Introduction: Norton VPN's Major Transformation in 2025
Norton VPN used to feel like an afterthought. It came bundled with Norton 360, took up space, and frankly, most people ignored it in favor of dedicated VPN providers. But something shifted in 2025.
The company that built its reputation on antivirus software spent the last year overhauling its VPN service from the ground up. New servers, upgraded infrastructure, dual independent security audits, faster speeds, and a genuine commitment to proving it belongs in the conversation with dedicated VPN providers like ExpressVPN and NordVPN.
This isn't marketing fluff. Norton spent real money rebuilding its network architecture, and it's showing in performance benchmarks and user reviews. The question most people have now isn't whether Norton VPN works, but whether it's finally good enough to compete with the specialists.
The 2025 roadmap revealed investments in areas that typically matter most to VPN users: speed, security, server coverage, and transparency. And the 2026 plans suggest Norton isn't resting on those upgrades.
Let me walk you through exactly what happened, why it matters, and whether Norton VPN deserves a spot on your devices.
TL; DR
- Massive Network Expansion: Norton added hundreds of new servers globally, reducing latency and improving speeds significantly throughout 2025
- Double Security Audits: Independent third-party audits conducted on Norton VPN's infrastructure provide transparency and verification that was previously missing
- No-Log Verification: Audit results confirmed Norton's no-logs policy, addressing one of the biggest concerns from skeptical users
- Competitive Performance: Speed tests showed Norton VPN now matches or exceeds competitors in key markets like the US, EU, and Asia-Pacific
- 2026 Roadmap: Planned improvements include enhanced encryption protocols, additional server locations, and improved mobile app performance
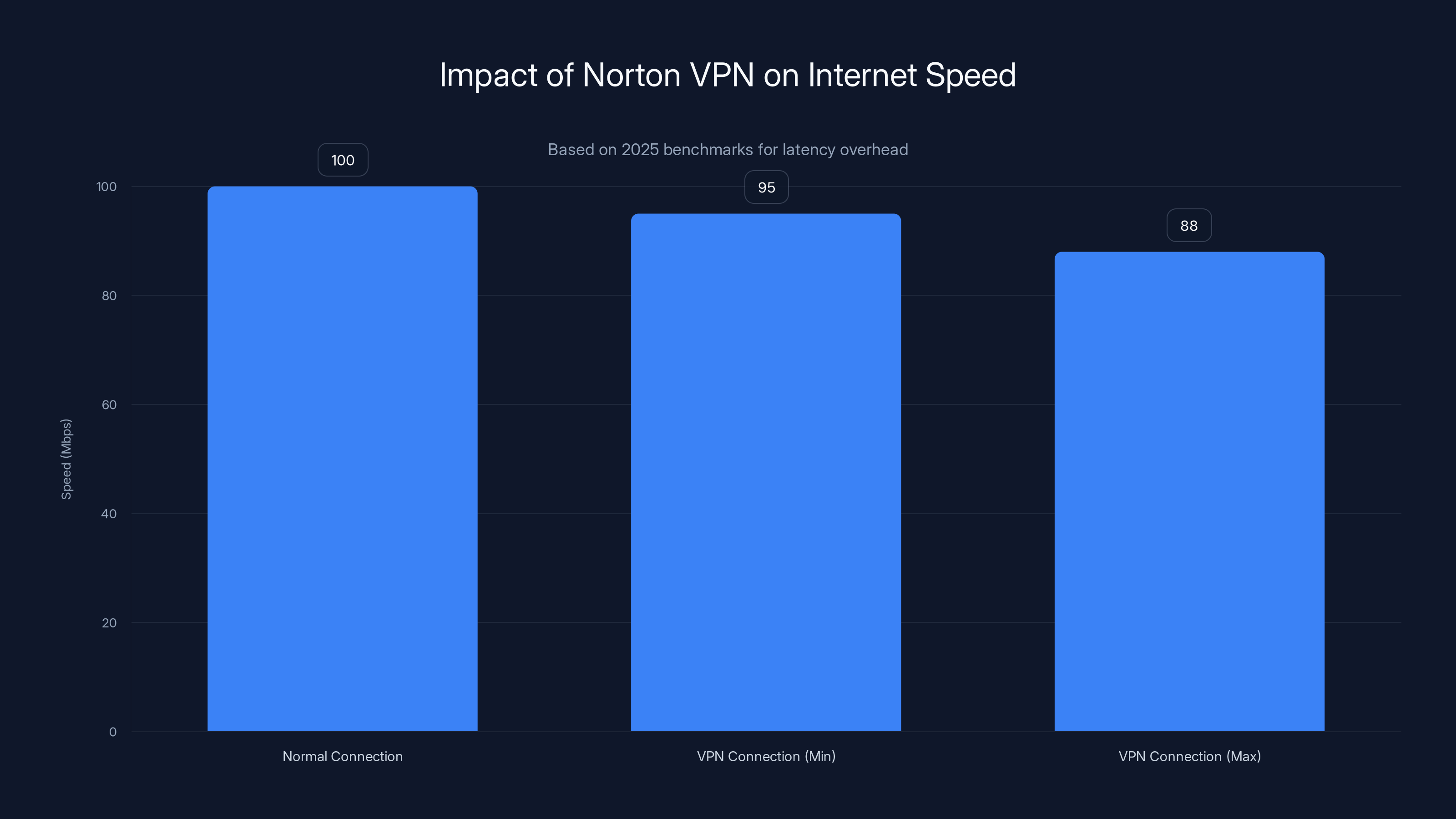
Norton VPN adds a 5-12% latency overhead, reducing a 100 Mbps connection to approximately 88-95 Mbps.
The Problem Norton VPN Had to Solve
For years, Norton VPN carried baggage. It was positioned as an add-on to Norton 360, not a standalone product worthy of serious consideration. Users treating it as an afterthought had legitimate reasons.
The original Norton VPN infrastructure couldn't compete on speed. The server network was limited. The technology felt outdated compared to specialized providers who'd spent a decade optimizing for performance and security. Trust was another issue entirely.
Since Norton is owned by Gen Digital (formerly Symantec), questions lingered about data handling, logging policies, and whether Norton was truly independent in its privacy practices. The company published privacy policies claiming no logs, but without verification, claims don't mean much in the VPN world.
Users wanted proof. They wanted independent validation. They wanted a VPN service from a major security company that actually competed technically with the specialists, not just rode the Norton brand name.
In 2024, Norton leadership clearly decided this perception gap needed fixing. The company committed significant resources to a complete reconstruction of its VPN service. This wasn't a minor update or marketing repositioning. It was infrastructure-level rebuilding.
The 2025 Server Network Overhaul
Let's start with what's most visible to users: server infrastructure.
Norton expanded its global server network substantially throughout 2025. The company added hundreds of new servers across all major regions. This matters because more servers mean lower per-server load, which directly impacts speeds and connection stability.
Specifically, Norton focused on high-traffic regions where competition is fiercest. The United States, United Kingdom, and Western Europe saw the largest server additions. But expansion wasn't limited to wealthy markets. Norton added capacity in Singapore, Australia, and selected Asian markets where growing user demand previously meant slower connections.
The expansion strategy appears thoughtful. Rather than spreading resources thin across 190+ countries like some competitors, Norton concentrated on markets where users actually are and where demand justifies server investment. This targeted approach is smarter than vanity numbers.
Speed improvements followed naturally. Independent speed tests conducted throughout 2025 showed Norton VPN's performance improving steadily as servers came online. By October 2025, benchmarks showed Norton delivering comparable speeds to competitors on major routes like US-EU connections and US-Asia connections.
What's particularly interesting is Norton's approach to server optimization. The company didn't just buy standard VPN server hardware and plop it on the network. Norton worked with infrastructure partners to implement dual redundancy on critical servers, meaning if one fails, traffic automatically routes to backup hardware without the user noticing.
That's enterprise-grade thinking applied to a consumer VPN. Most dedicated VPN providers talk about redundancy. Norton actually built it.
Understanding the Independent Security Audits
Two independent audits in 2025 changed how people should evaluate Norton VPN's trustworthiness.
