The AI Revolution Is Transforming Budget Consumer Electronics
The artificial intelligence boom has fundamentally reshaped how technology companies approach product development and pricing strategy across nearly every consumer electronics category. While discussions about AI's impact have largely centered on premium smartphones, high-end laptops, and cutting-edge gaming consoles, a quieter but equally significant transformation is occurring in the budget segment of televisions and audio equipment. This shift represents one of the most consequential changes in consumer electronics pricing and capability distribution in the past decade.
Budget-conscious consumers who traditionally settled for basic feature sets and limited performance are now facing a market in flux. The integration of artificial intelligence into even entry-level televisions and audio devices is creating unprecedented competitive pressure on manufacturers while simultaneously driving up production costs. Unlike premium markets where consumers expect continuous innovation and accept higher prices, the budget segment operates on fundamentally different economics. Consumers here prioritize value above all else, making them highly price-sensitive and quick to abandon brands that don't deliver expected performance at expected price points.
The paradox companies face is striking: implementing AI capabilities requires significant research and development investment, silicon engineering for specialized processors, software optimization, and testing infrastructure. Yet the budget market demands lower prices than ever before. This fundamental tension between rising development costs and price pressure is forcing manufacturers to make critical strategic decisions about which features to prioritize, which components to source, and how to justify price increases—or absorb costs by reducing profit margins.
The impact extends far beyond simple price tags. Consumer expectations around smart TV functionality, audio processing, picture quality enhancement, and seamless integration with smart home ecosystems have escalated dramatically. Budget products that would have been considered cutting-edge five years ago now feel basic without AI-powered features like automatic picture optimization, voice assistant integration, spatial audio processing, and machine learning-based content recommendations. Manufacturers can no longer compete on specifications alone; they must deliver intelligent features that were previously exclusive to premium tier products.
Understanding this transformation requires examining the specific technologies being deployed, analyzing how different manufacturers are approaching the budget segment, exploring the actual pricing implications, and evaluating whether these AI features deliver genuine value or represent marketing-driven feature inflation. The decisions made in this market segment will have lasting implications for consumer choice, brand loyalty, and the trajectory of technology democratization for millions of households globally.
How AI Integration Is Changing Manufacturing Economics
The introduction of artificial intelligence into budget consumer electronics has fundamentally altered the manufacturing landscape in ways many consumers don't fully appreciate. When a television or audio device incorporates AI capabilities, manufacturers must make strategic decisions about where AI processing occurs, which hardware components are required, and how software optimization impacts production complexity.
Neural Processing Units and Custom Silicon
Traditionally, budget televisions relied on simple, commodity processors designed primarily for video decoding and basic image upscaling. These processors were generic, widely available, and inexpensive—exactly what manufacturers needed to maintain razor-thin margins at budget price points. The introduction of AI-powered features requires either significantly more powerful general-purpose processors or specialized neural processing units (NPUs) designed specifically for machine learning inference.
Custom silicon development represents one of the largest cost factors in modern electronics manufacturing. Major manufacturers like Samsung, LG, and TCL have invested heavily in developing proprietary AI processing solutions specifically designed for television applications. These custom chips must handle picture quality enhancement through machine learning-based upscaling, real-time object detection for smart home integration, voice processing for natural language commands, and predictive content recommendations.
The manufacturing reality involves substantial non-recurring engineering costs that must be amortized across hundreds of thousands or millions of units. A manufacturer developing a new AI-enabled television processor might invest
Some manufacturers have chosen to license existing AI processing solutions from chip designers like Qualcomm, MediaTek, or Amlogic rather than developing proprietary solutions. This approach reduces development costs but increases per-unit licensing fees, which must be reflected in the final product price. Alternatively, manufacturers might implement AI processing through software optimization on existing processors, leveraging machine learning frameworks that run efficiently on older hardware architectures. This approach reduces silicon costs but requires more sophisticated software engineering and produces less impressive performance gains.
Software Complexity and Development Overhead
Beyond hardware, AI integration dramatically increases software complexity. A traditional television required relatively straightforward firmware for video decoding, menu navigation, and external input management. Modern AI-equipped televisions require machine learning model deployment, continuous optimization, cloud connectivity for model updates, and sophisticated user interface design for AI-powered features.
Manufacturers must maintain entire teams of machine learning engineers, data scientists, and software architects to develop and optimize these systems. The cost of maintaining and improving AI models post-launch extends far beyond the initial product development phase. Every software update requires testing across different content types, screen conditions, and use cases. Machine learning models require continuous refinement as they encounter edge cases and unusual viewing scenarios in the field.
For budget products, manufacturers often cannot justify the same level of post-launch support as premium tier devices. This creates a quality perception problem: consumers expect AI features to improve over time, similar to how premium smartphone manufacturers update their computational photography systems. Budget manufacturers, however, may ship a product with a fixed machine learning model that never substantially improves through software updates. This discrepancy creates consumer dissatisfaction even when the hardware is technically capable of receiving improvements.
Supply Chain Complexity
Integrating AI into budget electronics creates downstream supply chain challenges that ripple through manufacturing. Traditional television components came from established suppliers with proven quality and reliability records. Adding AI processing requirements means qualifying new suppliers, establishing quality control standards for NPU performance, and managing compatibility across different neural processing architectures.
This supply chain complexity increases inventory management costs, extends product development timelines, and creates risk exposure if suppliers fail to meet quality standards or experience production disruptions. Budget manufacturers, who typically operate with tight inventory buffers and rapid turnover requirements, find this added complexity particularly challenging. The flexibility that allows rapid product iterations and quick responses to market changes becomes constrained when suppliers cannot quickly adjust production volumes or introduce design variations.
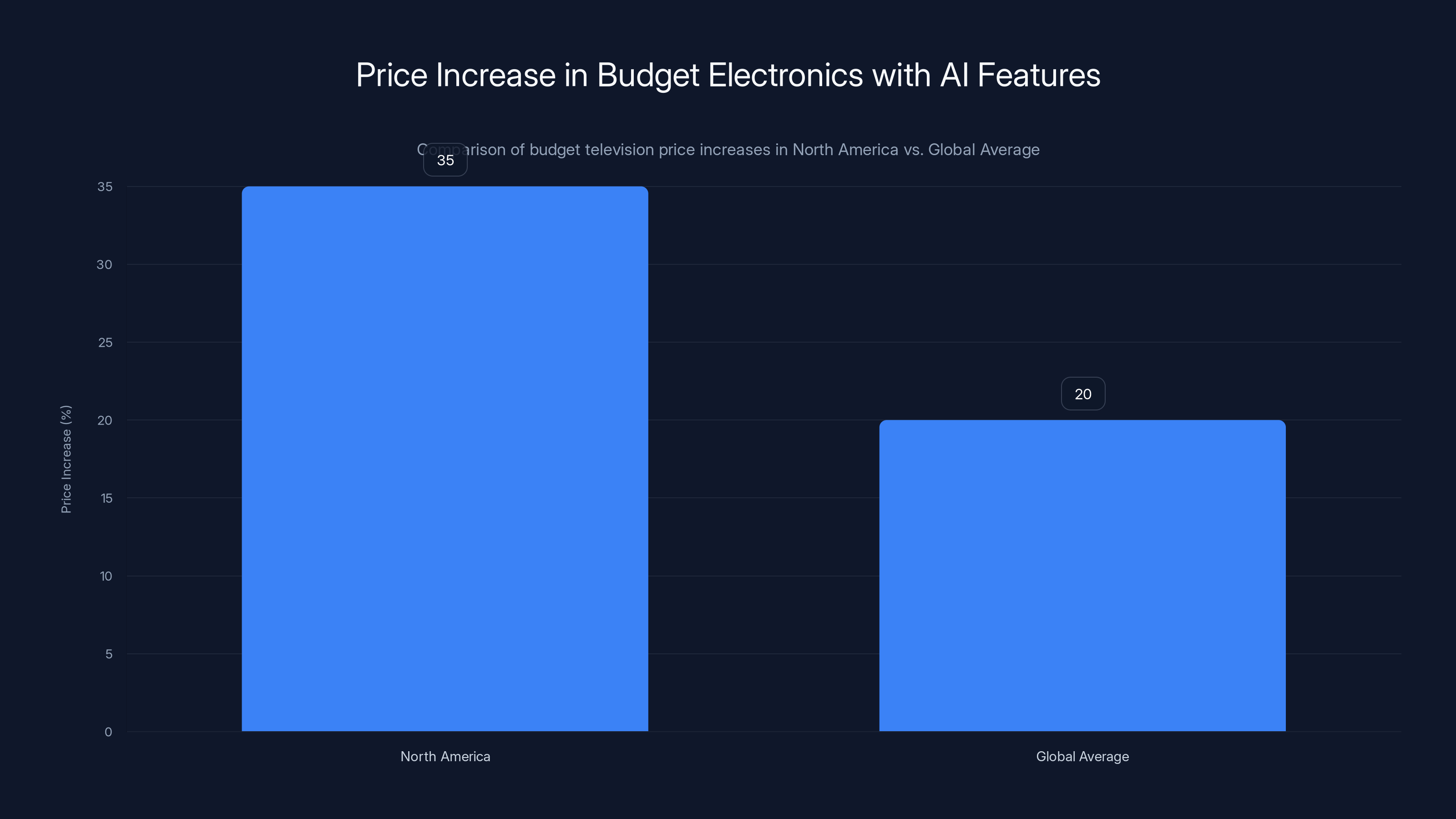
North American budget televisions with AI features are 30-40% more expensive than global averages, reflecting strong demand and affluent market positioning. Estimated data.
