CES 2026: The Year AI and Hardware Converged at Scale
CES 2026 marked a pivotal moment in technology history—not because of one breakthrough, but because of the convergence of AI adoption across every hardware category imaginable. The Consumer Electronics Show, held annually in Las Vegas, served as the industry's stage for demonstrating how artificial intelligence had moved beyond data centers and into the hands of consumers, manufacturers, and enterprises alike.
When industry watchers analyze technology inflection points, they often point to specific moments: the launch of the iPhone, the rise of cloud computing, or the introduction of GPUs to mainstream computing. CES 2026 may very well become one of those moments. What made this year's show different wasn't necessarily that groundbreaking products were announced, but rather that the maturation of AI technology had created an ecosystem where innovation could flourish across autonomous vehicles, household appliances, construction equipment, robotics, and consumer electronics simultaneously.
The show floor opened to the public following an intense schedule of press conferences and keynotes from technology giants. Major manufacturers used their platforms to demonstrate how they were integrating AI into their product roadmaps, with some focusing on custom silicon designed specifically for AI workloads, others emphasizing software partnerships, and still others highlighting the convergence of robotics and intelligent systems.
For developers and technology teams evaluating new tools and platforms, CES 2026 highlighted an important trend: the acceleration of automation technology across every industry vertical. This expansion has created new opportunities for teams seeking to automate workflows, generate content, and scale operations without proportional increases in headcount. Understanding what was announced at CES 2026 provides crucial context for making informed decisions about which technologies to adopt, which partnerships to pursue, and how to position your organization for the next wave of AI-driven transformation.
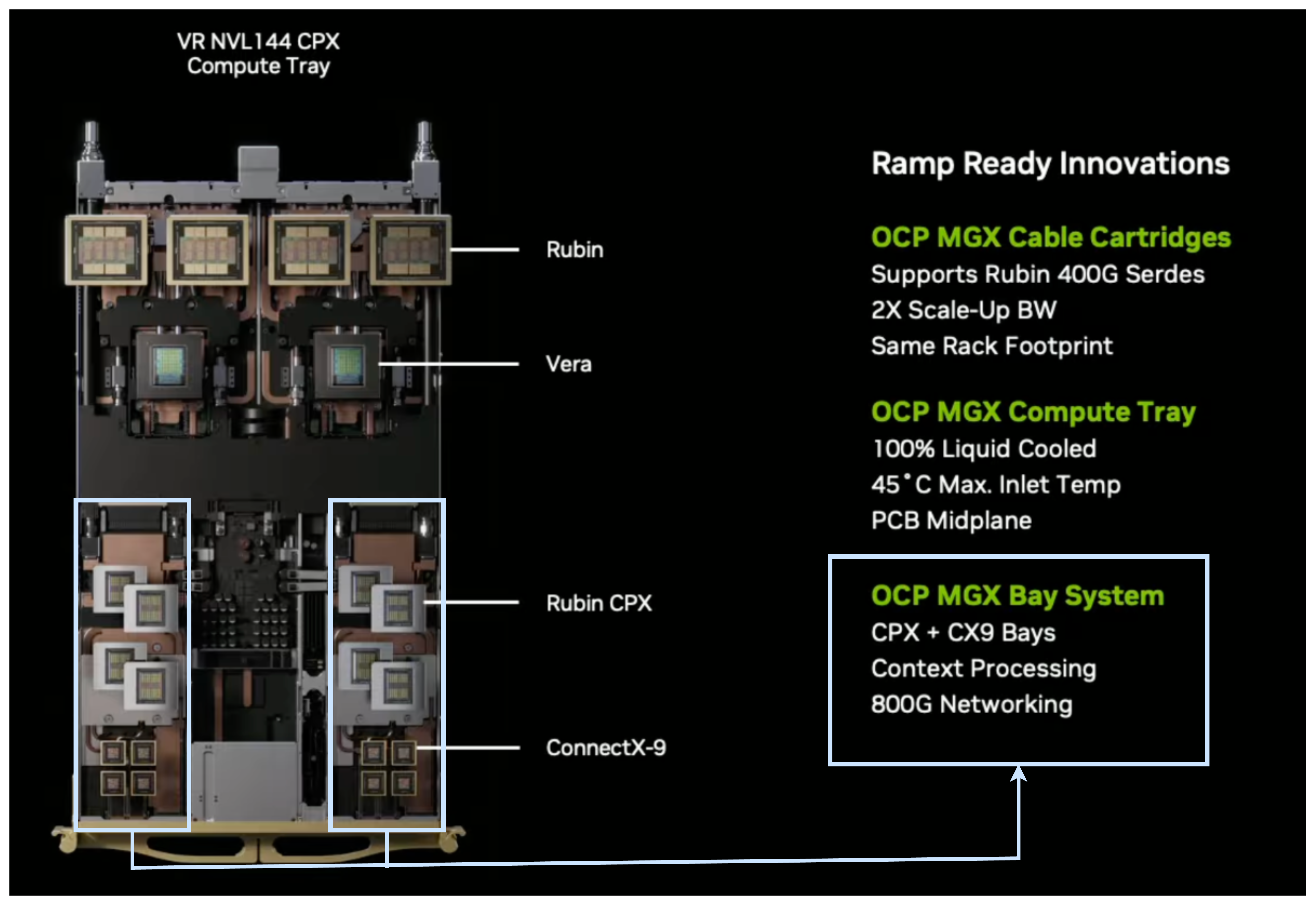
Nvidia's Rubin Architecture: The Next Generation of AI Computing Power
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang's keynote presentation at CES 2026 was, as expected, a comprehensive showcase of the company's strategic vision for the coming years. The star of the presentation was the announcement of the Rubin computing architecture, designed as the successor to the company's current-generation Blackwell architecture. This transition represents a significant engineering accomplishment and signals where Nvidia believes the compute demands of artificial intelligence are heading.
Understanding the Rubin Architecture's Design Philosophy
The Rubin architecture was engineered specifically to address what Nvidia has identified as the core bottleneck in AI systems: the gap between computational speed and data movement. While previous generations of chips had focused on raw processing power, Rubin takes a more balanced approach, increasing both compute capabilities and memory bandwidth proportionally.
The architecture introduces several technical innovations that are particularly relevant for teams running large-scale AI workloads. First, memory bandwidth improvements allow for faster data movement between the GPU and system memory, reducing the time processors spend waiting for data. Second, improved cache hierarchies mean that frequently accessed data can be stored closer to processing cores, reducing latency. Third, the architecture introduces new specialized tensor cores designed for specific AI operations, allowing them to complete in fewer clock cycles than previous generations.
From a practical standpoint, these improvements translate to tangible benefits for organizations running AI models. A model that took 100 hours to train on current infrastructure might complete in 70-75 hours on Rubin-based systems, depending on the workload. This 25-30% improvement in training speed compounds across the thousands of models being trained annually, translating to significant cost savings and faster time-to-market for AI-powered products.
Timeline and Integration Path for Rubin
Huang announced that Rubin would begin shipping in the second half of 2026, with expected volume production ramping through 2027. This timeline is important for organizations planning their infrastructure investments. The existing Blackwell generation will continue to be manufactured and sold, likely at reduced pricing as inventory shifts toward the newer architecture.
For teams currently evaluating GPU investments, this creates a strategic decision point. Organizations seeking maximum performance for new projects should consider waiting for Rubin availability, while those with immediate needs might find Blackwell offerings increasingly attractive at lower price points as Nvidia clears existing inventory.
Alpamayo: Bringing AI to Autonomous Vehicles
Beyond the Rubin announcement, Nvidia showcased its Alpamayo family of AI models and tools, specifically designed for autonomous vehicle development. Rather than creating a single monolithic model, Alpamayo represents a family of open-source models optimized for different aspects of autonomous driving—perception, prediction, planning, and control.
The significance of Alpamayo lies in Nvidia's strategic positioning. By open-sourcing these models, the company is following the Android playbook: create a reference implementation that manufacturers can build upon, customize, and improve. This approach creates an ecosystem where Nvidia benefits from increased adoption of its hardware (since these models are optimized to run on Nvidia processors) while allowing manufacturers the flexibility to differentiate their autonomous systems.
The Broader Robotics Vision
Throughout the keynote, Huang emphasized Nvidia's commitment to making AI infrastructure "the Android for generalist robots." This phrasing signals a fundamental shift in how Nvidia views its business. Rather than solely as a chip manufacturer, Nvidia is positioning itself as the foundational platform upon which the robotics revolution will be built.
This vision has profound implications for the technology landscape. If successful, Nvidia's software stack, middleware, and development tools become as important as the hardware itself. Organizations investing in Nvidia's ecosystem today are not just purchasing chips; they're positioning themselves for the robotics wave that Huang believes will define the coming decade.

