Introduction: The Chatbot That Refuses to Die
It's rare to see a software project become a genuine cultural phenomenon. Usually, AI chatbots get buried under mountains of hype, broken promises, and forgotten GitHub repositories. But Moltbot somehow managed to do the opposite. In the span of a few chaotic weeks, this open-source AI assistant went from relative obscurity to trending across Twitter, Reddit, and tech forums—surviving everything from community fraud to fake memecoin schemes along the way.
The story isn't about another venture-backed startup or a tech giant's latest product launch. It's about a grassroots project that captured the internet's imagination by being genuinely different. While ChatGPT and Claude focus on general-purpose usefulness, Moltbot positioned itself as deeply personalized, community-driven, and radically transparent. But that transparency came with a cost. The rebrand that catapulted Moltbot to viral fame also exposed it to chaos: scammers created fake tokens bearing its name, fraudsters launched copycat versions, and the community nearly fractured under the strain.
What makes this story essential reading is what it reveals about the future of AI development. We're entering an era where open-source AI tools are challenging closed corporate models. We're seeing communities—not venture capital—driving innovation. And we're learning that internet fame can be both a blessing and a nightmare, especially when you're building something designed to be deeply personal to each user.
Moltbot's journey tells us something critical about how AI will evolve. It's not going to be controlled entirely by a handful of major players. It's going to be messy, community-driven, and impossible to predict. This is the story of an AI chatbot that became the internet's favorite conversation starter—and why that matters for everyone building or using AI tools.
TL; DR
- Moltbot became unexpectedly viral after a rebrand positioning itself as a personalized, open-source alternative to closed corporate chatbots
- The project faced immediate challenges including fraudulent schemes, fake tokens, and copycat platforms trying to capitalize on the momentum
- Community-driven development proved both a strength and vulnerability, allowing rapid growth but enabling bad actors to exploit the openness
- Personalization at scale became Moltbot's core differentiator, letting users customize their AI assistant in ways competitors don't allow
- The rebrand story demonstrates how internet culture and AI development intersect in unpredictable, sometimes chaotic ways
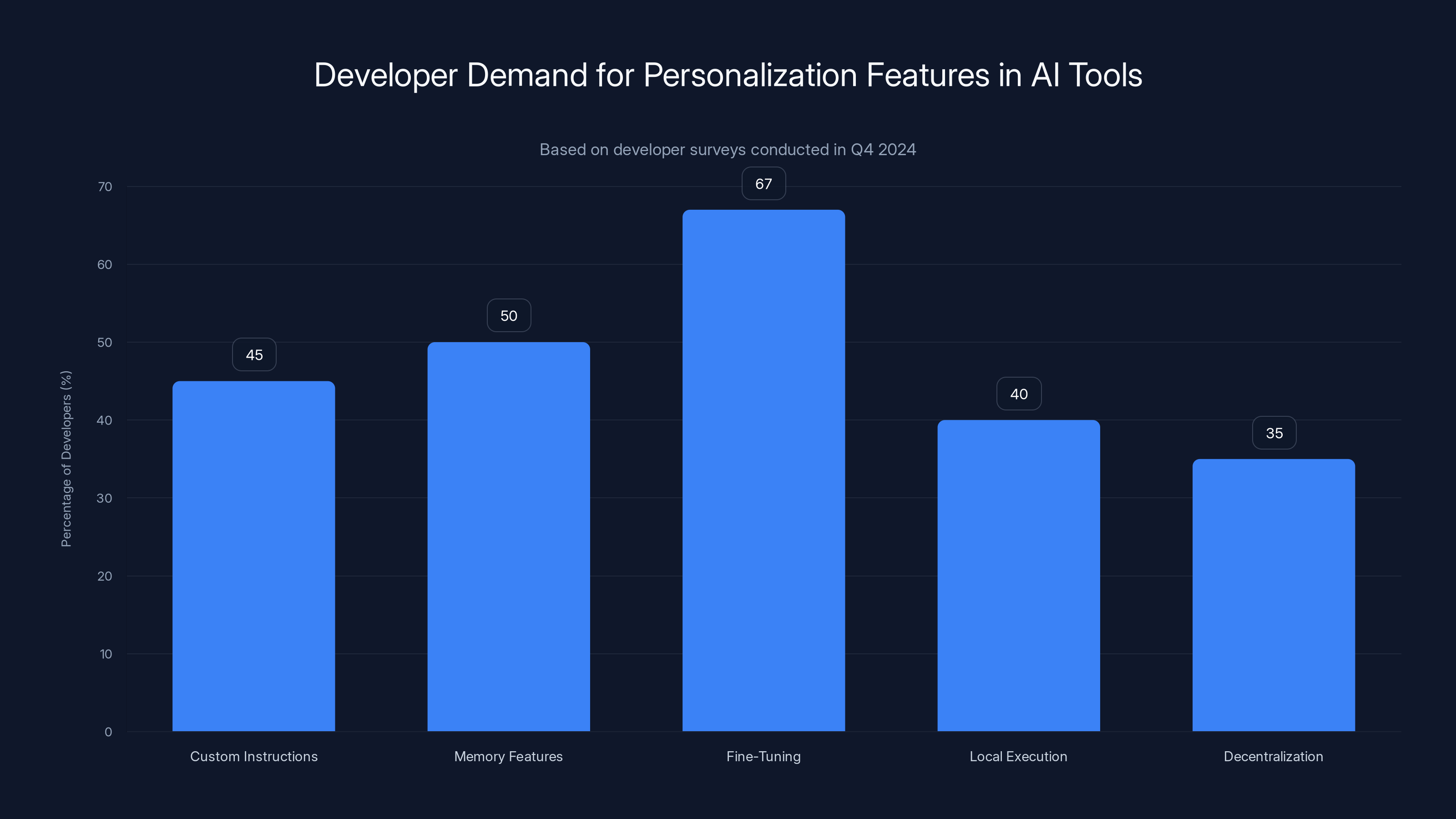
67% of developers desire fine-tuning capabilities, highlighting a significant demand for more personalized AI tools. Estimated data based on survey insights.
The Open-Source AI Revolution: Understanding the Landscape
Before we can understand why Moltbot's rebrand created such a seismic shift, we need to understand the broader context of open-source AI development. For years, the AI space has been dominated by a small number of well-funded companies. OpenAI controls ChatGPT. Google has Gemini. Anthropic developed Claude. These companies have massive budgets, enterprise security, and brand recognition. They also have centralized control.
But something changed around 2023 and 2024. Open-source models started becoming genuinely competitive. Projects like Mistral, Llama, and others proved that you didn't need billions in funding to create capable AI models. More importantly, you didn't need to centralize all decision-making in a corporate boardroom.
The appeal of open-source AI is straightforward: transparency, customization, and community ownership. When you build on open-source models, you're not beholden to a company's terms of service. You can modify the model. You can run it locally. You can build features that proprietary platforms would never allow. This freedom resonates deeply with developers and power users who are tired of opaque algorithms and corporate limitations.
Moltbot entered this landscape at precisely the right moment. The community was hungry for alternatives. People were frustrated by rate limits, privacy concerns, and the homogenized responses from mainstream chatbots. Enter Moltbot: a project promising radical customization, transparent development, and genuine community governance.