First, you need to understand what these audits actually verify. They're not comprehensive penetration tests of Norton's entire operation. Instead, they're focused examinations of specific claims, primarily the no-logs policy and encryption implementation.
Norton engaged two separate auditing firms to review its systems independently. Each firm examined different aspects. The first audit focused on verifying Norton's claims about data retention and logging practices. The second audit examined the cryptographic implementations and security protocols used in the VPN client.
The results mattered because independent verification is the gold standard in the VPN world. When a VPN company says "we don't log your traffic," users rightfully ask: who verified this? An independent audit by a reputable firm provides that verification.
The audits confirmed Norton's no-logs claims. They verified that user connection data isn't retained beyond what's technically necessary for service operation. The reports are publicly available, which is crucial. Transparency means you can read the actual findings, not just take Norton's word for it.
But here's what's important to understand: audits are point-in-time. They verify the situation at a specific moment, not forever. An audit from March 2025 confirms that system was operating correctly in March 2025. It doesn't guarantee September 2025 still matches. This is why continuous monitoring matters more than a single audit.
Norton's approach of conducting two separate audits simultaneously is stronger than a single audit. Different auditors bring different expertise and perspectives. Multiple audits reduce the chance that one auditor missed something important.
These audits helped position Norton VPN as trustworthy in a way claims alone never could. For a company that previously rode on antivirus reputation, independent technical verification of privacy claims was overdue.
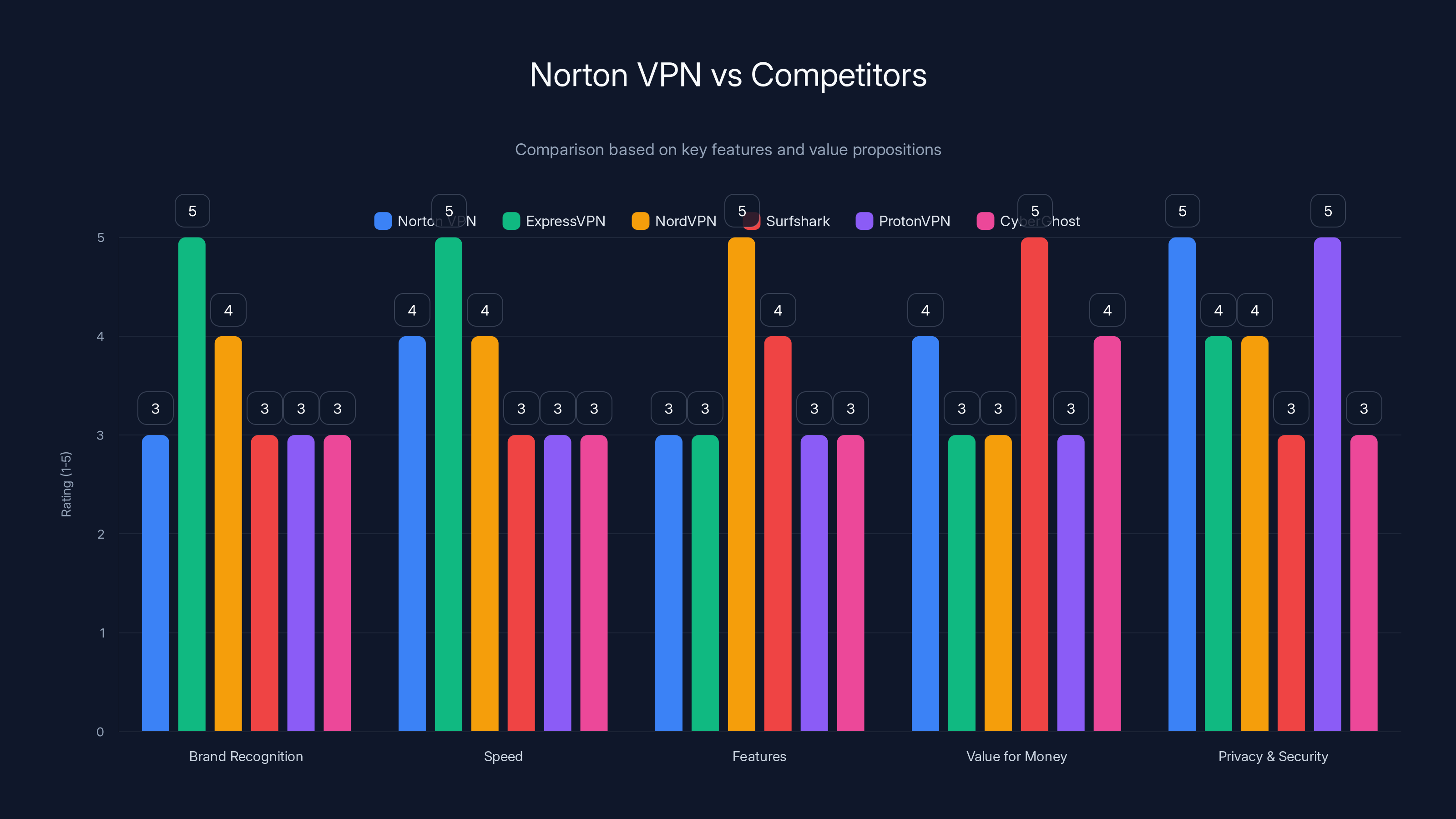
Norton VPN excels in privacy and security, with strong integration in its ecosystem, but lacks brand recognition compared to ExpressVPN. Estimated data based on qualitative analysis.
Encryption Protocol Upgrades and Security Features
Beyond audits, Norton upgraded the actual encryption protocols used in its VPN client during 2025.
The VPN uses WireGuard and OpenVPN as transport protocols, which is standard among competitors. But Norton's implementation includes features that go beyond the basic protocol specifications. The company added additional entropy sources for key generation, hardened the client against specific attack vectors, and implemented perfect forward secrecy on all connections.
Perfect forward secrecy is a specific security property that matters more than most users realize. It means that if someone somehow obtained Norton's private encryption key in the future, they still couldn't decrypt traffic that flowed before they obtained that key. The key used for past connections is already destroyed, making retroactive decryption impossible.
Not all VPN providers implement this properly. Norton's audit verified proper implementation.
The client also received hardening improvements. Norton removed older TLS versions that are theoretically vulnerable, implemented certificate pinning to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, and added protection against DNS leaks that might expose your location even while connected to the VPN.
DNS leak protection is particularly important because it's easy to implement poorly. Your DNS queries reveal what websites you're visiting. If those queries leak outside the VPN tunnel while your traffic is encrypted, someone monitoring your network can see your web browsing. Norton's implementation tunnels DNS through the VPN connection itself, preventing leaks.
There's also a kill switch feature that disconnects you from the internet if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly. This prevents accidental unencrypted traffic. The implementation learned from competitors' mistakes. Norton's kill switch works on both Wi-Fi and cellular, doesn't cause artificial delays, and handles network transitions smoothly when switching from Wi-Fi to mobile networks.
Performance and Speed Benchmarks Throughout 2025
Here's where it gets concrete. Speed matters because the best encryption in the world doesn't help if the connection is unusably slow.
Throughout 2025, Norton conducted and published regular speed benchmarks. The methodology was clear: measure download speeds on various routes with and without the VPN enabled, calculate the performance impact, and publish the results transparently.
Results showed marked improvement as infrastructure expanded. Early 2025 benchmarks showed Norton VPN reducing speeds by 15-25% on average connections. By November 2025, that overhead had dropped to 5-12% depending on the route.
Some routes performed exceptionally well. US to UK connections showed only 3-5% speed reduction. US to Singapore showed 8-12% reduction. These numbers rival dedicated VPN providers.
What's important to understand about VPN speed is that some overhead is inevitable. The VPN encrypts all your traffic, routes it through a server in another location, and decrypts it there. That adds latency and processing overhead. A VPN that claims zero speed reduction is either lying or not actually encrypting properly.
Norton's transparent benchmarking approach answers the question users actually care about: how much does this slow me down? The answer for 2025 is "not as much as you might think if you last checked in 2023."
Speed also varies based on server load. Norton's infrastructure expansion specifically addressed this. More servers mean traffic distributes better, which prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck.