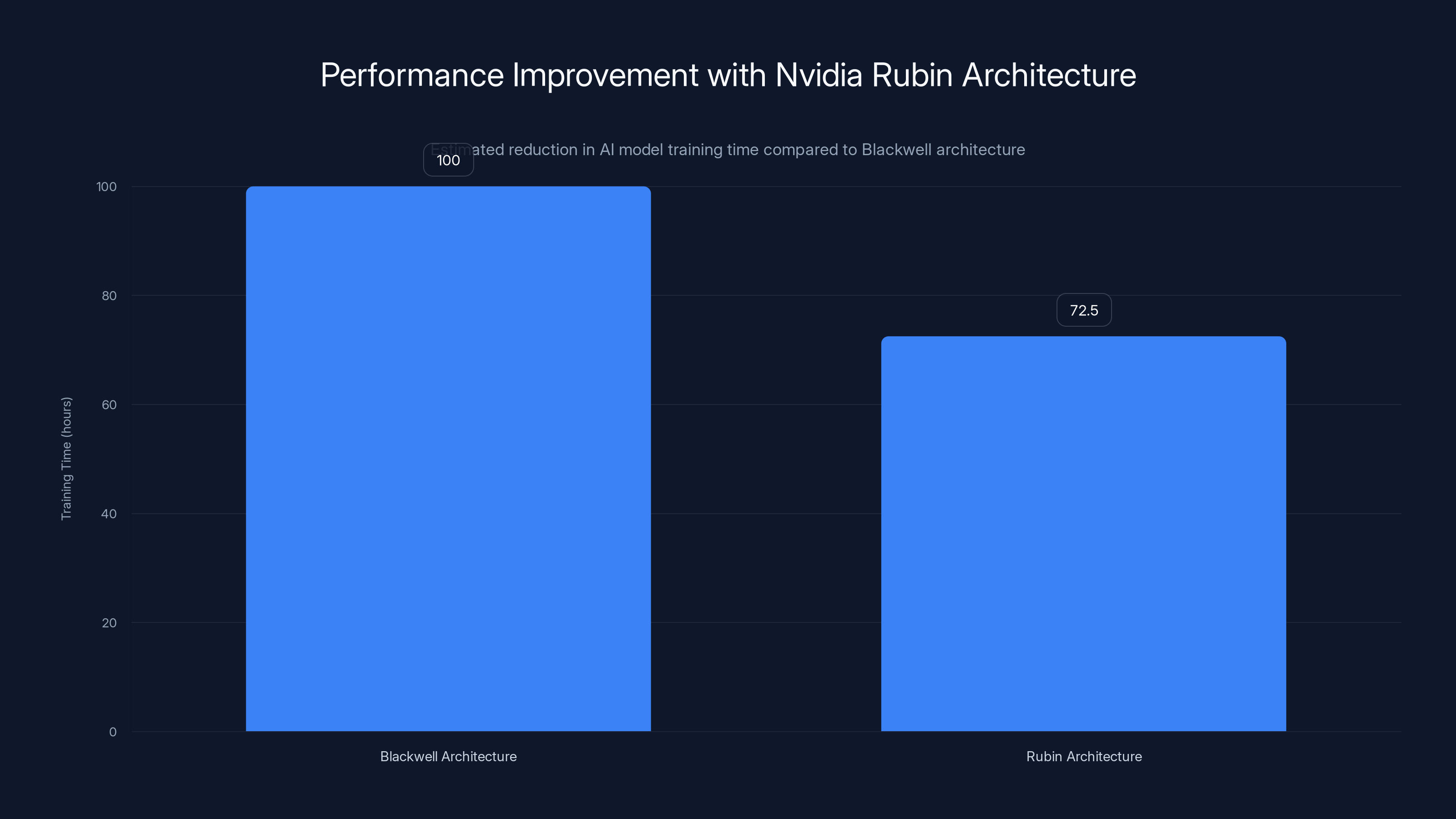
The Rubin architecture offers a 25-30% reduction in AI model training time compared to the Blackwell architecture, significantly enhancing efficiency. Estimated data.
AMD's Ryzen AI 400 Series: Democratizing AI at the Edge
AMD Chair and CEO Lisa Su opened CES 2026 with a keynote that took a notably different approach from Nvidia's vision. While Nvidia focused on data center-scale computing, AMD's presentation centered on bringing AI capabilities to personal computers and edge devices—the laptops, desktops, and embedded systems used by millions daily.
The Ryzen AI 400 Series Architecture
The Ryzen AI 400 Series processors represent AMD's answer to the question: how do we bring meaningful AI capabilities to consumer devices without requiring internet connectivity or access to powerful cloud services? The answer involves integrating specialized AI accelerator blocks directly into the processor alongside traditional CPU cores.
Unlike Nvidia's approach, which typically requires dedicated GPUs for AI workloads, AMD's solution integrates AI computation into the main processor die. This integration offers several advantages: reduced power consumption, improved latency (since data doesn't need to travel across separate memory hierarchies), and simplified system design for manufacturers.
Technically, the Ryzen AI 400 achieves this through a combination of strategies. First, the processors include dedicated NPUs (Neural Processing Units) capable of handling AI inference at speeds comparable to discrete solutions while consuming a fraction of the power. Second, the memory subsystem has been optimized for the access patterns typical of neural networks. Third, the instruction set includes new AI-specific instructions that allow certain operations to complete in fewer clock cycles.
On-Device AI: Privacy and Performance Implications
One of the most significant implications of AMD's approach is the shift toward on-device AI processing. Models running locally on a user's device offer distinct advantages: personal data remains private, latency is eliminated, and the system works offline. For sensitive applications like medical records analysis, financial planning tools, or personal productivity software, on-device processing represents a substantial privacy improvement.
AMD's keynote highlighted partnerships with software vendors eager to take advantage of these capabilities. Productivity software companies can now embed AI features—intelligent document summarization, image recognition, voice transcription—directly in their applications without requiring cloud connectivity. This shift has profound implications for how software is designed and distributed.
Market Positioning Against Nvidia
While Nvidia's data center-focused strategy targets the largest organizations and highest-performance workloads, AMD's personal computer approach targets a vastly larger addressable market. Billions of PCs will be sold in the coming years, and AMD's integration of AI capabilities directly into these devices means that AI-powered applications will become the default for consumers, whether they actively pursue them or not.
This creates an interesting competitive dynamic. Nvidia might own the high-end AI infrastructure market, but AMD could win by making AI ubiquitous at the consumer level. For organizations building AI applications, this suggests a future where users have local AI capabilities and cloud AI capabilities, and the optimal architecture involves coordinating between the two.
Strategic Partnerships and Ecosystem Building
AMD's keynote featured prominent partners including OpenAI, AI legend Fei-Fei Li, and Luma AI CEO Amit Jain. These partnerships signal AMD's strategy: rather than developing AI software in isolation, the company is positioning itself as the hardware platform for software vendors who are building the actual AI applications users care about.
This partnership approach differs strategically from Nvidia's more vertically integrated strategy. Where Nvidia develops its own software stacks and pushes them into the market, AMD is enabling third parties to build on top of Ryzen AI capabilities. For developers and organizations, this means more software options and less vendor lock-in—though it also means more fragmentation in how to optimize for AMD's platform.