The Television Market Transformation
Television manufacturing represents one of the most competitive and lowest-margin segments in consumer electronics. The global television market operates on brutal economics where price competition often overwhelms feature differentiation. A television's core function—displaying video content with acceptable picture quality—became commoditized over the past decade. Manufacturers differentiated through screen size, resolution, refresh rate, and panel technology, but these features followed predictable trajectories that compressed margins as technology matured.
Picture Quality Enhancement Through AI
Artificial intelligence offers television manufacturers a novel approach to differentiation through intelligent picture quality enhancement. Rather than competing on raw specifications, manufacturers can deploy machine learning models that analyze incoming video signals frame-by-frame, intelligently enhance picture quality, and adapt to content characteristics.
These AI upscaling systems work by analyzing low-resolution source material and using neural networks trained on high-resolution content to predict what additional detail should exist. A streaming service might deliver a television show at 1080p resolution, and the AI upscaling system analyzes the content, identifies likely textures, details, and fine structures based on its training data, and produces output that approaches 4K quality. The system learns from millions of example images what details typically appear in specific contexts, applying this knowledge to enhance standard-definition, high-definition, and compressed streaming content.
The performance difference is genuinely noticeable in real-world usage. An AI-enhanced 720p stream displayed on a 4K television looks substantially better than simple digital interpolation, which merely stretches pixels without adding detail. For consumers relying heavily on streaming services, cable television, or older content libraries, AI upscaling delivers tangible picture quality improvements without requiring higher-bandwidth sources.
Manufacturers have successfully marketed this capability as a key differentiator in the budget segment. A
HDR and Tone Mapping Intelligence
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content presents technical challenges for televisions, particularly budget models with limited local dimming zones or quantum dot capabilities. HDR content contains a much wider range of brightness levels than standard dynamic range video, requiring televisions to intelligently tone map this content to their specific display capabilities. A television capable of producing 1,500 nits peak brightness can display HDR content very differently than one limited to 300 nits.
Machine learning models trained on professional color grading examples can intelligently adapt HDR content to specific television capabilities, preserving artistic intent while optimizing for the display's characteristics. Rather than using simple tone mapping curves, AI systems learn the nuances of how professional colorists handle different content types and apply similar principles to HDR adaptation.
This capability has profound implications for budget televisions. Entry-level models without advanced local dimming or high peak brightness can now deliver surprisingly good HDR experiences through intelligent tone mapping. Manufacturers can advertise "AI-enhanced HDR" on budget products, which technically delivers superior results to non-AI competitors at the same price point.
Smart TV Integration and Voice Assistance
The budgetization of smart television functionality has been extraordinary over the past five years, with built-in smart platforms becoming standard even on
AI-powered voice processing allows budget televisions to handle voice commands more reliably than rigid keyword spotting systems. Rather than waiting for specific activation phrases, AI systems understand contextual intent, recognize different speaker voices, and differentiate between commands directed at the television versus ambient conversation. This requires neural network processing for natural language understanding, which traditionally required significant computational resources.
Manufacturers implementing this on budget devices must optimize heavily, often offloading complex voice processing to cloud servers. The television's local processor performs simple wake-word detection and audio capture, while sophisticated natural language understanding occurs remotely. This hybrid approach reduces local processing requirements while delivering user experiences approaching premium devices.
Gaming and Refresh Rate Intelligence
Gaming has become increasingly important even in the budget television segment. Console and PC gaming audiences have expanded beyond enthusiasts to casual players and families. Budget televisions increasingly include gaming-focused features like variable refresh rate support, motion smoothing, and input lag reduction.
AI systems can intelligently detect gaming content and automatically adjust display settings to optimize gaming experience—increasing refresh rate processing, reducing input lag, adjusting brightness for fast-moving content, and enabling specific color modes. Rather than requiring manual configuration, machine learning models analyze input characteristics and determine whether content is likely gaming, sports, movies, or standard television.
This intelligence appeals strongly to budget-conscious gamers who can't justify purchasing premium gaming displays but want decent gaming experiences on the television they're already buying. The AI features justify price increases that would be harder to sell on specifications alone.

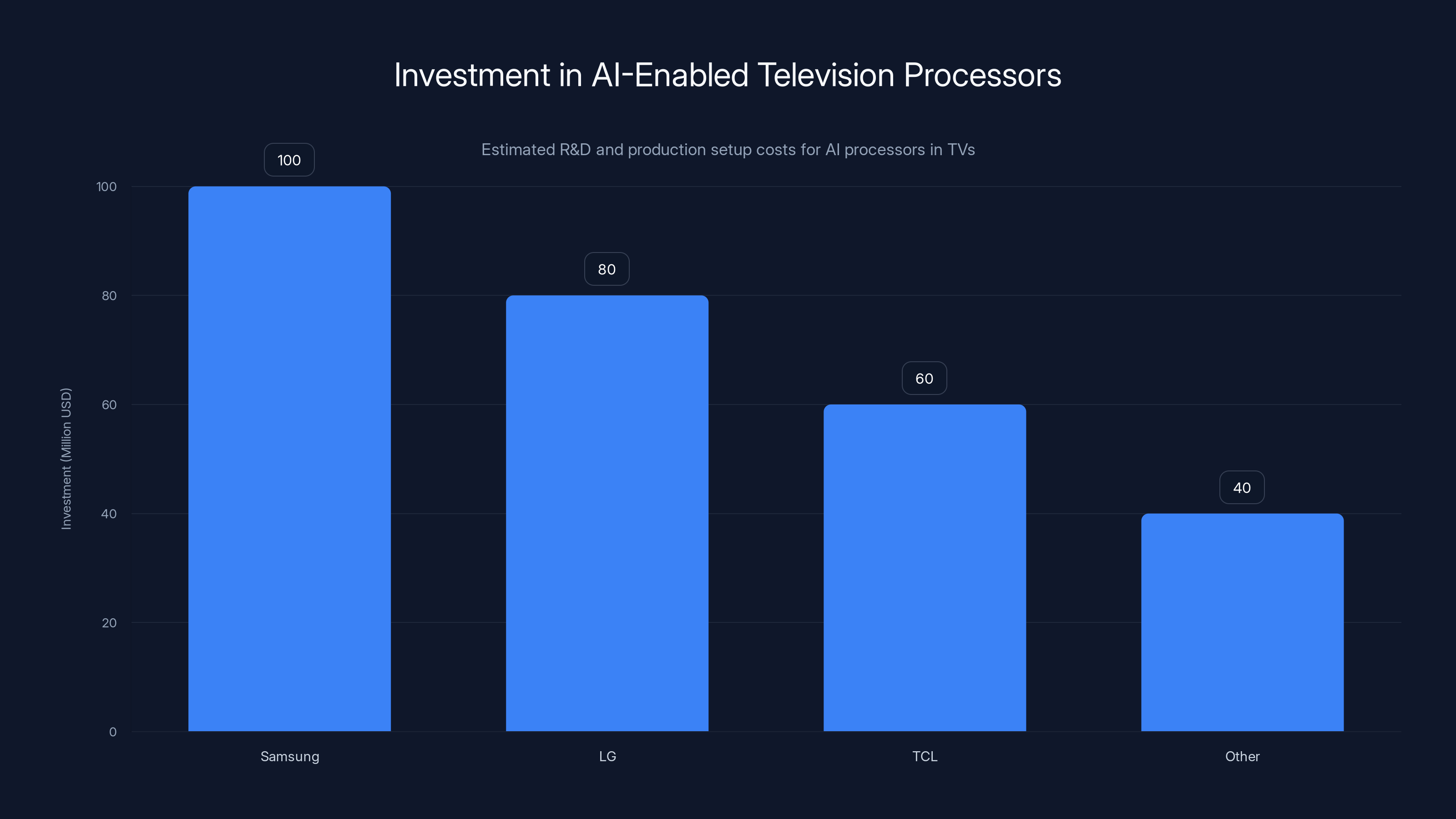
Major manufacturers invest heavily in AI processing solutions, with Samsung leading at an estimated $100 million. Estimated data.
Impact on Audio Equipment Economics
The audio equipment market has experienced different but equally significant disruption from AI integration. Unlike televisions, where manufacturers had some freedom to develop differentiated features, audio equipment manufacturers face competition from an entirely new category of AI-powered competitors: software-based audio enhancement applications.
