Tech News January 2025: Samsung S26 Upgrades, Garmin Whoop Clone & Industry Game-Changers
Introduction: Your Weekly Tech Update for January 31, 2025
The technology landscape continues its relentless march forward, and this week delivered seven significant announcements that deserve your attention. From flagship smartphone upgrades to wearable device innovations, the industry is signaling where it's headed in 2025. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a developer tracking emerging platforms, or simply someone interested in how devices will evolve, understanding these announcements helps contextualize the broader trends reshaping consumer electronics.
This week's tech news cycle was particularly dense because we're at a critical inflection point in the calendar. Companies are finalizing their spring product launches, refining software features for the year ahead, and investing heavily in artificial intelligence integration. The announcements we've tracked span multiple hardware categories—from personal electronics to fitness trackers—revealing that 2025 will be remembered as the year AI capabilities permeated nearly every device category.
What makes this week particularly noteworthy is the convergence of different manufacturers tackling similar problems from different angles. You'll see Samsung approaching smartphone AI differently than competitors, while Garmin's strategic move into the fitness tracker market suggests intensifying competition in wearables. This fragmentation actually benefits consumers because it drives innovation across price points and feature sets.
The seven stories covered here represent more than just product announcements—they're signals about where the tech industry is allocating resources, what problems engineers consider solvable, and which markets are heating up with competition. By understanding these announcements in context, you can make more informed purchasing decisions and anticipate which product categories might see significant improvements in the coming months.
Think of this weekly roundup as your firmware update for the tech world. Just as your devices need regular updates to stay current, your understanding of technology trends requires consistent exposure to industry developments. We've filtered through hundreds of announcements to bring you seven stories that matter—stories with real implications for your technology choices in 2025.

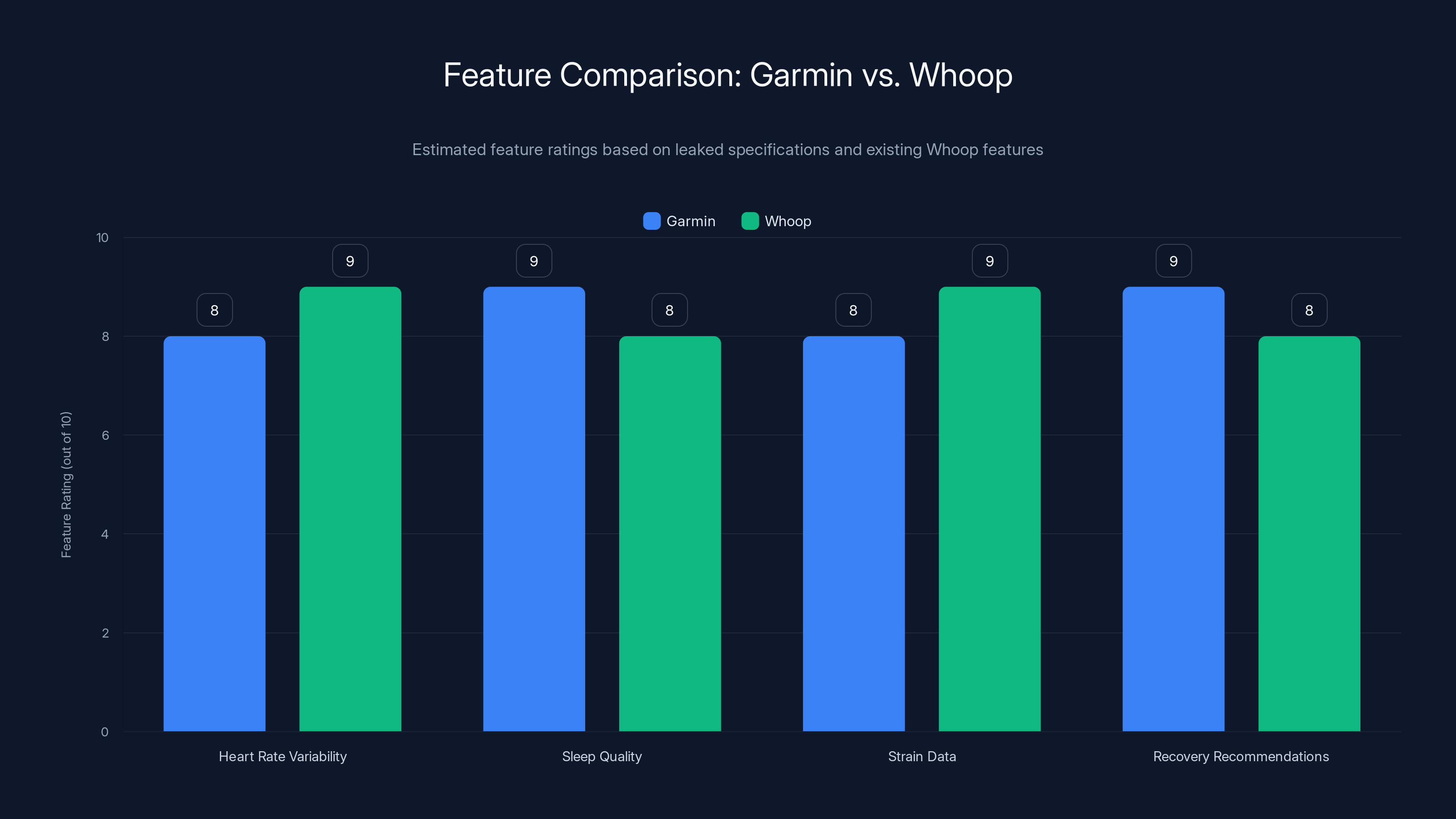
Garmin's new fitness tracker is estimated to closely match Whoop's feature set, potentially offering similar or enhanced capabilities in heart rate variability and recovery recommendations. Estimated data.
