Introduction: The Next Generation of TV Display Technology Is Here
If you've been paying attention to the TV market over the past few years, you know the display wars have been heating up. OLED dominated for years. Mini-LED gained serious traction. And now, something new is emerging from the shadows, ready to shake everything up.
RGB Mini-LED technology represents a fundamental shift in how premium televisions deliver picture quality. It's not an incremental improvement or a minor tweak to existing technology. This is a wholesale reimagining of the backlighting system that drives everything you see on your screen.
Here's the thing: traditional Mini-LED displays use white LEDs as their backlight source. RGB Mini-LED, by contrast, uses separate red, green, and blue mini-LED chips to create the backlight. This seemingly small technical difference creates enormous practical advantages that could genuinely reshape the premium TV landscape in 2026 and beyond.
The implications are substantial. We're talking about dramatically improved color accuracy. Unprecedented contrast ratios. Brightness levels that rival or exceed OLED displays. And the potential to deliver these improvements at price points that make premium picture quality accessible to a much broader audience.
But RGB Mini-LED isn't just about raw performance numbers. It's about fundamentally changing what people expect from their televisions. As streaming services deliver increasingly high-quality content, as gaming becomes more visually sophisticated, as consumers become more discerning about display quality, a technology that can deliver exceptional performance across all these domains becomes genuinely valuable.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore exactly what RGB Mini-LED is, how it works, why it matters, and what it means for the future of premium television. We'll break down the technical details without requiring an engineering degree. We'll compare it honestly against competing technologies. And we'll help you understand whether this is the next technology you should be watching as you plan your home entertainment setup.
TL; DR
- RGB Mini-LED uses separate red, green, and blue LED chips instead of white LEDs, enabling precise color control and exceptional picture quality
- Superior color accuracy and wider color gamut make RGB Mini-LED ideal for content creators, gamers, and video enthusiasts
- Contrast ratios and brightness levels exceed traditional Mini-LED while maintaining significantly lower power consumption than comparable OLED displays
- 2026 market predictions suggest RGB Mini-LED will capture 15-20% of the premium TV market as manufacturers perfect the technology and economies of scale reduce costs
- Price points are expected to drop substantially, potentially making RGB Mini-LED competitive with high-end QLED models while delivering superior picture quality
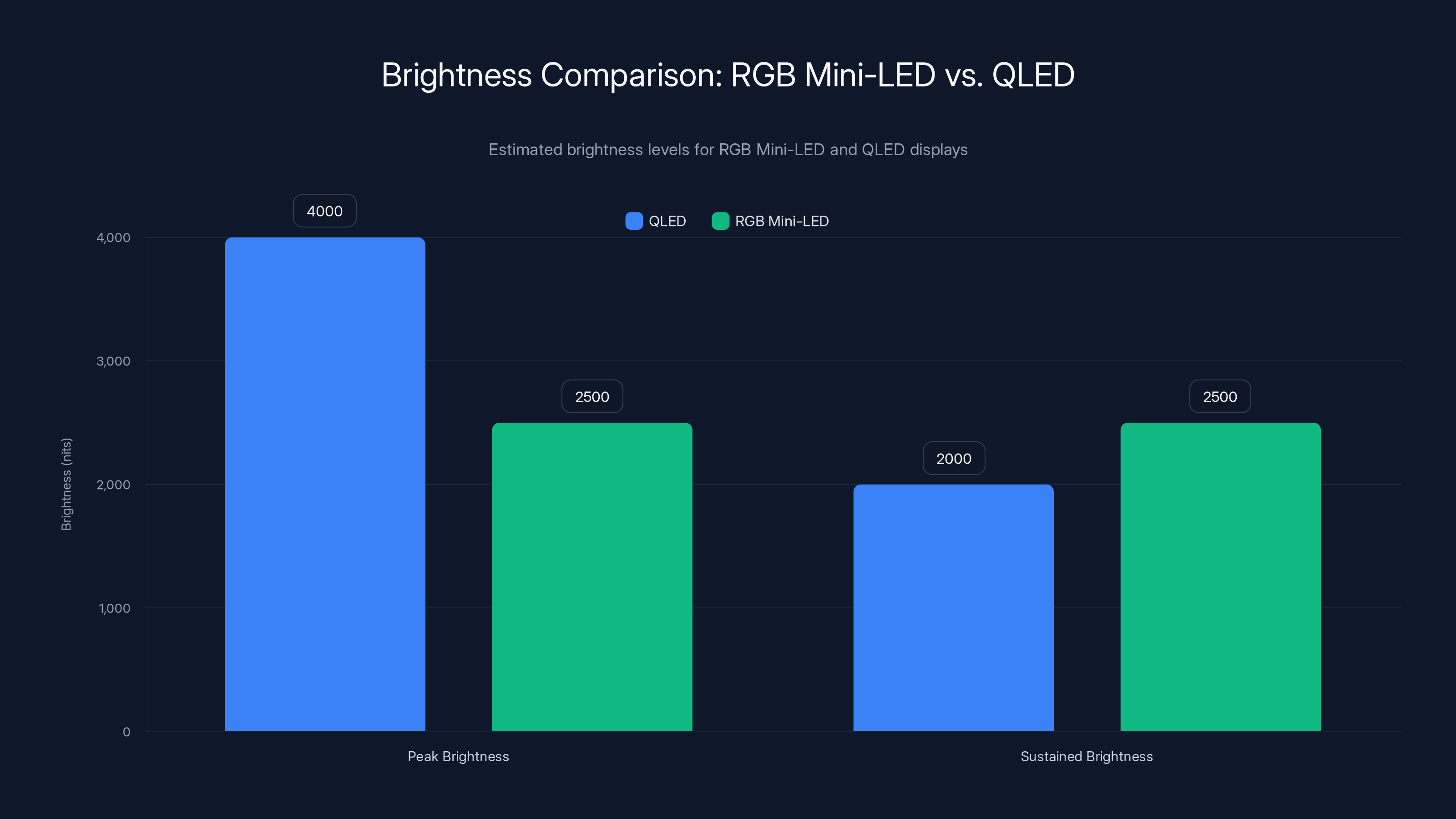
While QLED can achieve higher peak brightness, RGB Mini-LED offers more consistent sustained brightness, enhancing overall viewing experience. Estimated data.
What Is RGB Mini-LED? Understanding the Core Technology
Let's start with the fundamentals. To truly understand RGB Mini-LED, you need to know what came before it and why those earlier technologies had limitations that engineers have been trying to overcome.
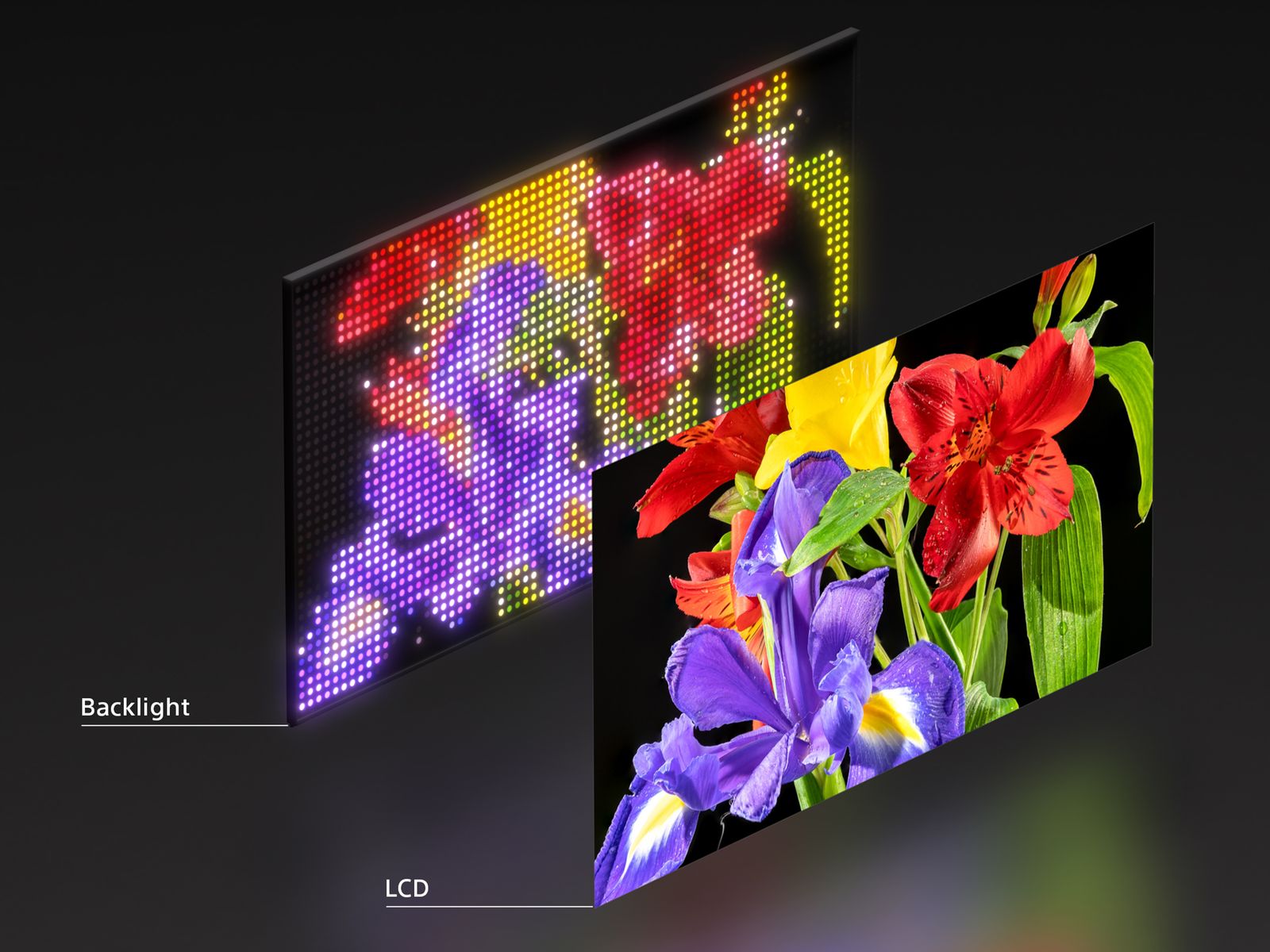
Traditional LCD televisions rely on a backlighting system. The LCD panel itself doesn't produce light. Instead, a separate light source shines through the liquid crystal layer, which can be electronically controlled to block or allow light to pass through. This is fundamentally different from OLED displays, where individual pixels produce their own light.
For decades, LCD TVs used fluorescent backlights, which were cheap but delivered mediocre color accuracy and contrast. LED backlights improved things substantially. Then came Mini-LED, which used thousands of tiny white LEDs arranged in zones behind the LCD panel. By dimming or brightening individual zones, manufacturers could achieve better contrast control and overall picture quality.
But here's the limitation that Mini-LED couldn't overcome: all those zones contained white LEDs. White light is created by combining red, green, and blue light. When you dim a white LED zone, you're dimming all three colors equally. This creates a situation where you lose color accuracy and can't achieve true color saturation at different brightness levels.
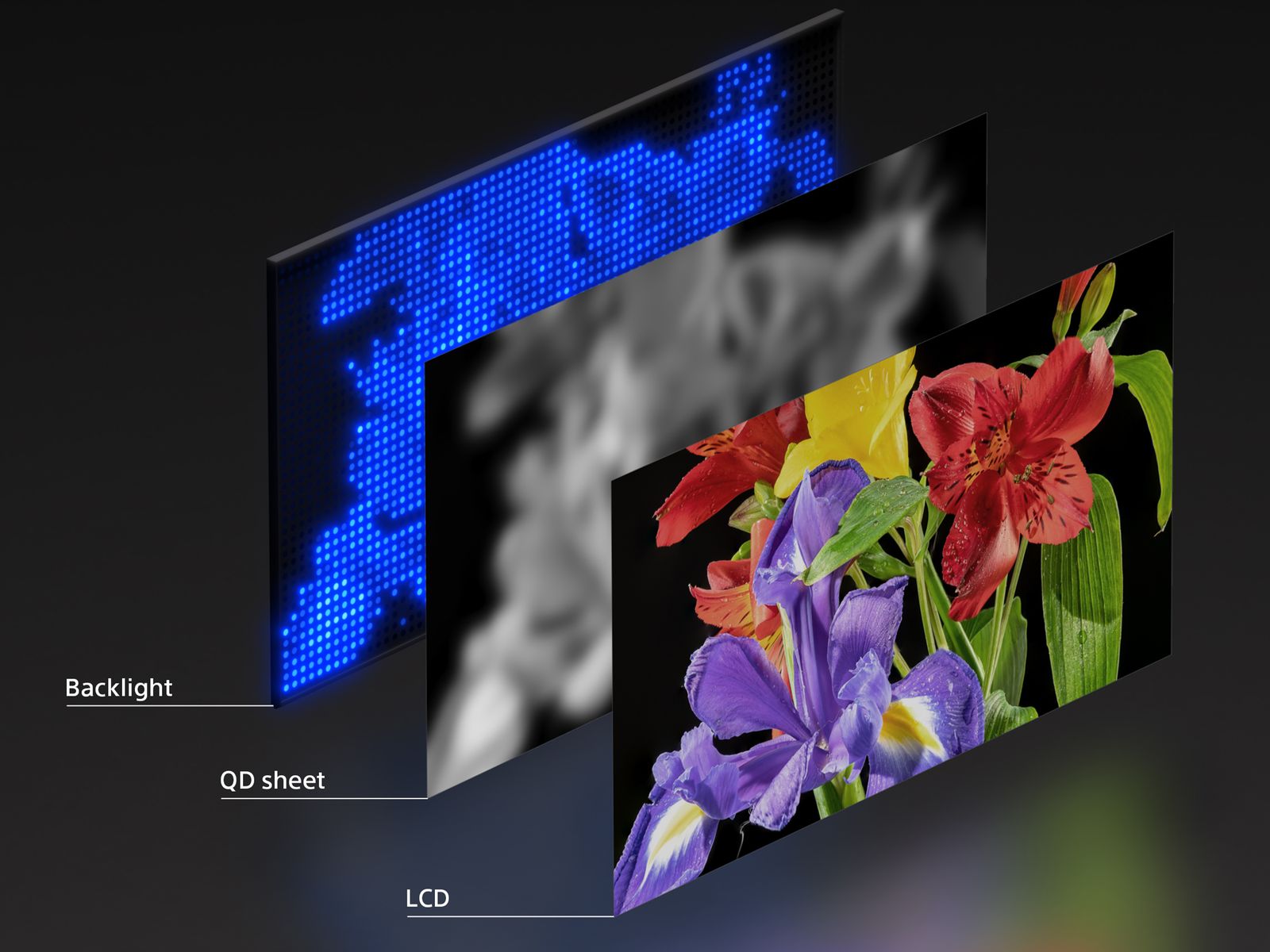
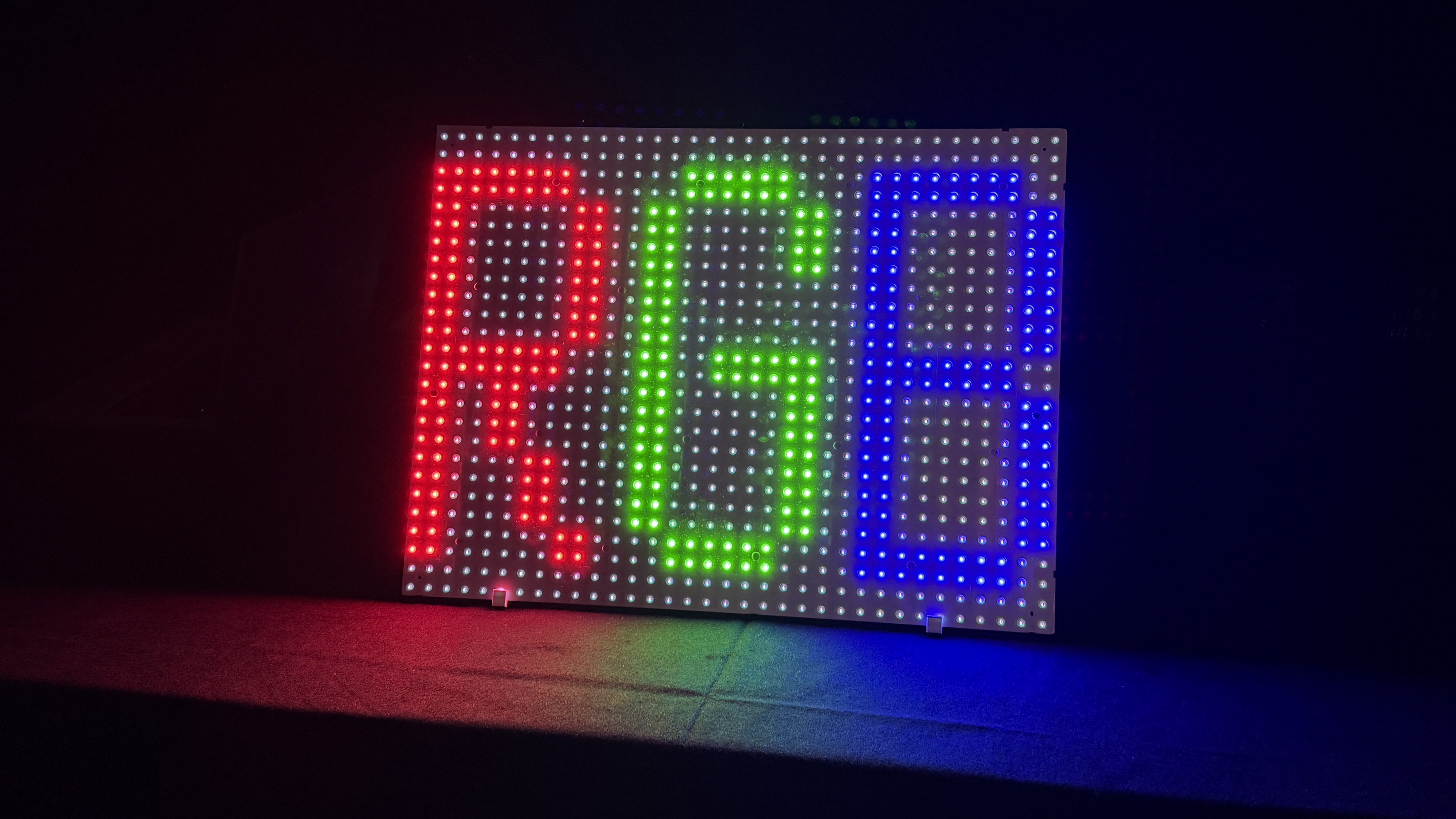
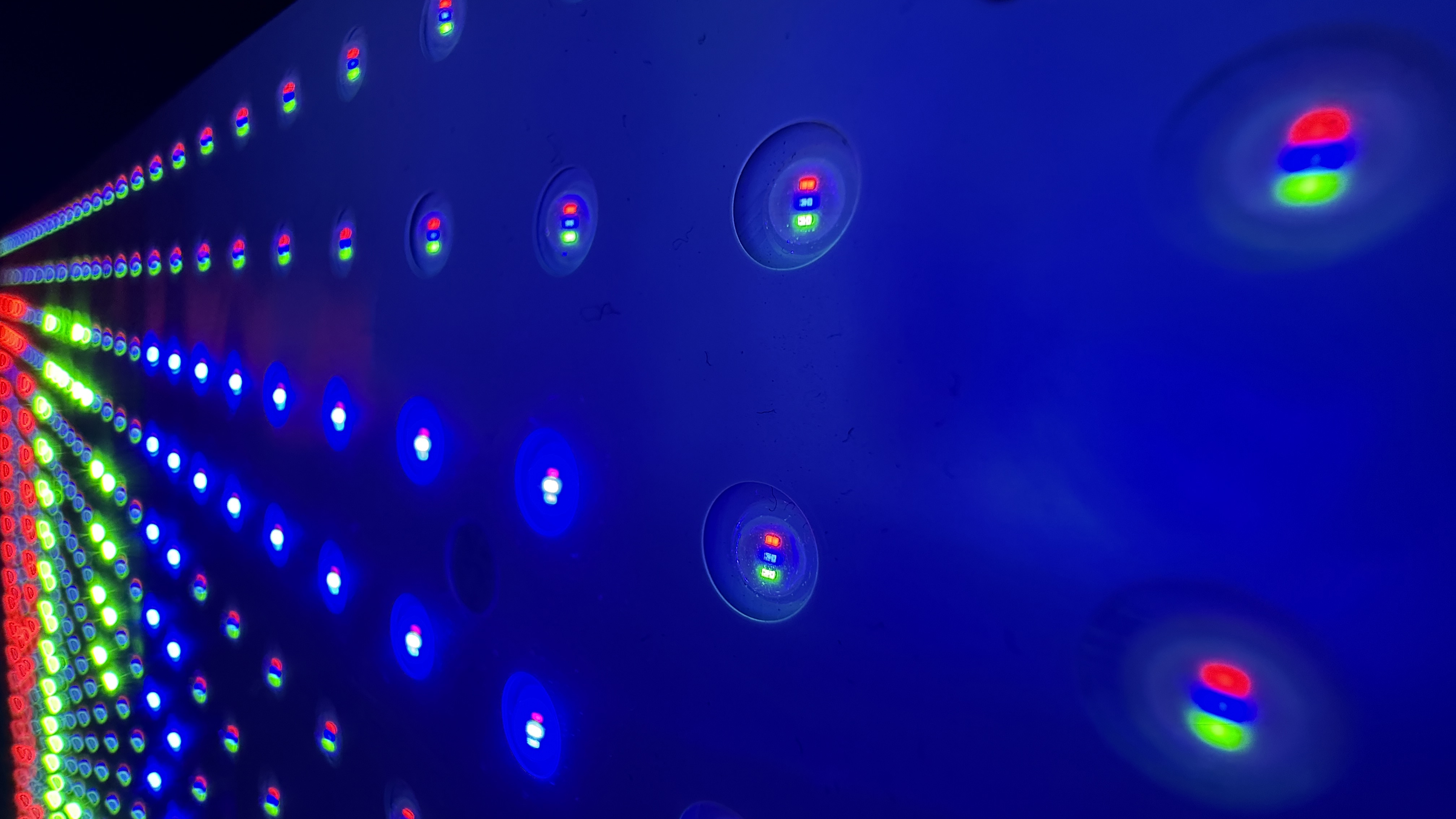
RGB Mini-LED solves this problem elegantly. Instead of using white LEDs, this technology uses separate red, green, and blue mini-LED chips. Each color has its own set of LEDs arranged in zones behind the LCD panel. This means you can control each color independently.
Think of it this way: with traditional Mini-LED, you're dimming or brightening white light. With RGB Mini-LED, you're composing the exact color and brightness you need by controlling red, green, and blue independently. It's the difference between adjusting a single knob and having three knobs where you can dial in exactly what you want.
The technical implementation is surprisingly elegant. Manufacturers take three separate mini-LED arrays (one for each color) and stack them behind the LCD panel. Advanced processing algorithms determine the optimal brightness level for each color in each zone based on the content being displayed. Modern processors handle this computation in real-time without any visible lag or processing artifacts.
What makes this particularly impressive is that RGB Mini-LED achieves these improvements while maintaining the fundamental advantages of the Mini-LED approach. You get thousands of independently controllable zones. You get the ability to deliver exceptional brightness. You get the energy efficiency that comes from being able to dim zones that aren't needed for specific content.
The size of the LEDs matters too. These aren't just shrunk-down versions of regular LEDs. Mini-LEDs typically measure between 0.03 and 0.3 millimeters in diameter, making them roughly the size of a grain of salt. This small size allows for the massive density required to create the thousands of zones that make zone-based dimming effective. RGB Mini-LED technology pushes this even further, requiring even more precise manufacturing and quality control.

