Windows 11 Storage Security Feature Explained [2025]
Introduction: A Lock on Your Disk Settings
Microsoft quietly rolled out a security change that's going to confuse a lot of people. If you've been poking around in Windows 11's Settings app lately, you might've noticed something strange: the Storage panel is now locked behind an admin gate. Non-administrators trying to access it get a notification saying they need elevated permissions. Sounds simple, right? Wrong.
Here's the thing—this isn't just some random UI tweak. It's part of a broader security strategy that Microsoft has been implementing across Windows 11 to tighten control over system-level changes. And while the intention is solid, the execution leaves plenty of room for confusion, especially in shared computers or workplace environments.
In this article, we're breaking down exactly what this feature does, why Microsoft implemented it, and what it means for you whether you're a home user, a small business owner, or an IT administrator managing a fleet of machines. We'll also walk through the practical implications, the workarounds, and whether you should even care about this change in the first place.
The core idea is elegant: prevent accidental or malicious modifications to disk partitions, formatting, and storage management. But the real-world impact is more nuanced than that. Some users will barely notice. Others will hit a wall. And administrators managing multiple devices will need to understand how this plays into their access control strategy.
Let's dig into what's actually happening under the hood and what you need to know to keep your system running smoothly.
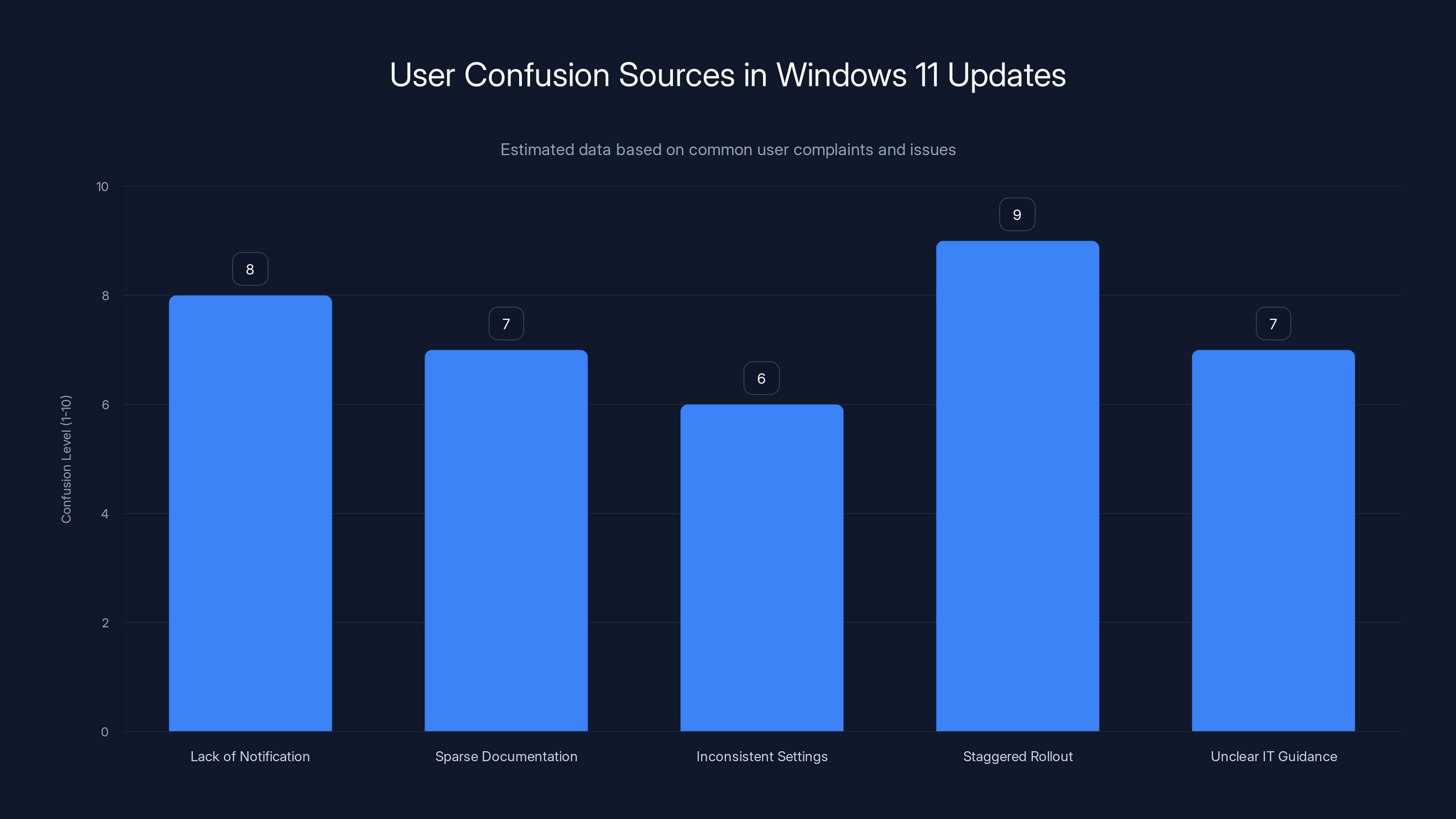
Estimated data shows that staggered rollout and lack of notification are major sources of user confusion in Windows 11 updates.
TL; DR
- Storage panel is now admin-protected: Non-admin users can't access disk management, partitioning, or formatting tools directly from Settings
- Prevents accidental or malicious changes: Stops standard users from reformatting drives or modifying storage configurations without authorization
- Affects shared computers most: Families and small offices with multiple user accounts will notice this restriction first
- Admin users aren't affected: If you're the primary account owner with admin privileges, nothing changes for you
- Workarounds exist but require technical knowledge: Users can request admin credentials temporarily or use alternative tools like Disk Management console
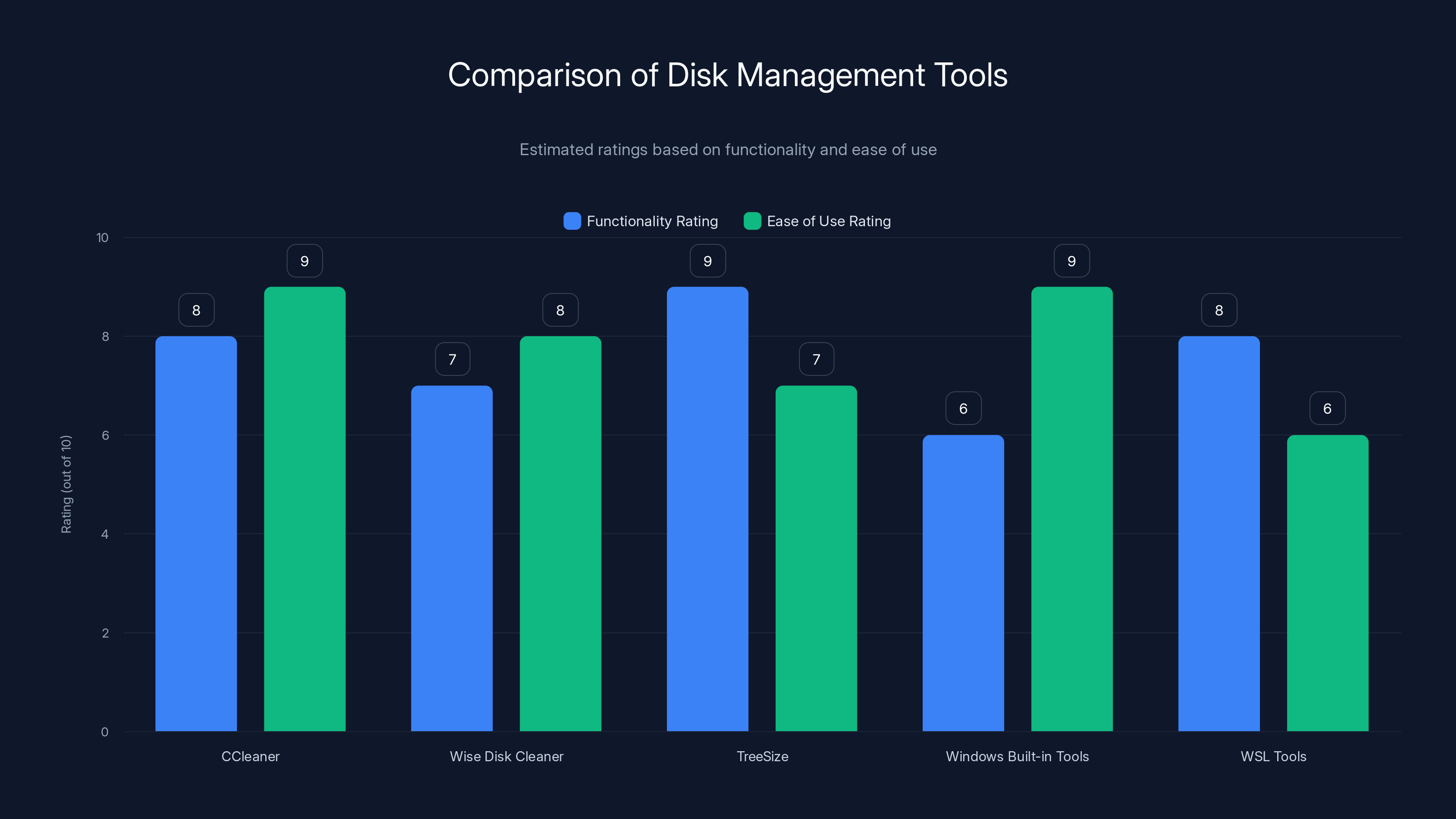
CCleaner and TreeSize offer high functionality, while Windows Built-in Tools are the easiest to use. Estimated data based on typical user reviews.