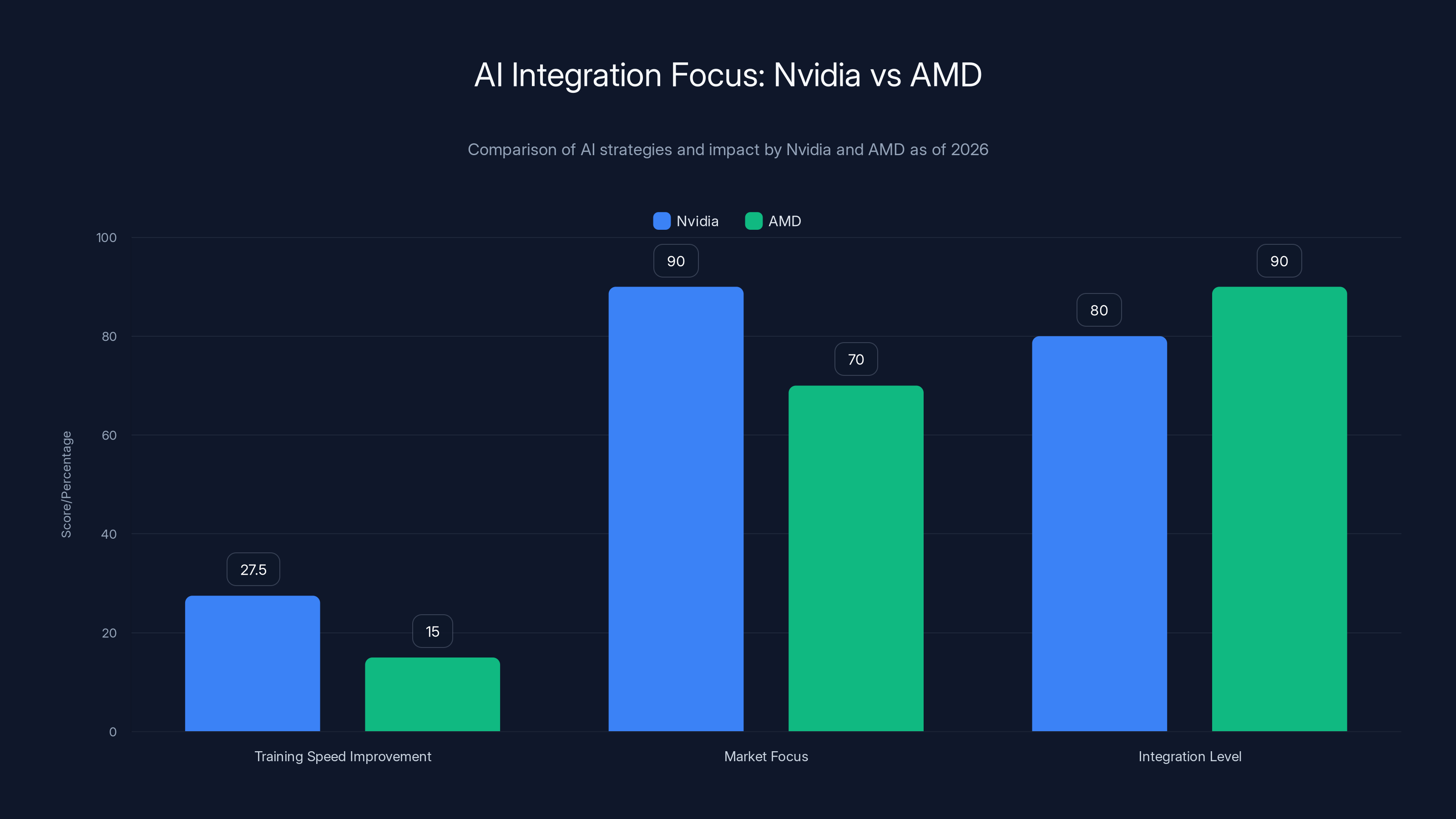
Nvidia's Rubin architecture offers a 25-30% improvement in AI training speed, focusing on data centers, while AMD targets consumer devices with high integration levels. Estimated data.
Autonomous Vehicles and AI Integration: The Physical World Meets Digital Intelligence
One of the most substantial themes running through CES 2026 was the acceleration of AI integration into autonomous systems. This wasn't limited to automobiles; robotics, construction equipment, and manufacturing systems all showed evidence of AI enhancement.
Ford's AI Assistant: The Automotive Future
Ford announced a significant strategic initiative at CES 2026: the deployment of an AI assistant that would first appear in the company's mobile app, with targeted integration into Ford vehicles by 2027. The assistant, built using off-the-shelf large language models and hosted on Google Cloud infrastructure, represents a shift in how automotive manufacturers are approaching software.
Historically, automakers developed proprietary software for their vehicles, creating closed ecosystems optimized for their specific hardware. Ford's approach, by contrast, leverages cloud infrastructure and commercial AI models, allowing the company to move faster and iterate more frequently than traditional in-house development would permit.
The strategic implication is important: automotive software is no longer a competitive advantage; it's table stakes. Manufacturers that can't integrate with cloud AI providers and deliver seamless voice interface experiences risk commoditization. Ford's partnership with Google signals a broader industry trend where automotive software becomes a collaboration between manufacturers, cloud providers, and AI companies rather than a fully in-house effort.
However, the announcement was notably light on details about what drivers should actually expect from their experience with the assistant. What can it do? How frequently will it update? How does it handle private data? These questions remain open, suggesting that Ford is still working through the user experience implications of embedding AI into the car itself.
Caterpillar and Nvidia's Construction AI: Expanding Beyond Consumer Applications
While Ford's announcement focused on consumer vehicles, Caterpillar and Nvidia's partnership demonstrated AI's expanding role in industrial applications. The companies announced a pilot program called "Cat AI Assistant," demonstrated on Caterpillar's excavator equipment at CES, combining real-time AI perception with construction planning tools.
The system works through a combination of hardware and software innovation. Caterpillar's equipment is fitted with sensors and cameras that feed real-time data to Nvidia-powered AI models running locally on the equipment. These models analyze the environment—identifying obstacles, measuring excavation progress, optimizing bucket positioning—and provide the operator with real-time guidance.
Simultaneously, Nvidia's Omniverse simulation technology is being used to plan construction projects. Before beginning actual work, planners can simulate the project in a digital environment, testing different equipment configurations and work sequences. This simulation-informed planning leads to more efficient execution and fewer costly mistakes on actual job sites.
For the construction industry, which hasn't seen dramatic productivity improvements in decades despite technological advances, AI-powered equipment represents a genuine breakthrough. Early data from pilot programs suggests that AI assistance can improve excavation accuracy by 15-20%, reduce fuel consumption by improving equipment efficiency, and enable safer operations by preventing operator errors.
The Broader Robotics and Automation Ecosystem
Both the Ford and Caterpillar announcements are symptoms of a larger shift: AI is moving from computational tasks (analyzing data, generating text) to physical tasks (driving, digging, moving). This expansion from digital to physical is profound, and it's accelerating faster than many predicted.
Organizations looking to stay competitive in any equipment-heavy industry should begin evaluating how AI could augment their current operations. This isn't just about buying new equipment; it's about reimagining workflows to take advantage of AI capabilities. A construction company using AI-assisted equipment might reorganize their planning, execution, and quality control processes to work in concert with the AI systems rather than against them.
Consumer Devices and the Return of Hardware Innovation: Clicks Communicator
CES has historically been showcased for new consumer electronics, yet in recent years, the show has increasingly focused on incremental improvements to existing product categories. The Clicks Communicator represented a refreshing departure from that trend—a genuinely novel consumer device that challenged assumptions about what modern phones should prioritize.
Why Physical Keyboards Are Having a Moment
Clicks Technology's
The resurgence of physical keyboards reflects a genuine insight about how people work. Developers, writers, journalists, and professionals who spend significant time typing have long complained that on-screen keyboards are inferior for text input. Typing on a physical keyboard enables faster composition, fewer errors, and more natural muscle memory. For a specific segment of users—professionals who prioritize text input over consuming media on their phones—physical keyboards represent a genuine productivity improvement.
Clicks' market research likely revealed that this professional segment was willing to accept a less sleek design and pay a premium price for better typing capabilities. The phone sacrifices some thinness and elegance for functionality, a trade-off that would be rejected by most consumers but embraced by power users.
Design and Manufacturing Excellence
The Communicator made a strong impression in hands-on demonstrations, which speaks to the care taken in its design and engineering. The contoured back improves grip, the elevated screen protects content, and the curved chin creates a protective recess for the keys. These details suggest that Clicks spent considerable time iterating on the design, moving through dozens of 3D-printed prototypes before arriving at the final form.
From a manufacturing perspective, the phone is technically complex. Creating a slim, usable keyboard requires precision engineering in components that are typically invisible to users—the actuation mechanism, the connection between keys and circuitry, the stiffening structure that allows the keyboard to withstand millions of keystrokes. The success of early production runs will determine whether Clicks can sustain demand and improve margins through manufacturing optimization.
Implications for the Smartphone Market
The Communicator's appeal is deliberately narrow, targeting professionals rather than mass market consumers. This niche positioning is actually strategically sound—rather than competing with Apple and Samsung across the entire market, Clicks is creating a new category where different optimization criteria apply.
If successful, the Communicator might inspire competitors to explore hardware differentiation in smartphone design. Instead of the current market structure, where phones differ primarily in processor speed, camera quality, and screen resolution, we might see more fundamental design divergence. Some phones optimized for productivity, others for entertainment, still others for specific professional applications.