The Rebrand: From Obscurity to Viral Sensation
Moltbot's original identity was somewhat generic. The project existed in the mid-tier of open-source AI tools: used by enthusiasts, known in certain developer circles, but not commanding mainstream attention. Then came the rebrand.
The new branding positioned Moltbot not just as another chatbot, but as a personal AI assistant that actually learns from individual users. The key differentiator wasn't raw capability—it was customization depth. While ChatGPT treats every user identically (unless you pay for advanced features), Moltbot could be trained on your personal writing style, your preferences, your context, and your unique needs.
This repositioning immediately resonated. The rebrand campaign launched with specific messaging: "Your AI shouldn't treat you like a number. It should know you." The timing was perfect. By late 2024, people were increasingly frustrated with generic AI responses. They wanted tools that actually understood their individual needs.
The rebrand announcement itself became viral. Within 48 hours, Moltbot was trending on Twitter. Reddit's r/Machine Learning and r/Open Source subreddits filled with discussions. Tech journalists started writing about it. The open-source community, which often moves in slow, methodical ways, suddenly mobilized around this project.
What made the viral moment genuine—rather than pure marketing hype—was that people actually tried it. The barrier to entry was zero. You could fork the repository, set it up locally, and start customizing your instance immediately. No sign-up forms. No corporate gatekeeping. Just code and community.

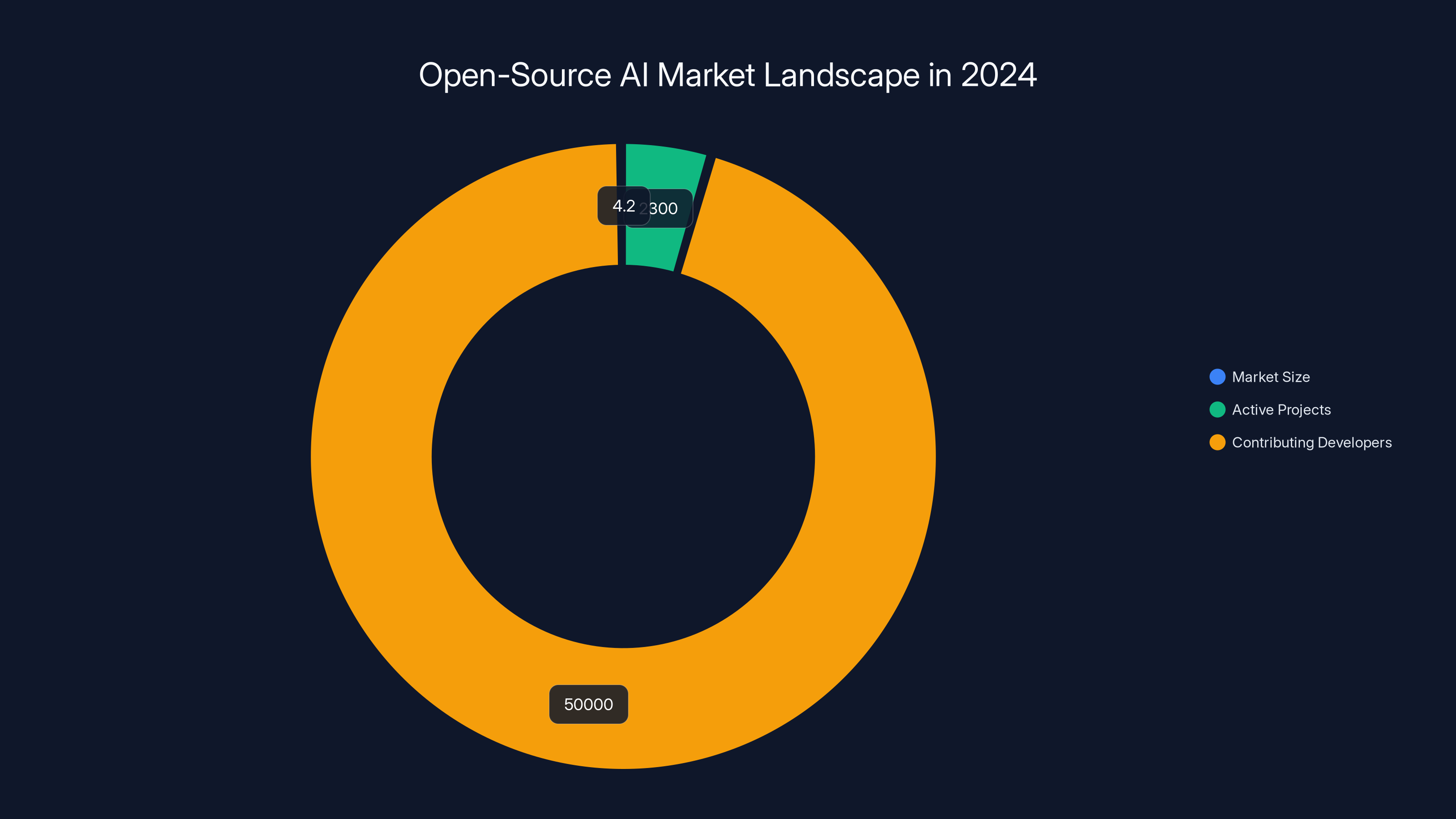
In 2024, the open-source AI market was valued at $4.2 billion, with over 2,300 active projects and contributions from more than 50,000 developers. Estimated data.
The Dark Side: Scams, Fraud, and Memecoin Chaos
Here's the thing about viral success in the AI space: bad actors move fast. Moltbot's unexpected fame created an obvious opportunity for fraudsters, and they didn't waste time exploiting it.
Within days of the rebrand announcement, fake tokens appeared. Scammers created cryptocurrencies named "Moltbot" or variations thereof, hoping to capitalize on confused investors who thought they were buying into the actual project. The project maintainers issued clear warnings: there is no official Moltbot token. There will never be a token. Any cryptocurrency claiming to represent Moltbot is a scam.
But the warnings didn't stop everyone. Telegram groups filled with users asking questions like "Is this the real Moltbot coin?" Some people lost money. The project maintainers found themselves spending more time fighting misinformation than they spent on actual development.
The fraud extended beyond crypto. Scammers created fake GitHub repositories that looked almost identical to the official Moltbot project. These fake versions included trojanized code designed to steal API keys or harvest user data. Unsuspecting developers cloned these malicious repositories and unknowingly deployed compromised versions of Moltbot.
Worse still, some individuals created knockoff "Moltbot" services. These were web applications that claimed to offer personalized AI experiences but actually just sold user data or inserted advertising. The official Moltbot project is ad-free and doesn't monetize user information. The counterfeits did exactly that.
The project leadership responded transparently. They published detailed post-mortems about the attacks. They created verification guides. They worked with GitHub and other platforms to take down malicious repositories. They even coordinated with cybersecurity researchers to analyze the fraudulent code and warn the community about specific attack vectors.
The irony is that these attacks validated Moltbot's core philosophy. Because the project is open-source and transparent, the community could collectively identify and respond to threats. With a closed proprietary platform, users would have no way to know if malicious code was introduced. Moltbot's openness became its best defense against fraud.

