How Biotics AI's FDA-Approved Fetal Ultrasound AI Changes Prenatal Care
There's a quiet crisis in American healthcare that doesn't make headlines the way other medical emergencies do. The United States has one of the worst prenatal outcomes among high-income nations. For Black women specifically, the maternal mortality rate sits at alarming levels, and one of the biggest culprits is something most people never think about: poor quality ultrasound imaging during pregnancy.
That's where Biotics AI comes in.
In January 2025, the startup announced something significant. After nearly three years navigating the FDA approval process, they received clearance for their AI-powered software designed to detect fetal abnormalities in ultrasound images. This isn't just another medical tech announcement. It represents a fundamental shift in how prenatal care could work across America, particularly for vulnerable populations where diagnostic disparities run deepest.
The company was founded by Robhy Bustami, whose personal connection to obstetrics runs deep. Raised in a family where his mother, sister, and uncle all worked as obstetricians, he spent his childhood in hospitals witnessing both the miracles and the gaps in maternal care firsthand. After studying computer science at UC Irvine and teaching himself to code, Bustami realized he could apply artificial intelligence to fix something the medical community had struggled with for decades: the inconsistency of ultrasound interpretation.
The Problem Biotics AI Actually Solves
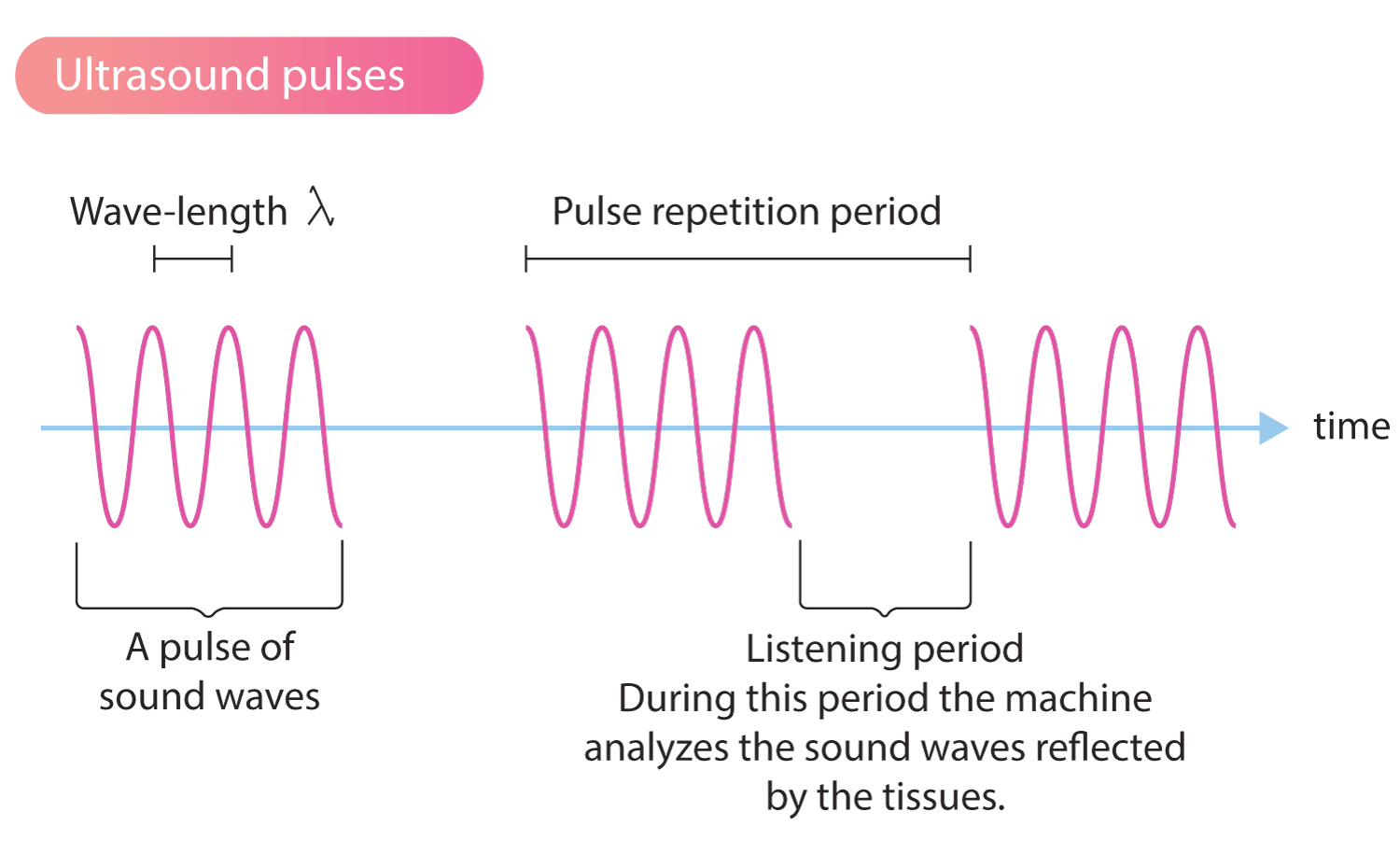
Here's what most people don't realize about ultrasounds: they're deceptively difficult to interpret correctly. An obstetrician or maternal-fetal medicine specialist might spend years learning to spot anatomical markers, abnormalities, and warning signs that can literally save a baby's life or prepare parents for serious complications ahead.
But here's the real issue. Not every ultrasound is performed by a specialist. Many are done by techs with varying levels of training, in settings with older equipment, by practitioners who might be tired after their eighth scan of the day. Image quality varies wildly. The interpretation can depend heavily on the individual performing the scan. Miss a critical marker, and a serious condition goes undiagnosed until delivery or later, when intervention becomes infinitely more complicated and expensive.
The prenatal ultrasound has become what experts call the "cornerstone" of pregnancy monitoring. It's the primary tool for detecting everything from structural abnormalities to growth restrictions to placental complications. But when image quality drops or critical anatomical views aren't captured, the entire system breaks down.
Bustami saw this problem firsthand. He understood that low-quality ultrasound images don't just cause inconvenience. They lead to missed diagnoses, delayed care, and preventable complications. They disproportionately affect communities with less access to top-tier medical centers, creating a vicious cycle where the people who most need good healthcare receive the worst quality imaging.
