Chat GPT Outages: What Causes Them and How to Prepare [2025]
It's 2 PM on a Wednesday. You're halfway through an important project, and you reach for Chat GPT to help you draft an email. The page won't load. You refresh. Still nothing. You check Twitter. Thousands of people are complaining. Chat GPT is down.
This scenario has played out dozens of times in the past year alone. And it's not just Chat GPT—nearly every major AI service experiences outages. Anthropic's Claude went down on the same day Chat GPT experienced issues in February 2025. When services relied on by millions of users go offline, the ripple effects are immediate and significant.
But here's what most people don't understand: these outages aren't random. They follow patterns. They happen for specific, predictable reasons. And knowing those reasons helps you plan accordingly.
In this guide, I'm breaking down what actually causes Chat GPT outages, how often they happen, how long they typically last, and most importantly, what you can do about it. Whether you're a casual user or running a business that depends on AI tools, understanding service reliability is non-negotiable.
TL; DR
- Chat GPT outages are common: Major disruptions happen every few months, with partial outages occurring more frequently
- Root causes are predictable: Infrastructure failures, traffic spikes, software bugs, and configuration errors account for 90% of downtime
- Typical duration ranges: Minor outages resolve in 15-30 minutes; major ones can last 2-6 hours or longer
- Tracking tools exist: Down Detector and status.openai.com provide real-time outage confirmation
- Prevention is possible: Implementing fallbacks, monitoring status pages, and using backup AI tools dramatically reduces workflow disruption
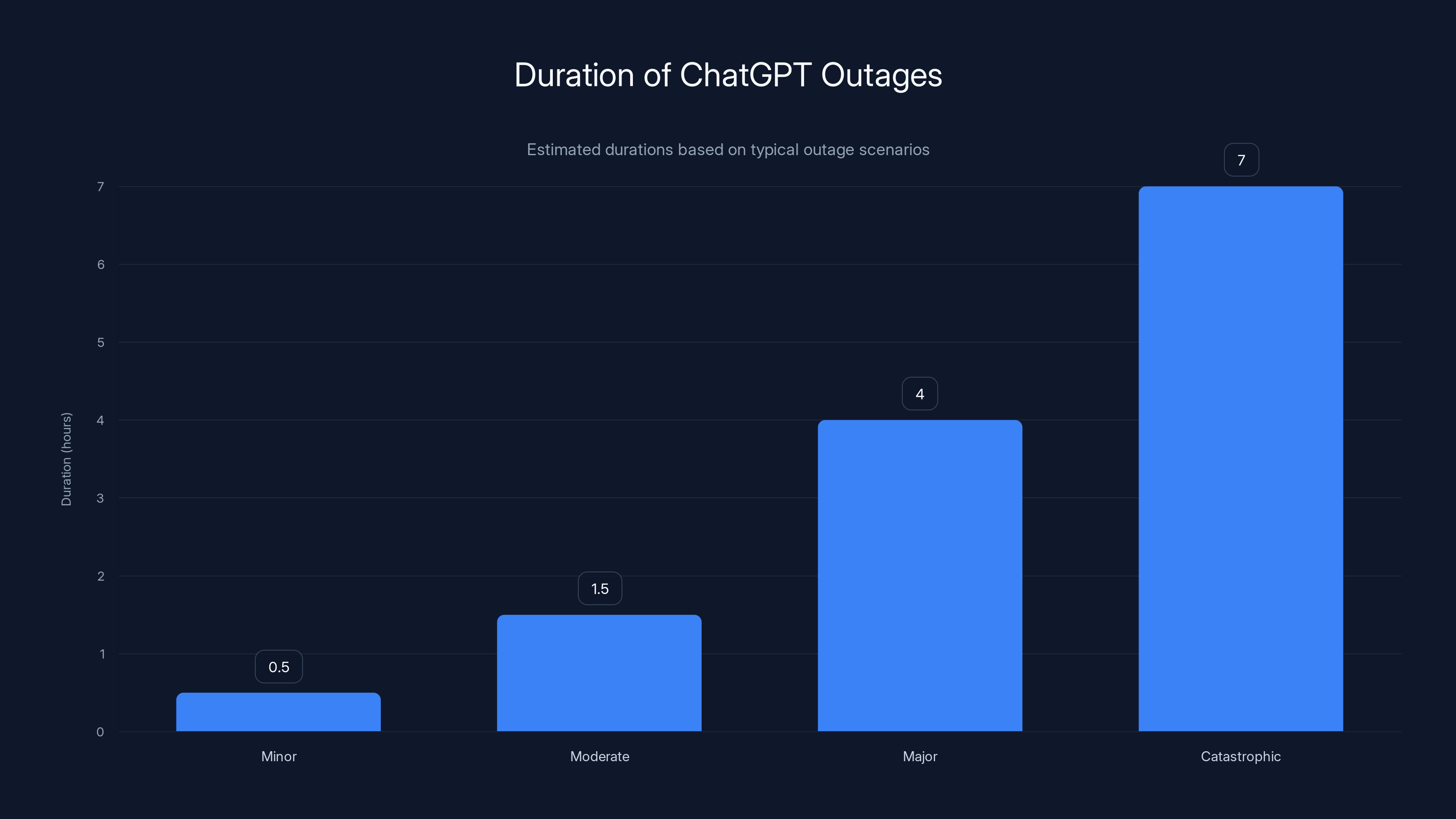
Minor outages often resolve within 30 minutes, while major outages can last up to 6 hours or more. Estimated data based on typical incidents.
Understanding AI Service Outages and Their Scale
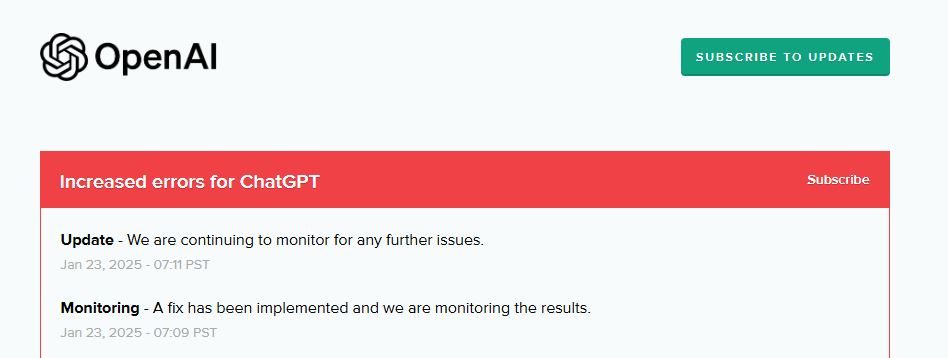
When Chat GPT went down in February 2025, Down Detector logged more than 12,000 reports at peak disruption. That number doesn't represent 12,000 individual users—it represents 12,000 people bothered enough to report the issue on a tracking website. The actual number of affected users was likely in the millions.
This wasn't a small glitch. It was a partial outage affecting a massive subset of Open AI's user base. The company posted a status update noting "elevated error rates" for both Chat GPT and its API platform. By 5:14 PM ET, they marked the primary issue as resolved. But a secondary issue persisted: the fine-tuning component of the API continued experiencing problems.
What's interesting is that the same day, Claude experienced a parallel outage with similar characteristics—elevated error rates across all models. Both services saw issues resolve within hours, but the fact that two competing services went down simultaneously suggests the problem might have been upstream, possibly involving shared infrastructure.
This is a critical insight: when multiple AI services experience outages at the same time, it usually points to a shared dependency. Maybe it's a cloud provider like AWS or Google Cloud. Maybe it's a DNS issue. Maybe it's a content delivery network like Cloudflare that both services rely on.
The scale of these outages matters. When a service with 200+ million users goes offline, even for an hour, it affects productivity across every industry. Financial analysts can't get market summaries. Customer support teams can't draft responses quickly. Students can't get help with assignments. Developers can't get code suggestions.