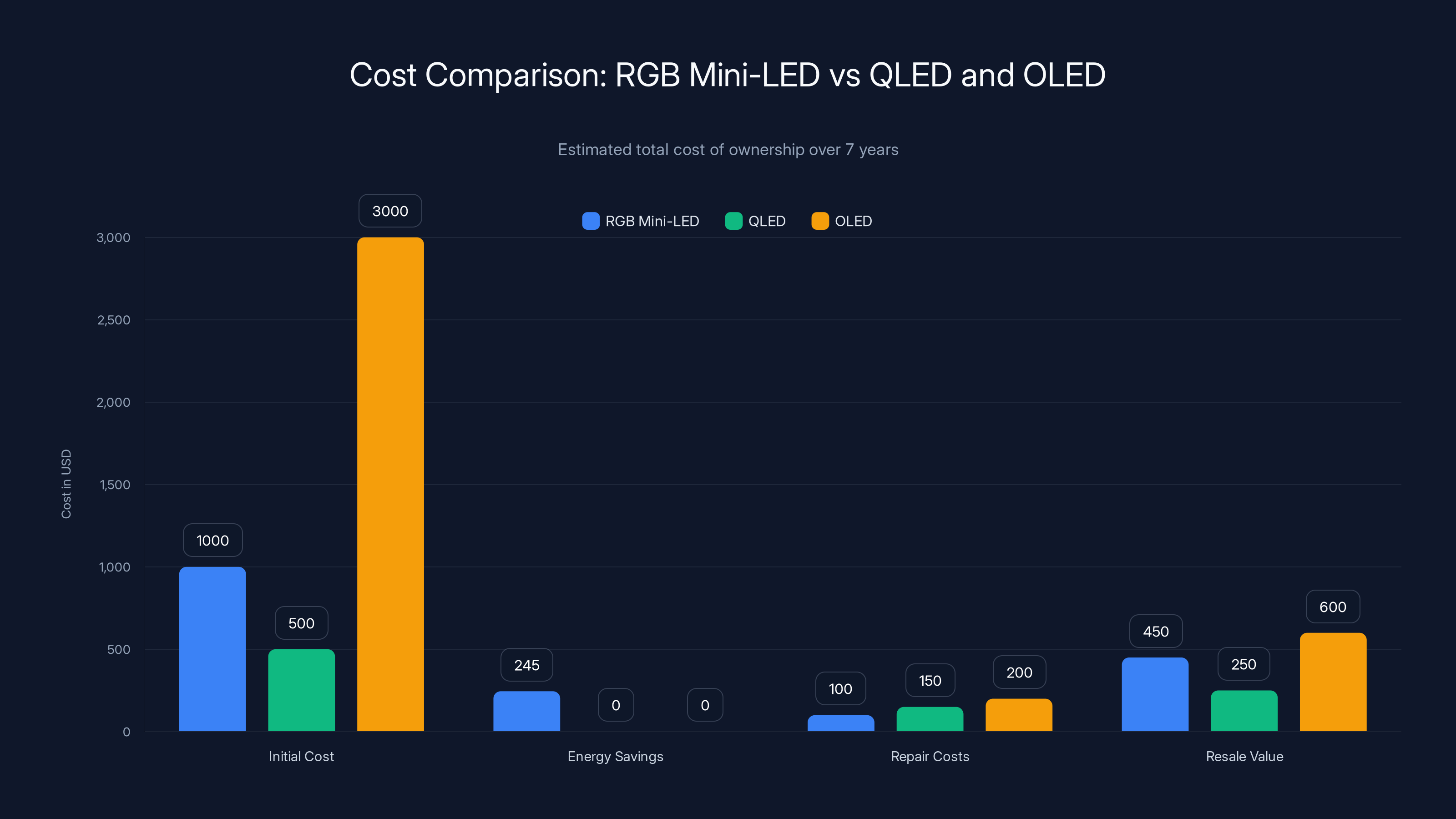
Estimated data shows RGB Mini-LED displays have a lower total cost of ownership over 7 years due to energy savings and higher resale value compared to QLED and OLED.
How RGB Mini-LED Backlighting Works in Practice
Understanding how RGB Mini-LED actually functions in a real television requires looking at the signal flow from content to your eyes.
When you're watching content on an RGB Mini-LED display, the television receives video data. This data is processed by the display's image processor, which analyzes the content frame by frame. For each frame, the processor determines the optimal brightness level for each color in each zone based on what's being displayed.
Here's where it gets interesting. The processor doesn't just dim or brighten zones uniformly. It applies sophisticated algorithms that consider factors like perceived brightness, color saturation, and even human visual perception. The algorithms understand that human eyes perceive brightness differently across the color spectrum. They know that red brightness appears different to our eyes than green or blue brightness at the same physical brightness level. This is called photometric calibration, and RGB Mini-LED systems apply it to each color independently.
The actual backlighting process involves three separate LED arrays working in concert. The red LED array projects red light through designated zones. The green LED array projects green light through the same zones. The blue LED array does the same. The LCD layer then modulates this combined light based on the pixel data.
This creates a situation that's genuinely unique in television technology. Each pixel can have light of a different spectral composition depending on what that pixel needs to display. A bright red area on the screen gets primarily red backlight, with minimal green and blue. A blue area gets primarily blue backlight. A white area gets balanced amounts of all three colors.
The contrast improvement comes from the ability to independently control each color. Imagine a scene with a bright white cloud against a dark blue sky. Traditional Mini-LED would brighten the entire zone, affecting both the cloud and the sky. RGB Mini-LED can brighten the red and green components for the cloud while keeping the blue dim for the sky. This creates dramatically better separation and perceived contrast.
The processing demands are substantial. Modern RGB Mini-LED televisions contain specialized processors dedicated solely to zone calculation and LED control. These processors must handle calculations for thousands of zones across three colors multiple times per second. A 120 Hz display means the processor recalculates zone values 120 times per second. At 4K resolution with advanced zone calculations, this requires substantial computing power.
Latency is also carefully managed. The time between when content is received and when the LEDs adjust must be minimal, typically in the single-digit millisecond range. This is why gaming performance on RGB Mini-LED displays is genuinely excellent. The backlighting can adjust quickly enough to keep pace with rapidly changing content.
Color accuracy depends heavily on the quality of the LED chips themselves and the calibration of the system. Manufacturers source mini-LEDs from specialized suppliers, as these components require extremely tight tolerances. A red LED that's even slightly shifted in wavelength can throw off the entire color gamut. This is why manufacturing RGB Mini-LED displays is significantly more complex than traditional Mini-LED production.
RGB Mini-LED vs. OLED: The Ultimate Showdown
When comparing display technologies, OLED is the elephant in the room. OLED displays have dominated the premium TV market for years, and for good reason. Each pixel produces its own light, enabling perfect blacks and exceptional contrast. But OLED has limitations, and RGB Mini-LED addresses many of them.
Let's talk brightness first. OLED displays struggle with sustained brightness. An OLED TV can peak at extremely bright levels for short bursts, but maintaining brightness across the full screen for extended periods causes the display to thermally throttle. This is why you might notice an OLED TV getting slightly less bright when you're watching a bright scene with lots of white. It's protecting itself from heat damage.
RGB Mini-LED doesn't have this limitation. Because the backlighting is separate from the LCD panel, heat dissipation is more manageable. Modern RGB Mini-LED displays can maintain peak brightness across the entire screen without thermal throttling. For watching bright content in well-lit rooms, RGB Mini-LED has a genuine advantage.
Contrast is where OLED traditionally dominated. Perfect blacks are hard to beat. But RGB Mini-LED is closing this gap. With thousands of dimming zones and the ability to control each color independently, RGB Mini-LED can achieve contrast ratios exceeding 200,000:1. While this isn't quite the infinite contrast of true OLED blacks, it's close enough that the difference is barely perceptible in most viewing scenarios.
Color accuracy is where RGB Mini-LED genuinely shines. Traditional Mini-LED has always struggled with color accuracy because the white backlighting compromises color saturation at different brightness levels. RGB Mini-LED eliminates this problem entirely. By controlling red, green, and blue independently, color saturation remains consistent regardless of brightness level. For color-critical applications like photo and video editing, RGB Mini-LED offers advantages that OLED simply can't match.
Consider the burn-in issue that plagues OLED displays. If you display the same image on an OLED screen for months or years, those pixels gradually degrade, leaving a permanent ghost image on the screen. This is a fundamental limitation of OLED technology. RGB Mini-LED doesn't have this problem. The backlighting is independent of the LCD panel's lifespan, and the LCD modulation layer experiences negligible wear from pixel-level variations.
Energy efficiency is more nuanced than most people realize. OLED displays don't actually use less power than RGB Mini-LED for all content. OLED excels with dark content because it can turn off pixels entirely. But for bright content with lots of white areas, OLED actually consumes more power because every pixel must generate its own light. RGB Mini-LED uses more efficient backlighting for bright scenes and can dim unused zones for dark content. Overall, modern RGB Mini-LED displays are comparable to OLED in energy efficiency and sometimes more efficient depending on content.
Response time matters for gaming. OLED displays have exceptional response times, typically below 1 millisecond. RGB Mini-LED response times depend on how quickly the backlighting can adjust. High-end models achieve response times in the 2-4 millisecond range, which is still excellent for gaming and barely perceptible to human eyes.
Price is where the largest difference currently exists. OLED displays are expensive because the manufacturing process requires precise alignment and quality control across millions of individual light-emitting pixels. RGB Mini-LED manufacturing, while complex, leverages more established processes and economies of scale that OLED hasn't yet achieved. This translates to lower costs.
The real question isn't which technology is objectively superior. It's which technology better serves your specific needs. Professional content creators prioritize color accuracy, making RGB Mini-LED compelling. Gamers value response time and contrast, where both technologies excel. Movie enthusiasts who watch in dark rooms might still prefer OLED's perfect blacks. And practical consumers concerned about burn-in, brightness, and long-term reliability increasingly see RGB Mini-LED as the smarter choice.
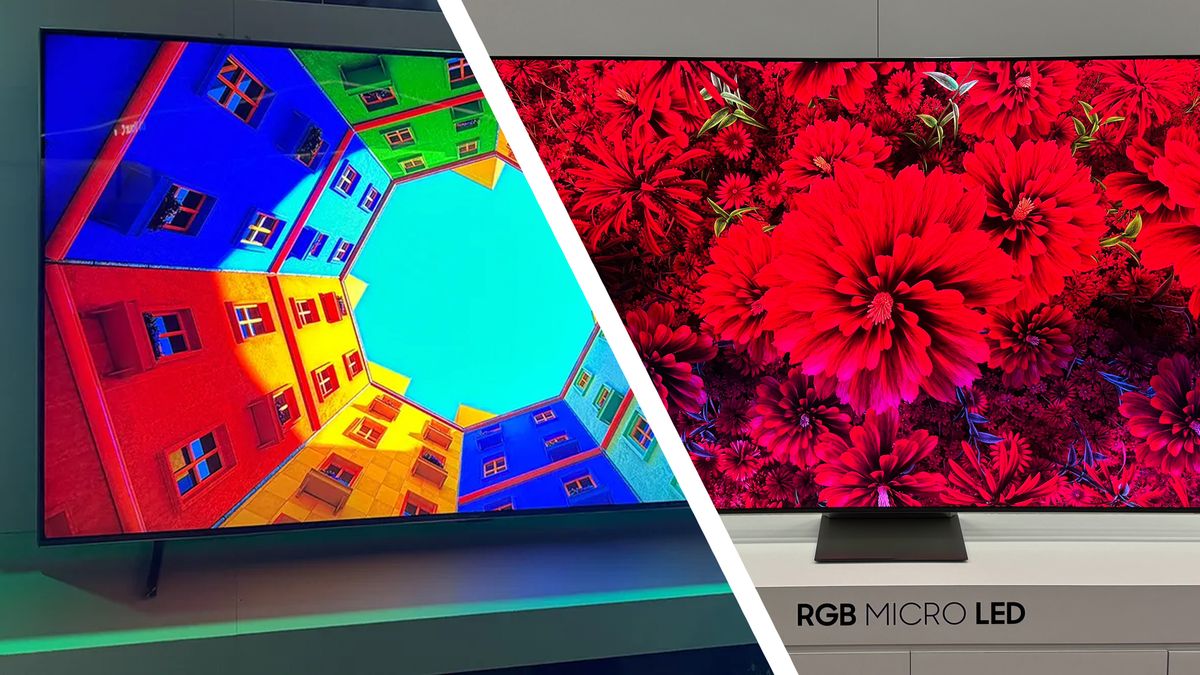