What Exactly Changed in Windows 11 Settings?
Let's start with the obvious question: what are we actually talking about here?
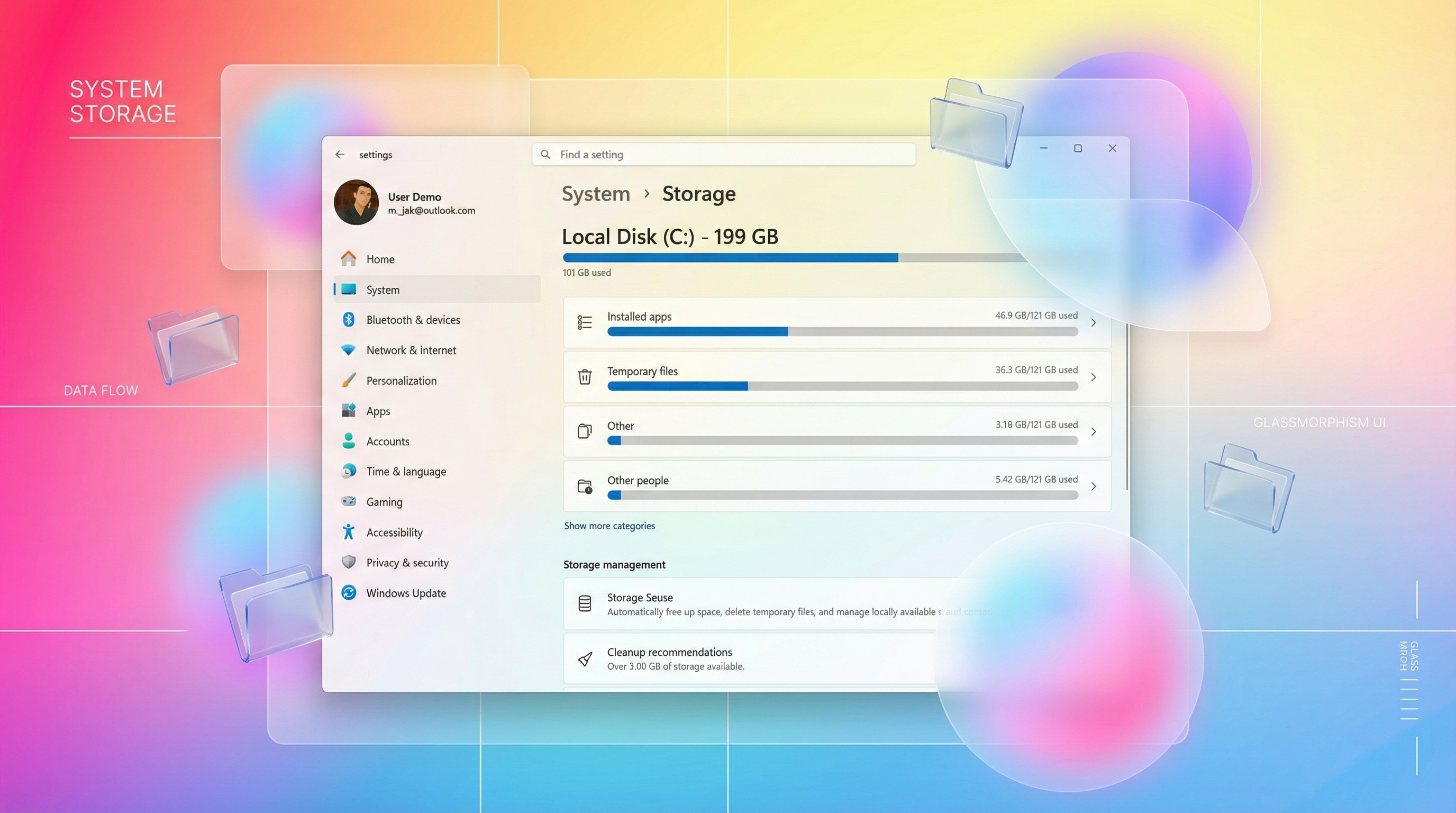
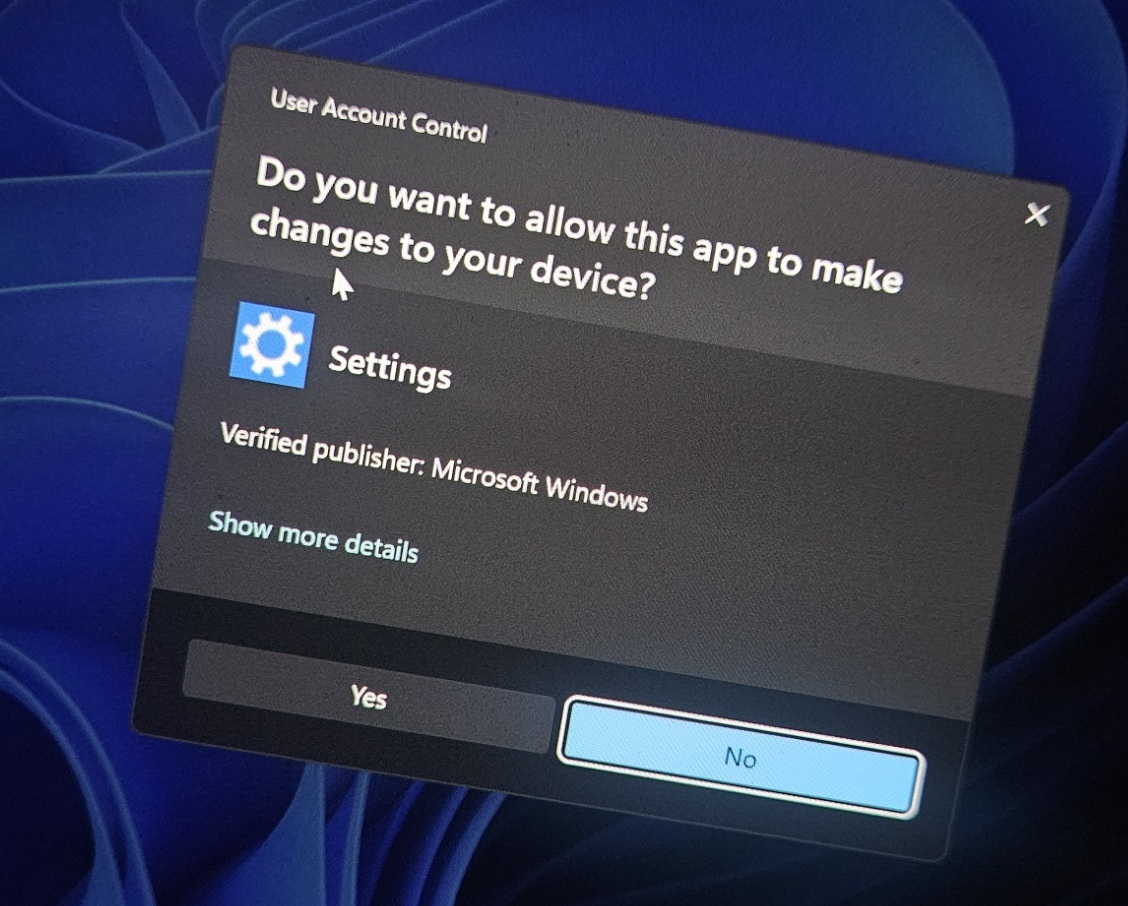
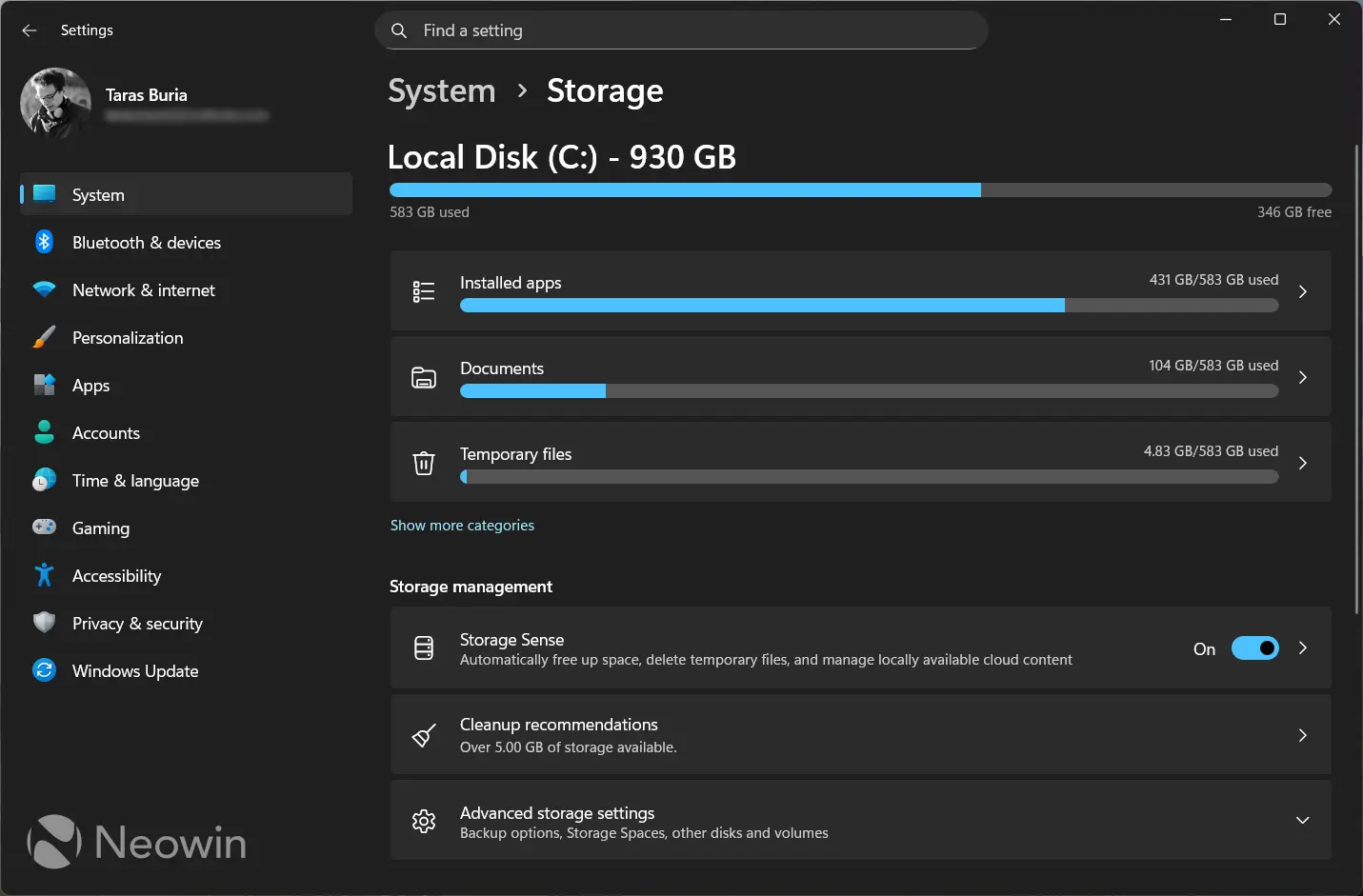
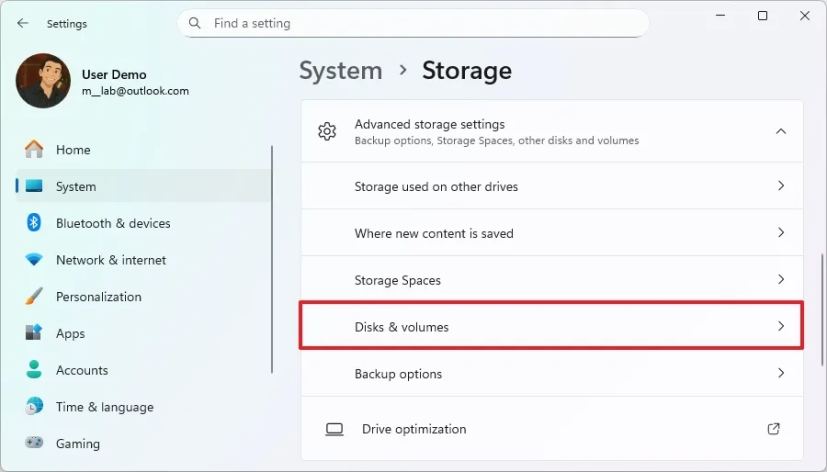
Microsoft moved the Storage panel in Settings to require administrator privileges. When you open Settings on Windows 11 and navigate to System > Storage, that page now requires elevation. If you're not logged in as an administrator, you'll see a notification that says something like "You don't have permission to view this folder" or "Contact your administrator."
This applies to the entire storage management section, which includes options like viewing disk usage, managing storage sense settings, and accessing advanced storage options. The restriction is comprehensive—you're not just blocked from dangerous operations. You can't even view detailed storage information without admin rights.
The change rolled out in recent Windows 11 updates, though not all users saw it simultaneously. Some reported seeing the lockdown in Build 22621.3737 and later, while others didn't encounter it until even more recent versions. This staggered rollout caused confusion because users weren't expecting the change, and Microsoft didn't make a huge announcement about it.
What's interesting is that this isn't entirely new behavior in Windows. Disk Management (the more advanced tool for partitioning and formatting) has always required admin rights. But the Settings app was previously more permissive—it let you view storage information even without admin access. Now those permissions have been tightened to match Disk Management.
The practical result: if you're a standard user on a shared family PC or a non-admin employee at a company, you can no longer even peek at how disk space is being allocated without asking someone else to log in.
Why Microsoft Made This Change: The Security Angle
