The Hidden Cost of AI Workslop: How Businesses Lose Hundreds of Hours Weekly
Here's the thing about artificial intelligence that nobody wants to admit out loud: it's noisy.
Your team adopts Chat GPT, Gemini, or Claude. They're excited. They prompt the model. Out comes content that looks polished, reads smoothly, and seems ready to ship. So they ship it. Then the customer calls. Or your compliance officer flags it. Or you find out the "facts" are completely made up.
Now you've got a problem that didn't exist before you started using AI.
This is what the industry is quietly calling "AI workslop"—the messy, error-ridden, context-blind output that AI tools produce at scale. And it's costing enterprises a fortune. According to a recent study, 58% of workers spend more than three hours every single week cleaning up AI-generated content. That's not a one-time onboarding cost. That's recurring labor waste, week after week, month after month.
But here's what makes this even worse: only 2% of workers say AI outputs need no revision. Not 50%. Not even 20%. Two percent. That means for 98% of people using these tools, there's a mandatory cleanup phase that kills the productivity promise.
So why is this happening? Why are companies adopting tools that actually create more work? And more importantly, how do you fix it?
TL; DR
- The Scale of the Problem: 58% of workers spend 3+ hours weekly fixing AI content, with 11% spending over 10 hours
- The Quality Gap: Only 2% report AI outputs need zero revision, despite 92% believing AI boosts overall productivity
- Real Business Impact: 28% have experienced rejected work, 27% encountered security issues, and 24% faced compliance problems
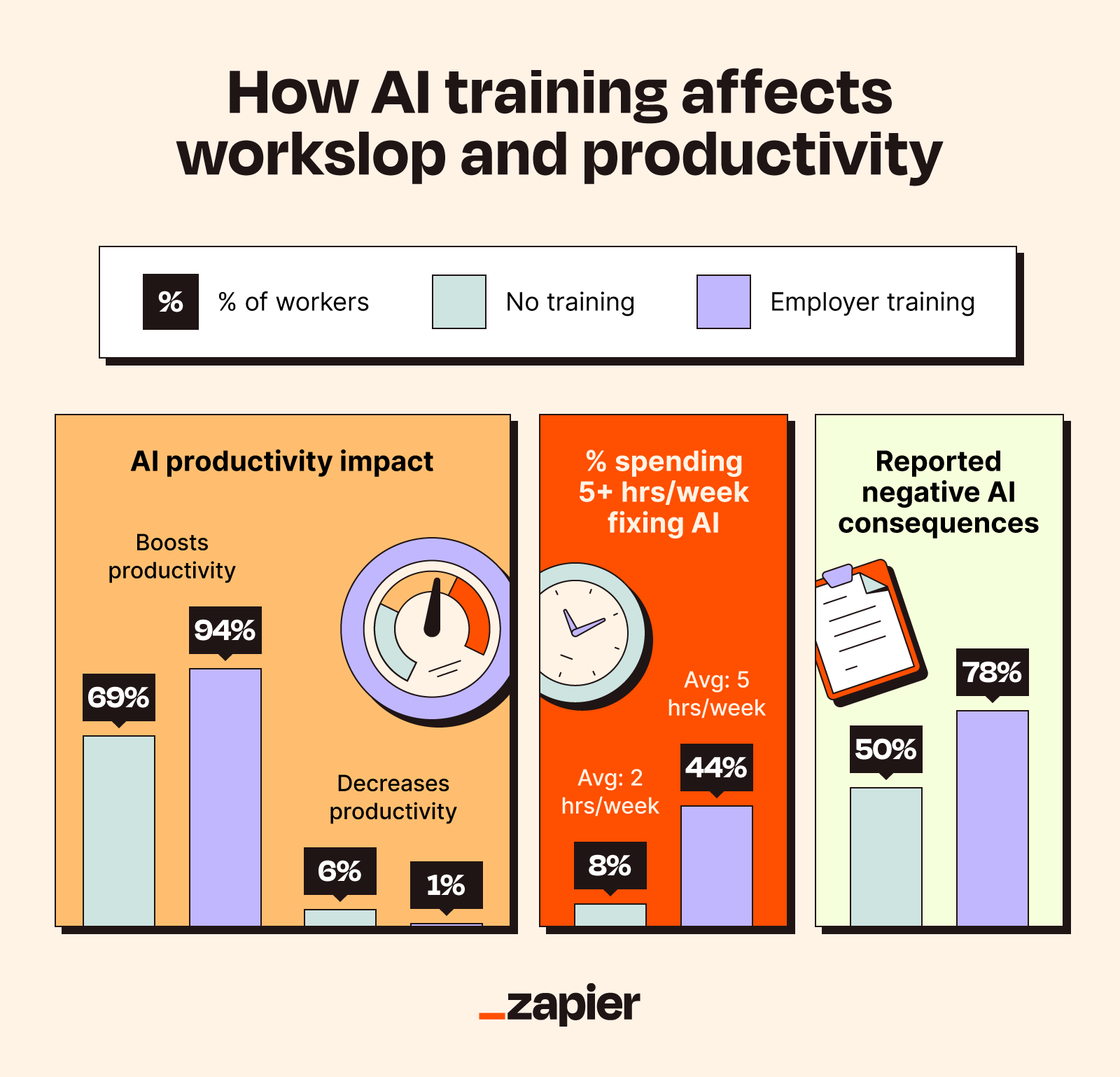
- The Training Difference: 94% of trained workers say AI boosts productivity vs. only 69% of untrained workers
- The Solution: Mandatory training, standardized processes, prompt templates, and proper orchestration tools are non-negotiable
Investing
Why AI Looks Great Until It Doesn't
The problem starts with how AI models are built and what they're optimized for. These large language models excel at pattern matching and text generation—they're trained to produce outputs that feel coherent and complete. A Chat GPT response doesn't stutter. It doesn't say "I'm not sure." It answers confidently, usually on the first try.
That confidence is seductive. It makes the output seem trustworthy even when it's completely wrong.
When you ask an AI model to "summarize the Q3 financial reports," it doesn't actually read your company's financial reports. It hallucinates plausible-sounding summaries based on patterns in its training data. If you ask it to "fact-check this claim," it doesn't verify anything—it generates text that sounds like a fact-check. And if you ask it to write marketing copy for your regulated industry, it'll confidently ignore compliance requirements because it was never trained specifically on your regulatory environment.
But none of this is obvious from looking at the output. That's the trap.
The research shows data analysis and visualization work (55%), research and fact-finding (52%), and long-form reporting (52%) are the hardest areas for AI to nail. These tasks require accuracy, context, and domain knowledge. They're exactly the opposite of what generative AI was designed to do.
The confidence problem gets even worse at scale. When one person uses AI and finds errors, they catch them. But when 50 people are using AI across different departments with different workflows and different levels of skepticism, problems compound. One person's hallucination about customer data becomes a data integrity issue. Another person's misunderstanding of compliance requirements becomes a legal liability.
Now you've got security incidents (27% of respondents reported these), privacy breaches (also 27%), customer complaints (25%), and actual compliance violations (24%). These aren't theoretical risks anymore—they're happening in real companies right now.
