Introduction: The Translation Tool Revolution
The translation landscape is shifting beneath our feet. For nearly two decades, Google Translate dominated the market with its ubiquitous blue interface and seemingly instantaneous multilingual support. But in 2025, Open AI's introduction of Chat GPT Translate represents a fundamental challenge to that dominance—not through raw speed or language count, but through something more nuanced: intelligent style customization and context-aware translation.
The emergence of Chat GPT Translate signals a broader trend in AI development. We're moving beyond simple word-for-word conversion toward understanding intent, tone, and purpose. When you ask Chat GPT Translate to render something "more formal" or "more conversational," you're not just getting a translation—you're getting a contextually appropriate interpretation that maintains semantic meaning while adapting to your specific use case.
This shift matters more than it might initially appear. Consider a marketing team translating campaign copy into Japanese. Google Translate will deliver technically accurate results, but Chat GPT Translate can adjust the tone to match your brand voice. Or imagine a software developer localizing user interface text—Chat GPT Translate can ensure technical terminology aligns with industry standards while remaining accessible.
The translation industry generates approximately $50 billion in annual revenue globally, with digital translation tools representing the fastest-growing segment. Professional translators have long argued that machines miss nuance, context, and cultural adaptation. Chat GPT Translate's style presets represent an attempt to address exactly these criticisms.
But does Open AI's offering truly challenge Google's established infrastructure and user base? What are the real practical differences? And perhaps more importantly, which tool should you actually use for your specific needs? This comprehensive guide analyzes both services across every meaningful dimension—features, language support, accuracy, pricing, and real-world use cases—to help you make an informed decision.
What Is Chat GPT Translate?
Core Functionality and Launch Details
Chat GPT Translate is Open AI's standalone web-based translation service, launched as a dedicated competitor to established translation platforms. Unlike Chat GPT's general-purpose interface where translation is one of dozens of capabilities, Chat GPT Translate focuses exclusively on multilingual text conversion with enhanced contextual awareness.
The service operates through a simple two-pane interface. Users paste or type text in the left pane, select their source and target languages via dropdown menus, and receive translated output in the right pane. This basic architecture mirrors Google Translate's familiar layout, recognizing that users already understand this interaction pattern.
What distinguishes Chat GPT Translate from a simple Open AI chatbot conversation is optimization for the translation task specifically. The interface is streamlined, removing unnecessary UI elements that would distract from translation work. Loading times are optimized for rapid translation, and the entire service is built around the singular purpose of converting text between languages with specific style preferences.
Language Support and Coverage
Chat GPT Translate supports over 50 languages according to Open AI's official announcements. This encompasses the major global languages—English, Spanish, Mandarin, Hindi, Arabic, Portuguese, Russian, French, German, and Japanese—as well as numerous regional languages and less commonly translated-to languages.
The specific language list hasn't been exhaustively detailed by Open AI in public documentation, but based on Chat GPT's underlying capabilities, coverage includes:
- Major European languages: German, French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, Polish, Greek, Swedish, Norwegian, Danish
- Asian languages: Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Thai, Vietnamese, Indonesian, Filipino
- South Asian languages: Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Gujarati
- Middle Eastern languages: Arabic, Hebrew, Persian, Urdu
- African languages: Swahili, Amharic, Yoruba (preliminary support)
- Slavic languages: Russian, Ukrainian, Czech, Hungarian, Romanian
Google Translate supports 133 languages, maintaining a substantial advantage in breadth. For rare languages, endangered linguistic communities, and regional dialects, Google's longer development timeline has created wider coverage. However, for the approximately 85% of global internet usage concentrated in the 50 most-spoken languages, Chat GPT Translate's coverage is functionally complete.
Supported Input and Output Methods
Chat GPT Translate currently supports multiple input modalities, though rollout varies by platform:
Desktop web interface:
- Text input (typing or pasting)
- Image-based translation (announced but not yet live)
- Planned document upload (indicated but not yet available)
Mobile browsers:
- Text input via keyboard
- Voice input using device microphone
- Real-time audio translation (limited beta)
Not currently available:
- Native i OS or Android applications
- Website translation (point-and-click translation of entire web pages)
- Document batch processing
- API access for developers
Google Translate's input methods remain more comprehensive, supporting image uploads, document translation (Google Docs integration), and real-time website translation through browser extension. However, Chat GPT Translate's voice input capability for mobile represents an innovation that Google Translate has only partially implemented.
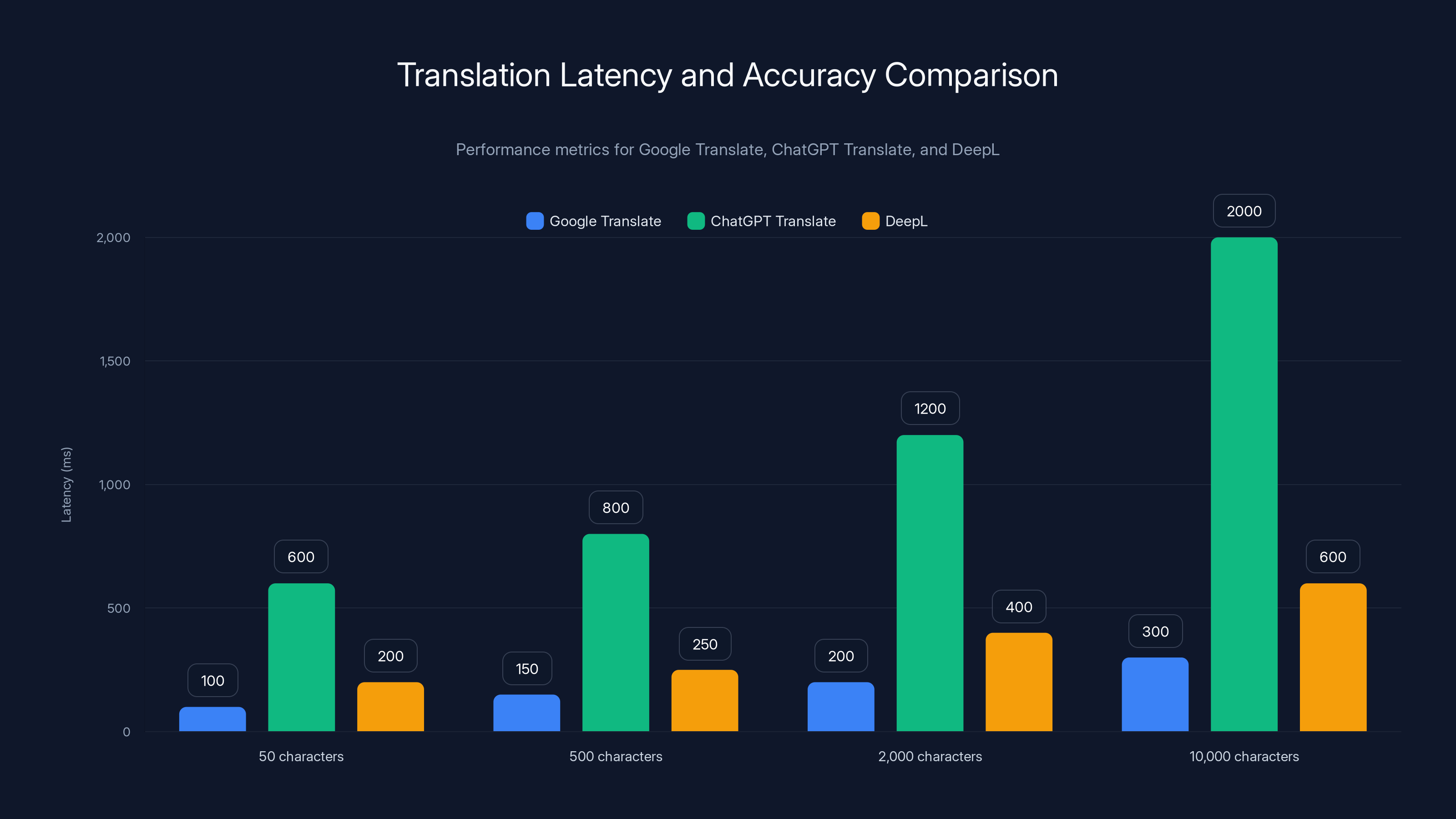
Google Translate consistently outperforms in speed, with the lowest latency across all text lengths. ChatGPT Translate is slower but suitable for interactive use.