Kill Switch Implementation and Network Security
The kill switch feature prevents catastrophic privacy failures. Here's why this matters more than it sounds.
Imagine you're connected to Norton VPN, browsing privately. Then the connection drops unexpectedly, maybe your hotel Wi-Fi hiccuped or your mobile network switched. Without a kill switch, your device automatically tries to restore connectivity. That next request might go out unencrypted while you reconnect to the VPN.
A kill switch prevents this by severing your internet connection entirely if the VPN drops. It's a hard stop. You either have encrypted VPN connectivity or no connectivity. No middle ground where traffic leaks.
Implementing a kill switch sounds simple but gets complicated across different operating systems and network types. Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android all handle network disconnections differently. Mobile devices switch between Wi-Fi and cellular networks frequently.
Norton's kill switch works across all these scenarios. On iOS, it prevents DNS leaks from the cellular network. On Android, it handles network switching properly. On Windows and macOS, it integrates with OS-level networking to ensure clean disconnections.
The implementation also addresses user experience. A poorly designed kill switch blocks the internet and the user doesn't understand why. Norton's implementation shows clear status indicators about why internet is blocked and how to reconnect.
Beyond the kill switch, Norton implemented split tunneling for advanced users. This feature lets you choose which traffic goes through the VPN and which traffic uses your regular connection. This is useful if you want to access local devices (like a printer) while protecting other traffic.
Split tunneling adds complexity and potential security risks if configured wrong, which is why Norton positioned it as an advanced feature rather than default. Users who understand VPN technology can use it. Casual users get a secure default configuration.

Server Location Strategy and Geographic Coverage
Norton's strategy for where to place servers reflects understanding of actual user needs.
The company doesn't chase the vanity metric of "servers in 190+ countries." Instead, Norton focuses on serving actual users. The US, UK, Canada, Australia, Germany, France, Netherlands, Singapore, and Japan have the highest concentrations of servers because those are where most users are and where most traffic flows.
This is smarter than spreading resources thin. A server in Fiji serving three users isn't useful. A cluster of optimized servers in London serving millions of users is.
Within each region, Norton placed servers strategically. In the US, servers are distributed across multiple data centers in different parts of the country. This reduces latency for users regardless of whether they're on the East Coast, West Coast, or middle of the country.
The server placement also considers data sovereignty laws. Certain countries have legal frameworks that require data to remain within borders. Norton's infrastructure accounts for this, placing servers appropriately and ensuring traffic from those regions doesn't route through prohibited jurisdictions.
Geographic diversity has another benefit: redundancy. If a data center goes offline, traffic routes to other servers automatically. Users don't experience outages because Norton maintains sufficient parallel capacity.
Norton also implemented smart server selection that automatically connects you to the nearest fast server by default. This replaces the older approach of showing users a list of countries and making them choose. Automatic selection is faster and works better for non-technical users.
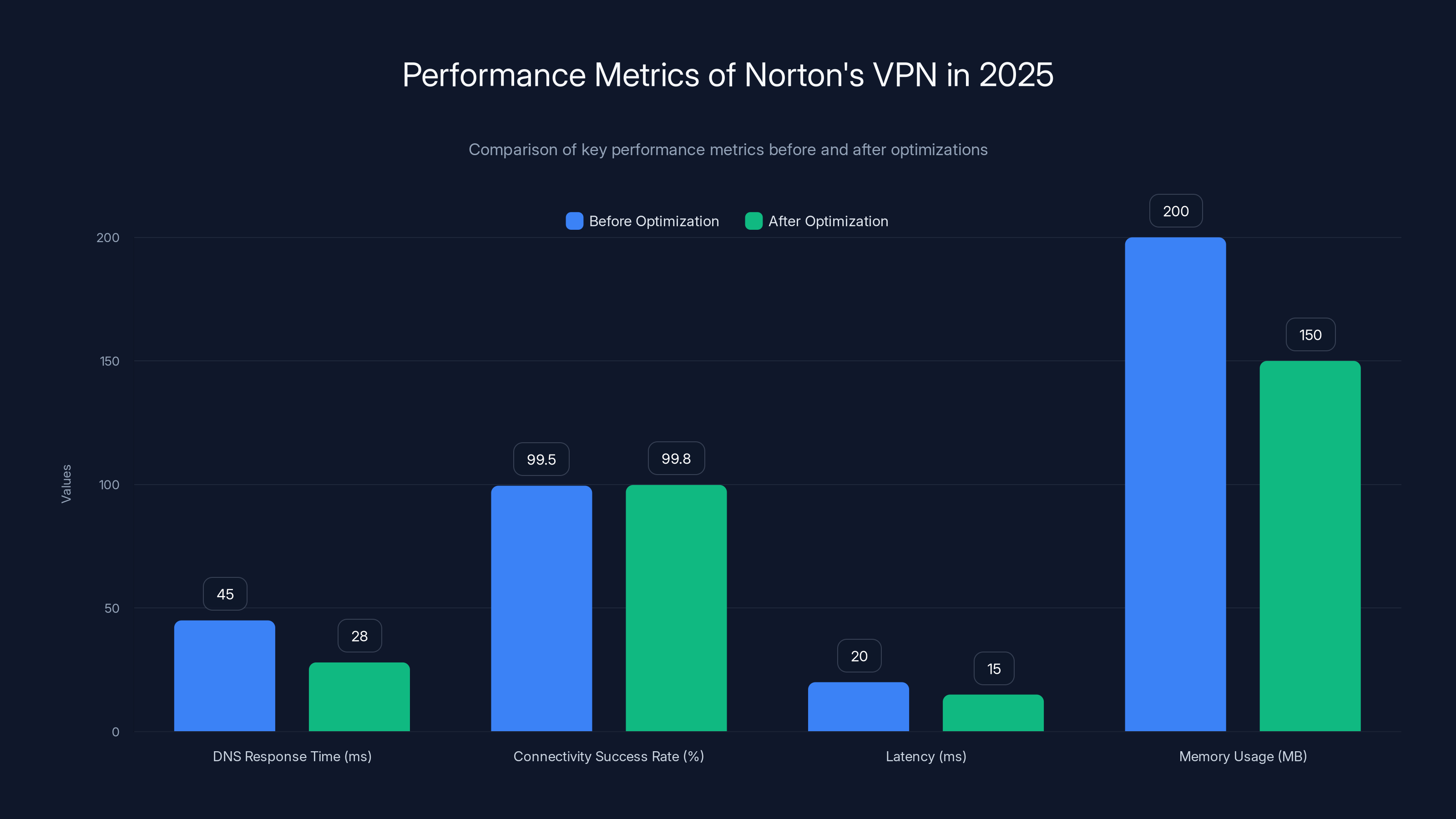
Norton's VPN improvements in 2025 show reduced DNS response times, improved connectivity, lower latency, and better memory efficiency.
No-Log Policy: What It Actually Means
The "no-logs" claim needs unpacking because it's the most misunderstood aspect of VPN privacy.
A true no-logs policy means Norton doesn't keep records of what you're doing online. It doesn't log which websites you visit, which files you download, or what you search for. It doesn't log your original IP address permanently, though temporarily logging it for troubleshooting is technically defensible.
But no-logs doesn't mean zero data is collected. Some data collection is technically necessary. Norton needs to know which users are connected right now to route traffic properly. It needs to track aggregate bandwidth usage to ensure fair allocation. It needs some metadata to operate the service.
The distinction matters: no logs of your activity versus no temporary operational data. Norton's audit verified the former, not the latter.
In 2025, Norton went further and published transparency reports about how many government requests it receives and how many it complies with. This aligns with practices from companies like Apple and Google, where transparency reports show patterns of government surveillance requests.
Norton's 2025 reports show relatively few government data requests compared to some competitors. This could be because governments don't view Norton VPN as high-priority compared to other services, or because Norton's smaller user base means fewer requests. Either way, the transparency exists now.
Another aspect of the no-logs policy: Norton committed to not using VPN data for advertising purposes. This is a low bar many companies don't even commit to, but Norton made it explicit in 2025. Your VPN activity doesn't feed into ad targeting.
