Understanding Articul 8: The Intel Spinout Revolutionizing Enterprise AI
Articul 8 represents a fascinating case study in how large technology corporations are leveraging internal AI expertise to create focused, specialized companies. Spun out from Intel in early 2024, this Santa Clara-based enterprise AI company has achieved remarkable momentum in a relatively short timeframe. The company recently announced securing over half of a planned
This trajectory raises important questions about the future of enterprise AI, particularly in regulated industries where precision, auditability, and data sovereignty matter more than cutting-edge model capabilities. Unlike many AI startups that chase general-purpose large language models, Articul 8 has taken a deliberately different path, focusing on specialized AI systems that operate within customers' own IT environments and are tailored to specific business functions.
The funding round leadership from Spain's Adara Ventures, with participation from India's Aditya Birla Ventures, signals growing international confidence in Articul 8's approach. CEO Arun K. Subramaniyan has explicitly stated the company is not under pressure to raise capital, describing Articul 8 as revenue-positive following a series of significant enterprise contracts. The company projects finishing the year with annual recurring revenue exceeding $57 million, with approximately 45-50% of that already recognized, demonstrating a business model that has moved well beyond the proof-of-concept stage.
What makes Articul 8's approach particularly relevant is the timing. As enterprises worldwide grapple with AI integration, the debate between general-purpose cloud-based AI solutions and specialized, on-premise systems continues to intensify. Articul 8's positioning at this intersection, combined with its focus on regulated industries, has attracted a customer base including Hitachi Energy, AWS, Franklin Templeton, and Intel itself—companies that cannot afford ambiguity in their AI systems.
The Evolution of Enterprise AI: From General-Purpose to Specialized Systems
The Shift Away from One-Size-Fits-All AI Models
For years, the AI industry operated under a fundamental assumption: larger, more general-purpose models trained on broader datasets would eventually solve every problem. This paradigm produced remarkable achievements in natural language processing, image generation, and creative applications. However, enterprise customers, particularly those in regulated industries, began identifying critical limitations with this approach.
General-purpose AI models, by their nature, optimize for average performance across diverse use cases. This creates several practical problems for enterprise customers. First, auditability becomes nearly impossible—when an AI system makes a decision, understanding exactly why becomes extraordinarily difficult. Second, data sovereignty concerns emerge when sensitive corporate information must be transmitted to shared cloud platforms. Third, the accuracy requirements for regulated industries often exceed what general-purpose models can reliably deliver, particularly for domain-specific tasks.
Articul 8's founders recognized these limitations and built the company around the premise that enterprise AI would eventually bifurcate into two categories: general-purpose solutions for commodity applications, and specialized systems for high-value, high-stakes business functions. This market segmentation has proven prescient, with enterprises increasingly willing to invest in customized AI solutions for critical operations.
Why Regulated Industries Demand Different Solutions
Regulated industries—energy, manufacturing, aerospace, financial services, and semiconductors—operate under constraints that fundamentally change AI requirements. In these sectors, regulators often require demonstrable understanding of how decisions were made. A recommendation engine can use black-box machine learning; a credit decision cannot. An energy company optimizing renewable integration needs explainable AI; a pharmaceutical manufacturer validating drug interactions absolutely requires it.
Articul 8's specialization strategy directly addresses these requirements. Rather than selling standalone models, the company packages technology as customized software applications and AI agents tailored to specific business functions. This approach allows enterprises to maintain control over their data while gaining the benefits of advanced AI capabilities. The distinction matters enormously: instead of sending proprietary data to cloud providers, customers deploy Articul 8's systems within their own IT environments, processing sensitive information locally.
This architecture also enables Articul 8 to build domain-specific knowledge into its systems. An AI agent designed for energy sector portfolio optimization can incorporate decades of domain expertise, regulatory knowledge, and industry-specific constraints from the outset. This produces dramatically higher accuracy and faster time-to-value compared to generic models that require extensive fine-tuning.
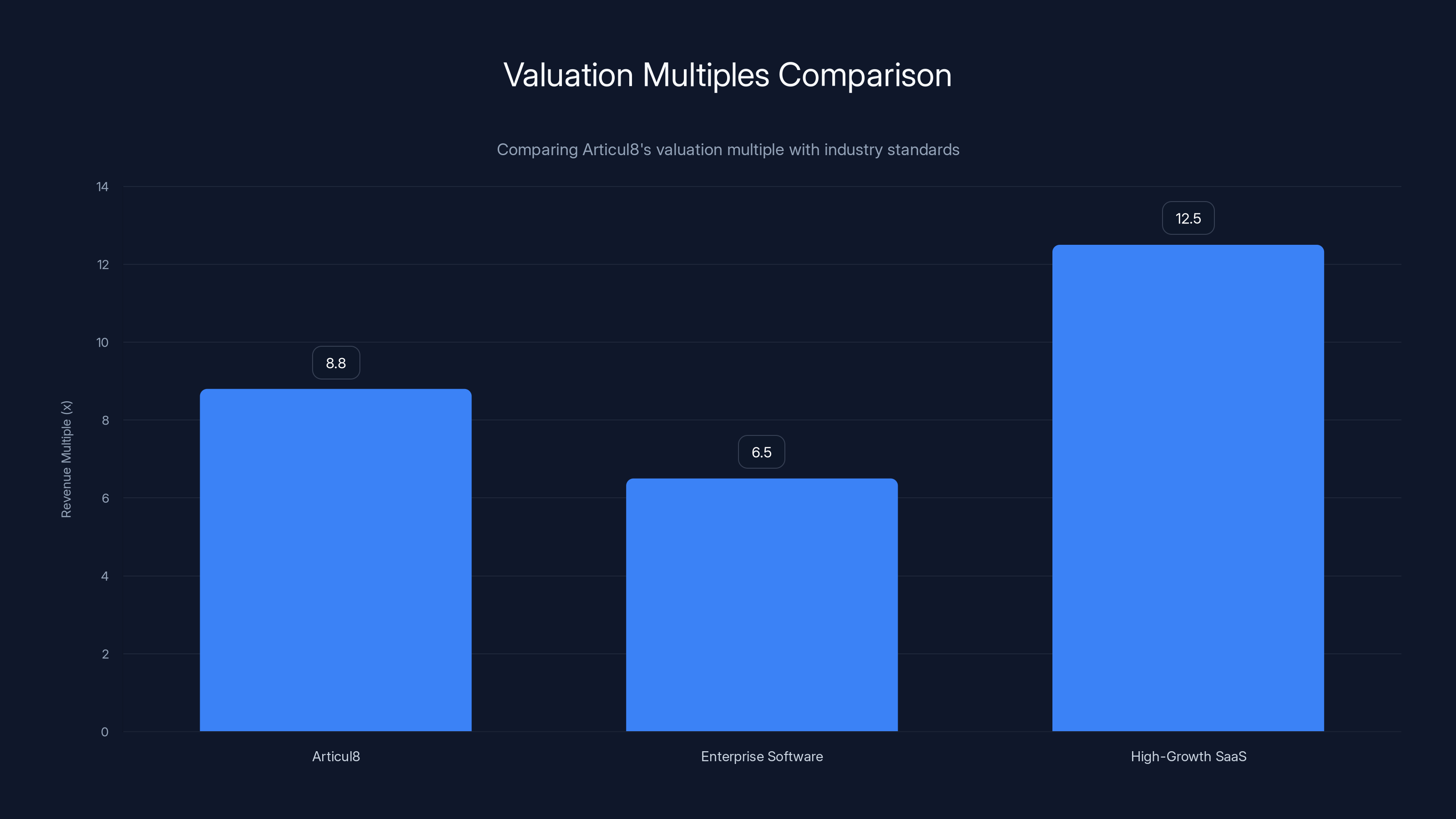
Articul8's revenue multiple of 8.8x is competitive, sitting between typical enterprise software (5-8x) and high-growth SaaS companies (10-15x). Estimated data.
Articul 8's Business Model: From Technology to Applications
The Software Application Packaging Strategy
Articul 8's business model represents a deliberate departure from how most AI companies monetize their technology. Instead of licensing AI models, the company sells fully-formed software applications powered by specialized AI. This distinction fundamentally changes the value proposition and customer relationship.
Consider the difference between selling an AI engine and selling a complete application. An enterprise purchasing an AI engine must invest significantly in integration, customization, domain knowledge encoding, and ongoing management. An enterprise purchasing a complete application receives immediate functionality. The difference parallels historical software adoption—enterprise applications succeeded when they provided business functionality, not when they provided raw technology components.
Articul 8's approach means customers can deploy meaningful AI capabilities in weeks rather than months. The company handles the integration, the domain expertise encoding, and the ongoing optimization. Customers focus on using the applications to solve business problems. This shift toward application-based monetization also improves unit economics, as application licenses typically command higher prices than raw technology while simultaneously reducing customer acquisition costs.
AI Agents: Automating Specialized Business Functions
Within its application framework, Articul 8 develops AI agents—autonomous systems designed to handle specific business functions with minimal human intervention. These agents differ fundamentally from traditional automation software. Whereas traditional automation requires explicit rules for every scenario, AI agents can reason about novel situations and adapt to changing conditions.