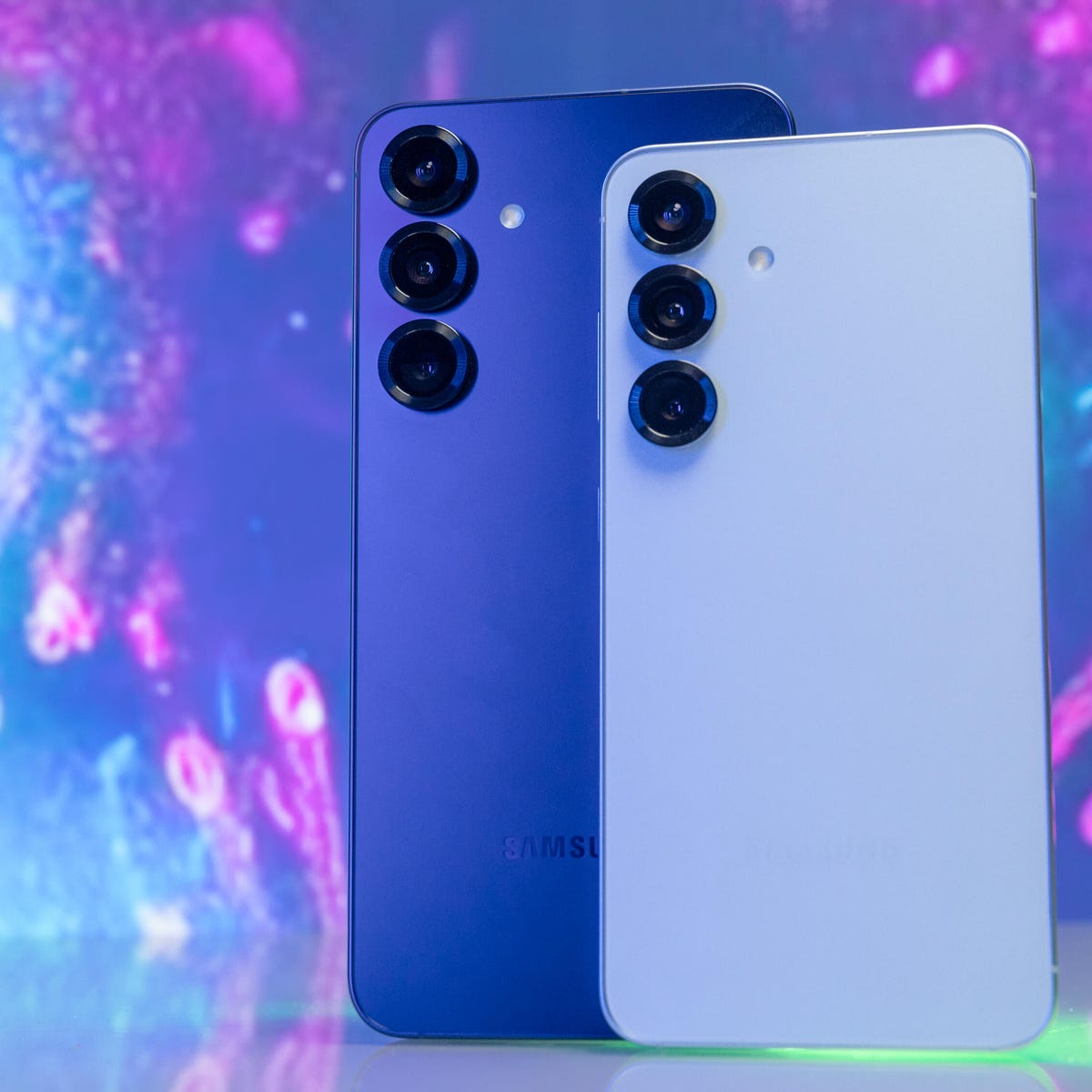
Story 1: Samsung Galaxy S26 Reveals Major AI Camera System Overhaul
Samsung's AI Photography Revolution
Samsung's forthcoming Galaxy S26 flagship represents a watershed moment for smartphone photography. The leaked specifications indicate that Samsung is fundamentally rethinking how computational photography works by integrating multiple AI neural networks directly into the device's image processing pipeline. This isn't merely an incremental improvement to existing features—it's an architectural redesign that could influence smartphone camera design industry-wide. According to PhoneArena, the S26's camera system reportedly utilizes dedicated AI accelerators that run inference tasks locally on-device, without requiring cloud processing. This approach has significant advantages: faster processing times, enhanced privacy (image data never leaves the device), and reduced dependency on network connectivity.
Specific capabilities leaked across multiple sources suggest the S26 will feature real-time object recognition that enables dynamic focus shifting during video recording. Imagine recording a video where the camera automatically tracks and maintains focus on a moving subject while keeping background elements artistically blurred. This type of dynamic depth-of-field adjustment during video capture has previously required expensive cinema equipment or complex post-production editing.
Technical Architecture Behind the Improvements
The underlying technology leverages transformer-based neural networks optimized for mobile hardware. Samsung has partnered with leading AI chip designers to ensure the processing power required for real-time AI inference doesn't drain battery life excessively. Thermal management emerged as a critical challenge—running intensive AI processing generates heat, and Samsung's solution involves intelligent scheduling that distributes computational load across multiple processor cores.
The image signal processor (ISP) in the S26 has been redesigned to handle AI tensor operations natively. Traditional smartphone image processors evolved to handle raw sensor data conversion and basic filtering. The S26's ISP now includes dedicated pathways for AI computations that work in parallel with traditional image processing, creating a hybrid architecture that excels at both conventional photography and AI-enhanced features.
One particularly impressive feature involves intelligent scene segmentation—the camera identifies different elements within a frame (sky, foliage, faces, buildings) and applies different processing algorithms optimized for each element type. A landscape photograph might apply one set of enhancements to the sky, completely different enhancements to trees and foliage, and yet another optimization for any faces in the frame. This selective enhancement produces more natural, well-balanced results compared to applying uniform filters across entire images.
Practical Implications for Mobile Photography
For photography enthusiasts, the S26 represents a significant quality leap. Night mode photography receives substantial improvements—the AI system can now identify sources of light pollution and correct for color temperature shifts automatically. Low-light scenarios that would previously result in grainy, color-shifted images should produce cleaner, more natural results.
Video recording capabilities expand considerably. The AI system can maintain consistent color grading across multiple video clips, allowing creators to film scenes with varying lighting conditions and have them appear as if shot under uniform illumination. This feature directly addresses one of professional videography's most time-consuming tasks: color correction across multiple takes.
Portrait mode receives a complete overhaul. Rather than simply blurring background elements, the new system understands face geometry well enough to apply selective sharpening to eyelashes, eyebrows, and other fine details while maintaining natural skin texture. This addresses a long-standing complaint about portrait mode—it often makes skin look overly processed or plastic-like.
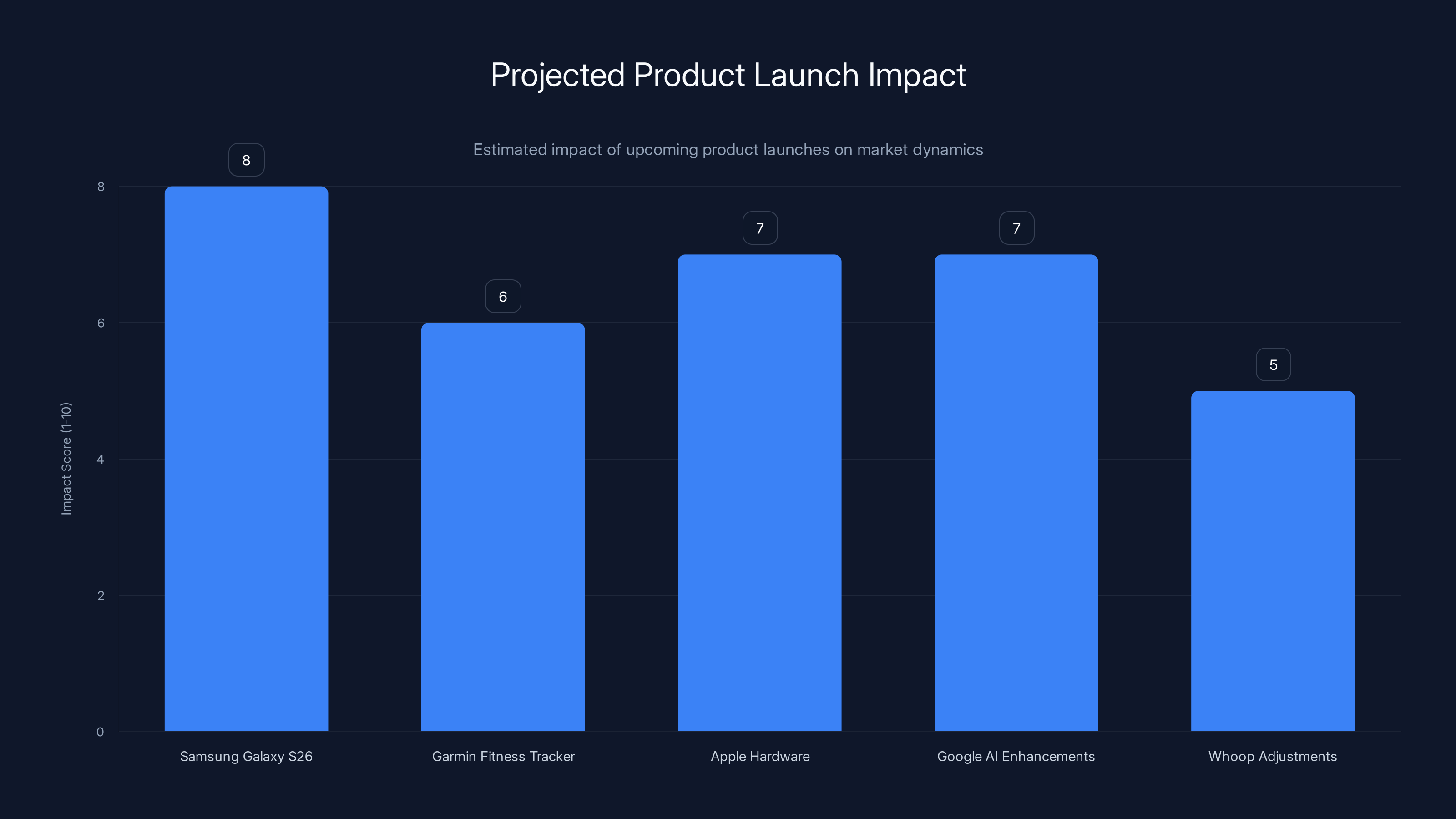
Estimated data: Samsung's Galaxy S26 is expected to have the highest impact due to its major event launch, while Whoop's response may have a moderate impact.