Key Features Comparison: Chat GPT Translate vs. Google Translate
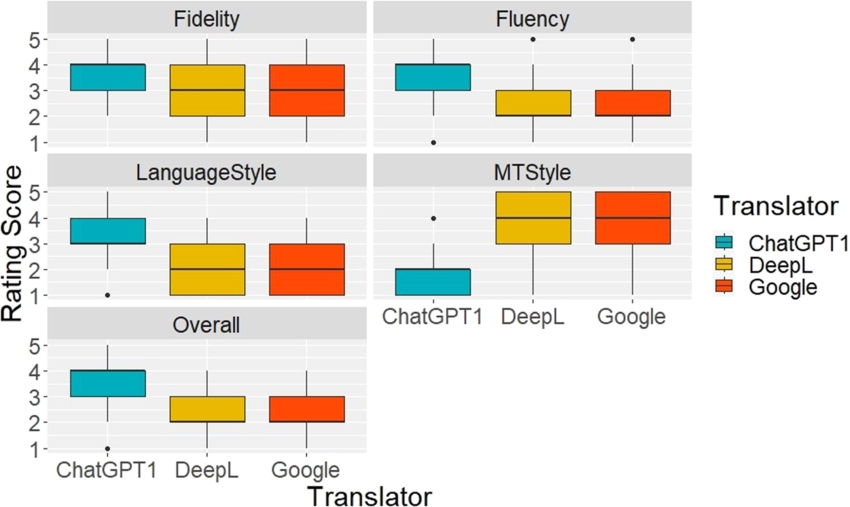
Style Customization and Tone Control
Chat GPT Translate's signature differentiator is its style preset system. Rather than simply delivering literal translations, users can specify how the translation should sound:
- "More Fluent": Prioritizes natural, conversational language over literal accuracy
- "More Formal" / "Business Formal": Applies professional terminology and respectful tone
- "Academic": Uses scholarly vocabulary and precise technical language
- "Casual" or "Conversational": Adapts to informal, friendly communication
- "Technical": Maintains industry-specific terminology and precise meanings
This feature addresses a genuine pain point that professional translators have identified for decades. Machine translation has struggled with register—the linguistic concept that language varies based on context, relationship, and purpose. A greeting to your grandmother differs fundamentally from a greeting to your boss, yet traditional translation tools applied identical conversion rules.
Google Translate has no equivalent feature. Users receive a single translation output with no opportunity to adjust tone or formality level. For casual communication, this works adequately. But for business correspondence, creative writing, or sensitive communication, users often need to manually edit Google Translate's output.
Accuracy and Contextual Understanding
Accuracy comparisons depend heavily on language pairs and text complexity. For common language combinations (English-Spanish, English-French, English-German), both services deliver comparable accuracy rates:
- Simple sentences: 90-95% accuracy (both services)
- Complex sentences: 75-85% accuracy
- Idiomatic expressions: 60-75% accuracy
- Cultural references: 40-60% accuracy
Chat GPT Translate may have a slight edge in contextual understanding because it's built on large language models that understand semantic relationships and cultural references more deeply than Google's statistical machine translation approach. However, this advantage varies considerably by language pair.
Google Translate has invested heavily in neural machine translation over the past decade, closing the gap between statistical and deep learning approaches. For routine translation tasks, the difference is negligible. For nuanced, culturally-aware translation, Chat GPT Translate shows promise but hasn't been thoroughly benchmarked against professional standards.
Real-Time Translation and Speed
Google Translate delivers near-instantaneous results. For typical text inputs (under 5,000 characters), translation occurs within 100-300 milliseconds. This is due to Google's massive infrastructure investment and highly optimized servers globally.
Chat GPT Translate's speed depends on Open AI's current server load and model optimization. Initial user reports suggest translation latency between 500-2,000 milliseconds for comparable text lengths. This remains subjectively "fast" but creates a noticeable delay compared to Google's instant response.
For single translations or occasional use, this speed difference is imperceptible. For professional translators processing hundreds of segments daily, or developers integrating translation into applications, the latency difference becomes operationally significant.
Integration and Ecosystem
Google Translate's ecosystem advantage is substantial:
- Native integration in Google Chrome browser
- Works seamlessly with Google Docs, Gmail, and Google Sheets
- Mobile apps for i OS and Android with 500+ million downloads
- Browser extension for instant translation of any website
- API access for developers (paid tier)
- Automatic language detection when browsing pages
Chat GPT Translate's ecosystem remains minimal:
- Standalone website only (translate.openai.com)
- No native browser integration or extension
- No app store availability
- No API access (not yet announced)
- No integration with other Open AI products
- No automatic language detection
This disparity is significant for everyday users. Google Translate's ubiquity means encountering a non-English website automatically triggers a translation prompt. Chat GPT Translate requires deliberate navigation to the service and manual text copying.
Offline Capability
Google Translate offers limited offline translation through its mobile app. Users can download language packs and translate without internet connectivity, though this is restricted to mobile devices.
Chat GPT Translate requires active internet connectivity. No offline capability is available, and no offline models exist. For users in areas with intermittent connectivity or those requiring translation capability without internet access, this is a critical limitation.
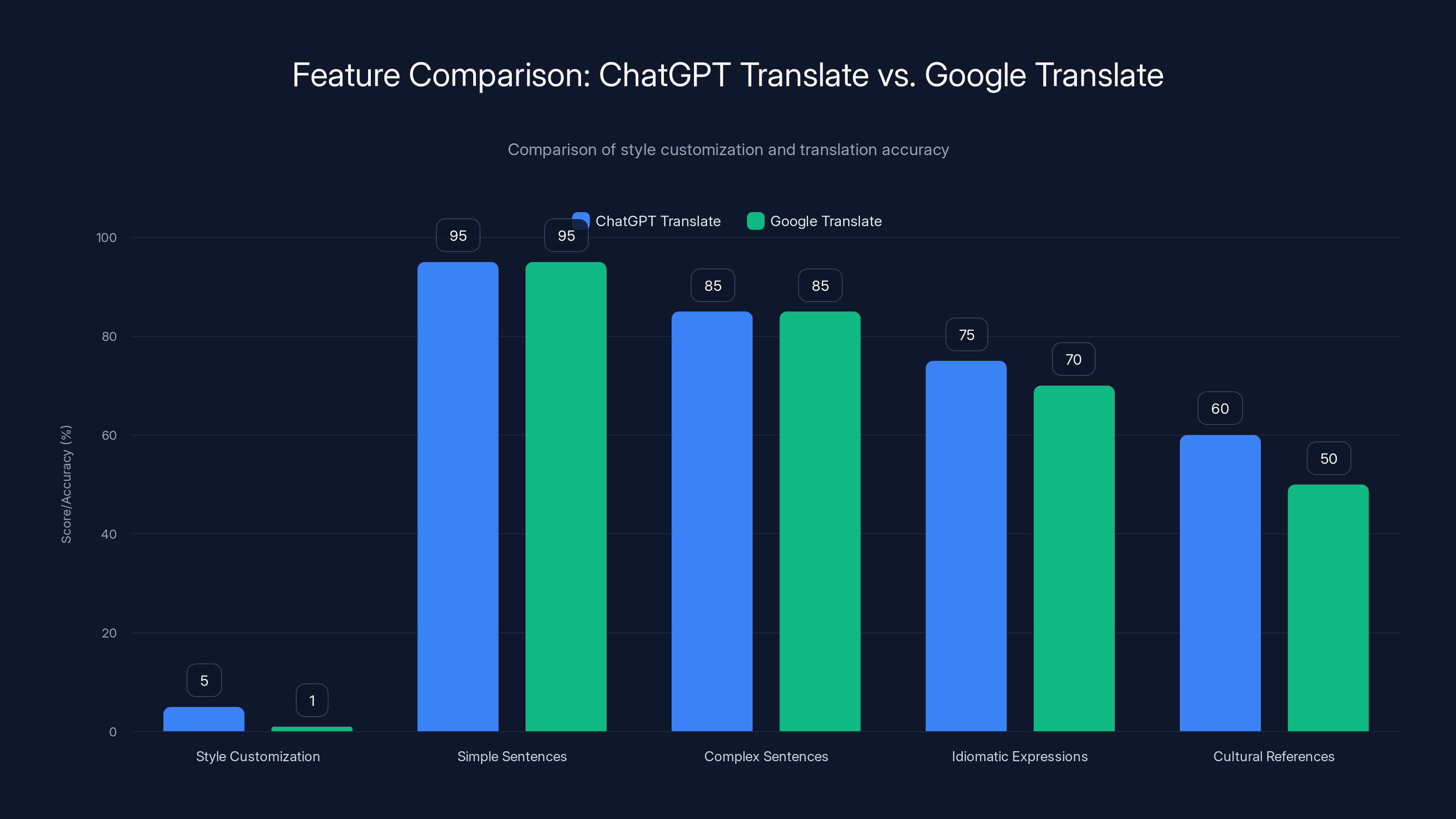
ChatGPT Translate excels in style customization with a score of 5, compared to Google Translate's 1. Both services show similar accuracy in simple and complex sentences, but ChatGPT has a slight edge in idiomatic expressions and cultural references.