The economic impact is harder to quantify but significant. If Chat GPT is down for 3 hours and you work for a company with 1,000 employees who each use it for 30 minutes of their workday, that's roughly 250 employee-hours of lost productivity. At an average rate of
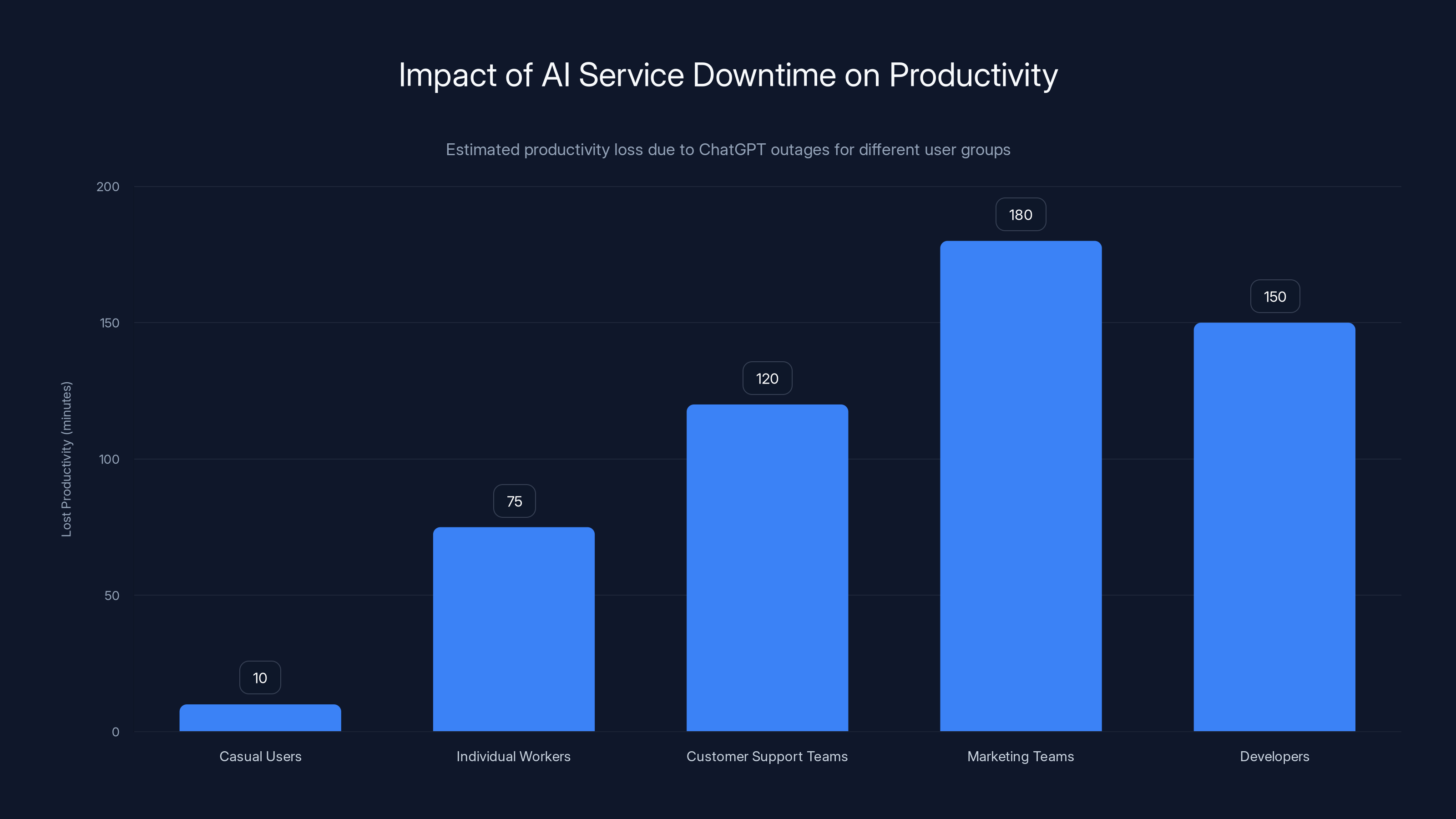
Estimated data shows that while casual users lose about 10 minutes, individual workers and business teams can lose between 75 to 180 minutes of productivity during a 2-hour ChatGPT outage.
What Actually Causes Chat GPT Outages
Chat GPT doesn't fail for mystical reasons. It fails because of the same issues that plague every large-scale software system: infrastructure problems, software bugs, traffic surges, and human error. Understanding which causes which type of outage helps you predict when problems are likely.
Infrastructure and Cloud Provider Issues
Chat GPT runs on cloud infrastructure, likely distributed across multiple data centers. When your application runs at this scale—serving requests from hundreds of millions of users daily—you're entirely dependent on the underlying infrastructure remaining stable.
Cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure maintain multiple availability zones in different geographic regions. The theory is simple: if one zone fails, traffic automatically routes to another. The practice is more complicated.
Infrastructure outages can be triggered by hardware failures, power losses, network issues, or cascading failures across multiple systems. A study by Gartner found that enterprise cloud services experience unplanned outages averaging 4.5 hours annually, even among companies with strong reliability practices.
For a service like Chat GPT, serving across multiple geographic regions, any infrastructure issue in even one region can create bottlenecks. If 20% of your capacity is offline, that remaining 80% gets hammered with traffic attempting to route around the failure. This can cause cascade effects where system overload brings down healthy infrastructure.
Open AI has been relatively quiet about their specific infrastructure setup, but industry standards suggest they likely use multiple cloud providers and regions to avoid single points of failure. However, no amount of redundancy eliminates risk entirely.
Traffic Spikes and Capacity Issues
Chat GPT's traffic patterns are unpredictable. A new feature release, media coverage, or a trending topic on social media can cause traffic to spike dramatically. When millions of users hit a service simultaneously, even well-provisioned infrastructure can buckle.
Capacity planning is a constant game of guessing. Open AI engineers must predict: How much traffic will we get tomorrow? Next week? Next month? If they provision for peak demand, they waste money on unused capacity on quiet days. If they provision for average demand, they can't handle spikes.
Most companies solve this through auto-scaling: when traffic increases, they automatically spin up more servers. But auto-scaling isn't instantaneous. It takes time to provision new infrastructure. If traffic spikes faster than servers can scale up, you hit a capacity wall.
During viral moments—when Chat GPT becomes trending on Twitter, or a major news outlet publishes a story about it—traffic can spike 3-5x above normal within minutes. The service becomes slow, then unresponsive, then offline. By the time new capacity comes online, the spike has usually passed.
Software Bugs and Configuration Errors
This is where things get interesting. Many Chat GPT outages aren't caused by infrastructure failures—they're caused by bugs in code that Open AI deployed.
Every software company releases code multiple times per day. Sometimes that code has bugs. Maybe a database query is inefficient and starts consuming resources faster than expected. Maybe a new feature has a memory leak that gradually consumes available memory until the service crashes. Maybe an API change wasn't fully tested against all consumer services.
One particularly illuminating case involved Cloudflare, a company that provides infrastructure services to hundreds of thousands of websites and applications, including Chat GPT. Cloudflare deployed a configuration change to handle threat traffic more efficiently. The configuration file was designed to filter malicious traffic. Instead, it triggered a crash in Cloudflare's software that handled traffic routing for their wider services.
The result: a "significant outage" that took down not just Chat GPT but Discord, Slack, Crunchyroll, and hundreds of other services. All because of a single misconfigured file.
This type of outage is particularly vicious because it's not obvious to the companies affected. Open AI engineers might spend 30 minutes investigating Chat GPT infrastructure before realizing the problem is upstream at Cloudflare. That 30 minutes of uncertainty can feel like an eternity when your service is down.
Configuration errors are particularly dangerous because they're often rolled out globally all at once. Unlike a bug in one service instance, which might only affect a percentage of traffic, a global configuration change can instantly break the entire service.
API Rate Limiting and Overload Protection
Chat GPT implements rate limiting to prevent abuse and manage capacity. When a user or application sends requests faster than the system can handle, those requests get throttled. Taken to an extreme, throttling becomes outages.
Rate limiting protects the service, but it can also make the service appear broken to users. If you're hitting a 429 "Too Many Requests" error, that's technically not an outage—the service is working, it's just telling you to slow down. But from the user's perspective, the service isn't working.
During high-traffic periods, rate limits can be very aggressive. The service might accept only 1 request per second per user, which feels like the service is offline if you're used to instant responses.
Human Error in Deployments
This is the most embarrassing cause of outages, which is why companies rarely admit to it. A developer accidentally deploys code to production instead of staging. A Dev Ops engineer misconfigures a load balancer. Someone deletes a database table that wasn't supposed to be deleted.
Major tech companies have systems in place to prevent human error: code review, automated testing, staging environments, canary deployments. But these systems aren't perfect. Humans are creative at finding ways to break things.