Spatial Audio and Surround Processing
Spatial audio—the illusion of three-dimensional sound from limited speaker arrays—has traditionally required either sophisticated hardware (multiple speaker drivers positioned precisely in space) or complex analog signal processing. Dolby Atmos and DTS: X brought surround sound to home theater, but achieving these capabilities required significant hardware investment.
Artificial intelligence offers a third approach: software-based spatial audio processing that analyzes mono or stereo audio and extracts directional cues, space information, and surround sound characteristics through machine learning. Neural networks trained on spatial audio examples can analyze stereo music and generate convincing surround sound illusions, creating the perception of sound coming from directions that don't correspond to actual speaker positions.
This capability democratizes surround sound for budget equipment. A
Manufacturers have heavily marketed these capabilities, introducing terminology like "virtual surround," "3D audio processing," and "AI-enhanced spatial sound" to budget product lines. The genuine technical capability beneath the marketing is significant: machine learning models performing real-time audio analysis and processing, delivered on budget hardware through careful optimization.
Noise Suppression and Clarity Enhancement
Particularly relevant in portable audio, gaming headsets, and speakerphone applications, AI-powered noise suppression has become increasingly sophisticated and accessible on budget equipment. Rather than simple noise gate circuits that mute quiet audio, modern AI systems intelligently distinguish between desired audio (speech, music, sound effects) and background noise (traffic, wind, mechanical sounds, crowd noise).
These systems work by analyzing audio characteristics—frequency content, temporal patterns, statistical properties—and learning to differentiate between speech and noise. Machine learning models trained on millions of hours of audio examples can identify noise even in complex acoustic environments and suppress it while preserving desired audio content and quality.
For budget headsets, portable speakers, and conferencing equipment, this capability has transformed user experience. A
Adaptive EQ and Frequency Response Optimization
Sound signature customization has traditionally been either absent from budget audio equipment or available as crude preset switches. AI systems enable sophisticated, automatic frequency response optimization that adapts to listening environment, content type, user hearing characteristics, and hearing damage or age-related hearing changes.
Artificial intelligence processes listening patterns, adjusts frequency response based on detected content characteristics, and continuously optimizes settings to match user preferences and hearing capabilities. Hearing test integration allows the system to detect hearing loss and compensate with targeted frequency response adjustments. Environmental analysis can detect whether the user is in a car, office, home, or outdoors and adjust audio processing accordingly.
This level of customization was previously exclusive to premium audiophile equipment or expensive hearing aid systems. Budget audio equipment now incorporates similar sophistication through efficient neural network models deployed on modest processors.
Battery Efficiency Through Predictive Processing
For portable audio equipment, battery life is paramount. AI systems can optimize power consumption by predictively adjusting processing intensity based on content characteristics, user behavior patterns, and environment. Rather than applying maximum computational effort constantly, intelligent systems reduce processing intensity during periods when complex processing provides minimal perceptual benefit.
Machine learning models predict listening patterns, anticipate content transitions, and optimize processor states preemptively. A portable speaker might reduce audio processing intensity during spoken word content while maintaining maximum quality during music, learning these patterns from user behavior. Similarly, systems might predict when environmental conditions will remain stable and reduce adaptive processing overhead.
These optimizations extend battery life by 10-20% without compromising perceived audio quality, a significant advantage in competitive budget markets where battery life directly influences purchase decisions.
Pricing Dynamics and Cost Pressures
The integration of AI into budget electronics creates complex pricing dynamics that benefit some consumers while disadvantaging others. Understanding these economics reveals why prices are shifting and what consumers should expect in the near term.
Component Cost Escalation
Historically, budget television and audio equipment benefited from mature component economies where standardized parts achieved low unit costs through massive production volumes. A basic television processor designed in 2015 and refined through billions of manufactured units achieved remarkable cost reduction—unit costs falling from $50+ to single digits as manufacturing scaled.
Introducing new AI-capable processors interrupts this trajectory. New silicon enters the market at high cost and only achieves cost reduction through production volumes over several years. Manufacturers introducing AI features early face 30-50% higher processor costs compared to incumbent solutions. For budget products where processor costs represent 8-12% of total BOM (Bill of Materials), this translates to
As production scales and multiple manufacturers adopt similar approaches, component costs will decline. However, the timeline for reaching mature cost levels stretches across 3-5 years. During this period, budget manufacturers face genuine cost escalation that must be absorbed through price increases, margin compression, or feature reduction.
Feature Consolidation and Tiering Strategy
Facing rising costs, many manufacturers have implemented feature consolidation strategies that bundle AI capabilities into specific product tiers while removing features from lower-tier models. Where a manufacturer previously offered five television models at
This tiering strategy accomplishes multiple objectives: it maintains psychological price points at round numbers (
Consumers at the absolute budget extreme find fewer feature options and sometimes less impressive picture quality or audio capability than in previous generations. However, consumers able to spend slightly more discover that the feature gap between budget and mid-range products has narrowed considerably, with
Market Consolidation Effects
Rising AI integration costs have accelerated market consolidation. Small to mid-sized manufacturers lack the R&D budgets to develop custom AI solutions and cannot achieve sufficient production volumes to justify licensing fees. This disadvantage is pushing them toward private label manufacturing or exit from independent brand competition.
The remaining competitors—Samsung, LG, TCL, Hisense, Sony, and a handful of others—can distribute AI development costs across larger production volumes and more product lines, achieving cost efficiency smaller competitors cannot match. This concentration is increasing, with consequences for consumer choice and competitive pricing pressure.
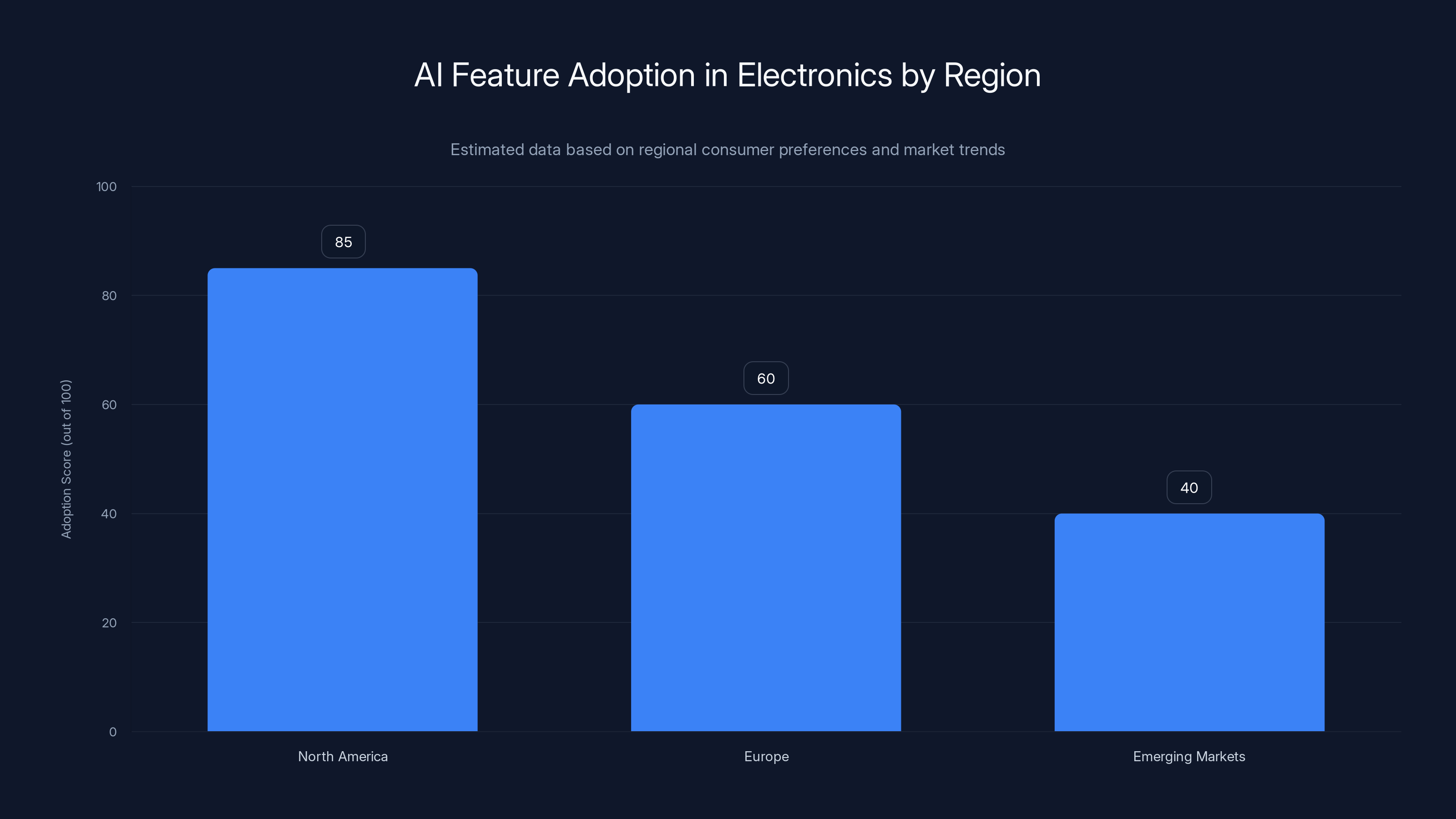
North America leads in AI feature adoption in electronics, driven by consumer enthusiasm and higher price acceptance. Europe shows moderate adoption due to privacy concerns, while emerging markets focus on affordability. Estimated data.
