mini emerges through ecosystem integration. Continuity features allowing users to start an activity on one device and seamlessly resume on another have become increasingly sophisticated. The iPhone Fold could introduce particularly compelling continuity scenarios: beginning document editing on the Fold's folded display, then unfolding it to continue work on the larger canvas, then handing off to an iPad Pro for final production.
Handoff features, universal clipboard, AirDrop file sharing, and automatic authentication through proximity all benefit the iPhone Fold. The device's integration into iCloud means photos, documents, and data synchronize automatically. Siri works consistently across devices. This unified experience remains Apple's most defensible advantage against alternative productivity solutions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Power Users
Power users including designers, photographers, and content creators face compelling financial calculus with the iPhone Fold. At
For users who don't currently maintain both an iPhone and iPad, the Fold's premium over a standard iPhone (

Impact on iPhone Lineup and Product Strategy
Positioning Within the iPhone 18 Generation
Apple will likely position the iPhone Fold as a separate product line rather than a direct replacement for Pro Max models. The iPhone 18 lineup might maintain the standard structure (base model, Plus, Pro, Pro Max), with the iPhone Fold existing as a premium alternative rather than a replacement. This strategy avoids cannibalizing Pro Max sales while offering innovation-focused consumers a novel option.
Pricing and positioning would position the Fold as a step above Pro Max, creating a clear hierarchy. Standard iPhone 18 at ~
Impact on iPad and Mac Product Lines
The iPhone Fold's introduction raises strategic questions about iPad positioning. If the Fold provides sufficient productivity capabilities for many users currently purchasing iPad minis, Apple risks cannibalizing iPad mini sales. However, this risk is mitigated by differentiation: the Fold remains a phone-sized device when closed, while the iPad mini remains a dedicated tablet optimized for extended productivity sessions.
Apple has historically managed overlapping product lines through differentiation rather than exclusive positioning. A user who demands both phone functionality and tablet functionality would choose the Fold. A user satisfied with either phone or tablet functionality would choose accordingly. The products could coexist similarly to how iPhone and iPad currently coexist despite overlapping capabilities.
The Mac remains unaffected by iPhone Fold introduction, as the Fold cannot replace laptop functionality. Professional creative work requiring multi-window applications, file system access, and external peripheral support remains firmly Mac territory. The Fold complements Mac as a portable companion device, similar to how iPhone currently functions.

Future Iterations and Evolution Path
Display Technology Roadmap
Beyond 2026, Apple will likely pursue continued display improvements. Crease elimination could achieve further refinement. Brightness might increase to 3,000 nits or beyond, enabling outdoor usability even in direct sunlight. Variable refresh rates could improve battery efficiency while maintaining high frame rates for motion content.
More speculative technologies on Apple's likely research roadmap include self-healing displays that automatically repair minor scratches through molecular processes, improved color rendering through advanced color science, and potential holographic display experiments that allow the internal display to project visible imagery without glasses.
Hinge Durability and Reliability Evolution
Subsequent generations will likely refine hinge design based on first-generation consumer feedback. Friction characteristics might be optimized for smoother operation. Durability testing will establish real-world lifespan capabilities. If first-generation devices demonstrate the hinge survives 500,000+ open-close cycles, confidence in longevity will grow substantially.
Apple might transition from Liquidmetal to alternative materials offering superior properties once manufacturing scales. Sapphire or ceramic hinge components might replace metal in future iterations if cost and manufacturing capabilities allow. The hinge remains an area of continuous innovation, and subsequent generations will likely show measurable improvements.
Software Capabilities and App Ecosystem Development
The app ecosystem will mature substantially after first-generation launch. Third-party developers will create applications specifically optimized for the foldable form factor, exploiting multitasking, split-view, and responsive design capabilities in ways that generic adaptations cannot match. Games designed for the larger screen, productivity apps with specialized foldable-optimized interfaces, and content apps with adaptive layouts will emerge.
Apple's framework development will accelerate responsively, with each iOS update adding capabilities that simplify foldable optimization for developers. By generation two or three, optimization for foldable form factors will become as routine as optimization for various standard iPhone sizes today.
Key Takeaways and What to Expect
The iPhone Fold represents Apple's evolution into the foldable category at a moment of proven consumer acceptance and technical maturity. Multiple enabling factors converge: crease-less display technology from Samsung, consumer familiarity with foldables through Samsung and Google products, supply chain capabilities developed through years of foldable manufacturing, and Apple's legendary ability to execute on complex hardware.
The expected fall 2026 timeframe provides Apple with two additional years of market observation, allowing the company to learn from millions of existing foldable users. This is classic Apple strategy: wait for technologies to mature, observe how consumers use them, then introduce a refined interpretation that often becomes the new category standard.
The technical challenges remain substantial: thermal management in a thin form factor, dust sealing without hindering the hinge, achieving crease-less display visibility, developing intuitive software that intelligently handles state transitions between folded and unfolded modes. Apple's engineering resources and historical problem-solving capabilities suggest these challenges are surmountable, though not without the possibility of delays if unforeseen obstacles emerge.
The market opportunity is clearly substantial. Premium consumers who value innovation, productivity, and ecosystem integration represent a segment of hundreds of millions globally. Even capturing 5-10% of iPhone's annual sales would represent 10-20 million units annually. The price premium ensures profitability regardless of absolute volume.
Competitors including Samsung, Google, and Motorola have established the foldable category viability. Apple's arrival will likely accelerate mainstream adoption, much as iPhone accelerated smartphones in 2007. Consumers intrigued by foldable technology but hesitant to adopt an unfamiliar category might finally convert once Apple validates the category through its participation.
For developers, designers, and product strategists, the iPhone Fold's arrival demands preparation. Applications must be designed with foldable form factors in mind. User experiences must account for crease zones and state transitions. Workflows that span multiple applications should optimize for split-view multitasking. The creative possibilities inherent in a device that transitions between phone and tablet represent an exciting frontier for digital product design.
Ultimately, the iPhone Fold represents not just a new product, but a philosophical statement about the future of mobile computing. Apple is betting that integrated devices—products that seamlessly transition between configurations to serve different use cases—represent the future. If the Fold succeeds, subsequent generations will likely refine this approach. If the Fold struggles, Apple will likely retreat to conventional form factors, having learned valuable lessons in the process. Either way, the product's development and introduction will meaningfully shape the smartphone industry's evolution for years to come.