One particularly famous incident happened at Amazon: an AWS employee was doing routine maintenance on a database server. They ran a command that was supposed to remove test data, but the command was slightly different than what they intended. It deleted production data instead. This single error took down the S3 service for hours and affected thousands of companies relying on AWS.
Open AI likely has similar safeguards, but safeguards fail. It's a numbers game: if you deploy code 50 times per day, and there's a 0.1% chance each deployment introduces a critical bug, you'll have an outage roughly every 20 days just from code deployments.
How Long Do Chat GPT Outages Actually Last
Outage duration varies wildly depending on root cause. Understanding typical durations helps you plan alternatives.
Minor Outages (15-30 minutes)
Minor partial outages—where some users experience degraded service but others don't—typically resolve quickly. These are usually caused by temporary traffic spikes or brief infrastructure hiccups. The system self-heals: traffic spikes pass, auto-scaling kicks in, or a transient network issue resolves itself.
In the February 2025 Chat GPT outage, the main issue was resolved within about 3 hours (from initial reports around 2 PM to resolution at 5:14 PM), but the affected user experience varied. Some users experienced complete unavailability, others experienced slow responses, and some didn't notice anything wrong.
Moderate Outages (30 minutes to 2 hours)
When a software bug is introduced that affects service stability, resolution typically takes 30 minutes to 2 hours. This is the time needed to:
- Detect the problem (usually 5-15 minutes)
- Understand the root cause (15-30 minutes)
- Develop a fix (15-30 minutes)
- Test the fix (10-15 minutes)
- Deploy the fix (5-10 minutes)
- Verify the fix works (5-10 minutes)
Or alternatively, if the fix is too complex, to roll back to the previous version of code (usually 10-30 minutes).
Rollbacks are faster than fixes, which is why you'll often see companies quickly revert a deployment instead of trying to fix the problem in place.
Major Outages (2-6 hours)
Larger issues take longer. If an infrastructure component fails—like a database becoming corrupted or a data center losing power—recovery can take hours. Engineers need to:
- Determine which infrastructure component failed
- Attempt to bring that component back online
- If that fails, migrate to backup infrastructure
- Restore data from backups if corruption occurred
- Gradually bring systems back online (rushing risks cascading failures)
A database restore from backup might take 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on database size. A data center failover might take 1-3 hours. During this time, the service is completely unavailable.
Catastrophic Outages (6+ hours)
Fortunately, these are rare. They usually involve:
- Simultaneous failures in multiple data centers
- Corruption of primary and backup data
- Infrastructure provider-level outages affecting multiple customers simultaneously
- Security incidents requiring investigation before service can resume
When Cloudflare's configuration error took down services, it impacted hundreds of companies globally. Resolution required:
- Identifying which configuration file was problematic (30+ minutes)
- Creating a fix (30+ minutes)
- Carefully deploying the fix to avoid re-triggering the crash (60+ minutes)
- Waiting for all affected services to come back online gradually
Total time: several hours.
The actual duration depends on:
Root Cause Severity
- Temporary issues: 15-30 minutes
- Software bugs: 30 minutes to 2 hours
- Infrastructure failures: 1-6 hours
- Data corruption: 3-12+ hours
Time of Day
- Business hours: Faster resolution (more engineers available)
- Off-hours: Slower resolution (fewer engineers on-call)
- Weekends: Slowest resolution (skeleton crew)
Complexity of Fix
- Simple rollback: 15-30 minutes
- Code patch: 30 minutes to 1 hour
- Infrastructure reconfiguration: 1-3 hours
- Data restoration: 2-6+ hours
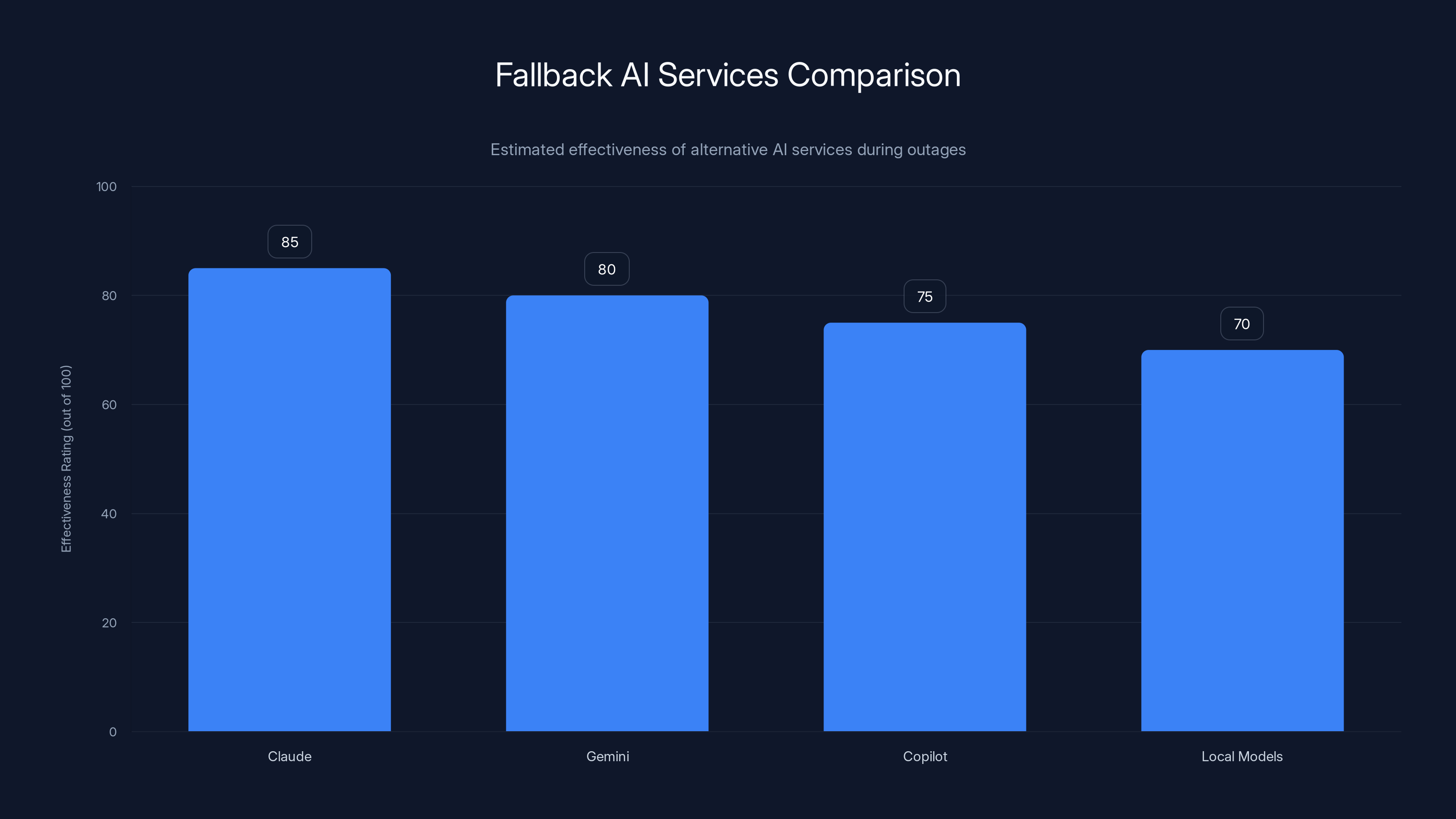
Claude offers the highest effectiveness as a fallback service during outages, followed by Gemini and Copilot. Local models provide basic functionality but are less effective. Estimated data based on typical service capabilities.
Real-World Impact of AI Service Downtime
Understanding how outages affect real users reveals why service reliability matters.
Impact on Individual Users
For casual users, a Chat GPT outage is an inconvenience. You close the browser and do something else. You lose maybe 10 minutes to troubleshooting.
But for users depending on Chat GPT for work, outages create immediate problems. A customer support representative can't draft responses quickly. A writer can't get help editing. A developer can't get code suggestions. Each minute the service is down represents lost productivity.
If your job involves running 5-10 Chat GPT queries per hour, a 2-hour outage costs you 10-20 queries of productivity. If each query saves 5 minutes, that's 50-100 minutes of lost efficiency. Multiply that across millions of users, and you're looking at meaningful productivity loss.