Regional Market Variations and Global Supply Chain Impact
AI integration in budget electronics has affected different global regions unequally, reflecting variations in content consumption patterns, consumer expectations, infrastructure, and manufacturer regional strategies.
North American Market Dynamics
North American consumers have embraced AI-powered television features rapidly, particularly AI upscaling and voice assistance. Streaming culture is deeply established, with consumers regularly consuming compressed streaming content that benefits substantially from AI enhancement. Voice assistant integration aligns with existing smart home ecosystems (Alexa, Google Home), making voice-controlled televisions appealing.
Manufacturers responded by positioning AI as a core feature even in budget segments, with aggressive marketing emphasizing "AI-powered picture quality" and "intelligent upscaling." North American budget television prices have increased more substantially than global averages, with base models 30-40% more expensive than equivalent models in other regions. This reflects both strong consumer demand for AI features and manufacturers' ability to achieve higher price positioning in affluent North American markets.
For audio equipment, spatial audio processing and voice-integrated soundbars have achieved strong market adoption. Budget soundbars incorporating AI spatial audio now dominate <$300 category, with traditional non-AI competitors largely displaced.
European Market Dynamics
European markets show different patterns. Privacy concerns limit adoption of certain AI features, particularly cloud-based voice assistance and data-intensive content analysis. European consumers are more skeptical of aggressive feature marketing and more sensitive to price increases. Regulations like GDPR impose compliance costs on AI systems that collect or process personal data, increasing development complexity.
European manufacturers have focused AI integration on privacy-respecting features: local processing-based picture quality enhancement, offline noise suppression, and mathematical audio processing rather than cloud-connected AI features. Pricing increases have been more modest, with manufacturers reluctant to price budget products at premiums that alienate cost-sensitive segments.
Asian Markets and Emerging Economies
In major Asian markets and emerging economies, budget segment dominates volume. Consumers are more price-sensitive and less willing to accept significant price increases for AI features. Manufacturers have pursued different strategies: some offer AI-featured products at aggressive pricing to drive adoption (particularly in China), while others maintain lower prices by omitting AI features or implementing minimal AI through software optimization of existing processors.
Content consumption patterns in emerging markets also differ, with cable and over-the-air television still significant. AI upscaling benefits from streaming sources, providing less compelling value for consumers relying on cable transmission or local broadcast, reducing manufacturer motivation for aggressive AI feature positioning.
Technology Deep Dive: What AI Actually Does in Budget Products
Understanding what AI features genuinely do in budget televisions and audio equipment requires examining the actual algorithms, processing approaches, and real-world performance implications.
Machine Learning Upscaling Algorithms
AI upscaling represents perhaps the most visible AI feature in budget televisions. The technology works by training deep neural networks on billions of image pairs—low-resolution sources and corresponding high-resolution reference images. The network learns to predict what high-resolution details should be reconstructed from low-resolution inputs.
These systems are trained using supervised learning where the network receives low-resolution input, generates a high-resolution prediction, and compares output to ground-truth high-resolution reference images. The network's weights are adjusted to minimize the difference between predicted and reference output. After training on diverse content (photographs, cinematography, digital art, mixed sources), the network generalizes to predict plausible high-resolution details from any low-resolution input.
The quality difference compared to traditional interpolation is substantial. Traditional upscaling merely duplicates or interpolates pixels mechanically. Machine learning upscaling analyzes patterns and context to predict realistic detail. A 720p video stream of a face upscaled through ML might generate realistic skin texture, hair detail, and eye definition that interpolation would miss entirely. For landscape photography, ML upscaling predicts tree foliage, grass texture, and distant detail with remarkable fidelity.
Budget television implementations often use pre-trained models from publicly available frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch) rather than developing proprietary models. This reduces development cost and achieves reasonable performance. However, it means manufacturers lack competitive differentiation through upscaling algorithms—all use similar underlying approaches and achieve comparable quality.
Voice Processing Pipeline
Voice assistance on budget televisions involves multiple processing stages deployed across local processors and cloud infrastructure. The local television processor performs wake-word detection, detecting specific phrases like "Alexa" or "OK Google" through simple neural networks consuming minimal power. This requires listening constantly without recording or transmitting audio.
Once wake-word detection triggers, the television records audio and transmits it to cloud servers where sophisticated speech recognition and natural language understanding occurs. Cloud-based processing handles complex speech recognition, semantic understanding, context retention across multiple utterances, and device control logic. The cloud-based approach is cost-effective for manufacturers since it offloads processing to cloud providers' infrastructure rather than requiring powerful local processors.
This architecture creates privacy concerns since audio must be transmitted to cloud servers. Some manufacturers offer local-only processing versions, running smaller natural language models entirely on-device, but this limits capability and requires more powerful local processors, increasing cost. Budget products typically employ the hybrid cloud-based approach despite privacy implications, since it minimizes hardware costs.
Spatial Audio Mathematics
Spatial audio processing that generates surround sound from stereo or mono sources relies on psychoacoustics—understanding how human hearing interprets audio spatial characteristics. The human auditory system determines sound direction through several cues: timing differences (sounds from the side reach one ear slightly before the other), frequency response differences (head shadowing affects high frequencies differently), and spectral characteristics (the ear's shape modifies high-frequency response depending on sound direction).
AI spatial audio systems analyze stereo audio and extract these directional cues, then synthesize surround channel information that creates convincing spatial illusions. The neural network is trained on spatial audio content with known directional characteristics, learning to identify patterns that correspond to specific sound directions and spatial positions.
For stereo music, the algorithm extracts directional information from phase differences, frequency balance differences, and other stereo characteristics, then generates convincing surround channels that expand the perceived sound field. The results are genuinely impressive—stereo recordings processed through AI spatial audio can produce convincing enveloping sound fields that feel three-dimensional.
Budget soundbars implement this through efficient neural networks running on basic processors. A Qualcomm Snapdragon processor in an affordable soundbar can execute spatial audio processing in real-time with minimal latency, delivering experiences approaching hardware-based surround systems costing significantly more.
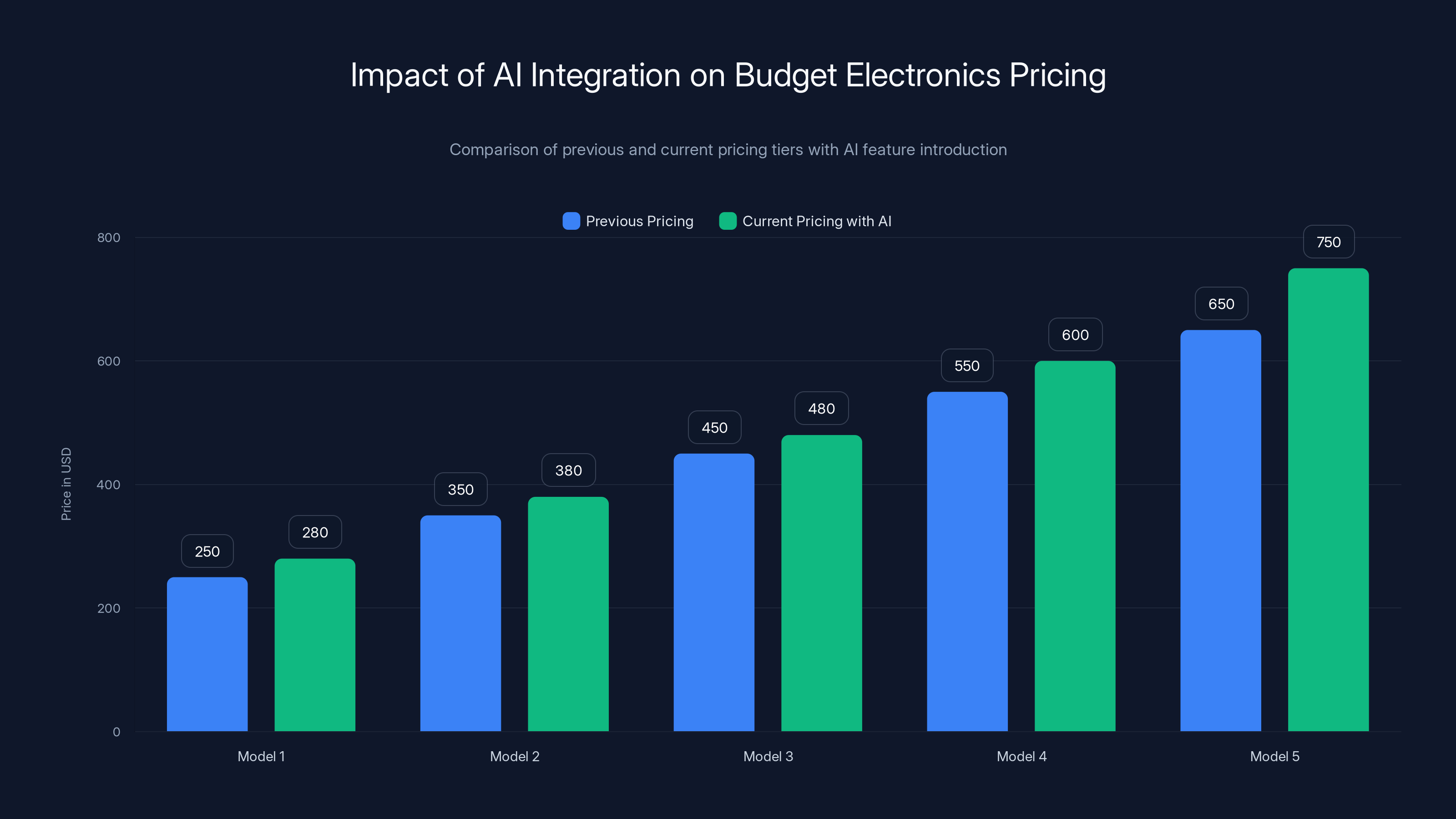
The introduction of AI features has led to a noticeable increase in pricing tiers for budget electronics, with AI capabilities starting at higher price points. Estimated data based on typical market adjustments.
