Open AI Chat GPT Military Access: What It Means for Defense [2025]
Last summer, something pretty significant happened in the AI world—and most people missed it. Open AI quietly announced that the US military would get access to Chat GPT. Not some watered-down version. Not a limited trial. Full-powered Chat GPT running on government cloud infrastructure, available for all lawful military uses.
This wasn't a snap decision. Open AI spent months wrestling with the ethical implications before signing off. And when they did, they made a pretty clear statement: "We believe the people responsible for defending the country should have access to the best tools available."
Here's the thing—this decision matters way more than a press release makes it sound. It signals a fundamental shift in how government agencies approach AI adoption. It opens doors (and raises concerns) about what happens when cutting-edge AI gets deployed in military contexts. And it sets a precedent that other nations and private contractors are watching closely.
So what's actually happening here? How does it work? What are the real implications? Let's dig into the details, because there's a lot more going on beneath the surface.
TL; DR
- Military AI Access: The US military now has access to Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil, the Pentagon's secure AI platform, for all lawful uses
- Infrastructure Security: Chat GPT runs on government cloud infrastructure with safeguards built into the model level, not just interface-level restrictions
- Unrestricted Use: Unlike civilian versions, military Chat GPT isn't technically restricted—safeguards are embedded in how the AI functions at its core
- Competitive Selection: Open AI won against rivals Google and x AI; Anthropic declined due to disagreement over operational control
- Government AI Evolution: This reflects broader Pentagon investment in AI through platforms like Gen AI.mil and represents a major shift in defense technology strategy

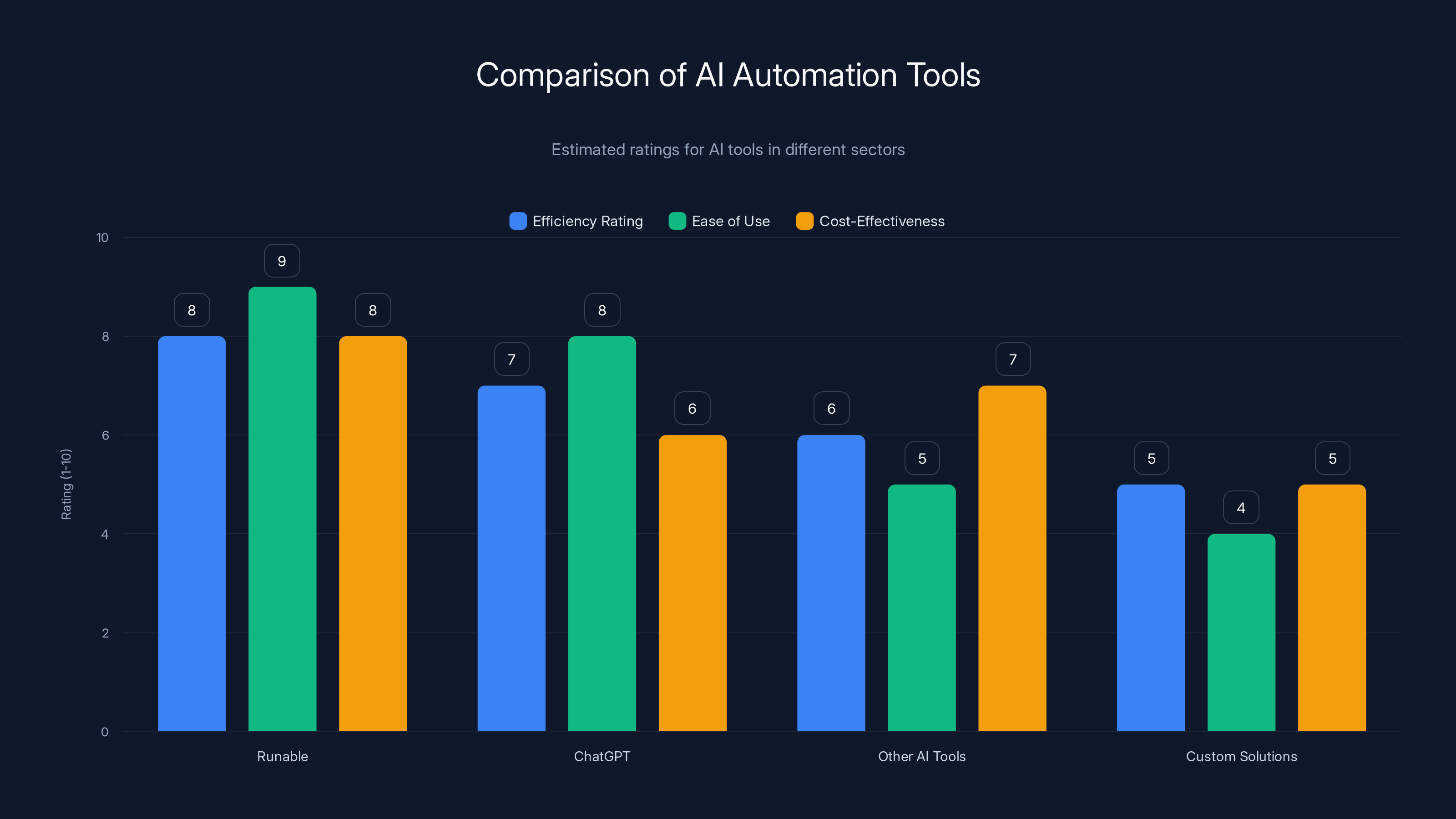
Runable is rated highly for ease of use and efficiency in AI automation, making it a strong choice for enterprises. Estimated data.
The Backstory: How Open AI Got Here
Open AI didn't just wake up one morning and decide to arm the military with Chat GPT. This was a calculated move after months of internal debate, policy discussions, and strategic positioning.
The company had already launched Open AI for Government back in July 2025. That platform was designed specifically for federal agencies—government cloud infrastructure, compliance with security requirements, the whole package. But military-specific access? That required a different conversation.
Open AI essentially asked itself: Do we want to be in the business of providing AI tools to the military? The answer, after deliberation, was yes. But with conditions. The company made clear that it would provide the "best tools available" to people defending the country, but it would build safeguards into the model itself rather than relying on usage restrictions at the interface level.
This is a critical distinction. You can't just block certain outputs on a user-facing dashboard and call it secure. Open AI's approach means the AI is trained and configured at a fundamental level to handle military contexts responsibly.
The decision also came at a moment when the Pentagon was actively searching for AI solutions. The military wasn't waiting around. They had already built Gen AI.mil—a comprehensive platform designed to bring AI capabilities to the Department of Defense. Chat GPT was just one piece of that larger puzzle.
Gen AI.mil: The Pentagon's AI Playground
Understanding Gen AI.mil is key to understanding why Chat GPT matters for the military. This isn't just some new app the Pentagon downloaded. It's an entire platform built from the ground up to serve as the secure AI infrastructure for the entire Department of Defense.
Think of Gen AI.mil as the military's answer to enterprise AI platforms. It's where authorized personnel go to access AI tools. Chat GPT is the anchor tenant, but it's not the only tenant. The platform is designed to integrate multiple AI systems, from different providers, all running in a controlled, monitored environment.
The platform itself is built on government cloud infrastructure. This matters enormously from a security perspective. Military data doesn't leave military-controlled systems. Everything runs inside government facilities, managed by government personnel, with government oversight.