Story 2: Garmin's Fitness Tracker: Directly Competing with Whoop
Garmin's Strategic Move into Premium Wearables
Garmin, traditionally known as a GPS navigation specialist and sports watch manufacturer, apparently has strategic ambitions to compete directly in Whoop's market segment. Whoop, founded in 2012, created an entirely new category of wearables focused on comprehensive biometric tracking and recovery coaching. The leaked details about Garmin's upcoming device suggest the company plans to match or exceed Whoop's feature set while leveraging its established expertise in sports metrics and battery optimization.
This represents a significant competitive development because Garmin brings manufacturing scale and distribution relationships that boutique wearable companies like Whoop lack. Whoop currently operates as a premium, subscription-focused business with a tight ecosystem. Garmin's entry could democratize access to similar features at potentially lower price points, disrupting Whoop's premium positioning.
The leaked specifications indicate Garmin's device will track similar metrics to Whoop: heart rate variability (HRV), sleep quality, strain data, and recovery recommendations. However, Garmin appears to be integrating these features into a broader ecosystem of sports watches, running watches, and fitness trackers rather than positioning it as a standalone device. This platform approach could prove more compelling to existing Garmin users who already own multiple fitness devices.
Technical Specifications and Sensor Architecture
Garmin's device reportedly utilizes an advanced optical heart rate sensor that operates across visible and near-infrared wavelengths simultaneously. This dual-wavelength approach improves accuracy during motion and provides better signal consistency compared to single-wavelength sensors. The sensor can measure HRV with greater precision—a critical metric for Whoop-style recovery analytics—by analyzing beat-to-beat variations in heart rhythm.
Battery life emerges as a major differentiator. Whoop users must charge their devices every 2-3 days. Garmin's device, according to leaks, targets 5-7 days of battery life between charges. This longevity stems from Garmin's expertise in power management for sports watches. The company has spent decades optimizing battery consumption in GPS-enabled devices, and they're applying that expertise to optical sensor management.
The device includes multiple sensing modalities: accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, and skin temperature sensors. The barometer enables altitude tracking and pressure trend analysis—useful for understanding how atmospheric conditions affect athletic performance. Skin temperature sensing provides real-time biometric data useful for detecting illness onset and monitoring recovery status.
Competitive Positioning Against Whoop
Whoop's strength lies in its sophisticated machine learning algorithms that correlate biometric data with real-world performance outcomes. Whoop's recommendation engine provides highly personalized guidance about training intensity, sleep optimization, and recovery protocols. Garmin needs to match this AI sophistication to be truly competitive.
Garmin likely has a significant advantage in the sports watch market. Many ultramarathon runners, triathletes, and serious fitness enthusiasts already own Garmin sports watches. If Garmin can integrate Whoop-like recovery analytics into their existing watch ecosystem, they could convert existing customers more easily than Whoop can expand its subscriber base.
Price points will prove decisive. Whoop's subscription costs
Story 3: Breakthrough Advances in Large Language Models and AI Reasoning
The Evolution of Reasoning Capabilities in AI
This week witnessed continued progress in large language model development, particularly around so-called "reasoning" capabilities. Recent breakthroughs demonstrate that language models can now work through complex multi-step problems more effectively than previous generations, moving beyond simple pattern matching toward something resembling genuine problem-solving.
The technical distinction matters significantly. Previous language models excelled at predicting the next most likely word in a sequence—essentially sophisticated pattern matching based on training data. Newer models incorporate architectural innovations that enable them to work through problems step-by-step, checking their reasoning at each stage and backtracking when they detect errors. This represents a fundamental shift in how AI systems approach difficult problems.
These reasoning advances have immediate practical implications. Developers can now use language models for complex code generation tasks that require multiple connected decisions. Mathematical problem-solving—particularly in calculus and discrete mathematics—shows substantial improvement. The models can now work through proofs, verify intermediate steps, and catch their own mistakes, resulting in higher accuracy rates than previous generation models.
Developer-Focused Applications
For developers and engineers, these reasoning advances mean language models become more useful as coding assistants. Rather than generating code snippets that require human review and debugging, newer models can now generate complete solutions to complex problems and often verify their own output for correctness. This capability accelerates development cycles considerably.
The improvement extends to systems design and architectural decisions. When developers use language models to work through infrastructure problems, the models can now propose solutions that account for multiple constraints simultaneously—scalability requirements, cost optimization, security considerations, and operational complexity. This holistic approach to problem-solving mirrors how experienced engineers think through system design.
Documentation generation receives substantial benefits. Models with improved reasoning can now generate documentation that accurately reflects complex systems because they can reason through how components interact. This reduces the time software engineers spend on documentation while improving accuracy and completeness.
Enterprise Implications and Adoption Patterns
Enterprises are beginning to deploy these reasoning-capable language models in mission-critical applications. Financial institutions use them for fraud detection and risk assessment. Healthcare organizations deploy them for diagnostic support. Manufacturing companies use them for quality control and predictive maintenance scheduling.
The key difference in enterprise adoption concerns safety and verification. Enterprises cannot simply deploy AI models and trust the output implicitly. Advanced reasoning capabilities actually make enterprise deployment easier because the models can now explain their reasoning process, enabling humans to audit and verify decisions before implementation. This transparency builds confidence in AI-assisted decision making.