Impact on Businesses Using Chat GPT
Businesses face worse consequences. A customer support team relying on AI-powered response drafting suddenly has to manually write responses. That service gets slower and lower quality. Customers wait longer, experience worse support, and some might churn.
A marketing team using AI to generate copy, headlines, and social media posts can't do their work. Campaigns get delayed. Posting schedules get disrupted. Revenue might be affected if campaigns miss optimal windows.
Developers using Chat GPT for code generation lose coding speed. A team that normally ships code 20% faster with AI assistance suddenly has to code manually. Productivity drops, deadlines slip, costs increase.
For companies with API-only usage (not the web interface), outages can completely block their services. If a startup's entire product is built on Chat GPT API calls, and the API is down, their product doesn't work. Their customers can't use their service. This is exceptionally bad.
Impact on API Customers
The February 2025 outage affected both the Chat GPT web interface and the API platform. For companies using the API to power their own products, this is critical.
Imagine you built a Saa S product that helps writers improve their content. Your product calls the Chat GPT API to analyze writing and suggest improvements. When Chat GPT's API is down, your product is broken. Your customers can't use it.
If the outage lasts 2 hours and you have 100,000 active users who each attempt to use your product once, you've created 100,000 bad experiences. Some of those users might abandon your product, thinking it's broken. Some might ask for refunds.
This is why serious API customers maintain fallback services. If the primary API is down, they automatically route requests to a secondary service. Claude, Mistral, or Cohere APIs can serve as backups. The response quality might be slightly different, but the service stays online.
Historical Patterns: How Often Do Outages Happen
Trying to pin down exact outage frequency is difficult because Open AI doesn't publish comprehensive reliability data. But based on user reports and public outage tracking, patterns emerge.
Tracking Outage Reports
Down Detector aggregates outage reports from users across the internet. While this data isn't perfect (user-reported outages include false positives like local connectivity issues), it provides a reasonable proxy for service reliability.
Looking at Chat GPT's outage history on Down Detector:
- February 2025: Partial outage affecting thousands of users, resolved within 3 hours
- Previous incidents: Various partial and complete outages occurring roughly every 1-2 months
- Pattern: Peak frequency during major news coverage or after new feature releases
This suggests Chat GPT experiences a significant outage (impacting thousands of users simultaneously) roughly every 4-8 weeks. Smaller issues affecting subsets of users or specific API endpoints occur more frequently.
Seasonal Patterns
Certain times are more likely to have outages:
Peak Usage Times (Higher Risk)
- Weekday mornings (9 AM - 12 PM)
- Mid-afternoon (2-5 PM)
- After major announcements or feature releases
Lower Risk Times
- Early mornings (3-6 AM)
- Weekends (fewer users, but fewer engineers on-call)
- Late night (1-3 AM local US time)
Open AI likely deploys new code during off-peak hours (early morning) to minimize impact. But if a deployment goes wrong, you've got a skeleton crew of engineers to fix it.
Comparative Reliability
How does Chat GPT's reliability compare to other services?
Cloud Platforms
- AWS: Publicly committed to 99.95% uptime (roughly 22 minutes of downtime per month)
- Azure: Similar SLA, 99.95% uptime commitment
- Google Cloud: Slightly higher at 99.99% uptime
Social Media Platforms
- Facebook: Typically experiences major outages 1-2 times per year
- Twitter/X: Variable reliability depending on current infrastructure status
AI Services
- Chat GPT: Major outages roughly every 4-8 weeks (estimated 98-99% uptime)
- Claude: Similar frequency to Chat GPT
- Google Gemini: Generally more stable (benefits from Google's infrastructure)
Chat GPT's reliability is worse than AWS but better than many consumer services. This makes sense: Chat GPT is scaling incredibly fast, Open AI isn't a traditional infrastructure company, and growth is prioritized over stability.
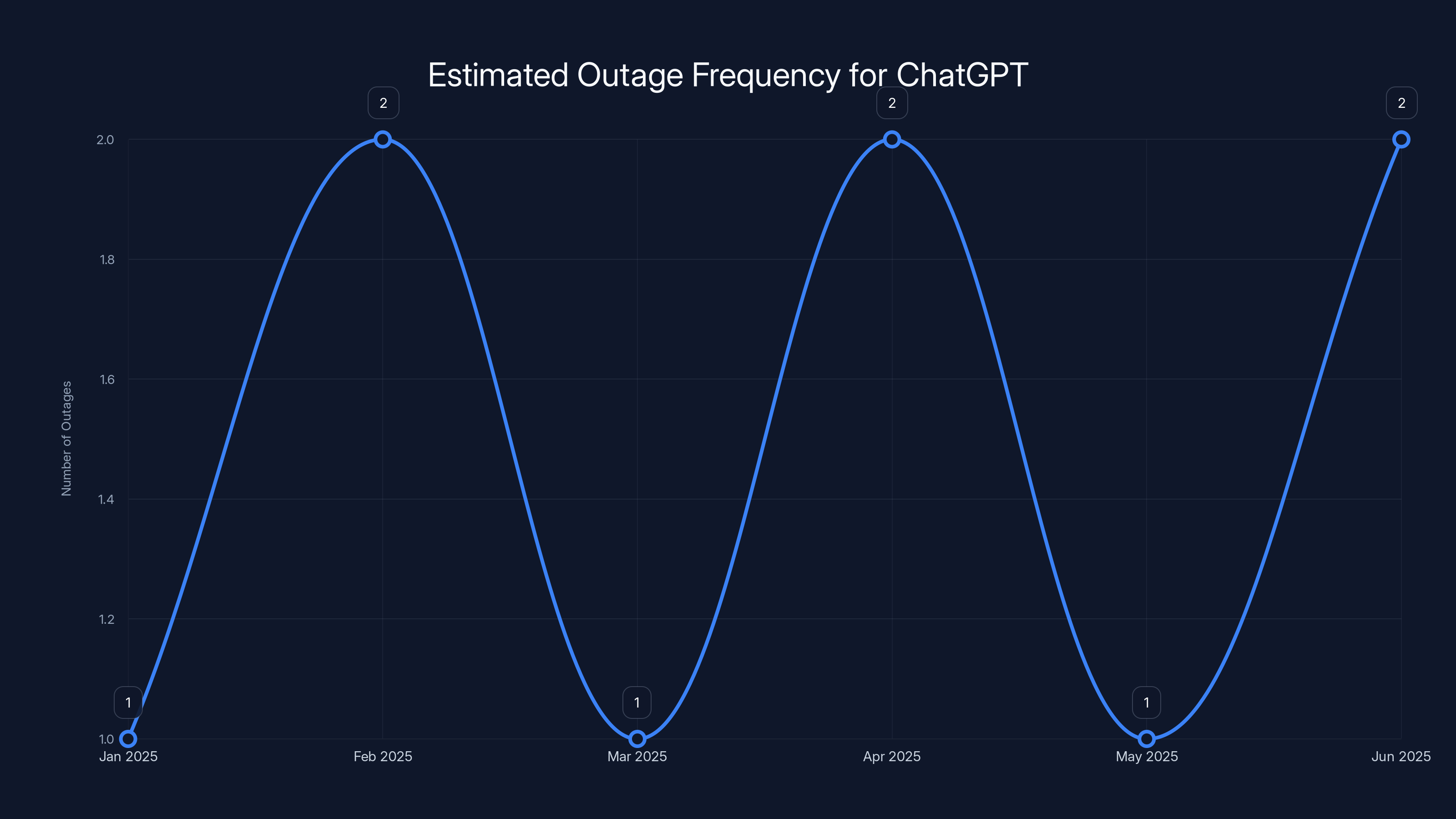
Estimated data suggests ChatGPT experiences significant outages roughly every 4-8 weeks, with higher frequency during peak usage times and after major announcements.
Monitoring and Early Detection: Knowing Before Everyone Else
The first person to know about an outage can prepare, while others are still confused. Here are tools and techniques to detect issues early.