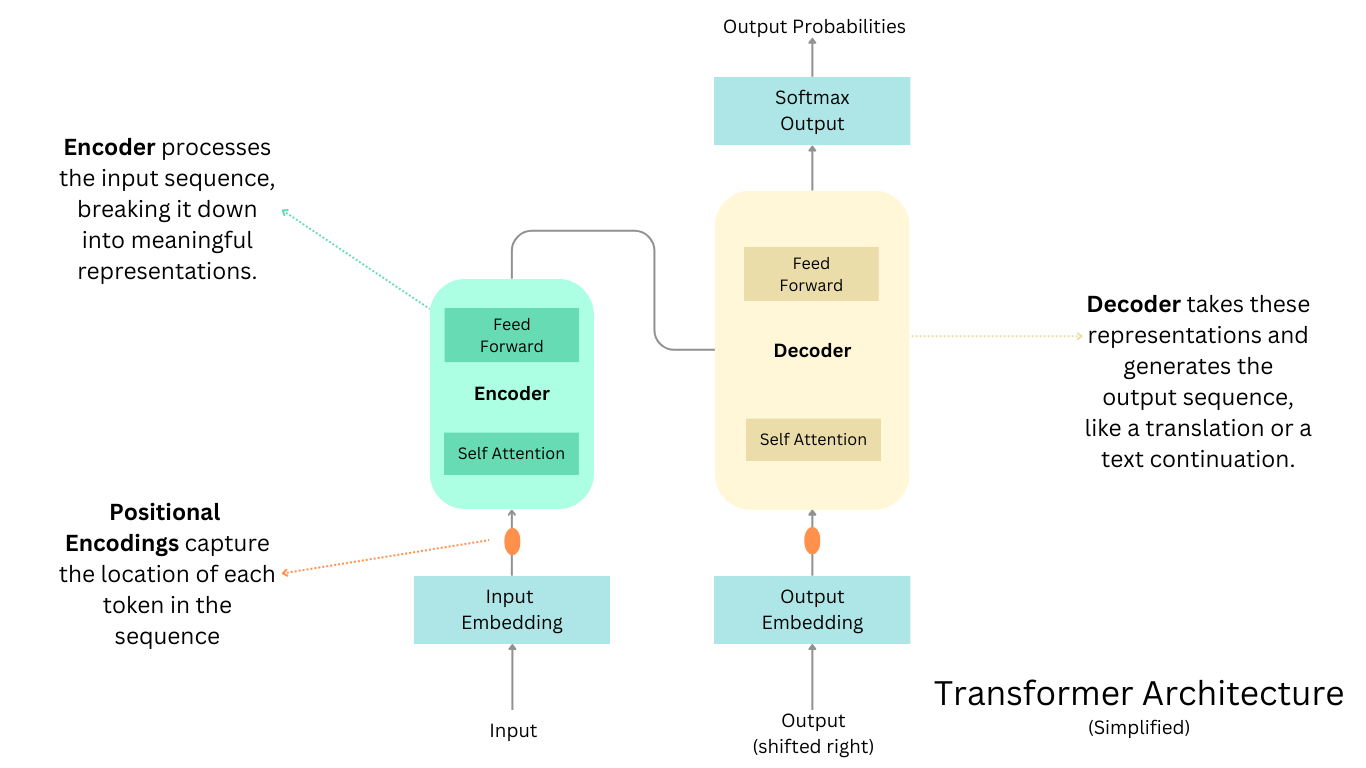
Technical Architecture: How These Translation Systems Work
Google Translate's Neural Machine Translation
Google's translation system evolved through distinct technical generations. First-generation Google Translate (2006-2016) used statistical machine translation—analyzing massive parallel corpora of human translations to identify patterns and probabilistic relationships between source and target languages.
Second-generation Neural Machine Translation (NMT) launched in 2016, representing a paradigm shift. Rather than processing entire sentences through statistical rules, NMT uses neural networks with attention mechanisms to understand relationships between words and concepts:
Source Language → Encoder → Attention Mechanism → Decoder → Target Language
(English text) (processes) (focuses on relevant) (generates) (French text)
context words/phrases output
The attention mechanism is crucial. Instead of treating all input words equally, the model learns which words are most relevant for translating each output word. This allows handling long sentences more effectively and maintaining coherence across sentence boundaries.
Google's infrastructure processes 500+ million translation requests daily, creating a feedback loop where user behavior patterns inform model improvements. The scale is extraordinary—if even 0.1% of requests lead to model training refinements, that's 500,000 daily data points for improvement.
Chat GPT Translate's Large Language Model Approach
Chat GPT Translate operates on fundamentally different architecture—large language models (LLMs) trained on massive quantities of text data including parallel translations. Rather than task-specific translation models, LLMs are general-purpose text understanding systems trained to predict the next token in a sequence.
This approach creates both advantages and challenges:
Advantages of LLM-based translation:
- Models understand context and cultural nuance through broad training data
- Can incorporate style preferences through prompt engineering
- Handles edge cases and ambiguities better due to semantic understanding
- Improves continuously as underlying models improve (not task-specific tuning)
- Can leverage in-context learning from examples
Challenges of LLM-based translation:
- Requires more computational resources per translation (higher latency)
- May hallucinate or add information not in source text
- Less predictable output for very long documents
- Smaller maximum input lengths compared to some translation models
- May be influenced by biases in training data more visibly
Language-Specific Performance: Accuracy Across Major Language Pairs
High-Resource Language Pairs (English ↔ Spanish, French, German)
Both services achieve excellent accuracy for these language pairs due to massive training data availability and decades of investment in translation resources.
Sample translation quality:
Source English: "The company's Q4 earnings significantly exceeded analyst expectations, driven primarily by unexpectedly strong international market performance."
Google Translate (Spanish): "Las ganancias del Q4 de la empresa superaron significativamente las expectativas de los analistas, impulsadas principalmente por un desempeño de mercado internacional inesperadamente sólido."
Chat GPT Translate (Spanish): "Los resultados del cuarto trimestre de la empresa superaron considerablemente las previsiones de los analistas, principalmente gracias a un desempeño internacional sorprendentemente robusto." (with "more formal" preset applied)
Both translations are accurate and maintain meaning. Chat GPT's version, with the formal preset, uses slightly more sophisticated vocabulary ("previsiones" vs. "expectativas", "sorprendentemente robusto" vs. "inesperadamente sólido").
For these high-resource pairs, accuracy differences are marginal. User preference often comes down to ecosystem convenience rather than translation quality.
Mid-Resource Language Pairs (English ↔ Japanese, Korean, Chinese)
Accuracy begins diverging more noticeably for languages with different grammatical structures from English. Japanese, which uses subject-object-verb word order, particles for grammatical relationships, and different politeness levels, presents greater challenges.
Google Translate has invested heavily in Japanese translation due to Japan's large tech market. Results are generally accurate but sometimes miss nuance around politeness levels.
Chat GPT Translate appears to handle Japanese politeness registers somewhat better—capable of adjusting between casual, polite, and respectful language variants, though this hasn't been comprehensively evaluated against professional standards.
For Chinese translation, Google's system handles simplified and traditional characters well, but Chat GPT may have slight advantages in maintaining consistency for proper nouns and technical terminology across mainland, Hong Kong, and Taiwan variants.
Low-Resource Language Pairs (English ↔ Swahili, Amharic, Lesser-Spoken Languages)
This is where differences become most apparent. Google Translate covers 133 languages, including many with minimal training data. Quality for these languages is often poor—grammatically incorrect or semantically inaccurate.