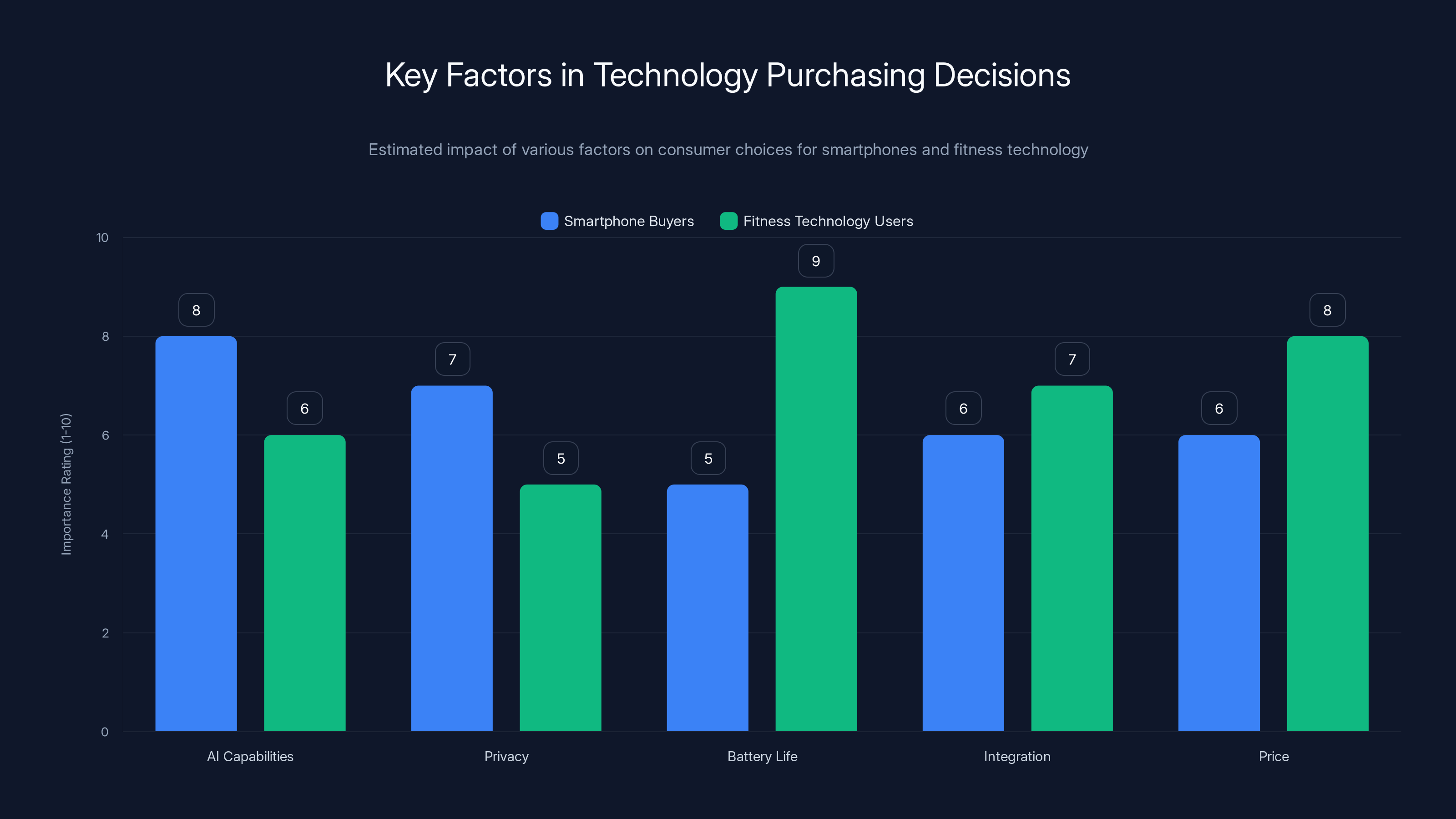
AI capabilities and privacy are crucial for smartphone buyers, while battery life and price are key for fitness tech users. Estimated data based on consumer trends.
Story 4: Apple Intelligence Expands to mac OS and i Pad Operating Systems
Integration Across the Apple Ecosystem
Apple continued its rollout of on-device AI capabilities—branded as "Apple Intelligence"—expanding these features from iPhone to Mac and iPad devices. This ecosystem-wide integration represents Apple's strategy to keep AI processing local to user devices rather than relying on cloud processing, a positioning advantage Apple emphasizes heavily in their marketing and product strategy.
The technical architecture involves specialized neural processing engines built into Apple's chips—the A-series processors for phones and tablets, and the M-series processors for Mac computers. Apple designed these chips specifically to handle machine learning workloads efficiently, enabling sophisticated AI features without excessive power consumption or thermal issues.
Why does this matter beyond Apple's ecosystem? Because Apple's bet on local processing—keeping AI inference on-device rather than sending data to cloud servers—represents a different philosophical approach than competitors like Google and Microsoft, who favor cloud-based AI processing. Apple's strategy emphasizes privacy (your data stays on your device) and performance (no network latency for AI features). This debate about on-device versus cloud processing will influence how the entire industry evolves.
Privacy-First Architecture
Apple's approach involves running AI models entirely on-device for most operations. Certain complex tasks that exceed on-device capability can optionally run on Apple's servers, but users have explicit control over whether to enable this cloud processing. For privacy-conscious users, the on-device-first approach addresses longstanding concerns about tech companies processing personal data on remote servers.
The implementation requires substantially more engineering than traditional cloud-based AI. Models must be compressed and optimized to run efficiently on consumer hardware with limited memory and processing power. Apple's investment in neural engine design—dedicated hardware for machine learning—enables this efficient on-device processing.
Developers building on the Apple ecosystem gain access to these AI capabilities through accessible APIs. Rather than forcing developers to implement complex machine learning code themselves, Apple provides high-level APIs that abstract away the complexity. A developer might call a single function to perform natural language processing, and the underlying system handles the neural network computation, optimization, and resource management.
Real-World Features Enabled by These Capabilities
Email applications become more intelligent. The system can automatically categorize incoming messages, prioritize important communications, and even draft response suggestions. Writing assistants built into all text input fields help users refine their writing, providing suggestions for tone adjustment and clarity improvements.
Photo organization receives substantial improvements. The system recognizes objects, scenes, and people in photos without uploading images to cloud servers. You can search your photo library for specific things ("photos with dogs" or "beach sunset photos") and get accurate results, entirely processed locally on your device.
Notification management becomes smarter. The system learns which notifications you typically engage with and which you dismiss, then automatically prioritizes notifications more intelligently. This capability reduces notification fatigue while ensuring important alerts still reach you promptly.

Story 5: Google's New AI Search Integration and Semantic Understanding Improvements
Transforming Search Through Generative AI
Google announced significant expansions to its AI-powered search capabilities, moving beyond traditional keyword matching toward generative AI that synthesizes information and provides direct answers rather than simply listing documents. This represents an existential competitive challenge to Google's existing search business model—search results that provide complete answers reduce the likelihood that users click through to external websites where Google displays advertisements.
The technical achievement involves training language models on the entire indexed web while maintaining the ability to cite sources and verify factual accuracy. This is substantially more difficult than training language models on generic internet text. Google's models must map generated responses back to specific source documents, enabling fact-checking and attribution.
For search users, the immediate impact means search results increasingly provide direct answers rather than requiring click-through to external websites. A query about "how to fix a leaky kitchen faucet" might generate a step-by-step guide directly in the search results, synthesized from multiple authoritative sources. This capability makes search more immediately useful for many common queries.
Semantic Understanding and Entity Recognition
Google's improvements to semantic understanding enable the search system to comprehend complex relationships between concepts. A search for "best hiking trails near me with water features" requires understanding the spatial relationship between the user's location, trail characteristics, and landscape features. Previous search systems struggled with these complex, multi-faceted queries.
The updated system performs entity recognition at a deeper level. When you search for information about a person, the system understands different contexts—a query for "President Lincoln" understands you might want biographical information, historical context, or references to Lincoln-related sites. The system disambiguates based on contextual clues and your search history.
Competitive Implications for Search and AI
Microsoft's Bing, powered by Open AI's language models, initiated this shift toward generative AI in search. Google's response was delayed but comprehensive—rather than replace their existing search algorithm, Google is layering generative capabilities on top of their existing ranking systems. This hybrid approach preserves what works while adding new capabilities.
But this transformation creates a paradox for Google: better AI-powered search results that answer questions directly may reduce advertising inventory if users no longer click through to external websites. This long-term business model challenge influences how aggressively Google can push generative search capabilities.