Microsoft's reasoning is sound, even if the implementation raises questions.
Storage management is powerful. If someone with bad intentions—or just clumsy fingers—gets into your disk settings, they can do serious damage. They could delete partitions, reformat drives, disable storage sense, or manipulate space allocation in ways that break your system. In a family environment or a workplace, giving every user access to these tools is like leaving your car keys on the kitchen counter—technically possible, but not recommended.
The company is prioritizing what security researchers call the principle of least privilege. This concept says users should only have access to the specific tools and settings they actually need to do their job. Your teenage kid doesn't need to be able to repartition the family hard drive. Your office intern doesn't need to access storage management on company machines. So why give them the ability?
Microsoft has been gradually implementing this principle across Windows 11. It's why they've been restricting access to other settings too—like system file management, registry editor controls, and service configurations. Each restriction alone seems minor. Together, they add up to a more locked-down system that's harder to accidentally break.
There's also a security angle beyond accidents. Malware and malicious actors often target storage settings to hide themselves or destroy evidence. By restricting access, Microsoft makes it harder for malicious code to modify disk configurations without being caught. If storage changes require admin elevation, every change gets logged and flagged more prominently.
It's worth noting that this aligns with how other operating systems handle storage management. mac OS restricts storage operations to administrators. Linux typically requires root access. So Windows is actually catching up to industry standards rather than inventing something new.