FAQ
What is the iPhone Fold and when will it launch?
The iPhone Fold is Apple's anticipated foldable smartphone, expected to launch in the second half of 2026. It will feature a book-style design similar to Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold series, with an external 5.5-inch display when folded and an internal 7.7-7.8-inch display when unfolded. The device represents Apple's entry into the established foldable smartphone category after years of speculation and development.
How does the iPhone Fold's crease-less display technology work?
Apple's iPhone Fold is expected to utilize Samsung Display's proprietary crease-less OLED technology showcased at CES 2026. This technology combines a flexible OLED layer with a laser-drilled metal support plate that distributes stress across thousands of microscopic channels when the device folds. This stress distribution prevents the formation of visible creasing that affects current foldable displays, creating a nearly imperceptible fold line under normal viewing conditions.
What is Liquidmetal and why is it used in the iPhone Fold's hinge?
Liquidmetal is a proprietary metallic glass alloy—essentially a metal with glass-like properties—that Apple uses in the iPhone Fold's hinge mechanism. Liquidmetal exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to titanium, exceptional resistance to deformation from repeated stress cycles, and hardness comparable to ceramics. These properties make it ideal for the foldable hinge, which must endure hundreds of thousands of open-close cycles throughout the device's operational lifetime without developing play, looseness, or plastic deformation.
What will the iPhone Fold's camera system look like?
The iPhone Fold will feature a four-camera setup: two rear cameras (48MP main and 48MP ultra-wide), one punch-hole camera on the external folded display, and one 24MP under-display camera on the internal unfolded screen. Notably, the device will use Touch ID integrated into the power button for authentication instead of Face ID, allowing both displays to remain uninterrupted by camera cutouts. The under-display camera represents a significant technical achievement, as current foldable devices typically use much lower-resolution sensors.
How much will the iPhone Fold cost?
Industry analysts expect the iPhone Fold to price between
How does the iPhone Fold compare to Samsung's Galaxy Z Fold?
While both devices utilize book-style foldable designs, Apple's iPhone Fold differentiates through crease-less display technology, Liquidmetal hinge construction, ecosystem integration with iPad and Mac, and Touch ID authentication instead of Face ID. Samsung's Z Fold lineup has proven the category's viability and refined the form factor through multiple generations. By 2026, the Z Fold will likely be on its eighth or ninth generation, while the iPhone Fold will launch as Apple's first foldable offering. Apple typically enters mature categories with premium pricing and refined execution rather than cost-competitive positioning.
Will the iPhone Fold replace the iPad mini?
The iPhone Fold and iPad mini serve different use cases despite overlapping screen sizes. The Fold provides a single device that transitions between phone and tablet functionality, while the iPad mini remains a dedicated tablet optimized for extended productivity sessions. Users choosing between them should evaluate whether they prefer integrated flexibility (Fold) or focused-purpose hardware (iPad mini). Many users will likely choose the Fold if they currently maintain both iPhone and iPad devices, potentially consolidating hardware. Users satisfied with either dedicated phone or tablet functionality would continue choosing traditional products.
What thermal management challenges does the iPhone Fold face?
The iPhone Fold's thin unfolded profile (4.5-5.6mm) constrains heat dissipation pathways significantly compared to standard iPhones. When running demanding applications like video editing or 8K video recording, Apple processors generate substantial heat that must dissipate through limited surface area. Apple likely employs graphite sheets, phase-change materials, and potentially vapor chamber technology to manage heat flow away from processing components. Thermal performance must remain competitive with standard iPhones despite greater space constraints—Apple's rigorous quality standards will demand consistent performance without thermal throttling under normal usage.
How will multitasking work on the unfolded iPhone Fold display?
The iPhone Fold's large unfolded display will support iOS multitasking similar to iPadOS, allowing multiple apps to run simultaneously in split-view and slide-over configurations. Apple's framework developers will provide responsive design abstractions that allow existing apps to adapt to the Fold's larger screen without explicit redesign. Apps specifically optimized for the foldable form factor can provide sophisticated multitasking experiences that leverage the additional screen real estate. The operating system must intelligently handle app state preservation when the device transitions between folded and unfolded states, and avoid placing critical interface elements over the crease zone.
What manufacturing challenges could delay the iPhone Fold launch?
Several technical hurdles could extend development timelines and push launch into 2027. The crease-less display, while demonstrated by Samsung, must meet Apple's exacting visual standards and durability requirements. The hinge mechanism must survive hundreds of thousands of open-close cycles under accelerated testing while remaining sealed against dust and moisture. Thermal dissipation must maintain performance consistency in a constrained form factor. Battery cell balancing across multiple cells requires sophisticated management electronics. If any of these systems require additional development cycles, Apple would likely delay launch rather than compromise on quality—the company prioritizes market readiness over aggressive timelines.