When you access Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil, you're not connecting to Open AI's consumer servers. You're connecting to a version of Chat GPT that lives entirely within the Pentagon's IT infrastructure. Open AI provides the AI engine, but the Pentagon controls the environment.
This is actually a pretty elegant solution to a security problem. The military gets access to state-of-the-art AI capabilities without having to send sensitive data to external servers. Open AI gets to serve a major government customer without compromising its security architecture.
Early adoption through Gen AI.mil is limited—the military is rolling this out carefully, testing it with specific units and departments before broader deployment. But the infrastructure is there. The pathway is open. And the precedent is being set.
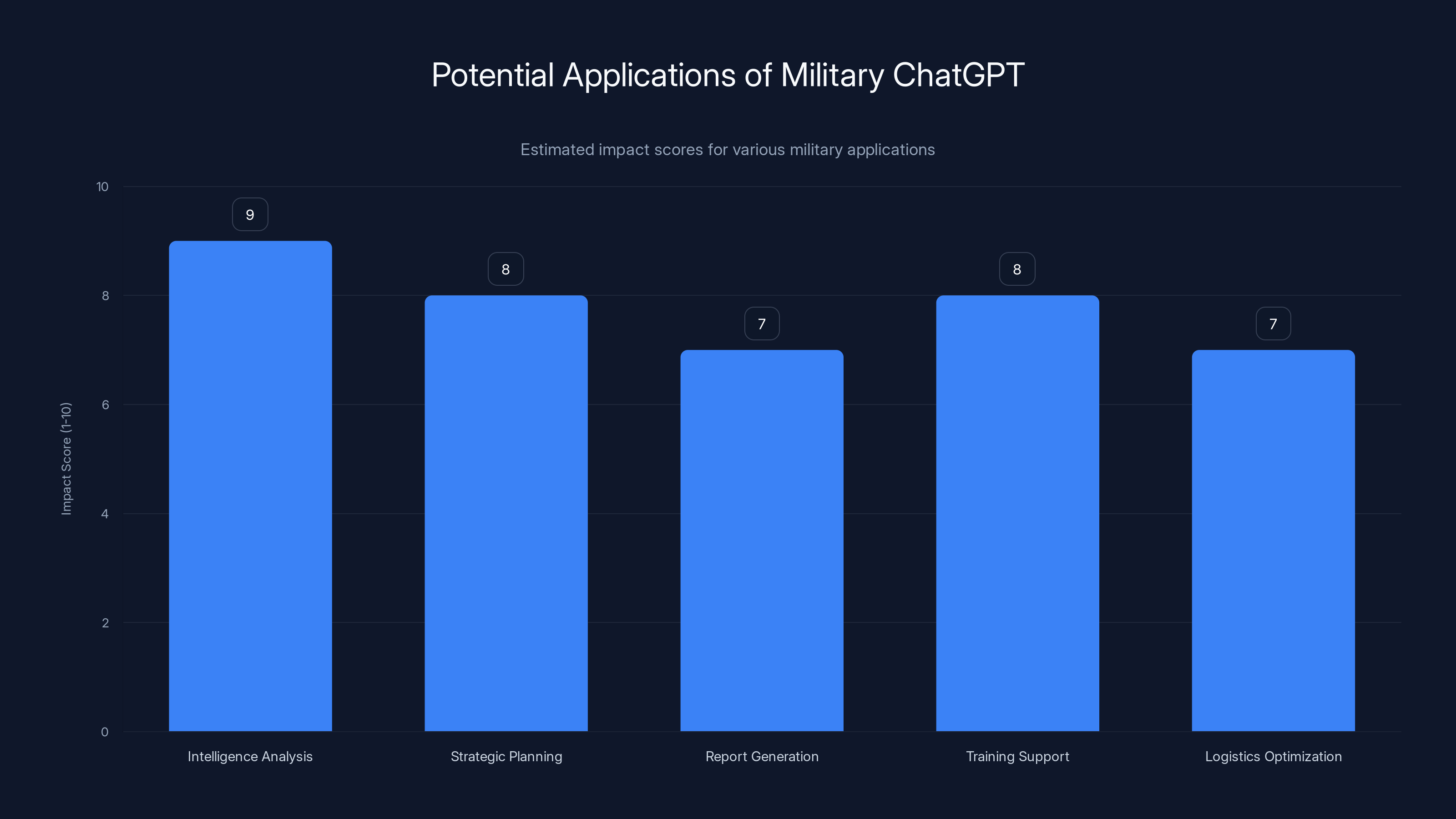
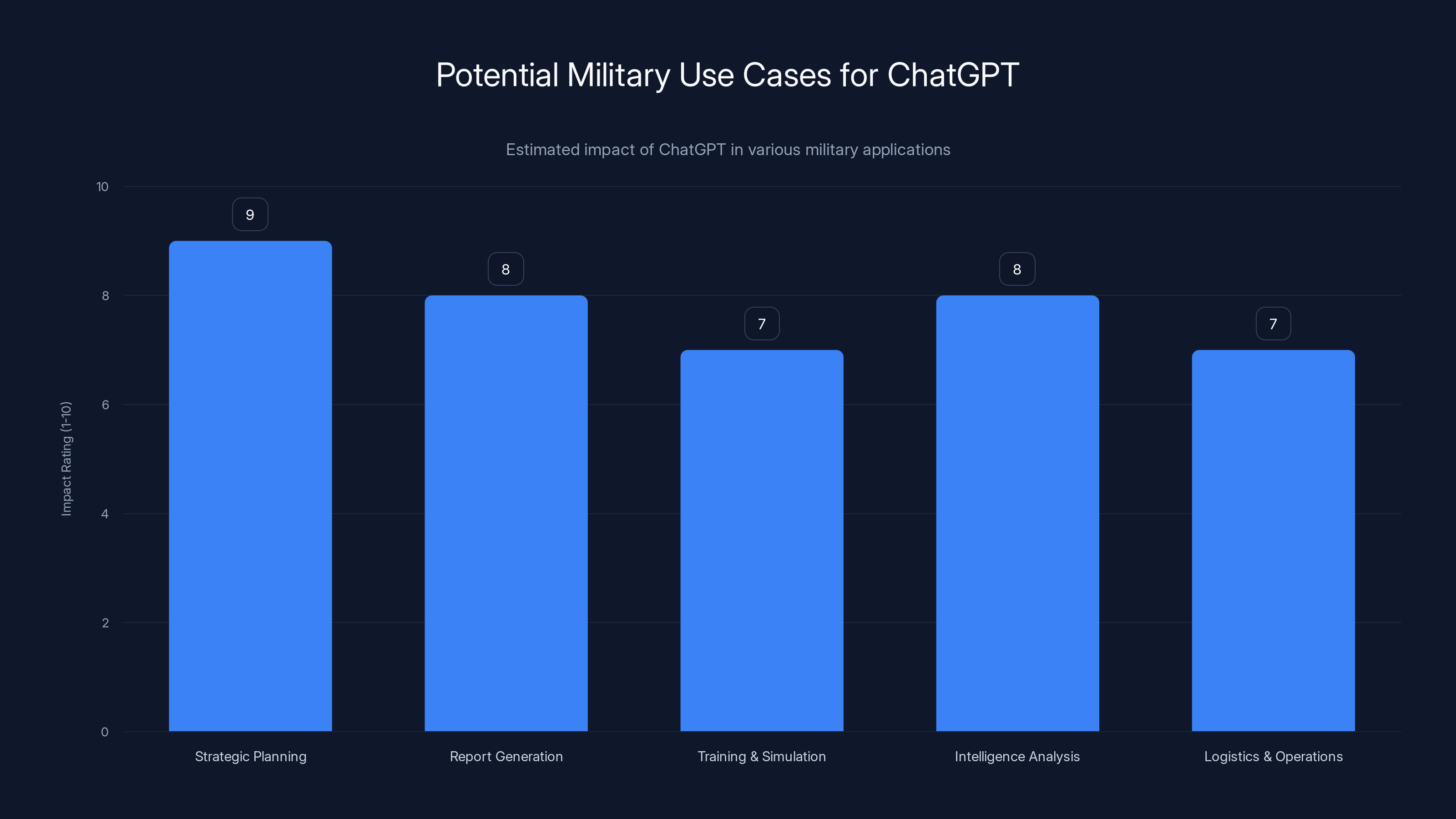
Military ChatGPT is projected to have the highest impact on intelligence analysis and strategic planning, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency. (Estimated data)
How Military Chat GPT Actually Works
So what's different about the military version of Chat GPT compared to what you're using right now?