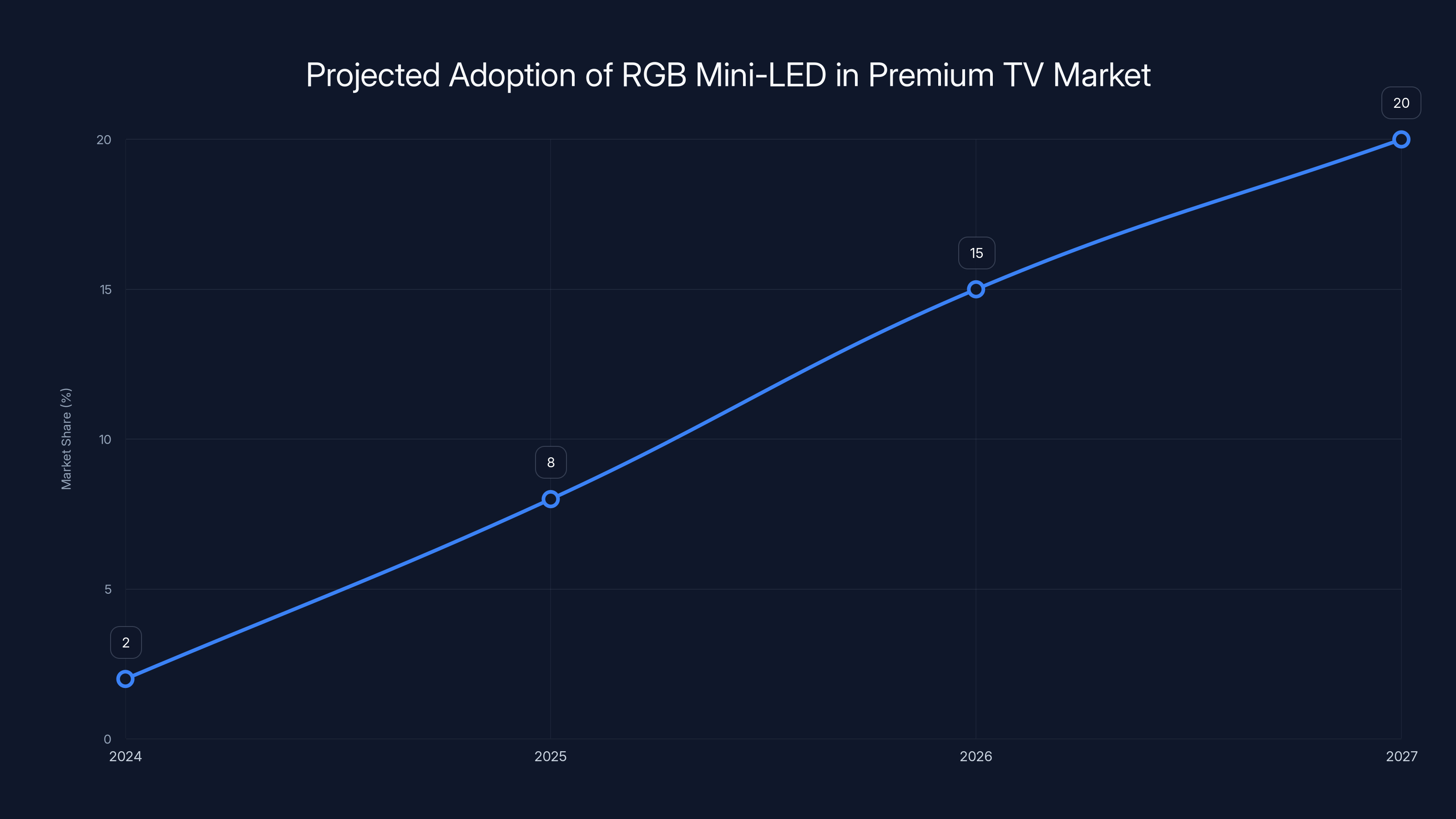
RGB Mini-LED displays are projected to grow from 2% market share in 2024 to 20% by 2027, indicating a rapid adoption curve. Estimated data.
RGB Mini-LED vs. Traditional QLED: Breaking Down the Differences
QLED (Quantum Dot LED) displays from manufacturers like Samsung and TCL represent the current mainstream premium TV technology. Understanding how RGB Mini-LED compares to QLED helps explain why RGB Mini-LED is generating so much industry excitement.
QLED uses quantum dots, which are tiny semiconductor particles that glow when exposed to light. A white Mini-LED backlight shines through the quantum dot layer, and the quantum dots convert that white light into a wider range of colors. This approach improves color volume and vibrancy compared to traditional LED displays.
The fundamental limitation is the same as traditional Mini-LED: white backlighting. Because the backlight is white, color accuracy at different brightness levels still suffers from the same constraints. You can brighten a zone, but you're brightening all colors equally, which limits color saturation when brightness is reduced.
RGB Mini-LED with quantum dots represents the next generation. Some manufacturers are experimenting with RGB backlights positioned behind quantum dot layers. This combines the color precision of RGB backlighting with the color volume of quantum dots, potentially offering the best of both approaches.
Brightness comparisons are interesting. A high-end QLED display might achieve peak brightness of 3,000-4,000 nits in small highlight areas. RGB Mini-LED displays typically achieve 2,000-2,500 nits sustained across the entire screen. For practical viewing, sustained brightness matters more than peak brightness. An RGB Mini-LED that maintains 2,500 nits across the entire display creates a brighter, more compelling image than a QLED that spikes to 4,000 nits in tiny areas but operates at 1,500-2,000 nits for most content.
Dimming zones tell a similar story. A typical high-end QLED display might have 300-500 dimming zones. Premium RGB Mini-LED displays feature 2,000-5,000 zones. More zones mean finer contrast control and fewer visible blooming artifacts (halos around bright objects against dark backgrounds).
Color gamut is where RGB Mini-LED truly separates itself. QLED achieves DCI-P3 coverage of roughly 90-95%. RGB Mini-LED displays achieve DCI-P3 coverage of 98-99% or higher. This means RGB Mini-LED can display colors that QLED simply cannot render.
Price-wise, high-end QLED and RGB Mini-LED are starting to converge. A top-tier QLED 65-inch display might cost
The question for consumers is whether the improvements justify the current price premium. For professional users, photographers, video editors, and serious gamers, the color accuracy and contrast improvements probably do. For casual viewers, the difference might be subtle enough that QLED represents better value.