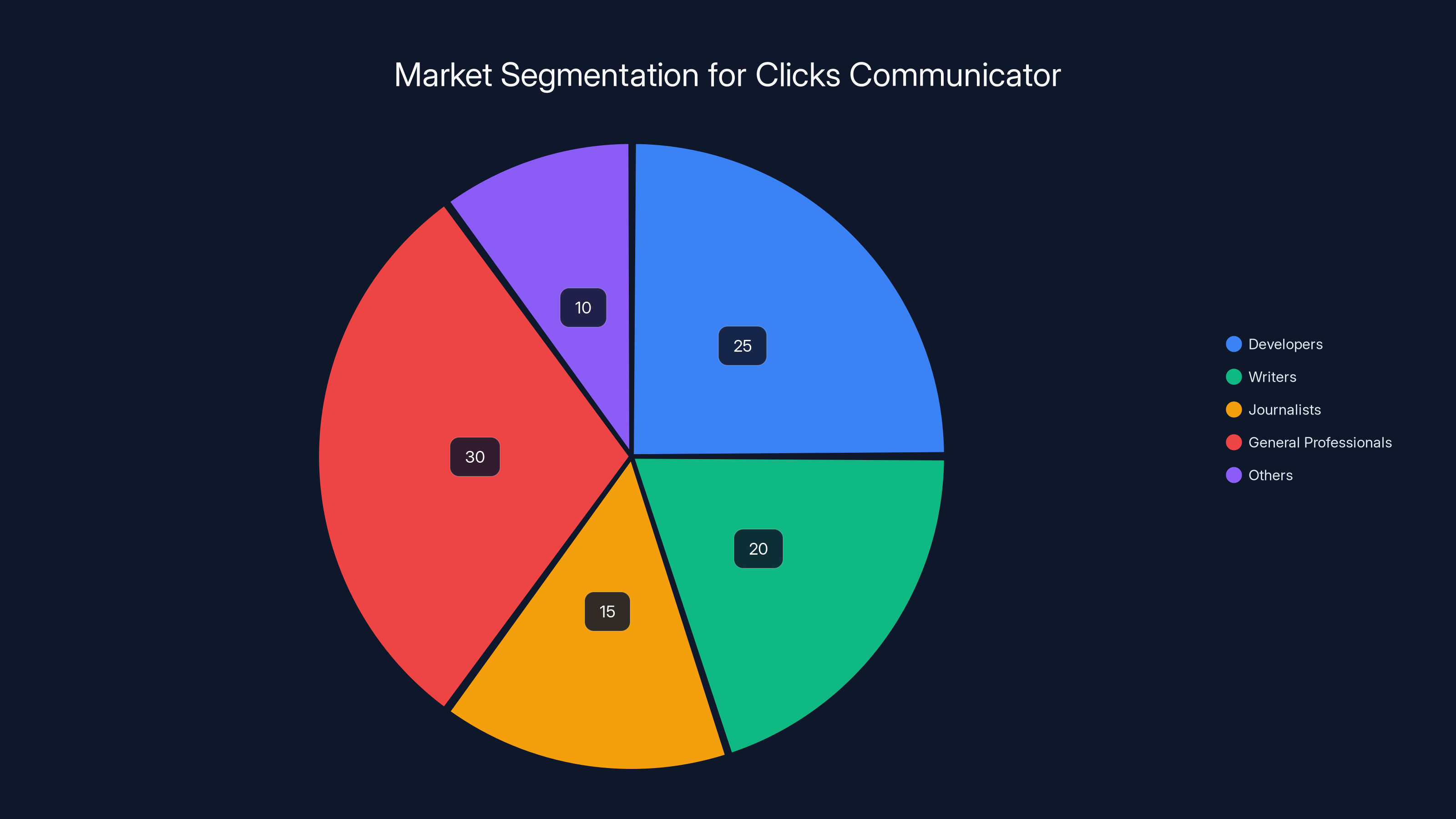
Estimated data suggests that developers, writers, and journalists form a significant portion of the market for physical keyboard smartphones, with general professionals also showing interest.
Smart Home Innovation: The Skylight Calendar 2
Among the more intriguing discoveries on the CES show floor was the Skylight Calendar 2, a family planning tool that represents the evolution of connected home devices beyond basic automation and notification.
Intelligent Calendar Systems and Multi-Source Data Integration
The Skylight Calendar 2 addresses a genuine pain point in household management: coordinating schedules across multiple family members, devices, and platforms. Most families use a jumble of solutions—Google Calendar, Apple Calendar, personal digital assistants, shared spreadsheets, and email reminders—to track their collective schedules and commitments.
Skylight's innovation is to create a unified interface that pulls data from these various sources, presents it in a format optimized for family planning (typically on a large wall-mounted display), and adds AI-powered features that traditional calendars lack. The device can analyze photos from family members' phones to identify events and automatically add them to the calendar. It can parse messages from group chats and extract scheduling information. It can suggest optimal times for family activities based on everyone's availability.
The AI capabilities go beyond simple data aggregation. The system learns family patterns—who typically has availability on weekends, which family members frequently schedule activities in the evenings, what types of events matter most to different family members. This learning enables the system to provide increasingly relevant suggestions and reminders over time.
Appointment Reminders and To-Do Integration
A seemingly simple feature—appointment reminders—becomes more sophisticated when combined with other data sources. Rather than just notifying someone that a dentist appointment is at 2 PM tomorrow, the system can provide context: commute time, reminders to bring insurance cards, suggestions to let other family members know you'll be gone. If a family member was planning to ask for help with a project during that time, the system can suggest an alternative window when both people are available.
The to-do functionality similarly benefits from multi-source integration. A photo shared in family chat becomes a to-do item. A message requesting help with a task becomes a to-do assigned to the relevant family member. Voice commands while cooking can create shopping list items. Over time, the system builds a comprehensive picture of what needs to happen in the household and proactively suggests optimizations.
The Broader Smart Home Ecosystem Implication
Skylight Calendar 2 represents a maturation of smart home technology beyond simple automation. Rather than just controlling lights and thermostats based on rules, next-generation smart home devices are becoming information hubs that help families manage complexity through AI-powered analysis and suggestion.
For organizations building smart home products, this signals a shift toward treating data integration and AI analysis as core capabilities rather than nice-to-have features. The most valuable smart home products of the future won't just control devices; they'll synthesize information from multiple sources and provide actionable intelligence.
Robotics and Boston Dynamics: The Hardware-AI Interface
Boston Dynamics made headlines at CES 2026 not for a new robot design, but for a strategic partnership that signals where advanced robotics is heading. The announcement that Boston Dynamics, owned by Hyundai, would partner with Google's AI research lab to train and operate Atlas robots represents a significant organizational and technical choice.
The Atlas Robot Evolution and Capabilities
The Atlas humanoid robot has been in development for over a decade, with incremental improvements in mobility, dexterity, and autonomy. Previous versions operated primarily in controlled environments with significant human oversight. The new generation of Atlas robots, combined with Google's AI training infrastructure, aims to move toward more autonomous operation in less structured environments.
The partnership represents a convergence of two capabilities: Boston Dynamics' mechanical engineering expertise and decades of learning about how to build robots that move like humans, and Google's AI training infrastructure and research capabilities. By combining these strengths, the partnership aims to develop robots that can handle real-world tasks without extensive human programming for every possible scenario.
From a technical perspective, this means developing AI systems that can: perceive complex environments using computer vision, reason about how to accomplish tasks given particular constraints, execute sequences of movements with high precision, and adapt when situations don't go exactly as planned.
Google Cloud and Training Scale
Google's role in this partnership extends beyond just providing AI expertise. The company has invested heavily in infrastructure for training large-scale AI models, including specialized hardware (TPUs) and software frameworks optimized for machine learning workloads. This infrastructure can process vast amounts of sensor data from robot trials, extract patterns about successful behaviors, and encode those patterns into neural networks.
This training infrastructure is a significant competitive advantage. A robotics company building on-premises cannot match the computational resources Google can allocate to training tasks. By partnering with Google, Boston Dynamics gets access to training capabilities that would take years and hundreds of millions of dollars to build independently.
Implications for the Robotics Industry
The Boston Dynamics-Google partnership signals that the future of advanced robotics will be built on the following formula: specialized hardware engineering + massive-scale AI training infrastructure + domain expertise in robotics-specific problems. No single company is likely to excel at all three simultaneously, suggesting that robotics will increasingly be a collaborative effort between hardware specialists, cloud infrastructure providers, and AI research organizations.
For organizations evaluating robotics solutions, this partnership highlights an important trend: the most advanced robots in the coming years will likely come from companies that can marshal these three capabilities, whether through in-house development or strategic partnerships.
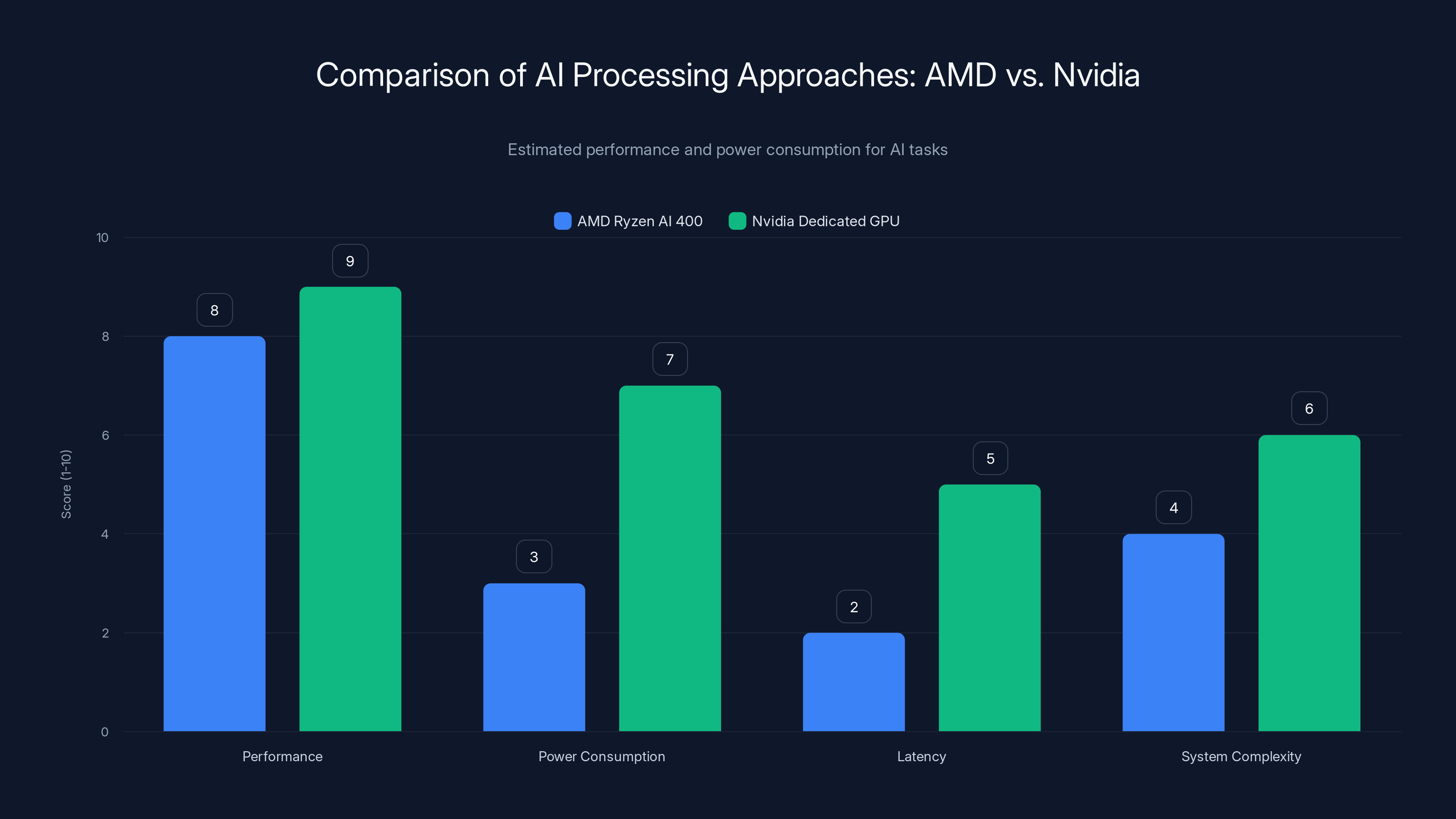
AMD's integrated AI solution offers lower power consumption and latency compared to Nvidia's dedicated GPU approach, while maintaining competitive performance. (Estimated data)
Consumer Electronics: Innovation in Hardware Design
Beyond the marquee announcements, CES 2026 featured numerous innovations in consumer electronics that signal broader trends about how hardware is evolving in the era of AI.
The Blurred Line Between Device Categories
Traditionally, CES has showcased clear product categories: smartphones, laptops, tablets, wearables, smart home devices, and so on. At CES 2026, the boundaries between these categories continued to blur. Devices increasingly featured the capabilities of multiple categories—a laptop might function as a tablet, a smartwatch might run full applications, a phone might have enterprise-grade processing capabilities.
This convergence is enabled by the increasing power and efficiency of processors. Moore's Law may be slowing, but the efficiency improvements in specialized silicon (AI accelerators, imaging processors, wireless modems) create new possibilities for what can fit into compact form factors while maintaining acceptable power consumption.
Display Technology and Always-On Computing
Display technology represented another area of innovation. E-ink displays continued to improve, with faster refresh rates enabling applications previously impossible on e-paper. LCD and OLED displays featured higher refresh rates, better color accuracy, and improved energy efficiency. Micro-LED displays began appearing in wearable applications, promising better brightness and smaller form factors than existing technologies.
These display improvements enable new computing paradigms. Always-on displays that consume minimal power when showing static information become practical with improved display technology. This means devices that can show useful information at a glance without draining batteries—a small shift in capability with substantial implications for how people interact with technology.
Battery Technology and Energy Density
Solid-state battery development continued to show promise at CES, with several companies demonstrating prototypes that offer higher energy density than lithium-ion cells currently in production. Energy density improvements are particularly important for wearable devices, where users want longer operational lifespans without significant weight or bulk penalties.
The path to commercialization for solid-state batteries remains challenging—manufacturing at scale, managing thermal properties, and achieving cost targets all present hurdles. However, the direction is clear: battery technology will continue to improve, enabling new form factors and use cases for portable electronics.