In energy sector applications, an Articul 8 agent might autonomously optimize renewable energy integration across a grid, making real-time decisions about load balancing while respecting transmission constraints and regulatory requirements. The agent learns from historical patterns and continuously optimizes performance. In financial services, an agent might automate investment due diligence, analyzing opportunities against risk parameters and regulatory constraints.
The sophistication of these agents depends on domain expertise encoding. Articul 8's advantage lies in its ability to codify specialized knowledge into agent behavior. An agent designed for semiconductor manufacturing quality control incorporates decades of process engineering knowledge. When deployed, the agent doesn't need to learn from scratch—it inherits the accumulated expertise of the domain.
Articul8's rapid valuation growth is driven by
Customer Traction: From Proof of Concept to Revenue Generation
The $90 Million Contract Value Milestone
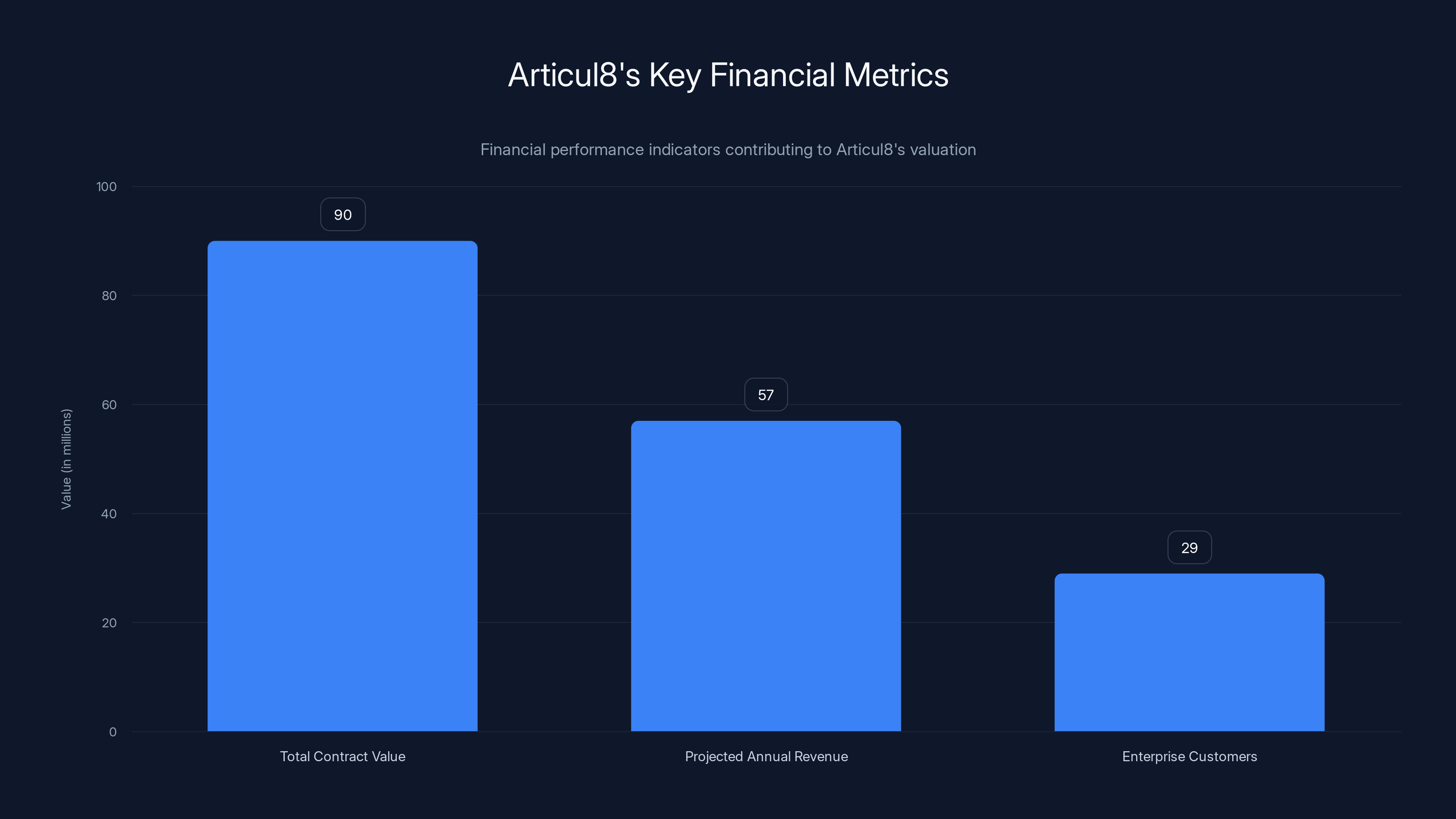
Articul 8's customer metrics reveal a business that has moved decisively beyond early-stage validation. With $90 million in total contract value across 29 paying customers, the company demonstrates strong enterprise sales traction. This figure—representing cumulative value of all signed customer contracts—indicates both deal size and customer acquisition success.
Breaking down the math, this implies an average contract value of approximately $3.1 million, suggesting these are substantial enterprise engagements, not small pilot projects. Many of these customers operate in sectors requiring extensive due diligence, procurement processes, and regulatory approval. The fact that Articul 8 has navigated these hurdles for 29 separate organizations indicates the company has developed effective enterprise sales and delivery capabilities.
The customer roster reveals strategic diversity. Hitachi Energy represents the energy sector, demonstrating deep penetration in a critical regulated industry. Franklin Templeton's participation validates demand in financial services. AWS being both a customer and partner indicates cloud providers themselves see value in specialized AI applications. Intel's presence as a customer speaks to the technology's maturity—the company that spun out Articul 8 still chooses to license its services.
Revenue Metrics and Growth Trajectory
Articul 8's projected annual recurring revenue of just over $57 million with 45-50% already recognized indicates a business model that has achieved significant scale efficiently. This projection for year-end represents approximately 63-65% of the total contract value, suggesting reasonable contract fulfillment and revenue recognition across the customer base.
The revenue recognition pattern carries important implications. When a company has committed to
For investors considering whether Articul 8 represents an attractive growth opportunity, these metrics prove critical. The company has moved beyond speculative valuations based on technology potential. Instead, Articul 8's valuation rests partly on demonstrated ability to win enterprise contracts and execute delivery. CEO Subramaniyan's comment that the company is "not cash-strapped" carries particular weight when analyzed against these numbers—a company generating $57 million in annual recurring revenue can self-fund operations and growth.

The Series B Funding: Strategic Capital for Scaled Growth
Two-Installment Structure and Timing
Articul 8's Series B structure merits analysis, as it reflects pragmatic negotiation around company growth stages. Rather than a single capital injection, the company has structured the funding in two installments, with the first led by Adara Ventures and the second expected to close in Q1 of the current year. This structure offers several advantages for both company and investors.
Two-installment funding aligns capital availability with business milestones. The company receives initial capital to pursue priority initiatives, then demonstrates progress before accessing the second tranche. This reduces investor risk by gating capital release behind achievement, while giving the company flexibility to adjust strategy based on market feedback and execution results.
Adara Ventures' leadership of the round carries strategic significance beyond capital provision. Based in Madrid with backing from the European Investment Fund, the firm brings European venture capital expertise and connections. Articul 8 plans to use Series B proceeds to expand internationally, with European expansion as a priority. Having a lead investor with deep European networks accelerates market entry and customer development.
Allocation Strategy: R&D, Product, and International Expansion
Company leadership has been explicit about Series B capital allocation priorities: expand research and product development, scale operations internationally, with focus on Europe and parts of Asia. This allocation strategy reveals how Articul 8 leadership thinks about competitive positioning and market opportunity.
Articul 8's emphasis on R&D and product development indicates confidence that product differentiation remains the primary competitive advantage. The company intends to deepen its technical moat rather than aggressively expand sales and marketing. With 75 total employees and approximately 80% focused on R&D, Articul 8 maintains an unusually engineering-heavy organization. This structure allows the company to continuously improve its AI systems, develop new domain applications, and maintain technical superiority over competitors.
International expansion targeting Europe and parts of Asia (specifically Japan and South Korea) reflects geographic risk diversification and market opportunity assessment. European enterprises face particularly stringent data privacy regulations (GDPR) and cybersecurity requirements, making Articul 8's on-premise deployment model exceptionally attractive. Japan and South Korea's manufacturing and electronics sectors represent massive opportunities for specialized AI applications.