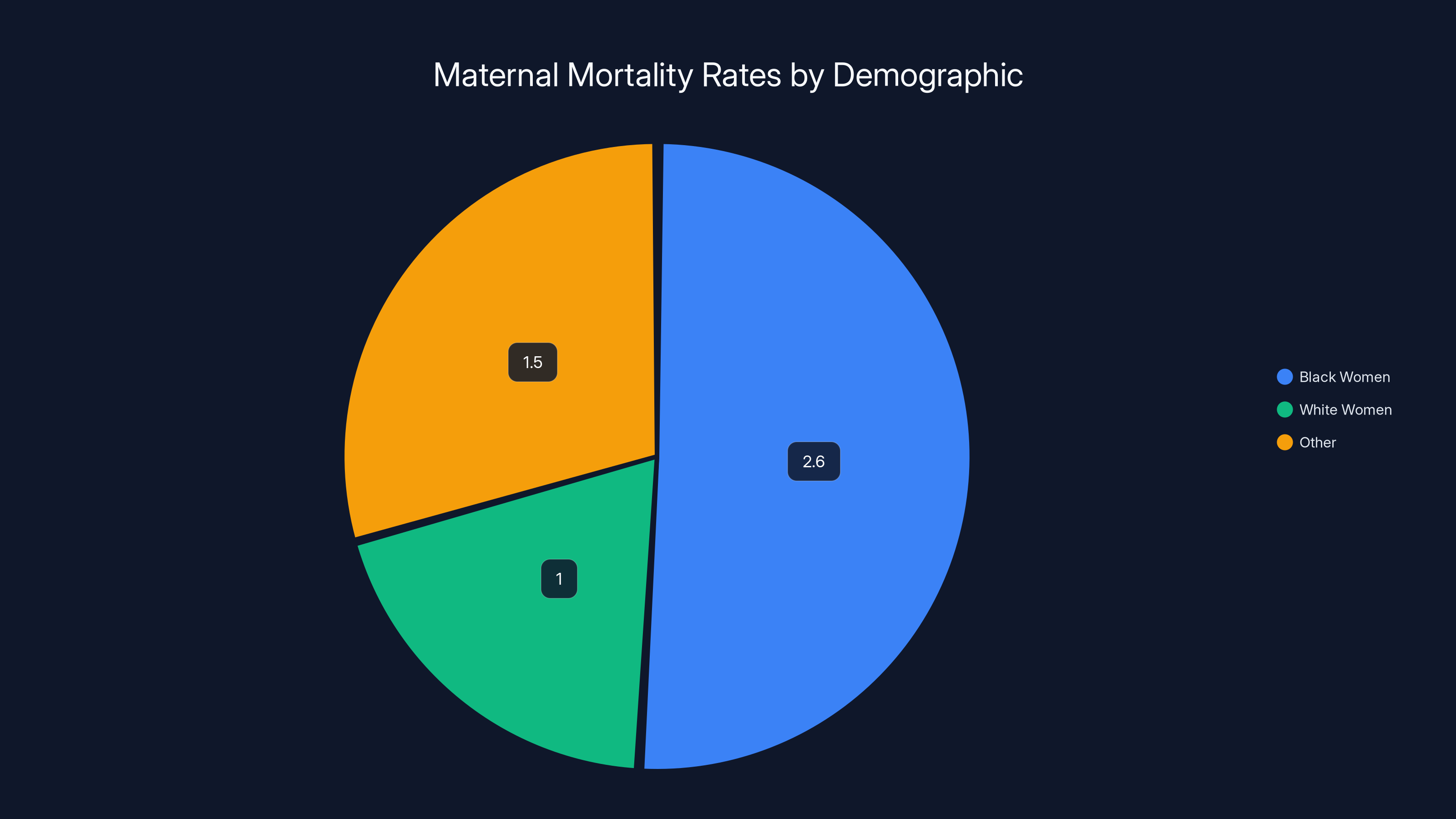
Black women face maternal mortality rates approximately 2.6 times higher than white women, highlighting significant healthcare disparities. Estimated data.
Building the Biotics AI Platform: Computer Vision Meets Obstetrics
When Bustami and his cofounders Salam Khan, Chaskin Saroff, and Dr. Hisham Elgammal founded Biotics AI in 2021, they started with a specific technical challenge: could they build a computer vision system that could evaluate ultrasound image quality, detect anatomical completeness, and identify potential abnormalities?
The technical approach sounds straightforward in theory. Train a deep learning model on thousands of ultrasounds, teach it to recognize patterns, deploy it to flag concerning images. In reality, this is extraordinarily complex.
First, there's the training data problem. To build a reliable AI system, you need examples of what normal looks like and what abnormal looks like. You need images from diverse populations, different equipment, different settings, and different skill levels. The company trained their models on over 11,000 ultrasounds, but that's just the starting point. The real challenge isn't the volume of data. It's the representativeness.
Bustami emphasized something critical during discussions about the FDA approval process: the hardest part wasn't building the actual AI models. It was ensuring the technology performed reliably in the real world, especially when it came to demographics with the highest risk for tragic outcomes. This distinction matters enormously.
Lots of AI systems work great in controlled settings with carefully curated data. They fail spectacularly when deployed to the messy reality of actual clinical practice. That's where demographics matter. If your training data overrepresents certain populations and underrepresents others, your system will perform beautifully for the majority and terribly for the minority. In obstetrics, this isn't acceptable. The women most at risk of maternal complications need the best technology, not the worst.
The FDA Approval Process: Why Three Years?
When someone asks why it took Biotics AI nearly three years to get FDA approval, the knee-jerk response is usually "regulatory burden" or "bureaucratic slow-walking." The real answer is more nuanced and actually reveals something important about how medical technology should be developed.
The FDA classification for Biotics AI's software is likely a Class II medical device or possibly a Class III, depending on the specific intended use and risk classification. This requires what's called "510(k) substantial equivalence" or potentially a Premarket Approval application. Either way, it means rigorous testing, comprehensive clinical validation, and proof that the technology performs as claimed, doesn't create unexpected harms, and works reliably across the populations it claims to serve.
Bustami said something revealing about why it took so long: it wasn't the regulatory work alone. It was how they organized their internal processes. The company discovered early on that engineering, product development, clinical validation, and regulatory strategy can't be sequential activities. They have to happen in parallel and be deeply integrated from the start.
Think about this from a regulatory perspective. If you build your product first, then do clinical testing, then figure out what regulatory pathway you need, you're guaranteed to hit massive snags. You'll discover during testing that you need to measure something you didn't build the system to measure. You'll realize the clinical evidence you need doesn't align with what your product can provide. You'll have to rebuild everything.
Bustami's team did the hard work upfront. They designed the product, planned the clinical validation, and mapped out the regulatory pathway simultaneously. This meant early conversations with the FDA, rapid iteration based on feedback, and building features from day one that would support evidence generation.