The Color Accuracy Advantage: Why This Matters
Color accuracy might seem like a technical specification, but it profoundly affects what you actually see on your screen. This is where RGB Mini-LED demonstrates a genuine and significant advantage.
Traditional display technologies struggle with something called color gamut mapping. When a display can't render a color that exists in the source content, it must approximate it with a nearby color it can render. With traditional Mini-LED or QLED, this approximation sometimes looks desaturated or shifted.
Consider a professional photographer working with images that contain highly saturated colors. When viewing their work on a traditional Mini-LED display, certain colors might appear duller than they actually are. The photographer adjusts the image to look right on their display, but when other people view the image on a display with a wider color gamut, it looks oversaturated.
RGB Mini-LED's wider color gamut means these color shifts happen less frequently and less noticeably. The wider the gamut, the fewer colors in typical content require approximation.
The practical impact extends to everyday content. Modern streaming services like Netflix and Disney+ increasingly deliver content in HDR (High Dynamic Range) with wider color gamuts. Watching this content on a display that can fully reproduce the intended colors creates a noticeably more vivid, more engaging experience.
Video gamers experience this too. Modern games often include content authored in extended color spaces. An RGB Mini-LED display renders these colors more accurately, making game worlds look more vibrant and more closely matching the developer's intent.
The technology that enables this color accuracy is what makes RGB Mini-LED special. By controlling red, green, and blue light independently, the display can achieve higher saturation at any given brightness level. Traditional white backlights can't do this because brightening a white backlight brightens all colors equally.
Calibration becomes more important with RGB Mini-LED because the display has more potential for both exceptional accuracy and potential color accuracy issues if not properly calibrated. Premium RGB Mini-LED displays include factory calibration and often include calibration tools that allow users to fine-tune color performance if desired.