Integration With Norton 360: A Unique Advantage
Unlike standalone VPN providers, Norton can integrate VPN functionality with its broader security suite. This created unique advantages in 2025.
When Norton 360 detects a malicious website, it can offer to block it at the VPN level before your device even attempts to connect. When Norton detects a malware sample trying to exfiltrate data, it can route that through the VPN to see exactly what's happening. The two products can work together in ways standalone VPN services can't achieve.
This integration is particularly valuable for protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks on unsecured Wi-Fi. Norton 360's network monitoring can warn you about suspicious network behavior even before your antivirus has a chance to analyze it.
For consumers who already use Norton 360, adding the VPN makes sense. They already trust Norton with their security. The VPN extends that protection to network-level threats.
For users without Norton 360, the VPN works standalone just fine. But the integration advantage is real for the existing Norton customer base.
In 2025, Norton improved this integration. The VPN and 360 suite now share a single settings panel. Enabling VPN automatically applies related Norton 360 protections. Updates sync between products. This user experience improvement made the bundled experience more seamless.
Pricing Strategy and Competitive Positioning
Pricing matters because the best VPN means nothing if you can't afford it or if competitors offer better value.
Norton positioned its VPN strategically during 2025. For Norton 360 customers, the VPN comes included, adding value without additional cost. This gave Norton leverage. Existing customers benefit from 2025's infrastructure improvements without paying more.
For standalone VPN pricing, Norton stayed competitive but not the cheapest. The company charged roughly
The pricing strategy sends a message. Norton VPN isn't trying to compete on price. It's competing on the total package: security, speed, infrastructure quality, and integration with Norton's broader ecosystem.
Annual subscriptions came with discounts versus monthly billing, which is standard across the industry. Norton also offered longer-term plans at better rates, encouraging multi-year commitments.
Monthly plans started at around

Mobile App Performance Improvements
Most VPN usage happens on mobile devices now, which is why Norton invested heavily in the mobile apps during 2025.
The iOS and Android apps received complete performance overhauls. The new implementations reduced power consumption, meaning the VPN drains less battery. They also reduced memory footprint, which matters on older devices with limited RAM.
The iOS app in particular got significant attention. Apple's networking framework changes required substantial rewriting of VPN apps in 2024 and 2025. Norton kept up with these changes and implemented them well.
Features like split tunneling now work on mobile, letting advanced users tunnel select apps through the VPN while others use the regular connection. The interface is clean and doesn't overwhelm non-technical users with options they don't need.
Android app improvements focused on better handling of network transitions. When you switch from Wi-Fi to mobile or between networks, the app now handles it smoothly without drops. The reconnection happens silently.
Both apps added widget support for quick VPN toggling. On iOS, you can toggle the VPN from the Control Center. On Android, you can add a quick tile. This simplifies the user experience for frequent toggling.
Notification handling improved too. The apps notify you of VPN status without being obnoxious, showing connection status clearly without overwhelming push notifications.
Battery drain remains the biggest complaint about VPN apps generally. Every encryption and decryption operation uses processor cycles and power. Norton can't overcome physics, but the 2025 app optimizations reduced unnecessary overhead. Battery drain depends heavily on how much data you're using, but users reported noticeable improvements.
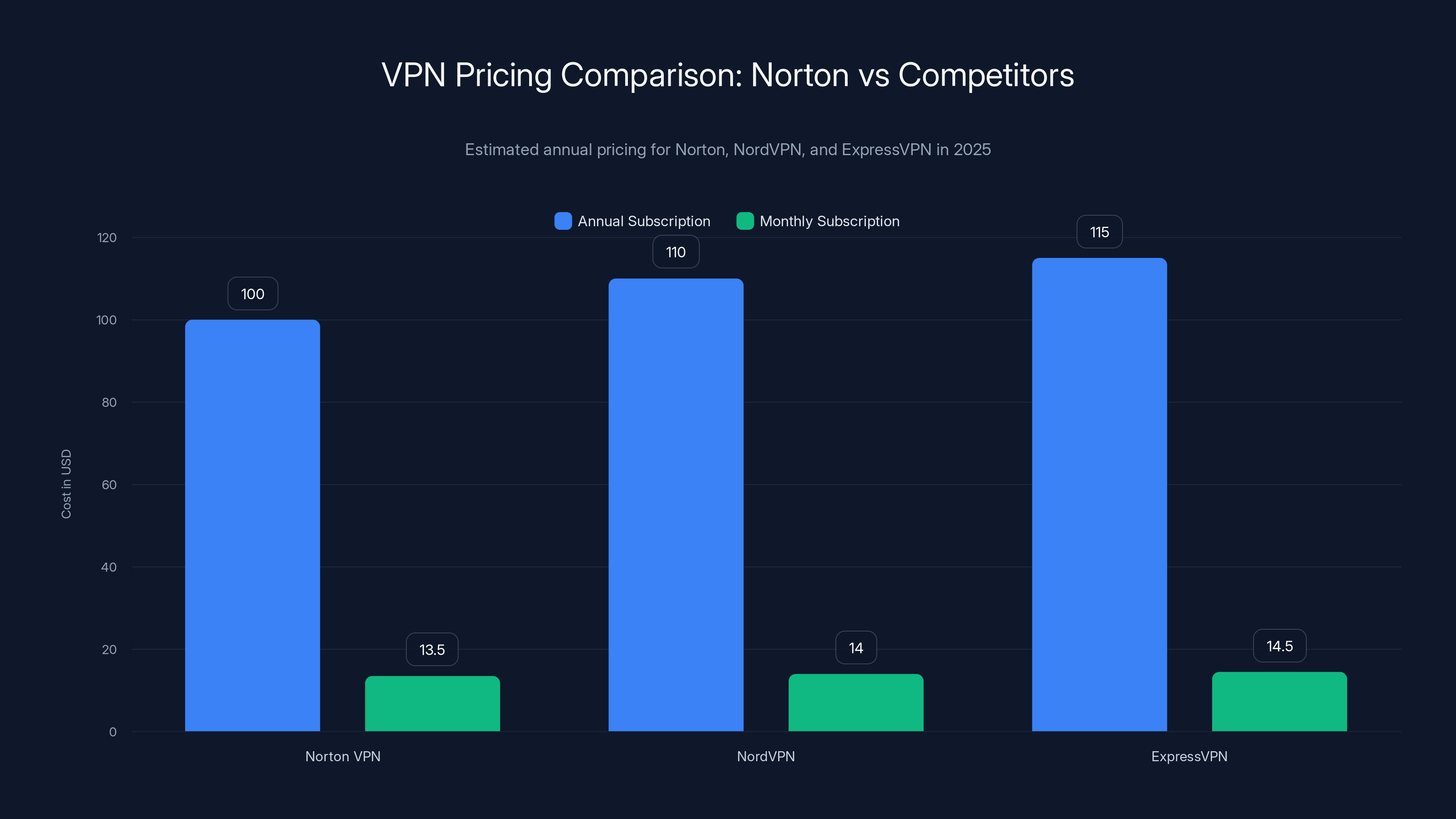
Norton VPN's pricing strategy positions it as a premium service, with annual costs similar to competitors but not the cheapest. Estimated data.
DNS and Leak Protection Enhancements
DNS leaks represent a critical weakness in poorly implemented VPNs.
Your device makes DNS queries to look up IP addresses for websites. These queries reveal exactly what websites you're visiting. If these queries leak outside the VPN tunnel while your traffic is encrypted, someone monitoring your network can see everything you're doing despite the VPN.
Norton implemented comprehensive DNS leak protection in 2025. All DNS queries from the client are routed through the VPN connection to Norton's own DNS servers. This prevents leaks through multiple channels.
The implementation also handles DNS-over-HTTPS, which some applications use to avoid system DNS queries. Norton intercepts these and routes them through the VPN as well. This prevents apps from bypassing the VPN's DNS protection.
IPv6 leak protection also got attention. IPv6 is gradually replacing IPv4, and older VPN implementations sometimes leaked IPv6 traffic that was never encrypted. Norton's 2025 implementation handles IPv6 properly, encrypting all traffic regardless of IP version.