Why Personalization Matters: The Technical Differentiator
Beyond the cultural moment, Moltbot's rebrand centered on a genuine technical innovation: efficient personalization at scale. Understanding why this matters requires understanding how most AI chatbots work today.
When you interact with ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, you're using a base model that's identical for every user. The service provider added some fine-tuning and instruction following during training, but the core model doesn't adapt to you individually. In recent versions, you can create custom GPTs or provide context, but this is bolted-on top of a fundamentally unchanging system.
Moltbot approached the problem differently. The architecture was designed around user-specific adaptation from the ground up. Rather than having a single model serve millions of identical requests, Moltbot could maintain lightweight personalization layers for individual users. This meant:
User Context Integration: Every interaction teaches the system something about how you communicate, what you value, and what kind of responses work best for you. After a few dozen conversations, Moltbot isn't just responding to your literal words—it's responding to your communication style, your domain expertise, and your unique constraints.
Style Transfer: You can provide samples of your writing, and Moltbot learns to match that voice. If you write technical documentation with specific terminology and structure, the AI adapts. If you prefer conversational, casual responses with analogies, it shifts accordingly. This isn't just cosmetic—it fundamentally changes the quality of the output because it's actually aligned with what you want.
Preference Learning: The system learns what matters to you. If you consistently deprioritize speed in favor of thoroughness, it adapts. If you value creative exploration over accuracy, it learns that. Most commercial chatbots treat all users identically. Moltbot treats users as individuals with unique preferences.
The technical implementation is clever. Rather than retraining massive models for each user (computationally impossible), Moltbot uses a combination of prompt engineering, lightweight adapter layers, and retrieval-augmented generation to create personalization effects without massive overhead. The result is that you get customization benefits without the computational cost.

The Community Governance Model: Decision-Making by Community
Another critical aspect of Moltbot's rebrand was the governance model. The project didn't just claim to be open-source—it actually ceded meaningful decision-making power to the community.
Most open-source projects have a benevolent dictator model: one or a few core maintainers make final decisions. This works, but it creates bottlenecks and doesn't align with the philosophical principles of open-source development. Moltbot attempted something different: actually implementing community governance.
Here's how it works: major feature decisions, architectural changes, and policy updates go to a community vote. Token holders (and yes, this is where token economics come in, though separate from the scam tokens) get voting power. The system is transparent—all discussions are public, all votes are auditable, and anyone can propose changes.
This has real implications. When the maintainers proposed a change to the default personalization settings, the community voted against it. The maintainers disagreed with the vote but implemented what the community wanted anyway. This kind of accountability is almost unheard of in software development.
Of course, community governance also creates challenges. Decision-making is slower. Sometimes the community votes for something technically suboptimal. Sometimes vocal minorities can outweigh the silent majority. Moltbot experienced all of these problems during the rebrand period.
But here's what made it work: the transparency meant that problems were visible and discussable. When a decision turned out badly, the community could propose a reversal. Bad decisions weren't locked in by corporate leadership with no accountability. They could be undone.
The rebrand actually strengthened the governance model. Before, community governance was mostly theoretical—a nice idea with limited actual impact on direction. During the rebrand chaos, governance became essential. The community had to collectively decide how to respond to fraud, how to prioritize security fixes, and how to communicate with new users. Governance that worked in theory got tested in practice.

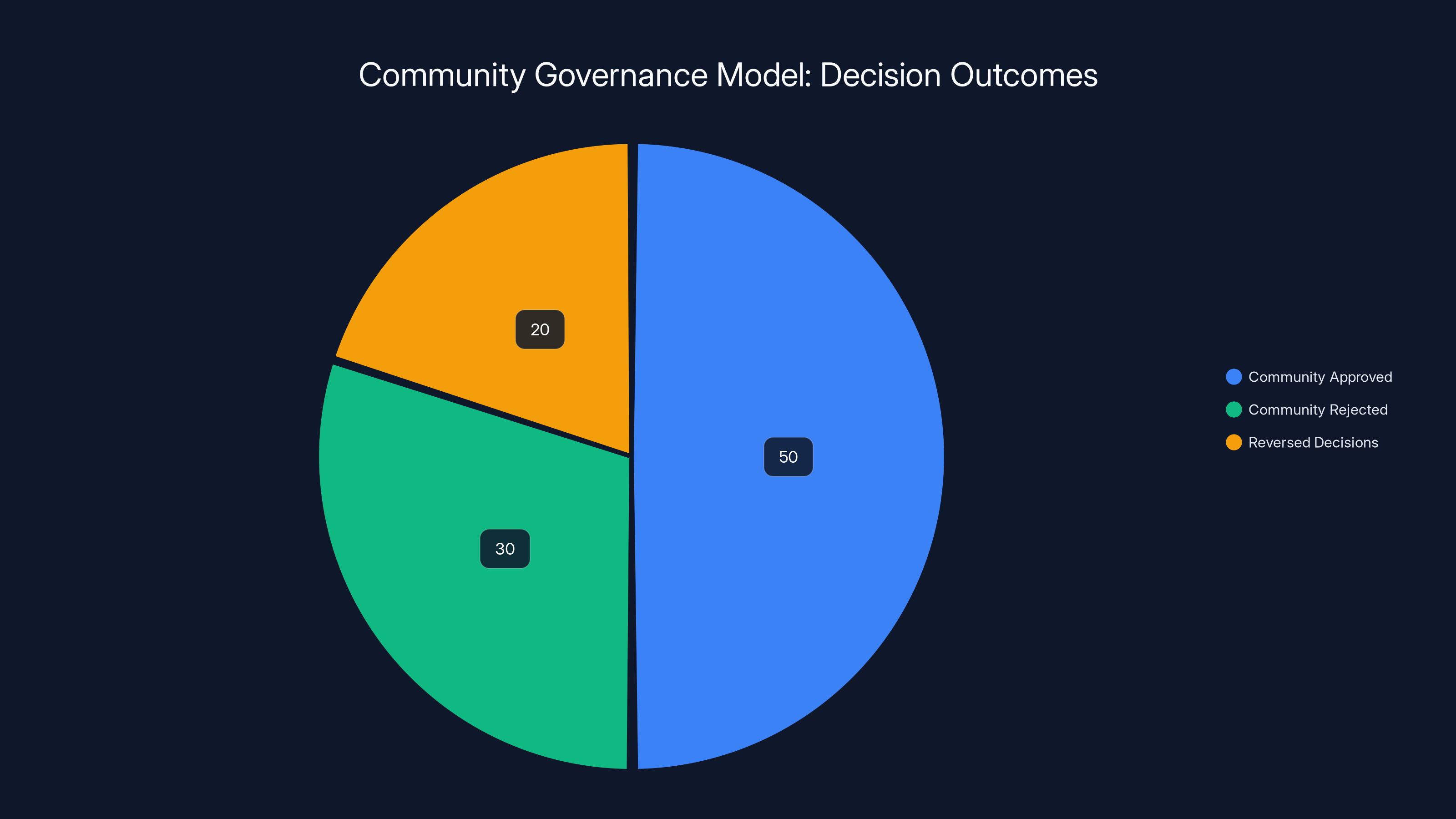
Estimated data shows that 50% of decisions were approved by the community, 30% were rejected, and 20% were reversed after initial approval, highlighting the dynamic nature of community governance.
The Viral Marketing Mechanics: How Internet Culture Amplified the Signal
Moltbot's viral moment wasn't random. It was the product of specific cultural conditions and genuine network effects, but it's worth understanding the mechanics of how something becomes unexpectedly popular.
First, there was genuine novelty. In a crowded AI chatbot market, Moltbot offered something visibly different. That difference was easy to explain and easy to experience. You didn't need a technical background to understand "it learns your preferences." You didn't need to read a white paper to test it out.
Second, there was community credibility. Open-source developers have genuine clout in tech communities. When respected developers started using Moltbot publicly, citing it as an actual improvement over commercial alternatives, that carried weight. It wasn't a company making claims—it was peers sharing experiences.
Third, the timing aligned with broader cultural shifts. By late 2024, there was growing skepticism about corporate AI. Concerns about data privacy, concerns about algorithmic bias, concerns about surveillance—all of these created an opening for a privacy-respecting alternative. Moltbot positioned itself in that gap.
Fourth, the rebrand messaging was emotionally resonant. "Your AI shouldn't treat you like a number" hit a nerve. People felt dismissed by generic AI tools. They wanted something that actually understood them. Moltbot promised exactly that.
Once the initial momentum started, network effects took over. Each person who tried Moltbot and had a good experience recommended it to friends. Each recommendation brought more people. More people meant more contributors to the project. More contributors meant faster improvements. Faster improvements meant more recommendations. The cycle continued.
But here's the important part: unlike manufactured viral moments, this one was genuine because the product actually delivered. People weren't just talking about Moltbot because the marketing was clever. They were talking about it because it worked and because it represented something they actually wanted.