On the surface, it does the same things. You ask questions. It generates answers. It can summarize documents, analyze data, draft reports, brainstorm strategies. The core functionality is identical.
But under the hood, there are meaningful differences. The military version operates under a different set of constraints and configurations.
First, the safeguards are baked into the model itself. This means the restrictions aren't rules applied after the fact—they're part of how the AI was trained and configured. Open AI doesn't describe exactly what these look like (for obvious security reasons), but the concept is sound: the AI is designed from the ground up to understand military operational contexts and behave appropriately within them.
Second, the platform allows for "all lawful uses." This is intentionally broad. The military doesn't want to fight with an AI that's constantly refusing to help because a particular task seems risky. As long as something is legal, Chat GPT should help with it. The legal bar is the constraint, not some vague AI-ethics judgment call.
Third, the deployment model is completely different. The system runs on government cloud infrastructure with military-grade logging, monitoring, and audit trails. Every query, every response, every interaction is recorded and auditable. This creates accountability while also building a data trail that can help the military understand how AI is being used across the organization.
Fourth, the version available to the military might have different training data or configurations than the public Chat GPT. We don't know the specifics, but it's reasonable to assume the military's instance was tuned for defense-relevant contexts and use cases.
The Competition: Why Open AI Won
Here's something important: Open AI wasn't the only option. The Pentagon had serious alternatives on the table.
Google was in the running. So was x AI. Both companies showed up ready to do business with the military, willing to accept the "all lawful uses" clause that would govern how their AI tools got deployed.
Then there was Anthropic. The company behind Claude reportedly pushed back. Anthropic wanted more control over how Claude could be used. They weren't comfortable with the broad "all lawful uses" framing. They wanted guarantees about what their AI wouldn't be used for. And when the Pentagon didn't offer those guarantees, Anthropic stepped aside.
This tells you something important about how different AI companies approach the ethics question. Open AI chose to engage with the military on the military's terms. Anthropic chose to draw a line. Both approaches are defensible, depending on your philosophy.
But from the Pentagon's perspective, Open AI's approach was more practical. The military needed a tool that could serve broad purposes across the organization. They didn't want an AI system that would say "no" to requests just because someone at the company decided it was philosophically uncomfortable.
Is Open AI now the Pentagon's preferred AI vendor? Not necessarily. The platform is designed to integrate multiple AI systems. Google's tools might show up on Gen AI.mil eventually. x AI's capabilities could be added alongside Chat GPT. The Pentagon isn't betting everything on Open AI. They're building a platform, and Open AI is the first major tenant.
But there's no denying that Open AI's willingness to work with the military, on the military's terms, gave them a significant head start and a high-profile deployment that demonstrates the real-world viability of their AI systems.
Military Use Cases: What Will Chat GPT Actually Do?
Okay, so the military has Chat GPT. What do they actually use it for?
The Pentagon was clear: "all lawful uses." That's broad intentionally. But let's think through the practical applications that make sense in a military context.
Strategic Planning and Analysis: One of the biggest use cases is going to be analysis. Military planners can feed Chat GPT historical data, current intelligence, geographic information, and ask it to identify patterns, suggest scenarios, analyze strategic options. An AI that can synthesize massive amounts of information and identify non-obvious patterns is genuinely useful for military strategy.
Report Generation and Documentation: The military generates an absurd amount of paperwork. After-action reports, strategic assessments, threat analyses, compliance documentation. Chat GPT can draft these, summarize source materials, ensure consistent formatting and language. This alone probably saves thousands of hours annually across the entire organization.
Training and Simulation: Military training often involves scenario-based learning. An AI can generate realistic scenarios, populate them with plausible interactions, help train personnel in decision-making under complex circumstances. Chat GPT could power a lot of military training applications.
Intelligence Analysis: Military intelligence analysts work with massive volumes of information. Chat GPT can help organize that information, identify key connections, flag anomalies, suggest interpretations. An analyst might feed the AI raw intelligence reports and ask it to identify patterns the human might have missed.
Logistics and Operations: Supply chains, resource allocation, operational planning—these are deeply computational tasks where an AI that can reason through complex constraints would be genuinely valuable. Chat GPT won't replace logistics planners, but it could dramatically accelerate their work.
Language and Communication: The military operates globally. Chat GPT's language capabilities could help with translation, communication analysis, cultural context analysis. If you're trying to understand communications in a foreign language or cultural context, an AI trained on global datasets is a real asset.
What won't happen: Chat GPT won't autonomously decide to launch weapons. It won't make tactical decisions in the field. It won't replace human judgment in life-or-death situations. These decisions remain with humans, using AI as a tool to accelerate their analysis and decision-making.