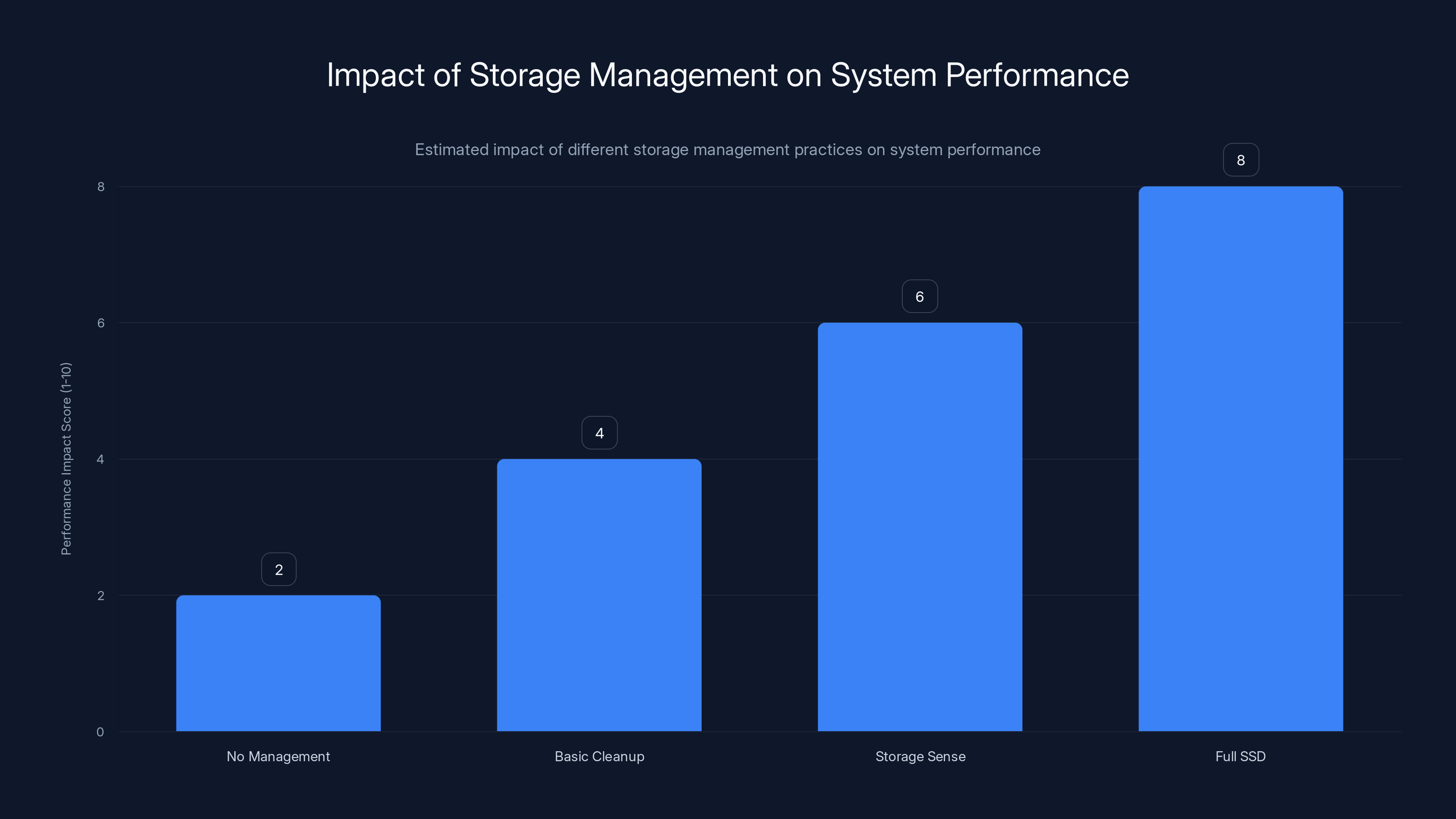
Estimated data shows that while basic cleanup and Storage Sense improve performance, modern SSDs inherently maintain performance, reducing the need for frequent management.
Who This Actually Affects: The Real-World Impact
Not everyone feels the impact of this change equally.
If you live alone and use your PC solo, this probably doesn't touch your life. You're the admin. You have access to everything. You won't see the restriction because it doesn't apply to you. You might not even know this feature exists.
But if you're in a household with multiple users—kids with their own accounts, a spouse with limited access, or guests who have temporary accounts—suddenly someone's going to hit this wall. They'll open Settings, click on Storage, and get blocked. Most people won't understand why. They'll think something's broken.
Small businesses feel this harder. If you're managing a network where employees have standard user accounts (which is a best practice), they suddenly can't access storage information without escalating privileges. This creates workflow friction. Someone wants to check how much space is left on a shared drive, and they have to submit a help ticket or ask an IT person to check for them.
It also affects system administrators managing Windows 11 devices. If you're using Group Policy or other management tools, you need to understand how this restriction interacts with your access control strategy. You might want to make exceptions for certain users or disable the restriction entirely in certain scenarios.
The confusion also comes from inconsistency. Other settings in Windows 11 still allow standard users to view information—they just can't modify it. Storage broke that pattern. You can't even look anymore.
For IT departments specifically, this creates a support burden. Users call helpdesk asking why they can't view their own disk usage. Support staff have to explain something that Microsoft didn't really publicize. That's a lot of unnecessary friction.
How to Access Storage Settings if You're Blocked
Okay, so you're locked out. Now what?
The obvious solution: use an admin account. If there's another account on the computer with administrator privileges, that person can access Storage settings. This works great if you're in a family with one admin managing the PC. Less great if you're in a workplace and IT is slow to respond.
If you're a standard user and you need temporary admin access, you can request elevation through a couple of methods. When you open Settings and try to access Storage, you might see a prompt asking for admin credentials. If an admin account is available, you can enter those credentials and get temporary elevated access to view storage settings.
For more advanced options, you can use Disk Management instead. This is the older, more powerful tool that's been around since Windows XP. Press Windows Key + X and select "Disk Management," or search for "Disk Management" in the Start menu. Disk Management also requires admin rights, but some people find it more reliable and feature-rich than the Settings app version. It gives you a graphical view of all partitions, free space, and allows you to manage volumes directly.
Another route: open File Explorer and right-click on a drive, then select Properties. You'll see storage information without needing admin access. You can't do advanced management operations this way, but you can see usage details. This is perfect if you just want to know how much space you're using.
If you're an IT administrator managing multiple machines, you can create Group Policy exceptions or use Windows 11 Pro management features to adjust who has access to storage settings. In domain environments, you can use Active Directory to push out specific access policies.
For home users, if you're frustrated with the restriction, you can create a second admin account and use it when you need to access storage settings. It's not ideal, but it works and is more secure than giving everyone admin access.