Security Implications: The Cost of Openness
The fraud and scam attempts that followed Moltbot's viral moment raise important questions about security in open-source projects. There's a persistent assumption that open-source is inherently less secure than proprietary software. The Moltbot situation actually complicates that narrative.
On one hand, the openness created obvious attack surfaces. Bad actors could fork the repository and modify it maliciously. They could create convincing counterfeits. They could operate with relatively little friction because there's no centralized authority to shut them down immediately.
On the other hand, the openness also enabled rapid detection and response. Security researchers in the community immediately analyzed fraudulent code. They published analyses of attack vectors. They created tools to help users distinguish legitimate Moltbot instances from counterfeits. The community's collective intelligence was a far more powerful defense than any corporate security team could have been.
The key difference is that with open-source, security is distributed and collective. With proprietary software, security depends entirely on the company's resources and priorities. Moltbot had both more vulnerabilities and more defenders.
Moreover, the transparency created accountability for security. Users could audit the code themselves. If the maintainers introduced a security vulnerability, users could spot it before it became widespread. This isn't theoretical—it's a known advantage of open-source security practices that has been validated repeatedly across decades of software development.
Moltbot's experience suggests that for security-conscious users, open-source tools that are actively maintained and have engaged communities are actually more trustworthy than proprietary alternatives, precisely because the openness enables collective scrutiny.

The Business Model Question: How Do You Monetize Personalization?
Moltbot's rebrand raised immediate questions about sustainability. Open-source projects need funding. Community governance is great, but it doesn't pay server costs or support full-time maintainers.
Moltbot's approach to this was deliberately anti-mainstream. Rather than pursuing venture capital or building a corporate product, the project committed to remaining sustainably funded through:
Community Support: Direct donations from users who benefit from the project. No corporate sponsors required. This keeps the project aligned with user interests rather than investor interests.
Cooperative Ownership: Token holders (the real ones, not the scam versions) who hold governance stakes also fund development. This aligns incentives—the people making decisions about direction are also invested in the project's success.
Services, Not Software: The core software remains free and open. Revenue comes from optional services: hosted versions for people who don't want to run their own servers, premium support, enhanced features. This preserves the free core while funding development.
The model is deliberately not venture-scale. The project isn't trying to raise hundreds of millions or achieve unicorn status. The goal is sustainable funding for a tool that serves a real community need. This contrasts sharply with most AI startups, which are designed around maximum growth and eventual acquisition or IPO.
During the rebrand chaos, this business model actually proved its value. Because Moltbot wasn't desperate for growth metrics, the maintainers could respond carefully to problems rather than rushing to capitalize on viral momentum. They could turn down proposals that would compromise the project's principles. They could prioritize community trust over maximum user acquisition.

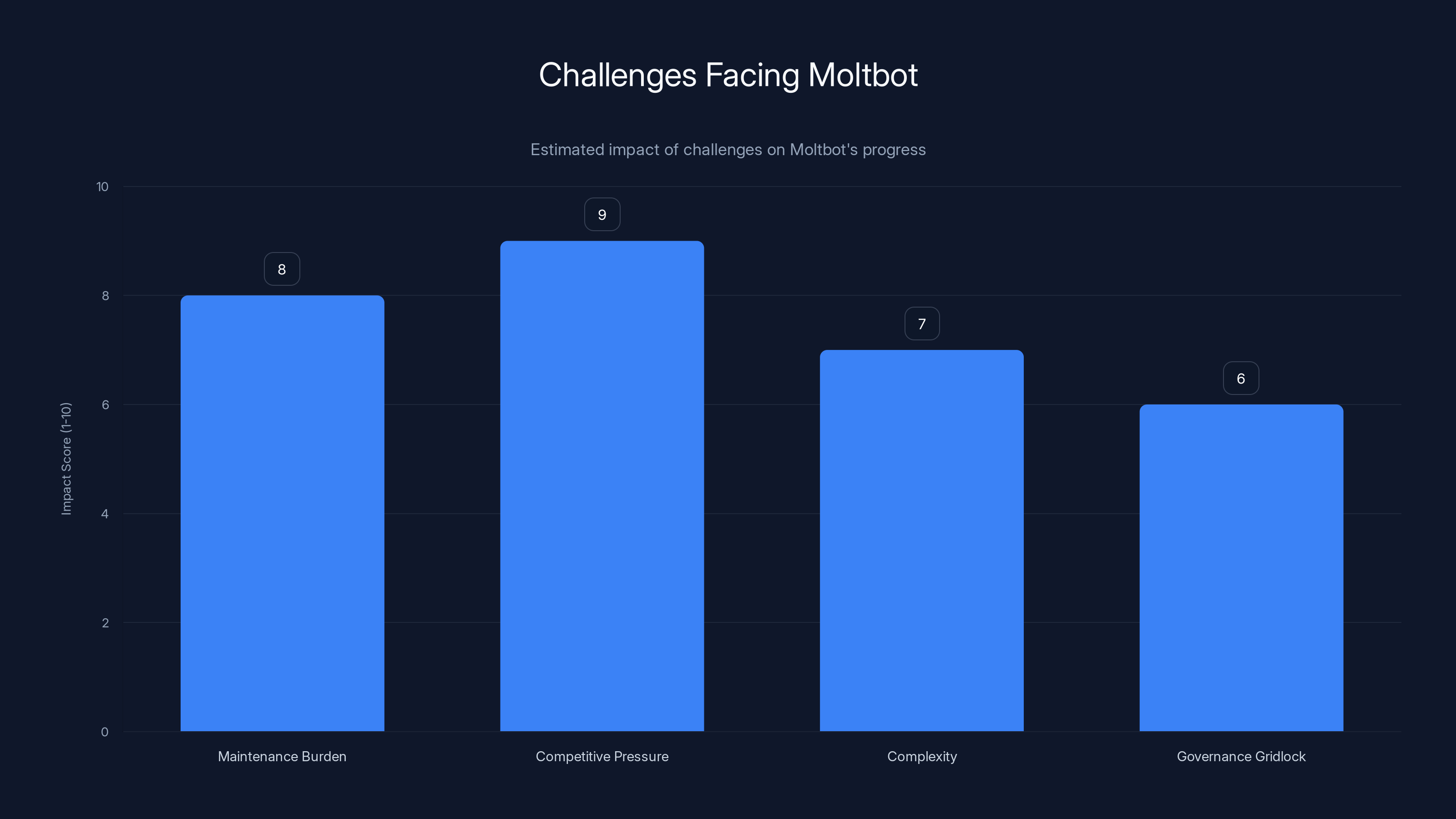
Competitive pressure and maintenance burden are estimated to have the highest impact on Moltbot's future success. Estimated data.