Consumer Impact and Purchasing Implications
How AI integration in budget electronics affects actual consumer experiences and purchasing decisions requires examining real-world scenarios and practical implications.
Picture Quality Perception and Content Dependency
AI upscaling provides genuine picture quality improvements for specific content types and viewing scenarios. Consumers streaming Netflix, YouTube, or other compressed sources see substantial benefits—720p streams appear noticeably sharper, more detailed, and more visually appealing than non-upscaled display. For cable television or over-the-air broadcast transmission at 1080i resolution, benefits are less dramatic but still noticeable.
However, AI upscaling cannot improve extremely compressed or heavily degraded source material. A heavily compressed video call or low-bitrate stream might contain insufficient information for accurate detail prediction, resulting in artifacts or false details. The algorithm must handle content gracefully even when appropriate high-resolution reconstruction is genuinely ambiguous.
Consumers' perception of AI picture quality improvements depends heavily on their primary content consumption patterns. Cord-cutting households relying on streaming services perceive substantial benefits and justify higher prices. Traditional cable television viewers notice improvements but may not perceive sufficient benefit to justify price premiums. Understanding your content sources before purchasing becomes important for evaluating AI television value.
Voice Assistant Utility and Implementation Quality
Voice assistance implementation varies substantially between manufacturers despite similar underlying technologies. Some implementations are highly responsive with accurate command recognition across diverse accents, dialects, and speech patterns. Others struggle with recognition accuracy, require precise enunciation, or fail with background noise.
These differences reflect optimization quality rather than fundamental algorithmic differences. Manufacturers investing in extensive voice training data and quality assurance achieve superior results. Budget manufacturers sometimes deploy voice assistance quickly without sufficient optimization, resulting in frustrating user experiences that discourage ongoing use.
Consumers considering budget televisions with voice assistance should test the feature in-store with diverse speakers, different accents, and background noise present. Visual inspection of specifications tells little about practical utility—hands-on testing reveals implementation quality.
Soundbar Audio Quality and Listening Context
AI-powered spatial audio in soundbars delivers impressive results for specific listening contexts. In living rooms with typical reverberation and acoustic characteristics, spatial audio processing creates convincing surround sound perception. In small spaces with short reverberation times, or locations with unusual acoustics, results may be less convincing.
Importantly, spatial audio processing is optimized for movie and television content featuring cinematic spatial mixes. Music listening experiences from AI-processed stereo differ substantially from cinematic content. Some listeners find the spatial field expansion appealing; others find it artificial or distracting. Personal listening preference becomes the determining factor in whether AI spatial audio features justify premium pricing.
For audio equipment, personal audition in environments similar to your home becomes crucial. Retail demonstrations often use specific content and acoustic environments optimized to showcase AI features. Evaluating the same products in your home's acoustic environment might produce quite different perceptions.
Manufacturer-Specific Approaches and Positioning
Different manufacturers have pursued distinct strategies for AI integration in budget products, reflecting different corporate philosophies, engineering capabilities, and market positioning.
Samsung's Aggressive AI Positioning
Samsung has positioned AI as central to its budget television strategy, emphasizing AI upscaling under the "AI Picture Quality" brand across budget lines. Samsung developed proprietary neural network architectures optimized for its processors, allowing them to claim competitive differentiation in AI capabilities. Their approach prioritizes visible feature marketing—prominently featuring AI in advertising, packaging, and product names.
Samsung's execution benefits from massive R&D budgets and extensive manufacturing scale allowing them to absorb AI development costs across enormous production volumes. Budget Samsung televisions often incorporate more sophisticated AI features than competitors' mid-range products, creating strong value perception.
LG's AI Integration Philosophy
LG has taken a more selective approach, implementing AI features in specific product lines while maintaining pure hardware differentiation at the absolute budget extreme. LG's AI implementation focuses on picture quality, particularly tone mapping and HDR optimization, rather than comprehensive smart TV intelligence.
LG's strategy reflects confidence in their display technology superiority through IPS and OLED implementations, positioning AI as a complementary enhancement rather than core differentiation. This approach appeals to consumers prioritizing display quality and audiovisual performance over broad feature sets.
TCL and Chinese Manufacturer Strategies
TCL and other Chinese manufacturers have pursued aggressive AI feature integration combined with aggressive pricing. Their budget products often incorporate more AI features than competitors while maintaining lower price points, reflecting lower development cost bases and different market strategies.
Chinese manufacturers benefit from proximity to semiconductor suppliers and manufacturing centers, reducing supply chain costs. Lower labor costs reduce software development expenses relative to Western competitors. These cost advantages allow feature-rich AI implementation at price points Western manufacturers cannot match profitably.
Such pricing advantages are narrowing as Western manufacturers improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce development costs. However, in many markets, Chinese manufacturers maintain price leadership, particularly in true budget segments.
Premium Brand AI Strategies
Sony and Panasonic, traditionally focused on premium positioning, have implemented minimal AI features in budget products, preferring to differentiate through brand reputation and build quality. Their budget products often lack the comprehensive AI feature sets that cheaper competitors offer, positioning them as simpler, more reliable alternatives rather than feature-rich budget options.
This strategy appeals to consumers prioritizing reliability and brand trust over comprehensive features. Sony and Panasonic customers often remain loyal despite feature disadvantages, and these manufacturers maintain premium pricing by offering heritage, reliability, and customer service rather than competing on features.