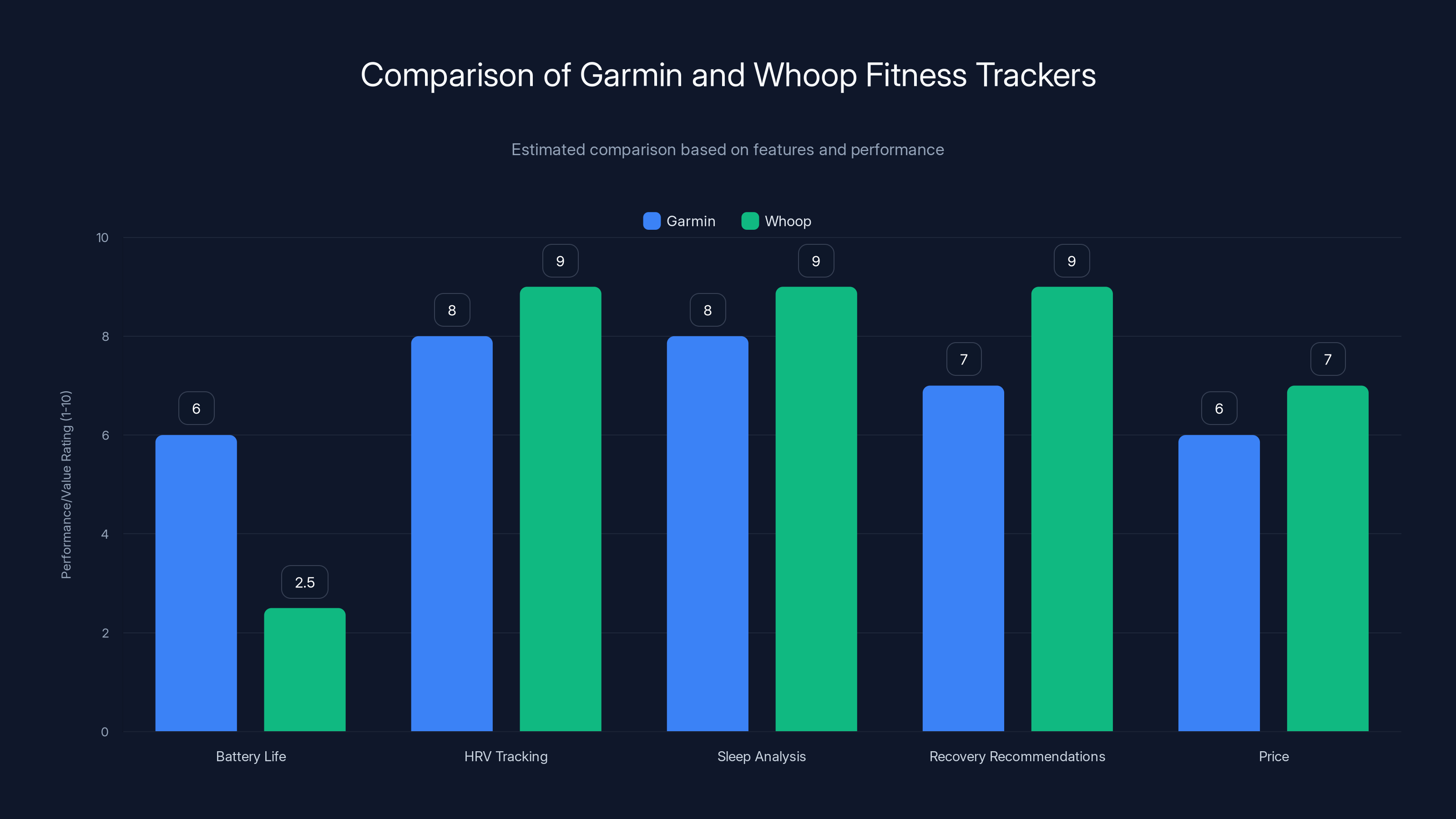
Garmin offers longer battery life and integration with its ecosystem, while Whoop excels in HRV tracking and personalized guidance. Estimated data based on available information.
Story 6: Meta's Latest AI Model Releases and Open-Source AI Strategy
Commitment to Open-Source AI Development
Meta (formerly Facebook) continues its commitment to open-source artificial intelligence by releasing new large language models and multimodal AI systems to the research community. This strategy diverges from competitors like Open AI and Google, which maintain tighter control over their AI models. Meta's approach involves making models available to researchers and developers, enabling broader AI experimentation and development.
Why adopt an open-source strategy in a competitive landscape? Meta's calculation appears to be that widespread AI adoption—even if some competitors use Meta's technology—benefits Meta by accelerating AI infrastructure development and creating large ecosystems around Meta-published models. Additionally, open-source development attracts top AI research talent and provides Meta credibility in the academic and research communities.
The released models include improvements in reasoning capabilities, multimodal understanding (processing images and text together), and efficiency optimizations that enable models to run on less powerful hardware. These improvements matter because they lower the barrier to AI adoption—researchers and companies with limited computing resources can now experiment with state-of-the-art models.
Practical Applications for Developers
Developers building AI-powered applications can now leverage Meta's models without building relationships with Meta's sales teams or accepting terms that restrict how models can be used. This democratization of AI models accelerates innovation in applications across multiple domains.
For companies evaluating AI infrastructure decisions, the availability of quality open-source models changes the calculation. Rather than committing to proprietary models from major cloud providers, companies can build on open-source foundations and maintain greater independence. This competitive dynamic pushes all AI providers to improve their offerings and reduce pricing, benefiting end users.
Startups particularly benefit from this open-source approach. Early-stage companies building AI-powered products can minimize infrastructure costs by using open-source models rather than expensive commercial APIs. As companies scale, they might eventually migrate to more sophisticated commercial offerings, but open-source models remove early-stage cost barriers.

Story 7: Quantum Computing Milestones and Practical Progress Toward Real-World Applications
Recent Breakthroughs in Quantum Error Correction
The quantum computing field achieved meaningful progress on error correction—one of the fundamental challenges preventing quantum computers from solving real-world problems. Quantum bits (qubits) are inherently fragile; environmental interference causes errors that accumulate and ultimately corrupt computation results. Error correction requires redundancy, but quantum systems cannot simply copy qubits (a consequence of quantum mechanics). Recent work demonstrated error correction schemes that actually reduce errors as more qubits are added to the system—a crucial milestone.
This breakthrough matters because it addresses the primary barrier preventing quantum computers from scaling. Previously, adding more qubits to a system increased total error rates. If you couldn't control errors, making quantum computers larger and more powerful was impossible. The new error correction approaches reverse this curve—systems with more qubits can have lower error rates than smaller systems, enabling exponential scaling of computational capability.
The technical achievement involved encoding quantum information across multiple qubits in ways that enable detection and correction of errors without measuring the data qubits themselves (measurement would destroy quantum states). These schemes use carefully designed parity checks analogous to classical error correction, but adapted for the quantum domain.
Timeline to Practical Quantum Computers
Experts suggest quantum computers capable of solving practically useful problems remain 5-10 years away, though this timeline continues to shift as progress accelerates or slows. The problems most likely to be solved first involve optimization (finding the best solution within enormous search spaces), molecular simulation (understanding how atoms interact), and specific machine learning tasks.
Industries paying close attention include pharmaceuticals (drug discovery), materials science (designing new materials with specific properties), and finance (optimization of portfolios and financial instruments). These domains have well-defined problems where quantum computers might provide advantages over classical computers.
For most organizations, quantum computing remains a long-term consideration rather than an immediate threat or opportunity. However, companies processing sensitive data or working in quantum-adjacent domains should begin monitoring developments and considering how quantum advances might impact their businesses 5-10 years forward.