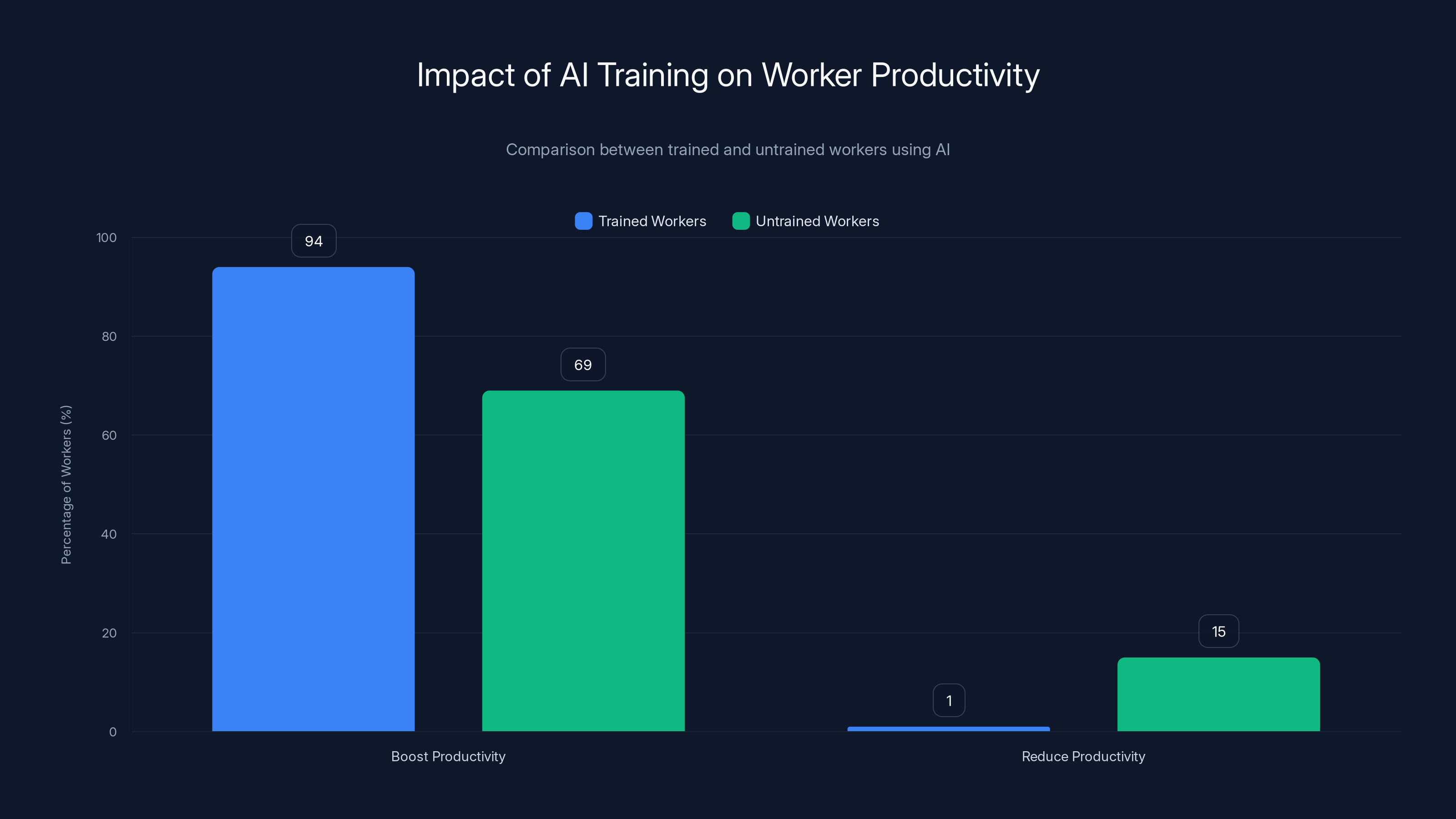
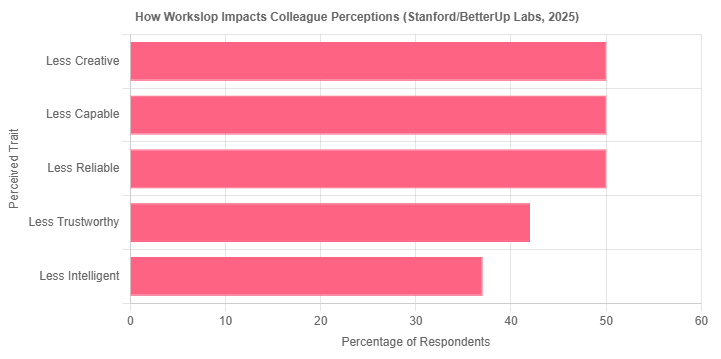
Training significantly enhances AI productivity benefits, with 94% of trained workers experiencing boosts compared to 69% of untrained workers. Estimated data for untrained workers' reduced productivity.
The Time Waste Is Staggering (And It's Getting Worse)
Let's put numbers to this because the scale is actually shocking.
58% of workers spend more than 3 hours per week cleaning up AI outputs. That's 12 hours per month, or 144 hours per year. For a
But wait, it gets worse.
35% of workers spend more than 5 hours per week on this cleanup work. That's 20 hours monthly, or 240 hours annually. For that same employee, that's $8,600 in wasted labor.
And then there's the hardcore 11% spending over 10 hours weekly on cleanup. That's more than 500 hours per year per person. For a
Now multiply that by your team size. A 50-person company where 11% of people spend 10+ hours weekly on AI cleanup is losing nearly
And this is happening right now, in 2025. Most CFOs have no idea this is even a line item in their budget.
The research from productivity automation platforms shows that companies aren't even capturing this data systematically. They're just accepting it as the cost of doing business with AI. "Yeah, Claude sometimes makes things up. Yeah, we have to review everything. That's just how it works," they say. But that's accepting a $5,000+ per employee annual tax on AI adoption.
Here's where it gets personal: if you're the person doing the cleanup, you're not actually being more productive. You're doing the same job you always did, plus now you're fact-checking an AI model. Your workload went up, not down. The AI "productivity boost" is a mirage.
When AI Generated Content Gets Rejected (And Why)
Let's get specific about what's actually breaking.
28% of workers have experienced rejected AI-generated work. Not revision. Rejection. The customer said no. The compliance officer blocked it. The legal team killed it. The work had to be redone from scratch.
Why does this happen? Because AI is fundamentally bad at a few critical things:
Accuracy in specialized domains: AI models know a little about everything and a lot about nothing. Ask a language model about general knowledge and it's decent. Ask it about your proprietary customer database schema, your company's specific compliance requirements, or the nuances of your industry's regulatory environment, and it hallucinates. It generates plausible-sounding nonsense because it was never trained on your specific context.
Security and privacy awareness: AI models were trained on public internet data. They don't understand the difference between public information and sensitive internal data. You prompt it with your customer data to "analyze trends" and it will gladly process that data and store it in its training feedback loops (depending on the tool's privacy settings). Many companies discovered this the hard way after their security teams got involved.
Compliance with regulations: GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, FINRA, export controls—these regulatory frameworks exist for a reason. AI models aren't trained to navigate them. They'll generate compliant-looking documents that completely miss the mark on regulatory requirements. 24% of respondents reported compliance or legal issues from AI-generated content.
Domain-specific context: Your industry has history, precedent, and unwritten rules. A logistics company knows that overnight shipping works differently than ground shipping. A healthcare provider knows that patient data requires different handling than general information. An AI model trained on general text has no idea about any of this.
When AI output gets rejected, the company loses the time investment twice. First, they spent time prompting the model and reviewing the output. Then they spend more time explaining to the AI why it failed, rewriting the prompt, trying again, or just doing the work manually.