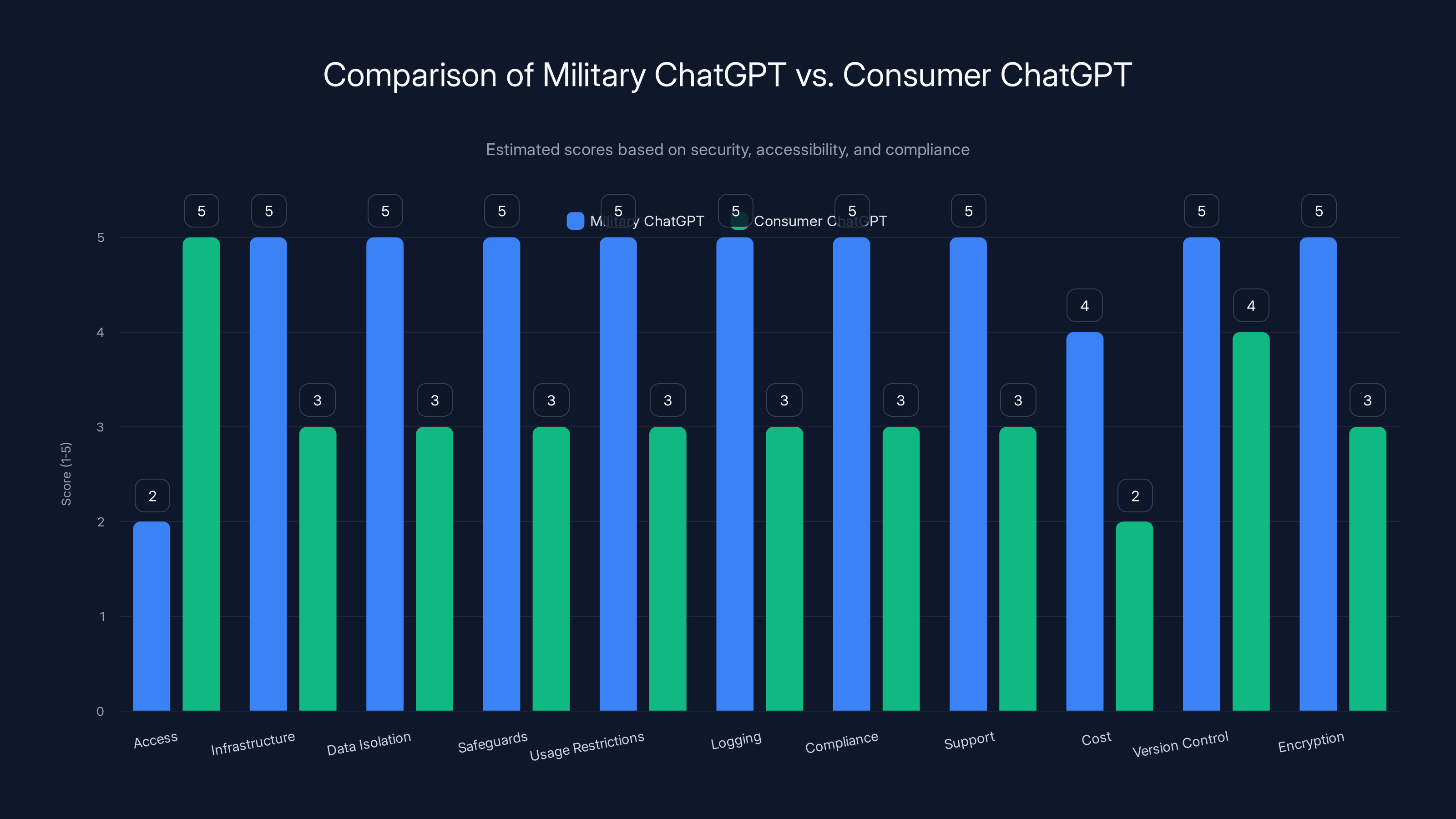
Military ChatGPT scores higher in security, compliance, and support, while Consumer ChatGPT excels in accessibility. Estimated data based on typical characteristics.
Security Architecture: How Is Military Chat GPT Actually Secure?
Let's talk about the elephant in the room: security.
The Pentagon doesn't give classified information to cloud services hosted by private companies. That's a fundamental rule. So how does military Chat GPT stay secure?
First, it runs entirely on government cloud infrastructure. The AWS Gov Cloud or similar government-certified cloud environments. These facilities are physically secured, controlled by government personnel, subject to government audit and oversight. No data leaves the government's control.
Second, the instance of Chat GPT running on government infrastructure is isolated. It's not the same instance serving civilians. It's a separate deployment, separate data, separate operations. This isolation is critical—it means there's no pathway for military queries to leak into civilian training data or vice versa.
Third, access control is strict. You don't just log into Gen AI.mil with a username and password. You're probably using a military identity and credential system, two-factor authentication, possibly biometric verification depending on the sensitivity of what you're accessing. Only authorized military personnel with the appropriate clearances get access.
Fourth, the data is encrypted. In transit, at rest, in memory. Chat GPT's responses to military queries are encrypted before they leave the server, encrypted while in transit, encrypted when stored. Only authorized personnel with the appropriate keys can decrypt it.
Fifth, everything is logged and auditable. Every query, every response, every access event is recorded in tamper-proof logs. If there's ever a question about what happened or whether a breach occurred, those logs provide accountability and traceability.
Sixth, the AI itself is constrained at the model level. Open AI built safeguards directly into how the AI functions. This isn't just a content filter that blocks bad outputs—it's a fundamental part of how the model was trained and configured.
But here's the honest part: no system is 100% secure. Sophisticated actors can potentially find ways to manipulate AI systems, extract information, or exploit vulnerabilities. The military knows this. That's why they're rolling this out cautiously, testing it with specific use cases first, monitoring how it performs, building in safeguards and controls.
The security model isn't "this is completely safe." The security model is "this is appropriately safe for the intended use cases, with controls that allow us to detect and respond to problems if they occur."
The Broader Pentagon AI Strategy
Chat GPT is important, but it's not the whole story. The military's interest in AI is much broader and reflects a long-term strategic bet.
The Pentagon has been investing heavily in AI for years. There's the Joint Artificial Intelligence Center, which coordinates AI initiatives across the entire Department of Defense. There are research projects exploring AI applications in everything from logistics to cybersecurity to combat operations.
Gen AI.mil is part of this broader strategy. It's the platform that brings generative AI capabilities to the military at scale. Chat GPT is the anchor application, but the platform is designed to integrate multiple AI systems over time.
Why is the Pentagon so interested in AI? Several reasons:
Speed: Modern military operations happen fast. AI can help human decision-makers process information faster, evaluate options faster, communicate decisions faster. In some contexts, speed is the difference between success and failure.
Analysis: Military problems are often data-intensive. You need to analyze terrain, weather, intelligence reports, supply chains, personnel capabilities. AI is good at finding patterns in data that humans might miss.
Adaptation: Military environments are uncertain and changing. AI systems can adapt to new information, adjust strategies, respond to unexpected situations. This is valuable in planning, logistics, and tactical operations.
Efficiency: The military has finite resources. If AI can help planners do their jobs faster, reduce paperwork burden, optimize logistics, that frees up personnel and resources for other tasks.
Competitiveness: Other major powers are investing in military AI. The US military sees AI as a necessary capability to maintain technological advantage. If China and Russia are deploying AI in their militaries, the US needs to keep pace.
Chat GPT is just one part of this larger strategic shift. But it's a significant part because it's a capability that directly benefits military personnel across the entire organization, not just specialized units or researchers.
Implications for Defense Industry and Contractors
When the military adopts a major new technology, the entire defense industry pays attention.
Chat GPT's availability through Gen AI.mil sends a signal to defense contractors and technology companies: the military is serious about AI adoption. They're ready to integrate generative AI into their operations. And they're willing to partner with leading technology companies to do it.
For companies like Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Raytheon, and others in the defense industry, this opens opportunities. They can build systems that integrate with Gen AI.mil. They can use Chat GPT and other AI tools available through the platform to improve their products and services. They can position themselves as bridge companies that help the military leverage AI effectively.
For tech companies outside the traditional defense sector, it's also interesting. Open AI just demonstrated that a pure-play AI company can successfully partner with the military. This opens doors for other tech companies to pursue government contracts. Google, Microsoft, Amazon—all have opportunities to position themselves as AI partners to the military.
For startups and smaller companies, the implications are more mixed. There are opportunities in niches and specialized applications. But competing for military contracts requires dealing with significant compliance, security, and regulatory requirements that smaller companies might struggle with.