Official Status Pages
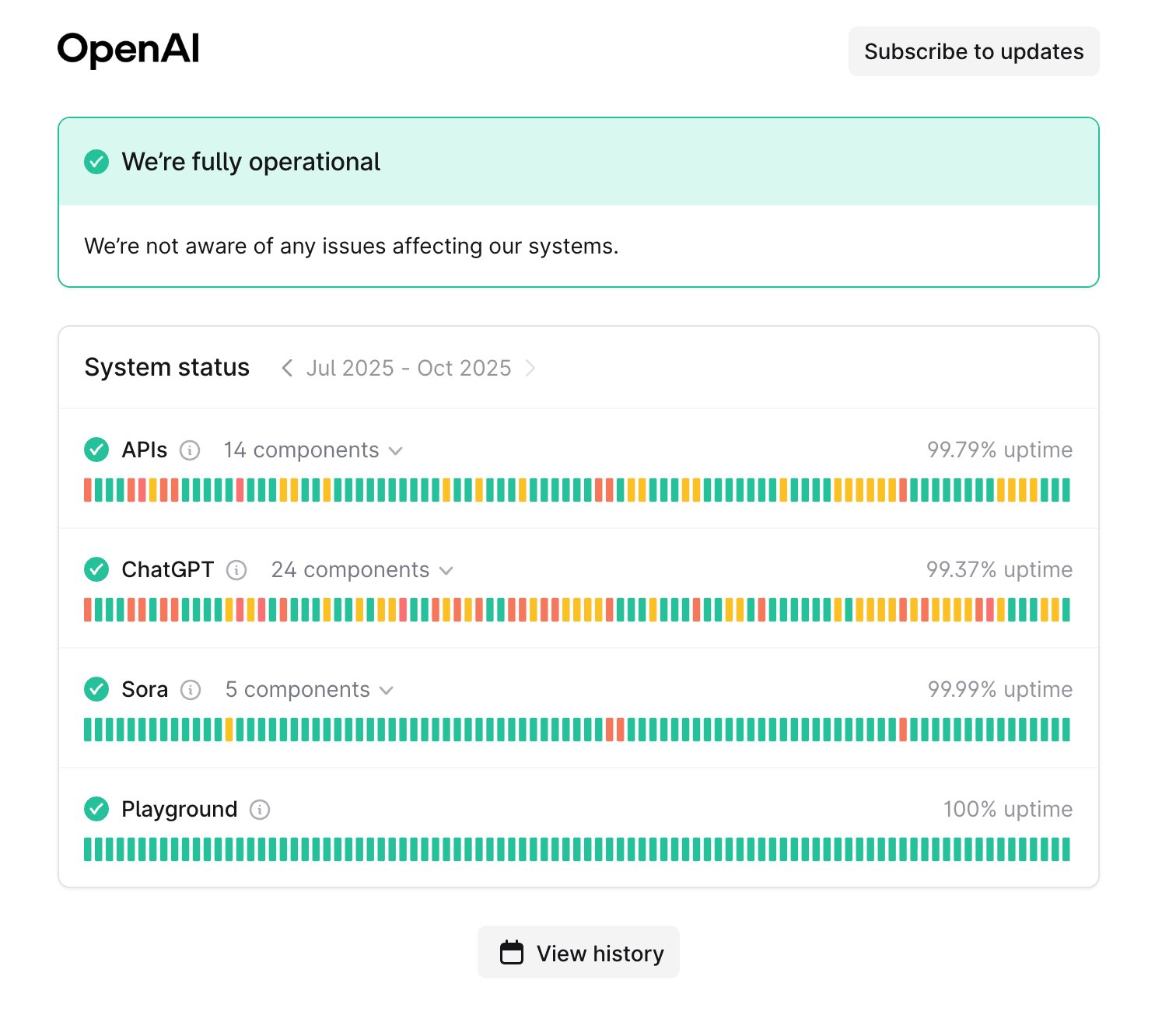
status.openai.com is the authoritative source for Chat GPT status. This page shows:
- Current service status (operational, degraded, or down)
- Active incidents with timestamps
- Recent incidents and resolution times
- Uptime metrics for the past 90 days
Checking this page should be your first step when Chat GPT seems broken. If status.openai.com says everything is operational but you can't access Chat GPT, the problem is likely local (your internet, your ISP, your browser, or a regional issue).
Open AI also sends status updates via email to registered users. If you use Chat GPT for work, subscribing to these notifications ensures you're informed of incidents in real-time.
Third-Party Monitoring Tools
Down Detector aggregates user reports of outages. When thousands of people experience an outage, reports flood in within minutes. Down Detector creates a spike in reported issues, often before companies have officially announced the outage.
How to use it:
- Go to downdetector.com/status/chatgpt
- Look at the chart showing reports over time
- A sharp spike indicates a current outage
- Read user comments for confirmation and details
- Check when the spike began to estimate how long ago the outage started
Other monitoring services include:
- Is It Down Right Now.com: Simple status checks
- Status Page.io: Third-party status page aggregator
- Twitter/X: Real-time user reports (search "Chat GPT down")
Proactive Monitoring for API Customers
If you depend on Chat GPT's API, you can implement proactive monitoring:
Heartbeat Monitoring
Every 60 seconds, send a test request to the API.
If it fails, log the failure and alert you via email/SMS.
If it fails 3 times in a row, trigger fallback to secondary service.
This gives you 60-120 seconds notice before users experience issues.
Detailed Logging Log every API call: timestamp, latency, response code, error message. When issues occur, you can analyze logs to pinpoint exactly when the service became unreliable.
Synthetic Testing Run synthetic tests that simulate real user workflows. If these tests fail, the service is degraded. This is different from just checking if the API responds—it tests actual functionality.
Building Resilience: Strategies to Minimize Outage Impact
Outages are inevitable. The question is: how much do they hurt your business? Here are strategies to minimize impact.
Strategy 1: Implement Fallback Services
The most effective protection is having an alternative service ready to use when primary service fails.
For Chat GPT users, consider:
- Claude (via Anthropic): Similar capabilities, often slightly better reasoning
- Gemini (via Google): Good general-purpose AI, benefits from Google's infrastructure
- Copilot (via Microsoft): Integrates with Microsoft products you might already use
- Local models (via Ollama or similar): Run your own AI model locally for basic use cases
When Chat GPT is down, you immediately switch to Claude. You lose 10 minutes to context-switching, but your workflow continues.
For API customers, implement automatic failover:
Try Chat GPT API call.
If it fails with error code 5XX (server error):
Wait 1 second, retry once.
If still fails:
Use Claude API as backup.
Alert team that backup is active.
If Claude also fails:
Use cached/default response.
Alert team that both services are down.
This ensures your service stays online even when primary dependencies fail.
Strategy 2: Design for Degradation
Not all features require AI. Some features can degrade gracefully when AI services are unavailable.
Example: A writing assistant with these features:
- Grammar checking (can work offline)
- Tone suggestions (requires AI)
- Content generation (requires AI)
When Chat GPT is down:
- Grammar checking continues working
- Tone and content features show a message: "This feature is temporarily unavailable. Please try again in a few minutes."
Users can continue using the app, just with reduced functionality. This is better than the entire app becoming unusable.
Strategy 3: Optimize Usage Patterns
Certain usage patterns create failure risk:
Risky Pattern: "Build everything on the API"
- Your entire product depends on Chat GPT working
- One outage breaks everything
- Dependency on external service you don't control
Better Pattern: "Use the API, but cache results"
- Cache API responses
- When API is unavailable, serve cached responses
- Slightly stale data is better than no data
- Most users won't notice the difference
Best Pattern: "Use the API for heavy lifting, local for fast path"
- Simple requests use fast local models
- Complex requests use Chat GPT API
- Load is distributed, reducing API dependency
- Faster responses for simple queries
Strategy 4: Maintain Offline Capabilities
For critical workflows, having offline alternatives is essential.
Examples:
- Keep a list of template responses for common customer service questions
- Maintain a knowledge base of frequently-needed information
- Have manual processes ready if AI tools become unavailable
- Document critical processes that don't require AI
If Chat GPT goes down, you can switch to manual processes without losing critical functionality.
Strategy 5: Choose Services with Strong SLAs
If you're evaluating AI services to depend on, SLA (Service Level Agreement) matters.
Compare:
- Uptime percentage: 99.9% (8.7 hours downtime/year) vs 99.95% (4.4 hours downtime/year)
- Response time SLAs: Average response under 200ms vs under 500ms
- Incident response time: Commitment to respond to incidents within 15 minutes
- Credit for downtime: Do they refund for SLA violations?
Services with strong SLAs typically have better infrastructure and more engineers dedicated to reliability.
