Introduction: Research Gets Smart
Remember when research meant opening 47 browser tabs, copying text into a docs file, and manually piecing together information from conflicting sources? Those days are fading.
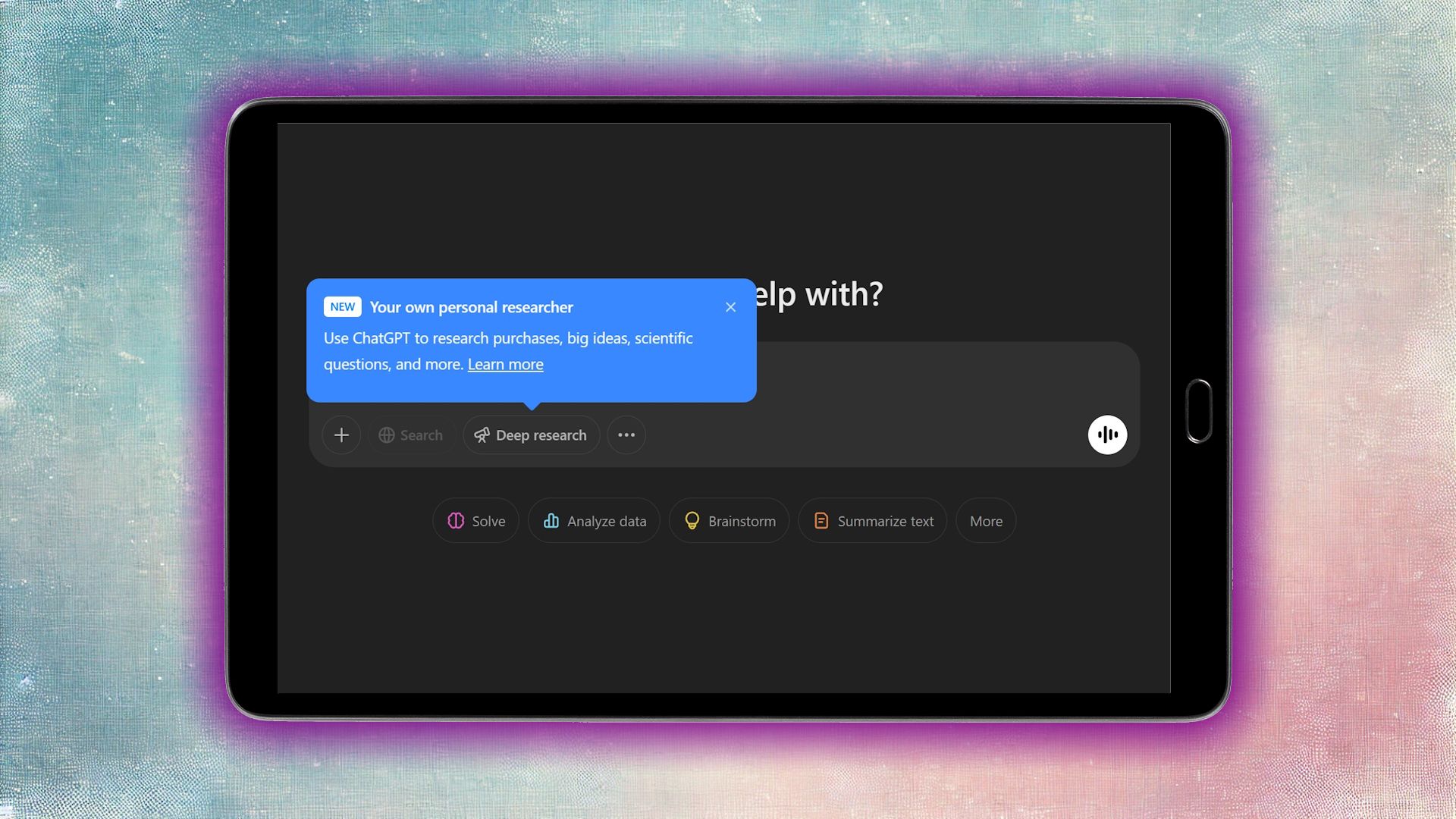
OpenAI's deep research tool has been quietly changing how people gather information. It's the feature that actually reads the internet for you, synthesizing thousands of sources into coherent, cited reports. But it's been missing something obvious: a decent way to actually read what it creates.
That just changed.
OpenAI rolled out a full-screen document viewer built directly into ChatGPT. It's not revolutionary. It's not flashy. But it's the kind of practical improvement that makes a tool stop feeling half-baked and start feeling like something you actually want to use every day.
Here's what matters: You can now watch your research compile in real-time. You can tweak the scope mid-process. You can download your report in Markdown, Word, or PDF. For Plus, Pro, and the new Go tier subscribers, this started rolling out immediately. Free users get it "in the coming days."
But the real story isn't just about a viewer. It's about what this means for how we work, how we research, and how AI is finally starting to understand that speed without usability is just noise.
Let me walk you through what this actually does, why it matters, and how it compares to the way you probably research right now.
TL; DR
- Full-screen viewer included: ChatGPT now shows research reports in a dedicated viewer with real-time progress tracking
- Multiple export formats: Download completed reports as Markdown, Word (.docx), or PDF
- Edit while researching: Modify research scope, add sources, or refocus on specific websites during the report generation process
- Rollout timeline: Plus/Pro users got access immediately; Go and free tier users receive it within days
- Time-saving feature: Eliminates manual copying, formatting, and document assembly from research workflows
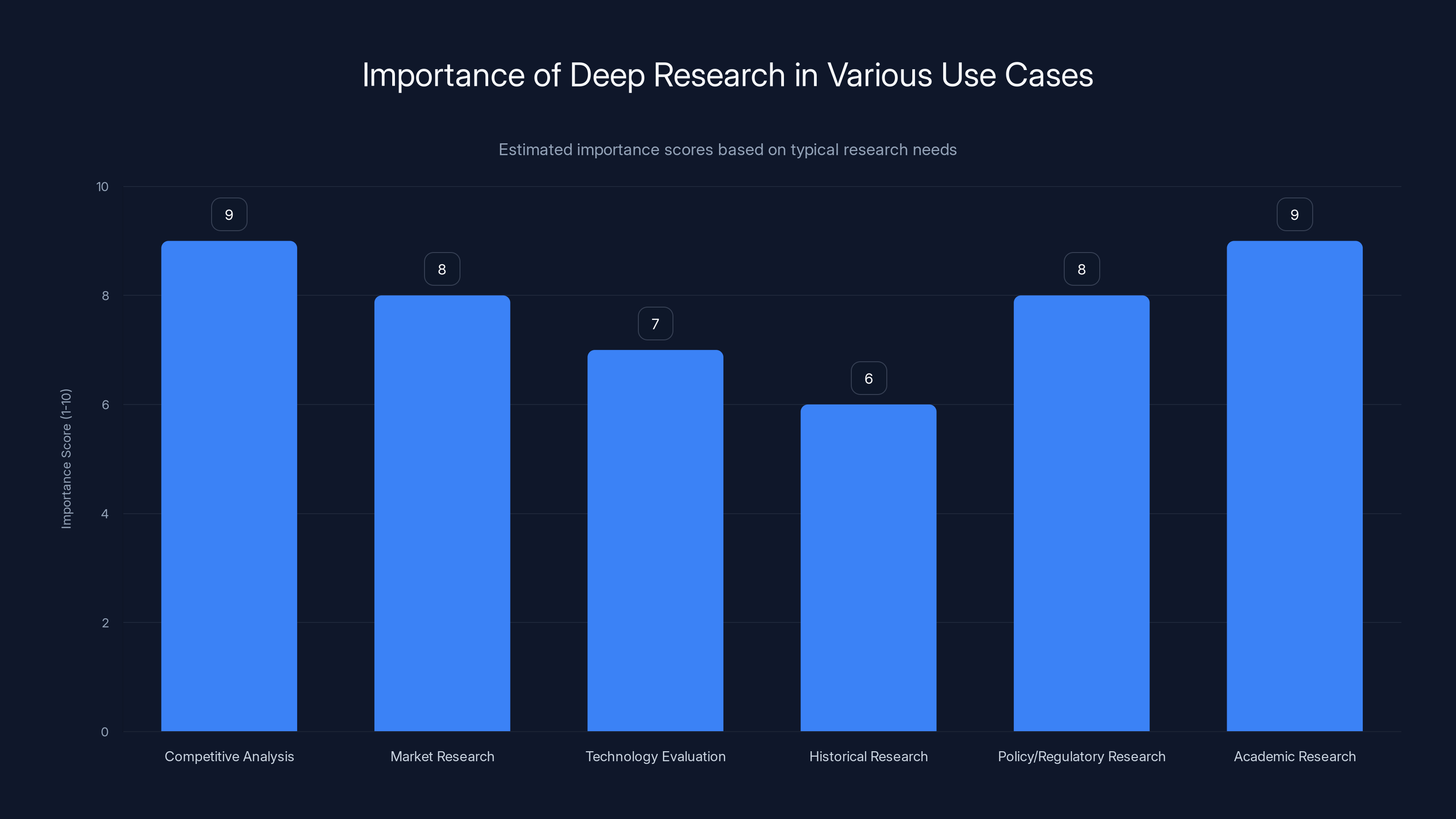
Deep research is crucial in competitive analysis and academic research, scoring highest in importance. Estimated data based on typical research needs.