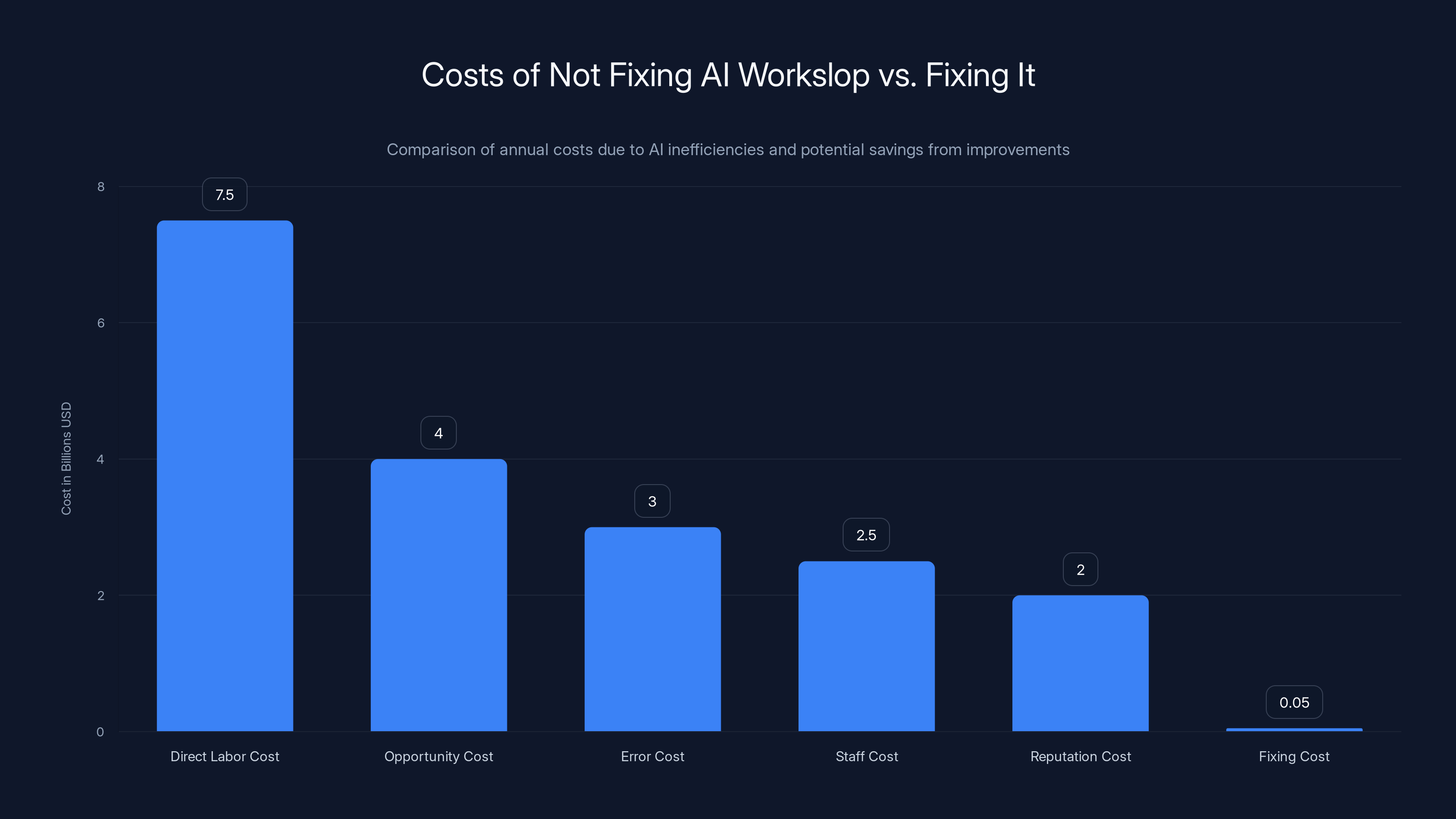
Estimated data shows that not addressing AI inefficiencies can lead to over
The Training Gap: Why Some Companies Actually Win With AI
Here's where it gets interesting, because there IS a path out of this mess.
The research reveals a massive gap between trained and untrained workers: 94% of trained workers say AI boosts their productivity. Compare that to 69% of untrained workers. That's a 25-percentage-point difference just from training.
More tellingly, only 1% of trained workers report that AI actually reduces their productivity. For untrained workers? It's much higher. They're fighting the tool, confused about how to use it, getting bad results, and then frustrated.
So what exactly is this training doing?
It's not magic. It's not even that complicated. Trained workers understand:
1. What the AI is actually good at (and what it isn't)
They know that language models are phenomenal for brainstorming, outlining, and generating first drafts. They're terrible for fact-checking, security decisions, and compliance work. Trained workers don't try to use a hammer as a screwdriver.
2. How to write effective prompts
AI models respond dramatically differently to prompt quality. A vague prompt gets vague output. A specific prompt with context gets better output. A prompt that includes constraints and requirements gets output that actually adheres to them. Trained workers know this intuitively after a few weeks of practice. Untrained workers just assume the AI is broken.
3. How to review AI output skeptically
Trained workers read AI output with a critical eye. They fact-check claims. They check the logic. They look for missing context. They know that confident-sounding text isn't the same as correct text. Untrained workers treat AI output like gospel.
4. How to use AI as one tool in a workflow, not the only tool
The companies seeing real benefits from AI aren't the ones trying to fully automate human work away. They're the ones using AI to speed up specific parts of workflows while keeping humans in the loop for judgment, verification, and decision-making.
Think about it from a workflow perspective: AI writes a first draft of a report (saves 2 hours). A trained human reviews it, fact-checks critical claims, adjusts tone and context (takes 1 hour instead of 4). Total time: 3 hours instead of 4. That's a real win.
Compare that to an untrained approach: AI writes a report (employee thinks it's done). Report gets rejected by compliance. Employee redoes the whole thing manually (takes 4 hours). Total time: 4+ hours.
The training fundamentally changes the human's relationship with the tool.
But here's the catch: most companies aren't providing this training. They're just handing employees Chat GPT logins and hoping for the best. "Go forth and be productive!" they say. Then they wonder why the AI cleanup work is overwhelming their teams.
The Quality Problem Is Systemic, Not Just Hallucinations
Everyone focuses on hallucinations—the false facts, the made-up citations, the completely wrong answers. But the quality problem is actually much broader than that.
AI output often lacks:
Contextual awareness: The AI doesn't understand your specific situation, your customer's situation, or the broader context in which the work will be used. It generates generic output that needs heavy customization.
Tone and voice matching: If your company has a specific tone (formal, casual, technical, accessible), the AI might not nail it. A report for investors needs different tone than a report for engineers. AI frequently misses these distinctions.
Completeness and depth: AI models are optimized for efficiency, not thoroughness. They'll generate output that hits the main points but misses important nuances, edge cases, or implications that a human expert would naturally include.
Accuracy in specialized areas: Beyond hallucinations, AI simply doesn't know your domain as well as experts do. A financial analyst knows which metrics matter most. A product manager knows which customer feedback is noise and which is signal. An AI model trained on general text doesn't have this intuition.
Customization to constraints: You might have specific requirements (must be under 500 words, must include these three data points, must avoid certain terminology). AI can follow instructions, but it frequently misses nuance or optimizes for the wrong thing.
All of this creates cleanup work.
The research found that data analysis and visualization (55%) and research and fact-finding (52%) are where AI struggles most. Why? Because these tasks require: domain expertise, verification from external sources, understanding of what data is reliable versus unreliable, and the ability to synthesize information rather than just summarizing it.
Generative AI is phenomenal at synthesis—combining patterns it has seen in training data. It's terrible at verification—it can't actually check whether something is true. It just sounds true based on training patterns.
For a marketing team writing copy, that's one problem. For a research team evaluating customer data, that's a much bigger problem. For a compliance team writing regulatory documentation, that's a legal liability.