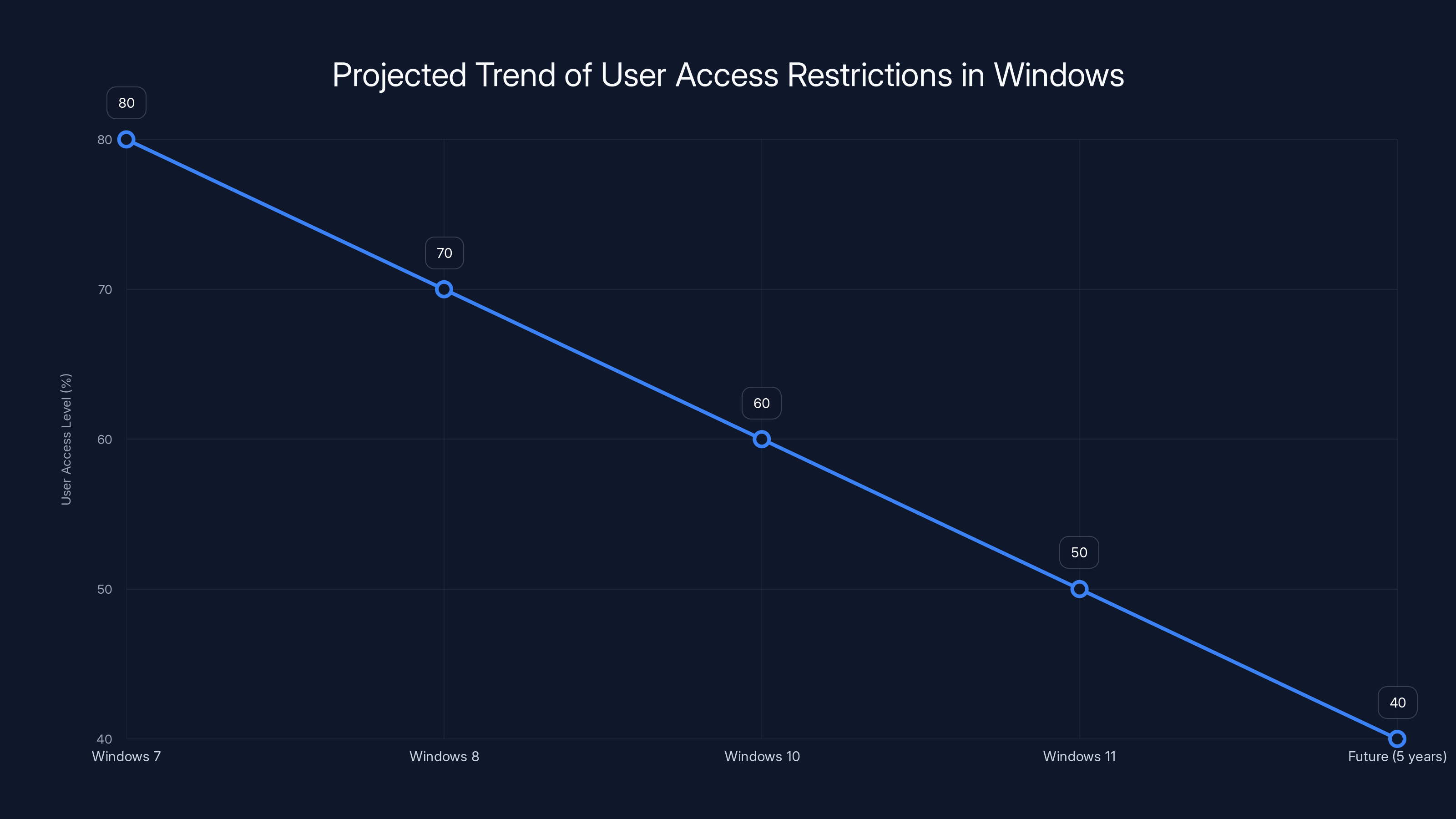
Estimated data shows a declining trend in user access levels, projecting further restrictions in the next five years.
The Technical Side: What's Actually Being Restricted?
When you can't access the Storage panel, what specifically are you blocked from doing?
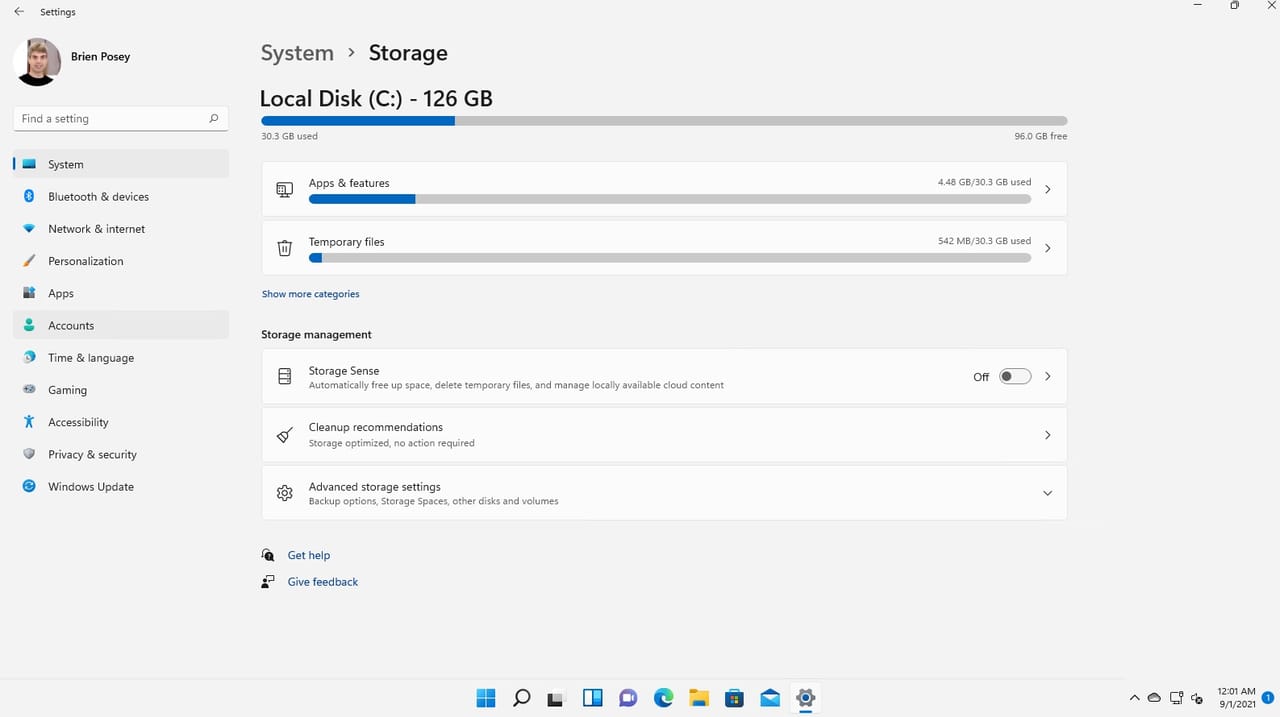
The restriction covers viewing and modifying several categories of storage information and operations. First, there's the overview data—you can't see a pie chart showing how disk space is allocated between apps, files, and system components. You can't see the total capacity, used space, or free space available. Even viewing is restricted.
Second, you're blocked from accessing Storage Sense settings. This is the automated cleanup tool that deletes temporary files, recycle bin contents, and cached data according to a schedule you set. Storage Sense is useful for keeping a system clean, so blocking standard users from adjusting it makes some security sense—they can't misconfigure it to delete important files or mess with system cleanup routines.
Third, you can't access advanced storage options. This includes things like installing apps to alternate drives, changing where new files are saved by default, or adjusting how different apps store their data. These are useful customizations, but they're considered system-level changes that require elevated privileges.
The restriction doesn't apply to personal file management. You can still copy, move, delete, and organize your own files in Documents, Downloads, Pictures, and Desktop. The block is specifically at the disk and partition level, not the file level.
What you also can't do without admin access: see which applications are using how much space. Windows provides an app storage usage breakdown that's incredibly useful for understanding what's hogging your disk. Now that's admin-only.
Interestingly, some storage-related operations in File Explorer still work for standard users. You can still pin items to Quick Access, create new folders, and manage file properties. It's just the system-level storage dashboard that's locked.
The technical implementation uses Windows security tokens and User Account Control (UAC). When a standard user tries to access Storage settings, Windows checks the user's security context, sees they don't have the required privileges, and blocks the operation. It's the same mechanism that's been used for protected operations since Windows Vista.
Why the Confusion? Mixed Messages from Microsoft
Part of the problem is that Microsoft didn't really explain this change clearly.
There's no prominent notification when the change rolls out. Users don't get a heads-up in Windows Update notifications explaining that storage access is now more restrictive. Instead, they discover it when they try to access the feature and get blocked. That discovery is frustrating, and worse, it makes people assume something's broken.
Microsoft's support documentation on this feature is sparse. If you search for "Windows 11 storage settings admin required," you'll find a few forum posts and reports, but no official Microsoft documentation explaining the decision or the workaround. That's a gap in communication.
There's also the issue of inconsistency across Windows. Other settings pages that deal with system configuration—like some networking settings or device settings—still allow standard users to view information even if they can't modify it. Storage breaks that pattern, which adds to the confusion. Users reasonably expect consistent behavior.
The timing of the rollout also contributed to confusion. It wasn't version-based or tied to a major update. It came in cumulative updates without headline attention. Some users got it early. Others got it later. This staggered rollout meant different people had different experiences with the same Windows version, creating a patchwork of bug reports across Reddit, Microsoft forums, and tech support channels.