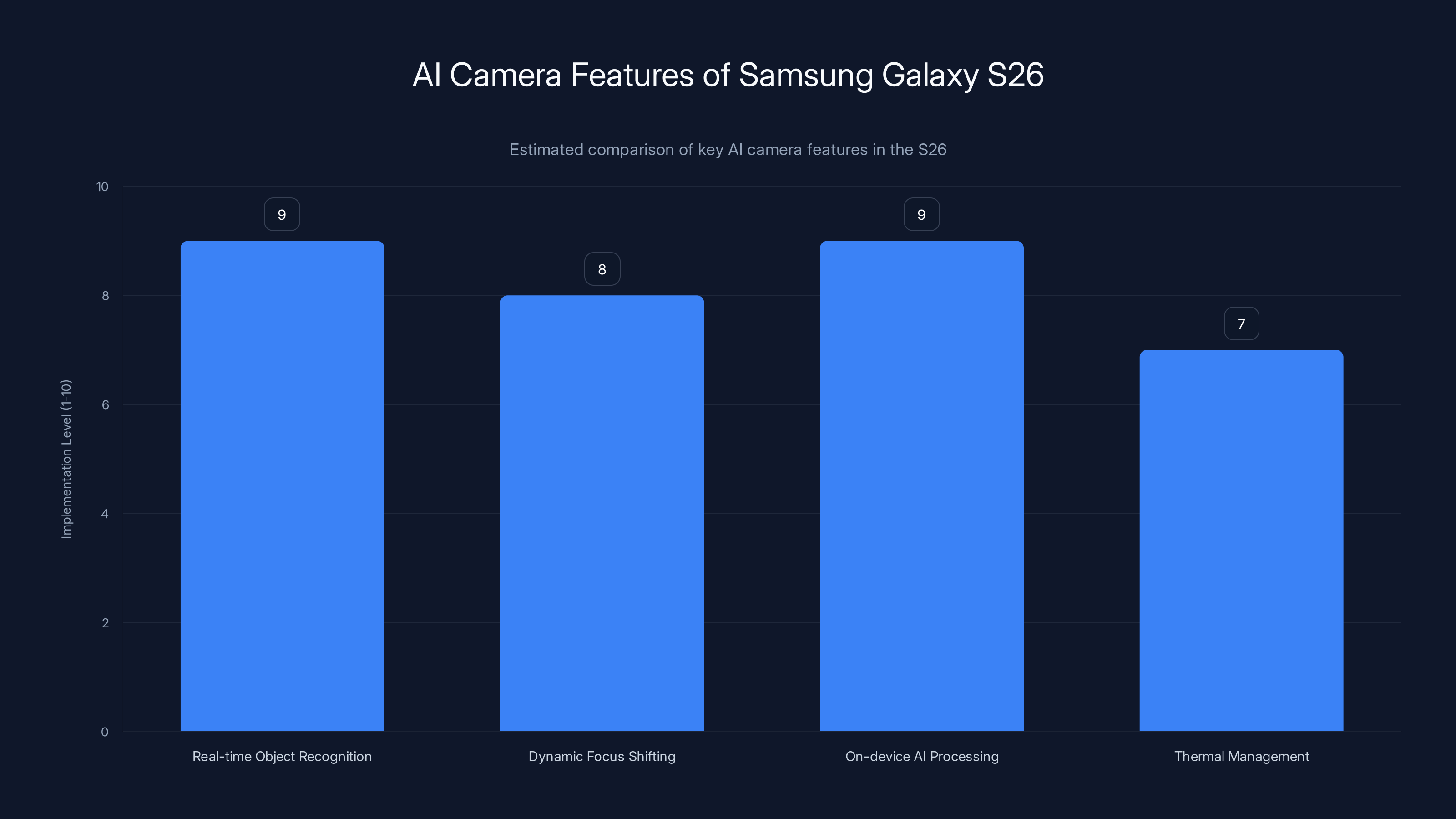
The Samsung Galaxy S26's AI camera system excels in real-time object recognition and on-device AI processing, setting a new standard for smartphone photography. Estimated data.
Story 8: Additional Developments Worth Your Attention
Emerging Technologies Reshaping Device Categories
Beyond the primary stories, this week included several secondary announcements indicating where manufacturers expect technology to evolve. Foldable device technology continued its maturation—multiple manufacturers announced incremental improvements in hinge durability and display crease reduction. These aren't revolutionary breakthroughs, but they suggest foldable devices are transitioning from novel prototypes to practical products.
Battery technology announcements indicate gradual improvements in energy density and charging speed. While no revolutionary battery chemistry breakthroughs occurred this week, incremental improvements from multiple manufacturers suggest the industry is making consistent progress. Energy density improvements of 5-15% annually might seem modest, but compound over multiple years into meaningful real-world improvements.
Augmented reality device development continued, with multiple companies announcing improvements to optical systems and processing power. AR glasses—the next potential breakthrough category in personal computing—remain challenged by manufacturing complexity and power consumption, but steady progress suggests commercial products might emerge within 3-5 years.
Market Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
This week also featured announcements of strategic partnerships and competitive positioning adjustments. These business developments often matter more than individual product announcements because they signal long-term strategic direction. Companies forming partnerships around AI infrastructure, cloud computing, or semiconductor manufacturing are essentially betting on which platforms and technologies will dominate future markets.
When major manufacturers announce partnerships around specific technology standards (like wireless charging, cloud storage, or AI processing), these announcements indicate which technology directions have industry consensus. This consensus shapes hardware design for years forward.

Understanding the Broader Tech Trends Driving These Announcements
The AI Integration Thesis
The fundamental theme threading through this week's announcements is comprehensive AI integration across device categories. Rather than AI as a separate feature or product, AI is becoming a foundational component of how devices function. This represents a paradigm shift from how technology has evolved previously.
Smartphones used to improve primarily through faster processors and better cameras. The newest generation of improvements focus on AI capabilities that enhance photography, personalization, and user interface responsiveness. This AI-first approach extends to smartwatches, fitness trackers, laptops, and even automotive systems.
This shift creates winner-take-most dynamics for companies with the best AI models and most efficient neural processing hardware. Companies that can run sophisticated AI locally on-device gain advantages in performance, privacy, and user experience. Companies that excel at training and optimizing neural networks gain competitive advantage across multiple product categories.
Computing Architecture Transformations
The announcements reveal fundamental shifts in computing architecture. Traditional approaches separated AI processing from application logic—AI ran in the cloud, applications ran locally. The newest trend involves embedding AI processing capability directly into devices through specialized hardware (neural engines, AI accelerators).
This architectural shift has implications for software development, power management, security, and system design. Engineers building applications must now understand neural network performance characteristics and can leverage AI capabilities more directly within their code. Operating systems must manage AI workload scheduling alongside traditional processes. Security considerations expand to include protecting machine learning models and the inference process.
Privacy and Data Sovereignty
These announcements reflect a broader industry trend toward processing sensitive data locally rather than sending it to cloud servers. This shift stems from regulatory pressure (privacy regulations like GDPR), competitive positioning (companies emphasizing privacy as a differentiator), and genuine user concerns about data privacy.
Local processing trades off some capabilities. Cloud-based AI can access unlimited computational resources and massive training datasets. On-device AI is constrained by available processing power and must rely on pre-trained models. However, users increasingly prefer limited functionality with strong privacy guarantees over more powerful features that require data transmission to remote servers.