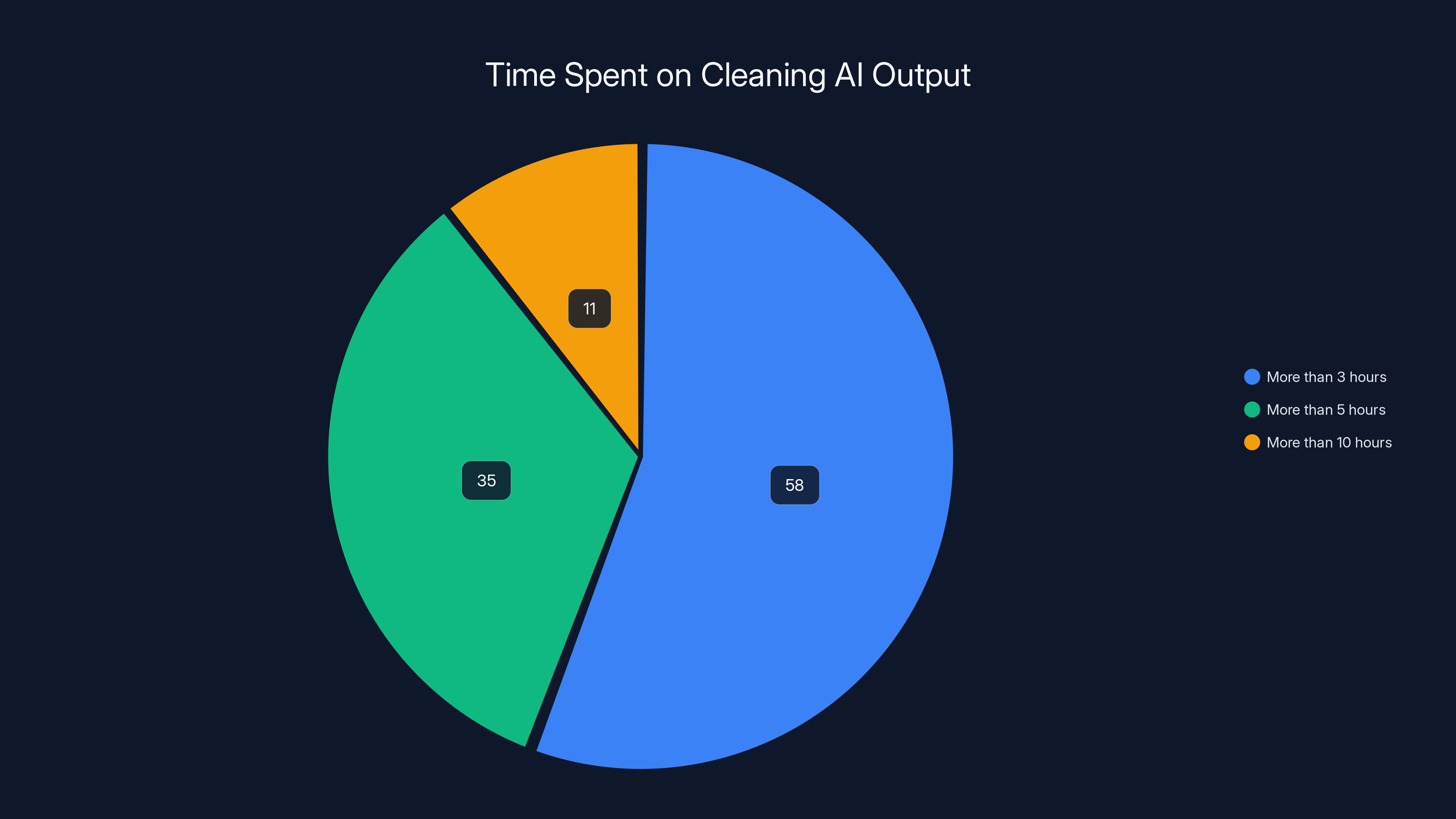
A significant portion of workers spend over 3 hours weekly cleaning AI output, with 11% dedicating more than 10 hours, indicating substantial time investment in ensuring content quality.
Security and Privacy: The Risks Nobody's Talking About
Let's talk about the elephant in the room: 27% of respondents reported security or privacy incidents related to AI usage.
That's not theoretical. That's actual security breaches happening right now.
Here's how it typically happens:
An employee has sensitive information (customer data, source code, internal strategies, employee information). They think "let me ask the AI to help me analyze this." They paste the data into Chat GPT or Claude or Gemini. The AI processes it. The employee gets their answer.
But now that data has been sent to the AI provider's servers. Depending on the tool's privacy policy and the employee's settings, that data might be:
- Stored for future model training
- Retained by the AI provider for an indefinite period
- Accessible by the AI provider's employees
- Subject to data retention laws in the jurisdiction where servers are hosted
- Potentially vulnerable to breach or unauthorized access
This is how companies accidentally violate GDPR (data about EU citizens), HIPAA (health information), or internal data governance policies.
Add to this the fact that many AI tools have default settings that share your data with third parties or use your queries to improve the model, and you've got a privacy disaster waiting to happen.
The other security issue is prompt injection attacks and model poisoning. Attackers can craft inputs that trick the AI into revealing information, changing its behavior, or compromising systems it's connected to. Companies that use AI as part of their security systems (like customer support chatbots that have access to internal data) are particularly vulnerable.
25% of respondents experienced customer complaints related to AI-generated content. Many of those complaints come from customers discovering factual errors, inappropriate tone, or information that shouldn't have been public. In a B2B context, this tanks trust. In a B2C context, it tanks brand reputation.
The companies winning with AI have solved this by:
- Data governance policies: Clear rules about what data can be used with AI tools
- Private AI deployments: Running AI models on-premises or with privacy-first providers
- Data anonymization: Removing sensitive information before feeding data to AI
- Access controls: Restricting which teams and employees can use AI tools with sensitive data
- Audit trails: Logging all AI usage so you can spot problems
If your company isn't doing these things, you're basically hoping you don't get caught.

Compliance and Legal Issues Are Real Risks
24% of respondents reported compliance or legal issues stemming from AI-generated content. That's not a small number.
Here's why this is happening:
AI models don't understand regulatory requirements. GDPR requires specific data handling practices. HIPAA requires specific security controls. SOX requires specific financial documentation standards. FINRA requires specific investment advisor disclosures. Export control regulations require specific restrictions on what information can leave the country.
An AI model trained on public internet data has no idea about any of these requirements. It will confidently generate documents that sound compliant while completely missing regulatory requirements.
Here are real examples of compliance failures with AI:
In financial services: A company used Chat GPT to generate investment recommendations for clients. The AI didn't include required disclosures about fees, risks, or conflicts of interest. When regulators reviewed the communications, they found violations. Fines ensued.
In healthcare: A provider used AI to draft patient communications. The AI included medical jargon that made it sound authoritative but was technically inaccurate. Patients relied on the bad information. When patients' conditions worsened, they sued based on the miscommunication.
In data privacy: A company used AI to process customer data for marketing insights. They didn't realize that their usage violated GDPR because the AI wasn't designed with GDPR compliance in mind. The data had been transferred to AI provider servers in the US, creating legal liability.
In marketing: A company used AI to generate social media content that made health claims about products. The AI's claims weren't substantiated. The FTC investigated for deceptive advertising.
In each case, the company thought they were just using helpful AI tools. They didn't realize they were creating legal liability.
The solution requires:
- Compliance review before deployment: Any AI system handling regulated data needs legal review
- Documentation of AI usage: You need to prove how the AI works, what safeguards you have, and how you validated output
- Training on compliance requirements: Employees need to understand which regulations apply to their work
- Validation processes: You need formal procedures to verify compliance before content ships
- Audit capabilities: You need the ability to trace back how content was generated and by whom
Without these guardrails, AI becomes a liability amplifier rather than a productivity tool.