Microsoft also didn't provide clear guidance for IT administrators on how this affects device management policies. If you're responsible for managing device fleets, it's unclear whether this restriction applies to group-managed devices, how to override it if necessary, or whether future updates might change the behavior. That lack of clarity creates planning uncertainty.

Estimated data suggests that Windows 11's storage restrictions have minimal impact on single users but significantly affect shared and managed environments.
Storage Settings vs. Disk Management: Understanding the Difference
Here's where it gets a bit confusing for users coming from older Windows versions.
Windows actually has two places where you can manage storage: the Settings app and Disk Management. They're different tools with different purposes, and they handle the admin restriction differently.
The Settings app Storage panel is the newer, consumer-friendly interface. It's designed for people who just want to see what's using space and clean up their disk without dealing with technical details. It shows you application sizes, file categories, and offers one-click cleanup options. It's visual, simple, and safe—there's not much you can accidentally break in Settings because it doesn't expose the truly dangerous operations.
Disk Management is the older, more powerful tool. It's been in Windows since the NT days and has barely changed visually since then. Here you can partition drives, extend volumes, create new volumes, and manage RAID configurations. It's where you go when you need to do serious storage operations. It looks like it was designed in 2003 because it kind of was.
Disk Management has always required admin privileges because it handles dangerous operations. You can format a drive and lose all data in Disk Management. That justifies the access restriction. Settings, by contrast, was designed to be less dangerous, so it never required admin access before. You could view your storage information without worry because you couldn't break anything.
Now Settings also requires admin access. This change doesn't really add security—if you're a standard user, you couldn't break anything in Settings anyway. What it does is create a more uniform access model where all storage management requires admin privileges.
For most users, this is fine. For IT environments, it's something to document in your access control policies. For home users who like to share PC access, it's just another thing to be aware of.
If you need to do actual storage management (resizing partitions, creating new volumes, etc.), Disk Management is where you'd go anyway. The Settings restriction mostly affects information viewing and simple cleanup options.
Managing Multiple User Accounts: The Family PC Problem
This feature hits hardest in family environments where multiple people use the same computer.
Typical scenario: you've set up your computer with one admin account (yours) and standard accounts for your spouse and kids. Everyone's got their own user profile, their own documents folder, their own desktop. This is actually the recommended setup for family PCs because it compartmentalizes things and prevents accidental damage.
But now your spouse or one of your kids hits Settings > Storage and gets blocked. They can't see disk usage. They can't run disk cleanup. They can't check if there's space for a large file download. This isn't a security threat—they could ask you to check, or you could set it up so they have access when needed. But it is an inconvenience.
If you want to give a family member occasional access to storage settings, there are a few approaches. You could temporarily elevate their account to admin, but that's overkill and reduces security. You could use the Windows 11 Guest Account feature, though that's limited in other ways. You could stick with the current restriction and just handle storage management yourself, which is what most families probably do anyway.
Alternatively, you could create a second admin account specifically for storage management tasks. Everyone in the family knows the password to this account. When someone needs to access storage settings, they log into this account, make their changes, and log back out. It's not perfect from a security standpoint, but it's a reasonable compromise between security and convenience.
Schools and community centers dealing with shared computers face similar challenges. They want student accounts to be restricted for obvious reasons, but they also want to provide access to tools students might legitimately need. Storage settings fall into a gray area—they're not essential for most users, but completely blocking them creates friction.
The bigger lesson here is that security often creates inconvenience trade-offs. You can have maximum security (everyone is standard users, admins manage everything) or you can have maximum convenience (everyone has admin access). Most real-world setups land somewhere in the middle, and this storage restriction requires you to think consciously about where your specific setup falls on that spectrum.
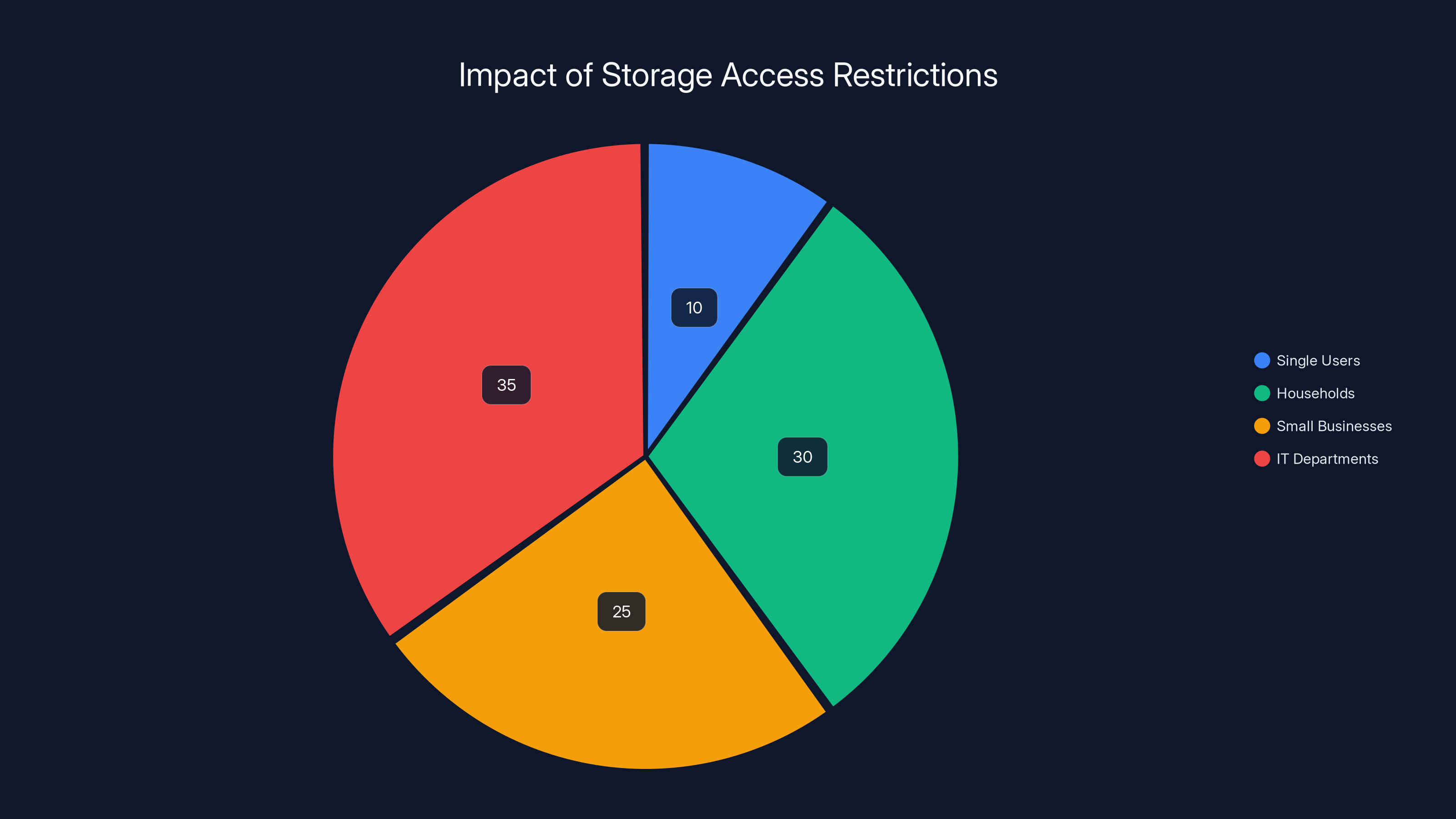
Estimated data shows IT departments and households are most affected by the new storage access restrictions, with small businesses also significantly impacted.
What This Means for Small Business IT
IT administrators managing Windows 11 devices in small business environments face practical decisions around this restriction.
The good news: this restriction actually aligns with security best practices. Standard users shouldn't have access to disk management. If an employee doesn't need to manage storage, they shouldn't be able to. This reduces the attack surface and limits what could go wrong if an account is compromised.
The challenging part: this restriction doesn't distinguish between "viewing information" and "making changes." If you're a security-conscious IT shop that allows standard users to view disk usage so they know when their drive is getting full, you're now blocked. You have to decide whether to give them admin access to view the info (bad idea) or manage storage concerns centrally (more work for IT).