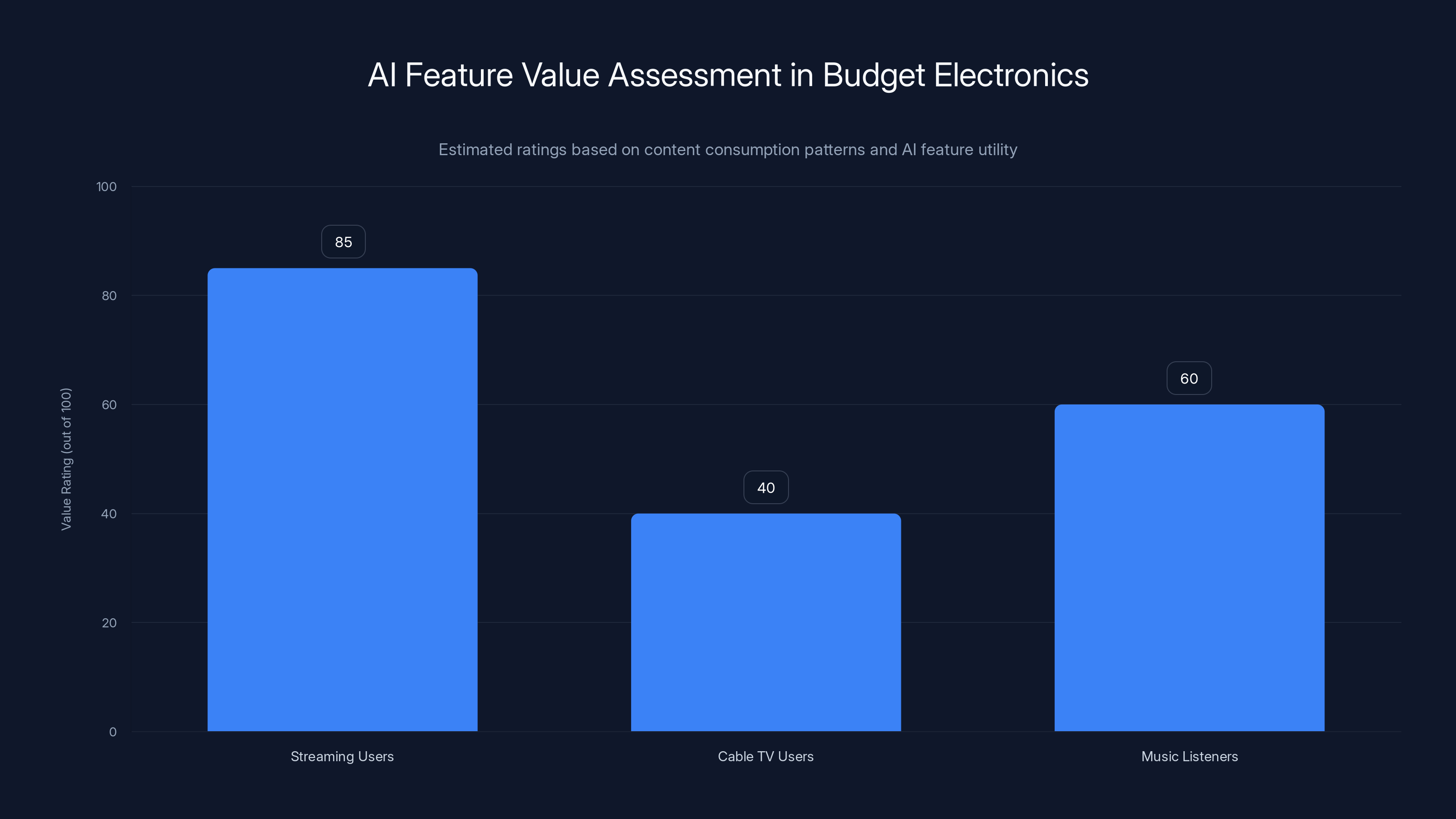
Estimated data suggests that AI features provide the most value to streaming users, with a high rating of 85 out of 100, compared to cable TV users who may not benefit as much.
Emerging Challenges and Quality Concerns
As AI integration becomes standard in budget products, certain challenges and quality concerns are emerging that impact long-term consumer satisfaction and product sustainability.
Model Obsolescence and Software Support
Machine learning models embedded in consumer electronics products have finite lifespans. As new content types emerge, encoding standards evolve, and customer use cases shift, models trained on historical data may perform increasingly poorly. A model trained on 2023 streaming content and compression standards might struggle with new streaming technologies or emerging content formats in 2025.
Unlike smartphones where software updates are expected and regularly deployed, television and audio equipment receive minimal post-purchase updates. Many budget products receive no meaningful updates after the first year. Consumers purchasing AI-equipped budget products today may find AI features degrading in quality as content landscapes change, with no mechanism to update the underlying models.
This creates a troubling scenario where newly purchased AI-equipped devices feel increasingly outdated not because hardware degrades, but because software models become unoptimized for current content. Manufacturers must address this through long-term update commitments, but budget products rarely receive such commitments.
Generalization Failures and Edge Cases
Machine learning models trained on diverse datasets sometimes fail in predictable ways when encountering unusual content, novel situations, or edge cases. A upscaling model trained on photographic and cinematographic content might produce artifacts when processing computer graphics, technical documentation, or unusual content types.
Budget products sometimes encounter these failures shortly after purchase as consumers discover use cases the development team didn't thoroughly test. Initial enthusiasm for AI features can transform to frustration when predictable failure modes become apparent.
Processor Thermal and Power Constraints
Neural network inference on processors designed for other purposes consumes disproportionate power and generates significant heat. Budget televisions and audio equipment use processors with limited thermal dissipation capabilities, constraining how intensively AI models can run continuously.
Many implementations use reduced-complexity models or limit AI processing to specific situations (pausing it during heavy processing or in thermal stress conditions) to manage power and thermal constraints. These limitations sometimes aren't apparent until after purchase, when consumers discover AI features disable themselves under normal usage conditions.

Future Trajectory and Long-Term Market Evolution
The current AI integration trajectory in budget electronics appears to have clear long-term patterns, though near-term volatility is substantial.
Component Cost Maturation Timeline
Neural processing capabilities for consumer electronics are undergoing rapid cost reduction similar to trajectories of previous technologies. Custom silicon costs will decline 20-30% annually as production volumes scale, component designs mature, and manufacturing processes improve. Current manufacturers' AI implementation costs will halve within 18-24 months as economies of scale activate.
This cost reduction will reduce pressure on budget product pricing. By 2026, AI upscaling, voice assistance, and spatial audio processing might be standard in
Feature Standardization and Differentiation Shifts
As AI features become standard across competitors, manufacturers will lose differentiation advantage, shifting competition toward other factors: picture quality, reliability, software update frequency, customer service, ecosystem integration, and design. AI will become a table-stakes feature rather than a premium differentiator.
This pattern followed previous technological innovations: surround sound, high-definition resolution, and smart TV functionality all eventually became standard. Budget products will incorporate comprehensive AI functionality while manufacturers differentiate through other advantages.
Software Update Commitments
Emerging competitive pressure will likely push manufacturers toward longer software update commitments for budget products. As consumers become more sophisticated about software support implications, manufacturers offering 3-5 year update commitments will gain competitive advantage over those offering minimal updates.
This shift will improve long-term product viability, reducing concerns about model obsolescence and improving consumer satisfaction with budget purchases.
Content Industry Adaptation
Content producers will increasingly optimize for AI processing capabilities, just as they currently optimize for specific resolution, frame rate, and compression standards. Streaming services might encode content specifically for optimal AI upscaling, music producers might mix content optimized for AI spatial processing, and filmmakers might produce content suited to AI tone mapping.
This co-evolution of AI algorithms and content production will create virtuous cycles where each advancement enables better utilization of capabilities, maximizing user experience improvements.
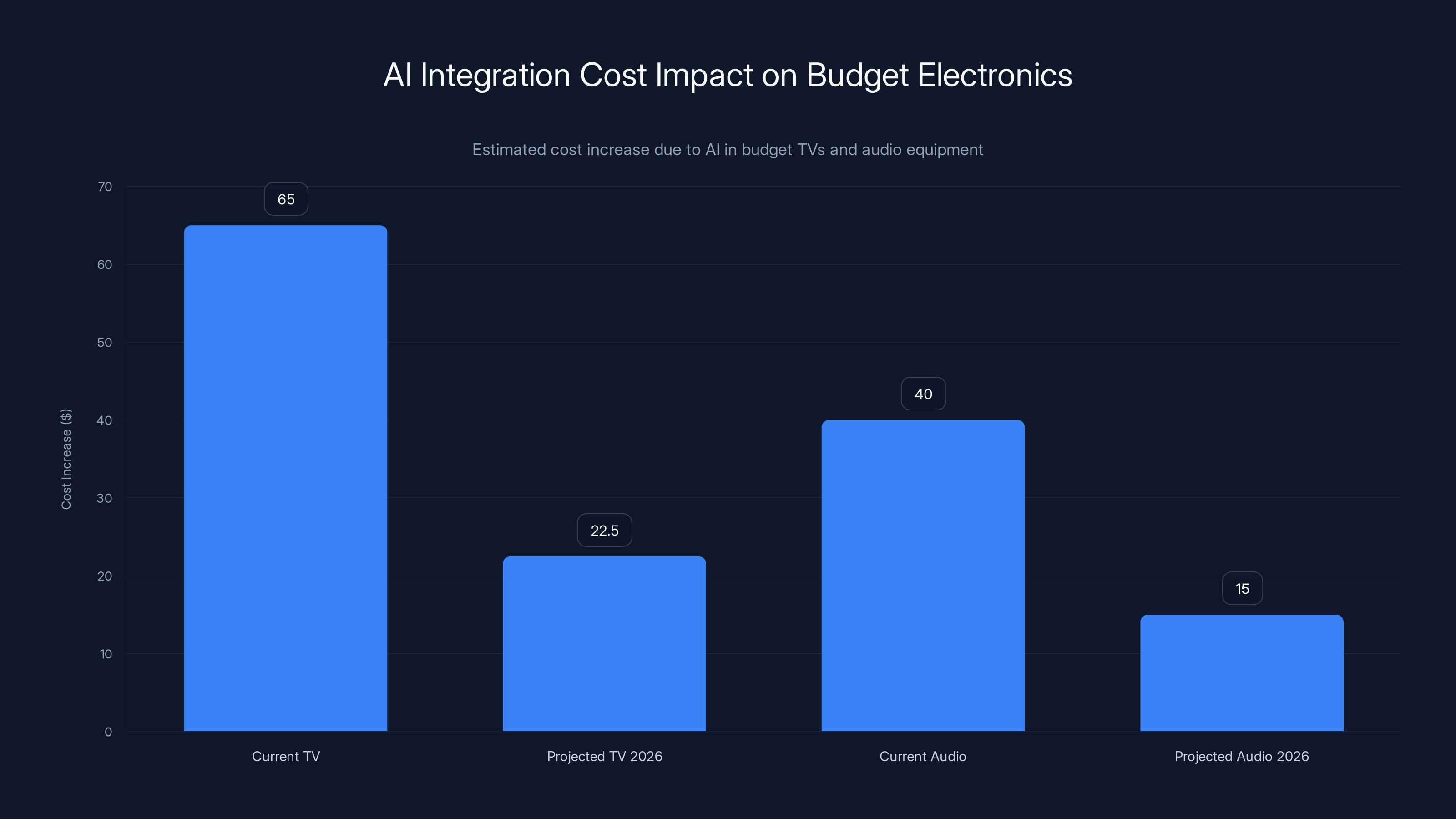
AI integration currently adds
Practical Guidance for Budget-Conscious Consumers
Navigating today's AI-integrated budget electronics market requires understanding value propositions, realistic feature assessment, and aligned purchasing decisions.