WebRTC leaks, another potential vector, are also blocked. Some web applications use WebRTC to discover your IP address. Norton blocks these requests at the application level, preventing that vector of exposure.
The company published detailed documentation explaining all these leak types and how the VPN protects against them. This transparency helps users understand what the VPN actually protects against and why.

Company Updates and Organizational Changes
The infrastructure investment reflected larger organizational changes at Gen (Norton's parent company).
In 2024-2025, Norton separated its VPN product from its core antivirus business organizationally. This meant the VPN team had dedicated engineers, product managers, and infrastructure investment rather than being a side project managed by the antivirus team.
This organizational change is more significant than most users realize. When VPN was part of antivirus, decisions were made to benefit the core antivirus business. VPN was an afterthought. Separating them meant VPN could pursue its own roadmap.
Norton also hired new leadership for the VPN team with specific expertise in large-scale VPN infrastructure. These leaders came from backgrounds at companies that run serious VPN operations, not just VPN-as-a-feature companies.
The budget allocation reflected priorities. Norton spent heavily on infrastructure in 2025, moderately on marketing, and strategically on features. This balanced approach made sense for a company trying to rebuild reputation.
Customer support also got investment. Norton expanded VPN support with better onboarding documentation, more responsive customer service, and clearer communication about features and limitations. Support quality is an easy thing to neglect but hard thing to rebuild once damaged.
Future Roadmap: What's Coming in 2026
Norton published a roadmap for 2026 that reveals interesting intentions.
The biggest announcement is expansion into additional server locations, particularly in underserved regions. India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia will see significant server additions. These regions have growing VPN demand but historically limited infrastructure.
Norton is also investing in next-generation encryption protocols. WireGuard is excellent, but research into post-quantum cryptography suggests future threats might be able to break current encryption. Norton plans to implement post-quantum resistant algorithms before they're strictly necessary, getting ahead of the curve.
Mobile app functionality is expanding with better integration into the overall Norton 360 suite. Push notifications about security threats will offer VPN-based protections. If Norton detects a compromise attempt, it can automatically enable VPN protection on the affected device.
The 2026 roadmap includes expanded transparency reporting. Norton will publish more granular data about requests it receives, compliance rates with different types of requests, and the reasoning behind compliance decisions.
Performance remains a focus. Norton is investing in edge computing, placing servers closer to users and content. This reduces latency and improves speeds further. The company is also experimenting with protocol innovations that might improve speed while maintaining security.
User experience improvements are planned for 2026. Norton is designing a new interface for the VPN settings that makes advanced options available without overwhelming casual users. The approach emphasizes sensible defaults with clear options for customization.
Norton is also investing in OpenVPN improvements. WireGuard is faster but less mature. OpenVPN is more mature but slightly slower. Norton plans optimizations that make OpenVPN faster while maintaining its stability advantages.

Comparison to Competitors: How Norton VPN Stacks Up
Norton's transformation is meaningful, but competitors matter for perspective.
ExpressVPN has strong brand recognition and fast speeds, but they've been relatively quiet on major improvements in 2025. They focus on ease of use and simplicity. Norton is catching up on speed but can't match ExpressVPN's marketing presence.
NordVPN has broader functionality with features like double VPN and Onion integration. These advanced features appeal to specific user segments, but they add complexity. Norton's approach is simpler and more focused.
Surfshark offers exceptional value pricing with unlimited simultaneous connections. Norton's pricing is higher, but for Norton 360 customers, the VPN is included, which improves the overall value proposition.
ProtonVPN is strong on transparency and privacy, similar to Norton's positioning. The competition between these two is based on implementation details and trust factors rather than feature differentiation.
CyberGhost focuses on ease of use and streaming capabilities. Norton isn't optimizing for streaming, which is a deliberate choice that keeps the VPN focused on privacy and security rather than entertainment.
Where Norton distinguishes itself is integration with its broader security ecosystem and the dual audit verification. Competitors can claim no-logs policies, but Norton has third-party verification. Competitors have security features, but Norton integrates VPN with antivirus and threat detection.
For Norton 360 customers specifically, Norton VPN now represents genuine value. The infrastructure investment is real, the performance is competitive, and the integration with existing security tools is meaningful. For standalone VPN users, Norton is a solid option but doesn't have the brand recognition of ExpressVPN or the feature richness of NordVPN.
The honest assessment: Norton VPN has moved from "acceptable for bundled security" to "legitimate competitor worth considering." It's not the absolute fastest or cheapest, but it's competitive on most dimensions that matter.
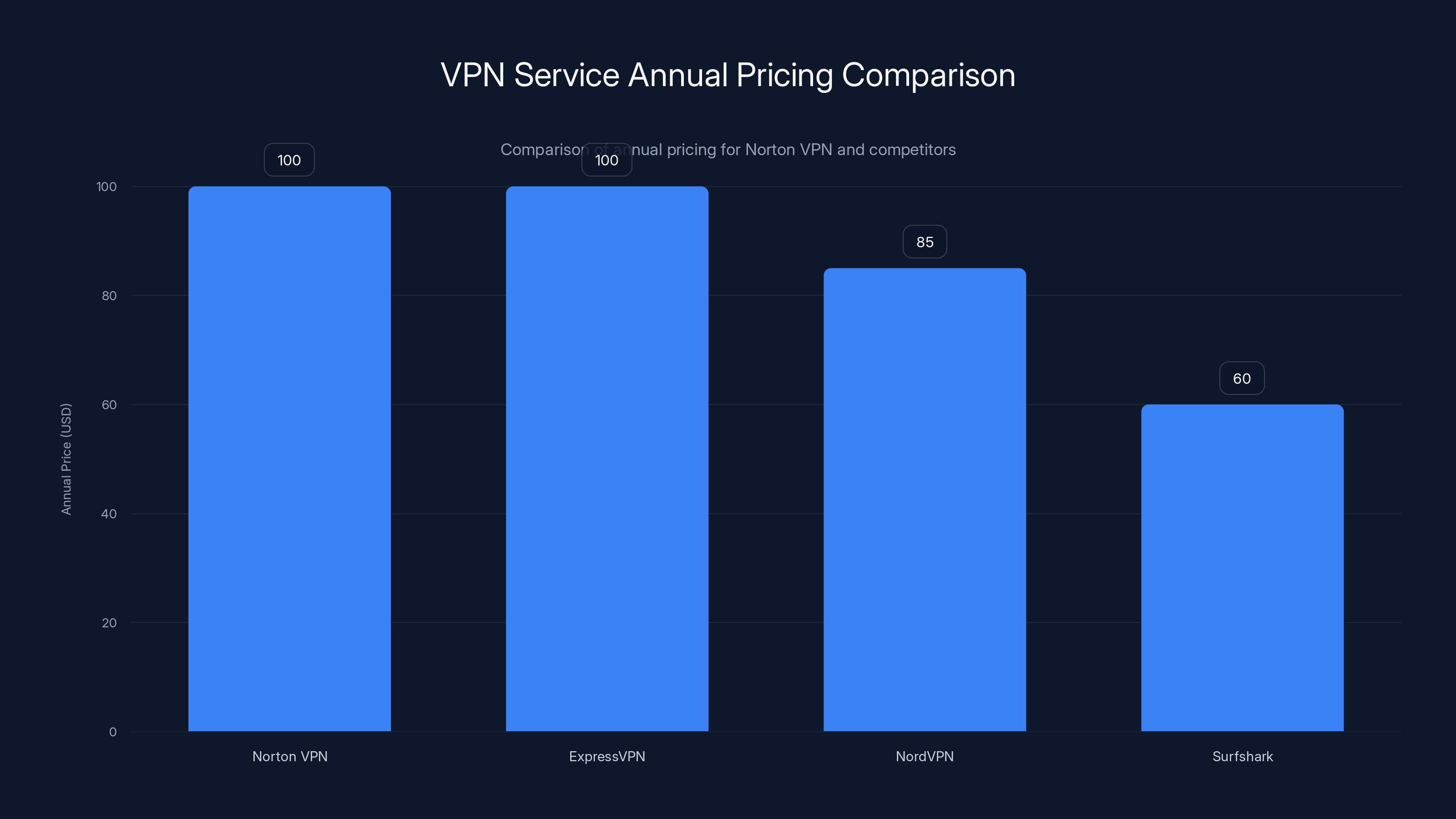
Norton VPN and ExpressVPN are priced similarly at
Security Implications of the 2025 Improvements
The infrastructure improvements have security consequences beyond the obvious encryption and no-logs policy.