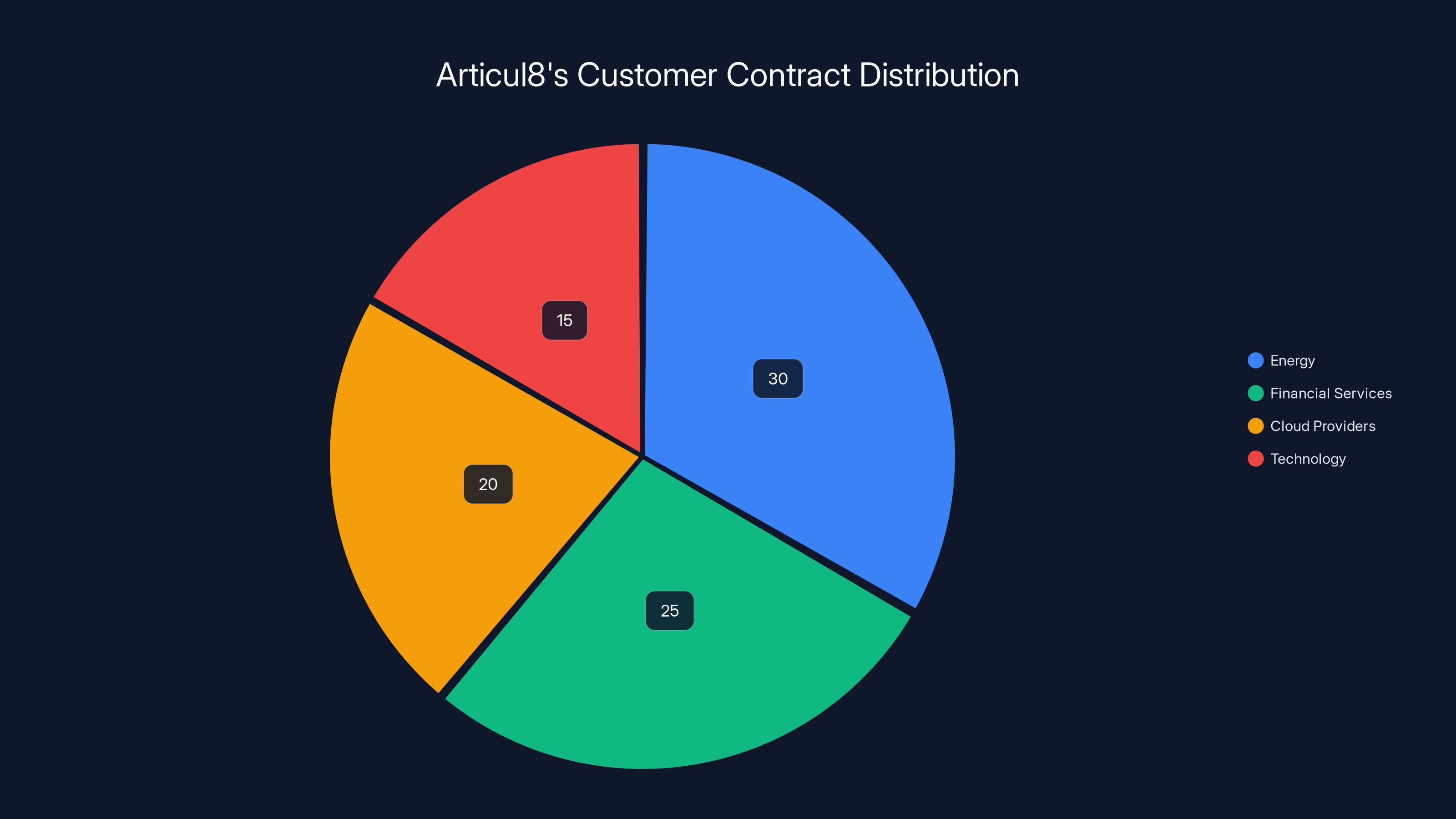
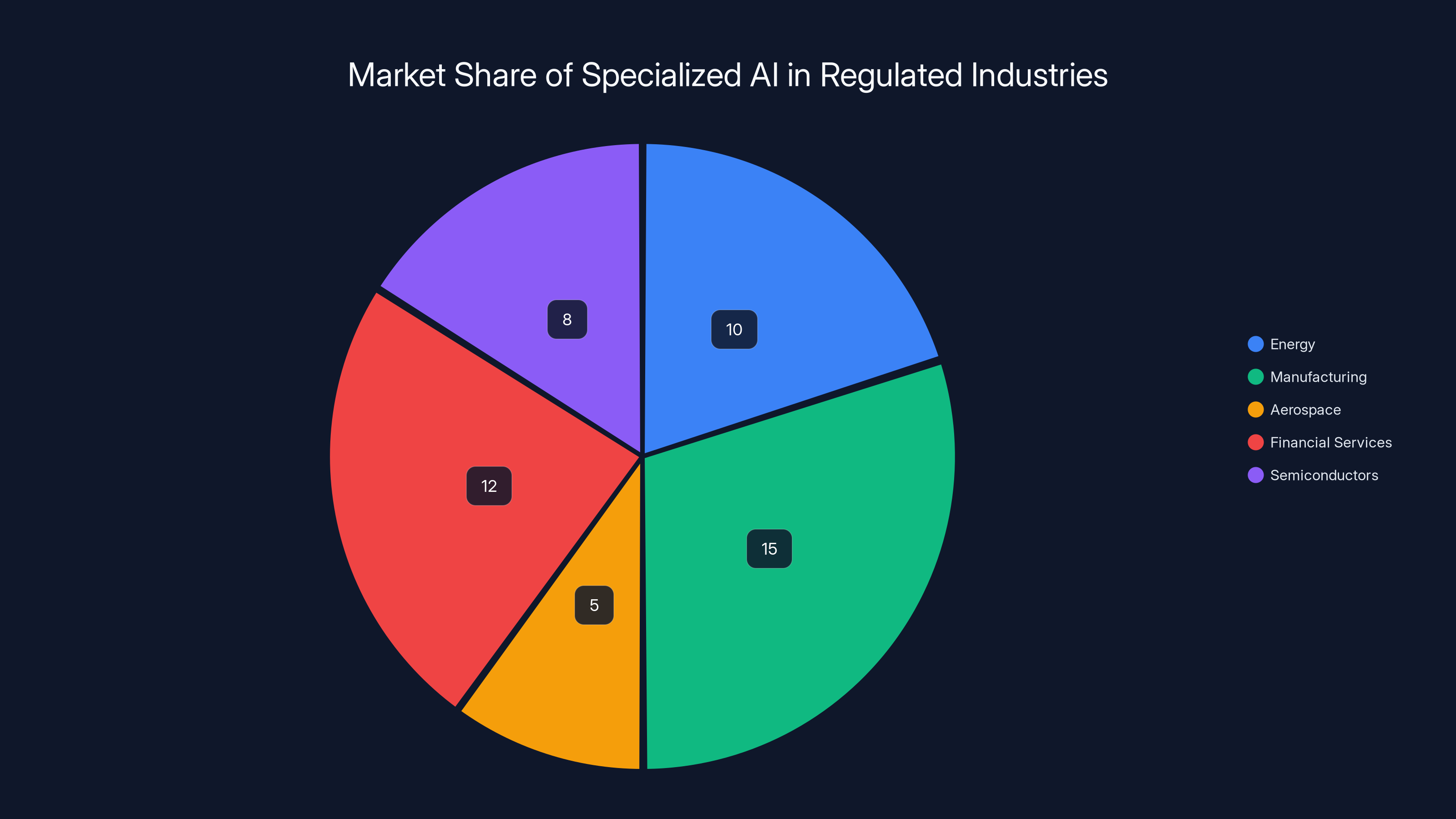
Articul8's $90 million in contracts is strategically distributed across key sectors, with energy and financial services leading at 30% and 25% respectively. (Estimated data)
Competitive Landscape: Who Really Competes with Articul 8?
Cloud Service Providers as Primary Competition
When asked about competition, CEO Subramaniyan offered a revealing perspective: "Our competition is pretty much everybody, but today, the major competitors are the cloud service providers, because they have realized that their model, as the general-purpose offerings, are all commodities." This statement reframes competitive dynamics in important ways.
Traditional competitors might include other AI companies or enterprise software vendors. However, Subramaniyan's assessment suggests the real competitive threat comes from organizations attempting to repurpose general-purpose AI into specialized applications. AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure all possess enormous resources, existing enterprise customer relationships, and sophisticated AI capabilities. These companies can theoretically develop specialized AI applications for any industry vertical.
However, cloud service providers face structural disadvantages in competing with specialized vendors like Articul 8. First, they must maintain neutrality across customer bases—AWS cannot optimize its AI agents specifically for energy companies without potentially disadvantaging manufacturing customers. Second, cloud providers' business models depend on commodity pricing and scale, while specialized applications command premium pricing. Third, organizational complexity increases friction—enterprise sales at AWS require navigating multiple business units and approval processes, while specialized vendors maintain focused go-to-market strategies.
Articul 8's advantage lies in specialization, single-minded focus, and alignment of incentives. Every decision prioritizes success in regulated industries. Every product enhancement targets domain-specific requirements. Organizational bandwidth concentrates on deepening relationships with target customers.
Distributed Competition Across Verticals
Beyond cloud providers, Articul 8 faces distributed competition across specific industry verticals. In energy, companies like Siemens operate energy management software platforms incorporating AI capabilities. In semiconductors, equipment manufacturers develop specialized analytics platforms. In financial services, established vendors like SAS and Refinitiv offer risk analytics platforms.
However, most of these competitors operate within traditional software paradigms, where AI represents an enhancement to existing platforms rather than the core value proposition. Articul 8's AI-first architecture creates different cost structures, deployment models, and capability trajectories. A traditional software vendor adding AI capabilities to legacy systems faces integration challenges. Articul 8, built from inception around AI, avoids legacy constraints.
The Open-Source Challenge and Specialized Model Emergence
Emerging competition comes from open-source AI models increasingly specialized to particular domains. As open-source language models improve, specialized variants optimized for legal analysis, scientific reasoning, or manufacturing process control emerge. Organizations with sufficient engineering resources can deploy these specialized models and build custom applications.