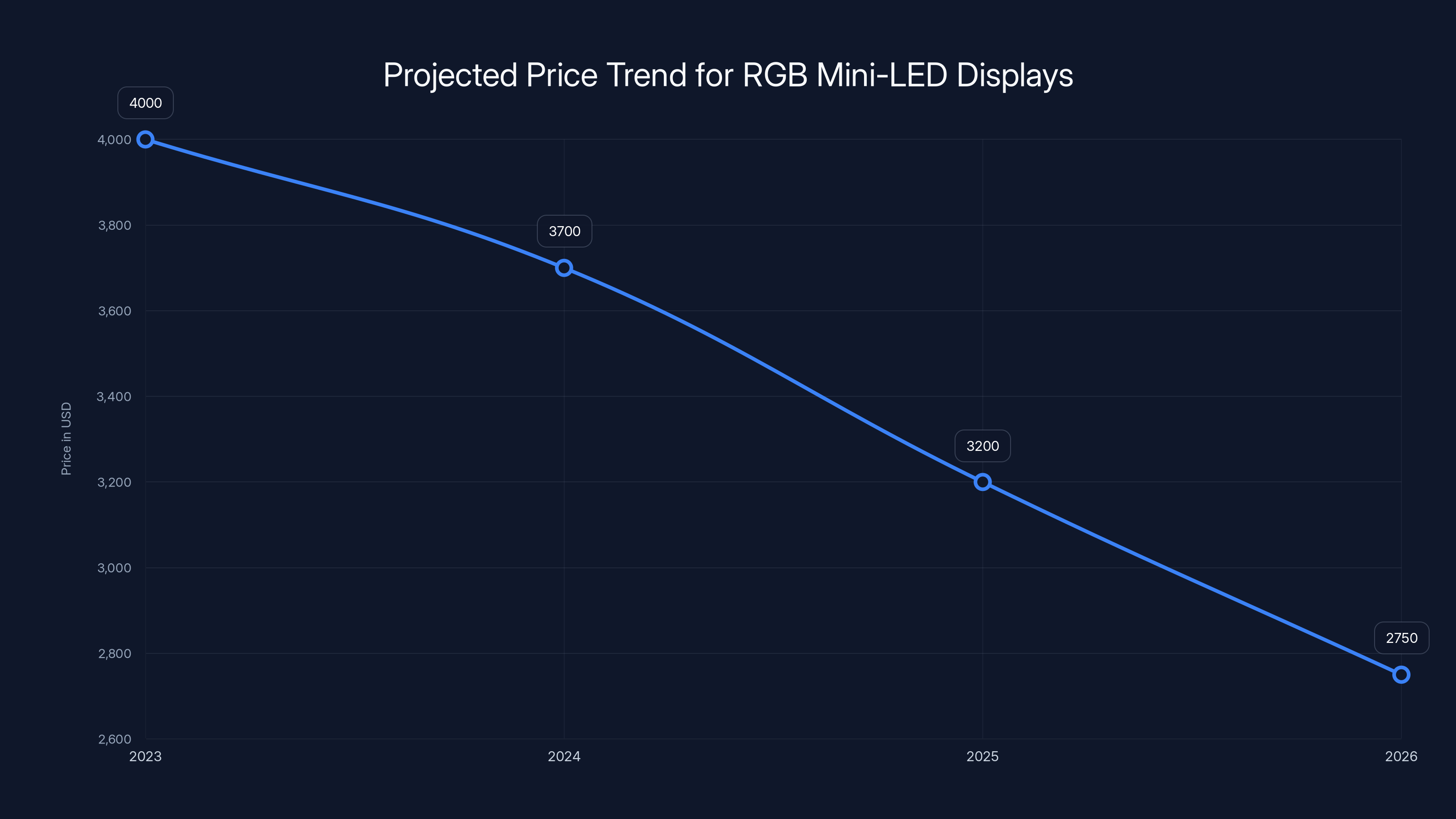
Estimated data shows RGB Mini-LED display prices are expected to decrease from
Contrast and Black Levels: The Complete Picture
When you're watching movies or gaming, contrast affects your emotional connection to the content. Deep blacks that feel truly dark enhance the dramatic impact of scenes. Bright highlights that pop without washing out create visual excitement.
OLED displays achieve infinite contrast through perfect blacks. Each pixel can turn completely off. RGB Mini-LED doesn't have this capability. But modern RGB Mini-LED achieves contrast ratios that are close enough to be imperceptible in most viewing scenarios.
The key is zone-based dimming combined with independent color control. When a zone is dark, all three color LEDs in that zone can be dimmed to nearly zero. This creates blacks that appear nearly as deep as OLED blacks. The difference becomes visible only in extreme conditions, like a completely dark room with a small bright object on a black background.
Contrast perception also depends on the viewing environment. In a bright room, the black level you can achieve on any display is limited by ambient light reflection. Both OLED and RGB Mini-LED displays appear to have lighter blacks in bright rooms. In dark rooms, where the ambient light level is essentially zero, the difference becomes more noticeable.
One advantage RGB Mini-LED has over OLED is the absence of blooming. Blooming occurs when light from a bright area spreads into adjacent dark areas. OLED doesn't have blooming because each pixel is independent. But with zone-based dimming, RGB Mini-LED can have visible halos around bright objects. High-end displays with thousands of zones minimize this dramatically.
Modern zone calculation algorithms are sophisticated enough to predict blooming and adjust zone brightness to minimize visible artifacts. This is where the computational power in RGB Mini-LED displays becomes critical.
For movie watching, the contrast improvements translate to better shadow detail and better highlight detail simultaneously. A dark scene where characters are talking in dim lighting preserves detail in their faces. A bright scene with sunlit landscapes maintains detail in bright areas without washing out. This dynamic range is precisely what HDR (High Dynamic Range) content is designed to showcase, and RGB Mini-LED displays excel at rendering HDR content.
Gaming benefits from high contrast too. When you're playing a fast-paced game in a dark environment, being able to see both dark shadows and bright highlights without losing detail in either improves your gameplay performance. The improved visual clarity translates to better awareness and faster reaction times.
Brightness Capabilities: Sustained Performance Matters
Brightness specifications for televisions are often misleading. Manufacturers publish peak brightness numbers measured in a small 10% window, which doesn't represent how the display performs during normal viewing.
RGB Mini-LED displays excel at sustained brightness. A high-quality RGB Mini-LED TV can maintain 2,000-2,500 nits of brightness across a 50% window (representing typical content with a mix of bright and dark areas). This sustained brightness matters more for real-world viewing than peak brightness measured in tiny highlight areas.
Why does brightness matter beyond just being able to see the picture? Brighter displays can better fight against ambient light. In a brightly lit living room, a dim display becomes hard to watch because you're competing against the room's light. A bright display punches through this ambient light and maintains visual impact.
Brightness also affects perceived contrast. When you're comparing a bright highlight to a dark shadow, the greater the absolute difference in luminance, the more dramatic the contrast appears. A display that can achieve higher brightness alongside deep blacks creates a more compelling visual experience.
HDR content is specifically designed to leverage high brightness. Movies and games authored in HDR assume a display with capability to achieve brightness that exceeds what standard dynamic range displays can produce. An RGB Mini-LED display with 2,000+ nits can render HDR content as it was intended.
One advantage of LED-based backlighting over OLED is thermal stability. An RGB Mini-LED display can maintain peak brightness indefinitely without thermal throttling. OLED displays, by contrast, reduce brightness during sustained high-brightness content to prevent heat damage. This is why an OLED might initially appear brighter, but an RGB Mini-LED maintains higher average brightness over time.
The practical impact varies by content. Watching bright sports events in a well-lit room, an RGB Mini-LED display with excellent sustained brightness outperforms OLED. Watching movies in a dark home theater, the difference becomes less noticeable.

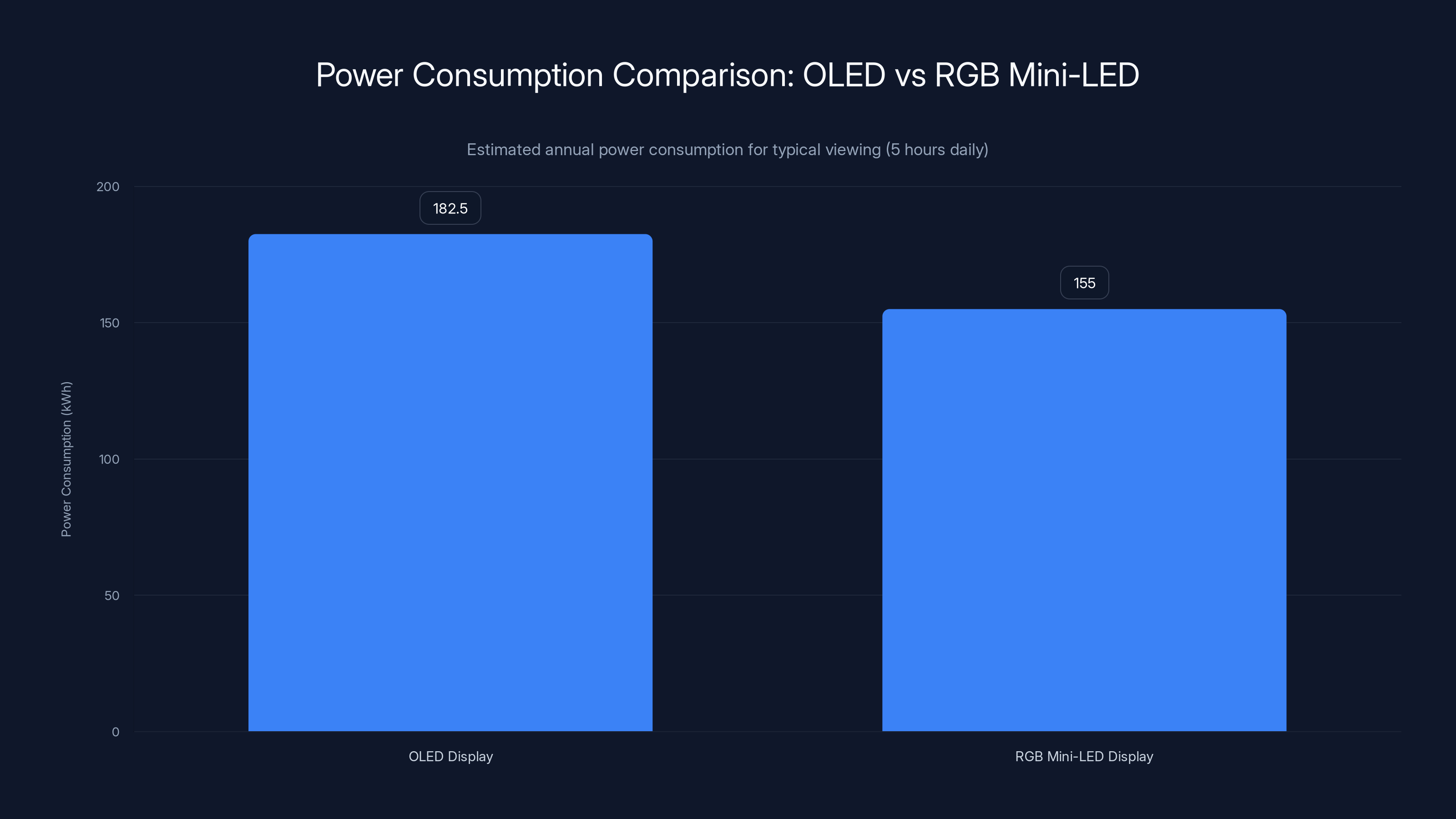
RGB Mini-LED displays consume approximately 15% less power annually compared to OLED displays, translating to savings of about
Energy Efficiency: The Often-Overlooked Factor
Energy consumption matters both for your electricity bill and for environmental impact. The common assumption is that LED-based displays consume more power than OLED, but this isn't entirely accurate.
OLED displays are extremely efficient for dark content because dark areas can turn off pixels entirely. But for bright content with large bright areas, OLED must power every pixel that's part of that bright area. Each pixel producing its own light requires substantial power.
RGB Mini-LED uses less power for bright content because the backlighting can serve multiple pixels simultaneously. Bright content that would require powering many OLED pixels instead requires brightening some LED zones, which is more efficient.
Typical power consumption comparisons show RGB Mini-LED using slightly less power than comparable OLED displays, especially when watching mixed-content like movies and television shows. The difference is roughly 10-20% in favor of RGB Mini-LED, though this varies based on content mix and display size.
Over a year of typical viewing (assuming 5 hours daily), this power difference translates to measurable savings. A display consuming 100 watts continuously used 5 hours daily for 365 days uses 182.5 kilowatt-hours annually. A comparable display consuming 85 watts uses 155 kilowatt-hours. At
This isn't a huge difference on a per-display basis, but aggregate across millions of displays sold annually, it represents meaningful energy savings.
RGB Mini-LED also enables more sophisticated power management algorithms. The backlighting can dim zones that aren't needed for specific content, achieving power savings that locked-zone approaches can't match. As AI and machine learning improve content analysis, future RGB Mini-LED displays will likely become even more efficient.