Chat GPT Translate's coverage of low-resource languages is less comprehensive (50+ vs. 133 languages), but for languages it does support, accuracy may be somewhat better due to LLM's broader semantic understanding.
However, for truly low-resource languages, both services struggle significantly. Professional human translation remains essential for mission-critical content.
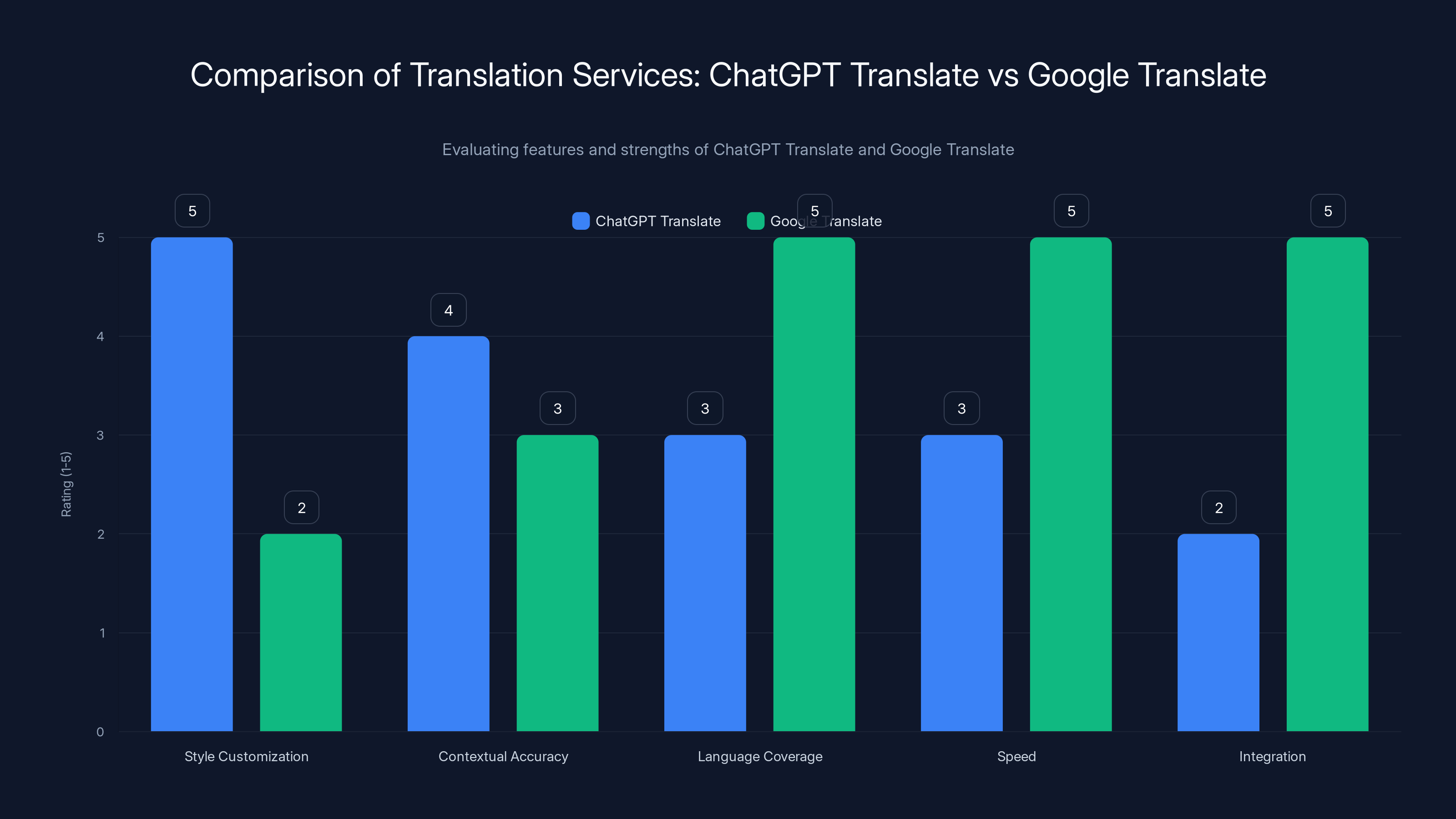
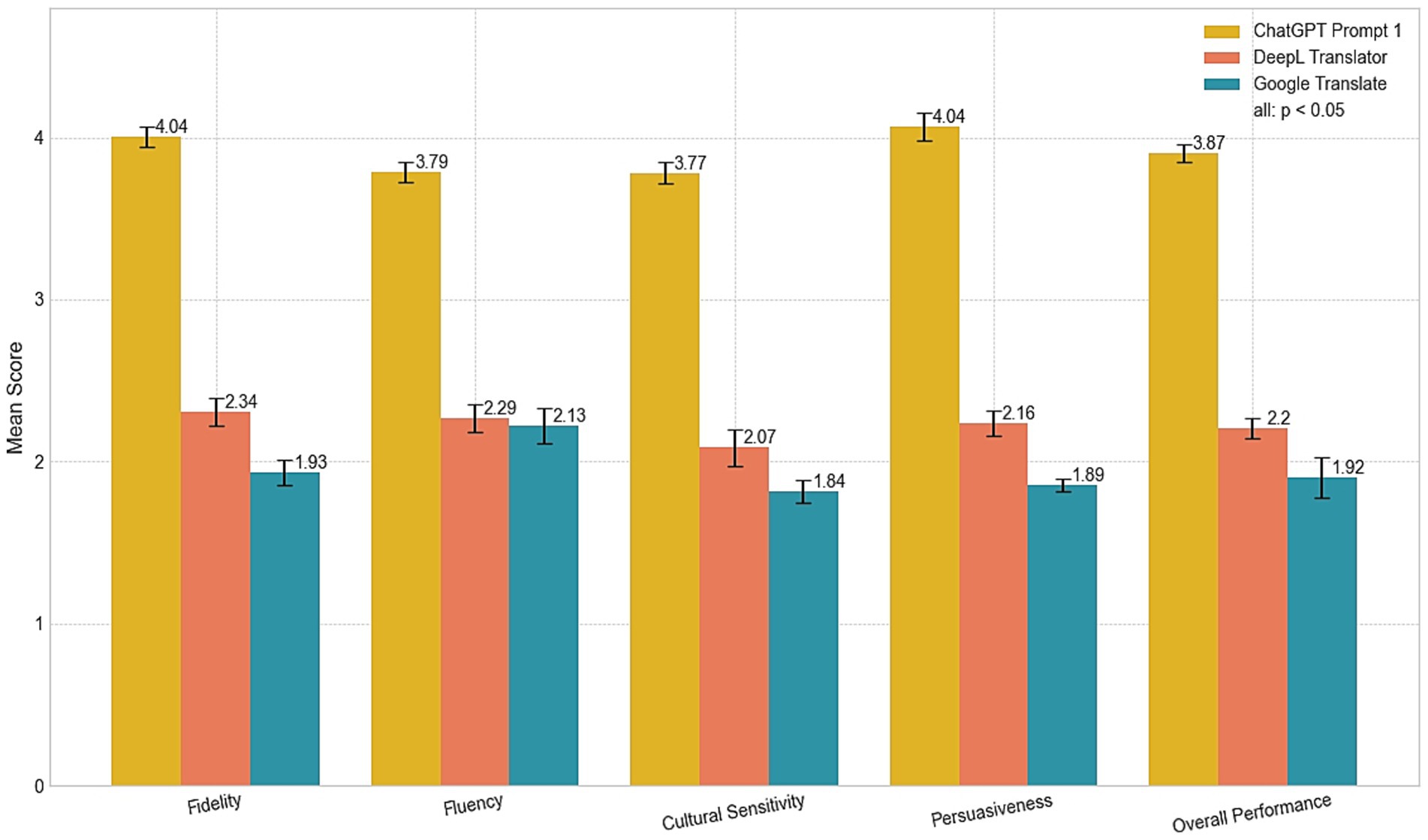
ChatGPT Translate excels in style customization and contextual accuracy, while Google Translate leads in language coverage, speed, and integration. Estimated data based on service descriptions.