However, open-source models represent a different competitive category. They provide raw capability requiring significant engineering investment to productize. Articul 8 sells finished applications with embedded domain expertise, regulatory compliance, and integration with customer IT infrastructure. The distance between "specialized open-source language model" and "production-grade AI agent operating manufacturing quality control" remains substantial.
Use Cases Across Regulated Industries
Energy Sector: Grid Optimization and Renewable Integration
The energy sector represents Articul 8's most developed vertical application area. Hitachi Energy's participation as a major customer validates the company's approach for this industry. Energy companies face increasingly complex operational challenges as renewable energy integration introduces variability into grids traditionally designed around baseload generation.
Traditional grid management relies on engineers and sophisticated SCADA systems making decisions based on predefined rules. However, modern grids with high renewable penetration require continuous optimization across thousands of variables: generation availability from wind and solar, transmission constraints, demand patterns, reserve requirements, and market prices. AI agents specifically designed for energy grid optimization can make decisions in milliseconds that would require human deliberation.
Articul 8's energy applications likely incorporate domain expertise in electrical engineering, power systems, renewable integration, regulatory requirements, and market operations. An AI agent designed for this domain inherits decades of collective knowledge about how to maintain grid stability while optimizing renewable utilization. The agent learns from real-time data, continuously improving performance while operating within regulatory and safety constraints.
The value proposition extends beyond operational optimization. Energy companies increasingly operate in competitive markets where margin optimization matters significantly. An AI system that reduces renewable curtailment by even small percentages generates millions in annual value. A system that optimizes transmission line utilization reduces infrastructure costs. These optimization opportunities justify investment in specialized AI agents.
Aerospace and Manufacturing: Quality Control and Process Optimization
Aerospace and manufacturing represent industrial sectors where quality failures carry extraordinary costs. In aerospace, failures can result in loss of human life and company reputation destruction. In semiconductor manufacturing, process variation directly impacts yield and profitability. These sectors demand AI systems that combine predictive accuracy with explainability—decision-makers must understand why the system recommended a particular action.
Articul 8's applications in these sectors likely focus on two primary use cases: quality control and process optimization. For quality control, AI agents analyze production data in real-time, identifying deviations from specifications before they result in defective products. The agent's decisions must be explainable—when flagging a part for rejection, the system must clearly indicate which measurements deviated from specifications and by how much.
For process optimization, agents continuously adjust manufacturing parameters to maximize quality and yield. In semiconductor manufacturing, thousands of parameters affect wafer yield—temperature profiles, chemical concentrations, timing sequences, equipment-specific variations. An AI agent specifically designed for semiconductor manufacturing incorporates process knowledge, equipment specifications, and historical yield data. The agent makes parameter adjustments that improve yield while remaining within equipment constraints and process safety limits.
These applications create measurable value: improved yield translates directly to profitability, reduced scrap improves margins, and quality improvements reduce warranty costs and reputational risk. Manufacturing executives understand these metrics intuitively, making Articul 8's sales cycle more straightforward than in sectors where AI benefits are less tangible.
Financial Services: Risk Analysis and Compliance Automation
Financial services present different but equally compelling use cases for specialized AI. Franklin Templeton's participation validates demand in this sector. Financial institutions operate under extensive regulatory oversight, with compliance failures carrying severe penalties. Simultaneously, competitive dynamics demand rapid decision-making—investment opportunities move quickly, and institutions unable to analyze opportunities efficiently lose market share.
Articul 8's financial services applications likely address use cases including due diligence automation, compliance monitoring, and risk analysis. Due diligence traditionally requires teams of analysts reviewing thousands of documents to identify risks, conflicts, and concerns. An AI agent specifically trained on financial analysis can accelerate this process dramatically, reviewing documentation, identifying relevant information, and highlighting potential issues for human review.
Compliance monitoring involves continuous surveillance of transactions, counterparties, and activities to identify potential regulatory violations. AI agents designed for this purpose incorporate regulatory frameworks, know-your-customer requirements, sanctions lists, and transaction monitoring rules. The agent flags suspicious activities while minimizing false positives that overwhelm compliance teams.
Risk analysis spans credit risk, market risk, operational risk, and other dimensions. AI agents can synthesize information from diverse sources—market data, company financials, economic indicators, industry trends—to assess risk. Financial institutions value these assessments when they're explainable and auditable, requirements Articul 8's architecture satisfies.
Semiconductors and Advanced Manufacturing: Deep Domain Specialization
Semiconductor manufacturing represents perhaps the most complex manufacturing environment, with process parameters numbering in the thousands and interactions between parameters often non-obvious. Equipment companies like ASML and equipment users like Intel and TSMC invest heavily in optimizing manufacturing processes. This environment creates tremendous opportunity for specialized AI agents.
Articul 8's semiconductor applications likely address equipment predictive maintenance, process yield optimization, and fab-level resource allocation. Equipment failures in chip manufacturing can halt production for millions of dollars in lost output. Predictive maintenance agents analyze equipment telemetry, identifying degradation patterns and recommending maintenance before failures occur.
Process yield optimization involves continuous tuning of manufacturing parameters to maximize the percentage of wafers meeting specifications. Given the complexity and number of parameters, AI agents can identify optimization opportunities that exceed human analytical capacity. The agent operates within constraints—equipment capabilities, material properties, safety requirements—while continuously learning from operational results.
Fab-level resource allocation involves scheduling thousands of wafer lots through equipment with different capabilities and constraints. An AI agent optimizing fab operations maximizes throughput while meeting delivery commitments and maintaining equipment utilization. This optimization typically generates single-digit yield improvements and utilization increases, which translate to millions in value given fab capital costs.
Estimated data suggests specialized AI applications could capture $20-50 billion annually, with significant shares in manufacturing and financial services.
Articul 8's Technical Architecture: On-Premise Specialization
The On-Premise Deployment Model Advantage
Articul 8's architectural choice to operate within customers' own IT environments carries profound implications for product design, competitive positioning, and customer value. This represents a deliberate rejection of the cloud-first, Saa S-native architecture dominating modern software companies.
On-premise deployment offers several distinct advantages in regulated industries. First, data never leaves the customer's network, addressing data sovereignty and privacy concerns. Companies operating under GDPR cannot necessarily transmit sensitive personal or business data to shared cloud infrastructure. Pharmaceutical companies cannot share drug development research with external parties. Energy companies cannot share grid operations data with competitors who might be cloud infrastructure co-tenants.
Second, audit trails and decision logs remain entirely under customer control. When regulators require understanding how an AI system made a critical decision, the customer can provide complete logs without involving external parties. Compliance audits become simpler when data and decision processes reside within the organization.
Third, integration with legacy systems becomes manageable. Many enterprises operate alongside decades-old systems not designed for cloud connectivity. On-premise deployment allows Articul 8 systems to integrate with these legacy systems without requiring complete infrastructure transformation. This dramatically reduces deployment friction and time-to-value.
Knowledge Graph Architecture
Articul 8 utilizes a knowledge graph architecture to structure domain-specific information and relationships. Knowledge graphs represent information as interconnected nodes (concepts) and edges (relationships), allowing systems to reason about complex relationships and dependencies. In regulated industries, this architecture enables sophisticated reasoning while maintaining explainability.
For example, in a financial services knowledge graph, nodes might represent companies, securities, executives, transactions, and regulations. Edges capture relationships—executive works at company, company issues security, transaction involves parties. An AI agent traversing this graph can reason about conflicts of interest, sanctions exposure, and regulatory compliance. When the agent recommends action, the reasoning path through the knowledge graph provides explainability.
Knowledge graphs also enable what might be called "structured learning"—the system learns relationships and patterns while constrained by domain structure. An AI agent might discover a new pattern in transaction data, but this discovery occurs within the context of existing relationships in the knowledge graph. This produces more reliable learning compared to unstructured pattern discovery.
Integration with Existing Enterprise Infrastructure
Successful enterprise software products provide seamless integration with existing infrastructure. Articul 8 systems integrate with customer data warehouses, enterprise resource planning systems, business intelligence platforms, and other established tools. This integration requirement shapes product architecture, as the system must efficiently extract data from diverse sources, process it, and feed results back to customer systems.
Articul 8's 80% R&D focus likely includes substantial effort on integration and interoperability. Integration complexity represents genuine technical challenge—data formats vary, systems update on different cadences, security models differ. Successfully operating within diverse customer IT environments requires architectural flexibility and robust integration capabilities.
Market Opportunity Assessment and Competitive Dynamics
Total Addressable Market in Regulated Industries
Estimating the total addressable market for specialized enterprise AI requires segmentation by industry and application. Regulated industries that Articul 8 targets—energy, manufacturing, aerospace, financial services, semiconductors—collectively represent sectors with combined annual spending exceeding $500 billion in enterprise IT and operations globally.
Within these sectors, specialized AI applications address a subset of challenges. However, that subset includes some highest-value opportunities. Energy companies spend billions annually on grid operations—improvements in efficiency create enormous value. Manufacturers constantly pursue yield and quality improvements. Financial institutions spend billions on risk management and compliance. These expenditures indicate willingness to invest in solutions that demonstrate clear ROI.
Conservative estimates suggest specialized AI applications could eventually capture $20-50 billion in annual spending across relevant verticals. This represents a market opportunity orders of magnitude larger than Articul 8's current revenue run rate, indicating substantial runway for growth.