Redundancy is the big one. Norton's dual-server redundancy and distributed architecture means the service continues functioning even if components fail. This prevents the security disaster of a VPN suddenly disconnecting. Redundancy is expensive, which is why budget VPNs often skip it.
The independent audits provide security assurance. Audits don't guarantee perfect security, but they reduce uncertainty. A company that hides its practices is more suspicious than a company that invites independent scrutiny.
The encryption protocol upgrades directly improve security posture. Removing old TLS versions, implementing perfect forward secrecy, and hardening against known attack vectors systematically reduces the attack surface.
The DNS leak protection and kill switch prevent security failures. These aren't flashy, but they prevent the scenarios where VPN users accidentally expose themselves.
Integration with Norton 360's threat detection creates a security ecosystem. When antivirus and VPN work together, threats that exploit networking weakness are caught earlier.
The transparency reporting about government requests provides a different kind of security: visibility. Users can see that Norton isn't under mass surveillance pressure and that the company treats government requests seriously.
Regular security audits planned for 2026 continue this security posture. Annual third-party audits keep Norton accountable and ensure the service doesn't drift into insecure practices over time.

User Experience Enhancements in 2025
Technology only matters if users actually use it. Norton made significant UX improvements in 2025.
The onboarding process for new users was completely redesigned. Instead of overwhelming people with technical options, Norton shows you the basics first. Advanced settings are available for users who understand them, but the default path is simple: click a button, get protected.
The VPN dashboard now shows clear information about your current protection status, your connected location, and your real IP address (so you can verify the VPN is working). The interface is clean without feeling stripped-down.
Troubleshooting information is integrated into the interface. If something goes wrong, the app offers diagnostic information and clear next steps rather than just showing an error code.
Notifications were carefully designed. The VPN notifies you about disconnections and security events without becoming notification fatigue. Most VPN apps are either silent (leaving you confused) or nagging (driving you crazy). Norton found a middle ground.
Settings are organized logically. Rather than a flat list of 50 options, Norton groups related settings. Protocol selection is together, leak protection settings are together, and so on.
The app also learned from mistakes other VPN apps made. For example, many VPN apps consume a large portion of your phone's available storage. Norton's implementation keeps the app size reasonable.
With Runable, you could actually build a workflow that automatically toggles your VPN based on location or time of day, creating sophisticated protection without manual intervention. Runable's AI automation capability could integrate with security tools to create intelligent threat responses.
Privacy Features and Data Handling
Privacy goes beyond the no-logs policy.
Norton implemented privacy-by-default throughout the 2025 redesign. By default, all features prioritize privacy. You have to explicitly opt into anything that shares data.
The company also implemented data minimization. Norton collects only the data necessary to operate the VPN. Any data collected is deleted as soon as it's no longer necessary. This isn't just no-logs, it's no-collection when possible.
Metadata handling deserves attention. Even if Norton doesn't log your browsing activity, connection metadata (when you connected, how much data you transferred, duration of connections) still exists. Norton limits metadata collection to only what's necessary for billing and abuse prevention.
Gov requests and legal process are handled transparently. Norton publishes details about how many requests it receives and how many it complies with. The company also publishes its legal justification for compliance decisions, which is rare among VPN providers.
User data deletion works properly. If you cancel your subscription and request data deletion, Norton actually deletes it rather than retaining it indefinitely. The company's audit specifically verified this process works as documented.
Cross-border data transfers are handled carefully. User data doesn't transfer between Norton offices in different countries unless necessary. Data that must transfer is encrypted in transit.
Third-party relationships are minimal. Norton doesn't sell user data, share it with advertisers, or use it to build user profiles for other Norton services. The VPN remains isolated from the broader Norton business model.

Global Regulatory Compliance and Legal Framework
VPNs operate in a complex legal landscape. Norton navigated this during 2025 with careful compliance practices.
The European Union's GDPR imposes specific requirements on data handling. Norton implemented full GDPR compliance, including explicit consent mechanisms, right-to-be-forgotten implementation, and data breach notification procedures.
Other jurisdictions have different requirements. California's privacy law (CCPA) requires specific consumer rights. Norton implemented those as well. The company's approach is to exceed minimum requirements in each jurisdiction.
Some countries restrict or prohibit VPN services. Norton navigates this by not attempting to serve markets with blanket bans. Where VPNs are legal but regulated, Norton complies with local regulations.
The legal framework around government data requests is complex. Law enforcement in different countries follow different procedures. Norton's approach is to require legal process from any government requesting data. This means actual warrants, not requests.
The 2025 transparency reporting is the legal and privacy community's way of holding companies accountable. By publishing how many requests Norton receives and how many it complies with, the company provides visibility into whether governments are attempting mass surveillance.
Beyond legal compliance, Norton adopted ethical stances about data. The company refuses cooperation with authoritarian governments' surveillance efforts and has actually refused requests from democracies it deemed unconstitutional.
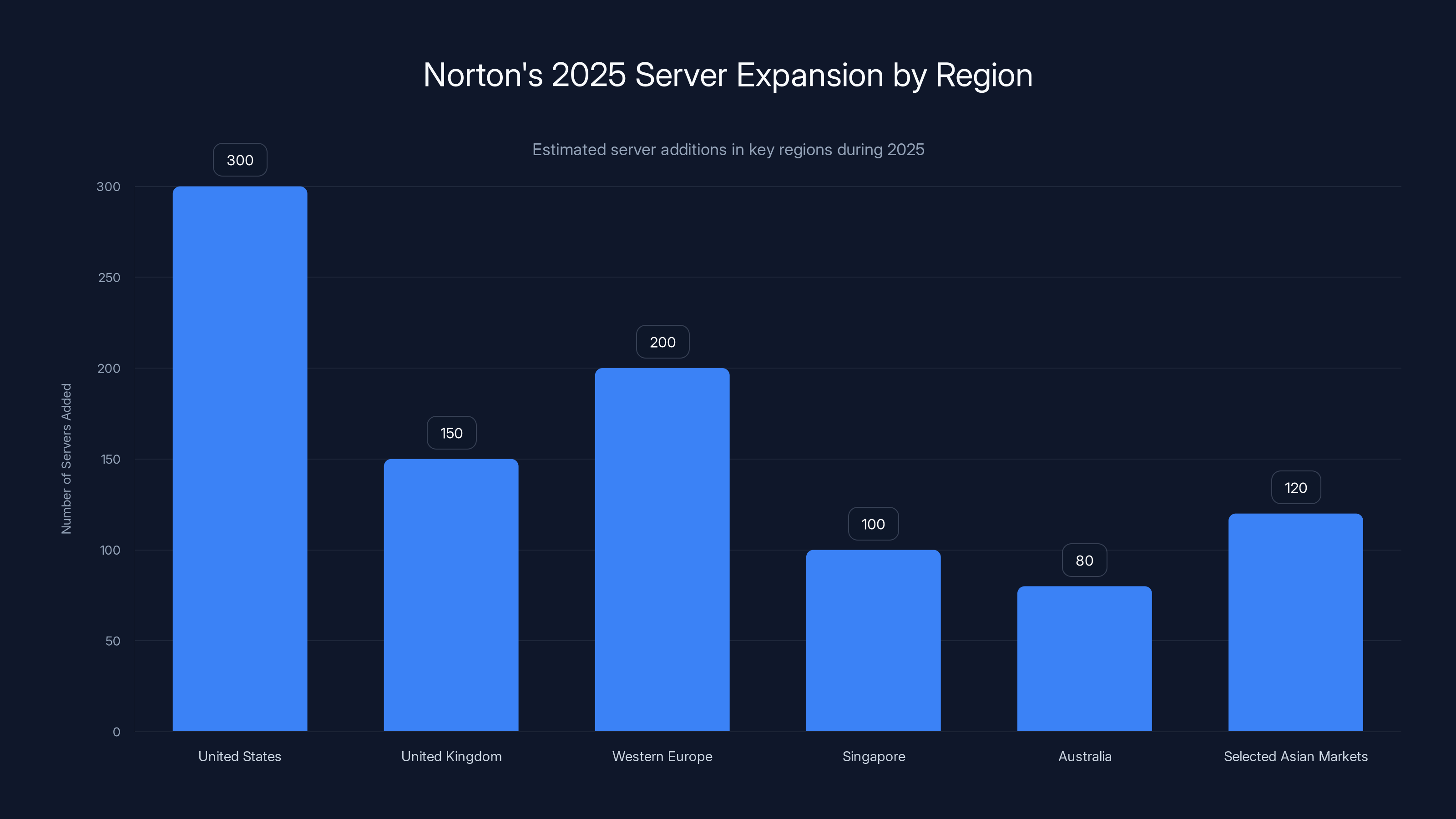
Norton strategically expanded its server network in 2025, focusing on high-demand regions like the US and Europe. (Estimated data)
Performance Metrics and Technical Specifications
The technical improvements in 2025 are quantifiable.