By structuring the work this way, "we were able to move quickly," according to Bustami. Three years still sounds long, but that's actually competitive for AI medical devices. Many take five to seven years. The difference is whether you're working with the regulatory process or against it.

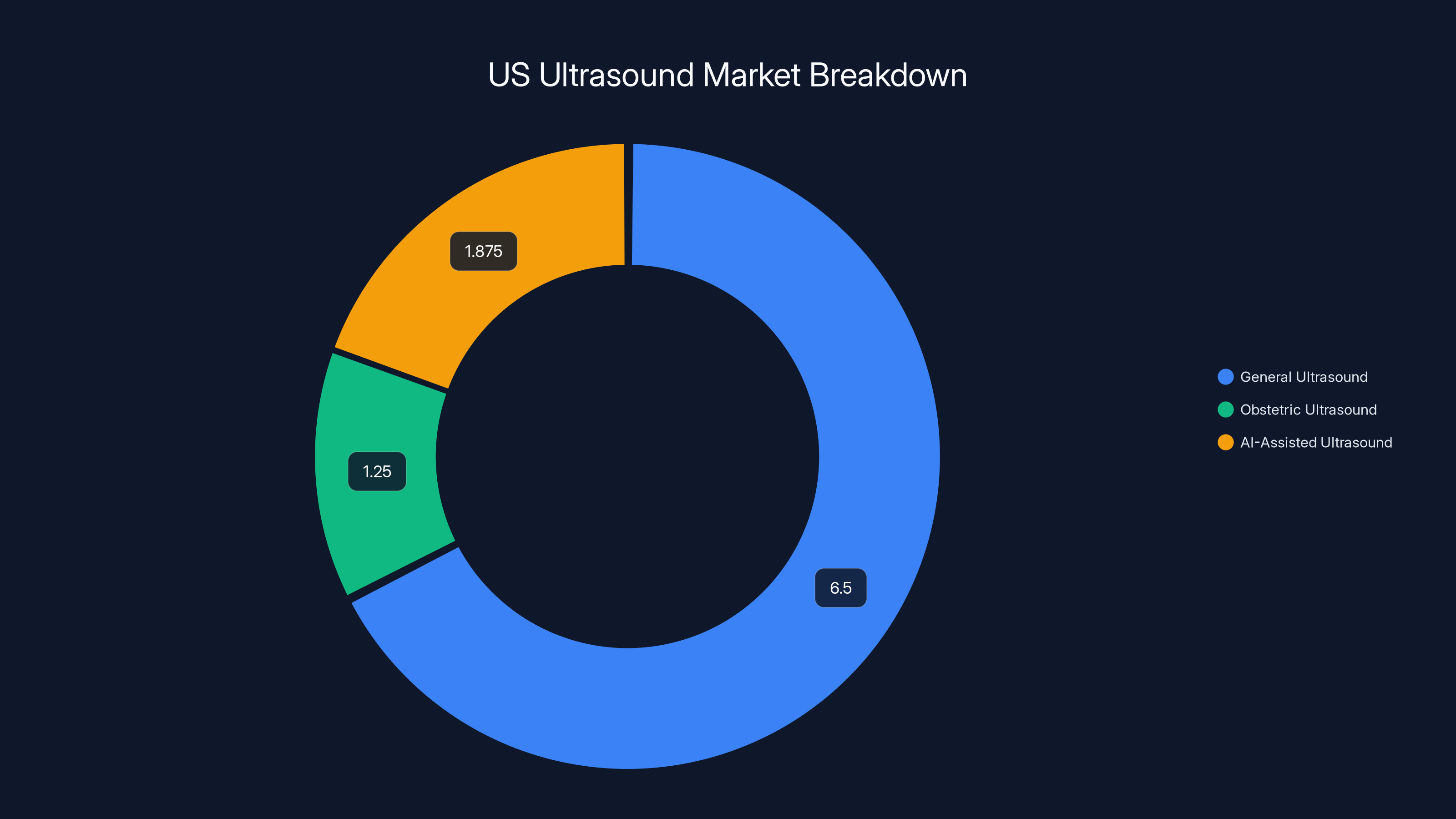
The US ultrasound market is valued at
How Biotics AI Actually Works in Practice
So what does the technology actually do when a clinician uses it? The Biotics AI platform provides several interconnected capabilities designed to work within existing clinical workflows rather than upending them.
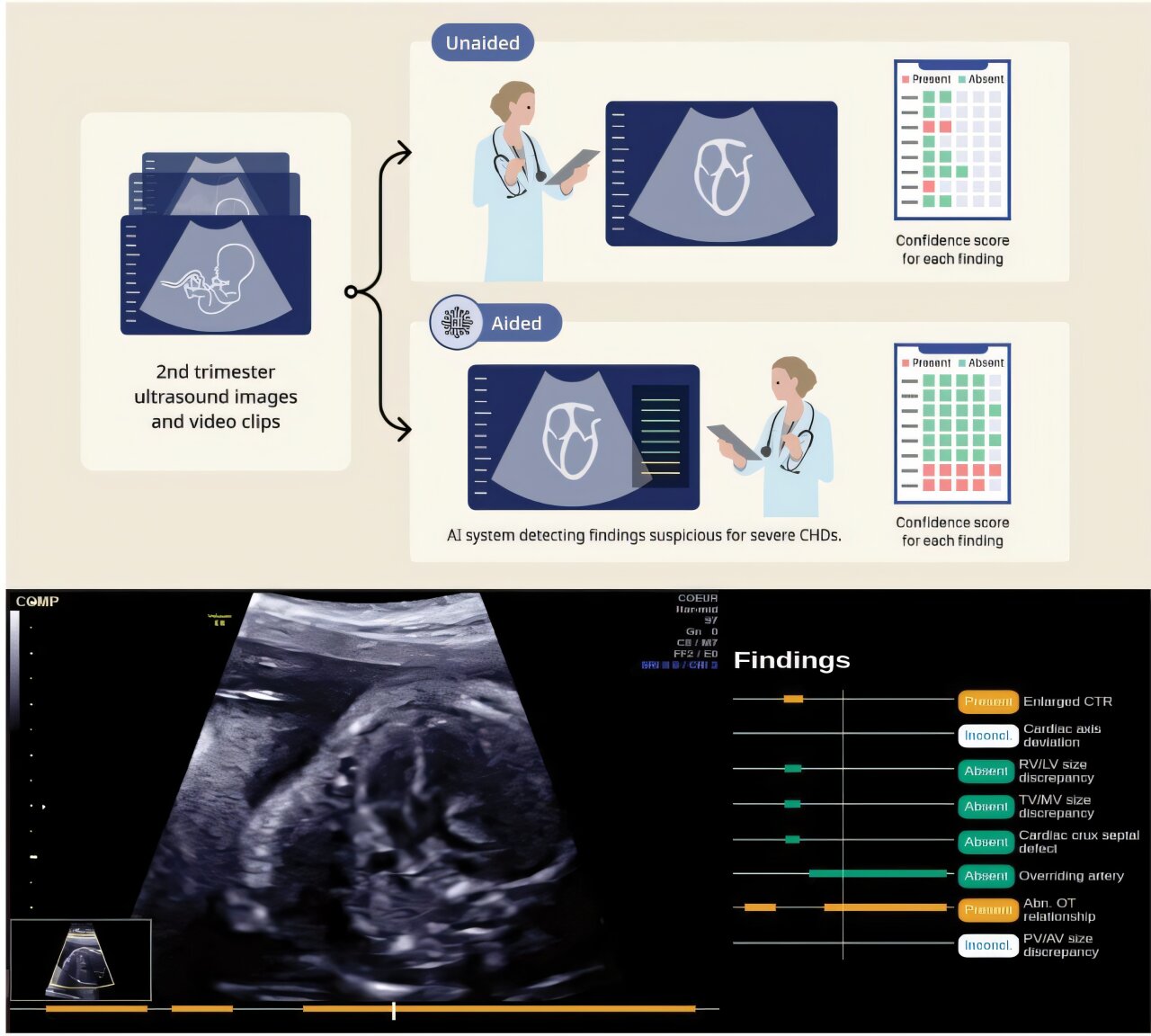
Fetal Ultrasound Quality Assessment: When an ultrasound image comes through the system, the AI evaluates whether the image quality is sufficient for diagnostic interpretation. It can detect if the image is too dark, blurry, shadowed, or otherwise compromised. This alone solves a real problem. Clinicians can immediately know whether they need to reposition, retry, or adjust settings rather than spending time trying to interpret a bad image.