What Deep Research Actually Does
Before diving into the viewer, you need to understand what you're viewing in the first place.
Deep research isn't ChatGPT making stuff up. It's ChatGPT becoming a research assistant that actually works. When you ask it to research something, the tool instructs ChatGPT to search the web systematically, gather relevant sources, cross-reference information, identify gaps, fill those gaps, and then synthesize everything into a cohesive report.
It's what you'd do if you had 10 hours and unlimited coffee. ChatGPT does it in 10 minutes.
The reports include citations. Real citations. Not the hallucinated variety that some AI systems famously produce. When deep research pulls information from a source, it tells you where it came from. You can verify it. You can follow up. You can trust it more than you trust random internet strangers (which, let's be honest, is a low bar).
But here's where the old version broke down: The output was trapped. You'd get a report, but reading it in the ChatGPT interface felt like reading a novel on a phone that only displays two sentences at a time. And then you'd have to manually copy sections into your own documents, format them, clean them up, and pretend you did the research yourself (you didn't, but nobody needs to know).
The deep research feature originally launched as a way to handle complex, multi-faceted questions that required synthesis across multiple domains. If you asked ChatGPT what the best programming language was for game development in 2025, it would give you an opinion based on its training data cutoff. But if you asked deep research the same question, it would actually go find current opinions from game developers, check what engines are using what languages, look at recent benchmarks, and build a report that's actually grounded in 2025 reality.
That's useful. That's different from the chat interface. And for the first time, it's actually readable.
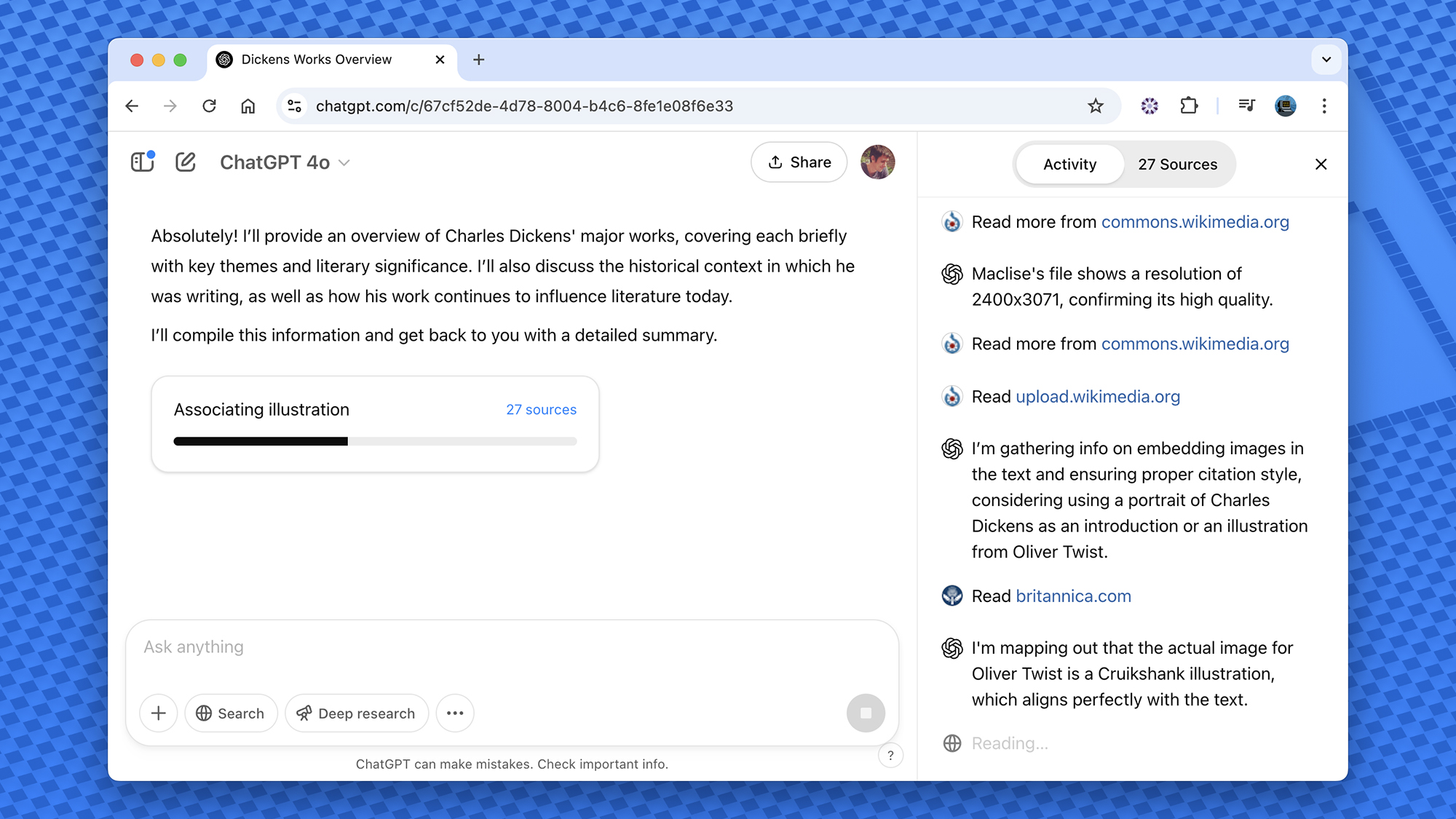
The New Document Viewer: Actually Readable Reports
Let's talk about the viewer itself. This is where the update matters.
OpenAI built a dedicated space for reading your research. It's full-screen. It has margins. It has breathing room. The text is actually legible. This sounds basic, but if you've ever tried to read a long ChatGPT response in the main chat interface, you know what a nightmare that is.
The viewer shows your report as it exists. If you want to download it, the option is right there. No hunting through menus. No confusion about where your file ended up. Click download, pick your format, and boom. Done.
But here's the part that's actually clever: You're not locked into watching the report appear one block at a time and hoping it turns into something useful. The viewer shows ChatGPT's progress in real-time. You see it gathering sources. You see it building sections. You see the work happening.
This matters more than it sounds. When ChatGPT takes 10 minutes to generate a report, watching nothing happen is anxiety-inducing. Are we actually researching? Did it freeze? Is it thinking about pizza instead of your question? Real-time progress kills that uncertainty.
The formatting comes through too. If deep research builds a report with headers, bullet points, and structure, the viewer preserves that. It's not everything getting dumped into one paragraph. It's actually organized. Your time isn't wasted scrolling through walls of text.
And if you're mid-research and you realize you've made a mistake? You can change things. OpenAI specifically mentioned that you can "edit the scope of its research or add new sources while the chatbot generates a report." So if deep research is halfway through and you decide you want more information about a specific angle, you don't have to start over. You just adjust. That's the kind of flexibility that makes tools actually usable instead of theoretical.