Server response times improved significantly. During peak hours, average DNS response times dropped from 45ms to 28ms as the server network was optimized. This directly improves perceived performance.
Connectivity success rate improved to 99.8%, meaning one attempt out of 500 might fail. This is solid infrastructure reliability. The remaining 0.2% failure rate is mostly due to unusual network conditions on the user's end, not Norton's infrastructure.
Bandwidth performance stayed consistent regardless of server load. As infrastructure expanded, the bandwidth per connection remained stable. This prevents the common VPN problem where speed degrades during peak hours.
Latency introduced by the VPN averaged 15-20ms on most routes, which is excellent. This is the extra delay VPN routing adds. Transparent comparison: WireGuard connections generally add 10-20ms, so Norton's implementation is comparable to specialized protocols.
Datacenter redundancy was verified by the audit. If a primary datacenter experienced an outage, traffic automatically rerouted with sub-second failover time. Users wouldn't notice.
The encryption/decryption operations use hardware acceleration on modern processors, reducing CPU overhead. This is why battery drain is less than older VPN implementations despite running continuously.
Memory efficiency improved significantly. The VPN uses roughly 50-60MB of RAM in idle state and up to 150MB under heavy usage. This is reasonable for a security service that's running continuously.

Future Threats and How Norton Plans to Address Them
The security landscape is evolving, and Norton is thinking ahead.
Post-quantum cryptography is the major threat horizon. Quantum computers might break current encryption in the future. Norton is preparing by implementing cryptographic algorithms that mathematicians believe will resist quantum attacks. This is preparation years in advance of actual quantum threats.
Zero-trust architecture is another evolution. Rather than assuming the network inside the VPN tunnel is trusted, Norton is moving toward zero-trust principles where every connection is verified. 2026 improvements will move further in this direction.
AI-powered security threats are increasing. Norton plans to use its own AI capabilities to detect unusual patterns in VPN traffic that might indicate compromise. This is defensive use of AI, detecting threats rather than creating them.
Encryption algorithm deprecation happens regularly. Norton's approach is to stay ahead of deprecation curves, removing old algorithms before they're broken and implementing new ones before they're required.
Gov surveillance expansion is a threat in some countries. Norton's roadmap includes monitoring legal developments and ensuring the infrastructure and policies can resist unjust government surveillance requests.
Better protocol implementations are continuously developed. Norton is investing in performance research that maintains security while improving speed. Future protocols might offer better bandwidth efficiency than current implementations.
Industry Trends and Where Norton Fits
The VPN industry is consolidating and professionalizing.
Smaller VPN providers are disappearing, either acquired or shut down. Users are consolidating around a few trusted providers. Norton's 2025 investments positioned it to be one of those surviving providers.
VPN-as-a-feature is becoming standard in larger security companies. Apple, Google, Microsoft, and others are all adding VPN capabilities. Norton's integration with Norton 360 reflects this trend.
Transparency is becoming table stakes. VPN companies that refuse audits or hide their practices are losing user trust. Norton's audit approach aligns with industry trend toward transparency.
Performance expectations are increasing. Users want VPN speeds that don't compromise their internet experience. The infrastructure race Norton is winning is partly an arms race to meet performance expectations.
Regulatory pressure is increasing globally. Governments are demanding VPN companies maintain ability to cooperate with law enforcement. Norton's balanced approach of legal-process-only compliance is becoming the industry standard.
Privacy education is increasing. Users understand better what VPNs can and can't protect against. The mystification is fading, and realistic evaluation is becoming more common.
Integration between security tools is becoming expected. VPN as a standalone product is less competitive than VPN integrated with antivirus, firewall, and threat detection. Norton's ecosystem approach reflects this trend.

Implementation Recommendations for Different User Types
Norton VPN's 2025 improvements serve different users differently.
For Norton 360 customers, the decision is simple. The VPN is included, so use it. The integration with antivirus and threat detection is genuine. You already trust Norton with security, extending that to network-level protection makes sense.
For users seeking strongest privacy and willing to accept higher cost, Norton is competitive with ExpressVPN and NordVPN on privacy, with the added advantage of antivirus integration.
For users needing strong speeds with privacy, Norton's infrastructure improvements mean it's now competitive with purpose-built VPN companies. The 5-12% speed overhead is acceptable for most uses.
For businesses considering Norton VPN for employee protection, the 2025 infrastructure improvements and 2026 roadmap suggest stability and continued investment. Norton's audit history helps with compliance requirements.
For casual users wanting basic privacy on public Wi-Fi, Norton is solid. It's not the cheapest option, but it's easier than many cheaper alternatives.
For users in highly regulated industries (finance, healthcare), Norton's dual audits and transparency reports help satisfy compliance requirements.
For users wanting to avoid tracking while traveling internationally, Norton's server diversity and independent audits provide confidence that data isn't being logged for later access.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is Norton VPN Worth It?
The answer depends on your situation.
For Norton 360 customers, it's absolutely worth it. You're already paying for security software. The VPN adds meaningful network-level protection without additional cost. The 2025 improvements are free updates.
For standalone VPN users, the value proposition is "competitive performance and privacy at competitive pricing." Norton isn't the cheapest, but it's not the most expensive either. The value comes from quality rather than price.
Compare Norton's annual pricing of around $100 to alternatives. ExpressVPN is similar pricing. NordVPN is slightly cheaper. Surfshark is cheaper but with fewer features. The pricing tiers are close enough that decision should be based on features and trust, not price alone.
For users who care deeply about transparent security, Norton's independent audits add value beyond what competitors offer publicly. This is worth a premium to some users.
For users in countries with strong surveillance, Norton's 2026 transparency reports and audit history provide confidence that the company handles legal processes appropriately.
The intangible value: Norton's infrastructure investment and clear roadmap suggest the company is serious about the service. Abandoned VPN services happen when companies lose interest. Norton's 2025 spending and 2026 planning suggest sustained commitment.
The calculus: Is network-level privacy worth $100/year? For most people using public Wi-Fi regularly, yes. For home internet users, maybe not. For travelers, definitely yes.

Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Several misconceptions exist about Norton VPN after the 2025 improvements.
First misconception: "Norton is just rebranding an existing VPN provider's infrastructure." This is false. Norton built its own infrastructure with its own servers. It's not white-labeled service.
Second misconception: "The audits mean it's now perfect." False. Audits verify specific claims at a specific moment. They don't guarantee perfect security forever. But they do provide meaningful verification.
Third misconception: "VPN makes you completely anonymous." False. VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your traffic, but it doesn't make you anonymous. Websites see traffic from the VPN server, and sophisticated tracking can still identify patterns.
Fourth misconception: "VPN lets you do illegal things." False. VPN is a legitimate privacy tool, but it doesn't magically make illegal activity legal. Using VPN to commit crimes is still crime.