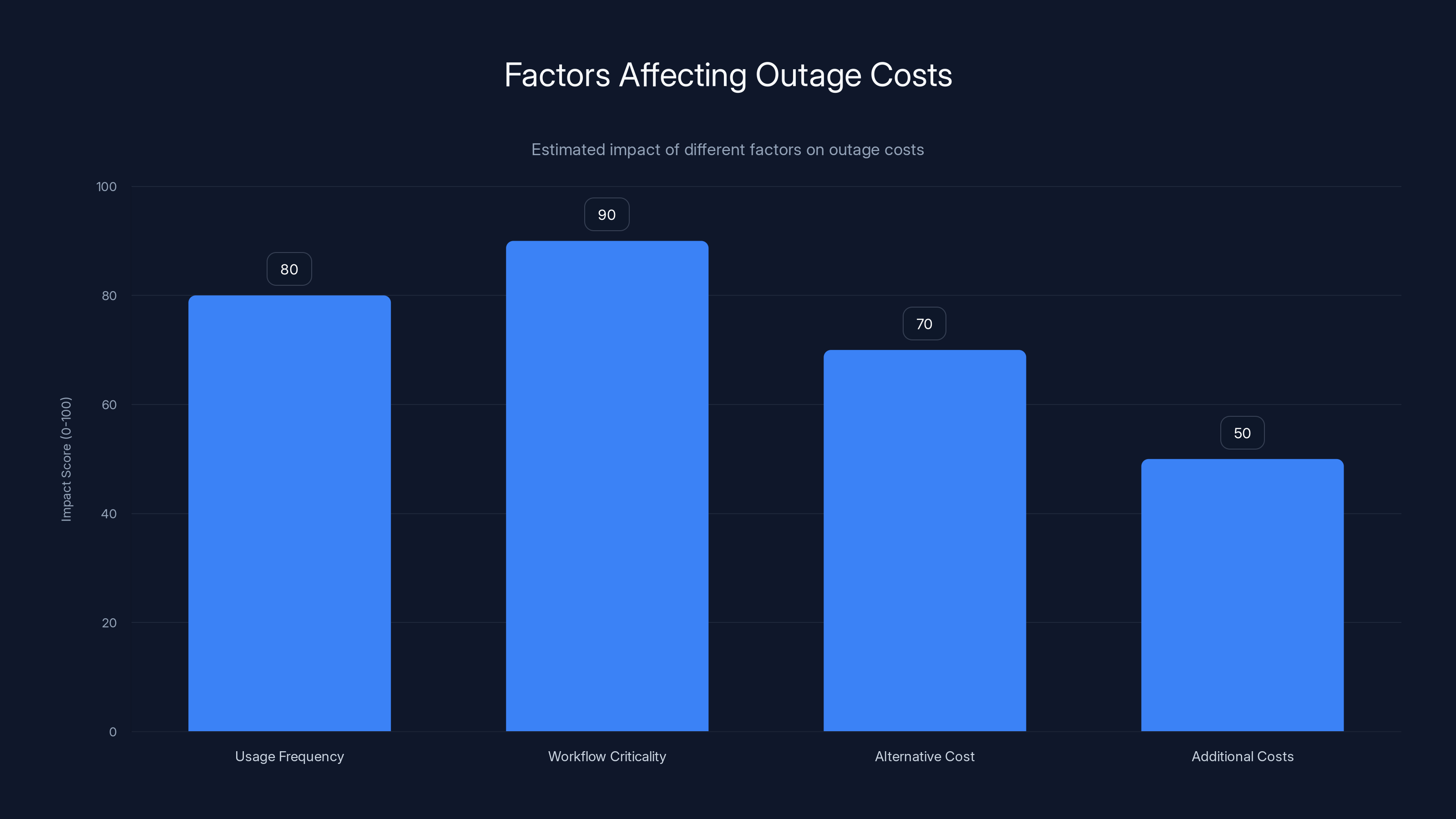
Estimated data shows that workflow criticality and usage frequency significantly impact outage costs, with alternative costs and additional costs also contributing.
The Economics of Outages: True Cost Analysis
Understanding the true cost of outages helps prioritize reliability investments.
Quantifying Productivity Loss
When Chat GPT is down, productivity loss depends on:
Usage frequency: How often do users query the service?
- High frequency (every 5 minutes): Greater impact from outages
- Low frequency (once per day): Minimal impact
Workflow criticality: How essential is the service?
- Critical path (blocks work): Cannot proceed without it
- Supporting tool (nice to have): Work continues, just slower
Alternative cost: What's the cost of alternatives?
- Free alternative available: Switch cost is low
- Paid alternative: Higher cost but can maintain SLA
- Manual process: Very high cost in time and quality
Formula for productivity cost:
Example:
- 1,000 users affected
- $50/hour average loaded cost (including benefits, overhead)
- 2 hours downtime
- 50% productivity loss (they can do other things while waiting)
This doesn't include additional costs like:
- Frustrated customers who churn
- Delayed projects missing revenue windows
- Customer support burden from users experiencing issues
- Opportunity cost of engineering time spent investigating
Real total cost is probably 30-50% higher.
Investment in Reliability
Given the cost of outages, companies invest heavily in reliability:
Engineering headcount: Companies like Google and AWS have teams of 50-200 engineers dedicated solely to reliability, monitoring, and disaster recovery.
Infrastructure redundancy: Building failover systems costs 50-100% extra in infrastructure.
Testing and simulation: Chaos engineering, load testing, and disaster recovery drills require continuous investment.
Monitoring and alerting: Setting up comprehensive monitoring across global infrastructure costs
A company might invest
Open AI is in a different position: they're growing incredibly fast and accepting some reliability tradeoffs to scale quickly. Stability is likely worth less to them than adding capacity to serve growing demand.

Future Reliability: Where Chat GPT is Headed
Chat GPT's outage frequency and duration reveal where the service is headed.
Short Term (Next 6 Months)
Expect current outage patterns to continue. As Open AI integrates new features, launches new model versions, and handles growing demand, reliability will be variable.
Major deployments (new features, model updates) might be scheduled for off-peak hours to minimize impact, but some disruptions are inevitable during active development.
Medium Term (6-18 Months)
Once Open AI finishes their current growth phase and infrastructure stabilizes, reliability should improve. This typically happens when:
- Infrastructure is sufficiently redundant
- Engineers shift focus from growth to reliability
- Monitoring and automation prevent common failures
Look for Open AI to publish SLA commitments around this timeframe.
Long Term (18+ Months)
Mature AI services will likely achieve 99.5-99.9% uptime, approaching current cloud provider standards. This requires:
- Geographic redundancy (multiple data centers in different regions)
- Infrastructure diversification (multiple cloud providers)
- Comprehensive automation and monitoring
- Dedicated reliability engineering teams
At maturity, Chat GPT will be as reliable as AWS or Google Cloud.