Longevity and Durability: The Long-Term Perspective
When you're spending $3,000-5,000 on a television, longevity matters. Will this display still look good in 5 years? 10 years? What's the realistic lifespan?
OLED displays have a known degradation issue. Over time, the light-emitting material gradually loses efficiency. After several years of use, especially with high brightness levels, OLED displays can experience noticeable brightness loss and color shift. This isn't a failure, but rather normal degradation.
RGB Mini-LED doesn't have this issue to the same degree. The LCD modulation layer experiences minimal degradation from pixel-level variations. The LEDs themselves degrade very slowly under normal operating conditions. Modern LED technology suggests useful lifespans of 30,000-50,000 hours, equivalent to 8-14 years of 5-hour daily use.
Burn-in is the critical differentiator. OLED displays can develop permanent image retention if you repeatedly display the same static image. This is why streaming services and gaming console manufacturers include static image warnings on OLED displays.
RGB Mini-LED doesn't suffer from burn-in because the LCD modulation layer is independent of the backlighting. You could theoretically display the same static image on an RGB Mini-LED screen continuously and never develop burn-in.
For practical use cases like using a television as a secondary display or gaming monitor where static UI elements appear constantly, this burn-in resistance is genuinely valuable.
Panel lifespan is just one component of overall reliability. Backlighting systems also have finite lifespans. However, LED backlighting is mature technology with proven reliability. Manufacturer warranties typically cover 5 years, and displays often last significantly longer with proper care.
Compare this to OLED, where the entire panel is at risk if the light-emitting material degrades. OLED panels are increasingly difficult and expensive to replace after warranty expiration, making a failed OLED display essentially unrepairable.
From a long-term total cost of ownership perspective, RGB Mini-LED offers superior economics. Lower initial cost plus lower maintenance costs and potentially longer useful lifespan make it an attractive choice for consumers planning to keep their displays 5+ years.

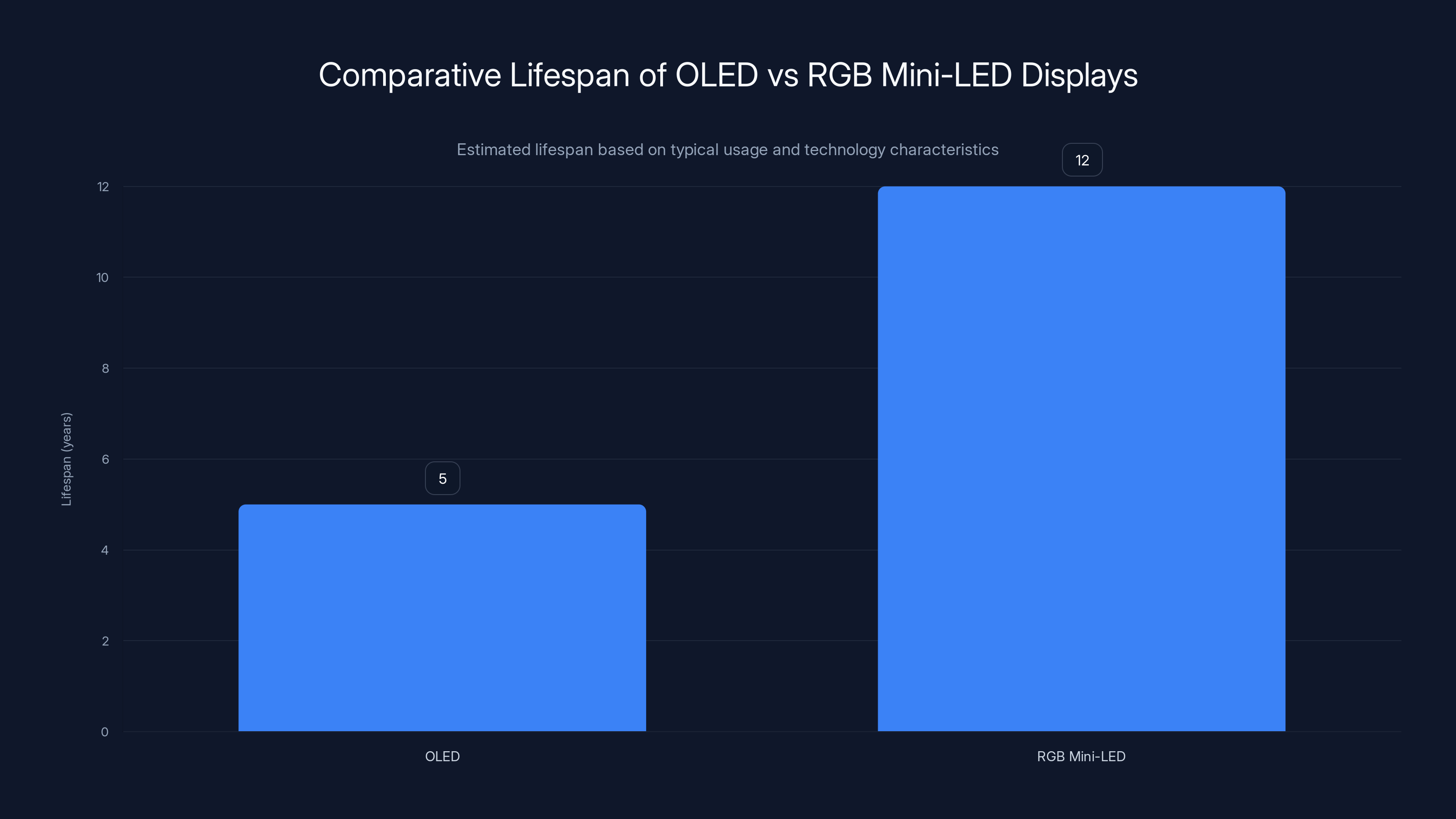
RGB Mini-LED displays have an estimated lifespan of 12 years, significantly longer than OLED displays, which last about 5 years under similar usage conditions. Estimated data.
Manufacturing and Production Challenges
While the technology is exciting, the manufacturing reality is complex. RGB Mini-LED requires significantly more precision than traditional Mini-LED or QLED production.
The fundamental challenge is alignment and calibration. You're stacking three separate LED arrays, and they must be perfectly aligned. Any misalignment creates color shifts and reduced contrast. The tolerances are in tens of micrometers, which is achievable but requires sophisticated manufacturing equipment.
LED sourcing is another challenge. RGB Mini-LED requires three separate types of mini-LEDs with tight wavelength specifications. Red, green, and blue LEDs must have consistent wavelengths across all units. Even small variations degrade color accuracy and require more complex calibration algorithms to compensate.
Manufacturers must source these components from reliable suppliers. Currently, very few companies manufacture mini-LEDs at the scale required for television production. This creates a bottleneck that limits production volume and drives up costs.
Quality control becomes more critical with RGB Mini-LED. Every display must be individually calibrated to ensure color accuracy. This calibration process is more complex and time-consuming than QLED or traditional Mini-LED calibration. Manufacturers are developing automated calibration systems to handle this, but they're expensive to implement.
Yield rates (the percentage of produced displays that meet quality standards) are another consideration. RGB Mini-LED manufacturing yields are currently lower than QLED or traditional Mini-LED, meaning a higher percentage of units don't meet quality standards and must be discarded or reworked. As manufacturing processes mature, yields improve and costs drop.
These manufacturing challenges explain the current high prices and why analysts predict costs will drop significantly as manufacturing volumes increase. What's expensive to manufacture in small quantities becomes much cheaper at scale.

The 2026 Market Landscape: Adoption Predictions
Where will RGB Mini-LED be in the TV market by 2026? The answer depends on manufacturing improvements, cost reductions, and consumer awareness.
Current estimates suggest RGB Mini-LED will capture roughly 10-15% of the premium TV market (displays over $2,000) by 2026. This might sound modest, but it represents genuine market shift from OLED and QLED dominance.
Manufacturers including BOE, TCL, Hisense, and others are investing heavily in RGB Mini-LED production. Samsung and LG are also developing RGB Mini-LED technologies. This competitive pressure should accelerate production scale and cost reductions.
Price projections suggest RGB Mini-LED displays will become price-competitive with high-end QLED models by 2026. A 65-inch RGB Mini-LED display that costs
Consumer awareness is the missing ingredient. Many people aren't aware that RGB Mini-LED exists or understand what advantages it offers. As manufacturers market these displays and reviewers highlight the superior picture quality, awareness and demand should increase.
The competitive landscape matters too. If OLED manufacturers successfully reduce prices below current levels, RGB Mini-LED adoption will be slower. If OLED prices hold steady while RGB Mini-LED prices drop, adoption will be faster. Current trends suggest RGB Mini-LED is becoming price-competitive faster than OLED is reducing prices.
Content availability will also influence adoption. As more streaming services deliver HDR content with extended color gamuts, the advantages of RGB Mini-LED become more apparent. Netflix, Disney+, and others are increasing HDR content production, which should drive consumer desire for displays that can fully render this content.
Gaming represents another growth driver. As gaming consoles and graphics cards become more powerful, games increasingly include extended color content. Gamers seeking the best possible image quality will be drawn to RGB Mini-LED displays.
Professional applications represent a smaller but growing market. Content creators, photographers, and video editors have budget for premium displays and understand the value of color accuracy. This professional segment could drive early adoption and help establish RGB Mini-LED credibility.