Technical Architecture: How Personalization Works Under the Hood
Understanding Moltbot's appeal requires getting into the technical details of how it actually achieves personalization. The system architecture is deceptively elegant.
At its core, Moltbot uses a base language model—typically a variant of Mistral or Llama—but wraps it with several layers of customization:
Adapter Layers: Small, trainable modules that sit between the input and the core model. These adapters learn user-specific patterns without modifying the base model. This keeps the core model identical across all users while enabling individual customization. The adapters are tiny compared to the full model, making them computationally efficient.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation: When you ask a question, the system doesn't just use the base model's training data. It retrieves relevant context from your personal interaction history, documents you've provided, and preferences you've set. This context gets injected into the prompt, effectively making the model "aware" of your specific situation.
Dynamic Prompting: Rather than using a static system prompt, Moltbot generates prompts dynamically based on your interaction history. If you've consistently asked for detailed explanations, the system prompt adapts. If you prefer brevity, it adapts. The model sees different instructions each time, tailored to what it knows about you.
Fine-Tuning on Demand: Users can optionally fine-tune the model on their own data. This is computationally expensive, but for power users with specific use cases, it's incredibly powerful. A programmer can fine-tune on their codebase. A writer can fine-tune on their published work. A researcher can fine-tune on their papers. The result is a model that truly understands their domain.
The genius of this architecture is that it provides personalization without requiring a new model per user. You don't have millions of separate models running. You have one efficient base model with millions of lightweight personalization layers.
Computationally, this means Moltbot can be run locally on consumer hardware. You don't need enterprise-grade servers. A laptop with a GPU can run the full system. This is revolutionary compared to centralized AI services that require expensive cloud infrastructure.
The Competition Response: How Chat GPT and Claude Adapted
Moltbot's unexpected success obviously created pressure on the dominant players. Both OpenAI and Anthropic announced personalization features in response, though the approaches differ significantly.
OpenAI's approach emphasizes custom instructions and memory—features that let you specify preferences and have ChatGPT remember previous conversations. It's useful, but it's fundamentally limited by ChatGPT's centralized architecture. You're still using OpenAI's servers. Your preferences are still stored on OpenAI's infrastructure. The personalization happens within OpenAI's controlled environment.
Anthropic similarly added memory and preference features to Claude. Again, useful for users, but constrained by the same architectural limitations. Claude can't truly adapt to your style because it's fundamentally the same model for every user.
Both companies have the capability to implement more sophisticated personalization. They could allow fine-tuning. They could run locally. They could decentralize control. They choose not to, for business reasons. Centralization provides data, control, and revenue opportunities. Decentralized personalization threatens that.
Moltbot's existence forced this conversation. It made clear to both companies and to users that real personalization is possible. Even if OpenAI and Anthropic don't fully embrace it, they now have to respond to users asking why their systems don't offer what Moltbot does.