Overall, Chat GPT's military deployment signals that AI is becoming a standard part of military technology infrastructure. Companies that can effectively integrate with and support AI systems will have advantages. Companies that ignore AI will fall behind.

ChatGPT is projected to have the highest impact in strategic planning and intelligence analysis, with significant contributions to report generation and logistics. Estimated data based on potential use cases.
International Response: What Other Nations Are Watching
The fact that the US military now has access to advanced AI doesn't go unnoticed globally.
China, for instance, is almost certainly accelerating its own military AI initiatives. Beijing sees the US military's AI adoption as both a threat and a validation of AI's strategic importance. Expect to see increased Chinese investment in military AI, likely including efforts to develop indigenous alternatives to systems like Chat GPT.
Russia is probably less focused on commercial AI partnerships (given sanctions and tech sector challenges) but definitely interested in military AI applications. Russia has publicly stated that AI is a strategic priority, though their ability to execute at the scale the US can afford is questionable.
European nations are taking a different approach. The EU has been more cautious about AI, with regulatory frameworks like the AI Act designed to govern AI development and deployment. European military adoption of AI is likely to be slower and more regulated than the US approach.
Israeli, Indian, and other allied nations are probably exploring similar arrangements with AI companies. If the US military can use Chat GPT, why shouldn't other allied militaries have similar access?
The geopolitical implication is clear: AI is becoming a military capability, just like advanced aircraft or naval vessels. Nations that effectively deploy AI in military contexts will have advantages. Nations that don't will fall behind. This is driving a new kind of arms race—not for nuclear weapons, but for AI capability.
Open AI's willingness to partner with the US military positions Open AI as the US government's preferred AI partner. This has strategic value for the US (access to cutting-edge AI), strategic value for Open AI (government contracts and validation), and strategic implications for other nations (signaling that they need their own AI capabilities).
Ethical and Political Controversy
Let's not pretend this decision was universally popular or ethically uncontroversial.
When it was announced that the military would get access to Chat GPT, some AI researchers and ethicists raised concerns. The argument goes like this: AI systems can be unpredictable or biased. Deploying them in military contexts could lead to unintended consequences. The military-industrial complex doesn't need better tools to wage war more effectively.
These are legitimate concerns worth taking seriously. An AI system that makes a classification error in a military context could potentially have real-world consequences. Bias in data could lead to biased recommendations. The AI's confidence could exceed its actual accuracy, leading decision-makers to trust its output more than they should.
Open AI's response to these concerns is essentially that:
- The military will use Chat GPT for lawful purposes, and it's not the AI company's job to second-guess what's lawful
- The safeguards built into the model mitigate many risks
- Human judgment remains with human decision-makers—AI is a tool, not an autonomous actor
- The military will use the system responsibly given their training and culture
- Refusing to provide AI tools to the military doesn't prevent the military from developing AI capabilities—it just means other countries might develop them first
Anthropic's approach was different. By pushing for more control over Claude's use, Anthropic was essentially saying: we'll support the military, but on terms that let us say "no" to applications we're uncomfortable with.
Both perspectives have merit. There's a real tension between providing access to the best available technology and maintaining ethical guardrails. Different companies resolve that tension differently.
What's likely true is that the military will use AI responsibly because:
- The military has strong institutional norms and chains of command
- The military understands the importance of human judgment in critical decisions
- The military has extensive experience managing complex, powerful technology
- There are oversight mechanisms and audit trails for military AI use
But it's also true that deploying AI in any high-stakes context carries risks. These risks are being managed, but not eliminated. The military is aware of this and is rolling out Chat GPT carefully, testing it, monitoring it, building safeguards.

Future Expansion: Will More Governments Get Access?
Open AI's statement hinted at future expansion: "Our goal is to help governments use AI effectively and safely."
This suggests that other governments could eventually get access to military-grade AI tools. But it'll probably take time and be selective.
Which governments might qualify?
- Close US allies: UK, Canada, Australia, other Five Eyes partners would probably be highest priority. These are countries with existing intelligence-sharing relationships and aligned strategic interests.
- NATO members: Other NATO nations might get access to support interoperability and alliance cooperation.
- Authorized partners: Countries with formal security relationships with the US might gain access.
Which governments probably won't get access?
- Adversarial nations: Definitely not China, Russia, or Iran.
- Countries with governance concerns: The US would probably be cautious about providing advanced AI to countries with governance issues or human rights concerns.
- Unstable regions: Countries in conflict zones or with unstable governments would likely be excluded.
The point is, Open AI isn't going to offer military-grade Chat GPT to everyone. Access will be selective, based on strategic relationships, governance standards, and alignment with US interests.
Over the next few years, expect to see:
- US military continues to expand and deepen its use of Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil
- Other government agencies (non-military) might get access through Open AI for Government
- Selected allied nations might negotiate access to similar capabilities
- Competitors to Open AI (Google, Anthropic, others) develop their own government-focused offerings
- Defense contractors integrate with Gen AI.mil to build systems that leverage Chat GPT and other available AI tools
The military AI market is nascent. We're probably five to ten years away from AI being as common in military operations as email is today. Chat GPT is just the beginning.
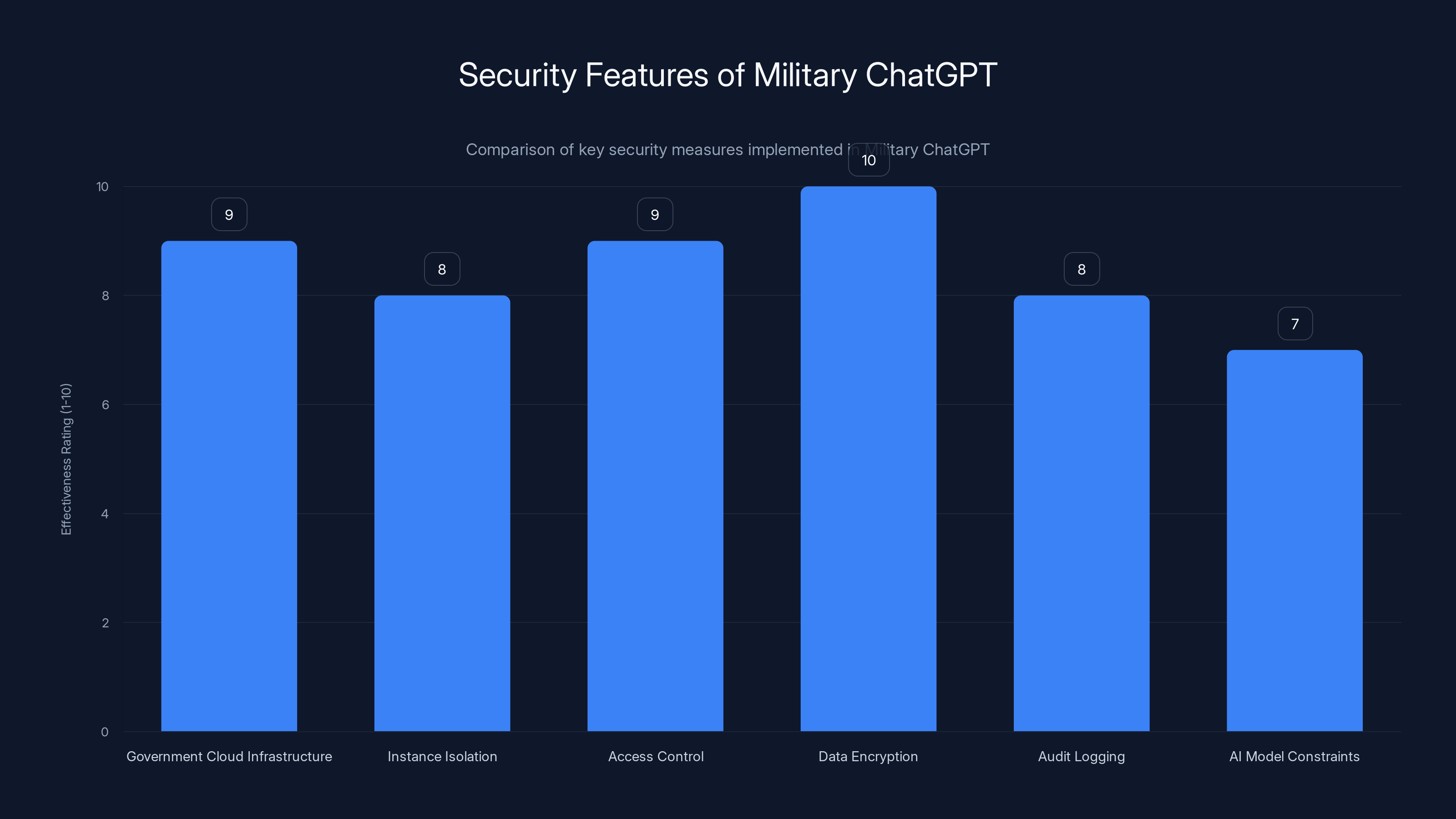
Military ChatGPT employs multiple layers of security, with data encryption and access control being the most effective measures. Estimated data based on typical security protocols.