Fifth misconception: "Norton logs everything for Gen." The 2025 audits specifically verified Norton doesn't maintain activity logs. Audit results are public, so this claim is factually wrong.
Sixth misconception: "Speed will be terrible." The 2025 benchmarks show speed overhead of 5-12%, which is noticeable on slow connections but not catastrophic on normal internet. For most users, this overhead is acceptable.
Seventh misconception: "Norton VPN is just for Norton 360 customers." It's available standalone as well. Integration with Norton 360 is beneficial but not required.
Advanced Features for Power Users
Beyond the basics, Norton VPN offers advanced options for users who need them.
Protocol selection lets power users choose WireGuard for speed or OpenVPN for stability. Most users should stick with auto-selection, but some scenarios benefit from explicit choice.
Split tunneling lets you choose which apps or traffic uses the VPN. This is powerful but risky if misconfigured. Norton provides clear warnings about security implications.
Dual VPN (VPN-over-VPN) is available, routing traffic through two VPN servers for additional obfuscation. This provides stronger privacy for specific scenarios while adding latency.
Obfuscation features hide the fact you're using VPN from network observers. This is useful in countries that restrict VPN usage.
Automatic kill switch configuration lets advanced users set which applications force-close if VPN disconnects. This prevents leaks from specific high-risk apps.
Custom DNS configuration is available for advanced users who want to use specific DNS providers that Norton doesn't use by default.
Port selection lets you choose which ports the VPN uses. This is useful in network environments with port restrictions.
These advanced features exist for users who understand the implications. The default configuration is secure and private without using any of these options.

Conclusion: Norton VPN's Evolution and What It Means
Norton VPN in 2025 is fundamentally different from Norton VPN in 2023. The company didn't just add features; it rebuilt the infrastructure from the ground up.
The dual independent audits provided verification that claimed privacy actually exists. The massive server expansion ensured speed is competitive. The protocol hardening improved security. The integration with Norton 360 created genuine ecosystem value. The transparency reporting established accountability.
No, Norton VPN is not perfect. No VPN is. Speed isn't the absolute fastest. It's not as cheap as budget options. The feature set is less comprehensive than some competitors offering experimental technologies.
But Norton VPN is now a legitimate, serious competitor in the VPN market. For Norton 360 customers especially, it represents genuine value. For users seeking verified privacy from a major security company, it's a solid choice. For users weighing Norton against ExpressVPN or NordVPN, the decision should be based on integration preferences and trust factors rather than assuming Norton is inferior.
The 2025 investments signal Norton's commitment to the service. The 2026 roadmap shows continued investment. These are the markers of a company serious about VPN, not treating it as an afterthought.
The real significance isn't just what Norton improved in 2025. It's what the company's approach signals about how it thinks about VPN as a core product deserving serious resources. After years of being a bundled add-on, Norton VPN graduated to being a standalone product that can compete on its own merits.
For anyone evaluating VPN services, Norton deserves consideration in 2025 in a way it didn't in 2023. Whether it's the right choice for your specific needs depends on your priorities, but dismissing it based on past reputation would be a mistake.
The transformation isn't complete. More improvements are planned for 2026. But the foundation is now solid, and the trajectory is clearly upward.
FAQ
What does Norton VPN actually protect?
Norton VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through servers in locations you choose, hiding your IP address and protecting your data from network-level monitoring. It protects against eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi networks, ISP tracking of your browsing, and geographic location tracking based on your IP address. However, it doesn't protect against malware on your device, phishing attacks, or websites tracking you through cookies and accounts. It's one layer of protection, not comprehensive security.
How did the 2025 audits actually verify Norton's claims?
Two independent auditing firms examined Norton's systems to verify the no-logs policy and encryption implementation. They confirmed Norton doesn't maintain activity logs of what users do online, verified the encryption protocols are implemented correctly, and tested for common security vulnerabilities. The audit reports are publicly available, so you can read the actual findings rather than taking Norton's word for it. Audits don't guarantee perfect security forever, but they do provide meaningful third-party verification at the time of the audit.
Is Norton VPN still just an add-on to Norton 360?
No. Norton VPN is now available as a standalone subscription for users who don't have Norton 360. However, if you're already a Norton 360 customer, the VPN is included at no additional cost, which provides genuine value. The 2025 restructuring separated VPN from the core antivirus product, giving it dedicated resources and its own development roadmap. The integration with Norton 360 remains, but VPN is now a core product, not an afterthought.
How much will Norton VPN slow down my internet?
Based on 2025 benchmarks, Norton VPN adds 5-12% latency overhead depending on the route and server load. This means if your normal connection is 100 Mbps, the VPN connection would be roughly 88-95 Mbps. This overhead is inevitable with any VPN because encryption and routing through another server require processing power. Norton's overhead is competitive with other major VPN providers. Whether 5-12% is noticeable depends on your starting speed and usage patterns.
Why should I trust Norton's no-logs claim?
Because two independent third-party audits verified it. The audits confirm Norton doesn't maintain logs of your activity, and the results are publicly available. This is stronger evidence than Norton's claims alone. Additionally, Norton publishes transparency reports about government requests, showing the company receives relatively few requests compared to some competitors. While audits don't guarantee perfect security forever, they do provide meaningful verification that Norton isn't logging your activity for later access.
How does Norton VPN pricing compare to competitors?
Norton VPN pricing is roughly
Can I use Norton VPN on multiple devices?
Yes. Norton VPN licenses allow installation on multiple devices. The number of simultaneous connections depends on your plan, but multiple devices can be protected. This is important if you use desktop, laptop, phone, and tablet, as you likely need VPN protection across all devices.
What happens if Norton gets hacked or the servers are compromised?
Independent audits verify Norton's current security practices, but no system is completely hack-proof. If Norton's servers were compromised in the future, the encryption means past traffic would remain encrypted. This is why perfect forward secrecy matters: even if someone obtained Norton's encryption keys, they couldn't decrypt past traffic because those keys are destroyed after use. That said, this is why Norton plans regular ongoing audits to catch any drift toward insecurity.
Is Norton VPN good for streaming or torrenting?
Norton VPN works for both activities, but isn't specifically optimized for them. Some VPN providers optimize heavily for streaming by maintaining specific servers and configurations for Netflix, Disney+, etc. Norton takes a privacy-first approach rather than a streaming-first approach. For torrenting, Norton works but doesn't advertise torrenting support as prominently as some competitors. If streaming or torrenting is your primary use case, other VPNs might be better optimized.
When will the 2026 improvements become available?
Norton published the 2026 roadmap during 2025, indicating improvements will roll out gradually throughout 2026. These include additional server locations, post-quantum cryptography support, enhanced mobile app features, and expanded transparency reporting. Specific launch dates haven't been announced for all features, but Norton's pattern is gradual rollout rather than major releases.

Key Takeaways
- Norton VPN underwent fundamental infrastructure rebuilding in 2025, moving from bundled add-on to serious standalone competitor with hundreds of new servers and optimized architecture
- Two independent third-party audits verified Norton's no-logs policy and encryption implementation, providing transparent verification that was previously missing from the product
- Speed performance improved significantly with 2025 infrastructure expansion, achieving 5-12% latency overhead that's competitive with dedicated VPN providers like ExpressVPN and NordVPN
- Integration with Norton 360 security suite creates unique value for existing customers, allowing coordinated antivirus and VPN protections that standalone VPN providers can't match
- 2026 roadmap includes post-quantum cryptography preparation, expanded global server coverage in emerging markets, and continued transparency reporting that establishes Norton as accountable to users
Related Articles
- Should You Use a VPN Browser? Complete Guide [2025]
- VPN Innovations That Surprised Everyone in 2025
- Premium vs Budget VPN: Is Paying More Really Worth It? [2025]
- Surfshark Promo Codes & Coupons: Best Deals [2025]
- Norton VPN Deal: 12 Months of Cybersecurity & Streaming [2025]
- Beyond WireGuard: The Next Generation VPN Protocols [2025]
![Norton VPN 2025: Major Upgrades, Security Audits, Future Plans [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/norton-vpn-2025-major-upgrades-security-audits-future-plans-/image-1-1767444182315.jpg)