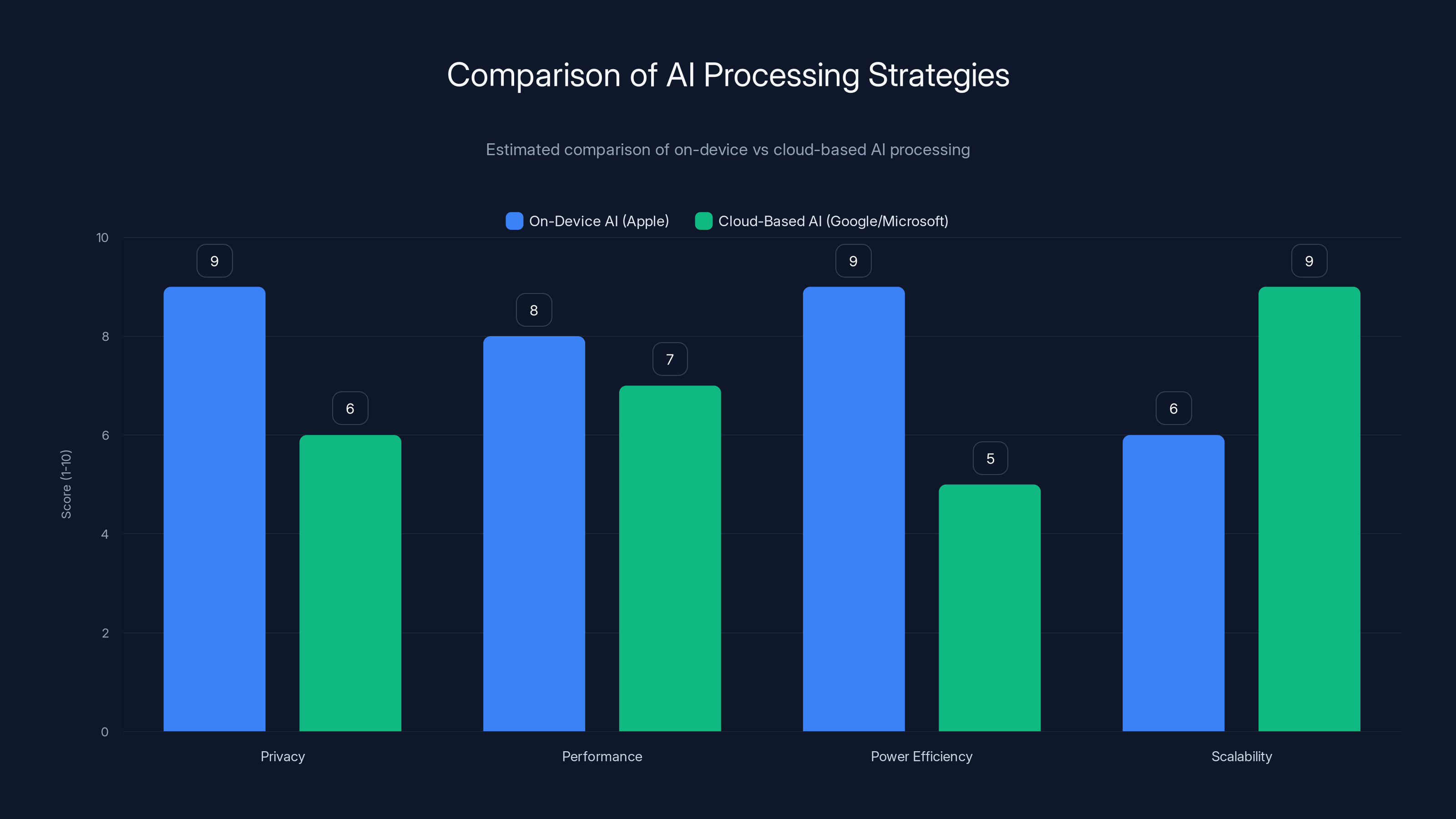
Apple's on-device AI strategy scores higher in privacy and power efficiency, while cloud-based AI excels in scalability. Estimated data.
Impact on Technology Purchasing Decisions and Consumer Strategies
Implications for Smartphone Buyers
These announcements should influence how you evaluate smartphones if you're considering an upgrade. AI capabilities are increasingly differentiating factor between devices. If you use smartphone photography extensively, the Samsung S26's AI photography improvements warrant serious consideration. If you're comparing smartphones, evaluate not just processor speed and camera megapixels, but how effectively each device's AI handles common tasks you perform regularly.
The on-device processing advantage Apple emphasizes in iPhone models appeals to privacy-conscious users. If data privacy is important to you, on-device AI processing eliminates the concern about your data being processed on remote servers. However, cloud-based processing (used by Android manufacturers more frequently) often provides more advanced features at the cost of data transmission.
Considerations for Fitness Technology Users
Garmin's new fitness tracker entry provides options for users previously committed to Whoop or seeking alternatives. If you're a fitness enthusiast considering wearables, the expanded competitive landscape means better options at various price points. Evaluate based on which metrics matter most to you (HRV, sleep analysis, training load, recovery recommendations) and which ecosystem integrates best with your other devices.
Battery life emerges as a practical consideration. If you're tired of charging devices every 2-3 days, Garmin's promise of 5-7 day battery life addresses a real pain point. However, ensure the device actually delivers on these claims before purchasing—battery life estimates often differ from real-world performance.
Developer Considerations for AI Integration
For developers evaluating which platforms to build on, this week's announcements clarify that AI capabilities are becoming table stakes. Platforms with better AI integration and more accessible AI APIs attract more development activity. If you're building applications, consider whether your app benefits from AI features like natural language processing, computer vision, or personalization.
The competition between open-source AI (Meta's approach) and proprietary models (Open AI, Google's approach) offers developers choice about which infrastructure to use. Open-source models provide freedom and independence but may require more technical expertise. Proprietary models provide simplicity and support but lock you into specific providers and pricing models.

The Week Ahead: What to Watch
Upcoming Product Launches
Based on this week's announcements, several products are likely to launch in coming weeks. Samsung's Galaxy S26 should appear at a major smartphone event, likely in February or March. Garmin's fitness tracker entry will probably reach availability for pre-order shortly after announcement. These launches provide opportunities to evaluate real hardware rather than leaked specifications.
Price announcements matter significantly. Leaked specifications tell you about features, but pricing determines who can actually afford the innovations. A 30% performance improvement might excite tech enthusiasts, but if it costs 50% more than previous models, adoption will remain limited. Watch for pricing announcements that might surprise either positively or negatively.
Market Reactions and Competitive Responses
Competitors will respond to this week's announcements. Apple might accelerate its own hardware improvements. Google will likely enhance its search and Android AI capabilities. Whoop may respond to Garmin's competitive entry with pricing adjustments or new features. Watching competitive responses often reveals which announcements companies actually consider threatening.
Investor reactions provide another data point. Stock price movements and analyst commentary reflect financial markets' assessment of whether announcements represent meaningful competitive advantages or minor incremental improvements. Markets often see through hype to identify which developments actually matter.

Preparing for the AI-Integrated Technology Future
Building Your Technology Stack
If you're building your personal technology ecosystem, these announcements suggest prioritizing devices from manufacturers leading in AI integration. While today's AI features might seem incremental, the trajectory points toward AI becoming essential for device usability and capability. Devices designed with AI as an afterthought will feel increasingly dated.
Consider compatibility and ecosystem integration. Apple devices work seamlessly together. Google devices and Android phones integrate well. If you're mixing ecosystems, ensure the devices you choose provide good compatibility. The benefits of ecosystem integration are becoming more significant as AI capabilities become more sophisticated.
Skill Development and Professional Preparation
For professionals, these announcements suggest growing importance of understanding AI capabilities and limitations. Engineers should develop skills in machine learning, neural network optimization, and AI-assisted development. Product managers should understand how AI features should be evaluated and designed. Marketing professionals should learn how to communicate AI capabilities accurately without overstating them.
The demand for professionals who understand both software engineering and machine learning is increasing faster than the supply of qualified people. Investing in these skills now positions you advantageously for career opportunities in coming years.

FAQ
What is the Samsung Galaxy S26 and why does it matter?
The Samsung Galaxy S26 is the upcoming flagship smartphone from Samsung, expected to launch in early 2025. It matters because it represents a significant redesign of smartphone photography capabilities through integrated AI systems. Unlike incremental camera improvements, the S26 fundamentally changes how computational photography works by running sophisticated AI processing directly on the device, enabling features like dynamic focus tracking during video and intelligent scene-based optimization. This architectural approach influences how the entire smartphone industry designs camera systems.