Evaluating AI Features in Your Use Case
Content Consumption Pattern Analysis: Before purchasing AI-equipped budget products, audit your actual content sources. Cord-cutting households streaming 80%+ of content derive substantial value from AI upscaling. Cable television viewers will notice less benefit. Music listeners should evaluate whether AI spatial audio aligns with listening preferences before accepting premium pricing.
Testing Procedures: Always test AI features in-store with content and scenarios matching your home usage. Request the salesperson test voice assistance with varied speakers, accents, and background noise. Listen to spatial audio processing with music samples matching your listening habits. Request playing content you actually watch regularly rather than manufacturer demonstration videos optimized to showcase features.
Implementation Quality Assessment: Don't assume identical feature names indicate identical performance across brands. Implementation quality varies substantially. Ask for detailed specifications of AI processors, model update frequencies, and local versus cloud processing approaches. These details reveal implementation sophistication.
Price-to-Value Calculations
Price Premium Attribution: When comparing products, identify the specific price premium attributable to AI features. A
Future-Proofing Considerations: Budget products lacking AI features now may feel increasingly outdated as content and services optimize for AI-enhanced viewing. However, content will remain accessible through non-AI devices indefinitely. Evaluate whether paying for future-proofing aligns with your replacement cycle expectations.
Total Cost of Ownership: Consider long-term total cost including maintenance, repairs, and replacement probability. AI-equipped products from reliable manufacturers may have better longevity through software updates, improving true cost per year of useful ownership.
Recommended Product Selection Approaches
For streaming-dominant households: Prioritize AI upscaling capability, even if it requires accepting higher prices or smaller screen sizes. AI upscaling delivers genuine quality improvements for your primary content source. Voice assistant capability is valuable secondary consideration if it aligns with your smart home ecosystem.
For cable television households: Evaluate AI features skeptically. Picture quality improvements will be less dramatic than streaming-focused use. Prioritize traditional quality factors: panel technology, brightness, color accuracy. If purchasing AI-equipped models, focus on reliability and update commitment rather than expecting transformative feature improvements.
For audio equipment: Test spatial audio processing in your listening environment, matching test content to your music and movie preferences. Prioritize implementation reliability—consistent performance across content types—over pure feature comprehensiveness. Noise suppression features matter primarily for communication use cases (headsets, speakerphone); evaluate honestly whether you need this capability.
For portable audio: Battery life and durability often matter more than advanced AI features. Evaluate whether AI features justify cost premium and whether they function reliably across your usage scenarios before committing to purchase.
Long-Term Ownership Perspectives
Budget electronics purchased today will likely receive minimal software updates in years 2-3 of ownership. Purchase with this expectation—don't assume AI features will improve substantially post-purchase through updates. Consider whether current feature implementation meets your needs without expecting future improvements.
Build replacement scenarios into purchase decisions. If planning to replace the product within 3-4 years, AI features matter less than if planning 5+ year ownership. Technology evolves rapidly; budgeting for earlier replacement reduces pressure on current features matching long-term expectations.
Consider brand update track records. Manufacturers with proven histories of extended software support for budget products deserve preference, even at modest price premiums. This investment in longevity translates directly to retained feature functionality over the ownership period.

Alternative Approaches and Competitive Solutions
Budget-conscious consumers seeking picture quality, audio capability, or smart functionality have alternatives to AI-integrated devices that sometimes offer compelling value.
Software-Based Enhancement Without Hardware AI
External streaming devices—Apple TV, Google Chromecast, Roku, Amazon Fire TV—incorporate sophisticated AI processing on the streaming device rather than the television. Connecting a smart streaming device with built-in AI upscaling and processing to any television delivers AI-enhanced picture quality without requiring an AI-equipped television.
This approach appeals to consumers with existing televisions they're satisfied with, or those seeking to upgrade smart capabilities without purchasing new televisions. A
For teams and organizations looking to systematize and streamline technology selection across multiple devices, automation platforms like Runable provide centralized management of smart devices, document generation for specifications, and workflow automation around device evaluation and procurement. This systematic approach helps large organizations make consistent purchasing decisions aligned with organizational standards and budgets.
Non-AI Quality-Focused Approaches
Manufacturers prioritizing display technology quality—panel selection, brightness, color accuracy, contrast ratio—sometimes offer superior overall picture quality despite lacking AI features. A quality IPS panel with 400 nits brightness might deliver better images than a mediocre VA panel with AI upscaling that can't achieve comparable brightness or color volume.
Evaluating display fundamentals—panel technology, brightness, color gamut coverage, contrast ratio—sometimes reveals that traditional quality factors matter more than AI features for specific viewing conditions. OLED televisions, for instance, achieve exceptional contrast through pixel-level control, making AI upscaling less critical than on LCD panels with limited contrast.
Used and Refurbished Premium Products
Budget constraints sometimes obscure better value in used or refurbished premium products than new budget alternatives. A refurbished 4-year-old premium television at
Refurbished audio equipment, particularly higher-end soundbars and receivers, similarly often represents better value than entry-level new products. Consumer electronics depreciation is substantial; previous-year premium models often represent exceptional value when purchased secondhand.

Key Takeaways for Navigating the AI-Equipped Budget Electronics Market
The integration of artificial intelligence into budget televisions and audio equipment represents a significant technological shift with real implications for pricing, capability, and consumer choice. Several core principles help navigate this complex landscape:
First, understand that AI features deliver genuine quality improvements for specific content types and use cases. AI upscaling meaningfully enhances streaming content, spatial audio provides convincing surround sound from limited speaker arrays, and voice processing enables convenient control. These aren't purely marketing features—they represent legitimate technological advances.
Second, recognize that AI integration is increasing budget product prices by $30-100 currently, though this premium will compress substantially as component costs mature. Evaluate whether current premiums align with your specific use cases and content consumption patterns. Premium prices are justified for streaming-dominant households; less justified for cable television viewers.
Third, acknowledge that implementation quality varies substantially across manufacturers. Identical feature names don't guarantee identical performance. In-store testing and research into specific processor choices, model architecture, and update commitments reveal actual implementation sophistication.
Fourth, understand that long-term software support for budget products remains limited. Don't purchase expecting AI features to improve substantially post-purchase. Purchase only if current implementation meets your needs.
Fifth, consider that cost-effective alternatives exist for accessing AI-enhanced picture quality and audio capability without purchasing fully AI-integrated products. Streaming devices with AI processing, quality-focused non-AI displays, and refurbished premium products sometimes represent better value than new AI-equipped budget options.
The AI explosion in budget electronics is genuine and consequential, delivering real capability improvements while simultaneously creating pricing pressure that ripples through consumer choice. Understanding these dynamics empowers informed purchasing decisions aligned with authentic needs rather than feature hype or marketing positioning.

FAQ
What specific AI technologies are most common in budget televisions?
The most prevalent AI technologies in budget televisions are neural network-based picture upscaling (using deep learning to enhance low-resolution source material to near 4K quality), voice assistant processing (for hands-free control), and intelligent tone mapping (AI algorithms optimize HDR content for specific display capabilities). These three capabilities account for the majority of AI implementation in budget segments, with some manufacturers adding more advanced features like game detection, content recommendation optimization, and frequency-specific color adjustment through machine learning.
How much does AI integration typically increase the price of budget televisions and audio equipment?
Current AI integration adds approximately
Which budget television manufacturers have the most sophisticated AI implementations?
Samsung, LG, TCL, and Hisense lead in budget television AI sophistication, though their approaches differ. Samsung emphasizes AI picture quality with proprietary upscaling algorithms, LG focuses on intelligent tone mapping and HDR optimization, while TCL aggressively bundles comprehensive AI features at competitive pricing. Implementation quality varies considerably—evaluation should focus on specific processor types, update commitment frequency, and honest in-store testing rather than brand assumptions. Smaller or regional manufacturers sometimes offer excellent AI implementation despite lower brand recognition, making hands-on evaluation important.
Will AI features in budget products require frequent software updates to remain effective?