Which Manufacturers Are Leading RGB Mini-LED Development?
Several manufacturers are making significant investments in RGB Mini-LED technology, each approaching it with slightly different strategies.
BOE (Beijing Orient Electronics) has been among the most aggressive in developing RGB Mini-LED. The company is investing billions in manufacturing infrastructure specifically for mini-LED and RGB mini-LED production. BOE currently supplies mini-LEDs for many television manufacturers and is moving aggressively into direct consumer display manufacturing.
TCL, particularly through its high-end TCL X-series displays, is incorporating RGB Mini-LED in premium models. The company is leveraging BOE's manufacturing capability while developing its own proprietary display processors for backlighting control.
Hisense is similarly investing in RGB Mini-LED technology and has announced plans to expand production significantly. The company is positioning RGB Mini-LED as a core technology for its premium product line.
Samsung is developing proprietary RGB Mini-LED variants that integrate with their quantum dot technology. Samsung's approach aims to combine the color volume of quantum dots with RGB Mini-LED's color accuracy.
LG, traditionally an OLED manufacturer, is also developing RGB Mini-LED technology as a hedge against potential OLED limitations. LG's approach leverages their display manufacturing expertise but is not yet as advanced as some competitors.
Ariseledtek and other specialized LED manufacturers are improving mini-LED production and wavelength consistency, which should gradually reduce costs and improve RGB Mini-LED display quality.
The competitive dynamics are interesting. Unlike OLED, where LG essentially owned the manufacturing infrastructure, multiple companies are investing in RGB Mini-LED manufacturing. This competition should benefit consumers through faster innovation and lower prices.

Practical Considerations: Should You Buy RGB Mini-LED Now?
If you're thinking about buying a premium TV in the next year, should you wait for RGB Mini-LED or buy an available QLED or OLED now?
The answer depends on your specific situation. If you need a new TV immediately and have the budget, current QLED and OLED options are excellent. You'll have a quality display regardless.
If you can wait until late 2024 or 2025, RGB Mini-LED options should become more available and potentially less expensive. The picture quality improvements are genuine and noticeable, especially for color-critical viewing.
Consider your use case. If you're primarily watching streaming content in a bright living room, RGB Mini-LED's superior brightness and color accuracy are compelling advantages. If you're building a dark home theater primarily for movies, an OLED's perfect blacks might still be preferable despite higher cost.
Gaming is another consideration. RGB Mini-LED displays with high refresh rates (120 Hz) and excellent response times are emerging. If you're a serious gamer, RGB Mini-LED offers advantages in color accuracy and sustained brightness.
Professional applications strongly favor RGB Mini-LED. If you're a photographer, video editor, or content creator, the color accuracy advantages justify waiting or paying a premium.
Budget constraints matter too. If you have a strict
Longevity considerations also apply. If you plan to keep your display 5+ years, RGB Mini-LED's lack of OLED burn-in concerns and lower degradation rates offer practical advantages.

Future Developments: What's Coming Next?
RGB Mini-LED technology is still evolving. Several developments could significantly impact its trajectory.
Micro-LED (where each pixel produces its own light like OLED but using inorganic LEDs) is being developed as an alternative. Micro-LED could eventually combine OLED's pixel-level control with LED's durability and efficiency. However, Micro-LED is still 3-5 years away from consumer market viability due to manufacturing complexity.
RGB Mini-LED with quantum dots is the likely next iteration. Combining RGB backlighting with quantum dot color conversion could create displays with the color accuracy of RGB Mini-LED and the color volume of current QLEDs.
AI-powered backlighting algorithms are becoming more sophisticated. Machine learning algorithms analyzing content in real-time can make smarter decisions about zone brightness allocation, reducing blooming artifacts and improving efficiency.
Variable refresh rate technology is becoming standard on premium displays. Future RGB Mini-LED displays will likely include variable refresh rates for gaming, reducing flicker and improving responsiveness.
Miniaturization of LED components continues. As mini-LEDs become smaller and more efficient, the number of zones possible will increase, further improving contrast control and reducing visible blooming.
Transparent displays incorporating RGB Mini-LED backlighting are being researched. These could revolutionize how displays are integrated into home environments.
Wide color gamut standards are expanding beyond DCI-P3 to even wider spaces. Future RGB Mini-LED displays might achieve coverage of newer standards like Rec. 2020, enabling even more precise color reproduction.
The fundamental trajectory is clear: RGB Mini-LED is evolving rapidly, with improvements in manufacturing efficiency, color accuracy, and processing capabilities happening at an accelerating pace.
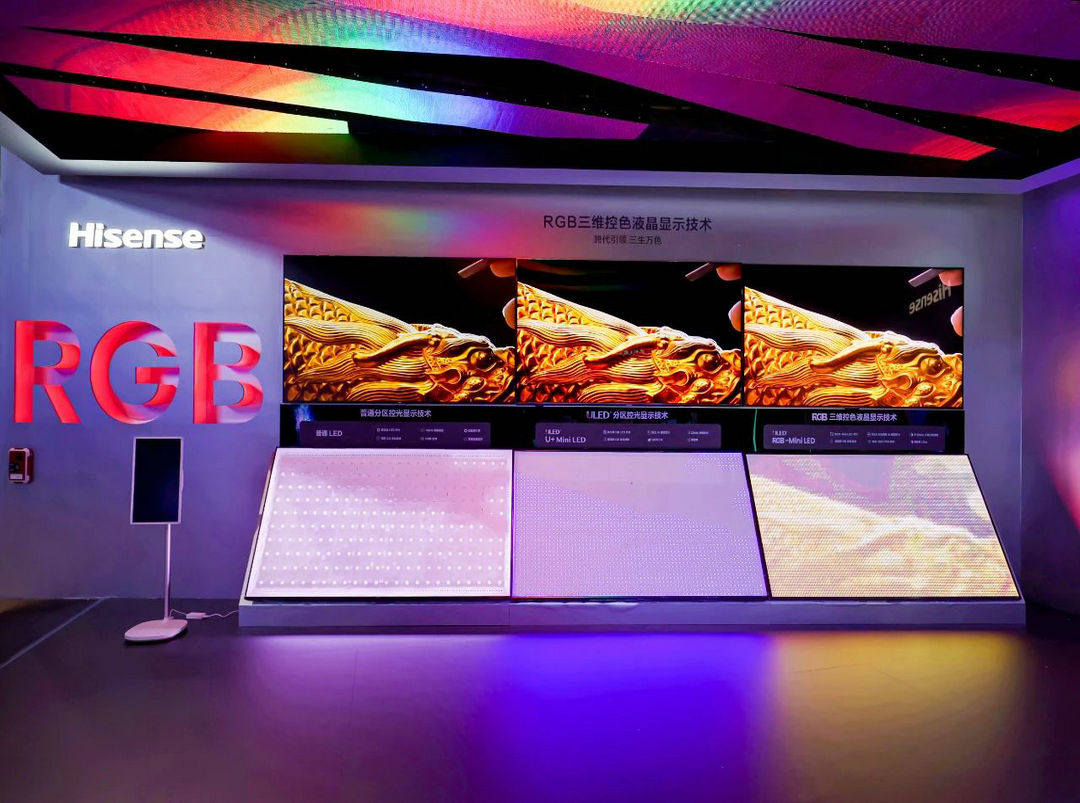

Regional Market Variations and Global Adoption
RGB Mini-LED adoption won't be uniform globally. Different regions have different preferences, different purchasing power, and different content consumption patterns.
Asia represents the largest and fastest-growing RGB Mini-LED market. Chinese manufacturers leading development (BOE, TCL, Hisense) have advantages in Asian markets where consumers are increasingly aware of display technology differences. Pricing in Asia is also expected to be lower, driving faster adoption.
In North America and Europe, OLED remains deeply entrenched. Premium consumers familiar with OLED may require substantial convincing to switch to RGB Mini-LED. However, the price advantage of RGB Mini-LED (when it materializes) could overcome this preference.
Professional markets in developed countries show strong interest in RGB Mini-LED due to color accuracy advantages. This segment will likely drive early adoption in North America and Europe.
Developing markets might leapfrog directly to RGB Mini-LED, skipping the QLED or OLED phase. As RGB Mini-LED prices drop, offering superior performance at lower cost than OLED, it becomes the natural choice for emerging markets.
Supply chain considerations affect regional adoption too. Regions closer to LED manufacturing (primarily Asia) will have easier access and lower transportation costs, driving faster adoption.
Regulatory considerations also play a role. Some regions have stricter power efficiency standards that favor LED-based displays, potentially accelerating RGB Mini-LED adoption in those markets.