Anatomical Completeness Verification: A comprehensive fetal ultrasound requires capturing specific anatomical views. There's a list of required images depending on gestational age. Getting all of them takes skill and experience. The AI can verify that the sonographer has captured the complete set of required views, similar to a quality checklist but automated and real-time.
Automated Abnormality Detection: The system can identify structural abnormalities and flag them for clinician review. This is where computer vision becomes genuinely powerful. The AI can process millions of pixel patterns and compare them to what it learned from training data. It might spot a marker of spina bifida, a sign of cardiac abnormality, or evidence of growth restriction faster than human review in some cases.
Automated Reporting: Rather than clinicians dictating or manually typing reports, the system can generate structured reports based on the images and findings. This reduces clerical work, standardizes reporting, and makes it easier for downstream clinicians to find critical information quickly.
Clinical Workflow Integration: This is crucial and often overlooked. The technology doesn't work in isolation. It integrates with existing hospital information systems, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), and EHRs (Electronic Health Records). Clinicians see the AI output within their normal workflow, not in a separate disconnected system.

The Clinical Validation and Testing That Earned FDA Clearance
Getting FDA approval means the company had to demonstrate several things through rigorous clinical testing. They needed to show that:
-
The system works as intended: When it identifies an abnormality, it actually identifies abnormalities. When it says an image quality is poor, the image actually is poor or acceptable. This requires sensitivity and specificity metrics showing how often the system is correct.
-
It works across diverse populations: This was the explicit focus for Biotics AI. They needed to prove the system performs reliably for different ethnic groups, different body habitus, different equipment manufacturers, and different settings. Regulatory agencies now require health equity analysis for medical devices, and this was central to Biotics AI's strategy.
-
It doesn't cause harm: New technology can introduce new failure modes. For instance, if the AI system confidently identifies a false abnormality, a clinician might make unnecessary interventions based on that false flag. The testing needed to characterize these risks.
-
Clinicians understand how to use it: The system needed documentation, training, and clear communication about what it can and can't do. Users need to understand when to trust the AI, when to override it, and when to seek additional evaluation.
-
It integrates properly with clinical workflows: They had to test real-world deployment in actual clinical settings to ensure the system didn't introduce workflow delays or errors.
This testing is expensive and time-consuming, which is why it takes years. But it's also why the resulting approval actually means something. It's not rubber-stamp approval. It's evidence-based validation.
Why Healthcare Disparities Matter: The Human Context
Bustami has been vocal about the healthcare disparities that motivated Biotics AI in the first place. In an environment where disparities in healthcare outcomes are well documented, it becomes ethically critical to demonstrate consistent performance across patient subgroups, not just in idealized cases.
Here's the problem in stark terms: if you build an AI system trained predominantly on imaging from wealthy hospitals with modern equipment and highly trained sonographers, it will work beautifully in wealthy hospitals with modern equipment and highly trained sonographers. It will fail in under-resourced clinics serving marginalized communities. The women who most need the technology's help receive the worst performance.
Bustami understood this from the beginning because he grew up watching his family provide maternal care to diverse populations. He saw firsthand how outcomes diverged based on access and quality. Building Biotics AI meant ensuring the system worked reliably for the communities where it mattered most, not just in the easiest cases.
This isn't corporate social responsibility window dressing. This is about fundamental product design. The company built diverse representation into the training data from day one. They tested extensively on underrepresented populations. They made this validation explicit in their FDA submission. This is how medical technology should be built.