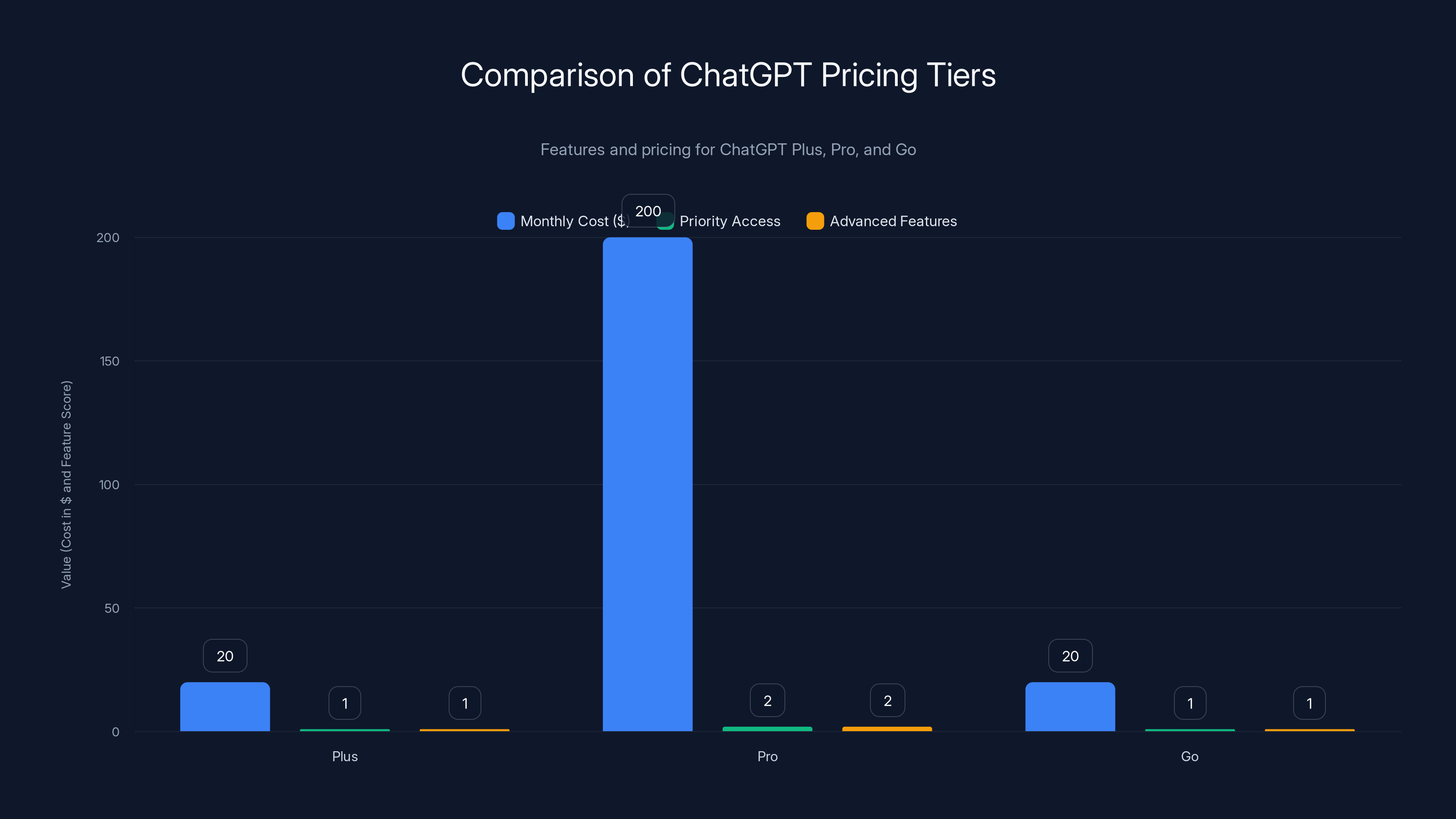
ChatGPT Pro offers the most advanced features and priority access at a higher cost, while Plus and Go provide essential features at a similar price point. Estimated data for feature scores.
Export Options: Multiple Formats for Multiple Workflows
Now we get to the practical part: actually using the research somewhere else.
The report needs to live somewhere. In your docs. In your notes. In an email to a colleague. And that means it needs to be in a format other than "text inside a web browser."
OpenAI built three export options:
Markdown is first. If you live in markdown (which increasingly, a lot of people do), this is your format. Markdown is what writers, developers, and people who understand the internet use. It's plain text but structured. It converts to everything. Web pages, PDFs, documents, presentations. Pick a markdown file and you've picked a format that works everywhere.
Word documents are for anyone who lives in the Microsoft ecosystem. You open the file, it's got your report, formatted and ready. You can edit it. You can add your own comments. You can share it with people who will definitely send you edits in tracked changes (because of course they will). It's not fancy, but it works, and half of the business world still runs on .docx files whether we like it or not.
PDF is for when you want the report to stop being a draft and become official. PDF locks everything in place. Formatting, fonts, layout. Nothing's changing. If you're creating something for presentation or archival, PDF is the move.
Having three options sounds like a small thing. It's not. Every research workflow is different. Some people are building docs and need text they can edit. Some people need a permanent record. Some people are building automation and need structured data. These three formats cover most situations.
The fact that all three work isn't luck. It's because OpenAI thought about how people actually use research. You're not just reading it in ChatGPT. You're building on it. You're sharing it. You're creating something else with it. The viewer is just the beginning.
Real-Time Progress Tracking: Watch the Sausage Get Made
One of the underrated features of the update is real-time progress tracking.
When you ask ChatGPT to deep research something, the system is doing a lot of work. It's formulating search queries. It's fetching results. It's evaluating sources. It's building an outline. It's writing sections. It's checking for gaps. It's filling gaps. It's cleaning up the final product. All of that takes time.
Before, you'd hit the research button and then just wait. The interface would show you a spinning animation and almost nothing else. You had no idea if the process was 20 seconds in or 9 minutes in. You had no idea if it was gathering sources or writing conclusions.
Now you see it. The viewer shows what stage the research is in. You're watching it work. That psychological element matters more than you'd think. When you can see progress, you're confident the system is actually doing something. Time feels shorter because you understand how it's being spent.
It also gives you an intervention point. If you're watching the progress and you realize halfway through that the research is going in a direction you don't want, you can pause and adjust. "Hey, I see you're focusing on enterprise solutions, but I actually need small-business options. Let me refocus that." And the research adapts. Instead of running to completion and then having to start over because it missed your actual intent, you course-correct on the fly.
That's the difference between a tool and a toy. Tools let you steer. Toys just do what they do.
Adding Sources and Focusing Research While It Happens
This is the feature that surprised people.
Most AI tools work like vending machines: You put in your input, you wait, you get your output. You don't talk to it while it's working. If the output is wrong, you start over.
Deep research is different. It's collaborative. You can interrupt it. You can say, "Also look at this website." You can say, "Focus more on this angle." You can say, "I've changed my mind about what I actually need."
This eliminates the frustration of running a full research cycle, getting a report that's 85% what you wanted, and realizing you could have gotten it exactly right if you'd just thought to mention one more thing at the beginning.
Now you can mention it whenever. Mid-process. And ChatGPT adjusts.
The specific implementation is straightforward. While a report is generating, you can add new sources. You can tell ChatGPT which websites or domains to focus on. You can say, "Only look at academic sources," or "Focus on recent articles, not 10-year-old data." The research doesn't blow up and restart. It incorporates your new parameters into the next phase of work.
This is particularly valuable when you realize you want information from a specific source that you know has good information, but ChatGPT might not have found it naturally. Want deep research about a specific company's strategy? Add their investor relations page as a source. Want information about a specific technology? Add the official documentation as a source. Instead of hoping ChatGPT discovers it, you ensure it gets included.