Privacy Architecture: Keeping User Data Actually Private
Personalization and privacy are typically in tension. To learn about your preferences, a system needs data about you. To keep that data private, a system needs to limit who accesses it. Moltbot's architecture attempts to thread this needle.
The core principle is that your personal data never leaves your control unless you explicitly choose to share it. If you run Moltbot locally, all your interaction data stays on your machine. The model learns from your conversations, but those conversations never touch a server you don't control.
If you use a hosted version of Moltbot, you're choosing to share data with the operators of that instance. But here's the key difference: you know exactly what's happening and who has access. With commercial chatbots, terms of service are deliberately opaque about data use. With Moltbot, if you're running it yourself, there is no central authority. If you're using a hosted version, the source code is public—you (or someone you trust) can audit it.
The implications are significant for regulated industries. Healthcare organizations can run Moltbot locally, train it on patient data, and maintain HIPAA compliance. Law firms can run it locally, fine-tune it on cases, and maintain attorney-client privilege. Financial services can do the same. Commercial chatbots make this essentially impossible because the vendors fundamentally cannot guarantee data isolation.
Moltbot's rebrand explicitly emphasized this privacy-first approach. In a moment where privacy concerns about AI are growing, having a tool that actually gives you control over your data resonated deeply.

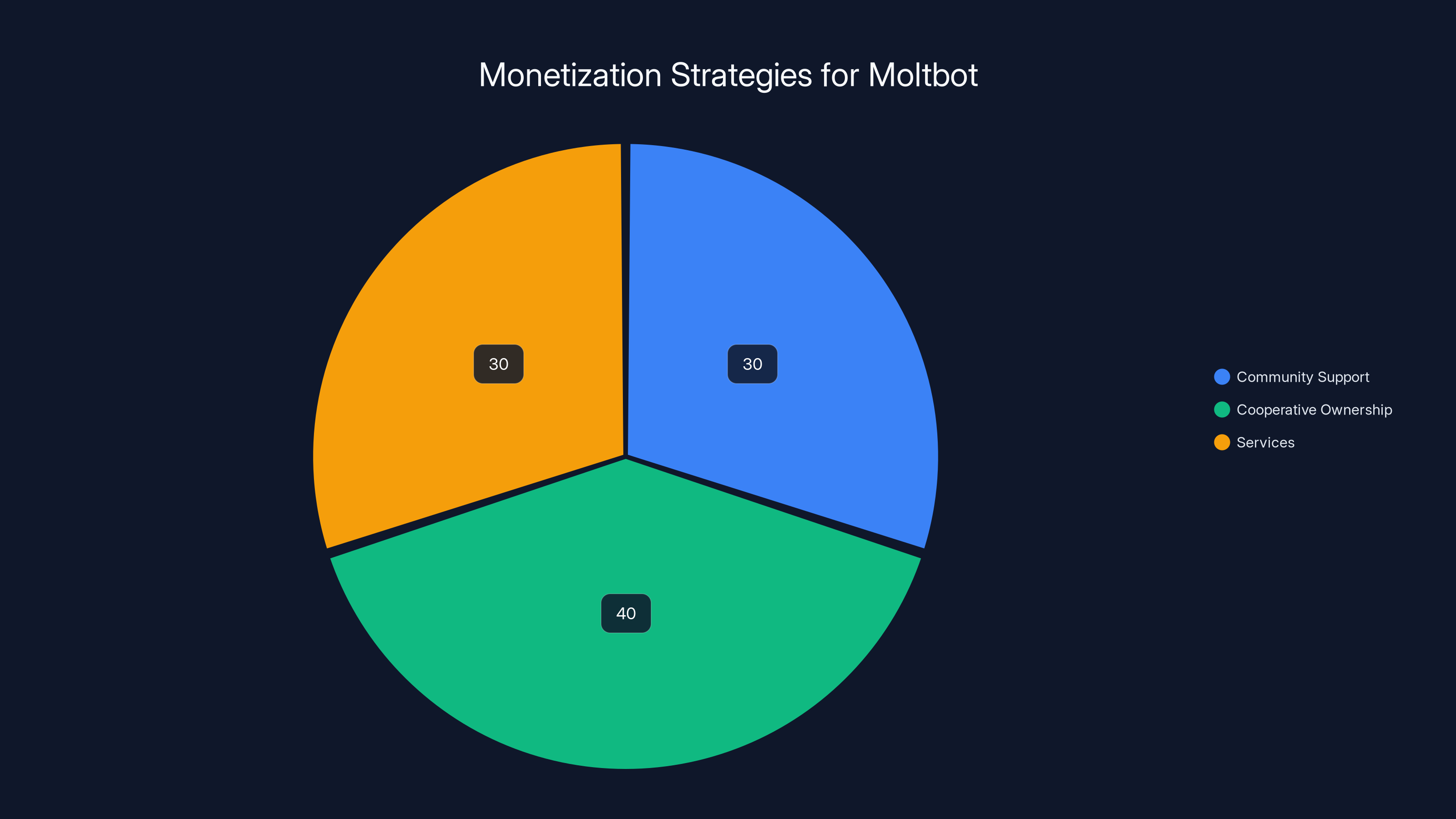
Moltbot's revenue is estimated to be evenly split between community support, cooperative ownership, and services, reflecting a balanced approach to sustainable funding. Estimated data.
User Experiences: Stories From the Rebrand Moment
The viral moment produced countless anecdotes about what Moltbot enabled. Understanding these stories helps explain why the rebrand resonated so deeply.
A data scientist described using Moltbot to accelerate research. She fine-tuned the model on her research papers and datasets, then used it as a research assistant. The personalized model understood her domain, her methodology, and her questions. It dramatically reduced the time she spent on literature review and problem formulation. She could ask domain-specific questions and get contextually appropriate answers.
A novelist fine-tuned Moltbot on his published works and used it as a writing assistant. The model learned his voice, his pacing, his character archetypes. When he started a new story, the assistant could suggest plot developments that felt consistent with his previous work. The personalization eliminated the awkward phase where a generic AI assistant learns how you write.
A developer ran Moltbot locally, fine-tuned it on her company's codebase, and used it for code review and documentation generation. The model understood her team's coding conventions, architectural patterns, and tech stack. Code suggestions were immediately applicable rather than generically correct.
These stories matter because they show that Moltbot's appeal wasn't theoretical. People genuinely had use cases that weren't well-served by existing tools. The rebrand created visibility for the solution.
The Sustainability Question: Can Open Source Scale?
Moltbot's success raised fundamental questions about the scalability of open-source AI development. Can a community-driven project with distributed governance actually build and maintain sophisticated AI systems?
The answer appears to be yes, with caveats. Moltbot demonstrated that you can build complex systems through community contribution. The technical quality of the codebase is high. The development velocity is fast. The community's collective capability exceeds what a small team could achieve.
But sustainability requires solving specific problems. First, funding. Open-source projects need money for infrastructure, full-time maintainers, and security audits. Moltbot's cooperative funding model works, but it requires discipline. The project must remain focused on genuine user value rather than chasing revenue.
Second, governance. Community governance is more legitimate than autocratic decision-making, but it's also slower and sometimes inconsistent. Moltbot experienced delays on critical decisions because the community voting process took time. This is acceptable for non-urgent matters but problematic for security issues.
Third, continuity. What happens when key maintainers burn out or move on? Moltbot's structure disperses critical knowledge across the community, which is good. But ensuring that knowledge persists and that new people can step in requires deliberate effort.
The rebrand moment forced Moltbot to confront these challenges directly. The viral success created pressure and opportunity simultaneously. The project had to scale while maintaining its values. That's difficult, and Moltbot is still working through it.

Future Trajectory: Where Moltbot Goes From Here
Moltbot's immediate future is defined by consolidation. The viral moment created massive interest, but converting interest into sustainable adoption requires work. The project is focusing on:
Stability: Ensuring that the core system remains reliable as more people use it. The rebrand brought an explosion of new users, and scaling infrastructure is expensive and complex.
Documentation: Making it easier for new users to get started. Community-driven projects often suffer from documentation gaps. Moltbot is investing heavily in how-to guides, tutorials, and troubleshooting resources.
Ecosystem: Building tools and integrations that extend Moltbot's capabilities. Rather than trying to do everything itself, Moltbot is becoming a platform that other developers can build on.
Security Maturity: Implementing formal security practices. Community projects often have informal security processes. As Moltbot grows, it's moving toward regular audits, penetration testing, and responsible disclosure programs.
Longer term, Moltbot could influence how AI development happens more broadly. If it succeeds, it demonstrates a viable alternative to venture-backed, closed-source AI companies. That's not to say VC-backed companies are bad—they have advantages in terms of resources and focus. But they shouldn't be the only option.
The most likely scenario is that Moltbot becomes part of a more diverse AI ecosystem. Some people will continue using ChatGPT and Claude for their convenience and capability. Others will run open-source models locally. Still others will use specialized tools for specific tasks. The monoculture of centralized AI services might be ending.