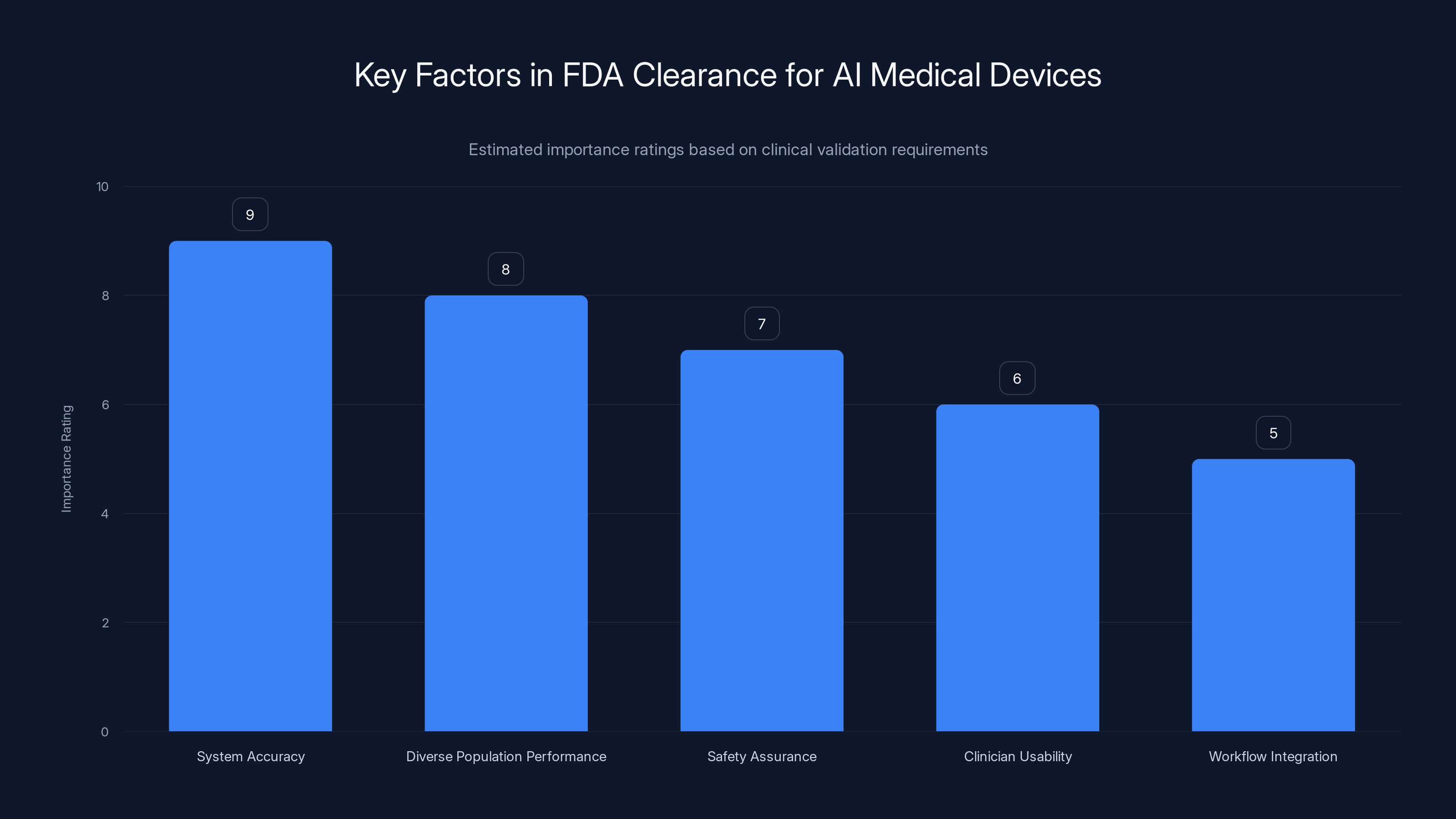
Estimated data showing the relative importance of different factors in achieving FDA clearance for AI medical devices. System accuracy and diverse population performance are top priorities.
Market Scale: What Comes Next
Now that Biotics AI has FDA clearance, the question becomes: how does the company scale? There are about 130,000 obstetric and gynecologic providers in the United States. Roughly 20 million pregnancies occur annually in America. The addressable market for ultrasound quality improvement, abnormality detection, and workflow automation is enormous.
Bustami has stated that the company's next focus is scaling across various health systems nationwide. This means a few things:
Hospital Partnerships: Biotics AI needs to partner with hospital networks and healthcare systems to deploy the technology. Each integration requires technical work, change management, and training. It's not fast, but it's profitable and sustainable.
Distribution Strategy: The company could work through ultrasound equipment manufacturers, through healthcare IT vendors who sell to hospitals, or through direct sales to health systems. The optimal strategy probably involves multiple channels.
Reimbursement: A critical question for any medical device is whether insurance will reimburse its use. The technology needs to demonstrate cost-effectiveness and improved outcomes that justify reimbursement codes. This is an area where Biotics AI will need to invest in health economic studies and real-world evidence.
Regulatory Expansion: FDA approval in the US is a start. Markets in Europe, Canada, and other developed nations have their own regulatory requirements. International expansion comes later but is part of scaling.
The Roadmap: Beyond Fetal Abnormality Detection
Bustami has signaled plans to add more features for fetal medicine and reproductive health beyond the core abnormality detection capability. This makes sense from both a product and business perspective.
Possible expansions might include:
Growth Assessment: AI could more precisely measure fetal growth markers and identify growth restriction earlier. The technology could automate the biometric measurements used to track fetal development.
Placental Analysis: The placenta is critical to pregnancy success, but placental abnormalities are often missed. AI could improve detection of placental insufficiency, abnormal invasion, or other complications.
Maternal Cardiovascular Assessment: Some clinical ultrasounds include assessment of maternal heart function and vascular changes in pregnancy. AI could support this analysis.
Extended Reproductive Health: Beyond pregnancy, the technology could potentially support gynecologic ultrasound interpretation, screening for pathology, or assessment of reproductive organs.
Each of these expansions would require separate clinical validation and likely separate FDA approvals. But they're all within the realm of ultrasound image analysis and abnormality detection, so the core technology foundation translates well.
The Competitive Landscape: Where Biotics AI Fits
Biotics AI isn't operating in a vacuum. Other companies are working on AI-powered ultrasound analysis, prenatal care improvement, and fetal medicine. However, FDA approval for fetal abnormality detection is still relatively rare, which gives Biotics AI a significant first-mover advantage in this specific indication.
Competitors might include:
Ultrasound Equipment Manufacturers: Companies like GE Healthcare and Philips are increasingly adding AI capabilities to their ultrasound machines. However, they tend to focus on image quality improvement rather than diagnosis support.
Standalone AI Companies: Various startups are building AI analysis tools for medical imaging, including ultrasound. However, many are more nascent and haven't navigated FDA approval yet.
Healthcare IT Platforms: Companies in the medical IT space might integrate or build AI ultrasound tools as part of broader clinical platforms. However, most don't have the specialized expertise in obstetric imaging.
Biotics AI's combination of obstetric domain expertise, AI sophistication, and FDA validation puts them in a strong position. The competitive advantage isn't permanent—others will get FDA approval eventually—but it provides a runway for market penetration and revenue growth.