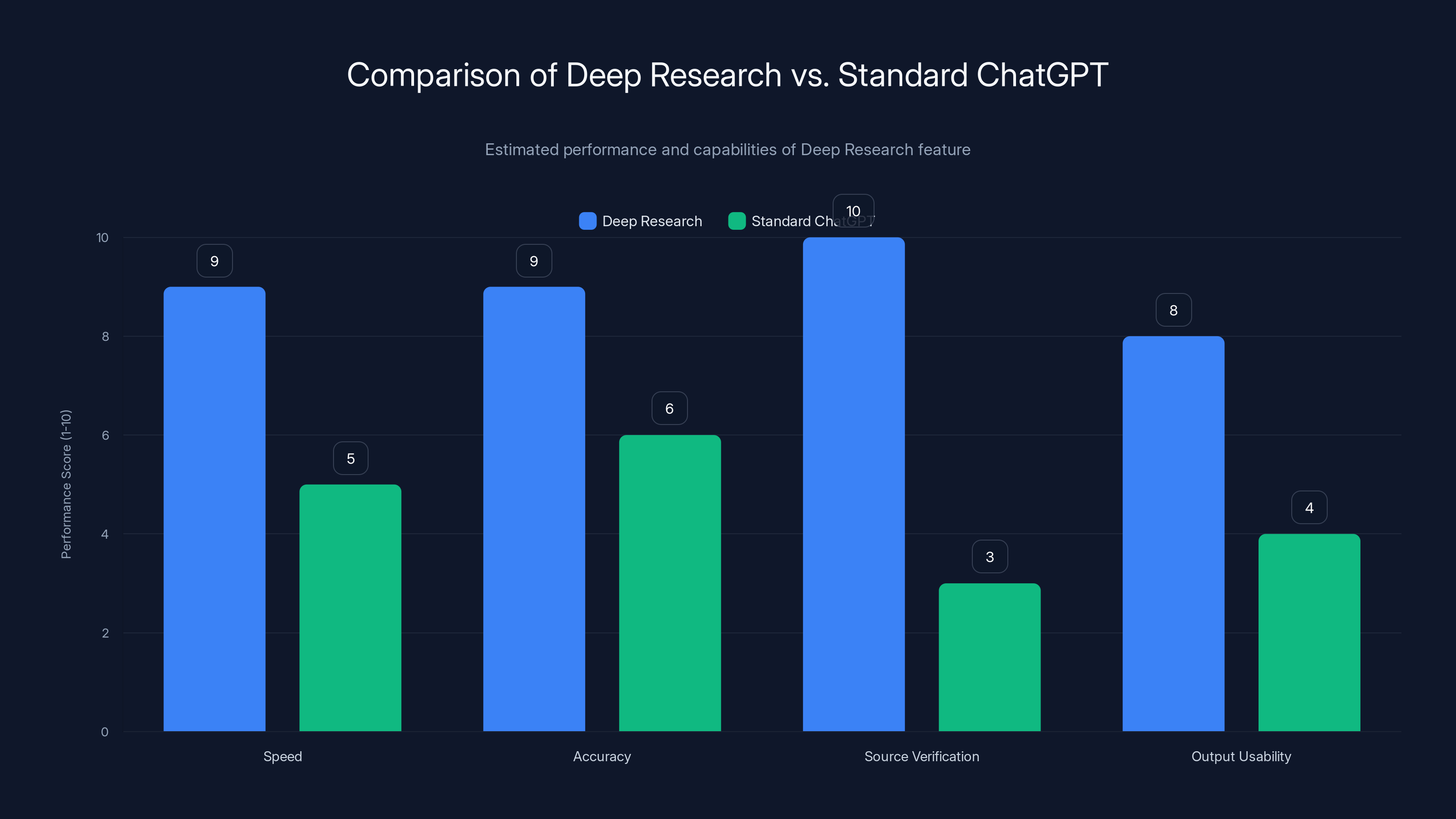
Deep Research significantly enhances ChatGPT's capabilities in speed, accuracy, source verification, and output usability. (Estimated data)
Rollout Timeline: Who Gets It When
Let's get practical about who can actually use this.
OpenAI rolled it out in tiers. If you're a ChatGPT Plus subscriber, you got access immediately. If you're a ChatGPT Pro subscriber (the most expensive tier), same thing. You got it right away.
The new ChatGPT Go tier (which sits between free and Plus in terms of pricing) is getting the update "in the coming days." Meaning within a week or so, probably. If you're not using Plus or Pro but didn't want to be stuck with the free tier, Go is the middle ground, and this feature is part of what you're paying for.
Free users also get deep research eventually, but it's coming later in the rollout. "In the coming days" per OpenAI's announcement. So free tier will get there, but paid users got the early access.
This makes sense from a business perspective. OpenAI has paid tiers now. They're rolling out features in a way that incentivizes upgrading. But they're not gate-locking features forever. The feature will be universal eventually.
Why? Because deep research is useful even with a free account. It's good public relations. It drives adoption. People get hooked on it, they upgrade to Plus for other features, and suddenly OpenAI has a paying customer. It's not malicious. It's just how software business models work.

Comparing to Traditional Research Workflows
Let's step back and ask the real question: How much better is this than what you're probably already doing?
The old way: You open Google, run 8-12 searches, open 20-30 tabs, skim articles, copy-paste text into a doc, organize it, format it, add citations manually (if you're good), edit it to sound like prose instead of a collection of excerpts, and then you've got a report. This takes 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on complexity.
The ChatGPT way: You ask deep research to research something, you watch it work for 5-15 minutes, you download the report, and you've got something that's already cited, already organized, already written in prose, and ready to use. You might edit it. You might add your own opinions. You might fact-check a few claims. But the heavy lifting is done.
The time delta is massive. We're talking about freeing up 1-2 hours per research task. For someone doing research professionally (analyst, journalist, academic, consultant, researcher), this is genuinely meaningful.
But there's a second benefit that's harder to quantify: accuracy. ChatGPT's deep research doesn't hallucinate the way the regular chat interface sometimes does. It finds real sources. It cites them. You can verify them. If ChatGPT makes a claim, you can click through and check if the claim is actually supported by the source. That's powerful. That means you can actually trust the output in a way you can't trust an uncited claim.

How This Compares to Perplexity and Other AI Research Tools
Now, OpenAI isn't the only company making AI research tools.
Perplexity also does real-time web search with citations. The difference is philosophical. Perplexity is built around search. You ask a question, Perplexity searches, it answers immediately, and you get a result with inline citations. It's fast and direct.
ChatGPT's deep research is more thorough. It's slower (5-15 minutes vs. 10-30 seconds for Perplexity), but it's designed to be more comprehensive. It's better for complex topics that need synthesis. Perplexity is better for quick answers where you want citations.
Google added an AI Overview feature to search results. That's Google's answer to AI research. But it's really just a summary of top results. It doesn't do deep research in the way that ChatGPT or Perplexity does.
Claude (made by Anthropic) doesn't have a deep research feature yet, though they have web access built into Claude 3.5 Sonnet and higher tiers.
What makes ChatGPT's approach different now is the workflow. You're not just getting a report. You're getting an interactive, editable, real-time, downloadable research experience. That's not trivial.