Competitive Intensity and Market Consolidation
As the opportunity becomes apparent, competitive intensity will increase. Established enterprise software vendors will develop specialized AI capabilities. Cloud providers will build vertical solutions. New startups will emerge targeting specific industries. This intensifying competition raises questions about Articul 8's defensibility.
Articul 8's defensibility rests on several factors. First, domain expertise compounds—each customer engagement teaches the company more about the industry. Competitors must acquire equivalent expertise through hiring or acquisition. Second, customer relationships create switching costs—replacing a system that's integrated deeply into operations is expensive. Third, continuous product improvement driven by 80% R&D focus maintains technical advantage.
However, larger competitors possess resources to overcome these advantages through investment and acquisition. The ultimate question is whether Articul 8 can maintain technical superiority and customer lock-in long enough to establish market leadership, particularly before cloud providers develop competitive offerings. Given the company's funding, customer traction, and growth trajectory, the company appears to be on this path, but execution risk remains substantial.
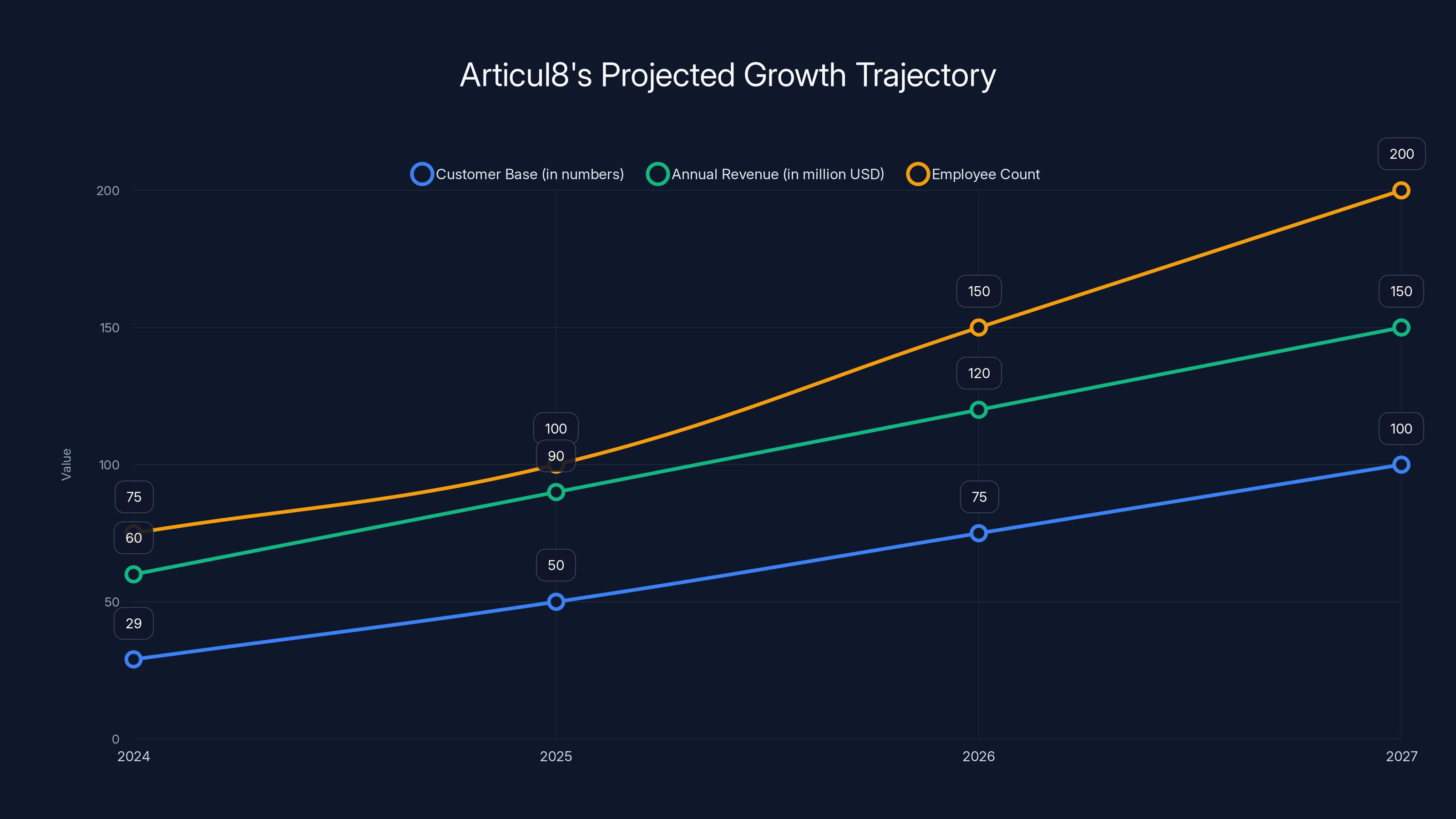
Articul8 is projected to significantly expand its customer base, revenue, and employee count by 2027, driven by geographic and vertical expansion. Estimated data.
Financial Performance and Investor Thesis
Valuation Metrics and Industry Comparison
Articul 8's
This valuation appears reasonable given Articul 8's characteristics. The company demonstrates strong customer traction (29 paying customers,
The fivefold increase in valuation from Series A to Series B (from
Revenue Sustainability and Growth Prospects
The claim that Articul 8 is "revenue-positive" merits scrutiny. Revenue-positive means revenue exceeds operating expenses, but it doesn't necessarily indicate strong cash flow given different revenue recognition timing versus cash collection. However, with
Growth prospects depend on several factors. Customer acquisition must accelerate beyond the current pace of 29 customers to achieve meaningful scale. International expansion in Europe and Asia requires building sales capabilities in new regions. Vertical expansion into additional regulated industries requires product development. All of these require capital, which the Series B funding provides.
The two-year projection likely shows continued revenue acceleration, with targets potentially reaching $100+ million in annual recurring revenue by year-end of next year. This would represent approximately 75% year-over-year growth, a pace that would support venture returns while remaining achievable given current traction.
Partnerships and Strategic Relationships
Cloud Provider Partnerships and Integration
Articul 8 maintains partnerships with major cloud providers including Nvidia and Google Cloud, while AWS functions as both customer and deployment partner. These relationships serve multiple purposes for Articul 8. Technically, cloud provider partnerships ensure Articul 8 systems integrate effectively with cloud infrastructure where customers increasingly operate. Commercially, cloud provider endorsements provide credibility and enable go-to-market collaboration.
The distinction between Articul 8's on-premise deployment model and cloud partnerships might appear contradictory. However, many enterprises operate hybrid environments—some workloads on-premise, others in cloud. Articul 8 systems can operate on-premise while integrating with cloud-based data sources and consuming cloud services like compute or storage where beneficial. This flexibility increases addressable market by accommodating diverse customer infrastructure approaches.
AWS's participation as both customer and partner deserves particular attention. AWS selecting Articul 8 as a customer indicates the company sees value in specialized AI agents for its own operations. AWS's participation as a deployment partner suggests AWS recognizes opportunities to integrate Articul 8's technology into AWS offerings, potentially expanding addressable market through AWS distribution channels.
Customer Partnerships and References
Articul 8's customer relationships extend beyond simple vendor-customer transactions to true partnerships. Major customers like Hitachi Energy, Franklin Templeton, and Intel have invested in implementing Articul 8 systems and presumably derived measurable value. These relationships provide crucial reference value—enterprise sales processes involve extensive due diligence, and recommendations from peer organizations carry enormous weight.
The presence of Intel as both founder and customer carries special significance. Intel's embrace of Articul 8 suggests confidence in the technology's maturity and commercial potential. Intel's experience provides feedback for product development and reference value with other enterprise prospects.