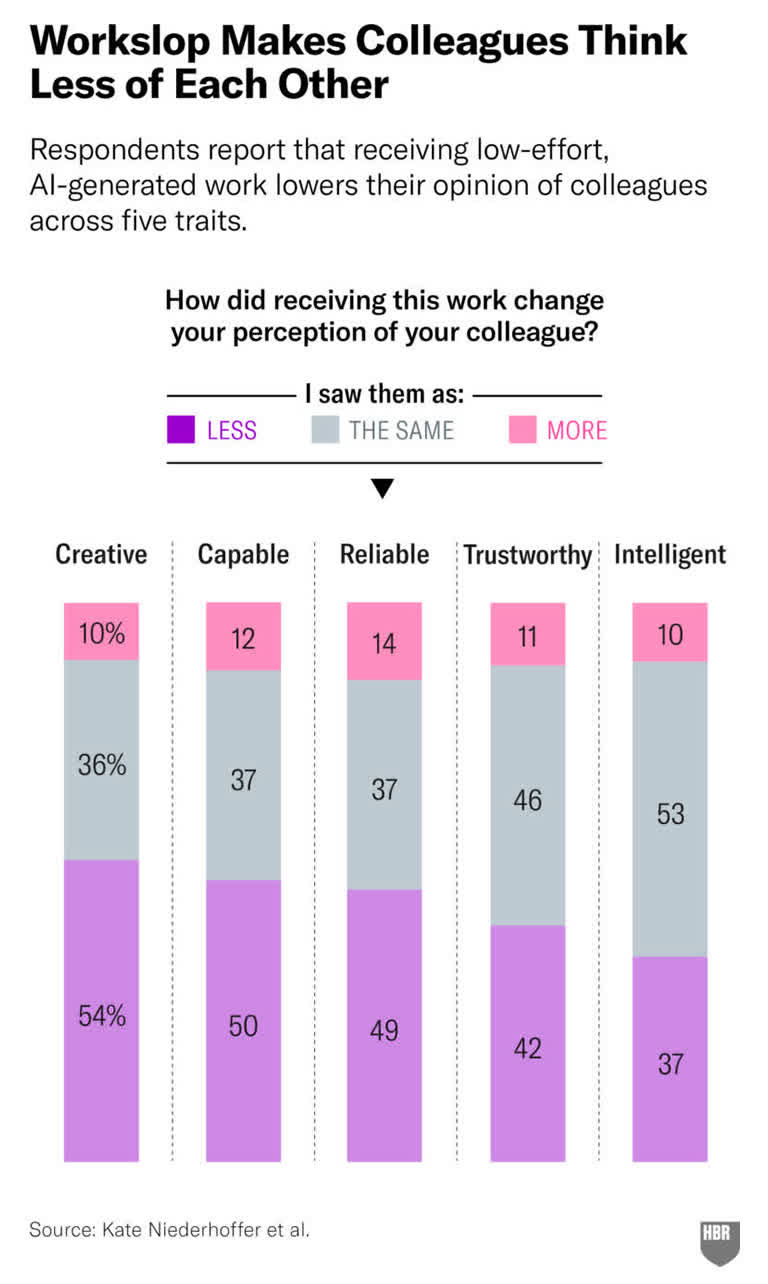
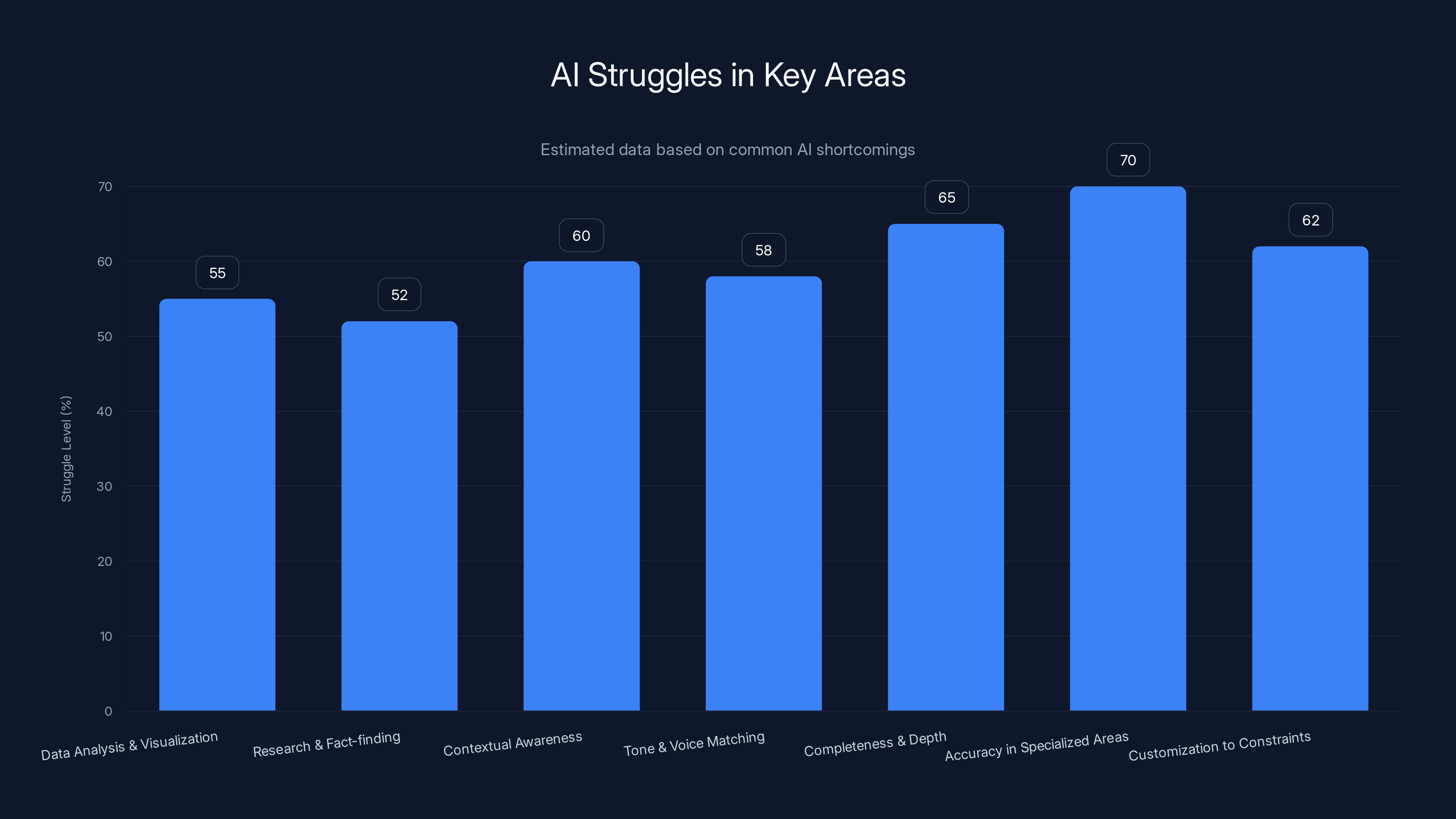
AI struggles most with accuracy in specialized areas and completeness, requiring significant human intervention. Estimated data based on common AI shortcomings.
How AI Workslop Spreads Through Organizations
Here's something critical that companies miss: AI quality problems compound across teams.
When one person in marketing uses AI to generate copy and doesn't fact-check it, that copy might go to the sales team. The sales team uses that copy in customer presentations. The customer believes the claims. When the claims turn out to be false, the customer is angry.
This is the cascading failure model. The initial AI quality problem creates downstream failures in teams that didn't even use AI directly.
Consider a common scenario:
- Product team uses Chat GPT to write a product specification. The AI includes features that aren't actually planned but sound good.
- Engineering team reads the spec and starts building those features, wasting months of development time.
- Marketing team uses the same spec to write marketing copy. They advertise features that don't actually exist.
- Sales team sells to customers based on marketing copy. Customers buy expecting features that don't exist.
- Customer support team gets flooded with complaints. They spend hundreds of hours dealing with customer disappointment.
The initial AI quality problem in step 1 created a cascade of failures that cost the company potentially millions of dollars.