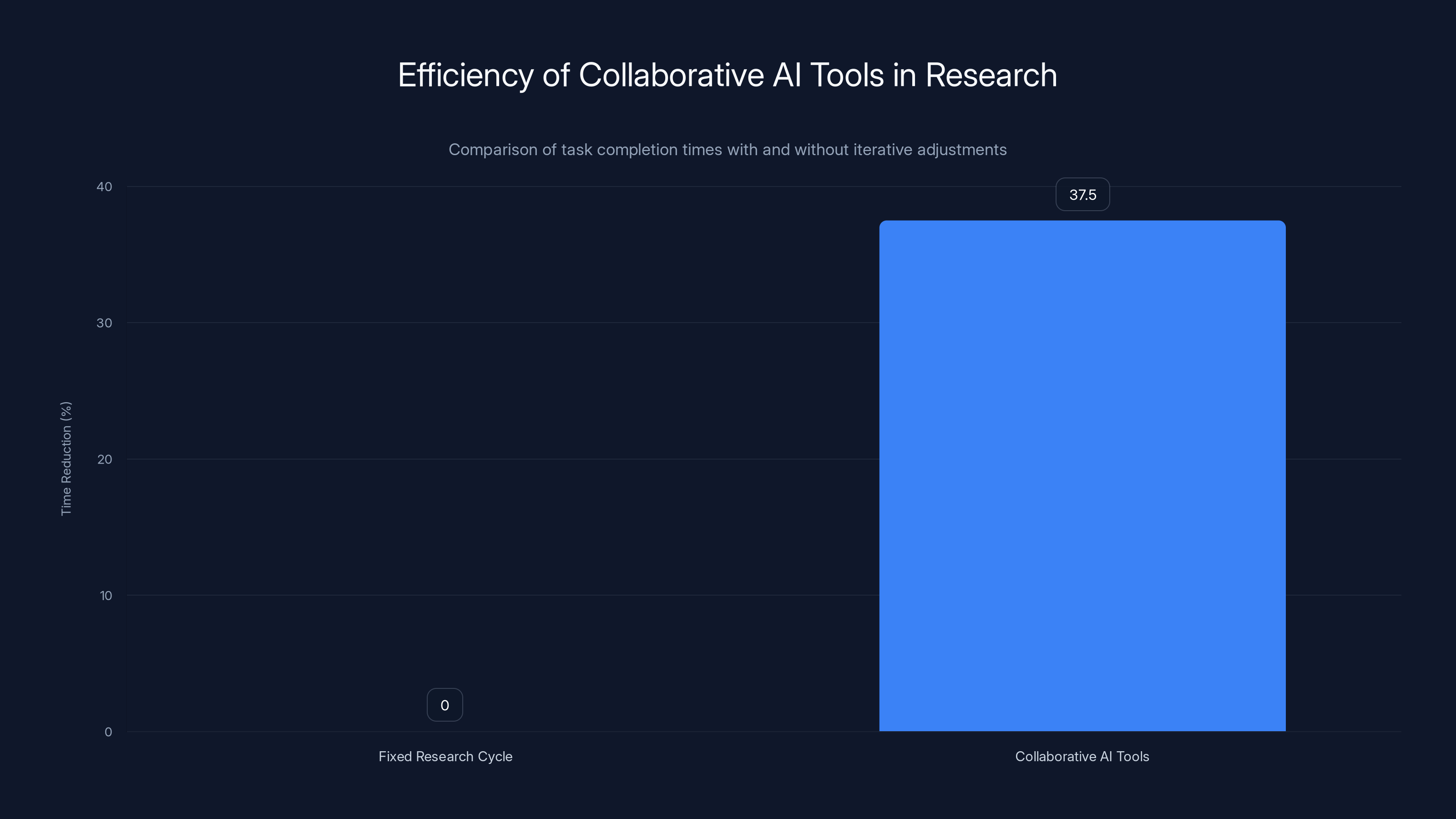
Collaborative AI tools allow users to iteratively adjust search scope and sources, resulting in a 35-40% faster task completion time compared to fixed research cycles. (Estimated data)
Use Cases Where Deep Research Actually Matters
Let's get specific about when this is worth your time.
Competitive analysis: You need to understand what competitors are doing. Deep research gathers information from their websites, recent news, product updates, and market positioning. You get a comprehensive report in one shot. Versus manually checking each competitor's site, reading all their recent press releases, and synthesizing it yourself.
Market research: You need to understand trends, market size, growth rates, and player positioning in an industry. Deep research finds relevant reports, news articles, analyst takes, and synthesizes a current snapshot. Much faster than clicking through industry databases.
Technology evaluation: You're trying to decide between two tools or technologies. Deep research can find benchmarks, user reviews, feature comparisons, and recent updates. You get a balanced overview instead of just reading marketing copy.
Historical research: You need to understand the history of something. Deep research can gather timeline information, key events, and important developments. It's like asking someone who read all the Wikipedia articles and then summarized them for you.
Policy or regulatory research: You need to understand regulations or policy changes. Deep research finds official documents, interpretations, expert analysis, and recent developments. Particularly valuable since regulations change and old information becomes outdated.
Academic research: You're writing a paper or thesis and need current information on a topic. Deep research finds recent studies, expert opinions, and conflicting viewpoints. You get citations you can follow up on.
Basically, anywhere you'd hire someone to research something for you, ChatGPT's deep research is now a substitute.

The Practical Workflow: Start to Finish
Let me walk you through what actually using this looks like.
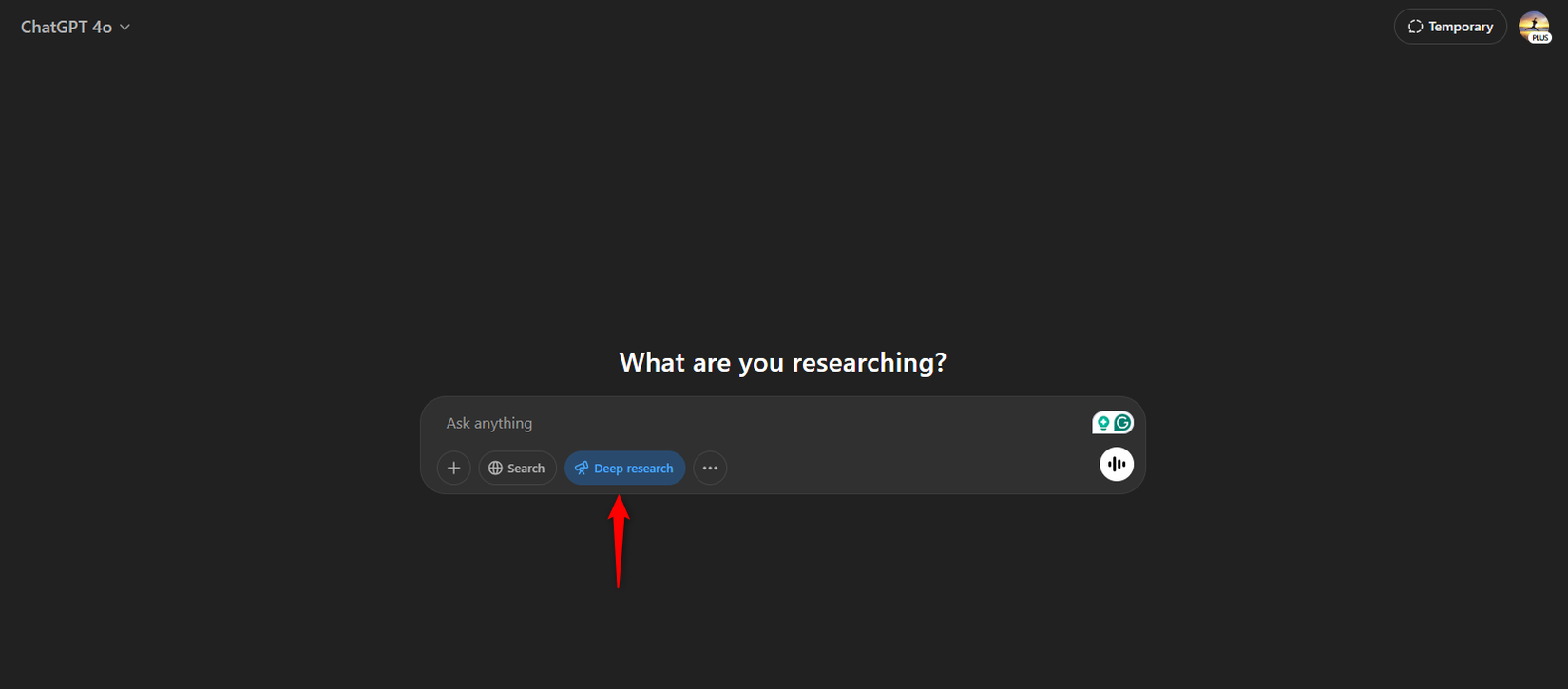
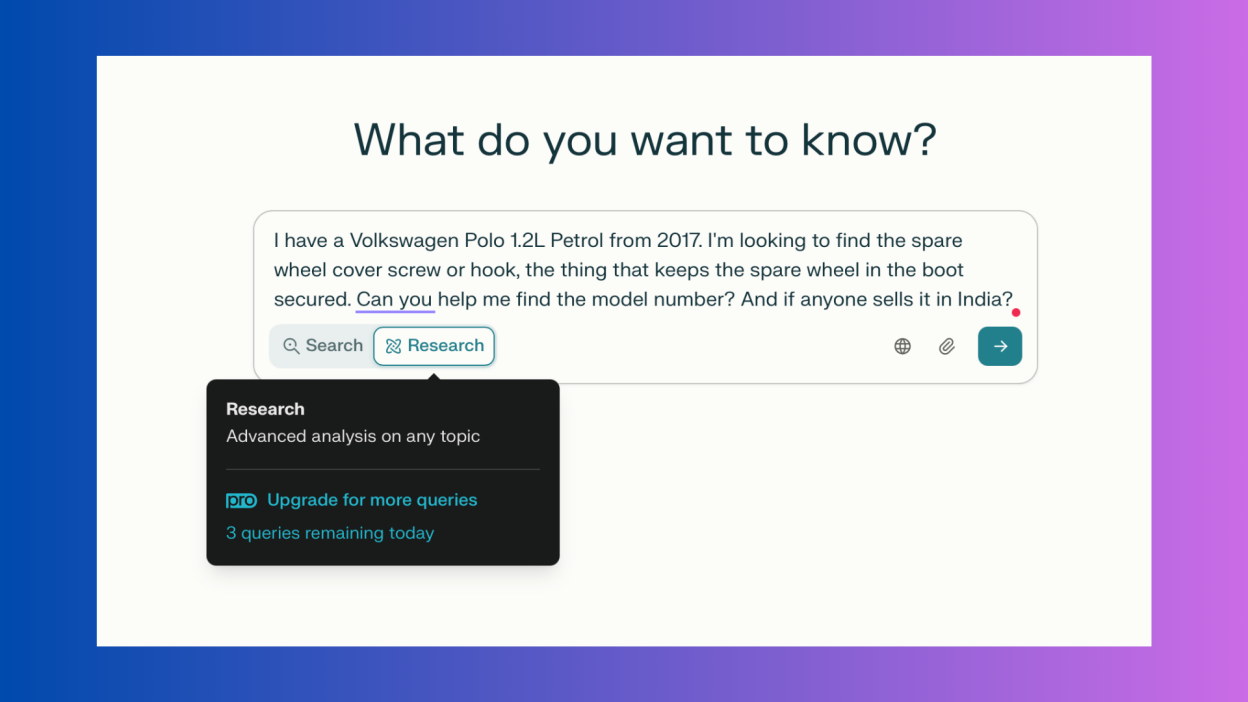
Step 1: Ask a question. You go to ChatGPT, select deep research (it's a distinct feature, not just regular chat), and type your question. Something like, "What are the current best practices for prompt engineering in LLM applications?"