For managed devices in corporate environments, IT can use group policies to adjust who has access to storage settings. You could create a custom security group and grant them elevated rights specifically for storage management. You could use Just-In-Time (JIT) access systems where employees can request temporary elevation for specific tasks. You could centralize storage monitoring through remote management tools and handle cleanup proactively.
The most common approach is probably to do nothing different. Employees request storage management through a help desk ticket, and IT handles the work. This is more supportable, more auditable, and aligns with security principles. It's also more time-consuming for IT staff.
Medium to large enterprises probably won't feel much impact because they likely have IT policies already in place that prevent standard users from accessing system settings. This change just formalizes what they were already enforcing through policy.
Small business environments with fewer IT resources might feel the pain. If employees have been managing their own storage cleanup, they're now dependent on IT for tasks that are normally routine. That creates a support burden.
From a policy documentation standpoint, IT should probably document that storage management access requires admin rights and create a formal process for handling storage-related requests. It clarifies expectations and prevents confusion when users hit the restriction.
Performance and System Impact: Is There a Difference?
Here's a question that doesn't get asked much: does restricting storage settings actually make your computer run better or safer?
The answer is nuanced. Preventing accidental modifications to storage configuration prevents problems that would make things run worse. If someone accidentally reformats your system drive, your computer stops working. If someone misconfigures storage sense to delete files you need, you have data loss. So preventing those accidents is protective.
But there's no performance improvement from the restriction itself. Your computer doesn't run faster or more efficiently because storage settings require admin access. The restriction is purely about access control, not optimization.
Storage Sense, the automated cleanup tool that's hidden behind the admin wall, actually does improve performance if configured well. It removes temporary files, recycle bin contents, and old downloads that waste space. By restricting access to Storage Sense, Microsoft is being slightly inconsistent—they're preventing users from accessing a feature that would help them, supposedly for security reasons.
From a practical standpoint, modern SSDs make storage management less critical than it used to be. Older mechanical hard drives suffered serious performance degradation when full. Modern SSDs maintain performance even at higher capacities. So the urgency of storage cleanup has decreased, making it less problematic to restrict access.
If you're curious about actual performance impact, you can check using built-in tools. Open Resource Monitor (search for "Resource Monitor" in Windows) and look at the Disk tab. You'll see what's accessing storage and how heavily. If nothing concerning appears, your storage system is healthy and you probably don't need to worry about frequent cleanup anyway.
Long-term, as SSDs become the default and capacities increase, storage management becomes less of a day-to-day concern. This restriction might feel less relevant in a few years when most systems have 2TB+ drives and minimal cleanup needs.
Third-Party Tools and Alternative Solutions
If you're frustrated with Microsoft's approach, you're not without options.
Third-party disk management and cleanup tools can do most of what Storage Sense does, and they typically don't require admin access to provide their core functionality. Tools like CCleaner, Wise Disk Cleaner, and Tree Size give you detailed storage information and cleanup capabilities. Some require admin access for all features, but others let you at least view storage information as a standard user.
These tools are double-edged swords though. They add capability, but they also add complexity and potential security considerations. You're installing additional software to work around a Windows limitation, which creates its own management burden.
For file-level management, built-in Windows tools work fine without admin access. File Explorer properties, folder statistics, and standard file operations don't require elevation. If you just need to see which files are biggest and delete them manually, you can do that without admin access.
The Windows Subsystem for Linux, if you use it for development, actually gives you more granular storage management options available without Windows admin access. If you're a technical user, WSL tools can provide storage insights in ways Windows itself now restricts.
For IT environments, remote management and monitoring solutions actually become more valuable with this restriction in place. If standard users can't access local storage information, IT needs better visibility through centralized monitoring tools to proactively manage disk space and prevent capacity issues.
Some power users have advocated for workarounds like creating a separate admin profile just for maintenance tasks or using Windows Task Scheduler to run cleanup operations with elevated privileges on a schedule. These are valid approaches, though they require more technical knowledge.
Really though, the most practical solution for most people is probably just accepting the restriction and planning accordingly. Give admin users the responsibility for storage management, establish a process for handling storage-related requests, and move on. It's not ideal, but it's simpler than trying to work around the system.

Future Implications: Will This Change More?
It's reasonable to wonder whether this is the start of a broader trend toward more restrictions in Windows 11.
Microsoft has been gradually tightening access controls across Windows 11. The storage settings restriction is one move in a larger direction toward limiting what standard users can do. Whether this is good or bad depends on your perspective.
From a security standpoint, limiting access is generally positive. Every tool you can't access is a tool that can't be used against you through a compromised account. From a user freedom standpoint, it's restrictive and paternalistic. Microsoft deciding what you should and shouldn't be able to do with your own computer rubs some people the wrong way.
Historically, Windows trends suggest more restrictions are coming. Windows 10 already moved toward limiting standard user access to various settings. Windows 11 continues that trajectory. Within five years, expect standard users to have access to even fewer system settings than they do today.
There's also the question of whether Microsoft will create a workaround or provide more granular controls. Enterprise customers with volume licenses might gain the ability to adjust these policies. Home users probably won't. The gap between what enterprise customers can control and what consumers can control is likely to widen.
One possibility: Microsoft could separate information viewing from modification. You could view storage information without needing admin rights, but making changes requires elevation. That would solve the problem elegantly. But it would require a UI redesign, and Microsoft hasn't indicated they're planning that.
More likely scenario: this is the new normal, and if people don't like it, they can use older Windows versions or choose different operating systems. Microsoft's direction is pretty clear, and the company isn't likely to reverse course on security-motivated restrictions.
Troubleshooting: When Something Goes Wrong
Occasionally, even admins encounter issues with storage access and settings.
If you're an admin and you suddenly can't access Storage settings even though you should be able to, the issue is usually a permissions corruption or a problem with User Account Control. Here's what to try.
First, restart your computer. This sounds obvious, but it genuinely fixes UAC-related issues sometimes. Many permission problems are temporary and resolve with a reboot.
Second, check that you're actually using an admin account. Search for "User Accounts" in Settings and verify that your account is listed as Administrator. If it shows as Standard User, you'll need to elevate yourself first.
Third, try running Settings as administrator. Right-click the Settings app and select "Run as administrator." This forces elevation and might bypass the permission issue. Alternatively, you can use the command line: right-click Command Prompt and select "Run as administrator," then type "start ms-settings: storageadvanced" to open the Storage settings directly with elevated privileges.
If you can't access Storage settings through Settings but you have admin privileges, try Disk Management instead. The two tools use slightly different permission systems, and Disk Management might work when Settings doesn't. Open Disk Management and see if it lets you access storage information.
If you're completely locked out and you need to regain access, your options are limited. You could create a new admin account using the command line in safe mode, though this is technical and requires Windows installation media in worst-case scenarios.
For non-admin users who need temporary access, the cleanest solution is to have an admin account holder grant temporary elevation through User Account Control. When you try to access Storage settings, UAC should prompt for admin credentials. If no admin account is available on the machine, you're out of luck until an admin is present.
If you're experiencing issues related to storage actually filling up and you can't access Storage settings, the most practical solution is to delete files manually through File Explorer until you have space, then ask an admin to help with cleanup tools.
Best Practices: Setting Up Your PC for Success
Knowing how to structure user accounts and access controls on your PC prevents problems down the line.
If you're the primary user, create an admin account for yourself and keep it secure. You're the system owner. You should have admin privileges. Use a strong password and don't share it unnecessarily.
For anyone else who uses the computer, create standard user accounts. This is the recommended setup even for family members. It limits what can go wrong and provides a layer of protection against accidental system changes. Yes, it means you're the person handling storage management, but that's actually not a bad thing.
If you need to give someone else admin access to specific tasks, do it temporarily. Create a separate admin account with a time-limited use case. Someone manages the computer while you're away? Give them temporary access. Once their task is done, revoke access. It's more secure than permanent elevation.
For regular maintenance, establish a schedule. Don't wait until your storage is full to think about cleanup. Run Storage Sense monthly or quarterly as a preventive measure. This prevents the scenario where someone urgently needs disk space and you're scrambling to free it up.
Document your setup. Write down which accounts have what access and what the passwords are. If something happens to you, someone else needs to be able to manage the computer. A simple document in your password manager covers this.
If you're managing multiple PCs, consider creating a standard account structure across all of them. Consistent setups are easier to manage and less confusing for users moving between machines.