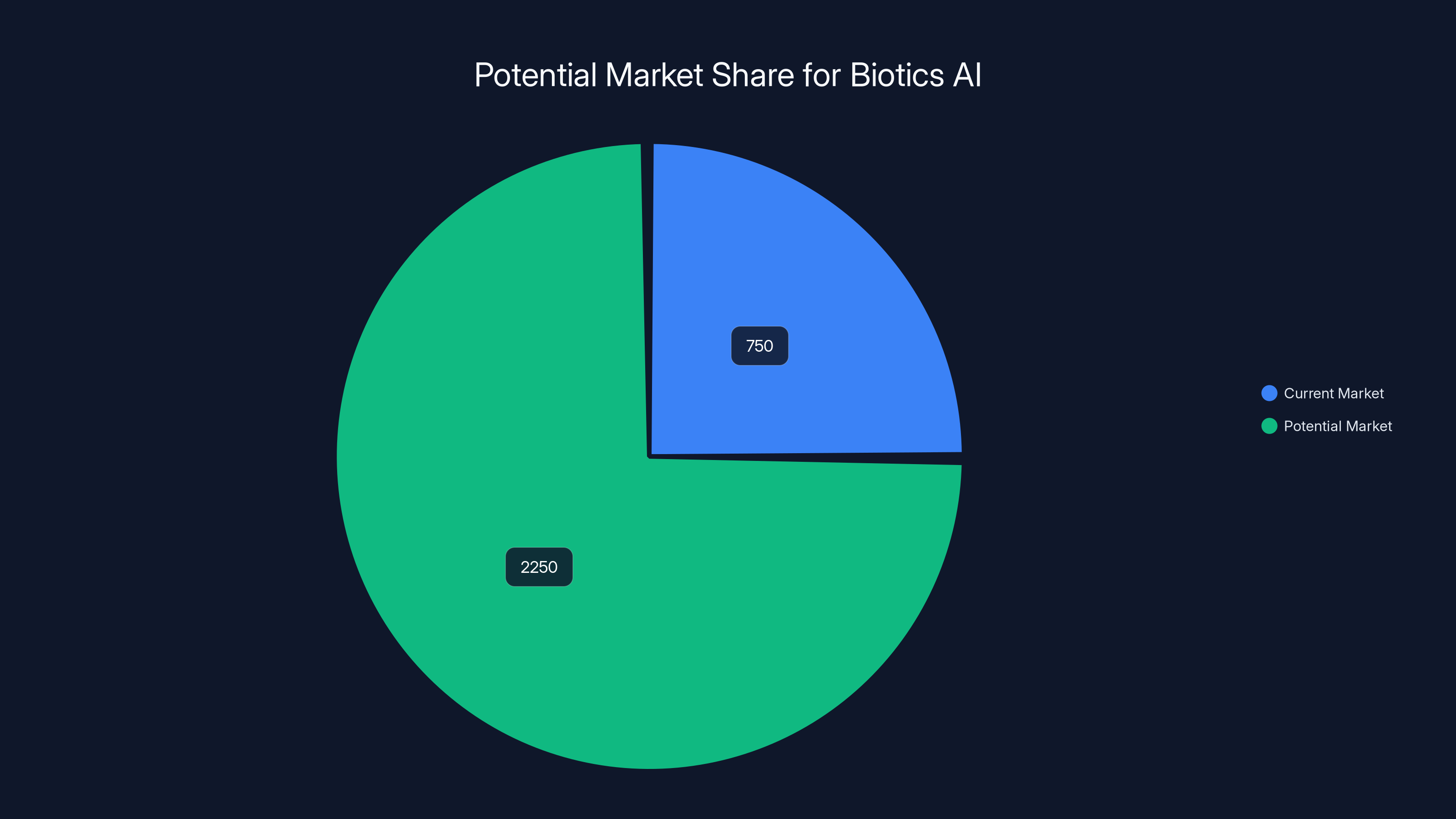
Biotics AI's addressable market ranges from
Real-World Impact: What FDA Approval Actually Changes
For clinicians wondering what FDA approval actually means for their daily work, here's the practical reality:
Liability Protection: With FDA approval, the device has undergone rigorous testing and validation. If a clinician uses the device appropriately and per its instructions, they have regulatory backing. This gives both clinicians and hospitals confidence to deploy the technology.
Reimbursement Eligibility: Hospital systems are more likely to invest in technology with FDA approval because reimbursement discussions become more grounded. The approval provides documentation that the technology is validated and appropriate.
Integration Possibilities: Approved medical devices can integrate more easily with hospital IT systems because compliance and security requirements are clearer. There are established pathways for integration.
Clinical Confidence: Clinicians are more likely to trust and use a technology that's been formally approved by the FDA. The approval carries weight in the clinical decision-making process.
Training and Adoption: FDA approval enables more sophisticated training and user education because the regulatory requirements ensure the material is accurate and complete.
From a patient perspective, FDA approval means that pregnant patients receiving ultrasounds at hospitals using Biotics AI have an additional layer of quality assurance and abnormality detection supporting their care.
The Broader Implications for AI in Healthcare
Biotics AI's FDA approval is part of a larger trend: the convergence of artificial intelligence and healthcare delivery. Several lessons emerge from Biotics AI's journey:
Integration Beats Innovation: The most successful medical AI isn't the most technically sophisticated. It's the AI that integrates seamlessly into how clinicians actually work and integrates with existing systems.
Equity Must Be Intentional: AI systems inherit the biases in their training data. Companies that want to build equitable technology must intentionally design for it, test for it, and validate it across populations.
Regulatory Clarity Accelerates Development: Companies that engage early with regulators and build regulatory requirements into product development move faster than those that iterate independently then face regulatory pushback.
Real-World Testing Is Non-Negotiable: Lab performance means nothing if the technology fails in clinical deployment. Any company developing medical AI needs to commit to extensive real-world validation.
Clinical Expertise Matters: Biotics AI succeeded partly because the founding team included clinicians who understood the actual problem. AI companies without domain expertise tend to build solutions to problems that don't really exist or that clinicians don't actually need solved.
The Numbers: Market Size and Opportunity
Let's put some numbers around what this market could look like. The US ultrasound market is worth roughly
These numbers assume reasonable penetration. They also assume that Biotics AI captures a meaningful market share, which depends on execution, partnerships, reimbursement success, and competitive response.