Step 2: Watch it work. The document viewer opens. You see progress: gathering sources, analyzing, building outline, writing, finalizing. It takes 5-15 minutes depending on complexity.
Step 3: Intervene if needed. Midway through, you realize you want to focus on security implications specifically. You can say that. ChatGPT adjusts the research.
Step 4: Review the report. Once done, the full report is right there in the viewer. Readable, formatted, with citations.
Step 5: Download. Click download, pick your format (Markdown, Word, or PDF), and your report is saved to your computer.
Step 6: Use it. You've now got a research artifact. You can share it, edit it, build on it, or cite it in your own work.
Total time: 15-30 minutes including download. Compare that to the 1-3 hours it would take to research manually. That's the value.
Integration with Other Tools and Workflows
Here's the thing nobody talks about: The report you get from deep research isn't the end product. It's the beginning.
You download it as Markdown, Word, or PDF. Then what?
If it's Markdown, you can paste it anywhere markdown works. GitHub, Notion, Obsidian, Medium, your own blog. You can commit it to version control. You can build on it programmatically.
If it's Word, you can drop it into any document ecosystem. Share it with colleagues who need to edit it. Track changes. Comment on it. It becomes a collaboration artifact.
If it's PDF, you've got an archival format. You can file it. You can send it to clients. It's official.
But more importantly, the fact that these formats export cleanly means deep research can be part of a larger workflow. You could theoretically use deep research reports as inputs to other tools. You could feed them into automation platforms like Runable to turn research reports into presentations or other formatted documents automatically.
That's the future. Not just reading reports inside ChatGPT. But using reports as building blocks for everything else you're making.
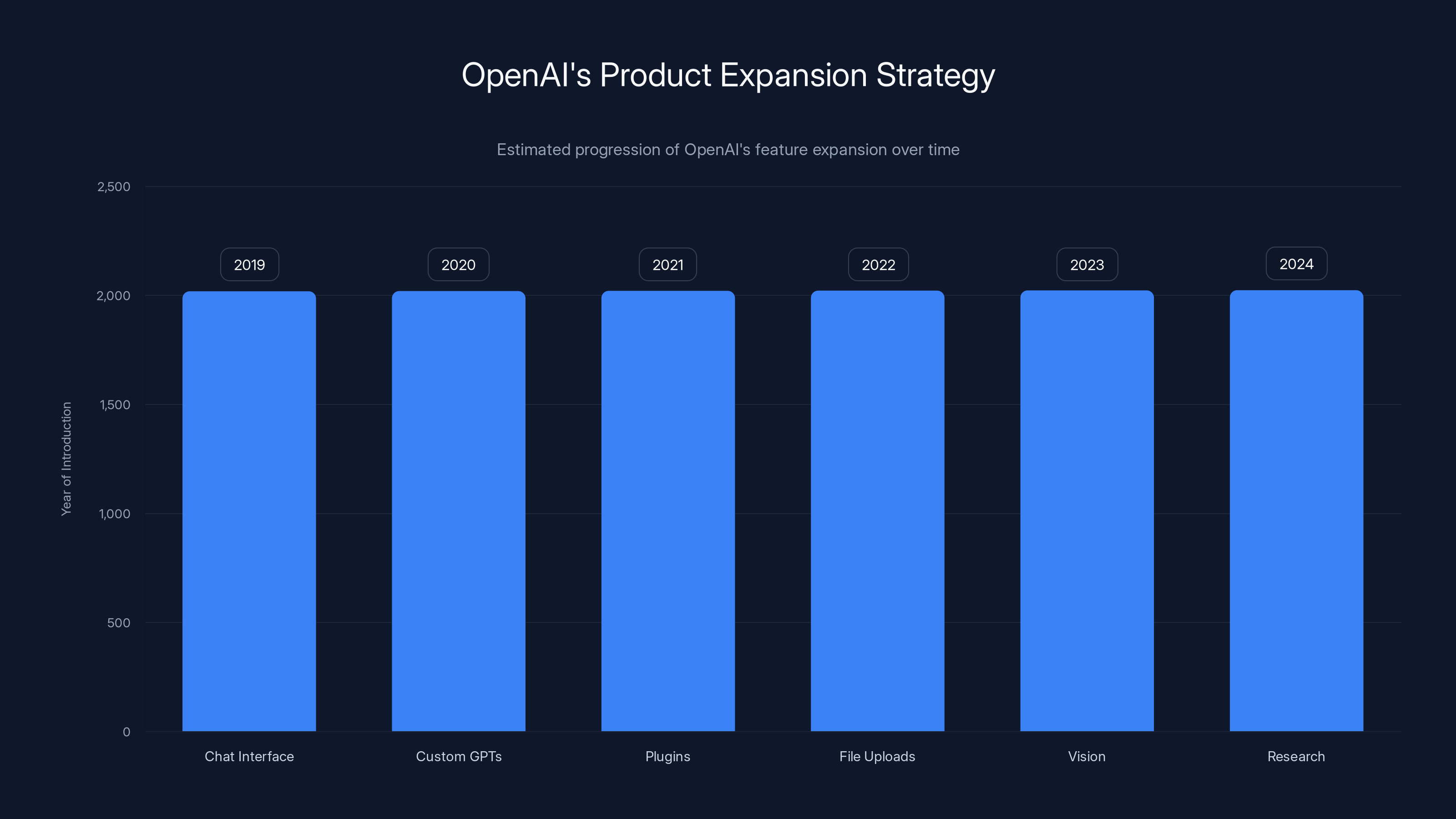
OpenAI has progressively expanded its product features from a simple chat interface in 2019 to advanced research capabilities by 2024. Estimated data.
The Security and Privacy Angle
One question people always ask: When ChatGPT's deep research crawls the web looking for information, what happens to that data?
OpenAI's public position is that they don't retain the individual sources you request deep research on. The research process itself doesn't involve storing your queries in a way that ties them to your account for training purposes. But the honest answer is more complex.
When you use deep research, you're telling OpenAI what you want to know about. That's logged. It's associated with your account. If you're researching something sensitive, confidential, or private, that query data exists somewhere in OpenAI's systems. Should you be concerned? That depends on your threat model and how you feel about OpenAI's data practices.
