Beware of Fake 7-Zip Installers Laced with Malware [2025]
Last week, a startling revelation shook the tech community: a malicious website posing as 7-Zip's official site was distributing malware-laden installers. This isn't just a cautionary tale; it's a wake-up call for everyone who downloads software online. Let's dive deep into how these scams operate, the risks involved, and how you can protect yourself.
TL; DR
- Fake Websites: Malicious sites mimic legitimate ones, distributing malware, as detailed in Malwarebytes' report.
- Malware Risks: Devices can be compromised and used for criminal activities, according to Help Net Security.
- Verification Tips: Always check the URL and source before downloading.
- Security Measures: Use robust antivirus and stay updated with security patches, as recommended by PCMag.
- Future Trends: Expect more sophisticated cyber threats as technology evolves, as discussed in Industrial Cyber.

The Rise of Fake Software Installers
In recent years, downloading software from the internet has become a double-edged sword. While it's convenient, it's also a playground for cybercriminals. The proliferation of fake installers, like the recent case with 7-Zip, highlights a growing threat where malefactors exploit popular software to spread malware, as noted by CyberPress.
How Fake Installers Work
Fake installers are designed to look like legitimate software downloads. Cybercriminals create websites that mimic official sites or embed download links in popular video tutorials and blog posts. Users, believing they are downloading genuine software, inadvertently install malicious programs.
Example: A fake site using a URL like 7zip-download.com offers what appears to be a legitimate 7-Zip installer. Upon installation, the malware could run a script to steal data, hijack the system, or enlist the device in a botnet, as explained in Manufacturing Business Technology.
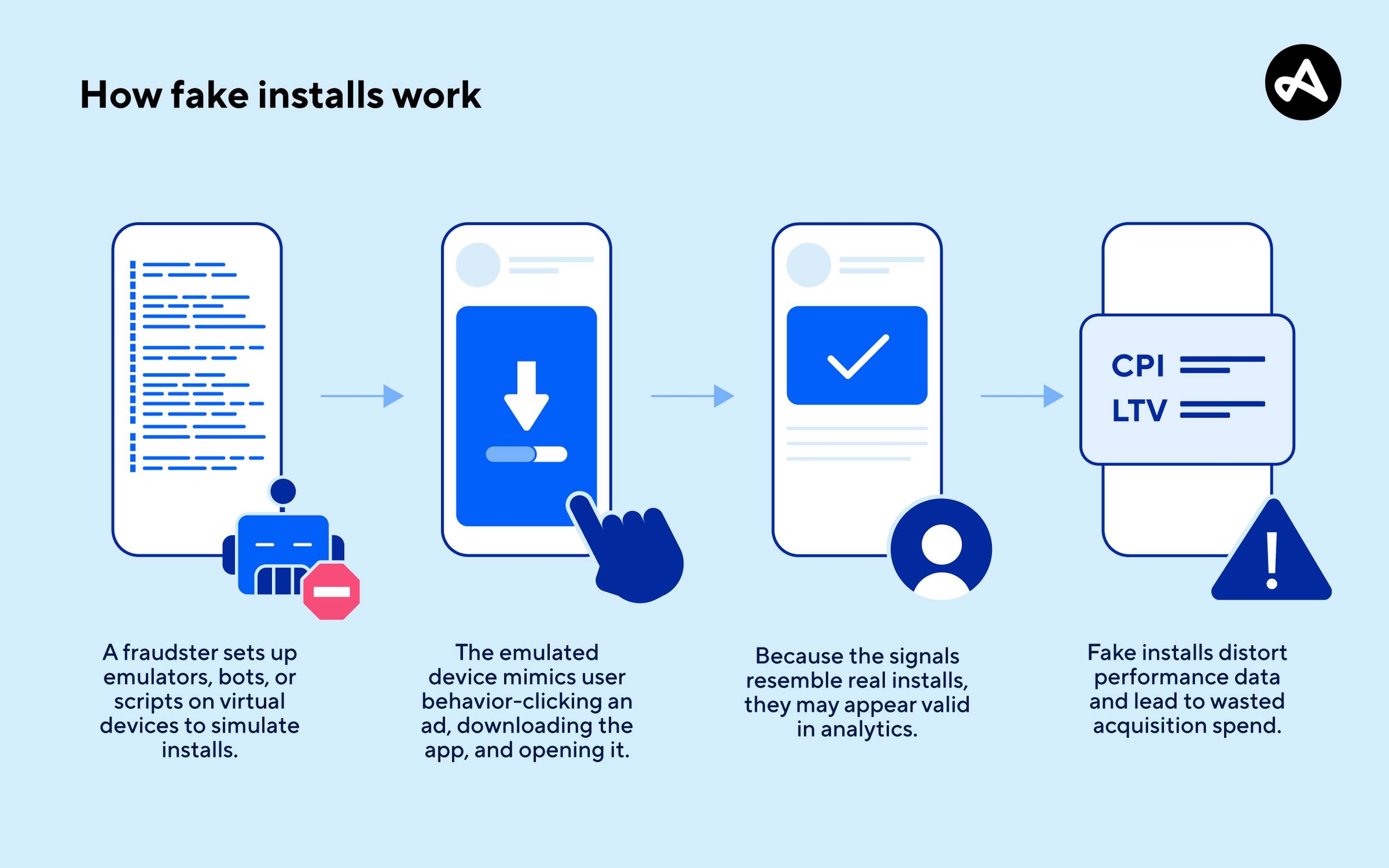
Understanding Malware Distribution
Malware distribution via fake software installers is a sophisticated operation. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
- Creation of Fake Websites: Cybercriminals design websites that closely resemble legitimate ones. They may use similar domain names to trick users, as highlighted by Microsoft Security Blog.