Comparison: Military Chat GPT vs. Consumer Chat GPT
It's worth understanding the differences between the military version and what civilians use.
| Aspect | Military Chat GPT | Consumer Chat GPT |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Limited to authorized military personnel | Public, anyone can sign up |
| Infrastructure | Government cloud (Gov Cloud or similar) | Open AI commercial servers |
| Data Isolation | Completely separate from civilian data | May use some data for training (with opt-out) |
| Safeguards | Model-level safeguards, integrated security | Interface-level content filters |
| Usage Restrictions | All lawful uses permitted | Company policy restrictions apply |
| Logging | Comprehensive, auditable logs | Standard Open AI logging |
| Compliance | Fed RAMP and military requirements | Standard commercial compliance |
| Support | Dedicated government support | Standard commercial support |
| Cost | Government contract terms | Subscription fees or free tier |
| Version Control | Controlled updates, testing before deployment | Rapid updates from Open AI |
| Encryption | Military-grade encryption standards | Standard TLS encryption |
The differences reflect the different use cases. Consumer Chat GPT is built for speed and broad accessibility. Military Chat GPT is built for security, compliance, and accountability. Both serve their purposes well within their respective contexts.
How Runable Fits Into the AI Automation Picture
While the military deployment of Chat GPT represents one important use case for advanced AI, enterprises and organizations across sectors are discovering that AI automation tools can dramatically improve productivity and efficiency.
Runable represents another category of AI-powered automation: enterprise-focused AI agents that help teams generate presentations, documents, reports, images, and videos automatically. Unlike Chat GPT, which is a general-purpose conversational AI, Runable is specifically built for workflow automation and content generation.
For organizations looking to implement AI automation without the complexity of integrating multiple tools, Runable offers an all-in-one AI automation platform. Starting at $9/month, it provides teams with AI agents that can automate repetitive content creation tasks, freeing up personnel to focus on higher-value work.
The military's adoption of AI tools demonstrates a broader trend: sophisticated organizations recognize that AI isn't just a luxury feature—it's becoming essential infrastructure for operational efficiency. Whether it's the Pentagon deploying Chat GPT for strategic analysis or a marketing team using Runable to automate report generation, the pattern is the same: AI augments human capability and accelerates decision-making.
Use Case: Automate your team's weekly reports and presentations in minutes instead of hours, with AI-generated content that's customizable and brand-aligned.
Try Runable For FreeThe Technical Reality: What Chat GPT Can and Cannot Do
Let's be concrete about the capabilities and limitations of Chat GPT, especially in military contexts.
What Chat GPT is genuinely good at:
- Pattern recognition in text: Feed it documents, let it identify themes, connections, anomalies
- Summarization: Take complex information and condense it to essential points
- Draft generation: Create starting points for reports, plans, communications
- Explanation: Help people understand complex concepts, translate technical information
- Brainstorming: Generate multiple options, perspectives, approaches to problems
- Information synthesis: Combine information from multiple sources into coherent analysis
What Chat GPT struggles with:
- Real-time information: It's trained on data with a knowledge cutoff; it doesn't know what's happening right now
- Perfect accuracy: It can confidently state things that are factually wrong
- Specialized domain knowledge: In some technical domains, it may lack depth
- Novel problems: Problems that don't resemble training data may not get good solutions
- Quantitative precision: It's not always reliable for specific numbers or calculations
- Context understanding: It can miss important context that a human expert would catch
What Chat GPT absolutely cannot do:
- Make autonomous military decisions: It's a tool, not an autonomous agent
- Access classified information: If the information isn't in its training data, it can't access it
- Predict specific future events: It can't reliably forecast what will happen next month
- Understand classified operations: It doesn't have access to classified materials
- Replace human judgment: It supports human decision-making, not replaces it
The military understands these limitations. They're using Chat GPT as a tool to augment human capability, not to automate critical decisions. A military strategist uses Chat GPT to help analyze options, not to decide military strategy. An intelligence analyst uses it to help synthesize information, not to make final intelligence judgments.
This appropriate use of AI—as a tool to accelerate human work, not replace human judgment—is probably the key to successful military AI deployment.