For most people, most of the time, this is fine. For people working with trade secrets, medical information, or other sensitive data, you might want to think twice about using deep research on anything confidential. Read OpenAI's privacy policy. Understand what data they're collecting. Make your own decision.
There's also the question of the sources themselves. When deep research visits a website, that website sees a request coming from OpenAI. Most sites are fine with this. Some aren't. Some have terms of service that don't allow automated crawling. Is that a legal risk? Probably not for you as the user, but it's worth being aware of.

Limitations You Should Know About
Deep research isn't magic. It's really good, but it has real constraints.
Real-time only goes so far. Deep research searches the web for recent information, but it's still subject to search indexing delays. Very new information (published in the last few hours) might not show up. If you need truly up-to-the-minute data, a regular web search might be faster.
Synthesis quality depends on source quality. If the web has mostly bad information about a topic, deep research will synthesize bad information better than humans would, but you're still getting bad information. Garbage in, garbage out, just more coherent.
Behind paywalls is out. A lot of valuable information lives behind paywalls. Academic journals. Subscription news sites. Industry reports. Deep research can't access most of that. It only sees what's publicly available. That limits what it can research.
Knowledge cutoff still matters. ChatGPT's underlying training data has a knowledge cutoff. Deep research can find recent information, but it's still ChatGPT doing the synthesis. For topics where understanding historical context is important, you might get less historical depth than you'd like.
Opinions still get baked in. ChatGPT tries to be neutral, but synthesis is an act of judgment. Which sources get weighted heavily? Which claims get emphasized? These decisions involve choices. The report isn't purely objective. No report is. But if you're looking for pure, unfiltered source material, you'd be better served by a list of links than a synthesized report.
Hallucinations can still happen. Deep research is more reliable than regular ChatGPT because it's grounded in actual sources. But if ChatGPT makes a mistake in how it interprets a source, that mistake makes it into the report. You still need to verify important claims.

How This Fits Into OpenAI's Larger Product Strategy
You need context to understand why OpenAI is pushing deep research this hard.
For years, OpenAI's ChatGPT was a chat interface. That's it. You talked to it, it talked back. Simple. But chat isn't how people actually work. People work in documents, spreadsheets, presentations, reports, code editors, and a dozen other formats.
OpenAI realized they needed to expand beyond chat. They launched custom GPTs. They added plugins. They added file uploads. They added vision. And now they're adding research.
The strategy is clear: Make ChatGPT not just a tool you talk to, but an interface for doing actual work. Research is just the beginning. Eventually, ChatGPT might be your interface for everything. You tell it what you need, it does the research, compiles the report, formats it how you want, and hands it back ready to use.
That's the end state OpenAI is building toward.
The new ChatGPT Go tier is part of this strategy too. It's priced to be accessible ($20/month for unlimited) while still being profitable. It's trying to build a massive user base using advanced features to drive upgrades from free to Go to Plus to Pro.
Deep research with a document viewer isn't just a feature. It's a signal that OpenAI is serious about being the platform you use to get work done, not just the chatbot you ask for advice.

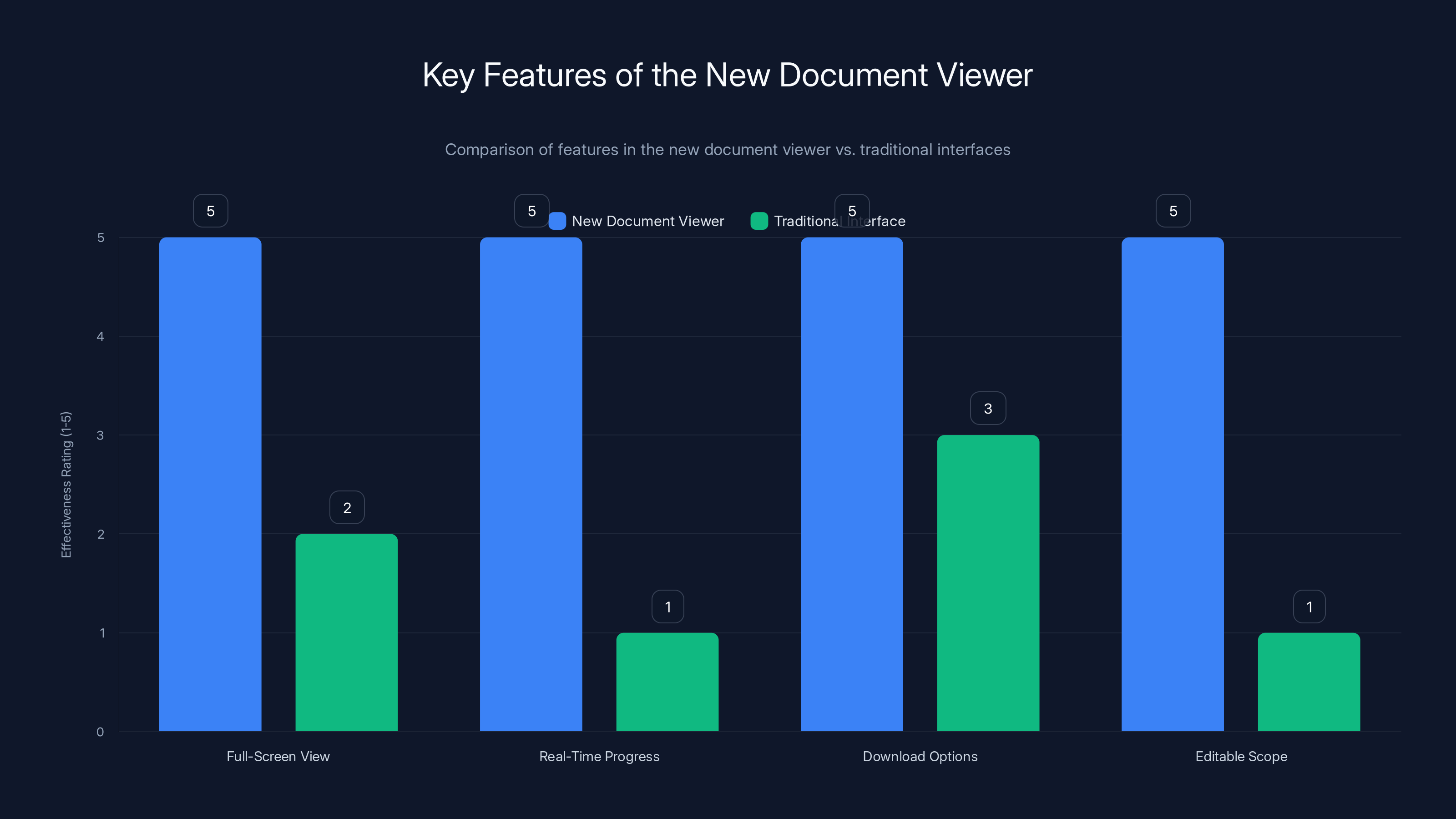
The new document viewer significantly enhances user experience with features like real-time progress and editable scope, compared to traditional interfaces. Estimated data.
The Future of AI Research Tools
Where does this go from here?
Obviously, the research features will improve. Better source quality. Faster generation. More reliable citations. Those are table stakes. Everyone's building in that direction.
The more interesting direction is integration. Imagine deep research that doesn't just generate a report but automatically formats it into a slide deck. Or that creates an interactive webpage. Or that breaks down the findings into a runnable workflow. The viewer is just the start.
We're probably seeing a future where you don't ask ChatGPT to "research" something. You ask it to "research and create a presentation," or "research and create a document I can share with clients," or "research and give me a summary I can use as a tweet thread."
The research is the input. The output format is your choice.
That's the direction this is moving. And when it gets there, research stops being something you do and becomes something that just happens as a side effect of asking for the output you actually want.
For now, though, the document viewer is a huge step forward. It takes a tool that was theoretically useful and makes it practically usable.
ChatGPT Plus, Pro, and Go: Pricing Context
Let's talk about whether it's worth paying for.
ChatGPT Plus is $20/month. You get GPT-4, which is smarter than the free version. You get faster response times. You get some features (like voice) that aren't available free. Deep research is included.
ChatGPT Pro is the new premium tier at $200/month. You get even smarter models, more priority access, and integration with Canvas (a separate editor for code and long-form documents). Deep research is included here too, obviously.