AI Infrastructure and the Data Center Refresh Cycle
While consumer electronics grabbed headlines, the real economic impact of CES 2026 was the clear validation that data centers worldwide would undergo significant refresh cycles to support AI workloads. Both Nvidia and AMD used their keynotes to position their products as the foundation for this transformation.
The $1 Trillion Data Center Refresh
Analysts estimated that global data center operators would invest over $1 trillion in the coming five years to build out AI infrastructure. This represents a massive capital cycle, driven by the realization that existing computational infrastructure, optimized for traditional workloads like web services and databases, is not optimal for training and running AI models at scale.
This investment cycle has ripple effects throughout the technology ecosystem. Power infrastructure, cooling systems, networking equipment, storage devices, and software licensing all represent opportunities for vendors to participate in the buildout. Companies that position themselves well in this cycle—whether as hardware manufacturers, software providers, or systems integrators—will capture substantial value.
Implications for Existing Data Centers
Data center operators face a strategic choice: continue optimizing existing infrastructure for traditional workloads, or invest heavily in AI-capable infrastructure. For some operators, the answer is both—creating hybrid environments where legacy workloads continue on existing hardware while new AI workloads run on specialized infrastructure.
This hybrid approach creates complexity and operational challenges but often makes financial sense. Existing hardware has been fully depreciated, so continuing to use it for workloads it was designed for offers good returns. New hardware optimized for AI offers better efficiency for AI workloads but requires significant upfront capital investment.
The Consolidation of Infrastructure Among Cloud Giants
One likely outcome of this capital-intensive refresh cycle is further consolidation of computing power among the largest cloud providers. Companies like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have the financial resources to make massive infrastructure investments faster than competitors. Their scale enables them to negotiate better terms with hardware vendors and spread fixed costs across more customers.
For startups and smaller organizations, this consolidation trend suggests that building custom hardware or specialized data center infrastructure is increasingly risky. The cloud giants can invest in optimization and achieve economies of scale that private operators cannot match. This drives customers toward cloud services, further increasing the concentration of computational power among a small number of companies.

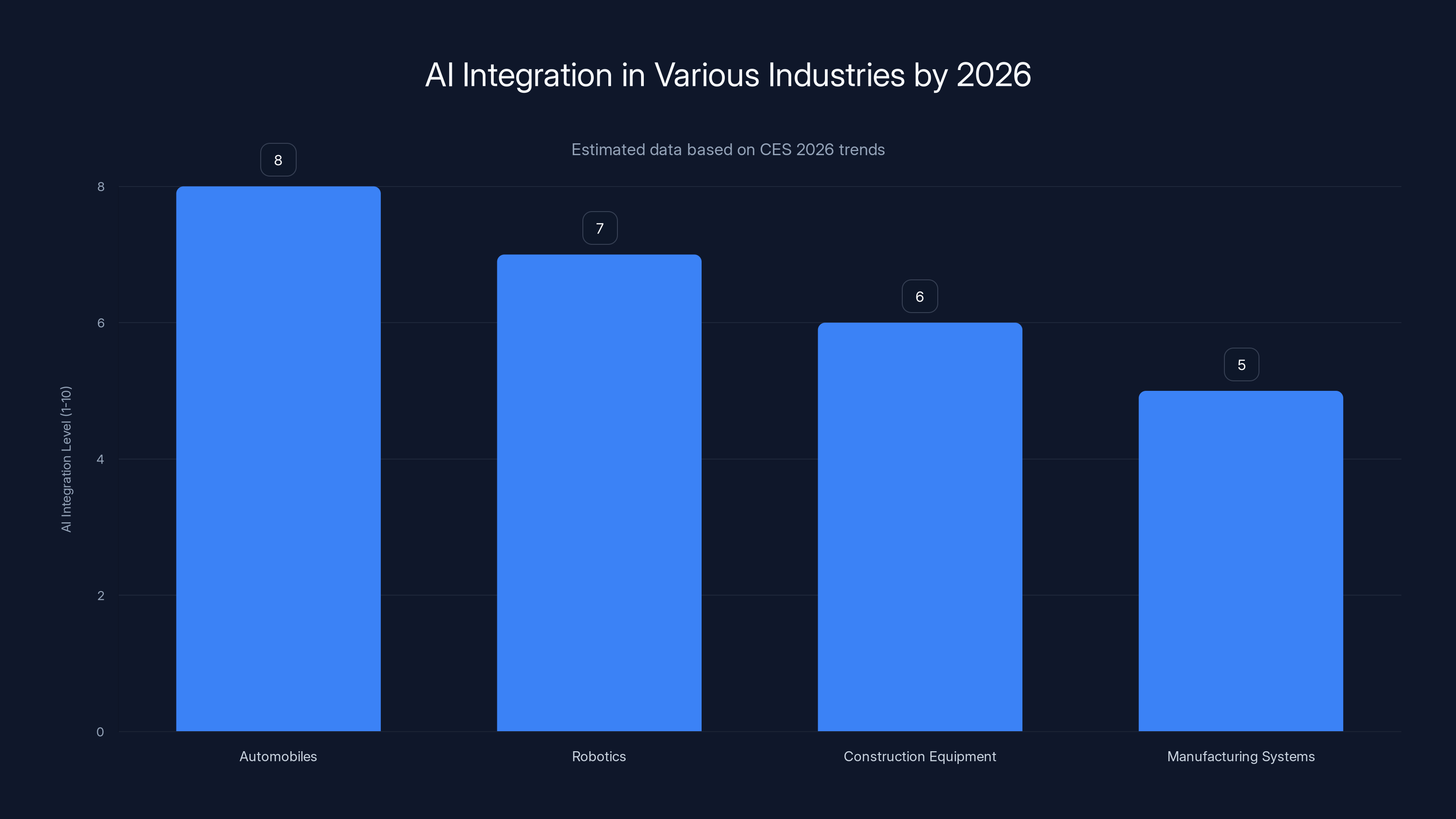
AI integration is highest in automobiles, followed by robotics, construction equipment, and manufacturing systems, indicating a trend towards digital intelligence across sectors. (Estimated data)
Industry-Specific Applications and Vertical Solutions
CES 2026 made clear that AI's impact would not be uniform across industries. Instead, vertical-specific solutions were emerging that tackled industry-particular problems using AI.
Manufacturing and Production Optimization
Beyond construction, other manufacturing sectors are experiencing AI integration. Computer vision systems can inspect manufactured goods with accuracy exceeding human inspectors, quality control processes can be automated, and production schedules can be optimized using predictive AI models.
Companies implementing AI in manufacturing report significant benefits: defect rates drop by 30-50%, production scheduling becomes more efficient, and downtime decreases as predictive maintenance systems identify equipment issues before failures occur. These improvements drive down manufacturing costs, making products more competitive and improving profit margins.
Healthcare and Diagnostic Applications
AI-powered diagnostic systems continue to improve, with systems approaching or exceeding human radiologist accuracy on specific imaging tasks. Healthcare providers are increasingly deploying these systems to accelerate diagnosis, reduce variability, and free up expert physicians to focus on complex cases and patient interaction.
While regulatory challenges remain, the trajectory is clear: AI will become integral to clinical workflows, assisting in diagnosis, treatment planning, and outcome prediction. Healthcare organizations that successfully integrate AI into workflows will improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency; those that resist adoption risk falling behind.
Financial Services and Risk Analysis
Financial institutions have been among the earliest adopters of AI, using machine learning models for fraud detection, risk assessment, and investment analysis. CES 2026 highlighted continuing advances in these applications, with more sophisticated models achieving better accuracy on complex prediction tasks.
For financial organizations, the challenge is no longer whether to use AI but how to use it most effectively. This involves developing internal AI capabilities, selecting appropriate vendors and platforms, and managing the regulatory and compliance implications of automated decision-making.