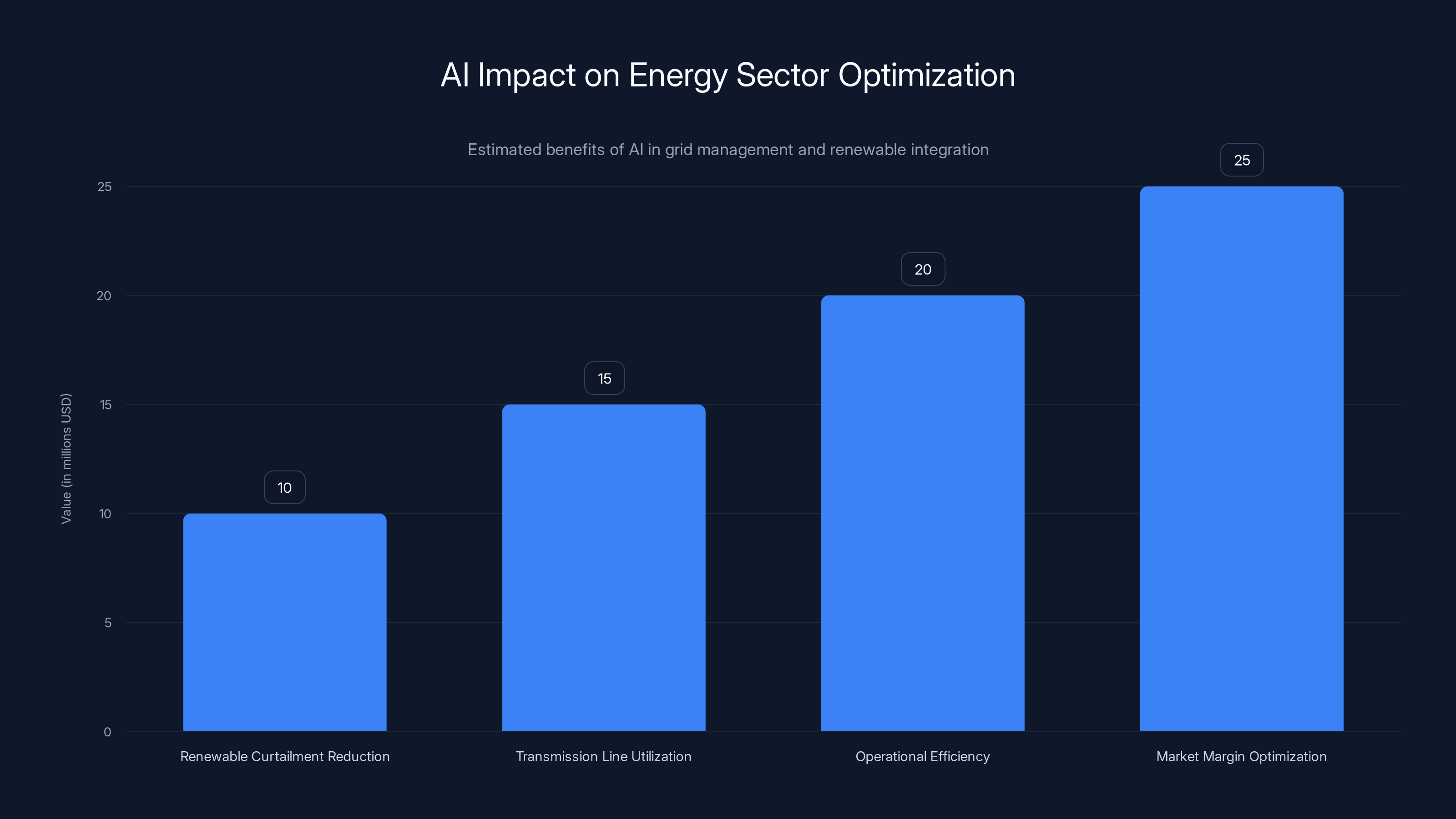
AI-driven optimization in the energy sector can significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency, with potential annual savings in the millions. (Estimated data)
Global Expansion Strategy and Market Entry
European Market Focus and Regulatory Tailwinds
Articul 8's emphasis on European expansion reflects strategic market assessment. European enterprises face particularly stringent regulatory environments—GDPR for data privacy, critical infrastructure protection regulations, sector-specific compliance frameworks. These regulatory requirements create tailwinds for Articul 8's on-premise deployment model and specialized, explainable AI systems.
Europe also represents a developed market with substantial enterprise IT spending. European energy companies, manufacturing firms, and financial institutions all match Articul 8's target customer profile. Additionally, European venture capital through Adara Ventures provides credibility and connections for market entry. The decision to use Series B proceeds partly for European expansion shows capital discipline—investing in markets where regulatory and market conditions favor the company's approach.
Asia-Pacific Expansion and Japan/South Korea Priorities
Articul 8's targeting of Japan and South Korea reflects different strategic considerations than European expansion. These countries host world-class manufacturing sectors—Japan in automotive and electronics, South Korea in semiconductors and electronics. Both countries invest heavily in manufacturing technology and digitalization, creating receptive markets for advanced AI applications.
Japan's manufacturing culture emphasizes continuous improvement and quality optimization, aligning perfectly with Articul 8's product focus. South Korea's semiconductor industry, centered on companies like Samsung and SK Hynix, represents enormous opportunity for specialized AI agents. The company's statement that it "has begun working with large enterprise customers" in these markets suggests initial traction that expansion capital can accelerate.
India Operations as R&D Hub
Articul 8 maintains significant operations in India with teams contributing to R&D. India provides several advantages: access to large engineering talent pools, lower operational costs enabling greater R&D investment, and technical expertise in AI and software development. India-based R&D teams work across all geographies, contributing to product development globally rather than just serving local markets.
This distributed R&D model, while creating coordination challenges, provides organizational flexibility. The company can scale engineering capacity in lower-cost geographies while maintaining customer-facing teams in higher-cost markets. This approach improves margins while funding accelerated R&D investment.

Organizational Structure and Talent Strategy
R&D-Heavy Organization Design
Articul 8's decision to concentrate approximately 80% of its 75-person team on R&D reflects clear strategic priorities. This organizational structure resembles research-heavy companies more than typical enterprise software vendors. A traditional enterprise software company of similar revenue might maintain 40-50% in R&D, allocating more resources to sales, customer success, and operations.
Articul 8's structure indicates leadership believes product differentiation remains the critical competitive advantage. Maintaining technical superiority over larger competitors requires constant innovation. This R&D focus suggests the company is investing heavily in expanding capability depth—developing new domain applications, improving AI agent sophistication, and advancing integration capabilities.
This approach carries risk. If product development delivers less value than anticipated, the company will have underinvested in go-to-market activities that could accelerate growth. However, given early customer traction and strong retention indicators, the approach appears justified.
Geographic Distribution and Collaboration
Articul 8's teams spread across the U. S., Brazil, and India indicate both geographic diversification and deliberate talent sourcing strategy. The U. S. presence houses headquarters and likely customer-facing operations. Brazil's presence might reflect either specific customer opportunities or access to Spanish-speaking talent (relevant for European expansion). India's presence contributes to R&D scale.
Distributed teams introduce operational complexity—time zone coordination, communication challenges, and culture alignment require deliberate management. However, they also enable access to global talent and reduce operational costs. For a company focused on achieving scale rapidly, this structure makes sense.
Challenges and Risks
Competitive Escalation from Cloud Providers
Articul 8's most significant competitive risk comes from cloud providers' inevitable response to market opportunity. AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft possess enormous resources and existing customer relationships. Each company is increasingly investing in vertical solutions and specialized applications. Should they decide to prioritize specialized AI agents for regulated industries, they could mobilize resources that dwarf Articul 8's.
However, cloud providers face structural challenges in competing directly. Their existing business model depends on commodity cloud services. Vertical specialization requires different go-to-market, pricing, and organizational structures. Many large organizations implement specialization poorly, encountering internal friction and slower execution. Articul 8's advantage lies in remaining more nimble and specialized than large incumbents can easily become.
Customer Concentration Risk
With 29 paying customers and
The risk is mitigated somewhat by the nature of regulated industries, where switching costs are high once systems are deeply integrated. However, customers can reduce spending or cancel during economic downturns or if they believe competitive alternatives have emerged.
Technical Risk and Knowledge Codification Challenges
Articul 8's competitive advantage rests substantially on the ability to codify specialized domain knowledge into AI systems. This process is inherently complex—domain expertise often resides with limited numbers of experts, and translating expertise into trainable AI systems requires specialized talent and methodologies.
If Articul 8's knowledge codification approaches prove less effective than anticipated, or if the company fails to hire sufficient domain expertise, product differentiation could erode quickly. Additionally, as AI capabilities broadly improve, the competitive advantage from specialized training could diminish.
Regulatory Risk
Regulated industries present regulatory risk alongside opportunity. Changes in regulations—particularly regarding AI use in regulated contexts—could impact addressable market. For instance, if regulators impose restrictions on AI decision-making authority or requirements that exceed Articul 8's current architecture capabilities, the company could face challenges.
However, Articul 8's focus on explainability and auditability aligns well with likely regulatory evolution. The company appears well-positioned for regulation that emphasizes understanding and controlling AI behavior.

Strategic Implications and Industry Trends
The Enterprise AI Market Bifurcation
Articul 8's success, if it continues, will validate a thesis about enterprise AI market structure: the market will bifurcate into general-purpose commodity solutions (provided by cloud giants and open-source models) and specialized vertical applications (provided by focused vendors). This bifurcation parallels historical software market development, where infrastructure commoditized while application layer remained specialized.
If this thesis proves correct, venture investors should expect emergence of multiple specialized vendors across different verticals. Articul 8's current advantage lies in moving early into this market structure and establishing leadership in regulated industries. First-mover advantages in enterprise software are real but not deterministic—execution quality and customer relationships matter as much as timing.
Implications for Legacy Enterprise Software Vendors
Articul 8's emergence poses questions for traditional enterprise software vendors. Companies like SAP, Oracle, and Salesforce built enormous businesses by providing comprehensive solutions to specific industries. Now they face competition from specialized AI-native vendors that provide narrow solutions solving specific problems with superior AI capabilities.
Established vendors have advantages—customer relationships, implementation expertise, integration with existing systems—but disadvantages in organizational agility and AI specialization. The competitive outcome remains uncertain, but likely involves:
- Established vendors acquiring specialized AI companies to incorporate capabilities
- Established vendors developing in-house specialized solutions through significant investment
- Specialized vendors growing independently and eventually achieving acquisition-scale valuations
Articul 8 appears positioned for success under any of these scenarios, though long-term outcomes depend on execution quality.
The Future of Enterprise AI Architecture
Articul 8's on-premise deployment model and architectural choices suggest evolving thinking about enterprise AI architecture. Rather than centralized AI platforms serving all use cases, enterprises will increasingly deploy specialized AI systems optimized for particular business functions. These systems will operate within customer infrastructure, integrate with existing systems, and be tailored to specific domains.