Conclusion
The iPhone Fold represents a watershed moment for both Apple and the broader smartphone industry. After years of speculation and multiple delays, Apple's anticipated entry into the foldable category signals confidence that the technology has matured sufficiently for mainstream adoption. The convergence of enabling technologies—crease-less displays, refined hinge mechanisms, advanced thermal management solutions—creates genuine engineering feasibility for a product that would have been impossible just years earlier.
For Apple specifically, the iPhone Fold embodies the company's evolved product philosophy. No longer can Apple simply rely on iteration of established form factors. To maintain innovation momentum and capture premium consumer segments' excitement, Apple must venture into genuinely novel categories. The foldable smartphone, proven viable by Samsung and Google, now awaits Apple's interpretation and refinement.
The technical challenges remain substantial but surmountable. Apple's engineering resources, manufacturing partnerships, and historical problem-solving capabilities position the company well for success. The company's insistence on crease-less displays, dust sealing, thermal performance, and software optimization reflects the uncompromising quality standards that have defined Apple's best products. These standards will likely produce a foldable device that elevates category expectations, much as the original iPhone elevated smartphone expectations when it arrived in 2007.
For consumers, the iPhone Fold offers a compelling proposition: a single device that provides both premium smartphone functionality and tablet-like productivity capabilities. The
The competitive landscape will shift substantially once Apple validates foldable smartphones for mainstream audiences. Samsung's market position may strengthen further through first-mover advantages now fully established. Google's Pixel Fold may struggle to differentiate without Apple's ecosystem advantages. Emerging competitors from Chinese manufacturers may face accelerated pressure. The overall category, however, will almost certainly expand as Apple's participation elevates foldable phones from "innovative alternative" to "legitimate mainstream option."
Looking forward, the iPhone Fold's introduction opens broader questions about the future of mobile computing. Will subsequent foldable iterations refine the book-style design or explore alternative form factors? Will crease-less displays eventually become standard across all foldables, or will visible creasing remain a permanent trade-off? How will software design evolve as developers gain experience optimizing for foldable form factors? These questions will drive innovation throughout the 2026-2030 period.
For developers, designers, and product managers, the iPhone Fold's arrival demands immediate preparation. Understanding foldable form factor constraints, designing for state transitions between folded and unfolded configurations, optimizing layouts for crease zones, and leveraging multitasking capabilities will become essential skills. The applications that best exploit the iPhone Fold's unique capabilities will define the next generation of mobile software experiences.
Ultimately, the iPhone Fold's success depends not on raw specifications or feature comparisons, but on whether it meaningfully improves how people use mobile devices for work, creativity, and communication. Apple's historical success has always rested on this principle: the best technology aligns with how humans actually work and live. If the iPhone Fold achieves this alignment—if it truly makes people's lives better through its unique combination of portable phone functionality and tablet-class productivity—then it will succeed regardless of competitive comparisons or specifications disputes. If the device remains primarily a novelty appeal rather than a genuine productivity tool, then subsequent iterations will need to prove stronger value propositions. Either way, the iPhone Fold's introduction represents a pivotal chapter in Apple's ongoing evolution and the smartphone industry's continued transformation.

Related Articles
- iPhone 17e MagSafe A19 Chip Launch 2025 Guide
- Apple's 2026 Hardware Roadmap: MacBook Pro, iPad, iPhone 17e [2026]
- First-Gen AirTags Deal: $64 Four-Pack Guide [2025]
- Tech Gear News This Week: Pixel 10a, Valve Delays, New Apps [2025]
- Samsung Galaxy S26: What Customers Really Want [2025]
- Inside the Trump Phone T1: Design, Specs, and Delays [2025]