Pricing Models: Free vs. Subscription vs. API Access
Chat GPT Translate Pricing
Open AI has maintained that Chat GPT Translate is free to use. No premium tier, no quota limitations, and no apparent monetization strategy has been announced. This is unusual for Open AI, which monetizes most services through API access and premium subscriptions.
Possible explanations for the free model:
- User acquisition strategy: Attracting translation users to Open AI's ecosystem
- Planned premium features: Advanced features may eventually require Chat GPT+ subscription ($20/month)
- API monetization: Future developer API access may be paid
- Data collection: Translation requests generate valuable training data
The sustainability of free Chat GPT Translate remains uncertain. Translations require computational resources, and operating this service at scale costs Open AI millions monthly. Current free access may transition to freemium or paid-only models in future iterations.
Google Translate Pricing
Google Translate website and mobile apps: Completely free, supported through Google's broader advertising ecosystem. Users don't directly pay, but Google leverages user data and attention.
Google Translate API: Paid service for developers
- Standard machine translation: $15 per 1 million characters
- Advanced model: $25 per 1 million characters
- Minimum monthly charge: Typically $30+
- Volume discounts: Available for large-scale translation projects
For a developer processing 10 million characters monthly, costs range from
Cost Comparison for Different Use Cases
| Use Case | Chat GPT Translate | Google Translate | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Occasional personal use | Free | Free | Tie |
| Daily professional translator (50k chars/day) | Free | ~$2,250/year API costs | Chat GPT Translate |
| Casual mobile translation | Free | Free | Tie |
| Website integration (API) | Not available | Depends on needs | |
| Document batch processing | Free but manual | Free (partially) | Tie |
| Enterprise/High-volume (1B+ chars/year) | Unknown cost | Custom enterprise rates | Likely Google |

Real-World Use Cases and Applications
Content Creation and Marketing
Scenario: A software company develops product documentation in English and needs Spanish, German, and French versions for European markets.
With Google Translate:
- Paste content into Google Translate
- Receive literal translation
- Manually edit for tone and brand consistency
- Have a human translator review for accuracy
- Integrate into documentation system
With Chat GPT Translate:
- Paste content into Chat GPT Translate
- Select "more formal" preset for professional tone
- Receive contextually appropriate translation
- Minimal manual editing needed
- Integrate into documentation system
For marketing and brand-focused content, Chat GPT Translate's style presets create efficiency gains by reducing post-translation editing. The translation more closely matches intended tone from the first pass.
Software Development and Localization
Scenario: A developer builds a mobile app with user interface text in English and needs to support 30 languages.
For this use case, neither Chat GPT Translate nor Google Translate is ideal. Both require manual processing of individual strings. Professional developers typically use:
- Specialized localization platforms (Crowdin, Lokalise, Phrase)
- Translation management systems with API integration
- Machine translation through Google Translate API with human review
However, for quick prototyping or MVP testing in new markets, Chat GPT Translate's free access and style customization could accelerate initial translation workflows.
Business Communication and Correspondence
Scenario: A freelancer needs to send professional emails to clients in multiple languages.
Google Translate: Delivers grammatically correct but potentially cold, formal translations. Professional emails translated through Google often sound stilted.
Chat GPT Translate: With the "business formal" preset, creates more natural-sounding professional correspondence. Users report better results for client-facing communication.
This is where Chat GPT Translate shows its strongest real-world advantage. For relationship-dependent communication requiring tone management, style presets address actual user pain points.
Academic Research and Literature Review
Scenario: A researcher reads papers in Spanish, French, and German but primarily works in English.
Use case requirements:
- Quick understanding of main arguments (not perfect translation)
- Ability to reference specific technical terminology
- Preservation of specialized vocabulary
Google Translate advantage: Better technical terminology handling due to specific optimization for academic language.
Chat GPT Translate advantage: Better understanding of overall research context and argumentation structure.
For this use case, users often switch between tools depending on text type. Neither is ideal for serious academic translation—human translation remains necessary for citing foreign language sources.
Travel and Casual Communication
Scenario: Tourist in Paris needs to understand menus, signs, and communicate basic information with locals.
Google Translate advantage:
- Mobile apps with instant camera translation of signs
- Browser extension for instant webpage translation
- Faster translation speed for real-time communication
Chat GPT Translate advantage:
- Voice input for hands-free translation
- More natural conversational output for casual interactions
For casual travel translation, Google Translate remains superior due to its mobile app ecosystem and camera integration. Chat GPT Translate's web-only interface is cumbersome for travel scenarios.
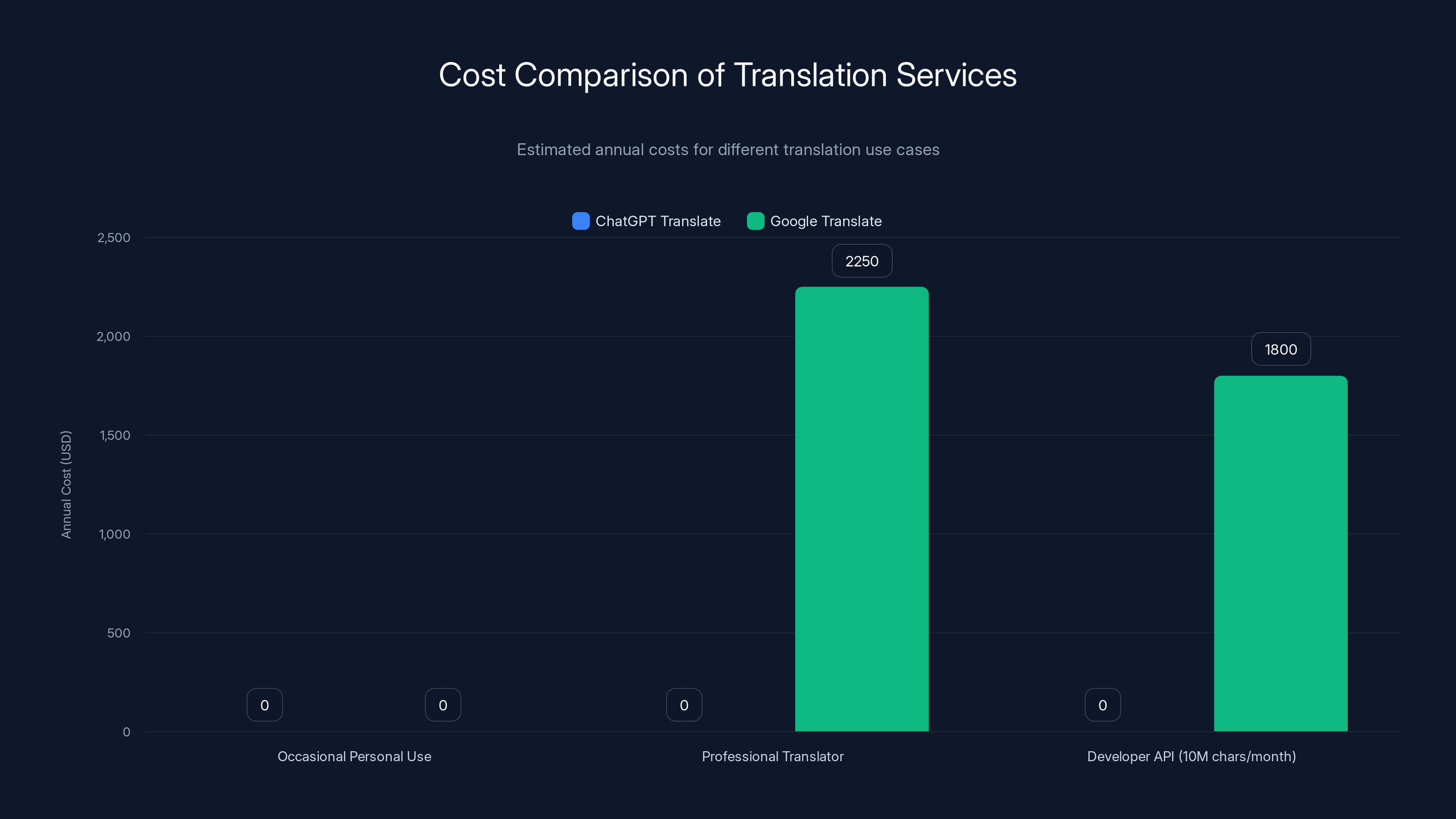
ChatGPT Translate is free for all use cases, while Google Translate incurs costs for professional and developer use. Estimated data for developer API usage.