This is exactly why untrained workers have such poor results with AI: they're not just affecting their own work; they're propagating errors through the organization.
In contrast, well-trained teams implement quality gates. They fact-check AI output before it propagates. They maintain single sources of truth. They use AI as a speed-up mechanism within a process that includes verification steps.
The Case for Mandatory AI Training
The research makes a clear argument: AI training should be compulsory for any worker who touches AI tools.
Here's why this makes financial sense:
A typical 4-8 hour AI training program costs roughly
But if that training reduces AI cleanup time from 10 hours per week to 3 hours per week, you've saved 7 hours per week per person. That's 350 hours saved per week across 50 people. At an average fully-loaded cost of
The training pays for itself in 6-15 weeks.
Over a year, if you factor in the compounding benefits (fewer errors, fewer rejections, fewer security incidents, fewer compliance issues), trained workers are probably
Yet most companies aren't doing this training. Why? Usually because executives don't see AI productivity problems clearly. The cleanup work is distributed across teams and invisible. Nobody's tracking it in the budget. Nobody's correlating it to training investments.
The research suggests training should be prioritized by:
- High-risk teams first: Teams handling sensitive data (finance, HR, legal, compliance) should be trained first
- High-volume AI users second: Teams that use AI most frequently should be trained to maximize impact
- Customer-facing functions third: Teams that interact with customers and whose AI mistakes create customer-facing risks
- Everyone else: Even individual contributors benefit from AI training
Effective AI training should cover:
1. What AI can and can't do: Understanding the strengths and limitations prevents misuse
2. How to write effective prompts: Good prompts get better results, dramatically reducing cleanup time
3. How to review AI output critically: Knowing what to look for when fact-checking
4. Domain-specific considerations: How AI works with your company's specific tools, data, and workflows
5. Security and privacy best practices: What data can be shared with AI tools and what can't
6. Compliance and governance: How AI usage fits with your regulatory requirements
7. Ethical considerations: When it's appropriate to use AI and when it isn't
8. Practical workflow integration: How to use AI as part of your actual daily work
This isn't one-time training that employees complete and forget about. It's ongoing because AI tools evolve, best practices improve, and employees need refreshers.

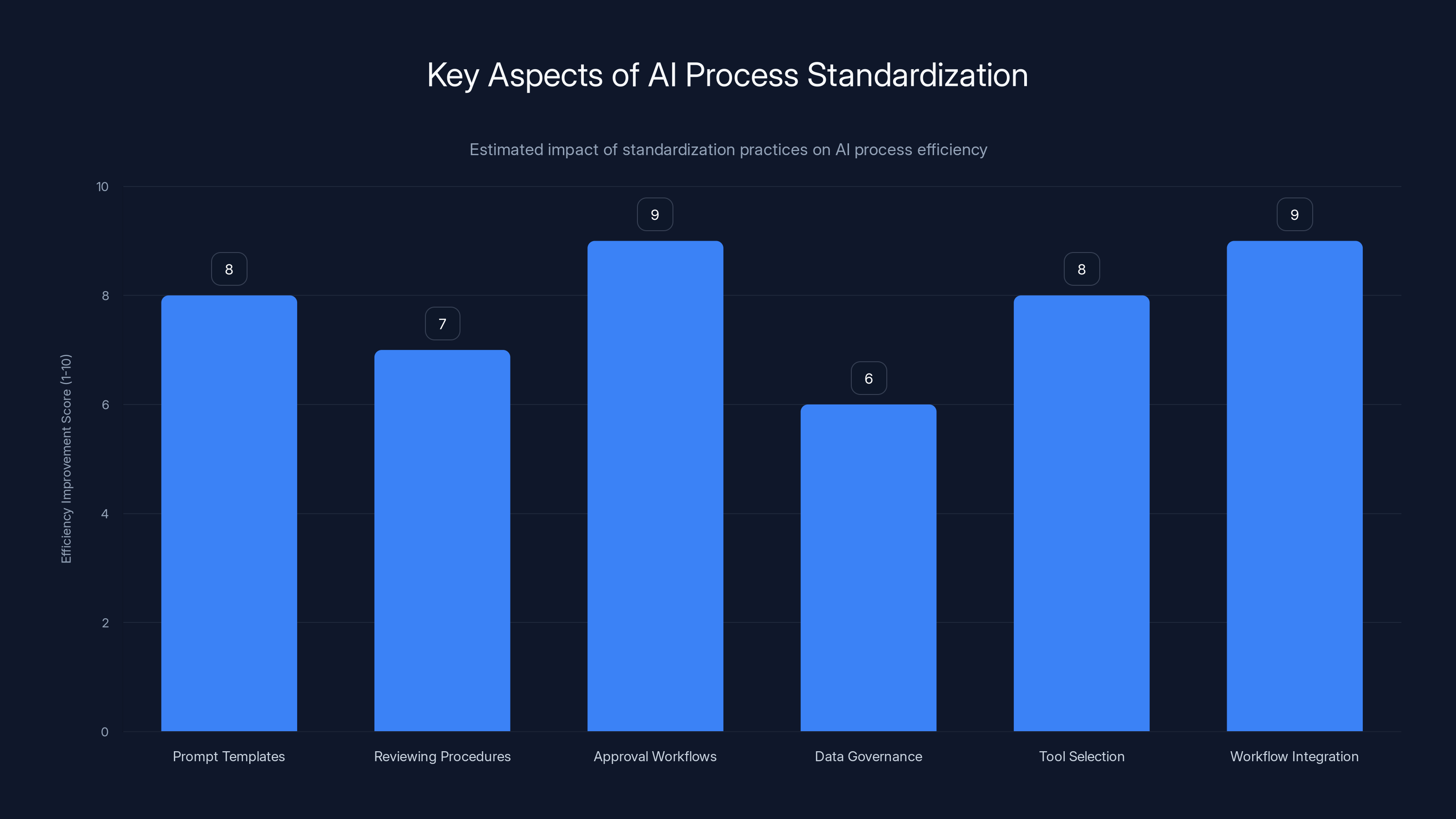
Standardizing AI processes significantly improves efficiency, with approval workflows and workflow integration showing the highest impact. Estimated data based on typical industry practices.
Standardizing AI Processes: From Chaos to Orchestration
Trained workers are step one. Standardized processes are step two.
The best companies aren't just training people; they're formalizing how AI gets used. Here's what standardization means in practice:
Prompt templates: Instead of each person writing their own prompts from scratch, teams maintain templates for common tasks. "Here's the template for market research prompts." "Here's the template for customer complaint analysis." "Here's the template for code review." Templates ensure consistency and quality.
Reviewing procedures: Formal processes specify who reviews AI output and what they're looking for. Different content types need different review criteria. Marketing content needs different review than financial documentation.
Approval workflows: Some output needs approval from specific people before it goes live. A financial report needs CFO review. A customer communication needs legal review. A security document needs security team review. Workflows ensure the right people see the right work.
Data governance: Clear policies about what data can be used with AI tools and which tools are approved for which data types. "Customer data cannot go to cloud-based AI tools." "Financial data requires sanitization before AI processing."
Tool selection: Instead of everyone using whatever AI tool they want, companies standardize on specific tools. This creates:
- Easier training (everyone learns the same tools)
- Better security (you can centrally manage one tool's security)
- Better integration (one tool integrates with your systems)
- Better compliance (you know what one tool's privacy practices are)
Integration with existing workflows: The best companies integrate AI into workflows that already have quality gates. They don't bolt AI on top of existing processes; they redesign processes around AI.
Consider a customer service workflow:
Old workflow: Customer email arrives → Support rep reads → Rep writes response → Response sent
Better workflow: Customer email arrives → AI suggests response based on templates → Support rep reviews → Rep sends or modifies → Response sent
Even better workflow: Customer email arrives → AI determines category and urgency → AI suggests response from library of proven responses → Rep reviews → Rep sends with one-click approval if content is good → Response sent
The AI is enhancing the workflow, not replacing the human judgment. The human is still in control. The quality gates are still there. But the process is faster.