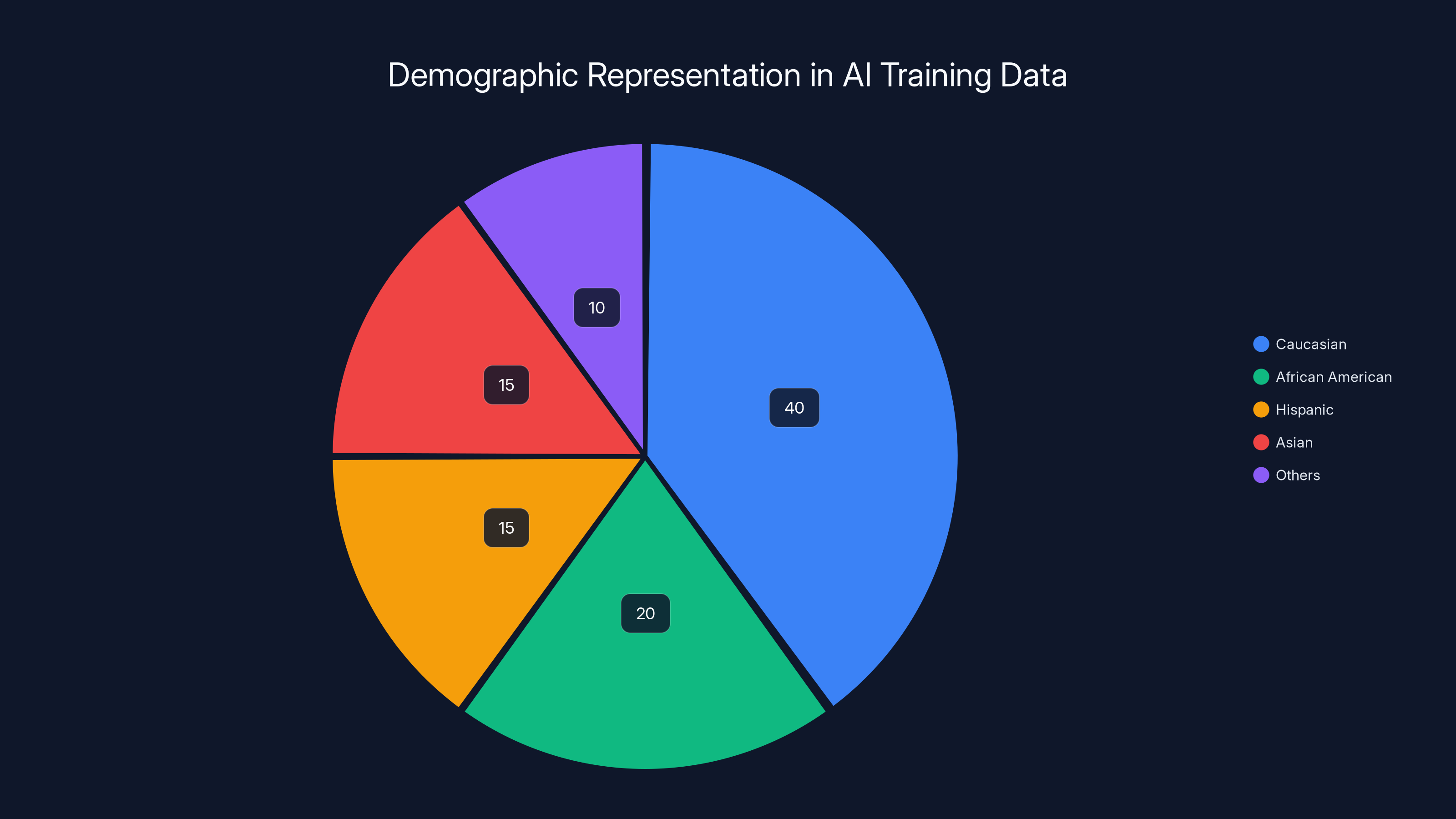
Estimated data shows potential underrepresentation of minority groups in AI training datasets, highlighting the importance of diverse data for reliable AI performance in obstetrics.
Future Trajectories: What Could Go Right or Wrong
What Could Go Right:
- Rapid adoption at major hospital networks leads to strong revenue growth
- Real-world evidence demonstrates improved outcomes and earlier abnormality detection
- Reimbursement gets established, making adoption a financial no-brainer
- The company successfully expands to other ultrasound applications
- International expansion accelerates growth
- The technology becomes considered standard of care for obstetric imaging
What Could Go Wrong:
- Clinicians resist adoption despite FDA approval due to workflow concerns or skepticism
- Reimbursement doesn't materialize, limiting hospital economics
- Competitive entrants with similar or better technology capture market share
- A high-profile failure or missed abnormality triggers liability concerns
- Integration challenges with legacy hospital IT systems slow deployment
- The company struggles to raise capital for scaling if early customer acquisition disappoints
The next 18-24 months will be critical for determining which trajectory the company follows.

The Startup Origin Story: From Disrupt to FDA Approval
Biotics AI's path from Tech Crunch Disrupt Battlefield competition winner to FDA-approved medical device is itself instructive. The Battlefield is where Tech Crunch showcases early-stage startups competing for recognition and media attention. Most startups that win Battlefield competitions get a boost in visibility but face the reality that most startups fail regardless of awards.
For Biotics AI to go from Battlefield recognition in 2023 to FDA approval by early 2025—roughly 18 months—suggests execution speed and focus. The team didn't get distracted chasing other applications or pivoting based on investor feedback. They stayed disciplined around the core mission: building AI that improves prenatal ultrasound quality and abnormality detection.
This kind of startup trajectory has become more common for AI-based healthcare companies. The technology is mature enough that building sophisticated AI systems is no longer the rate-limiting step. Regulatory approval and clinical validation are now the key bottlenecks. Companies that accept this reality and invest accordingly move faster than those trying to optimize purely for technical performance.
Implementation Considerations for Healthcare Systems
If you're a hospital administrator or department head considering Biotics AI deployment, here are key implementation questions:
Technical Integration: How does the software integrate with your existing PACS system, EHR, and ultrasound machines? What's the deployment timeline?
Training Requirements: How much staff training is needed? What's the learning curve? Do different types of staff (sonographers, physicians, administrators) need different training?
Workflow Impact: How does the tool change actual clinical workflows? Does it speed things up or introduce delays? Does it create new steps or eliminate them?
Liability and Credentialing: How should clinicians be credentialed to use the tool? What's the liability framework if the AI misses something?
Cost Analysis: What's the actual cost per ultrasound with the system? Does it improve reimbursement rates? What's the ROI timeline?
Change Management: How do you handle clinician resistance? What's your adoption strategy? Who are your early adopters and champions?
Outcome Tracking: How will you measure whether the implementation is actually improving patient outcomes? What metrics matter?
These questions are less about the technology itself and more about organizational readiness to implement it.
The Bigger Picture: AI-Driven Prenatal Care Transformation
Zoom out from Biotics AI specifically and think about what AI-powered prenatal care could look like in five or ten years:
Early Detection: AI systems improve early detection of issues that currently go undiagnosed until delivery or later in pregnancy, allowing for better preparation and intervention.
Remote Specialist Access: AI assistance could enable specialists to review ultrasounds asynchronously, improving access to expert interpretation for patients in underserved areas.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing ultrasound data in combination with other clinical information, AI could predict which pregnancies are at highest risk for complications, enabling preventive interventions.