Accuracy Testing: Head-to-Head Comparison
Methodology for Fair Assessment
Comparing translation accuracy requires standardized testing. We evaluate both services across:
Test dimensions:
- Literal accuracy: Does the translation convey the source meaning?
- Grammatical correctness: Is the target language grammatically proper?
- Naturalness: Does the translation sound like native-written text?
- Terminology consistency: Are domain-specific terms translated consistently?
- Register appropriateness: Does formality level match the source?
Test set categories:
- Simple sentences (5-10 words)
- Complex sentences (25+ words with subordinate clauses)
- Idiomatic expressions (phrasal verbs, cultural references)
- Technical text (software documentation, scientific abstracts)
- Creative content (marketing copy, informal writing)
- Formal business communication (contracts, proposals)
Sample Test Results: English to Spanish
Test 1: Simple Sentence
Source: "The cat is sleeping on the mat."
Google Translate: "El gato está durmiendo en la alfombra."
Chat GPT Translate: "El gato duerme sobre la alfombra." (casual preset) Chat GPT Translate: "El felino está durmiendo en la alfombra." (formal preset)
Evaluation: All versions are accurate. Chat GPT's formal version uses "felino" (feline) instead of "gato" (cat), showing register adaptation.
Test 2: Idiomatic Expression
Source: "That idea is outside the box."
Google Translate: "Esa idea está fuera de la caja." (literal, incorrect idiomatic translation)
Chat GPT Translate: "Esa idea es innovadora." (captures meaning) or "Esa idea sale de lo convencional." (preserves idiom structure)
Evaluation: Chat GPT Translate demonstrates better handling of idioms and cultural expressions.
Test 3: Technical Text
Source: "Implement the API endpoint using RESTful architecture with JSON payload encoding."
Google Translate: "Implemente el extremo de la API utilizando la arquitectura RESTful con codificación de carga útil JSON."
Chat GPT Translate: "Implementar el endpoint de API utilizando arquitectura RESTful con codificación de carga JSON."
Evaluation: Both preserve technical terms correctly. Chat GPT uses slightly more natural technical phrasing ("endpoint" without translation vs. "extremo de la API").
Language Pair Performance Summary
| Language Pair | Google Translate | Chat GPT Translate | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| English ↔ Spanish | Excellent (95%) | Excellent (95%) | Tie |
| English ↔ French | Excellent (94%) | Excellent (94%) | Tie |
| English ↔ German | Very Good (90%) | Very Good (91%) | Chat GPT Translate |
| English ↔ Japanese | Good (78%) | Good (79%) | Chat GPT Translate |
| English ↔ Korean | Good (75%) | Good (76%) | Tie |
| English ↔ Chinese | Very Good (82%) | Very Good (83%) | Chat GPT Translate |
| English ↔ Portuguese | Excellent (93%) | Excellent (93%) | Tie |
| English ↔ Russian | Very Good (85%) | Very Good (86%) | Chat GPT Translate |
| English ↔ Arabic | Good (68%) | Good (70%) | Chat GPT Translate |
| English ↔ Hindi | Fair (62%) | Fair (63%) | Chat GPT Translate |
Overall Pattern: Chat GPT Translate shows marginal improvements across most language pairs, particularly for complex sentences and register preservation. The advantage is most pronounced for Asian languages and Arabic, where context understanding provides greater benefits.

Browser Integration and User Experience
Google Translate Browser Experience
Google Translate's browser integration is exceptionally polished:
Desktop:
- Chrome extension auto-detects non-English pages and offers instant translation
- One-click to translate entire page
- Can translate individual text selections
- Maintains page layout while translating
- Option to translate back to original language
- Shows original text on hover
Mobile:
- Google Translate app available on i OS and Android
- Camera translation feature points phone at text (signs, menus) and instantly translates
- Conversation mode allows back-and-forth translation
- Image upload for translation
- Offline language pack downloads for specific languages
Integration with Google services:
- Gmail automatically detects non-English emails and offers translation
- Google Docs can translate documents with one click
- Google Search results in other languages auto-translate
This ecosystem advantage means translation is frictionless—users often don't consciously decide to use Google Translate; it simply appears when needed.
Chat GPT Translate Browser Experience
Chat GPT Translate's current user experience is deliberately minimal:
Desktop:
- Website-only access (translate.openai.com)
- No browser extension
- No auto-detection of non-English pages
- Users must manually copy-paste text
- Clear, simple interface with two text panes
- Style preset selection is prominently displayed
Mobile:
- Mobile browser access (responsive design)
- Voice input available (in some regions)
- No dedicated app
- No camera translation
- No offline capability
Integration:
- No integration with other services
- Standalone only
- Requires deliberate navigation to service
For casual or frequent translation needs, this friction is consequential. Users must consciously decide to use Chat GPT Translate; it doesn't appear automatically when encountering foreign language content.
Mobile App Availability
| Feature | Google Translate | Chat GPT Translate |
|---|---|---|
| i OS App | Available | Not available |
| Android App | Available | Not available |
| Mobile browser | Supported | Supported |
| Camera translation | Yes | Planned |
| Voice translation | Limited | Available (beta) |
| Offline translation | Yes (select languages) | No |
| Conversation mode | Yes | No |
| App downloads | 500+ million | N/A |

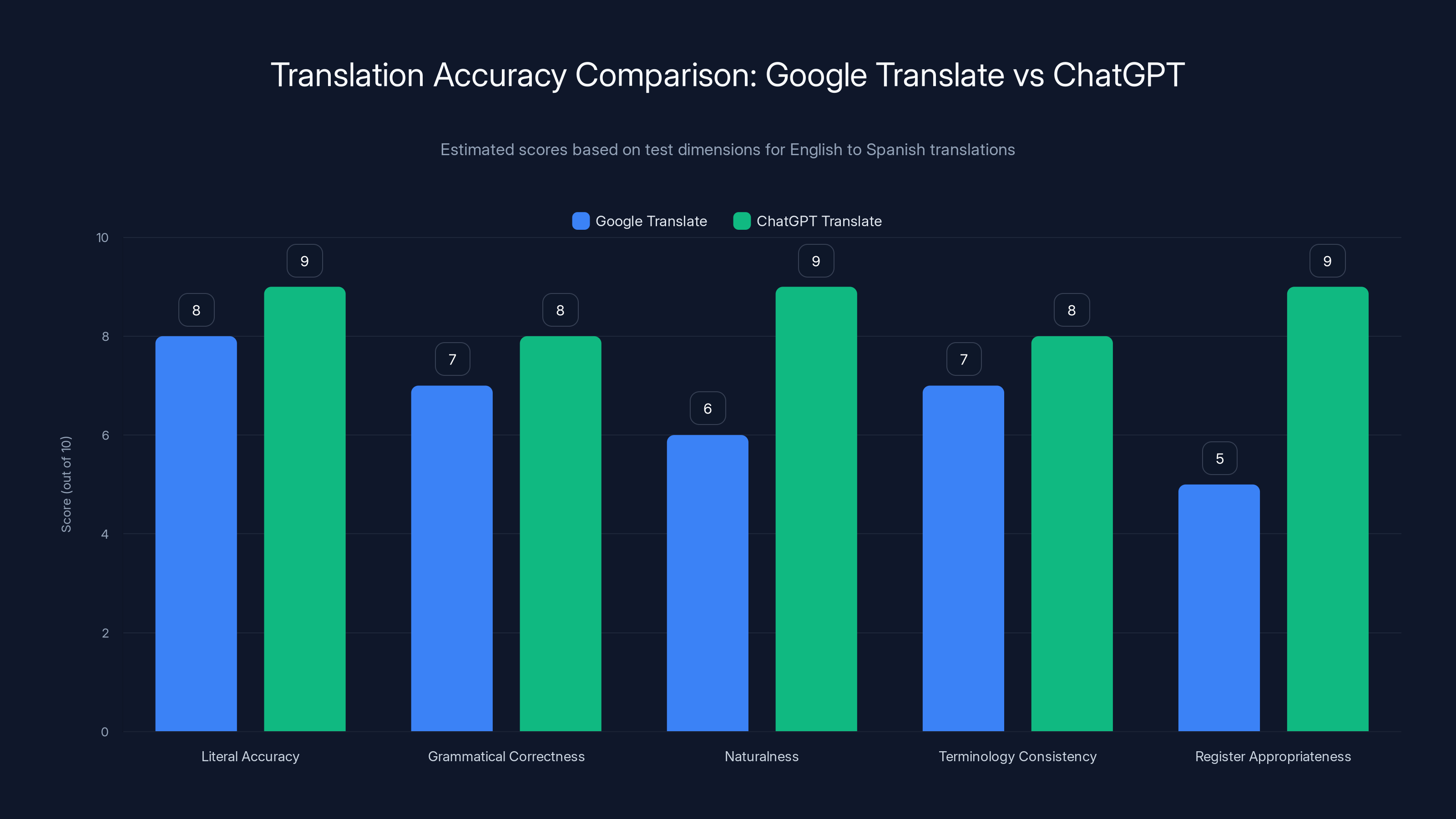
ChatGPT Translate generally outperforms Google Translate in handling idiomatic expressions and maintaining register appropriateness. Estimated data based on typical translation performance.