This is what companies mean by "orchestration." It's not just using AI; it's orchestrating AI within a process that maintains quality and safety.
Tools That Reduce AI Workslop
Software can help with AI workslop, but it's not a silver bullet. The right tools make it easier to verify output, maintain quality gates, and track AI usage.
Tools for AI quality management include:
AI verification platforms: Services that fact-check AI output, verify citations, and flag potential hallucinations. These aren't perfect, but they catch obvious errors automatically.
Workflow automation tools: Platforms that let you build formal workflows around AI. You can set up approval steps, assign reviewers, maintain audit trails, and enforce your processes.
Prompt management systems: Tools that store and organize your best prompts, so teams aren't starting from scratch each time. These often include collaboration features and version control.
Data governance platforms: Tools that classify data, enforce access controls, and prevent sensitive data from leaving your systems. These prevent the "accidental data leak" problem.
Compliance and audit tools: Platforms that track AI usage, document what models were used, what inputs were provided, and what outputs were generated. This creates accountability and compliance documentation.
Model comparison tools: When you have multiple AI options, these tools let you test them on your specific use cases and compare output quality side by side.
For teams looking to automate AI workflows end-to-end, platforms like Runable provide AI-powered automation for creating presentations, documents, reports, images, and videos. Rather than dealing with messy text output and requiring hours of human cleanup, these tools handle the generation and formatting in a structured way that's designed for enterprise workflows from day one.
The key thing about tools is this: tools aren't a substitute for training and processes. A bad process with fancy tools is still a bad process. A trained team with simple tools often outperforms an untrained team with sophisticated tools.
But a trained team using good processes with appropriate tools? That's when you actually see AI productivity gains.

Creating a Prompt Template Library
One of the highest-ROI things a company can do is build a library of effective prompts.
Here's why: prompt quality dramatically affects output quality. A vague prompt gets vague output. A specific prompt with constraints gets better output.
A template-based approach means:
- First person figures it out: The first person who needs to summarize quarterly earnings learns through trial and error how to write a prompt that produces good summaries
- They document it: They save their best prompt as a template
- Everyone else uses the template: The next person doesn't start from scratch; they use the existing template
- Teams improve it over time: Each person's feedback makes the template better
A prompt template for market research might look like:
You are a market research analyst with expertise in [INDUSTRY].
Analyze the following market data and identify:
1. Top 3 market trends
2. Key competitive threats
3. Opportunities for differentiation
4. Recommended strategic focus areas
Provide specific data points and cite sources where possible.
Market data:
[INSERT DATA]
Our company position:
[INSERT CONTEXT]
Constraints to consider:
[INSERT REQUIREMENTS]
Format your response as:
- Executive summary (2-3 sentences)
- Detailed analysis with bullet points
- Recommended actions with estimated impact
Notice this template:
- Establishes role and expertise
- Specifies exactly what you want
- Provides structure for the response
- Includes placeholders for customization
- Defines output format
- Mentions constraints
When someone uses this template instead of writing a prompt from scratch, they get dramatically better results. And crucially, they get consistent results across the team.
Building a library takes effort upfront, but the payoff is substantial: new employees can use proven prompts immediately, quality improves across the board, and cleanup time drops significantly.

Setting Up Review and Approval Workflows
Formal review processes reduce errors, ensure consistency, and maintain accountability.
Here's how to think about review workflows:
Content type determines review criteria: A social media post needs different review than a legal document. A blog outline needs different review than customer-facing communication.
Risk level determines review depth: High-risk content (anything customer-facing, anything with legal implications, anything with financial claims, anything with safety implications) needs thorough review. Low-risk content (internal working documents, brainstorms, research notes) needs lighter review.
Reviewer expertise matters: The person reviewing needs expertise relevant to the content. AI-generated financial reports should be reviewed by someone who understands financial accounting. AI-generated legal documents should be reviewed by someone who understands applicable law.
A formal review workflow might look like:
- AI generates output based on prompt template and specific request
- Creator reviews for obvious errors, poor quality, or misalignment with request
- Domain expert reviews for accuracy, completeness, and compliance with requirements
- Approver approves before content goes public/ships/goes to customer
- Audit log records who reviewed, what they checked, and when they approved
This sounds labor-intensive, but compare it to the current situation: AI generates something, people use it, errors propagate downstream, you spend hours cleaning up the mess. Formal review prevents that.
Many companies implement this in workflow tools where:
- AI output is automatically routed to the appropriate reviewer
- Reviewers can comment, request changes, or approve
- Approval chains ensure the right people are involved
- Audit trails document everything
- Templates standardize what reviewers look for
The best companies actually use this as a learning tool: they examine patterns in what reviewers catch and use that to improve prompts and training.

The Economics of Not Fixing This
If companies don't address AI workslop, the economic impact compounds.
Consider the costs:
Direct labor cost of cleanup work: 58% of workers spending 3+ hours weekly on cleanup = 150+ million hours annually across the US workforce (extrapolated from 150 million knowledge workers). At an average fully-loaded labor cost of
Opportunity cost: If 58% of workers are spending hours weekly on cleanup, they're not spending that time on higher-value work. Strategic initiatives are delayed. Innovation suffers. Competitive advantage erodes.
Error cost: 28% experiencing rejected work, 27% experiencing security incidents, 25% experiencing customer complaints, 24% experiencing compliance issues. Each of these has costs: rework, incident response, customer service, legal fees, fines.
Staff cost: Frustrated workers with frustrating tools eventually leave. Turnover is expensive: recruiting, hiring, training. The workers most likely to leave are the skilled ones, since they have options.
Reputation cost: When customers experience problems caused by poorly reviewed AI output, they tell other customers. Brand damage is hard to quantify but significant.
In contrast, the cost of fixing this is modest:
- Training investment: 5,000 per employee, one-time (mostly)
- Process design and documentation: 100-200 hours for a team, one-time
- Tool investment: 500 per employee annually, depending on what tools you choose
- Ongoing management: 5-10% of time for one person on the team
The math is simple: spending
This is why the research emphasizes that "the solution isn't fewer tools, it's better infrastructure." Companies aren't going to stop using AI. But they can absolutely improve the infrastructure around AI to make it work better.

Implementing AI Governance Right Now
If you've read this far, you're probably thinking "okay, so how do I actually start?"
Here's a practical roadmap:
Month 1: Assess and document
- Map where AI is currently being used in your organization
- Track time spent on AI-related cleanup work
- Identify your highest-volume and highest-risk AI use cases
- Document what's working well and what's causing problems
Month 2: Design governance framework
- Define which teams get priority for training
- Design AI training curriculum (or find external training)
- Plan prompt template library
- Design review and approval workflows for your most critical processes
- Document data governance policies
Month 3: Implement and train
- Roll out training to first priority group
- Build prompt template library with that group
- Implement review workflows
- Establish tool standards
- Create documentation and runbooks
Month 4 onwards: Monitor and iterate
- Track metrics: hours spent on cleanup, error rates, rejection rates
- Gather feedback from teams
- Refine templates based on what's working
- Expand training and processes to other teams
- Celebrate wins and share best practices
This doesn't require massive investment. It requires thoughtfulness and follow-through.