For small business environments, invest in centralized user management if you have more than a few devices. Windows 11 Pro and Enterprise support domain-joined devices that get user policies centrally from a server. This lets you define roles and permissions once and apply them across all machines. It's more work initially but saves enormous amounts of time managing policies individually on each device.
Comparing Across Operating Systems: How Windows Stacks Up
Windows isn't alone in restricting system management. Let's see how this compares to other operating systems.
On mac OS, storage management operations require admin privileges. You can't partition drives or manage volumes without providing an admin password. But viewing storage information is available to all users. You can see disk usage, storage breakdown, and available space without elevation. So mac OS is actually more permissive than Windows 11 in this regard. You can view freely, but modify only with permission.
Linux varies by distribution, but generally gives you granular permission controls. You can view storage information as a regular user. Modifying storage requires root access, which is like admin access in Windows. Some Linux systems make storage information particularly accessible because it's assumed that information transparency is important.
Chromebooks don't really have traditional storage management because cloud storage is central to their design. You don't manage local partitions the way you do in Windows or mac OS. It's a completely different model.
i Pad OS restricts you from managing storage almost entirely. You can see how much space each app uses, but you can't partition drives or do storage-level operations. i OS even more so. But that's partly because these are not intended to be admin-capable devices. You're expected to let the system manage storage automatically.
The interesting takeaway: Windows is becoming more restrictive around storage than it used to be, moving slightly toward mac OS's model of view-but-don't-modify for standard users. But it's not quite there yet. mac OS lets you at least see what's happening. Windows hides it.
If you value the ability to see detailed system information, other operating systems might actually be more permissive. If you value centralized control and preventing accidental changes, Windows 11's approach is reasonable.
The User Perspective: What People Are Actually Experiencing
Beyond the technical details, let's look at what actual users are reporting about this change.
Most casual PC users haven't noticed. They're running Windows 11, they never look at Storage settings, and they're totally unaffected. For them, this change is irrelevant.
Power users and tech enthusiasts are more aware. They're hitting the restriction when they try to check storage details, and many are frustrated. They see it as unnecessary paternalism—Microsoft assuming people are incompetent and restricting them for their own good. This group often complains on Reddit and tech forums.
IT professionals and system administrators recognize it as part of a security trend, though many find it creates unnecessary support overhead. If they're going to restrict access, many argue Microsoft should at least provide better tools for delegating access or provide clearer documentation about how to manage it.
Family members on shared computers feel the impact directly. Someone gets blocked, they ask the admin what's wrong, and the admin has to explain that Windows won't let non-admins access storage information. It's a friction point that didn't exist before.
Employees in small to medium businesses often don't even know the restriction is there because IT handles storage management for them anyway. But if they're used to managing their own systems, it's jarring.
Interestingly, most people don't have strong opinions about it once they understand the reasoning. The initial reaction is confusion and frustration, but when you explain that it's a security measure to prevent accidental damage, most people accept it. It's a reasonable trade-off if explained properly.
Microsoft's failure wasn't in implementing the restriction. It was in not explaining it clearly when rolling it out. A simple notification explaining the change and the reasoning would have prevented most of the backlash.

FAQ
What is the Windows 11 storage settings restriction?
The Windows 11 storage settings restriction is a security policy that prevents non-administrator users from accessing the Storage panel in Settings. This blocks standard users from viewing disk usage information, managing storage sense settings, or accessing advanced storage options without admin credentials. Only users with administrator privileges can access these features.
How does the storage settings restriction work?
When a non-admin user tries to open the Storage panel in Settings (System > Storage), Windows checks their security token through User Account Control. If the user lacks administrator privileges, Windows blocks access and displays a permission error message. Admin users bypass this check entirely and access the storage panel normally.
Why did Microsoft implement this restriction?
Microsoft implemented this restriction following the principle of least privilege, which is a security best practice. By limiting storage management to administrators only, the company prevents standard users from accidentally (or maliciously) modifying critical disk configurations, formatting drives, or misconfiguring storage settings that could damage the system. It also reduces the attack surface if a standard user account is compromised.
Who is affected by this restriction?
Primarily, non-administrator users on shared computers are affected. This includes family members on home PCs with standard accounts, employees with non-admin accounts at small businesses, and students using school computers. Single-user computers where the owner is the administrator are unaffected. Users can still see storage information through File Explorer drive properties without admin access.
What can I do if I'm blocked from storage settings?
If you're a standard user, you can request that an administrator with an elevated account access Storage settings for you. If you're an administrator who should have access but is being blocked, try restarting your computer, checking that you have admin privileges in User Accounts, or running Settings as administrator. You can also use Disk Management as an alternative tool with similar capabilities.
How does this compare to previous Windows versions?
In Windows 10 and earlier, the Storage panel was accessible to all users, though advanced operations required admin rights. Windows 11 changed this to require admin rights just to view storage information. Disk Management, the more advanced tool, has always required admin access. This change essentially unified the permission model across both interfaces.
Can IT administrators override this restriction?
Yes. In enterprise environments with Windows 11 Pro or Enterprise, administrators can use Group Policy to adjust storage access controls. They can create exceptions for specific users or groups, or they can disable the restriction entirely if their security policies allow it. Home and small business users without domain management capabilities cannot easily override this at the policy level without third-party tools.
Is there any security risk from this restriction?
No. The restriction actually increases security by preventing unauthorized modifications to disk configuration. A compromised standard user account cannot use storage settings to hide malware or destroy evidence because it lacks the permissions to access those settings. The risk is minimal and the benefit is a more locked-down system.

Conclusion: Living With the New Reality
Windows 11's storage settings restriction is one of those changes that seems small until you run into it. For most users, it's completely irrelevant. For shared computers and managed environments, it requires some adjustment to workflows and access policies.
The core reasoning is sound. Storage management should be restricted to people who understand the consequences. Preventing accidental reformatting or data loss is a legitimate security goal. The execution is reasonable too, even if it's not what users expected.
The real problem was communication. Microsoft rolled this out without clearly explaining why or how users should adapt. A clearer rollout and better documentation would have prevented much of the confusion and frustration.
Moving forward, expect more restrictions like this. Windows 11 is deliberately more locked down than Windows 10. If you're managing multiple computers, think ahead about how these restrictions fit into your access control strategy. Create admin accounts where needed. Document your setup. Establish processes for handling system management requests.
If you're a single user, honestly, you probably don't need to do anything. You're already running as an admin, so this doesn't affect you. Just be aware that if you set up other accounts on your computer, they'll hit this restriction. Plan accordingly.
The principle behind this restriction will likely expand to other Windows settings in the future. Microsoft is moving toward a model where regular users have less access to system configuration. Whether that's good or bad depends on your perspective, but it's the direction the company is heading. Understanding this change now helps you prepare for similar restrictions later.
Ultimately, Windows 11's storage security feature is a reasonable implementation of a good security principle. It might cause some friction if you're not prepared for it. But with proper setup and clear understanding of the reasoning, it's an acceptable trade-off for a more secure system.
Key Takeaways
- Windows 11 now requires admin privileges to access Storage settings, blocking non-admin users from viewing disk usage and managing storage sense
- The restriction implements the principle of least privilege, a security best practice that prevents accidental or malicious disk modifications
- Most impact falls on shared computers and small business environments; single-user PCs are unaffected since administrators retain full access
- Workarounds include requesting admin elevation through UAC, using Disk Management instead, or checking storage through File Explorer properties
- This change reflects Microsoft's broader trend toward more restrictive access controls in Windows 11 for enhanced security
Related Articles
- Windows 11 February 2025 Update: All Features & What to Expect
- Windows 11 Users Skeptical of Microsoft's AI Plans: Why Trust is Broken [2025]
- Windows 11 Taskbar Still Stuck? PowerToys Movable Taskbar Fix [2025]
- Windows 11 Improvements 2025: Microsoft's Real Fixes Beyond AI [2025]
- Microsoft's Top Menu Bar for Windows 11: Everything You Need to Know [2025]
- Windows 11 Hits 1 Billion Users: What This Milestone Means [2025]
![Windows 11 Storage Security Feature Explained [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/windows-11-storage-security-feature-explained-2025/image-1-1770379618176.jpg)