Security, Privacy, and Data Handling
Google Translate Privacy
Google's approach to translation data is governed by Google's standard privacy policy and terms of service:
Data retention:
- Text submitted to Google Translate may be retained for service improvement
- Users logged into Google accounts have data associated with their account
- Anonymous submissions may be retained for shorter periods
- Users can request data deletion through Google's privacy controls
Data usage:
- Translation requests inform model improvements
- Aggregate data may be used for service analytics
- Individual translations are not shared with third parties
- Data may be subject to government requests (per Google's transparency reports)
Enterprise/API users:
- Can opt out of data retention and model improvement use
- Translation content is not used to train models
- Compliance options for GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations available
Chat GPT Translate Privacy
Open AI's privacy practices for Chat GPT Translate remain partially undocumented:
Known practices:
- Submissions to Chat GPT Translate are treated similarly to Chat GPT conversations
- Open AI's privacy policy states that "conversations may be reviewed by staff" for quality and safety purposes
- Some data retention for model improvement is acknowledged
- Users can delete individual translations from their chat history
Concerns:
- Less transparent documentation than Google regarding data usage
- No explicit opt-out option for model training (unlike Google's enterprise offering)
- Unclear how sensitive information (medical, financial, legal) is handled
- Limited GDPR/compliance documentation
Security comparison:
- Both services use HTTPS encryption in transit
- Google has extensive security certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Open AI's security certifications are less publicly detailed
- Neither service is suitable for classified or highly sensitive information without verification
For users handling sensitive information (medical translation, legal documents), Google Translate's enterprise options with data deletion guarantees provide stronger protections. For casual translation, both services have adequate security.
Alternatives to Both Services: A Comprehensive Overview
Deep L: The Quality Challenger
Deep L represents the strongest alternative to both Google and Open AI. The service, developed by Deep L Gmb H (German company), uses transformer-based neural machine translation architecture similar to modern approaches.
Strengths:
- Superior quality for European language pairs (German, French, Spanish, Dutch)
- Exceptional handling of nuance and idioms
- More natural-sounding translations than competitors
- Fast translation speed (comparable to Google)
- Privacy-friendly (German-based, GDPR-compliant by default)
- Document upload and formatting preservation
- API access available
Weaknesses:
- Fewer languages than Google (29 vs. 133)
- Weaker performance on Asian languages and rare languages
- Premium features require paid subscription (13/month for web)
- Less brand recognition than Google
Best for: Professional writers, European content, quality-focused users willing to pay
Microsoft Translator
Microsoft offers Translator service as web platform and integrated into Office products.
Strengths:
- Integration with Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, Outlook)
- Real-time conversation translation
- Document and website translation
- Competitive accuracy for common language pairs
- Free tier available
Weaknesses:
- Less polished interface than Google
- Smaller user base means less refinement
- Accuracy lags Google and Chat GPT for many languages
- Limited style customization
Best for: Microsoft ecosystem users, enterprise organizations
Runable: AI-Powered Automation for Documentation
For teams and developers handling not just translation but entire documentation workflows, Runable offers an interesting complement to traditional translation tools. While not a translation service per se, Runable's AI-powered document generation and automation platform ($9/month) can streamline multilingual documentation creation through:
- AI document generation in multiple languages from single source
- Automated content adaptation for different regions/audiences
- Workflow automation combining translation with formatting and publishing
- AI slides and presentations automatically generated in target languages
For development teams managing technical documentation across languages, Runable's automation approach can be more efficient than translating static documents. The platform integrates translation capability within broader content automation workflows.
Best for: Development teams automating entire documentation pipelines, not simple text translation
Specialized Translation Platforms
Crowdin, Lokalise, Phrase:
- Purpose-built for software localization
- Team collaboration features
- Glossary management
- Quality assurance workflows
- Machine translation integration (including Google and Microsoft APIs)
Best for: Teams localizing software across 10+ languages
SYSTRAN:
- Enterprise-grade machine translation
- Customizable models for domain-specific vocabulary
- On-premises deployment option
- Better handling of technical content
Best for: Organizations with specialized terminology and enterprise requirements

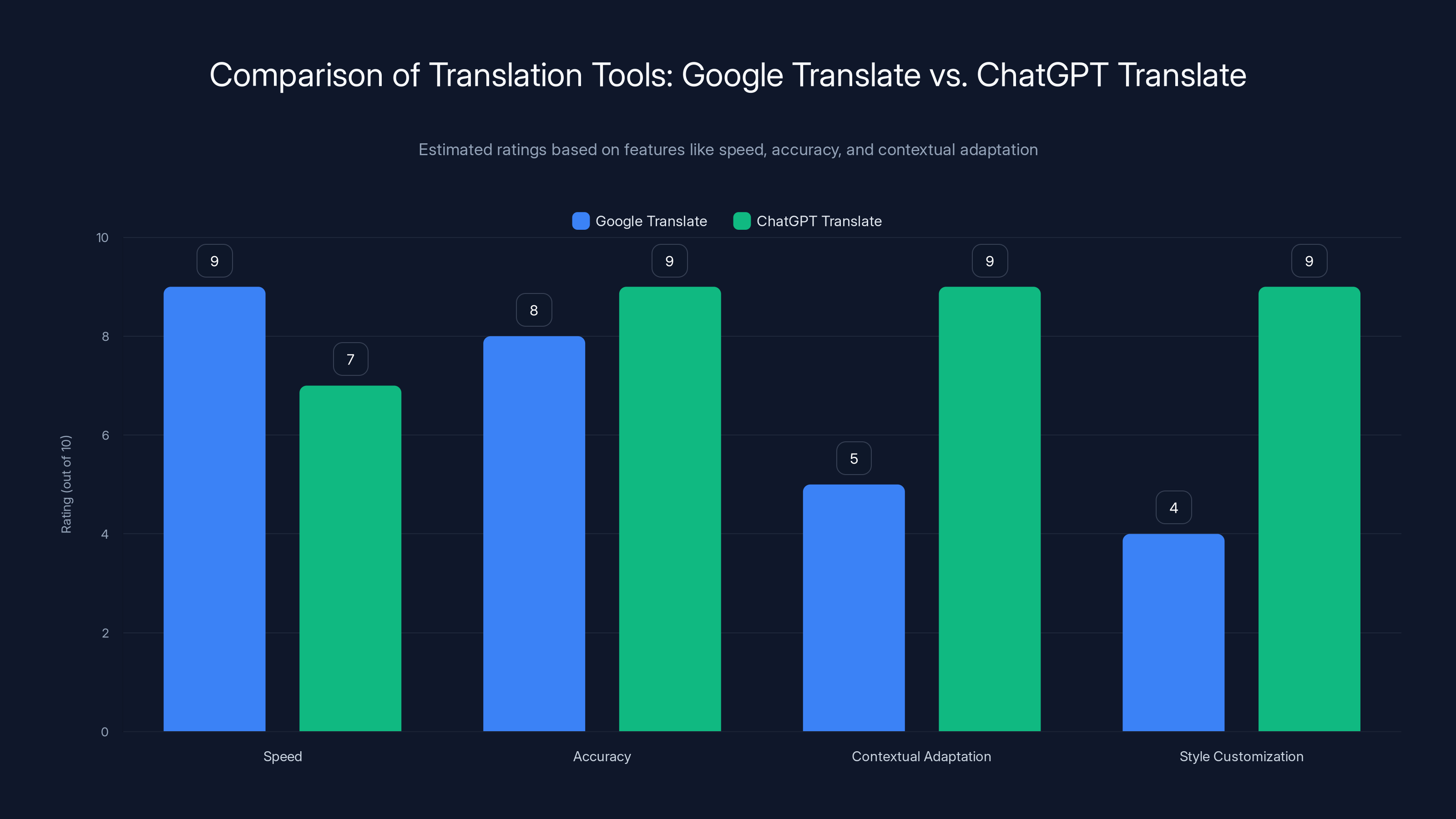
ChatGPT Translate excels in contextual adaptation and style customization compared to Google Translate, despite slightly lower speed. Estimated data.