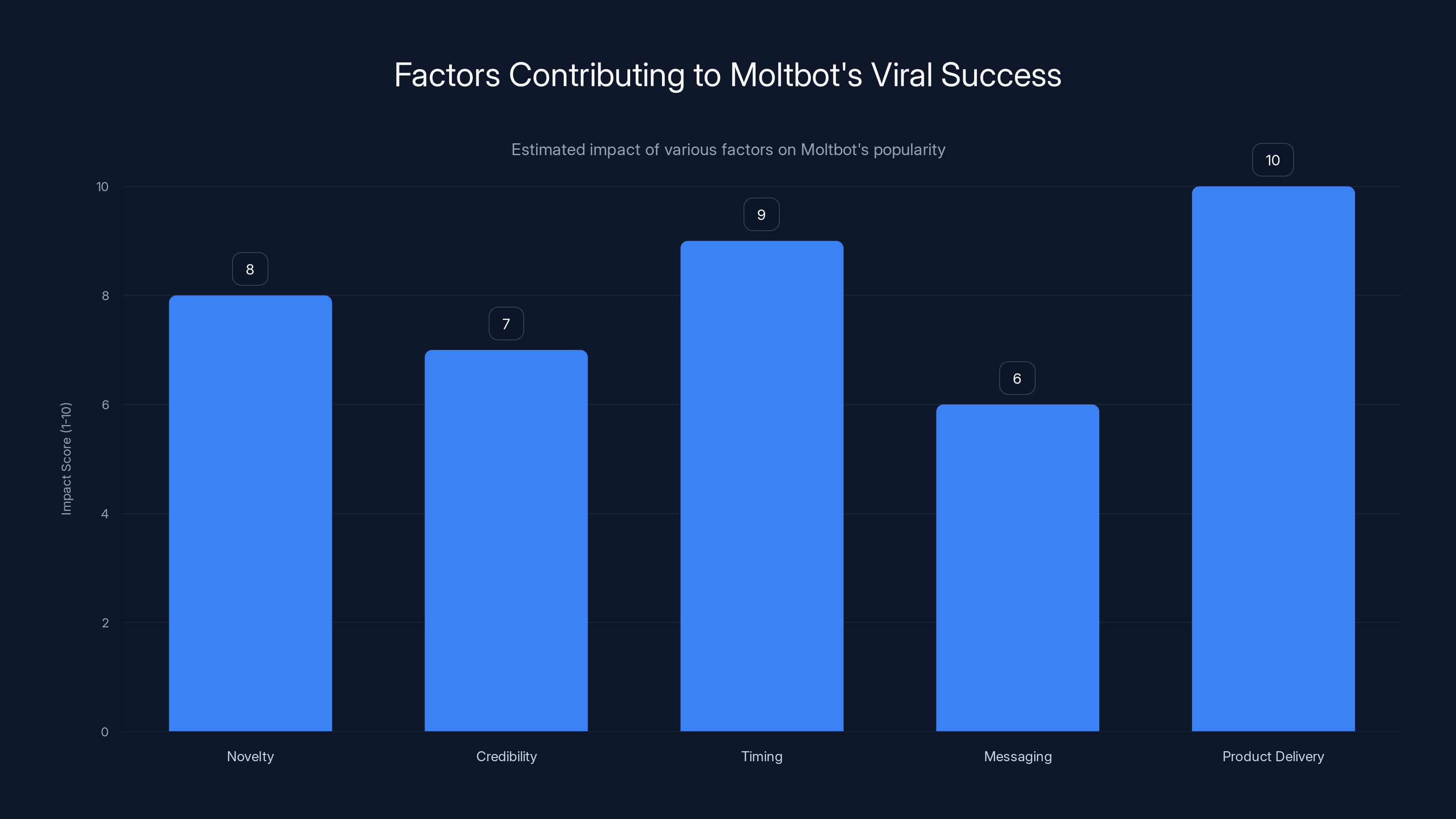
Moltbot's viral success was driven by its genuine novelty, strong credibility, perfect timing, resonant messaging, and effective product delivery. (Estimated data)
Lessons for AI Development: What Moltbot Teaches Us
Beyond the specific story, Moltbot offers several lessons for how AI development might evolve:
Personalization Is Real: The difference between generic AI and personalized AI is not theoretical. Users notice. Users value it. If a system learns about them, they get better results. This should push the industry toward more adaptive systems.
Transparency Matters: Users care about how systems work. They want to understand what data is being used. They want auditability. Open-source projects, despite their vulnerabilities, build trust through transparency in ways closed systems can't.
Communities Can Build Complex Things: The assumption that only well-funded companies can build sophisticated software is increasingly wrong. Communities can coordinate complex development. They can maintain high standards. They can compete with commercial products.
Governance Is Hard But Important: Community-driven projects that make decision-making transparent and inclusive earn loyalty. Autocratic projects, even if technically superior, lack that alignment with user interests. As AI systems become more consequential, governance legitimacy becomes more important.
Control and Privacy Are Competitive Advantages: As concerns about surveillance and data exploitation grow, tools that give users actual control become increasingly valuable. This is not a niche preference—it's a fundamental human concern.
Moltbot's rebrand moment captured all of these lessons in a single viral event. It showed what becomes possible when you prioritize users, transparency, and community over maximizing growth and revenue.

The Broader Context: AI Culture in 2025
Moltbot's success also reflects broader cultural shifts in how people think about AI. By 2025, the novelty of AI has worn off. People are moving past "wow, AI can do things" to "AI is becoming infrastructure. Now what?"
That shift creates different priorities. In 2022 and 2023, people cared about capability. Can the AI do the task? With Moltbot's rebrand, the focus shifted to value and alignment. Does the AI do what I need, in the way I prefer? Does it respect my data and my control?
This cultural shift advantages projects like Moltbot. They're not competing on raw capability. They're competing on control, customization, and values alignment. Those are different competitive dynamics.
It also explains why the rebrand resonated with fraud and scams as easily as it resonated with genuine interest. When something becomes culturally significant, bad actors will try to exploit it. That's not a flaw in Moltbot—it's a sign that people genuinely care about what it represents.

Challenges Ahead: Realistic Assessment
It would be inaccurate to suggest that Moltbot's future is guaranteed. The project faces real challenges:
Maintenance Burden: The explosion of interest created more users, more issues, more demands. Community members may burn out. Critical contributors may leave. Without full-time staff (and Moltbot's model prevents that), maintaining momentum is difficult.
Competitive Pressure: OpenAI and Anthropic are not standing still. They're improving their personalization features, reducing costs, and adding capabilities. They have resources that Moltbot can't match. The gap might widen rather than narrow.
Complexity: Personalization adds complexity. Getting the architecture right is harder than building a generic chatbot. Maintainers might make mistakes. Performance might suffer. Users might have frustrating experiences.
Governance Gridlock: Community voting can lead to indecision or decisions that satisfy no one. Moltbot might find itself unable to move quickly when speed matters.
These aren't hypotheticals. Open-source projects fail regularly despite strong initial momentum. The fact that Moltbot is aware of these risks and actively working to mitigate them is encouraging, but execution is everything.

Practical Implications: Should You Use Moltbot?
For different users, the answer is different. Moltbot is genuinely useful if:
You want control: You don't want your interactions stored on corporate servers. You want to run the system yourself.
You have specialized needs: Your use case is narrow enough that personalization provides real value. A writing tool, a coding assistant, a research helper that actually understands your domain.
You value transparency: You want to understand how the system works. You want the option to audit the code. You want to know exactly what data is being used.
You're technically capable: Moltbot requires some technical chops. You need to be comfortable with command lines, model files, and infrastructure decisions. It's becoming more user-friendly, but it's not yet as simple as ChatGPT.
Moltbot is probably not ideal if:
You want simplicity: ChatGPT is easier. You open it, type a question, get an answer. Moltbot requires initial setup and ongoing maintenance.
You need maximum capability: OpenAI's larger models (GPT-4) have capabilities that open-source models don't match. If you need state-of-the-art performance, Moltbot might fall short.
You want a finished product: Moltbot is still evolving. Hosted services for commercial AI have SLAs, support teams, and stability guarantees. Moltbot has a community and goodwill.
You can't handle community governance: If you want something that just works without worrying about politics and community decision-making, commercial products are simpler.