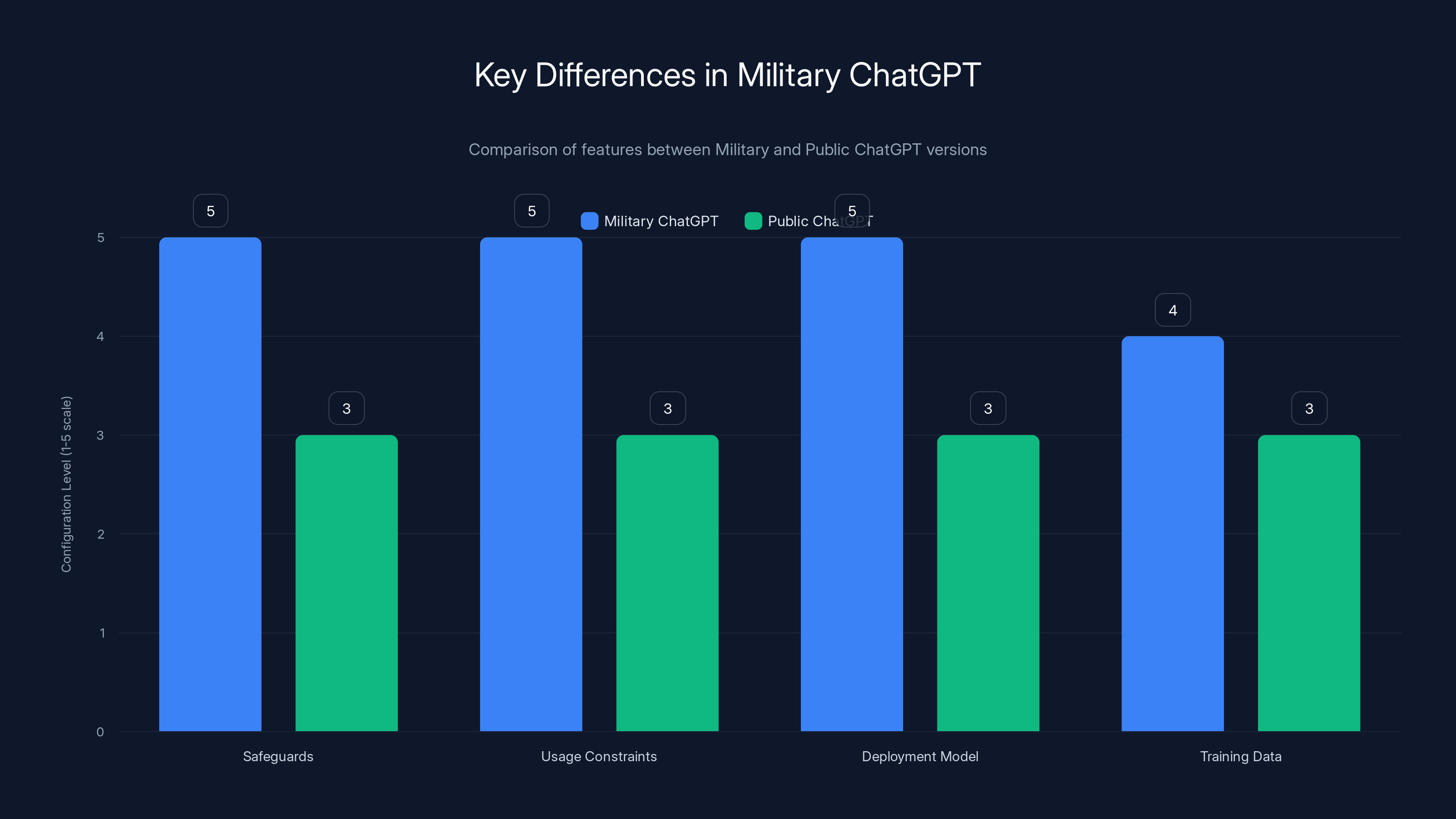
Military ChatGPT is configured with enhanced safeguards, broader usage constraints, secure deployment, and potentially specialized training data compared to the public version. Estimated data based on described differences.
Training and Implementation Challenges
Getting military personnel to effectively use Chat GPT is going to be a challenge.
First, there's the cultural factor. The military has institutional processes and ways of doing things that have been refined over decades. Introducing a new tool, especially an AI tool, requires training, habit change, and adjustment.
Second, there's the trust factor. Not all military personnel will immediately trust AI to help with important work. They'll need to test it, validate it, understand when it's reliable and when it isn't. This takes time.
Third, there's the security awareness factor. Military personnel are trained to protect information. An AI tool is a new potential information vulnerability. They need to understand what information is safe to input into Chat GPT and what isn't.
The Pentagon's approach to this is methodical:
- Pilot programs: Start with specific units, departments, and use cases
- Training: Provide education on how to use Chat GPT effectively and securely
- Monitoring: Track how the system is being used, what problems emerge
- Feedback loops: Adjust policies and training based on real-world experience
- Scaling: Gradually expand access as confidence grows
This isn't a rollout where everyone gets access on day one. It's a careful, methodical introduction of a new capability, with each stage informing the next.
The timeline probably looks like:
- Year 1-2: Pilot programs, training, validation of use cases
- Year 2-3: Expanded access to more units and departments
- Year 3-5: Broad organizational adoption, integration with other systems
- Year 5+: Mature deployment, evolved capabilities, potential integration of new AI tools
This timeline seems aggressive, but reasonable given the Pentagon's resources and the importance they place on AI adoption.
Competitive Implications: Where Does This Leave Other AI Companies?
Open AI just landed what might be the most high-profile military contract in the AI space. What does this mean for competitors?
Google has government-focused AI offerings and strong enterprise relationships with major defense contractors. They're not out of the game. But they missed this particular opportunity.
Microsoft has deep integration with both Open AI and the US government (through Azure and cloud services). They could still be significant players in military AI deployment, even if Chat GPT is the face of the effort.
Anthropic chose a different path by negotiating harder. This might pay off in other contexts where their more cautious approach to AI deployment resonates.
x AI lost out on this contract, but the field is young. Future government AI procurement will offer more opportunities.
The broader implication: the government AI market is real, it's substantial, and there's room for multiple vendors. Chat GPT is the anchor tenant in Gen AI.mil, but it won't be the only AI system available through that platform.
For AI companies, the lesson is clear: if you want to serve government and military customers, you need to:
- Build products that government can actually deploy (cloud infrastructure, security, compliance)
- Be willing to engage with government on government's terms
- Build trust through transparent operations and clear safety practices
- Demonstrate that your AI works reliably in government contexts
- Support integration with government systems and workflows
Open AI did all of this. That's why they won.

Looking Forward: The Evolution of Military AI
Chat GPT is just the beginning of a much larger evolution in military AI capabilities.
Over the next decade, expect to see:
More specialized military AI systems built specifically for defense use cases rather than adapted from civilian tools. These might focus on logistics, intelligence analysis, threat detection, operational planning, or other specific domains.
Better integration between humans and AI as the military learns how to effectively incorporate AI into decision-making processes. This includes things like improved interfaces, better training, clearer guidelines about when to trust AI recommendations.
More distributed AI deployment where AI systems run at the edge (forward operating bases, ships, aircraft) rather than only in central command centers. This enables faster decision-making in operational environments.
Evolved safeguards as the military gains experience with AI. Initial safeguards might prove either too restrictive or insufficient, leading to refinements based on real-world experience.
International competition as other nations develop military AI capabilities. This will drive continued US investment in military AI to maintain technological advantage.
Ethical frameworks and policies that govern military AI use. As capabilities expand, so will policies governing what AI systems can and cannot do.
Continued human decision-making at all critical points. The military will maintain the principle that humans make final decisions on matters of military consequence.
The overall trajectory is clear: AI is becoming a standard part of military infrastructure, just like computers and communications systems are today. Organizations that effectively integrate AI into their operations will have advantages. Organizations that don't will fall behind.
Key Takeaways and Implications
Let's synthesize what this all means.
The strategic significance: The US military now has access to one of the world's most advanced AI systems. This is a genuine capability advantage that the military will use to improve analysis, accelerate decision-making, and improve efficiency across the organization.
The technical accomplishment: Open AI successfully deployed a large language model in a secure government environment, running on government cloud infrastructure, with safeguards built in at the model level. This is a non-trivial achievement that demonstrates real capability.
The precedent: Open AI proved that a commercial AI company can successfully partner with the military. This opens the door for other tech companies to pursue government contracts and for the military to adopt civilian AI technology at scale.