How does Garmin's new fitness tracker compete with Whoop?
Garmin's new fitness tracker targets the same market segment as Whoop by offering comprehensive biometric tracking including heart rate variability (HRV), sleep analysis, recovery recommendations, and strain metrics. The key competitive advantages Garmin brings are significantly longer battery life (5-7 days versus 2-3 days for Whoop), integration with Garmin's existing sports watch ecosystem, and potentially lower pricing. However, Whoop's sophisticated machine learning algorithms for personalized guidance remain a competitive strength that Garmin must match to be truly competitive.
What are the benefits of on-device AI processing versus cloud-based AI?
On-device AI processing, emphasized by Apple and now expanding across other manufacturers, keeps your data local and doesn't require internet connectivity for features to work. This approach offers faster response times since processing happens immediately on your device without network latency. However, cloud-based AI processing can access unlimited computational resources and massive training datasets, enabling more sophisticated features. The trade-off is between privacy and capability—on-device processing is more private but sometimes less powerful, while cloud processing is more capable but requires data transmission to remote servers.
Why is AI error correction important for quantum computing?
Quantum error correction is crucial because qubits are fragile and easily corrupted by environmental interference. Without effective error correction, quantum computers become less reliable as you add more qubits—the opposite of classical computers where more processing power improves capability. Recent breakthroughs demonstrated error correction schemes that actually reduce errors as the system grows, enabling quantum computers to eventually scale to practical sizes. This represents the primary technical barrier preventing quantum computers from solving real-world problems, so progress here is genuinely significant.
What does "semantic understanding" mean in the context of Google's search improvements?
Semantic understanding refers to the ability to comprehend meaning and relationships between concepts, rather than just matching keywords. Traditional search systems looked for exact keyword matches. Modern semantic search understands intent, context, and relationships. When you search for "best hiking trails near me with water features," semantic understanding means the system grasps the spatial relationship between your location, trail characteristics, and landscape features. This enables more accurate results for complex, multi-faceted queries that don't have exact keyword matches.
How does Meta's open-source AI strategy differ from competitors?
Meta releases large language models and AI systems to the research community with open-source licensing, while competitors like Open AI and Google maintain tighter control. Meta's strategy assumes that widespread AI adoption—even if some competitors benefit—accelerates the overall AI ecosystem and attracts top talent to Meta. The approach democratizes AI by making high-quality models available to researchers and developers who might not have access to expensive proprietary models. However, competitors argue that openly releasing advanced models potentially aids competitors and reduces technical differentiation.
What timeline should I expect for quantum computers solving practical problems?
Most experts estimate quantum computers capable of solving practically useful problems remain 5-10 years away, though this timeline has been relatively consistent for several years (experts said "5-10 years away" five years ago and still say that today). The most likely first applications involve optimization problems, molecular simulation for drug discovery, and specific machine learning tasks. However, significant technical challenges remain before quantum computers transition from research curiosities to practical tools solving real business problems.
Which manufacturers are currently leading in AI-integrated device development?
Apple leads in on-device AI capabilities with Apple Intelligence features integrated across iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Samsung is clearly pushing hard with AI photography improvements in the S26. Google continues advancing AI in search and Android devices. Meta is advancing open-source AI models available to broader development communities. Garmin is making a competitive entry in AI-enabled fitness tracking. Leadership varies by device category and whether you prioritize local processing versus cloud capabilities.
How should I evaluate which smartphone to purchase given these AI improvements?
Consider how you actually use your smartphone. If photography is important to you, AI photography improvements matter significantly. If privacy is paramount, on-device processing is a key consideration. Evaluate the specific AI features against your actual use cases—sometimes marketed features sound impressive but won't impact your daily experience. Compare battery life, pricing, ecosystem integration with other devices you own, and long-term support plans. Don't choose a phone solely based on AI features without considering these broader factors.
Are there any risks or downsides to increased AI integration in devices?
Some legitimate concerns exist. As AI becomes more sophisticated, it becomes harder to understand why devices make particular decisions. A smartphone might choose to enhance certain colors in your photos, and it becomes difficult to predict these choices or override them when they miss the mark. There are also questions about whether AI features require more training and data collection, potentially raising privacy concerns despite on-device processing marketing claims. Additionally, increased complexity in AI systems means increased potential for bugs and unexpected behaviors. The industry is still learning how to safely deploy AI at scale.

Conclusion: Navigating the Technology Evolution of 2025
This week's seven technology stories collectively paint a picture of an industry in transition toward AI-integrated, locally-processed, and ecosystem-integrated devices. The announcements from Samsung, Garmin, Google, Meta, Apple, and quantum computing researchers aren't isolated developments—they represent coordinated movement by the industry toward a shared future where AI capabilities are foundational rather than supplementary.
Understanding these developments helps you make more informed technology purchasing decisions and prepares you for an environment where AI capabilities are increasingly expected rather than optional. The smartphone you purchase this year will incorporate AI features you haven't even considered yet. The fitness tracker you evaluate will be compared based on how well its AI understands your individual physiology and training patterns. The software development work you do will be amplified or limited by which AI tools you leverage.
The convergence of on-device processing, improved AI reasoning capabilities, and specialized hardware designed specifically for neural network computation suggests that 2025 will be remembered as an inflection point. Future devices will look back at today's technology as the moment when AI became pervasive rather than optional, when manufacturers stopped asking "should we add AI features" and started asking "which AI capabilities are essential."
For technology enthusiasts, professionals in tech fields, and consumers simply trying to make good purchasing decisions, the lesson is clear: AI capabilities should be a primary evaluation criterion when choosing new devices. Not as the only criterion—battery life, price, design, ecosystem integration, and support matter too—but as a major factor equivalent to processor power and camera quality.
The next six months will reveal how effectively manufacturers deliver on this week's promises. Samsung will launch the S26 and prove whether AI photography truly provides the leap forward that leaks suggest. Garmin will launch its fitness tracker and demonstrate whether it can compete effectively against Whoop's sophisticated algorithms. Google, Meta, and others will roll out their AI improvements and face real-world testing by millions of users. These launches provide concrete data points for evaluating whether this week's announcements represent genuine advancement or marketing hype. Keep watching as these products launch and reach users' hands—that's when we'll understand which promises hold up and which announcements were premature.

Key Takeaways
- Samsung S26 fundamentally redesigns smartphone photography through integrated AI that runs locally on-device without cloud processing
- Garmin's fitness tracker entry disrupts Whoop's premium positioning with longer battery life and comparable biometric tracking features
- 2025 marks an inflection point where AI capabilities transition from optional features to foundational device components across all categories
- On-device AI processing represents the industry's shift toward privacy-first computing, trading some capability for better data protection
- Google, Apple, Meta, and others are competing aggressively on AI capabilities, creating a winner-take-most dynamic for companies with the best models
- Quantum computing breakthroughs in error correction remove the primary technical barrier preventing practical quantum computers in 5-10 years
- Developers should prioritize understanding AI capabilities and limitations as these features become table stakes for competitive applications
- For consumers, AI capabilities should now be a primary evaluation criterion when choosing phones, watches, and other connected devices
Related Articles
- Apple & Google AI Partnership: Why This Changes Everything [2025]
- Apple's AI Pin Strategy: Why It Misses the Mark [2025]
- Garmin Cirqa Smart Band: Complete Analysis & Alternatives [2025]
- Experian's AI Evolution: Credit Scores, Privacy & Data Ethics in 2025
- AMI Labs: Inside Yann LeCun's World Model Startup [2025]
- Apple's Siri AI Chatbot Revolution: What Changed & Alternatives