Cost Analysis: ROI and Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating whether to choose RGB Mini-LED, understanding the financial implications matters.
Initial purchase price is the obvious cost component. Currently, RGB Mini-LED displays cost
Expected price trajectories suggest this premium will compress. By 2026, RGB Mini-LED should cost roughly the same as high-end QLED and 30-40% less than comparable OLED.
Energy costs matter over time. The 10-20% lower power consumption of RGB Mini-LED versus OLED translates to roughly $30-40 annually in electricity savings for typical usage patterns.
Longevity impacts total cost. An RGB Mini-LED display lasting 8-10 years with minimal degradation versus an OLED lasting 6-8 years with noticeable degradation changes the cost calculation. Over a 10-year lifespan, the RGB Mini-LED display costs less per year.
Repair costs are relevant too. When displays fail out of warranty, repair costs can be substantial. RGB Mini-LED's simpler architecture and more established repair infrastructure (since LED backlighting is more common than OLED) could mean lower repair costs.
Resale value is harder to predict but historically important. Technology that ages better commands higher resale prices. An RGB Mini-LED display that maintains excellent performance after 5 years might resell for 40-50% of original price, while an OLED with noticeable degradation might resell for only 20-30%.
Making a financial comparison between RGB Mini-LED and alternatives requires quantifying your expected usage patterns and time horizon. For a 7-year ownership period with 5 hours daily usage:
- RGB Mini-LED 65": 35/year energy = $4,245 total + potential repairs
- OLED 65": 45/year energy = $5,815 total + higher repair risk
The RGB Mini-LED comes out significantly ahead financially in this scenario.
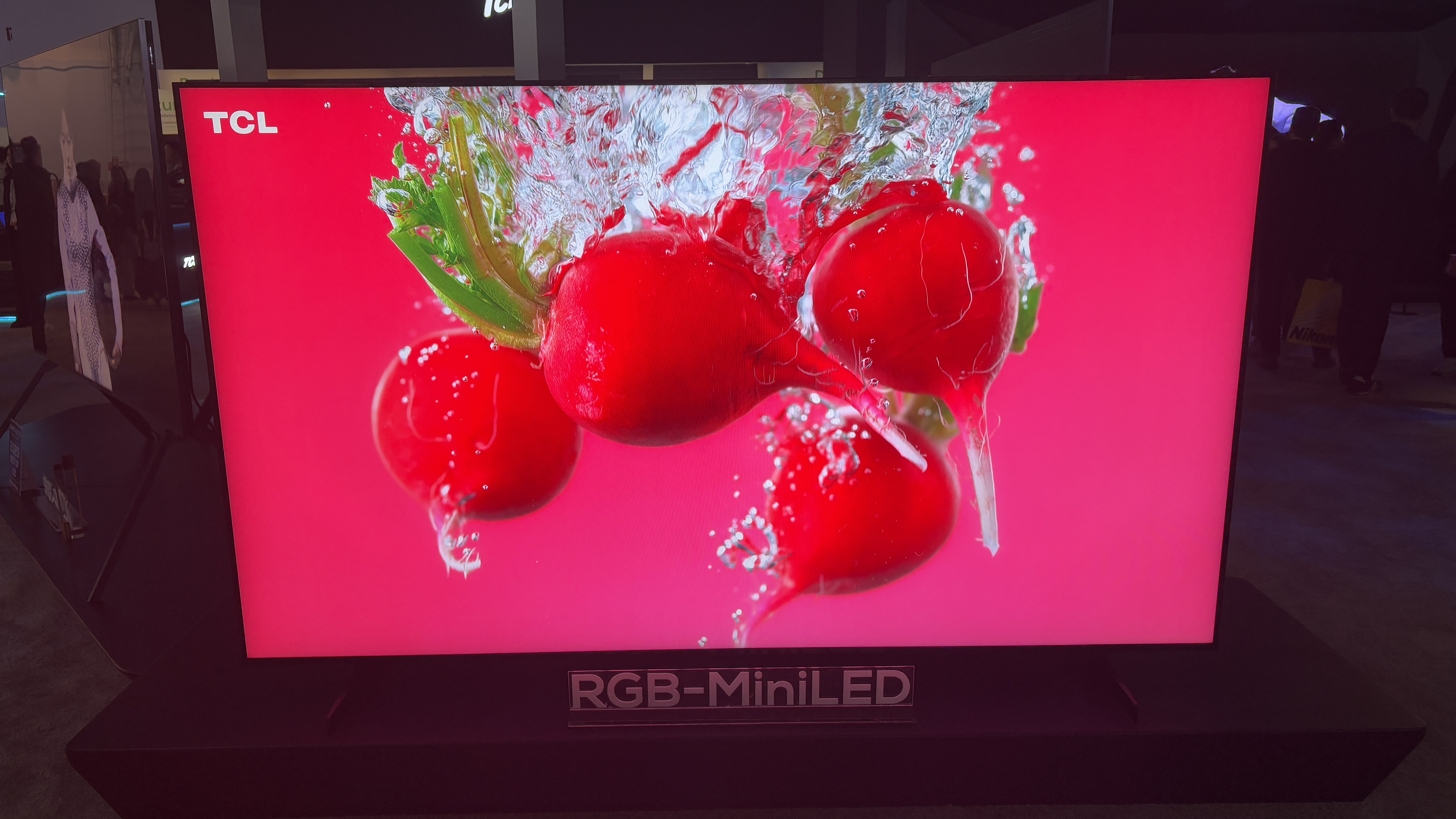

Conclusion: The RGB Mini-LED Revolution Is Here
RGB Mini-LED represents a genuine innovation in display technology. By combining the zone-based dimming of Mini-LED with independent red, green, and blue color control, manufacturers have created a display technology that rivals OLED in contrast and appearance while offering superior color accuracy, brightness, efficiency, and durability.
The impact on the premium TV landscape will be substantial. By 2026, expect RGB Mini-LED to capture 15-20% of the premium display market. Prices should drop to be competitive with high-end QLED while significantly undercutting OLED. Manufacturing improvements should continue enhancing color accuracy and reducing blooming artifacts.
For consumers, this creates genuine choice. OLED remains excellent for dark-room movie watching. QLED continues to offer good value at mid-tier price points. But RGB Mini-LED emerges as the compelling choice for people who want the best color accuracy, don't want to worry about burn-in, desire sustained brightness, and plan to keep their display long-term.
Professional content creators, serious gamers, and discerning consumers should absolutely be watching RGB Mini-LED development closely. This isn't a marginal improvement or a minor variant on existing technology. This is genuinely the next generation of premium television technology.
Whether you buy now or wait depends on your specific situation, budget, and timeline. But understand that the television landscape is shifting. RGB Mini-LED isn't a hypothetical future technology anymore. It's available now from multiple manufacturers, improving rapidly, and becoming more affordable. By 2026, it will likely be the dominant premium display technology.
The question isn't whether RGB Mini-LED will transform the premium TV landscape. It clearly will. The question is whether you'll be ready to take advantage of it when it does.

FAQ
What is RGB Mini-LED?
RGB Mini-LED is a backlighting technology that uses separate red, green, and blue mini-LED chips instead of white LEDs. This enables precise control of each color independently, resulting in superior color accuracy, contrast, and brightness compared to traditional Mini-LED or QLED displays. Each color can be controlled individually in thousands of dimming zones behind the LCD panel, creating exceptional picture quality across all content types.
How does RGB Mini-LED differ from traditional Mini-LED?
Traditional Mini-LED uses white LEDs that brighten or dim all colors equally. RGB Mini-LED uses three separate LED arrays (red, green, blue) that can be independently controlled. This means you can brighten red light while dimming blue light in the same zone, enabling significantly better color accuracy and color saturation at different brightness levels. Traditional Mini-LED is limited by the inability to control colors independently.
Is RGB Mini-LED better than OLED?
Both technologies have strengths. RGB Mini-LED offers superior color accuracy, brightness, and eliminates OLED's burn-in concerns. OLED offers perfect blacks and exceptional contrast in dark viewing environments. For professional content creation and bright-room viewing, RGB Mini-LED is superior. For dark-room movie watching, some people prefer OLED's perfect blacks. The best choice depends on your specific use case and viewing environment.
What is the current pricing for RGB Mini-LED displays?
RGB Mini-LED TVs currently cost
Does RGB Mini-LED suffer from burn-in like OLED?
No. RGB Mini-LED uses LCD panel modulation with independent backlighting, so static images cannot cause permanent burn-in. The LCD panel is fundamentally different from OLED's light-emitting structure, which makes OLED susceptible to burn-in. You can display static images on RGB Mini-LED indefinitely without risk of permanent image retention.
Which manufacturers are currently producing RGB Mini-LED displays?
BOE, TCL, Hisense, and other manufacturers are actively producing RGB Mini-LED displays. Samsung and LG are developing proprietary RGB Mini-LED variants. BOE is the primary supplier of mini-LED components and is also manufacturing complete displays. TCL and Hisense leverage BOE's manufacturing while developing their own display processing and calibration systems. More manufacturers will enter the market as production scales.
When will RGB Mini-LED prices drop to mainstream levels?
Market analysts predict RGB Mini-LED prices will become competitive with high-end QLED by 2025-2026 as manufacturing volumes increase. Mainstream adoption (mid-tier pricing) likely won't occur until 2027-2028. Currently, the technology is in the premium segment, where prices are necessarily high due to manufacturing complexity and lower production volumes.
Should I buy RGB Mini-LED now or wait for prices to drop?
If you need a television immediately and have the budget, current RGB Mini-LED displays are excellent and worth buying. If you can wait until late 2025 or 2026, prices should be significantly lower and more display options will be available. For price-conscious buyers, waiting is likely the better choice. For early adopters or professionals who value color accuracy, buying now is justified despite premium pricing.
How many dimming zones do RGB Mini-LED displays have?
High-quality RGB Mini-LED displays currently feature 2,000-5,000 dimming zones. More zones mean finer contrast control and fewer visible blooming artifacts (halos around bright objects). When evaluating displays, check the zone count specification. Generally, 3,000+ zones is considered excellent. Future displays are expected to feature 10,000+ zones, approaching pixel-level control.
What is the lifespan of an RGB Mini-LED display?
Modern RGB Mini-LED displays have expected functional lifespans of 8-14 years with typical 5-hour daily usage, based on LED technology's 30,000-50,000 hour lifespan. The LCD modulation layer experiences minimal degradation from pixel variations. Unlike OLED displays, which experience gradual light-emitting material degradation, RGB Mini-LED displays maintain consistent brightness and color throughout their functional lifespan.

Summary
RGB Mini-LED represents a transformative technology that bridges the gap between OLED's superior contrast and traditional Mini-LED's manufacturing advantages. By deploying separate red, green, and blue LED arrays controlled independently, manufacturers have created a display technology that excels in color accuracy, brightness, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
The market implications are substantial. By 2026, RGB Mini-LED is projected to capture 15-20% of the premium TV market as prices normalize and manufacturing improves. For consumers, this creates genuine choice backed by superior technology.
Whether you're a professional content creator prioritizing color accuracy, a gamer seeking exceptional performance, or a consumer wanting the best long-term display value, RGB Mini-LED deserves serious consideration as the premium display technology of the next generation.

Key Takeaways
- RGB Mini-LED uses separate red, green, and blue LED arrays for independent color control, enabling superior color accuracy and contrast compared to white-LED Mini-LED displays
- RGB Mini-LED maintains sustained brightness levels exceeding 2,000 nits while achieving contrast ratios over 200,000:1, rivaling OLED performance without burn-in concerns
- Professional content creators benefit most from RGB Mini-LED's exceptional color gamut coverage (98-99% DCI-P3) and Delta E color accuracy below 3
- Market projections suggest RGB Mini-LED will capture 15-20% of the premium TV market by 2026 as manufacturing scales and prices drop to become competitive with high-end QLED
- RGB Mini-LED displays are expected to cost 3,500-5,000 pricing, offering superior value compared to OLED while outperforming QLED in color accuracy
Related Articles
- Rodeo: The AI App for Making Plans With Friends [2025]
- What Startups & VCs Should Expect in 2026: Investor Predictions [2025]
- Ninja Foodi PossibleCooker Review: Multi-Cooker Game-Changer [2025]
- Why Apple Won't Make a Foldable iPhone Until They're Perfect [2025]
- Best iPad Accessories for Every User [2026]
- Watch Death in Paradise 2025 Christmas Special Online [2025]
![RGB Mini-LED TVs: The Future of Premium Display Technology [2026]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/rgb-mini-led-tvs-the-future-of-premium-display-technology-20/image-1-1766777835590.jpg)