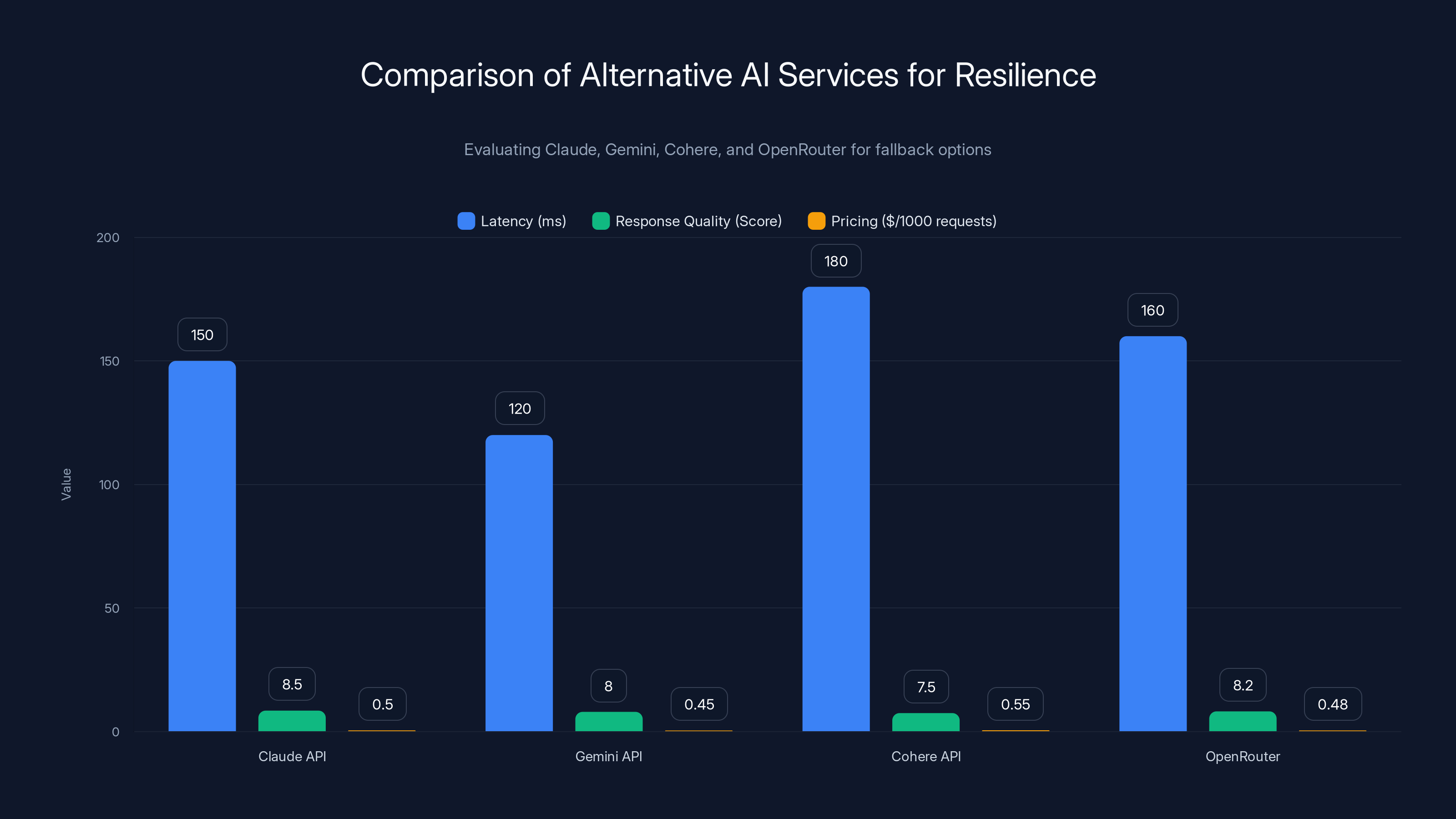
This chart compares latency, response quality, and pricing of four AI services as potential fallback options. Claude API has the highest response quality, while Gemini API offers the lowest latency. Pricing is competitive across all options. Estimated data.
Comparing AI Services: Reliability Across the Landscape
Chat GPT isn't the only AI service experiencing outages. Here's how the major players compare.
Chat GPT (Open AI)
Outage frequency: Major issues every 4-8 weeks Average MTTR: 30 minutes to 2 hours Uptime estimate: 98-99% (rough estimate based on user reports) Trend: Improving as infrastructure matures
Strengths:
- Excellent base model quality
- Wide API availability
- Strong developer ecosystem
Weaknesses:
- Variable reliability during scaling
- Less infrastructure maturity than cloud providers
- Limited public SLA commitments
Claude (Anthropic)
Outage frequency: Similar to Chat GPT, usually within hours Average MTTR: 30 minutes to 2 hours Uptime estimate: 98-99% Trend: Comparable to Chat GPT
Strengths:
- Good reasoning capabilities
- Comparable reliability to Chat GPT
- Strong developer support
Weaknesses:
- Smaller team means fewer resources for reliability
- Less mature infrastructure
- Fewer deployment locations than Chat GPT
Google Gemini
Outage frequency: Less frequent than Chat GPT Average MTTR: 15-45 minutes Uptime estimate: 99.5%+ (benefits from Google's infrastructure) Trend: More stable due to Google's mature infrastructure
Strengths:
- Exceptional infrastructure reliability
- Integration with Google ecosystem
- Advanced monitoring and automation
Weaknesses:
- Less optimized for certain tasks compared to Chat GPT
- Smaller third-party developer ecosystem
- Variable API availability
Microsoft Copilot
Outage frequency: Rare major outages Average MTTR: 15-30 minutes when issues occur Uptime estimate: 99.5%+ Trend: Stable due to Azure infrastructure
Strengths:
- Excellent uptime (benefits from Azure)
- Office integration
- Enterprise-grade support
Weaknesses:
- Less customizable than Chat GPT API
- Fewer advanced features
- Limited for certain specialized use cases

Creating Your Resilience Plan: Practical Steps
If you depend on Chat GPT or similar AI services, here's a step-by-step resilience plan.
Step 1: Assess Your Dependency (Week 1)
Identify every place in your workflow or business that depends on Chat GPT.
Questions to answer:
- Which features require Chat GPT?
- What happens when Chat GPT is unavailable?
- How long can you operate without it?
- What's the cost per hour of unavailability?
Document results in a simple spreadsheet listing:
- Workflow / feature
- Criticality (essential / important / nice-to-have)
- Duration tolerance (must work within 5 minutes / hour / day)
- Annual cost of unavailability
Step 2: Implement Monitoring (Week 2)
Set up alerts so you know immediately when issues occur.
For web users:
- Subscribe to status.openai.com notifications
- Follow Open AI's status account on social media
- Set up a Down Detector alert
For API users:
- Implement heartbeat monitoring (test request every 60 seconds)
- Log all failures with timestamps
- Set up email/SMS alerts for consecutive failures
- Create dashboards showing API health
Step 3: Establish Fallback Services (Week 3-4)
Identify and test alternative services.
Evaluate alternatives:
- Claude API (similar capabilities)
- Gemini API (good general purpose)
- Cohere API (specialized use cases)
- Open Router (multi-model aggregator)
For each alternative:
- Create a test account
- Migrate critical prompts/workflows
- Test latency and response quality
- Understand pricing and rate limits
- Document API differences
Step 4: Implement Automatic Failover (Week 4-6)
For API-dependent services, implement automatic failover code.
Basic example (pseudocode):
function get AIResponse(prompt) {
try {
return call Chat GPT(prompt);
} catch (error) {
if (error.status === 'unavailable') {
log('Chat GPT unavailable, trying Claude');
return call Claude(prompt);
}
throw error;
}
}
More sophisticated approach:
- Try primary service
- If timeout, try secondary service
- If secondary also times out, use cached response
- If no cache, return graceful failure message
- Log all failures for analysis
Step 5: Document Critical Processes (Week 6)
For truly critical workflows, document manual alternatives.
Example: Customer support team using AI for response drafting
When Chat GPT is down:
- Use template responses for common issues
- Consult knowledge base for detailed answers
- Write responses manually if templates don't apply
- Escalate complex issues to senior team members
- Resume AI-assisted workflow once service is restored
Step 6: Test Regularly (Ongoing)
Monthly testing ensures fallbacks actually work when needed.
Testing checklist:
- Verify fallback service still works
- Confirm latency is acceptable
- Test automatic failover in staging environment
- Review logs from previous month for patterns
- Update documentation if anything has changed
- Brief team on outage procedures
Emerging Solutions: Next-Generation Reliability
The AI industry is evolving to address reliability concerns.
Multi-Model Routing Platforms
Services like Open Router and similar platforms automatically route requests across multiple AI models and providers. If one model is unavailable, requests automatically route to an alternative.
This eliminates single-provider dependency entirely. Your application makes a single API call, and Open Router handles routing behind the scenes.
Serverless AI Inference
Platforms like Runway and Banana offer containerized AI inference that you can deploy to your own infrastructure. You're not dependent on any single provider's uptime.
Tradeoff: you manage infrastructure yourself, which introduces different reliability challenges.
Local Model Deployment
Open-source models like Llama, Mistral, and others can be deployed locally using tools like Ollama. You trade model quality for absolute reliability (your own hardware must be online, but you're not dependent on external services).
This is compelling for organizations with:
- Strong internal infrastructure
- Strict data privacy requirements
- Willingness to manage their own infrastructure
Advice for Different User Types
For Casual Users
Don't overthink outages. Chat GPT is usually available, and when it's not, wait 30 minutes and try again.
Best practices:
- Bookmark status.openai.com for quick checks
- Have a secondary browser tab ready with Claude if you need immediate help
- Accept that occasional unavailability is normal for free services
- Save important conversations (export them) in case you lose access
For Power Users (Heavy Daily Usage)
You should have a fallback plan because outages directly impact your productivity.
Best practices:
- Subscribe to status notifications
- Maintain a free Claude account as fallback
- Cache important prompts and responses
- Design critical workflows to not depend solely on Chat GPT
- Consider a paid Claude Pro account for backup
For Business/API Users
Reliability is non-negotiable. You should have robust fallback and monitoring.