Software and Platform Announcements: Building the AI Stack
Hardware announcements naturally dominated CES's press coverage, but software and platform innovations were equally significant for organizations building AI systems.
Development Frameworks and Tools
Software frameworks for building, training, and deploying AI models continued to evolve. These frameworks—including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and others—allow developers to write AI applications without needing to understand every detail of how computations are distributed across hardware. This abstraction is crucial for productivity, allowing developers to focus on algorithm and application-level problems rather than low-level hardware optimization.
At CES 2026, announcements about new frameworks and improvements to existing ones signaled continued investment in making AI development more accessible. Better debugging tools, improved performance profiling, and more intuitive APIs all reduce the barrier to entry for organizations building AI applications.
Cloud Service Enhancements
Cloud providers announced various enhancements to their AI services. These included improved pricing for AI workloads, new managed services for common AI tasks, and better integration between AI services and traditional enterprise applications.
The competitive dynamic among cloud providers—AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud—drives continuous innovation. Each provider invests heavily in differentiating their AI offerings, knowing that AI workloads represent a growing portion of cloud revenue. This competition benefits customers, who get better tools and services at competitive prices.
Open Source AI Models and Ecosystem
Open source AI models continued to proliferate, with new models released regularly by research institutions, companies, and communities. The availability of high-quality open source models democratizes AI—organizations no longer need to fund massive training efforts to get effective models; they can fine-tune existing models for their specific tasks.
This open source movement has profound implications for competition in AI. Instead of dominant companies controlling access to AI capabilities through proprietary models, the ecosystem is becoming more distributed, with multiple high-quality options available to developers. This competition improves the overall quality of available tools and reduces vendor lock-in risk.

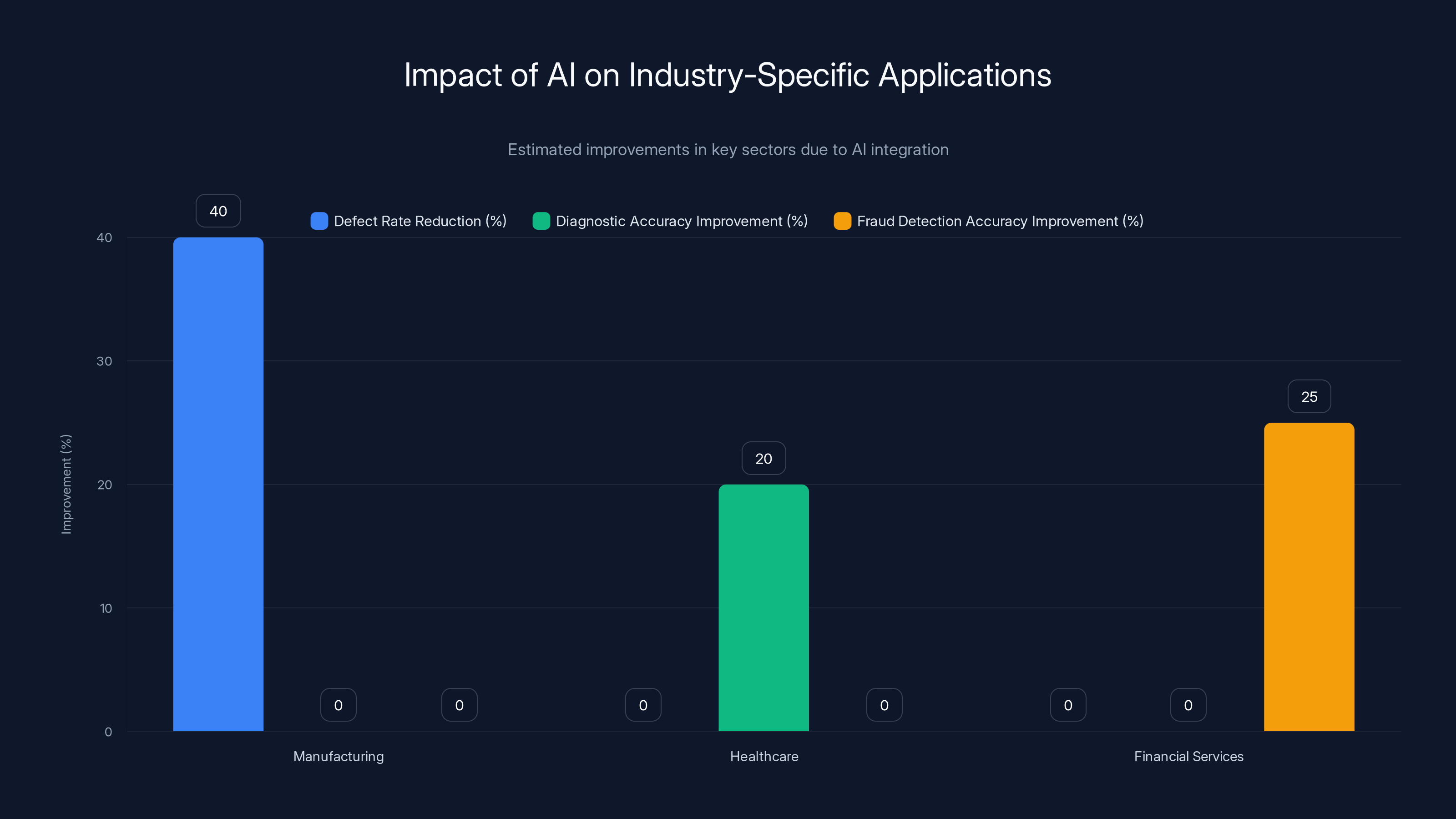
AI integration leads to significant improvements: manufacturing sees a 40% reduction in defect rates, healthcare diagnostic accuracy improves by 20%, and financial fraud detection accuracy increases by 25%. Estimated data.
Enterprise Software and Productivity Tools: The AI-Enhanced Office
While much of CES focused on consumer devices and infrastructure, enterprise software companies are increasingly using AI to enhance productivity tools that billions of workers rely on daily.
AI-Powered Document Generation and Summarization
Enterprise software vendors demonstrated AI capabilities for generating documents, summarizing lengthy materials, and extracting key information from unstructured data. These capabilities directly impact worker productivity—instead of spending hours writing reports or summarizing meetings, workers can have AI assist with these routine tasks, freeing time for higher-value activities.
The effectiveness of these tools varies depending on task complexity and domain specificity. For standard reports following predictable formats, AI generation can be highly accurate. For complex analysis requiring deep domain expertise, AI tools work best as assistants that generate drafts for human refinement.
For development teams and organizations managing content creation, AI-powered tools dramatically accelerate output. Teams that previously required dedicated technical writers, documentation specialists, and content creators can accomplish more with smaller teams augmented by AI tools. This scalability has profound economic implications, allowing organizations to maintain documentation quality while reducing costs.
Workflow Automation and Integration
Beyond document generation, AI is being applied to workflow automation—automatically routing documents, scheduling meetings based on participant availability, flagging items requiring human attention, and executing repetitive tasks. These automation capabilities build on traditional workflow tools but add intelligent decision-making that adapts to context.
The economic value of these tools lies in their ability to reduce manual work on routine tasks. An organization might have dozens of workers spending 10% of their time on routine administrative tasks. Automating even half of these tasks through AI-enhanced workflow tools can free up significant productive capacity equivalent to several full-time employees.
Accessibility and Natural Interaction
AI-enhanced productivity tools often feature natural language interfaces—workers can describe what they need in plain language rather than clicking through menus or writing code. This accessibility extends AI benefits beyond specialized technical users to the broader workforce. This democratization of AI tools means more workers can take advantage of automation and AI-assisted productivity.