This architectural evolution carries implications for cloud providers, software vendors, and enterprises themselves. Cloud providers must adapt business models to accommodate on-premise deployment. Enterprises must develop governance, security, and integration approaches for managing multiple specialized AI systems. Traditional vendors must develop new capabilities and organizational structures.
Comparing Specialized Enterprise AI Solutions
Articul 8 vs. General-Purpose AI Platforms
| Dimension | Articul 8 Specialized Approach | General-Purpose AI Platforms | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | On-premise customer infrastructure | Cloud-based shared services | Data sovereignty vs. simplicity |
| Customization | Extensively domain-specialized | Minimal customization available | Accuracy vs. flexibility |
| Pricing | Premium application licensing | Consumption-based or seat licenses | Higher CAC, better retention |
| Implementation | Weeks for configured deployments | Months for custom implementations | Time-to-value vs. flexibility |
| Explainability | Designed for regulatory compliance | Limited transparency on decision reasoning | Compliance vs. capability |
| Scaling | Vertical specialization first, then other industries | Horizontal across all use cases | Depth vs. breadth |
Target Customer Segments
Articul 8's target customers share common characteristics that influence vendor selection:
- Regulation-intensive industries requiring explainability and data control
- Large enterprises with sufficient budgets for specialized solutions
- Digital-forward organizations willing to adopt new AI approaches
- Companies with integration complexity benefiting from on-premise deployment
- Risk-averse buyers in high-consequence industries
General-purpose AI platforms appeal to different segments:
- Cloud-native startups with minimal legacy infrastructure
- Cost-conscious buyers in non-regulated sectors
- Organizations prioritizing speed over customization
- Broad application needs across multiple use cases
- Simple integration requirements with existing cloud infrastructure
Alternative Vendor Approaches
Other vendors pursue different specialization strategies:
Vertical Cloud Solutions: Companies like Veeva Systems specialize in life sciences cloud, incorporating AI into purpose-built platforms. This approach combines specialization with cloud deployment, contrasting with Articul 8's on-premise focus.
Consulting-Led AI Implementation: Firms like Deloitte and Accenture develop specialized AI capabilities through consulting engagements. They lack the product focus of dedicated vendors but offer implementation breadth and customer relationships.
Legacy Vendor AI Extensions: Oracle, SAP, and Salesforce extend existing platforms with AI capabilities. They leverage existing customer relationships but face organizational complexity and slower innovation cycles.
Open-Source Specialization: Organizations like Hugging Face develop specialized open-source models for specific domains. This approach provides flexibility and cost-efficiency but requires significant internal engineering capability for deployment and customization.

Emerging Alternatives for Specialized Enterprise AI Needs
AI-Powered Automation Platforms as Complementary Solutions
While Articul 8 focuses on specialized vertical applications, emerging AI-powered automation platforms serve complementary needs for enterprises managing multiple tools and workflows. These platforms automate routine business processes using AI agents, enabling organizations to improve efficiency across diverse functions without deploying purpose-built applications for each process.
Platforms like Runable offer flexible, cost-effective automation capabilities at the enterprise level. Starting at $9/month, Runable provides AI agents for document generation, content creation, and workflow automation—capabilities that many enterprises need across multiple departments. Organizations using Articul 8's specialized vertical applications might simultaneously deploy Runable for broader automation needs—internal report generation, documentation, content creation—that don't justify purpose-built applications.
This complementary positioning suggests enterprises won't adopt single monolithic solutions but will assemble toolkits combining specialized applications (like Articul 8) with general automation platforms (like Runable) and legacy systems (ERP, CRM, etc.). The ability to integrate across this ecosystem becomes critical.
Workflow Automation and Developer-Focused Tools
Developer-focused automation platforms represent another emerging category. As enterprises increasingly employ development teams to integrate and customize enterprise AI, platforms that enable developers to rapidly build and deploy AI agents become valuable. Runable's positioning as a developer-centric automation platform with AI slide generation, AI documentation, and automated workflow capabilities addresses this emerging need.
For technical teams at enterprise customers of Articul 8, tools like Runable provide lightweight automation capabilities for operational tasks. A team deploying Articul 8's energy grid optimization AI agent might use Runable to automate related tasks—generating daily reports, creating presentations for stakeholder meetings, or managing documentation. This integration between specialized vertical applications and general automation platforms represents the practical reality of enterprise AI deployment.
Cost Efficiency and Implementation Speed
Organizations evaluating enterprise AI solutions increasingly emphasize cost efficiency and time-to-value. Articul 8's strength lies in providing comprehensive, purpose-built applications for high-value use cases. However, enterprises also need to address numerous lower-value automation opportunities that don't justify specialized application development. This is where cost-effective platforms like Runable provide value—enabling automation of routine tasks at minimal cost.
A financial services firm deploying Articul 8 for sophisticated risk analysis might simultaneously deploy Runable for automating routine report generation and documentation—tasks that currently consume administrative staff time but don't justify custom development. This approach balances sophisticated capabilities for critical decisions with cost-effective automation for routine operations.
Future Outlook: Articul 8's Growth Trajectory
Medium-Term Projections (Next 2-3 Years)
Based on current metrics and market dynamics, Articul 8 likely achieves several milestones within the next 2-3 years:
Customer Base Expansion: Growing from 29 to 75-100+ paying customers, with deeper penetration in target verticals and geographic expansion to Europe and Asia driving volume growth.
Revenue Acceleration: Annual recurring revenue likely reaches $120-150 million by year-end of 2027, representing 100%+ growth from current projections. This growth comes from customer expansion, increased spend per customer as new AI agents are deployed, and geographic expansion.
Product Portfolio Expansion: Articul 8 likely develops applications for additional regulated industry verticals, deepening addressable market. Vertical expansion into healthcare, insurance, and telecommunications could open entirely new markets.
Organizational Scaling: Employee count likely doubles or triples to 150-200, with increased investment in sales, customer success, and operations as the company matures. The R&D percentage might moderate from 80% to 60-70% as go-to-market teams expand.
Long-Term Strategic Options
Articul 8 faces several strategic options beyond year 3:
Independence and Continued Growth: The company could remain independent, continuing to grow until reaching
Strategic Acquisition: Cloud providers or established enterprise software vendors might acquire Articul 8 to expand specialized AI capabilities. Acquisition valuations for high-growth enterprise software companies typically reach $2-5 billion, representing substantial venture returns.
Consolidation and Ecosystem Building: Articul 8 could acquire competing or complementary vendors, building a consolidated platform across multiple verticals. This approach accelerates geographic expansion and capability breadth but requires capital and integration execution.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Evolution
Articul 8's ultimate success depends on several external factors:
Cloud Provider Response: If AWS, Google, and Microsoft seriously prioritize vertical specialization, they could eventually capture market share. However, structural factors favor focused vendors over generalists.
Regulatory Evolution: Regulations favoring explainability and data control could accelerate Articul 8's market. Conversely, regulations enabling cloud-based AI could favor general-purpose solutions.
Open-Source Model Evolution: Improvements in open-source AI models could enable more organizations to build in-house specialized capabilities, potentially reducing addressable market for specialized vendors.
Economic Cycles: Enterprise AI adoption typically accelerates during growth periods and slows during downturns. Articul 8's success depends partly on continued economic growth and enterprise investment capacity.