AI features in budget products will eventually benefit from software updates but currently receive minimal post-purchase updates. Most budget televisions and audio equipment receive one or two software updates in the first year, then minimal attention after that period. However, this situation is changing as manufacturers recognize software support competitive advantages. Premium brands are beginning to commit to 3-5 year update schedules for budget products, improving long-term model relevance. Plan purchases assuming minimal updates, but evaluate manufacturer update track records—those with proven commitment to extended support deserve preference despite modest price premiums.
How do I determine whether AI features in budget audio equipment actually improve sound quality for my listening preferences?
Personal audition in your home's acoustic environment is essential, as retail demonstrations often use specific content and optimized acoustics. Test spatial audio with music matching your actual listening habits—the technology works well for cinematic surround mixes but can sound artificial for certain music genres. Test noise suppression with recording from environments you actually use (home office, coffee shop, car). Request extended demo periods where possible, allowing several days of home use before purchase commitment. Unlike specifications, audio quality perception is entirely subjective; features justified for one listener might be wasted for another with different preferences.
Can I achieve comparable AI image enhancement with a smart TV streaming device instead of purchasing an AI-equipped television?
Yes, absolutely—external streaming devices like Apple TV, Google Chromecast, and Roku now incorporate sophisticated AI upscaling that delivers comparable picture quality improvements to dedicated television AI systems. For consumers with existing televisions they're satisfied with, adding a $50-150 smart streaming device with AI capabilities often provides better value than replacing the television entirely. This approach works particularly well for streaming-focused content consumption. However, this method requires the smart device to remain connected between the content source and television, and introduces additional equipment into home theater setups. Direct television AI integration provides more seamless experience but at higher cost.
What happens to budget television and audio product performance as AI models become outdated?
As machine learning models age and content landscapes shift, pre-trained models optimized for 2024-era content may perform increasingly suboptimally for future content types and encoding standards. For example, if new streaming compression standards emerge that the fixed AI model wasn't trained on, performance degrades. This obsolescence is more pronounced in budget products receiving no software updates. However, graceful degradation typically occurs—features don't disappear entirely but may perform less impressively. You won't suddenly have non-functional devices, but over 4-5 year ownership, AI features may feel increasingly dated and less optimized for current content. Manufacturer software update commitment history is valuable predictor of long-term AI feature relevance.
How do AI-powered features in budget products compare to premium products' AI implementations?
Budget and premium products often use fundamentally similar AI technologies—same neural network architectures, similar machine learning frameworks, comparable algorithms—but premium products invest in model sophistication, larger training datasets, more extensive optimization, and better hardware support for efficient inference. A
Are there significant differences in AI implementation between Chinese and Western manufacturers in the budget segment?
Yes, meaningful differences exist reflecting different engineering priorities and cost structures. Chinese manufacturers often integrate more comprehensive AI features in budget segments while maintaining lower prices through lower development cost bases and manufacturing efficiency advantages. Western manufacturers frequently implement AI more selectively, sometimes omitting certain features from budget products entirely. Chinese implementations are increasingly sophisticated and reliable, though consistency varies across brands. The differentiation continues narrowing as Western manufacturers improve efficiency and Chinese manufacturers expand globally, facing more stringent quality expectations. Evaluate specific products individually rather than assuming quality based on manufacturer origin.
What should budget-conscious consumers prioritize when choosing between AI-equipped and non-AI products?
Prioritization depends entirely on authentic use cases and content consumption patterns. Streaming-dominant households should prioritize AI upscaling capability even at price premiums, as genuine quality improvements justify premium costs. Cable television viewers should evaluate AI features more skeptically, focusing on traditional quality factors instead. For audio, test spatial audio in your listening environment with your music preferences; don't assume industry hype applies to your personal situation. Consider your replacement timeline—products purchased for 3-4 year ownership cycles matter less about future software support than longer-term commitments. Budget available for products, then evaluate feature packages offering best value for your specific situation rather than feature comprehensiveness or brand prestige.

Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions in Today's AI-Integrated Electronics Market
The artificial intelligence revolution in budget consumer electronics represents both genuine technological advancement and significant market disruption. Unlike discussions of AI transforming premium segments—where consumers expect continuous innovation and accept escalating costs—AI's infiltration into budget markets creates more complex economics and more nuanced consumer implications.
The fundamental tension driving this market transformation is clear: AI capabilities require substantial development investment, specialized hardware, sophisticated software engineering, and ongoing maintenance. Yet the budget market demands lower prices than ever before. Manufacturers attempting to balance these contradictory demands are reshaping product lineups, adjusting pricing strategies, and fundamentally altering what capabilities consumers receive at each price point.
We've examined how neural processing units and custom silicon development increase manufacturing costs, how software complexity escalates development overhead, and how supply chain changes amplify production challenges. We've analyzed specific AI implementations in televisions—upscaling, HDR tone mapping, voice processing—and in audio equipment—spatial processing, noise suppression, adaptive EQ—demonstrating that these features deliver genuine capability improvements despite occasional marketing hyperbole.
Regional variations in AI adoption reflect different consumer expectations, regulatory environments, and manufacturer strategies. North American markets have embraced AI features most enthusiastically, resulting in more substantial price increases. European markets show greater skepticism, particularly around privacy implications. Emerging markets prioritize price competitiveness over feature comprehensiveness.
Manufacturer-specific strategies reveal different approaches to this market transformation. Samsung aggressively positions AI as central differentiator, LG implements AI selectively while prioritizing display technology, Chinese manufacturers bundle comprehensive features at competitive pricing, while premium brands maintain selective positioning. No single strategy has emerged as definitively optimal—different approaches resonate with different consumer segments.
The practical implications for budget-conscious consumers are substantial but navigable. Understanding that AI features deliver genuine value for specific use cases—particularly streaming content consumption—helps evaluate whether price premiums are justified. Recognizing implementation quality variation encourages hands-on evaluation rather than feature name comparison. Acknowledging limited post-purchase software support for budget products manages expectations about long-term feature evolution.
Alternative approaches deserve serious consideration: streaming devices with integrated AI upscaling, quality-focused non-AI displays, and refurbished premium products sometimes provide superior value than new AI-equipped budget products at seemingly cheaper price points. The presence of alternatives ensures consumers aren't forced to accept AI integration at arbitrary price premiums.
Looking forward, the trajectory is predictable though timeline remains uncertain. Component costs for neural processing will decline substantially as manufacturing scales and competition intensifies. Within 24-36 months, AI capabilities expected to justify $50-100 premiums today will become standard in budget segments at minimal additional cost. AI features will transition from differentiators to table-stakes capabilities. Manufacturers will shift competitive emphasis toward other factors: reliability, software update longevity, ecosystem integration, design, and customer service.
This inevitable cost reduction will democratize AI technology further, extending capabilities to even lower price points. The features exciting consumers today as premium differentiators will become baseline expectations. This pattern has repeated throughout electronics history: surround sound, high-definition resolution, smart connectivity, all eventually became standard across price segments.
The current moment represents a transition period where AI integration is sufficiently mature to deliver real functionality yet sufficiently novel to command premium pricing. For consumers navigating this transition, the principles outlined in this analysis—authentic use case evaluation, hands-on feature testing, realistic software support expectations, and consideration of alternative approaches—provide frameworks for making informed decisions aligned with genuine needs rather than marketing momentum.
The AI explosion in budget electronics is neither purely beneficial nor problematic—it represents technological maturation creating both opportunities and challenges. Informed consumers who understand the underlying economics, implementation approaches, and practical limitations can make purchasing decisions that deliver genuine value. Those purchasing reactively, assuming AI features represent unambiguous improvement, risk overpaying for capabilities misaligned with actual needs.
As this market continues evolving, maintaining this informed, skeptical approach remains essential. Technology should serve consumer needs, not the reverse. The most sophisticated purchasing decision involves honest assessment of what you actually watch, how you listen, what features matter for your lifestyle, and whether price premiums deliver value for your situation. Everything else—marketing positioning, feature comprehensiveness, brand prestige—should remain secondary to this fundamental consumer-centric evaluation.
The electronics market will continue transforming as AI matures and costs decline. Consumers who understand these dynamics, evaluate products skeptically, and prioritize authentic needs over feature marketing will consistently make better purchasing decisions regardless of how technology markets evolve. This analytical framework transcends specific products or companies, providing lasting value as the technology landscape continues shifting.

Related Articles
- Framework Desktop PC Price Hike: Why RAM Costs Are Crushing PC Builders [2025]
- How to Train AI SDRs That Actually Work: Clone Your Best Human [2025]
- AI PCs Are Reshaping Enterprise Work: Here's What You Need to Know [2025]
- Samsung TV Price Hikes: AI Chip Shortage Impact [2025]
- Best Soundbars of 2026: Dolby Atmos FlexConnect & Premium Audio [2026]
- AirPods Pro 3 Hit Record-Low Price: Save $50 on Apple's Best [2025]