Privacy, Security, and Governance Considerations
As AI systems proliferate across consumer and enterprise applications, questions about privacy, security, and governance became increasingly pressing at CES 2026.
On-Device Processing and Privacy Preservation
AMD's emphasis on on-device AI processing reflects broader industry recognition that privacy is increasingly valuable to consumers. Systems that process data locally, without sending it to cloud servers, offer stronger privacy guarantees. This is particularly important for sensitive data like medical records, financial information, or personal communications.
The shift toward on-device processing also offers security advantages. Data that never leaves a device cannot be compromised in cloud breaches. For healthcare providers, financial institutions, and enterprises handling sensitive information, on-device processing can reduce compliance burden and improve security posture.
Algorithmic Transparency and Explainability
As AI systems make increasingly important decisions—from loan approvals to medical diagnoses—there's growing pressure for transparency about how these decisions are made. Regulators are paying attention, with rules like the EU AI Act establishing requirements for algorithmic explanation and transparency.
At CES 2026, companies demonstrated tools and approaches for explaining AI decisions, making models more interpretable, and documenting AI system behavior. This emphasis on explainability will likely increase as regulations tighten and liability concerns grow.
Data Governance and Compliance
Organizations deploying AI systems must manage the data that powers these systems. This involves collecting data ethically, obtaining appropriate consent, securing data against unauthorized access, and complying with regulations governing data retention and deletion.
For enterprises building AI systems, data governance is increasingly complex. The data used to train models must be properly documented, the models themselves must be version-controlled and traceable, and the decisions made by AI systems must be auditable. Tools and practices for managing this complexity represent a growing market segment.

The Future of CES and Technology Announcements
Reflecting on CES 2026, several observations about the future of technology innovation and product announcements emerge.
The Permanence of AI as a Core Technology
CES 2025 was often described as the "Year of AI," with AI announcements dominating coverage. By CES 2026, this language had shifted. AI was no longer special or noteworthy simply because it was present; it was expected. The discussion moved from whether AI would be integrated into products to how AI should be integrated and what value it created.
This normalization of AI suggests that future CES shows will feature AI in nearly every major product announcement. The question for vendors is no longer whether to use AI but how to use it meaningfully, creating actual value for customers rather than using AI as a marketing buzzword.
Hardware-Software Convergence
CES 2026 highlighted the increasingly tight coupling between hardware and software. Specialized hardware accelerators for AI only make sense paired with software optimized to use them. Similarly, AI software capabilities are limited by available hardware. This convergence means that competitive advantage in many categories will require excellence in both hardware engineering and software development—a challenging combination.
For organizations evaluating technology partners and platforms, this suggests that integrated solutions (hardware plus optimized software) may increasingly outcompete pure hardware or pure software offerings that haven't been closely integrated.
The Role of Open Source and Community
Open source software and models continued to democratize access to advanced technology. Companies that successfully contributed to and leveraged open source communities were gaining competitive advantages through community contributions, improved tools, and access to talent. This trend will likely accelerate, with open source becoming even more central to technology development.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Among the more subtle but important themes at CES 2026 was energy efficiency. As AI systems consume more electricity for training and inference, concerns about power consumption and environmental impact are growing. Companies highlighting energy-efficient processors, improved cooling systems, and more efficient algorithms were positioning themselves well for a future where energy consumption becomes a key competitive factor.

Emerging Trends and Lessons for Organizations
For development teams, content creators, and organizations of all sizes, CES 2026 offered clear lessons about technology direction and strategic positioning.
The Acceleration of AI Integration
Organizations that haven't begun integrating AI into their core processes and products risk falling behind. CES 2026 made clear that AI is moving beyond experimental projects to becoming central to how products are built and services are delivered. Waiting to adopt AI is increasingly a strategic liability.
The Value of Specialization and Niche Innovation
While consumer electronics from major manufacturers continued to dominate market share, innovative niche products like the Clicks Communicator demonstrated that specialization and unique value propositions could succeed. Organizations that deeply understand specific customer segments and build products optimally tailored to those segments can compete effectively against generalists.
The Importance of Platform Partnerships
Successful companies at CES 2026 typically built on partnerships with infrastructure providers, cloud services, and software platforms. Rather than building everything in-house, successful organizations chose strategic partnerships that allowed them to focus on their core differentiation while leveraging partners' strengths.
Investment in Data and Training Infrastructure
The competitive advantages in AI increasingly accrue to organizations that can invest in training infrastructure and gather high-quality data. This creates a potential winner-take-most dynamic where leading companies in each category can outinvest competitors in training systems and data acquisition.

For Development Teams: Automation and Productivity Tools
One of the most relevant themes at CES 2026 for development teams was the continued expansion of automation and AI-assisted productivity tools. As organizations manage increasingly complex systems and accelerate release cycles, tools that automate routine tasks become increasingly valuable.
Content Generation and Documentation
Developers and technical teams face constant pressure to maintain documentation, create release notes, generate API documentation, and produce technical content. AI-powered tools can significantly accelerate these tasks, generating first drafts that developers can review and refine. Platforms like Runable, which focuses specifically on AI-powered content generation for developers, offer automation capabilities that teams can integrate into their workflows.
These tools work best for routine, structured content like API documentation, release notes, and technical specifications. They accelerate the creation process while still maintaining human oversight and quality control.
Workflow Automation and CI/CD Enhancement
Modern software development involves numerous repetitive tasks: running tests, deploying to staging environments, notifying teams of changes, managing dependencies. AI-enhanced workflow automation can intelligently execute many of these tasks, freeing developers to focus on writing code and solving problems.
For teams managing complex release processes, this automation directly impacts velocity. Faster feedback loops, earlier error detection, and automatic routing of tasks reduce the friction in development workflows and allow teams to ship features more frequently.
Knowledge Management and Search
Development teams accumulate vast amounts of knowledge: architecture decisions, API documentation, code examples, deployment procedures, incident postmortems. Making this knowledge discoverable and actionable becomes increasingly challenging as organizations grow. AI-powered search and knowledge management tools can organize this information and surface relevant knowledge when developers need it.

Strategic Implications for Organizations
CES 2026 demonstrated several clear strategic implications for organizations across all sectors.
Vertical Integration Becoming Increasingly Competitive
Companies that successfully integrate custom silicon, optimized software, and domain expertise (as Nvidia does) or companies that partner strategically across these capabilities (like Boston Dynamics with Google) demonstrate competitive advantages that pure software or pure hardware players struggle to match.
Speed of Iteration and Learning
Organizations that can experiment quickly with AI technologies, learn from results, and iterate rapidly will outpace competitors. This advantage accrues to teams that: (1) have access to sufficient computational resources for experimentation, (2) understand their customers deeply enough to identify valuable AI applications, and (3) can execute rapidly to bring innovations to market.
Ecosystem and Partnership Strategies
Successful companies at CES 2026 typically operated within ecosystems of partners rather than attempting to build everything independently. For organizations evaluating technology strategies, this suggests that building strong partnerships with complementary providers (cloud services, software platforms, research institutions) creates more value than attempting full vertical integration.
The Permanent Nature of the AI Refresh Cycle
Unlike previous technology cycles that eventually reached equilibrium, AI capabilities are improving at a relentless pace. This means organizations cannot implement an AI strategy once and rest; instead, they need to continuously evaluate new capabilities, experiment with emerging tools, and refresh their approaches regularly.