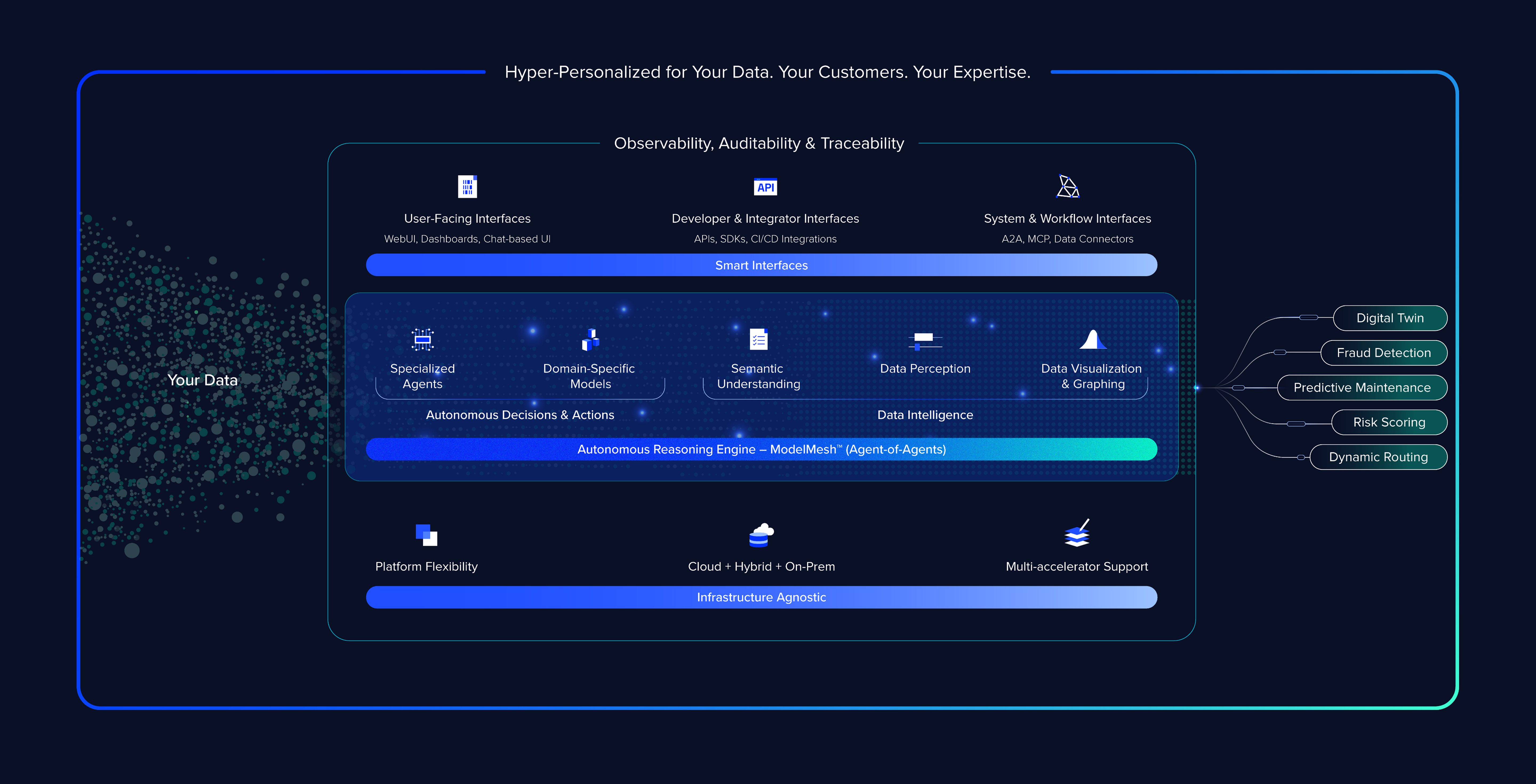
Conclusion: Strategic Implications and Investment Perspective
Articul 8's Series B funding round and $500 million valuation reflect broader trends in enterprise AI market development. The company represents a bet that enterprise AI will bifurcate into specialized applications and commodity platforms, with successful specialists commanding significant value. This thesis appears reasonable given market dynamics and regulatory evolution.
The company's execution has been impressive—establishing a customer base generating $90 million in contract value and achieving revenue positivity within 18 months of spinout demonstrates operational excellence. Geographic expansion backed by strategic investors with regional expertise suggests thoughtful capital allocation.
However, substantial risks remain. Competitive response from cloud providers, potential regulatory restrictions, and challenges in expanding specialization to adjacent verticals could limit ultimate scale. The distinction between a $500 million acquisition and a multi-billion-dollar independent company depends on execution quality and market conditions over the next 2-3 years.
For enterprises in regulated industries seeking specialized AI solutions, Articul 8 represents a credible option with proven customer traction and technical capability. For investors evaluating enterprise AI opportunities, Articul 8 exemplifies the specialized vendor thesis and provides early returns if the market structure develops as expected.
The company's story remains in early chapters. Scaling from
For teams evaluating enterprise automation needs more broadly, platforms like Runable complement Articul 8-type specialized solutions, addressing the full spectrum of automation requirements from high-value domain-specific applications to routine operational tasks requiring cost-effective automation. The future enterprise AI stack likely combines specialized vendors for critical functions with flexible, developer-friendly automation platforms for routine operations.
FAQ
What is Articul 8 and how does it differ from general-purpose AI solutions?
Articul 8 is an enterprise AI company spun out from Intel in early 2024 that develops specialized AI systems for regulated industries rather than general-purpose models. Unlike cloud-based AI platforms that optimize for broad use cases, Articul 8 creates domain-specific applications and AI agents tailored to particular business functions in energy, manufacturing, aerospace, financial services, and semiconductors. The company deploys systems within customers' own IT environments rather than relying on shared cloud infrastructure, providing superior data sovereignty, auditability, and regulatory compliance.
How has Articul 8 achieved its $500 million valuation so quickly?
Articul 8's valuation reflects strong execution across several metrics:
What are the advantages of Articul 8's on-premise deployment model for enterprise customers?
On-premise deployment provides several critical advantages for regulated industries: data sovereignty (sensitive information never leaves customer networks), complete audit trails and decision logging under customer control, integration with legacy systems without requiring cloud connectivity, and regulatory compliance aligned with industry-specific requirements. These advantages are particularly valuable for energy, manufacturing, and financial services companies where data residency, compliance, and system control are non-negotiable requirements.
Which industries and use cases benefit most from Articul 8's specialized AI agents?
Articul 8 primarily targets regulated industries including energy (grid optimization and renewable integration), manufacturing and semiconductors (quality control and process optimization), aerospace (defect detection and safety assurance), and financial services (due diligence and compliance automation). Within these sectors, use cases involving high-consequence decisions, regulatory requirements for explainability, or complex domain-specific optimization create the strongest value propositions for specialized AI agents.
How does Articul 8's business model generate revenue compared to other enterprise AI companies?
Unlike AI companies selling models or licenses, Articul 8 sells fully-formed software applications and AI agents as recurring license fees rather than consumption-based pricing. This application-centric model enables higher pricing, reduces customer acquisition friction (no integration required), and improves unit economics. With
What competitive threats does Articul 8 face from cloud service providers?
The primary competitive risk comes from AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure developing specialized AI applications for regulated industries. However, cloud providers face structural disadvantages: their business models depend on commodity pricing rather than vertical specialization, organizational complexity slows decision-making, and they must maintain neutrality across customer bases. Articul 8's advantage lies in focused specialization, rapid iteration, and alignment of all incentives toward success in target verticals, advantages difficult for large organizations to replicate.
How is Articul 8 using Series B funding to accelerate growth?
Articul 8 plans to allocate Series B proceeds primarily to research and product development (maintaining technical differentiation and expanding domain applications) and international expansion with emphasis on Europe and Asia. The two-installment structure reflects pragmatic capital gating—the company receives initial funding to pursue priorities, then demonstrates milestone achievement before accessing additional capital. European expansion leadership from Adara Ventures (backed by the European Investment Fund) signals strategic alignment with regulatory environments favoring Articul 8's on-premise, explainable AI approach.
What alternatives exist to Articul 8 for organizations seeking enterprise AI solutions?
Alternatives span several categories: cloud-based vertical solutions like Veeva Systems for specific industries, legacy vendor AI extensions from Oracle, SAP, and Salesforce that add AI capabilities to existing platforms, consulting-led implementations from firms like Deloitte, and general automation platforms like Runable that address broad automation needs at lower cost ($9/month). For organizations with diverse automation requirements spanning specialized applications and routine operational tasks, combining Articul 8-type specialized solutions with flexible automation platforms like Runable often provides optimal coverage.
How does Articul 8's knowledge graph architecture improve AI explainability and regulatory compliance?
Articul 8's knowledge graph architecture represents information as interconnected concepts and relationships, enabling AI agents to reason about complex dependencies while maintaining explainability. When an agent makes a decision, the reasoning path through the knowledge graph provides clear justification—critical for regulated industries where regulators and auditors require understanding of how decisions were made. This structured reasoning approach also enables more reliable learning constrained by domain structure, producing more trustworthy AI systems than unstructured pattern discovery methods.
What factors will determine Articul 8's long-term success or acquisition likelihood?
Success depends on sustained execution across several dimensions: customer acquisition acceleration to diversify beyond current 29 customers, product expansion into adjacent verticals creating additional revenue streams, geographic scaling in Europe and Asia maintaining growth rates, and technical differentiation maintenance through continuous R&D investment. The company could pursue independence building toward multi-billion-dollar scale, strategic acquisition by cloud or enterprise software companies at $2-5 billion valuations, or consolidation through acquiring competing vendors. Medium-term metrics (customer count, revenue growth, geographic expansion pace) will indicate which path becomes most likely within 24-36 months.

Key Takeaways
- Articul8 achieves 90M contract value, $57M ARR) and enterprise sales success in 18 months
- Specialized AI agents for regulated industries command premium pricing and demonstrate stronger enterprise adoption than general-purpose AI models
- On-premise deployment model provides critical advantages for data sovereignty, auditability, and regulatory compliance in regulated sectors
- Cloud providers represent primary competitive threat but face structural disadvantages compared to focused specialized vendors
- International expansion in Europe and Asia-Pacific, backed by strategic investors, positions Articul8 for significant scaling
- Enterprise automation needs increasingly require combining specialized applications (like Articul8) with flexible automation platforms (like Runable) rather than single monolithic solutions
- Knowledge graph architecture enables explainable AI reasoning critical for regulated industries and compliance requirements
- Company's 80% R&D focus indicates confidence that product differentiation remains primary competitive advantage against larger incumbents
Related Articles
- Grok Business and Enterprise: Elon Musk's Answer to ChatGPT [2025]
- Why Navan's IPO Flopped While AI Companies Soar: The B2B SaaS Reckoning [2025]
- Nvidia Cosmos Reason 2: Physical AI Reasoning Models [2025]
- Nvidia Vera Rubin AI Computing Platform at CES 2026 [2025]
- EU Tech Enforcement 2026: What Trump's Retaliation Threats Mean [2025]
- Data Sovereignty for Business Leaders [2025]