Best practices:
- Implement heartbeat monitoring with alerts
- Use multi-model routing platforms like Open Router
- Contract with multiple AI service providers
- Design for graceful degradation
- Maintain SLA commitments to your own customers
- Conduct regular disaster recovery testing
- Document critical processes that can be done manually
For Enterprises
You need enterprise-grade reliability with contractual guarantees.
Best practices:
- Negotiate SLAs with vendors (if possible)
- Use Microsoft's enterprise offerings with guaranteed uptime
- Implement geographic redundancy
- Use multiple cloud providers to avoid single-provider dependency
- Maintain internal AI models as fallback
- Invest in automated failover systems
- Conduct regular chaos engineering exercises
The Bigger Picture: AI Infrastructure Maturity
Chat GPT's outages are a symptom of an immature industry. AI infrastructure is still nascent.
Compare to cloud platforms:
- Cloud infrastructure reached widespread adoption in 2010-2015
- By 2020, enterprise clouds had 99.9%+ uptime
- This required 10-15 years of infrastructure investment
AI services are currently at the 2010-2015 maturity level. We're 3-5 years away from enterprise-grade reliability being standard.
What this means:
- Current outages and reliability issues are normal and expected
- Don't make critical business decisions assuming Chat GPT will always be available
- Build for multi-provider scenarios
- Expect reliability to improve significantly over the next 5 years
- Early adopters accepting outages will be rewarded with cost advantages once market stabilizes
The companies succeeding now are those treating AI as an optimization ("nice to have") rather than a requirement ("must have"). Once AI infrastructure matures, the economics change completely.

Conclusion: Building for Uncertainty
Chat GPT outages aren't exceptional. They're part of using a service that's simultaneously being scaled globally while delivering cutting-edge AI capabilities.
The February 2025 outage—with 12,000+ reported users and a resolution time of 3 hours—is exactly what we should expect from an immature service handling explosive growth. It's not a failure; it's completely normal.
What matters is how you respond. Users who had fallback plans barely noticed. Users who depended entirely on Chat GPT lost 3 hours of productivity. The difference comes down to planning.
You can't prevent outages. But you can minimize their impact:
- Monitor constantly: Know when issues start, not when users complain
- Plan alternatives: Have secondary services ready to activate
- Design for failure: Build systems that degrade gracefully instead of breaking completely
- Test regularly: Don't assume your fallback plans work until you've tested them
- Document procedures: Don't rely on memory when systems are down
- Stay informed: Subscribe to status updates and industry news
Outages are learning experiences. Each incident reveals fragility in systems, which you can then fix. Companies that treat outages as opportunities to improve reliability end up with better systems than companies that ignore them.
Chat GPT and similar AI services will become increasingly reliable as the industry matures. But in 2025, expecting 100% uptime is unrealistic. Plan accordingly, and you'll navigate the inevitable disruptions with minimal impact.
FAQ
What is a Chat GPT outage?
A Chat GPT outage is a period when the service becomes unavailable or significantly degraded for some or all users. This can range from partial outages affecting certain features or geographic regions to complete outages where the service is entirely non-functional. Outages can last from minutes to hours.
How do I know if Chat GPT is down?
The most reliable way to check is visiting status.openai.com, which shows current service status. For real-time user reports, check Down Detector's Chat GPT page. You can also search social media like Twitter/X for "Chat GPT down" to see if others are experiencing issues. If you can load the page but get error messages when submitting queries, you're likely experiencing a service outage rather than a local connectivity problem.
How long do Chat GPT outages usually last?
Minor outages typically resolve in 15-30 minutes as traffic spikes pass and auto-scaling kicks in. Moderate outages lasting 30 minutes to 2 hours usually indicate a software bug requiring code fixes or rollbacks. Major outages lasting 2-6 hours typically involve infrastructure failures or data issues. Catastrophic outages lasting 6+ hours are rare but can occur with simultaneous multi-system failures. The February 2025 outage lasted approximately 3 hours for most users, which is typical for moderate incidents.
What causes Chat GPT outages?
Chat GPT outages are caused by infrastructure failures (hardware/network issues), traffic spikes exceeding capacity, software bugs introduced in code deployments, configuration errors, database problems, or human errors. Sometimes issues are caused upstream at dependency services like Cloudflare or cloud providers that Chat GPT relies on. Root cause analysis is often only released after the outage is resolved, sometimes never publicly disclosed.
How often does Chat GPT experience outages?
Based on public outage tracking, Chat GPT experiences major outages (affecting thousands of users) roughly every 4-8 weeks. Smaller partial outages affecting specific regions or features occur more frequently—possibly weekly. This frequency is normal for a service at Chat GPT's scale and maturity level. Expect reliability to improve as Open AI's infrastructure matures. For context, enterprise cloud platforms like AWS experience outages less frequently due to 10-15 years of infrastructure investment.
What should I do when Chat GPT is down?
First, verify the outage by checking status.openai.com. If confirmed, switch to alternative services like Claude or Gemini for immediate needs. For non-urgent tasks, wait for the service to recover rather than switching contexts. Consider using this time to review previous Chat GPT conversations, improve your prompts, or work on other tasks. If you depend on Chat GPT for critical work, having a fallback service like Claude available before issues occur prevents panic.
Can I reduce my dependence on Chat GPT?
Yes, through several strategies. Implement automatic failover to alternative services like Claude. Design workflows that degrade gracefully—features work without AI, just slower or with less capability. Cache frequently-used responses to avoid repeated API calls. Use local models like Ollama for non-sensitive work. For critical business workflows, maintain manual processes or templates that work when AI services are unavailable. The most mature approach is treating AI as an optimization that makes work faster and better, not a requirement that makes work possible.
Is Chat GPT's reliability improving?
Yes, generally. As Open AI scales infrastructure and moves past explosive growth phase, reliability should improve steadily. Historical pattern shows services like AWS achieved 99.95%+ uptime after 10-15 years of operations. Chat GPT is roughly 3-5 years into this maturation cycle. Within 2-3 years, Chat GPT's uptime should match enterprise cloud standards (99.5-99.95%), meaning roughly 2-22 minutes of unplanned downtime per month instead of several hours.
Should I pay for Chat GPT Plus for better reliability?
Not primarily for reliability. Chat GPT Plus and the free Chat GPT tier experience the same outages—paying doesn't provide SLA protection. However, Chat GPT Plus includes benefits like faster response times and earlier access to new features. If you depend on Chat GPT for work, the faster responses might be worth the monthly cost independent of reliability. For absolute reliability, implement fallback services (Claude, Gemini) and monitoring rather than expecting any single service to be 100% available.
Runable CTA Section
Building AI-powered workflows that need to stay online? Runable offers AI-powered automation for creating presentations, documents, reports, and images with built-in reliability features designed for teams that can't afford downtime.
Use Case: Automate your weekly report generation with multi-service fallbacks to ensure reports get created even when primary AI services experience outages.
Try Runable For Free
Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT outages happen every 4-8 weeks due to infrastructure failures, software bugs, traffic spikes, and configuration errors
- Most outages resolve within 30 minutes to 2 hours, though major incidents can last 3-6 hours or longer
- Implementing fallback services (Claude, Gemini) and automatic failover prevents single-point-of-failure dependencies
- Monitoring tools like DownDetector and status.openai.com provide early outage detection before widespread user impact
- Economic cost of unplanned downtime can reach $50,000+ per hour across affected organizations, making resilience planning essential
- AI services currently have 98-99% uptime compared to enterprise cloud platforms at 99.95%, reflecting earlier infrastructure maturity
- Multi-provider routing platforms and graceful degradation design patterns minimize outage impact without eliminating risk
Related Articles
- TikTok's U.S. Infrastructure Crisis: What Happened and Why It Matters [2025]
- Claude Code Outage: What Happened and Why AI Tool Reliability Matters [2025]
- Internet Outages in 2025: Why Infrastructure Keeps Failing [2025]
- TikTok Outage in USA [2025]: Why It Failed and What Happened
- TikTok Data Center Outage: What Really Happened [2025]
- GameStop Outage January 2026: Everything You Need to Know [2026]
![ChatGPT Outages: What Causes Them and How to Prepare [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/chatgpt-outages-what-causes-them-and-how-to-prepare-2025/image-1-1770162030963.png)