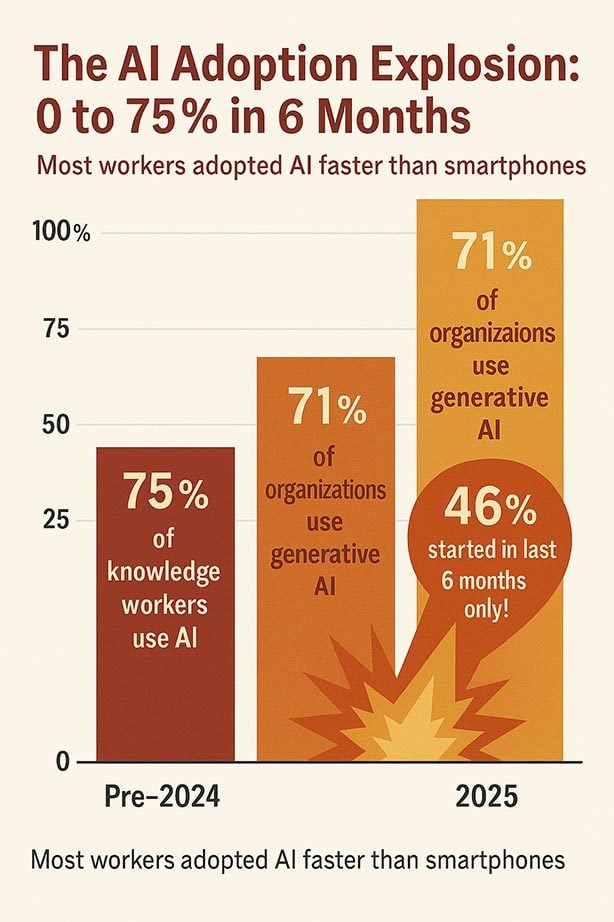
Future: AI Quality Will Improve, but So Will Adoption Speed
Looking ahead, there's reason for optimism and reason for caution.
The optimism: AI models are improving. GPT-5 and beyond will be better than GPT-4. Claude will improve. Gemini will improve. The underlying technology is advancing rapidly. Hallucination rates are dropping. Reasoning is improving. Accuracy on specific domains is getting better.
In 2-3 years, the quality problems we're discussing today will be partially solved by better models.
The caution: Companies will adopt AI faster than quality improves. They'll use it in more places, more recklessly, with less oversight. The 2% that need zero revision might become 10% or 20% as models improve, but 80%+ will still need review. And the adoption will expand into areas where accuracy matters even more.
So even as AI tools get better, the organizational challenge of managing AI workslop will probably stay relevant for the next 3-5 years. Maybe longer.
This is why the training and governance investments matter now. Companies that build good AI practices and culture now will be in position to benefit faster and more fully as models improve. Companies that are just letting AI run wild will eventually face either crisis or massive rework.
The Bottom Line: AI Productivity Is Real, But the Setup Matters
Let's come back to where we started: AI is noisy, and cleaning up the noise costs businesses hundreds of hours every week.
But here's what the research actually shows: when companies invest in training, processes, and governance, AI absolutely does boost productivity.
94% of trained workers report AI productivity benefits. Only 1% report productivity declines. That's the real promise of AI.
The companies getting actual value aren't the ones that casually adopted AI. They're the ones that:
- Trained their people on how to use AI effectively
- Built formal processes and quality gates
- Established governance and security standards
- Created prompt templates and best practices
- Maintained human judgment and review
- Tracked outcomes and iterated
They treated AI adoption as an operational change, not a magic switch.
If your company isn't doing these things, you're not going to see the promised productivity gains. You're going to see the hidden cost: hundreds of hours weekly spent cleaning up AI workslop.
The good news? This is fixable. You don't need massive budgets or fancy tools. You need thoughtful training, documented processes, and governance that actually works.
The sooner you start, the sooner you can move AI from "interesting experiment that creates more work" to "genuine productivity multiplier."
Use Case: Automating your weekly reports and documentation with AI while maintaining quality and compliance standards.
Try Runable For Free
FAQ
What is AI workslop?
AI workslop refers to the messy, error-ridden, or context-blind output that AI tools generate that requires significant human cleanup and revision before being usable. It's the difference between what AI produces and what's actually suitable for use, including hallucinations, inaccuracies, missing context, and tone mismatches.
Why do companies spend so much time cleaning up AI output?
AI models are optimized for pattern matching and fluent text generation, not accuracy or domain-specific context. They generate confident-sounding output that looks correct but often contains factual errors, misses important context, or doesn't align with specific requirements. Since 98% of AI outputs need revision, companies must invest significant time in fact-checking, customization, and quality assurance.
What's the difference between trained and untrained workers with AI?
94% of trained workers report that AI boosts their productivity, compared to only 69% of untrained workers. Trained workers understand what AI is good at (brainstorming, drafting, first-pass content) versus what it's bad at (fact-checking, security decisions, compliance work). They know how to write effective prompts, review output critically, and integrate AI into proper workflows with quality gates.
How much time do workers spend cleaning up AI output?
Research shows 58% of workers spend more than 3 hours per week cleaning up AI content, 35% spend more than 5 hours weekly, and 11% spend over 10 hours weekly. This translates to roughly
What security and privacy risks come with AI adoption?
27% of workers have experienced security or privacy incidents related to AI use. Common risks include accidentally sending sensitive data to cloud-based AI providers, data being retained for model training, sharing information that violates GDPR or HIPAA, and exposing proprietary information. These issues can be mitigated through data governance policies, using private AI deployments, anonymizing data before sharing with AI, and maintaining audit trails.
What compliance issues come from AI-generated content?
24% of respondents reported compliance or legal issues. AI models don't understand regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, or FINRA. They'll generate content that sounds compliant while missing critical regulatory requirements, creating legal liability. Content handling regulated data needs formal review by people with legal or compliance expertise before deployment.
What's the best way to implement AI governance?
Effective AI governance includes mandatory training for AI users, standardized processes and templates, formal review and approval workflows, clear data governance policies, tool standardization, and ongoing monitoring. Companies should prioritize high-risk teams (finance, legal, compliance) and high-volume users first, then expand to other groups.
Should companies invest in AI management tools?
While tools can help (prompt management systems, workflow platforms, verification tools), they're not a substitute for training and good processes. A trained team with simple processes often outperforms an untrained team with sophisticated tools. Tools work best when paired with training, governance, and clear processes.
How do prompt templates reduce AI cleanup time?
Prompt quality dramatically affects output quality. When teams build templates for common tasks with clear instructions, examples, and constraints, everyone gets consistent, higher-quality results. New employees can use proven prompts immediately instead of starting from scratch, which improves quality and reduces iteration time.
What's the ROI on AI training investments?
A 4-8 hour training program costs roughly

Key Takeaways
- 58% of workers spend 3+ hours weekly cleaning up AI-generated content; 11% spend over 10 hours, representing 18K annual labor waste per employee
- Only 2% of workers report AI outputs need zero revision, despite 92% believing AI boosts overall productivity, revealing a quality-to-perception gap
- Trained workers show 94% AI productivity benefits vs 69% for untrained workers, with training paying for itself in 6-15 weeks through reduced cleanup
- Organizations experience real business impacts: 28% rejected work, 27% security incidents, 25% customer complaints, 24% compliance issues from AI usage
- Success requires mandatory AI training, standardized processes, formal review workflows, and proper governance—not just better tools or hoping AI improves
Related Articles
- Anthropic's Economic Index 2025: What AI Really Does for Work [Data]
- Responsible AI in 2026: The Business Blueprint for Trustworthy Innovation [2025]
- Claude Cowork Now Available to Pro Subscribers: What Changed [2025]
- Anthropic's Claude Cowork: The AI Agent That Actually Works [2025]
- AI Coding Agents and Developer Burnout: 10 Lessons [2025]
- AI Bubble Myth: Understanding 3 Distinct Layers & Timelines
![The Hidden Cost of AI Workslop: How Businesses Lose Hundreds of Hours Weekly [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/the-hidden-cost-of-ai-workslop-how-businesses-lose-hundreds-/image-1-1768833421430.jpg)