FAQ
What exactly is Moltbot?
Moltbot is an open-source AI chatbot designed to provide personalized, adaptive responses by learning from individual user interactions and preferences. Unlike centralized services like ChatGPT, Moltbot can be run locally or self-hosted, allowing users to maintain control over their data while benefiting from customized AI assistance that adapts to their unique communication style, domain knowledge, and specific needs.
How does Moltbot personalize responses?
Moltbot uses several techniques to achieve personalization without requiring separate models for each user. Adapter layers add lightweight customization on top of the base model, retrieval-augmented generation pulls relevant context from your interaction history, and dynamic prompting tailors system instructions based on your established preferences. For power users, optional fine-tuning on personal data creates even deeper specialization, allowing the model to understand your specific domain, writing style, or expertise.
What happened during Moltbot's rebrand?
The rebrand repositioned Moltbot from a generic open-source chatbot to a personalization-focused AI assistant, emphasizing user control and customization. This triggered massive viral interest across tech communities. However, the visibility also attracted fraud: scammers created fake Moltbot cryptocurrencies, cloned the GitHub repository with malicious code, and launched counterfeit services. The community responded collectively through transparency and collaborative security efforts, ultimately validating the advantages of open-source development.
Why did Moltbot become so viral?
Several factors combined: genuine novelty in a crowded market, credibility within developer communities, perfect timing with growing skepticism about corporate AI, emotionally resonant messaging about user control, and most importantly, a product that actually delivered on its promises. Network effects amplified the signal as users recommended it to peers, contributing developers added improvements, and visibility continued growing. Unlike manufactured viral moments, this one sustained because the underlying product remained useful.
How is Moltbot different from ChatGPT or Claude?
The core differences are architectural and philosophical. Moltbot is open-source and can run locally, giving you complete control over your data. It's designed for deep personalization at the system level, not as an add-on. It uses community governance for decisions rather than corporate leadership. Most crucially, with Moltbot, you're not dependent on a company's terms of service, server infrastructure, or data handling policies. You can customize everything. That flexibility comes with responsibility—you manage your own infrastructure—but you gain privacy and control in return.
What are the security risks of using Moltbot?
Because Moltbot is open-source, bad actors can clone and modify it, potentially introducing malicious code. If you download from untrusted sources, you risk trojanized versions. However, the transparency also enables the community to rapidly identify and counter threats through code audits and security analysis. If you run Moltbot locally from the official GitHub repository, the security profile is actually superior to centralized services because you control the environment and can audit the code yourself. Using a hosted Moltbot instance depends entirely on trusting that specific operator's security practices.
Can Moltbot work offline?
Yes, that's one of its core advantages. You can run Moltbot entirely locally on your own hardware with no internet connection required beyond the initial model download. The model files are large (typically 7GB to 40GB depending on the model version), and the initial setup requires some technical configuration, but once running, it operates completely offline. This is impossible with ChatGPT or Claude, which require cloud connectivity and server access.
How much does Moltbot cost?
The core software is completely free and open-source. You only pay for infrastructure: either the hardware to run it locally or the costs of hosting it on a cloud provider. If you want a hosted version managed by the community, there are optional support tiers and commercial services, but the base model and code remain free. This is fundamentally different from ChatGPT, which charges per API call or subscription, or Claude, which requires a paid subscription for the best models.
Why should developers care about Moltbot?
For developers specifically, Moltbot offers customization impossible with commercial tools. You can fine-tune it on your codebase, making it understand your architecture and conventions. You can run it locally without worrying about API rate limits or costs scaling with usage. You can integrate it directly into your development environment. Most importantly, you can modify the code itself—adding features, changing behavior, or fixing issues without waiting for the company to push updates. This level of control is revolutionary for power users.
What's the long-term vision for Moltbot?
The project aims to demonstrate that open-source, community-driven AI development can be a viable alternative to venture-backed companies. The goal isn't to replace ChatGPT or Claude but to prove that users deserve choice and that decentralized, transparent AI systems can be competitive. Long-term success looks like Moltbot becoming part of a diverse AI ecosystem where users select tools based on their specific needs rather than defaulting to centralized services by default.
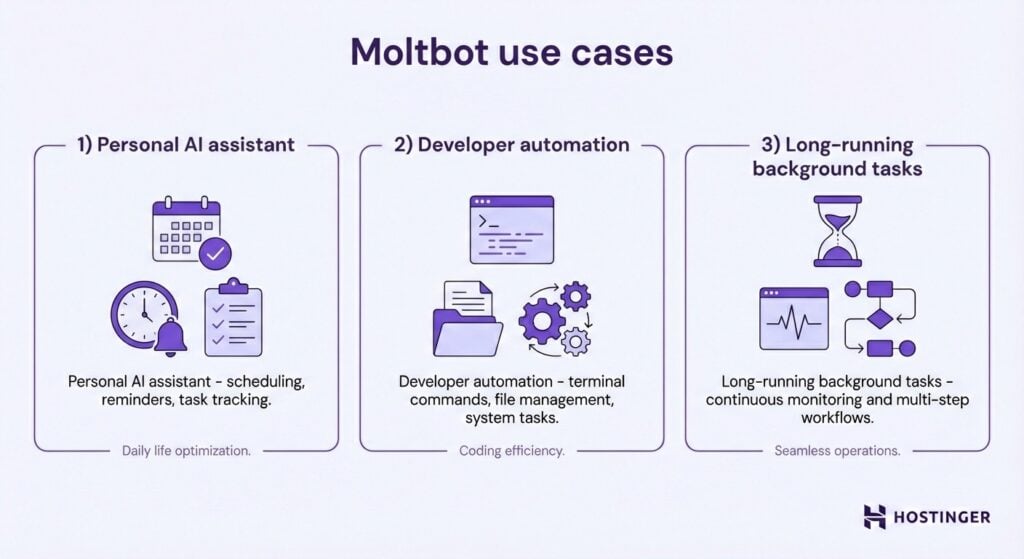
Conclusion: The Chatbot That Changed the Conversation
Moltbot's rebrand and subsequent viral moment represent something larger than a single project's success. It's evidence that the era of centralized AI monoculture might be ending. Users are increasingly aware that they have options. They're increasingly willing to trade convenience for control. They're increasingly skeptical of corporate narratives about AI inevitability.
The fraud and scams that followed the rebrand don't diminish this moment. If anything, they reinforce it. The scams existed because people suddenly cared deeply about what Moltbot represented. Fraudsters exploit what's valuable. The fact that bad actors tried to capitalize on the moment proves that the moment was real.
For the AI industry broadly, Moltbot serves as a warning and an opportunity. The warning is that dominance through network effects and massive resources is not guaranteed. If your users feel trapped or exploited, they'll embrace alternatives, even inconvenient ones. The opportunity is that there's genuine demand for tools that respect user autonomy, transparency, and control.
The technical achievement—building personalization that actually works at scale without centralized infrastructure—is remarkable. But the social achievement might matter more. Moltbot proved that a community can collectively maintain complex software, make governance decisions democratically, and respond to crises transparently. In 2025, those capabilities might be more valuable than raw capability.
It remains to be seen whether Moltbot can sustain this moment. The project faces genuine challenges. Competitors have more resources. Maintaining community momentum over years is harder than benefiting from initial viral excitement. Governance is harder than autocracy. But if any project can pull it off, the one with the most engaged, motivated community might be the one to do it.
Moltbot's story isn't finished. It's entering the phase where viral interest becomes either sustainable adoption or forgotten trend. The next chapters will determine whether this moment was a cultural blip or the beginning of something larger.
For anyone watching the AI industry evolve, Moltbot is essential to understand. It's not the future of AI—no single tool is. But it's evidence that the future will include more options, more transparency, and more user control than the present. That future benefits everyone, including people who never use Moltbot directly, because competition and alternatives make the entire industry better.
Key Takeaways
- Moltbot achieved viral success by offering genuine personalization and user control where centralized AI services only provided generic responses
- Open-source transparency proved both a vulnerability (fraud, scams) and strength (community-driven security response)
- Community governance and sustainable funding models represent viable alternatives to venture-backed AI companies
- Users increasingly value privacy, control, and understanding how AI systems work over pure convenience
- Moltbot demonstrates that specialized, personalized tools can compete with massive platforms if they solve real user problems
Related Articles
- Moltbot: The Open Source AI Assistant Taking Over—And Why It's Dangerous [2025]
- Moltbot (Clawdbot): The Viral AI Assistant Explained [2025]
- Moltbot AI Agent: How It Works & Critical Security Risks [2025]
- Moltbot AI Assistant: The Future of Desktop Automation (And Why You Should Be Careful) [2025]
- ChatGPT Go vs Plus: Is the Budget Tier Worth It? [2025]
- Wikipedia's 25-Year Journey: Inside the Lives of Global Volunteer Editors [2025]
![Moltbot's Viral Rebrand: How an AI Chatbot Became Internet Sensation [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/moltbot-s-viral-rebrand-how-an-ai-chatbot-became-internet-se/image-1-1769744225941.jpg)