Standardized Quality: AI ensures ultrasound quality and completeness is consistent across all settings, reducing diagnostic disparities based on where the scan is performed.
Reduced Maternal Mortality: If these improvements actually translate to better outcomes, the impact on maternal mortality—particularly among Black women and other marginalized groups—could be substantial.
Biotics AI is one piece of this larger transformation. But it's a meaningful piece because it tackles a core problem: the quality and interpretation of the fundamental diagnostic tool for prenatal care.
TL; DR
- FDA Approval Milestone: Biotics AI achieved FDA clearance for its AI software that detects fetal abnormalities in ultrasound images, marking significant progress in addressing prenatal healthcare disparities.
- Addressing Health Disparities: The technology was specifically designed and validated to work reliably across diverse populations, directly tackling maternal mortality disparities that disproportionately affect Black women.
- Three-Year FDA Process: What took three years wasn't bureaucratic delay but deliberate integration of product design, clinical validation, and regulatory strategy from the start, enabling faster approval than typical for medical devices.
- Scalable Market Opportunity: With roughly 20 million pregnancies annually in the US and addressable market potentially worth 3 billion, the scaling phase will determine whether Biotics AI becomes standard practice or remains niche.
- Blueprint for Medical AI: The company's approach demonstrates how successful healthcare AI companies combine domain expertise, regulatory collaboration, equity focus, and workflow integration rather than pure technical sophistication.
FAQ
What exactly is Biotics AI and what does it do?
Biotics AI is a healthcare technology company that developed FDA-approved AI software to analyze fetal ultrasound images. The system evaluates image quality, verifies that required anatomical views are captured, detects potential fetal abnormalities, and generates automated reports. The technology is designed to improve diagnostic accuracy and consistency in prenatal care, particularly for patients who might otherwise receive lower-quality imaging.
How did Biotics AI get its FDA approval?
Biotics AI navigated the FDA approval process over nearly three years by integrating product design, clinical validation, and regulatory planning simultaneously rather than sequentially. The company trained its AI models on over 11,000 diverse ultrasounds and validated performance across different patient populations to ensure equitable performance. This integrated approach and commitment to demographic representation helped the company move through FDA requirements more efficiently than typical AI medical device timelines.
Why does Biotics AI focus on demographic representation in its AI training?
The company explicitly addresses healthcare disparities by ensuring its technology performs reliably for all patient populations, particularly those at highest risk for adverse outcomes. Black women face maternal mortality rates approximately 2.6 times higher than white women. AI systems trained on unrepresentative data perform poorly on underrepresented populations, which would exacerbate existing disparities. Biotics AI made equitable performance central to product design and FDA validation.
What does FDA approval mean for hospitals considering Biotics AI deployment?
FDA approval indicates the technology has undergone rigorous clinical validation and demonstrated safety and effectiveness. For hospitals, this means stronger liability protections when using the device as intended, better reimbursement discussion groundwork, clearer integration pathways with existing IT systems, and greater clinician confidence in adoption. The approval enables hospitals to move forward with confidence that the technology meets regulatory standards.
How will Biotics AI integrate into existing clinical workflows?
The platform is designed to work within existing hospital systems including PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), EHRs (Electronic Health Records), and ultrasound machines. The AI output appears in clinicians' normal workflow rather than requiring them to switch to separate systems. Implementation requires technical integration work and staff training, but the goal is to support existing processes rather than disrupting them.
What are the next steps for Biotics AI after FDA approval?
Bustami indicated the company will focus on scaling across hospital networks nationwide through partnerships with health systems. Additional priorities include establishing reimbursement pathways, expanding features for fetal medicine and reproductive health, and potentially pursuing international regulatory approvals. The company will likely expand its addressable market beyond the core fetal abnormality detection capability.
How big could the market for Biotics AI become?
With roughly 20 million pregnancies annually in the US and approximately 15,000-20,000 locations performing obstetric ultrasound, the addressable market for AI-assisted ultrasound analysis could reach
What makes Biotics AI different from competitors working on AI ultrasound technology?
While other companies are developing AI ultrasound tools, Biotics AI has specifically achieved FDA approval for fetal abnormality detection with demonstrated equitable performance across demographics. The combination of regulatory clearance, clinical validation, and focus on healthcare equity creates a significant first-mover advantage in this specific indication, though competitive threats will emerge as other companies pursue similar approvals.
Why did the FDA approval process take three years when some companies claim faster timelines?
Biotics AI's three-year timeline is actually competitive for AI medical devices, many of which take five to seven years. The company invested heavily in comprehensive clinical validation, demographic representation analysis, and workflow integration testing. These activities took time but also enabled efficient regulatory review because the company presented complete, well-organized evidence rather than iterating during FDA review cycles.
Could Biotics AI's technology eventually become standard of care for obstetric ultrasound?
If real-world deployment demonstrates consistent improvements in abnormality detection and earlier diagnosis, and if reimbursement gets established, the technology could become standard of care. This trajectory requires successful hospital partnerships, positive clinical outcomes data, and continued competitive advantage. Healthcare adoption cycles move slowly, but favorable indicators suggest widespread adoption is plausible within five years if execution succeeds.
Key Takeaways
- Biotics AI achieved FDA clearance for its AI software that detects fetal abnormalities in ultrasound images after nearly three years of rigorous clinical validation and regulatory coordination
- The company intentionally designed its AI training with 11,000 diverse ultrasounds to ensure equitable performance across demographics, directly addressing maternal mortality disparities affecting Black women
- Integrated product design with regulatory strategy enabled Biotics AI to move through FDA approval faster than typical medical device timelines by avoiding sequential iteration cycles
- The technology improves ultrasound quality assessment, verifies anatomical completeness, detects abnormalities, and generates automated reports while integrating into existing clinical workflows
- The addressable market for AI-assisted obstetric ultrasound could reach 3 billion if adoption becomes widespread, representing substantial scaling opportunity
Related Articles
- AI Healthcare Revolution: Why Tech Giants Are Racing Into Medicine [2025]
- AI Bubble Myth: Understanding 3 Distinct Layers & Timelines
- 7 Biggest Tech Stories: Apple Loses to Google, Meta Abandons VR [2025]
- ChatGPT Ads Are Coming: Everything You Need to Know [2025]
- Grok's Unsafe Image Generation Problem Persists Despite Restrictions [2025]
- Anthropic's Claude Cowork: The AI Agent That Actually Works [2025]
![Biotics AI Wins FDA Approval for AI-Powered Fetal Ultrasound Detection [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/biotics-ai-wins-fda-approval-for-ai-powered-fetal-ultrasound/image-1-1768837096108.jpg)