The new ChatGPT Go tier is $20/month but positioned as unlimited ChatGPT access. It sits between free and Plus. It includes deep research.
The pricing is structured so that deep research isn't some expensive premium feature. It's available at the Plus level ($20/month) and higher. For someone doing research work, that's probably worth it just for this one feature.
But is it worth it for casual users? Probably not. The free tier will get deep research eventually, and if you only research occasionally, waiting is fine.
For professionals doing research work regularly? A $20/month subscription that saves you 1-2 hours per research task pays for itself in about 10 hours of saved time. At standard professional rates, you're breaking even in one week of usage.

Best Practices for Using Deep Research Effectively
Now that you know how to use it, here's how to use it well.
Be specific about what you want. "Research productivity tools" is vague. "Research project management tools that have free tiers, support team collaboration, and integrate with Slack" is specific. Specificity means better results.
Include context when helpful. If you need research for a specific use case, say so. "Research cloud storage options for a startup with 50 employees storing mostly documents and video files" will give you better results than "Research cloud storage."
Know what you're looking for before you start. What would "good research" look like? What questions do you need answered? What gaps do you need filled? Think about this before you start the research, not after you get the report.
Watch the progress, but don't hover. You can intervene if the research is going sideways, but micromanaging every step wastes time. Let it work, check in periodically, adjust if needed.
Verify important claims. Deep research is reliable, but it's not perfect. If the research supports a decision you're about to make, verify 2-3 key claims. Click through to the sources. Confirm they say what ChatGPT claims they say.
Export and save immediately. Once the research is done, download it. Don't rely on having it available in ChatGPT. Browser history gets cleared. Accounts get hacked. Export it, save it, back it up.
Use the right export format for your workflow. Markdown if you're editing or versioning. Word if you're collaborating. PDF if it's final.
Build on top of it. Don't treat the report as the finished product. Treat it as a starting point. Add your own analysis. Add your own opinions. Use it as the foundation for something bigger.
Automation and Integration Possibilities
Here's something worth thinking about: What if you automated this?
Let's say you want competitive intelligence every week. You could set up a workflow that automatically asks ChatGPT to deep research what your competitors are doing, exports the report, and drops it into a Slack channel or Google Drive. You're getting weekly competitive research reports with zero manual work.
Or imagine automated market research. Every Monday, research what's trending in your industry. Export it. Share it. Done.
This is possible with tools like Zapier or Runable, which offers AI automation for creating documents and reports. You could connect ChatGPT's API output to these tools, and suddenly your research is being compiled, formatted, and distributed automatically.
We're not quite there yet with deep research specifically (it's not exposed through the API in a clean way), but it's coming. And when it does, research stops being a manual task and becomes a scheduled, automated background process.
That's the future. Research tools that don't need you to remember to use them. They just happen.

FAQ
What is ChatGPT's deep research tool?
ChatGPT's deep research is a feature that systematically searches the web, gathers information from multiple sources, synthesizes the findings, and generates a comprehensive, cited report on a topic of your choosing. Unlike regular ChatGPT responses, which are based on training data with a knowledge cutoff, deep research provides current information grounded in real, verifiable sources.
How does the document viewer improve the deep research experience?
The full-screen document viewer provides a dedicated, readable interface for viewing research reports as they're generated. It shows real-time progress as ChatGPT gathers sources and builds the report, allows you to edit the research scope mid-process, and enables one-click downloading in multiple formats (Markdown, Word, PDF). This eliminates the frustration of reading long reports in the regular chat interface.
Can I edit my research while it's being generated?
Yes. While deep research is running, you can modify the scope by specifying which websites to focus on, adding new sources, or redirecting the research toward different angles. The system integrates these adjustments into the ongoing research process rather than forcing you to start over.
What file formats can I export deep research reports in?
You can export reports in three formats: Markdown (for editing and version control), Word (.docx for collaboration), and PDF (for archival and sharing). The choice depends on your workflow and what you'll do with the report next.
Who has access to the deep research document viewer right now?
ChatGPT Plus and Pro subscribers got immediate access when the feature rolled out. The new ChatGPT Go tier is receiving it within days, and free users will get access shortly after.
How long does deep research usually take?
Most deep research reports take between 5 and 15 minutes to generate, depending on the complexity of the topic and how many sources need to be gathered and synthesized. Simple queries might be faster, while research on complex topics requiring synthesis across multiple domains usually takes longer.
Can I trust the citations in deep research reports?
Deep research cites actual sources rather than hallucinating citations like some AI systems do. However, you should still verify important claims by clicking through to the sources themselves. While the research is generally reliable, it's based on ChatGPT's interpretation of what those sources say, and mistakes can happen.
Is deep research suitable for academic or professional work?
Deep research is useful for gathering information and synthesizing it quickly, making it valuable for initial research phases. However, for academic work, you'll likely need to follow your institution's citation requirements and possibly use primary sources. For professional work, the cited sources allow you to verify claims and share the report with confidence.
How does deep research compare to just using Google Search or other research tools?
Google Search gives you links. Perplexity gives you fast answers with citations. Deep research gives you comprehensive, synthesized reports with real-time progress tracking and real-time editing capabilities. It's best for complex topics requiring synthesis across multiple sources. For quick answers, faster tools might be better.
What are the privacy implications of using deep research?
Your research queries are logged and associated with your account. OpenAI doesn't retain individual sources for training purposes, but your research interest data exists in their systems. For sensitive or confidential research, review OpenAI's privacy policy to understand their data practices before proceeding.
Conclusion: Research Gets Practical
We're living through a moment where research tools are finally becoming usable.
For years, AI was interesting in theory. ChatGPT talked well. It had great ideas. But actually getting work done with it? That required workarounds and compromises. You'd use it as a starting point and finish manually. You'd use it for brainstorming and research elsewhere. You'd use it for drafts and edit heavily.
The document viewer is small. It's not revolutionary. But it signals that OpenAI is moving from theory to practice.
Research should be accessible. It should be fast. It should be reliable. It should produce outputs you can actually use. The new deep research tool, with its full-screen viewer, real-time progress tracking, interactive scope editing, and multi-format exports, hits all four of those things.
For anyone doing research work, this is worth your time to try. For professionals, it's worth the $20/month for ChatGPT Plus. For casual users, wait for the free tier access and try it then.
But here's the bigger picture: This is the direction everything's moving. Research today. Tomorrow it's analysis. Then it's synthesis. Then it's action. AI isn't becoming your replacement. It's becoming your interface for doing work.
The document viewer is just showing us what that future looks like.
If you're looking for ways to combine research with other workflows like presentation creation or document generation, platforms like Runable are now making it possible to automate the next step, taking deep research reports and transforming them into presentations, formatted documents, or other useful outputs without manual work.
That's the real future: Research not as an end product, but as an input to everything else you're building.
Use Case: Turn your deep research reports into polished presentations or formatted documents automatically with AI automation.
Try Runable For Free
Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT's new document viewer makes deep research reports readable in full-screen with real-time progress tracking and one-click downloads in Markdown, Word, or PDF
- You can edit research scope mid-process by adding sources, focusing on specific websites, or redirecting research toward different angles without starting over
- Deep research saves 1-2 hours per research task compared to manual web research, making the $20/month ChatGPT Plus subscription cost-effective for professionals
- Export formats enable integration into larger workflows: Markdown for editing and version control, Word for team collaboration, PDF for archival and sharing
- Deep research is most valuable for competitive analysis, market research, technology evaluation, and policy research where current information across multiple sources matters
Related Articles
- OpenAI's ChatGPT Ads Strategy: What You Need to Know [2025]
- OpenAI Prism: AI-Powered Scientific Research Platform [2025]
- ChatGPT Ads 2025: Complete Guide to OpenAI's Advertising Strategy
- OpenAI's ChatGPT Ads: What It Means for AI's Future [2025]
- Best AI Notetakers [2026]: Tested, Compared & Reviewed
- ChatGPT Caricature Trend: How Well Does AI Really Know You? [2025]
![ChatGPT's Deep Research Tool: Document Viewer & Report Features [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/chatgpt-s-deep-research-tool-document-viewer-report-features/image-1-1770766582258.jpg)