- SEO Manipulation: To increase visibility, these sites may employ SEO tactics to appear higher in search results.
- Social Engineering: Links to these fake installers are often shared on social media, forums, or embedded in video tutorials, exploiting the trust users place in these platforms.
Why Malware from Installers is Dangerous
Malware from fake installers can have devastating effects:
- Data Theft: Personal information, including passwords and banking details, can be stolen.
- Device Hijacking: Your device could become part of a botnet, used for DDoS attacks or cryptojacking.
- Privacy Invasion: Malware might access files, emails, and other sensitive data without your consent.
Best Practices for Safe Software Downloads
To protect yourself, follow these best practices:
- Verify URLs: Always ensure the URL matches the official website. For 7-Zip, the correct URL is
7-zip.org. - Check for HTTPS: Secure sites use HTTPS. Look for a padlock icon in the address bar.
- Read Reviews: Check user reviews and forum discussions for any red flags about the download source.
Implementing Security Measures
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Invest in reputable antivirus and anti-malware software. These tools can detect and remove threats before they cause harm.
Popular Options:
- Norton Antivirus: Known for comprehensive protection and regular updates.
- Malwarebytes: Specializes in malware removal and offers real-time protection.
- Bitdefender: Offers robust virus protection and minimal system impact.
Keeping Software Updated
Regular updates patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malware. Enable automatic updates for your operating system and applications.
Example: Windows Update and macOS Software Update provide critical security patches routinely.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Falling for Phishing Scams
Phishing emails often contain links to fake software downloads. Be cautious of unexpected emails and verify the sender before clicking any links.
Ignoring Security Warnings
Browsers and operating systems often warn users about potentially harmful downloads. Don’t ignore these warnings.
Solution: Investigate the warning, and if in doubt, do not proceed with the download.
The Future of Cybersecurity
As technology evolves, so do cyber threats. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, using AI and machine learning to create more convincing scams, as discussed in MSN News.
Trends to Watch
- AI-Driven Attacks: AI can automate personalized phishing attacks, making them harder to detect.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: As IoT devices proliferate, they present new targets for malware.
- Blockchain Security: While blockchain is secure, the platforms and exchanges around it are not immune to attacks.
Recommendations for Staying Safe
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and trends.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Back-Up Data Regularly: In case of an attack, backups ensure you don’t lose important information.
Conclusion
Fake software installers are a significant threat, but with vigilance and the right security measures, you can protect yourself. Always verify your sources, stay informed about potential threats, and use robust security tools to safeguard your devices and data.
FAQ
What is a fake software installer?
A fake software installer is a malicious program disguised as a legitimate software download. It aims to trick users into installing malware on their devices.
How can I identify a fake website?
Look for discrepancies in the URL, absence of HTTPS, and poor website design. Cross-reference the URL with the official website.
What should I do if I accidentally download malware?
Immediately disconnect from the internet, run a full antivirus scan, and remove any detected threats. Change passwords for sensitive accounts.
Why is malware from installers particularly dangerous?
Because it can compromise your device, steal sensitive data, and enlist your device in botnets without your knowledge.
How can I protect my system from malware?
Use reputable antivirus software, keep your system updated, and verify download sources before installing any software.
What are the future trends in cybersecurity?
Expect more AI-driven attacks, increased focus on IoT security, and challenges in securing blockchain platforms.
How does malware affect device performance?
Malware can significantly slow down your device, cause crashes, and lead to unexpected behavior as it consumes system resources.
What role does education play in cybersecurity?
Education is crucial. Understanding common threats and best practices can help individuals and organizations avoid falling victim to cyberattacks.
Use Case: Automatically generate security reports to identify potential threats using AI-powered tools.
Try Runable For FreeKey Takeaways
- Fake software installers spread malware posing as legitimate software.
- Verify URLs and use trusted sources to avoid downloading malicious software.
- Invest in robust antivirus solutions for real-time protection.
- Stay informed about evolving cybersecurity threats and trends.
- Implement two-factor authentication for enhanced security.
Related Articles
- Proton VPN 70% Off Deal: Complete Breakdown [2025]
- Volvo Conduent Data Breach: 17,000 Customers Exposed [2025]
- SmarterTools Ransomware Breach: How One Unpatched VM Compromised Everything [2025]
- Wikipedia vs Archive.today: The DDoS Controversy Explained [2025]
- Google's Enhanced Safety Tools Remove More Personal Data [2025]
- Vega Security Raises $120M Series B: Rethinking Enterprise Threat Detection [2025]
![Beware of Fake 7-Zip Installers Laced with Malware [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/beware-of-fake-7-zip-installers-laced-with-malware-2025/image-1-1770822819922.jpg)