The broader context: Military AI adoption is part of a larger trend where AI is becoming a standard tool across sectors. The military is an early and major adopter, but other organizations are following similar paths.
The international dimension: Other nations are watching the US military's AI adoption closely. This is driving international competition in military AI development and creating pressure for allied nations to develop or acquire similar capabilities.
The human element: Despite all the AI capability, humans remain the decision-makers. AI augments human capability but doesn't replace human judgment at critical decision points.
The ongoing evolution: This is not a settled story. Military AI capabilities will continue to evolve, policies will be refined, new tools will be deployed, and the understanding of how to effectively use AI in military contexts will deepen.
The military's adoption of Chat GPT marks a significant moment in the history of AI. It's the point where advanced AI moved from the realm of research and commercial applications into explicit military operational capability. The implications of this shift will play out over years and decades.

FAQ
What is Chat GPT and how does the military version differ from the consumer version?
Chat GPT is an advanced language model developed by Open AI that can generate human-like text responses, answer questions, draft documents, and perform various language-based tasks. The military version runs on government cloud infrastructure with safeguards built directly into the model rather than just at the interface level. The military version is authorized for "all lawful uses" without the content restrictions found in the consumer version, and all interactions are logged and auditable for compliance purposes.
How does the military access Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil?
Authorized military personnel access Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil, the Pentagon's secure AI platform. This platform runs entirely on government cloud infrastructure, meaning data never leaves military-controlled systems. Access requires military credentials and appropriate security clearances, with all queries encrypted and logged. The platform integrates Chat GPT with other AI systems and tools, providing a unified interface for military personnel across the Department of Defense.
What specific military applications will benefit most from Chat GPT?
Military Chat GPT will likely be most valuable for intelligence analysis (synthesizing large volumes of information), strategic planning (analyzing scenarios and identifying patterns), report generation (drafting documentation and summaries), training support (creating realistic scenarios and educational content), and logistics optimization (analyzing resource allocation and supply chain problems). Chat GPT accelerates human decision-making by automating analysis, suggesting options, and identifying non-obvious patterns in complex data.
Why did Open AI win the military AI contract over competitors like Google and Anthropic?
Open AI won because it was willing to provide Chat GPT for "all lawful uses" without significant restrictions. Google bid but wasn't selected as the primary vendor. Anthropic stepped aside because it wanted more control over how Claude could be used and wasn't comfortable with the broad usage permissions the military requested. Open AI chose to prioritize access to the best available tools for military personnel over maintaining strict usage controls.
What safeguards protect against misuse of military Chat GPT?
Safeguards operate at multiple levels: model-level constraints built into how Chat GPT was trained and configured, infrastructure-level security through government cloud services, access controls requiring military credentials and clearances, comprehensive logging and audit trails of all interactions, encryption of data in transit and at rest, and human oversight of military decision-making processes. The system is designed so that safeguards are embedded in the AI's functioning, not just applied after responses are generated.
Could other countries get military access to Chat GPT?
Open AI indicated interest in helping "governments use AI effectively and safely," suggesting future international expansion. However, access will likely be selective, granted to close US allies like the UK, Canada, and Australia, potentially NATO members, and countries with formal security relationships with the United States. Countries viewed as adversarial or with governance concerns would likely be excluded from military-grade AI access.
How will the military train personnel to use Chat GPT effectively and securely?
The Pentagon is taking a phased approach: starting with pilot programs in specific units and departments, providing targeted training on effective and secure Chat GPT use, monitoring how the system is deployed, gathering feedback from users, and gradually expanding access as confidence grows. Military personnel will learn what types of queries are appropriate, what information is safe to input, how to validate Chat GPT outputs, and when to rely on AI recommendations versus human judgment.
What are the limitations and risks of military Chat GPT deployment?
Key limitations include knowledge cutoff dates (Chat GPT doesn't know current events), potential inaccuracies stated with confidence, lack of access to classified information, and limitations in specialized technical domains. Risks include the possibility of AI-generated content being misunderstood or misapplied, bias in training data affecting recommendations, and the false sense of certainty AI outputs can create. The military mitigates these through oversight, careful deployment, and continuous monitoring.
How does military Chat GPT deployment affect the broader defense industry?
It signals that the military is serious about AI adoption, creating opportunities for defense contractors to build systems integrating with Gen AI.mil, tech companies to pursue government contracts, and companies to position themselves as AI integration partners. It also drives competition in the government AI market, encouraging companies like Google and Anthropic to develop government-focused AI offerings.
What does this mean for international competition in military AI?
The US military's adoption of Chat GPT signals to other nations that AI is a strategic military capability. This is likely driving acceleration of military AI programs in China, Russia, and other peer competitors. It's also pressuring allied nations to develop or acquire similar AI capabilities to maintain interoperability and technological competitiveness. The long-term implication is an international competition in military AI capability similar to past competition in nuclear weapons or advanced aircraft.
Will Chat GPT eventually replace human military personnel?
No. Chat GPT is a tool that augments human capability, not a replacement for human judgment. Military culture, training, and policy maintain the principle that humans make final decisions on matters of military consequence. Chat GPT will accelerate decision-making, improve analysis, and help personnel work more efficiently, but humans remain the ultimate decision-makers in all critical military contexts.
Conclusion: The AI-Augmented Military
The US military's adoption of Chat GPT through Gen AI.mil represents a watershed moment in military technology. For the first time, one of the world's most advanced AI systems is explicitly integrated into military operations, available to authorized personnel across the Department of Defense.
This isn't about building a robot army or creating autonomous weapons. It's about augmenting human capability. Military strategists who used to spend hours analyzing documents can now ask Chat GPT to synthesize information and identify patterns. Intelligence analysts drowning in information can use AI to help organize and understand that information. Logisticians planning complex supply chains can get AI assistance in analyzing constraints and identifying solutions.
The change is subtle but profound. It's the difference between a military analyst working at human speed and a military analyst working at augmented speed, leveraging AI to accelerate their thinking and decision-making.
Open AI's willingness to provide Chat GPT to the military, combined with the Pentagon's careful, methodical approach to deployment, suggests that this partnership will be successful. The military gets access to powerful AI technology. Open AI gets validation in one of the most important sectors. And the technology world learns that commercial AI systems can be effectively and securely deployed in government and military contexts.
Over the coming years, expect to see military AI capabilities expand. More tools will be integrated into Gen AI.mil. More use cases will be developed. More military personnel will be trained to use AI effectively. The military's organizational culture will evolve to incorporate AI as a normal part of operations.
This isn't the beginning of a science fiction scenario where AI runs the military. It's the beginning of a practical reality where AI becomes a standard tool for military personnel, helping humans make better decisions faster.
The real significance of Chat GPT's military deployment isn't the system itself—it's what it signals about the future. AI isn't coming to the military. It's already here. And it's going to change how military organizations operate, just as it's changing organizations everywhere.
The question now isn't whether military AI will happen. The question is how effectively will organizations deploy it, how carefully will they manage the risks, and how successfully will they maintain human decision-making authority in critical domains. Based on the Pentagon's approach so far, there's reason for cautious optimism that they'll get it right.

![OpenAI ChatGPT Military Access: What It Means for Defense [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/openai-chatgpt-military-access-what-it-means-for-defense-202/image-1-1770923244335.jpg)