Conclusion: Navigating the Post-CES 2026 Landscape
CES 2026 represented a transition point in technology evolution. The show demonstrated that AI had moved from emerging technology to fundamental infrastructure. The question for most organizations is no longer whether to adopt AI but how to adopt it most effectively for their specific needs and circumstances.
For development teams, CES 2026 highlighted the expanding availability of AI-powered tools designed to automate routine tasks, accelerate content creation, and enhance productivity. Teams that strategically adopt these tools—using them to augment rather than replace human expertise—will see measurable improvements in output velocity and quality.
For organizations building consumer products, CES 2026 demonstrated that AI integration is becoming table stakes. Products without meaningful AI features will be perceived as less advanced than those with them. However, AI integration must be thoughtful and user-focused; AI for its own sake doesn't create value.
For infrastructure and platform companies, CES 2026 validated the massive investment opportunity in supporting AI workloads. The $1 trillion data center refresh cycle will create substantial opportunities for vendors that can provide efficient infrastructure, developer-friendly platforms, and specialized tools for AI applications.
For enterprises managing complex operations, CES 2026 highlighted how AI can optimize workflows, improve decision-making, and free up human talent for higher-value activities. Organizations beginning their AI journey should start with high-impact, well-defined problems where AI can create measurable value.
The technology landscape continues to accelerate. CES 2027 will likely showcase advances that seemed impossible a few years prior. Organizations that stay informed about technology trends, maintain flexibility in their technology choices, and build partnerships with capable vendors will navigate this acceleration successfully. Those that wait and watch risk falling behind in a market where the pace of change shows no signs of slowing.

FAQ
What was the main focus of CES 2026?
CES 2026 primarily focused on the widespread integration of artificial intelligence across all product categories, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment. The show demonstrated that AI had evolved from an emerging technology to a fundamental component of modern products and services. Major announcements included Nvidia's Rubin architecture for data center AI workloads, AMD's Ryzen AI 400 Series for consumer devices, autonomous vehicle systems, and various robotics applications, signaling that AI adoption had reached a critical inflection point across industries.
What is Nvidia's Rubin architecture and why is it significant?
Nvidia's Rubin architecture is the next-generation computing platform designed to succeed the current Blackwell architecture, optimized specifically for handling the computational demands of large-scale artificial intelligence systems. Rubin improves upon previous generations by increasing memory bandwidth, implementing better cache hierarchies, and including specialized tensor cores for AI operations. The significance lies in its 25-30% improvement in training speed for AI models and its planned rollout beginning in the second half of 2026, indicating substantial investment cycles ahead in data center infrastructure refresh globally.
How does AMD's approach to AI differ from Nvidia's?
While Nvidia focuses on powerful data center processors for training large AI models, AMD's Ryzen AI 400 Series integrates AI capabilities directly into consumer-level processors like those found in laptops and personal computers. This on-device processing approach offers advantages including improved privacy (data stays local), reduced latency, and enables AI features without cloud connectivity. AMD's strategy targets the broader consumer market and emphasizes edge computing, whereas Nvidia dominates the high-performance training infrastructure market.
What are the benefits of on-device AI processing as highlighted at CES 2026?
On-device AI processing offers several critical benefits: enhanced privacy since personal data remains on the user's device rather than being transmitted to cloud servers, elimination of latency that accompanies cloud-based inference, continued functionality offline, and reduced dependency on internet connectivity. For sensitive applications like medical records analysis, financial planning, and personal productivity tools, on-device processing represents a substantial privacy and security improvement. Additionally, it enables faster response times and reduces bandwidth requirements for connected devices.
What is the significance of Ford's AI assistant announcement?
Ford's announcement of an AI assistant debuting in its mobile app (with vehicle integration planned for 2027) signals a strategic shift in automotive software development. Rather than building proprietary in-house solutions, Ford leveraged off-the-shelf large language models and Google Cloud infrastructure. This approach enables faster iteration and broader feature capabilities than traditional automotive software development would allow. The announcement demonstrates that automotive software is transitioning from a proprietary competitive advantage to a collaborative effort among manufacturers, cloud providers, and AI companies.
How will Caterpillar's partnership with Nvidia change construction operations?
The Cat AI Assistant pilot program combines real-time AI perception with construction planning simulation. On-site sensors feed data to Nvidia-powered AI models that analyze the environment, suggest optimal equipment positioning, and identify obstacles. Simultaneously, Nvidia's Omniverse simulation platform enables planners to virtually test construction sequences before execution. This integration yields early results showing 15-20% improvements in excavation accuracy, 10-15% reductions in fuel consumption, and enhanced safety through operator error prevention. The partnership suggests how AI will revolutionize traditionally stagnant productivity levels in construction and heavy equipment industries.
What makes the Clicks Communicator different from standard smartphones?
The Clicks Communicator differentiates itself through an integrated physical QWERTY keyboard, addressing a specific professional segment: developers, writers, and journalists who prioritize text input efficiency. At
What is the Skylight Calendar 2 and how does it use AI?
The Skylight Calendar 2 is a family planning tool displayed on a wall-mounted screen that unifies scheduling across multiple family members, devices, and platforms including Google Calendar, Apple Calendar, and email. Its AI capabilities include automatically parsing photos to identify events, extracting scheduling information from group chat messages, providing context-aware appointment reminders, and suggesting optimal times for family activities based on analyzed availability patterns. The device learns family behaviors over time, becoming increasingly relevant in its suggestions and reminders, effectively solving the household coordination challenge that traditional calendar systems address only partially.
What does the Boston Dynamics-Google partnership signify for robotics?
The Boston Dynamics-Google partnership demonstrates that cutting-edge robotics will require collaboration among mechanical engineering specialists, cloud infrastructure providers with AI training capabilities, and AI research organizations. Boston Dynamics brings decades of experience in humanoid robot design and movement, while Google contributes massive-scale AI training infrastructure and advanced research capabilities. This partnership model suggests the future of advanced robotics will increasingly involve specialized hardware companies partnering with tech giants, rather than single companies attempting to excel at mechanical engineering, software development, and AI research simultaneously.
What are the expected investment cycles following CES 2026 announcements?
Analysts projected over $1 trillion in global data center investments over the next five years as operators refresh infrastructure to support AI workloads. This massive capital cycle impacts power infrastructure, cooling systems, networking equipment, storage devices, and software licensing. Additionally, hardware manufacturers expect significant consumer refresh cycles as organizations and individuals upgrade to AI-capable devices. Software vendors will invest in AI-enhanced features. These interconnected investment cycles will reshape technology markets and create competitive advantages for companies positioned to capture value across the entire ecosystem.
How should organizations approach AI adoption following CES 2026?
Organizations should begin by identifying high-impact, well-defined problems where AI creates measurable value rather than pursuing AI adoption for marketing purposes. Strategic partnerships with cloud providers, software platforms, and specialized vendors often deliver better results than attempting full vertical integration. Development teams should evaluate AI-powered productivity tools that automate routine tasks, such as documentation generation and workflow automation, to accelerate delivery. Finally, organizations should maintain flexibility in technology choices and continuously evaluate emerging capabilities, recognizing that AI advancement shows no signs of slowing and periodic technology refresh cycles are now permanent features of the landscape.

Key Takeaways
-
AI Integration is Now Standard: CES 2026 demonstrated that AI has evolved from emerging technology to fundamental infrastructure expected in nearly all product categories, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment.
-
Hardware-Software Convergence Drives Competition: The most competitive products increasingly combine specialized hardware, optimized software, and deep domain expertise. Pure hardware or pure software plays face challenges competing against integrated solutions.
-
Privacy and On-Device Processing Matter: AMD's emphasis on on-device AI processing reflects growing consumer concern about data privacy. Systems processing data locally offer security advantages and eliminate cloud connectivity requirements.
-
Niche Innovation Remains Viable: The Clicks Communicator and Skylight Calendar 2 demonstrate that even in mature markets dominated by tech giants, specialized products serving specific customer segments with unique value propositions can succeed.
-
Data Center Infrastructure Refresh Cycle: The projected $1 trillion investment in AI-capable data center infrastructure over five years creates substantial opportunities for vendors and signals continued acceleration of AI workload deployment.
-
Robotics and Physical AI are Accelerating: Partnerships like Boston Dynamics-Google and Caterpillar-Nvidia show AI is moving from computational tasks to physical world applications, with significant industrial and economic implications.
-
Strategic Partnerships Over Vertical Integration: Successful companies increasingly build through partnerships with cloud providers, software platforms, and research organizations rather than attempting to develop all capabilities in-house.
-
AI Productivity Tools Are Essential: For development teams and content-focused organizations, AI-powered automation tools for documentation, content generation, and workflow management directly improve output velocity and team efficiency.
-
Continuous Evolution is Permanent: Unlike past technology cycles that reached equilibrium, AI improvement velocity shows no signs of slowing, requiring organizations to continuously evaluate new capabilities and refresh approaches regularly.

Related Articles
- Best Tech of CES 2026: 15 Innovations That Matter [2025]
- Cyera's $9B Valuation: How Data Security Became Tech's Hottest Market [2025]
- Lumus Smartglasses FOV Revolution at CES 2026 [2025]
- DDR5 Memory Prices Could Hit $500 by 2026: What You Need to Know [2025]
- CES 2026 TV Announcements: Micro RGB, OLED & Mini LED Guide [2026]
- Fender Audio's Mix Headphones & Ellie Speakers at CES 2026 [2025]