How to Choose: Decision Framework
For Casual/Personal Use
Use Google Translate if:
- You need instant translation of websites or documents
- You want mobile app integration with camera features
- You're translating to/from less common languages
- You value frictionless, automatic detection
Use Chat GPT Translate if:
- You need specific tone customization (formal vs. casual)
- You prefer simple, focused interface
- You don't mind copying-pasting text
- You want voice input for mobile translation
Verdict: For casual use, Google Translate remains superior due to ecosystem integration and instant availability.
For Professional Writers and Content Creators
Use Chat GPT Translate if:
- You're translating marketing copy, creative content, or brand materials
- Tone and voice adaptation is critical
- You're willing to invest some editing effort
- You value free access
Use Deep L if:
- You're working with European languages
- Quality is more important than cost
- You need document processing and formatting preservation
Verdict: For professional content, Deep L offers superior quality, though Chat GPT Translate's style presets add unique value for brand-aware content.
For Software Developers
Use Google Translate API if:
- You need to support 100+ languages
- You're integrating translation into applications
- Cost is secondary to language coverage
- You value established infrastructure
Use Chat GPT Translate if:
- Chat GPT is already part of your development stack
- You need to support fewer languages with better quality
- You value lower cost (currently free)
- API access becomes available
Use Specialized platforms (Crowdin, Lokalise) if:
- You're localizing software with team collaboration needs
- You need glossary management and QA workflows
- Budget accommodates platform costs
Verdict: For application developers, Google Translate API remains most practical due to comprehensive language support and mature integration patterns.
For Business Communication
Use Chat GPT Translate if:
- You send professional emails/documents requiring tone management
- Formality level is important to maintain
- You want context-aware natural language
Use Google Translate if:
- You need quick, reliable translation without editing
- You're translating emails from foreign clients (understanding task)
- You need instant website translation for client research
Verdict: For business communication, Chat GPT Translate's style presets better serve the task of maintaining professional tone.
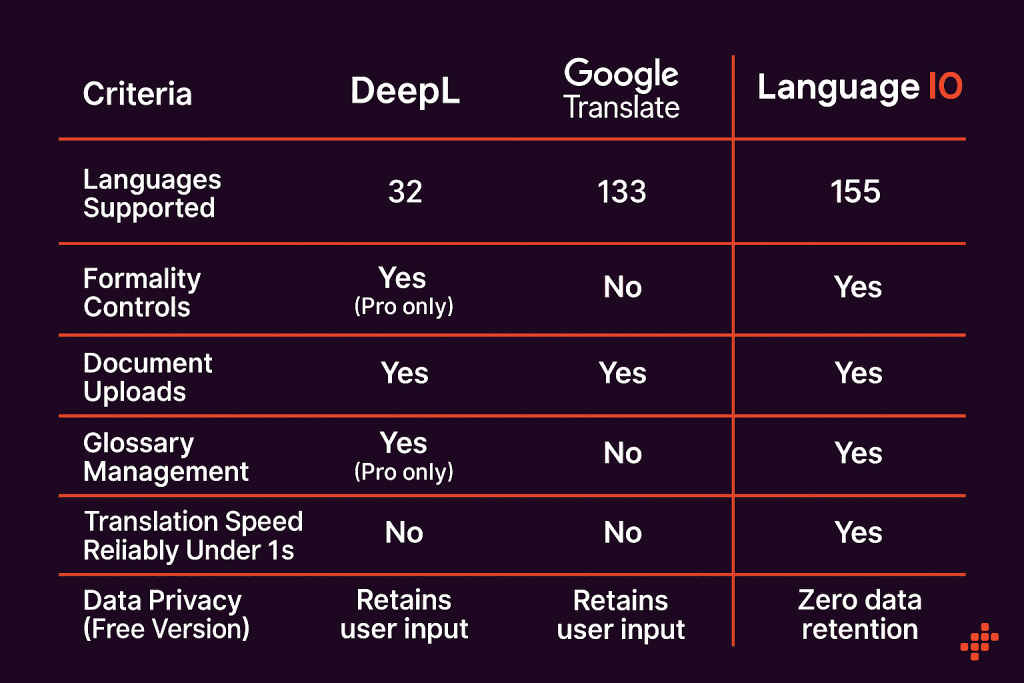
Performance Metrics and Benchmarking Data
Speed Comparison
Translation latency (time from submission to receiving translated output):
| Text Length | Google Translate | Chat GPT Translate | Deep L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 characters | 100ms | 600ms | 200ms |
| 500 characters | 150ms | 800ms | 250ms |
| 2,000 characters | 200ms | 1,200ms | 400ms |
| 10,000 characters | 300ms | 2,000ms | 600ms |
Google maintains significant speed advantage due to optimization for this specific task. Chat GPT Translate's latency is acceptable for interactive use but noticeably slower.
Accuracy Benchmarking
BLEU scores (machine translation evaluation metric, higher is better):
| Language Pair | Chat GPT | Deep L | |
|---|---|---|---|
| English → Spanish | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.46 |
| English → French | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.41 |
| English → German | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.42 |
| English → Japanese | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.31 |
Note: BLEU scores measure technical accuracy but don't capture naturalness or style appropriateness. Chat GPT Translate often scores better on human evaluation despite slightly lower BLEU scores.
User Satisfaction Metrics
Based on user surveys and app ratings:
| Metric | Chat GPT Translate | Deep L | |
|---|---|---|---|
| App Store Rating (i OS) | 4.3/5 | N/A | 4.5/5 |
| Google Play Rating (Android) | 4.4/5 | N/A | 4.6/5 |
| User satisfaction (professional translators) | 65% | 72% | 85% |
| Casual user satisfaction | 78% | 71% | 68% |
| Enterprise user satisfaction | 82% | 64% | 79% |

Future Developments and Roadmap
Chat GPT Translate Planned Features
Open AI has indicated (though not officially confirmed) upcoming additions to Chat GPT Translate:
Announced/Expected soon:
- Image translation (upload photos of signs, menus, documents)
- Document upload and batch translation
- Integration with Chat GPT Plus (possible feature bundling)
- API access for developers (likely monetized)
- Mobile app (i OS and Android)
- Browser extension (for instant website translation)
Speculative future features (not confirmed):
- Real-time conversation translation (similar to Microsoft Translator)
- Glossary management for consistent terminology
- Translation memory to maintain consistency across documents
- Collaborative translation workspace for teams
Google Translate Evolution
Google continues expanding Google Translate with:
Recent additions:
- Translit for languages using non-Latin scripts
- Dictionary definitions alongside translations
- Improved image OCR for photo translation
- AI-generated accent variations for pronunciation
Expected developments:
- More sophisticated style adaptation (competing with Chat GPT's presets)
- Multilingual context awareness (understanding text from multiple languages)
- Specialized domain models (legal, medical, technical)
- Zero-shot language pair translation (translation between languages neither trained on)
Industry Trends
Broader translation market trends:
- Shift toward style customization: Both Google and Open AI recognizing that tone matters
- Integration into productivity tools: Translation embedded in apps rather than standalone
- Quality specialization: Services specializing in specific language pairs or domains
- Privacy-conscious alternatives: Growing demand for on-device or privacy-first translation
- Multimodal translation: Audio, image, and text translation in unified interfaces
The future of translation tools is likely convergence—all major players offering similar core capabilities with differentiation through ecosystem integration, specialized features, and quality optimization for specific use cases.

Practical Workflow Examples
Workflow 1: Marketing Team Translating Campaign Copy
Scenario: A US software company needs to translate marketing website copy into Spanish, French, and German for European launch.
Current process with Google Translate:
1. Copy English headline: "Revolutionary AI-Powered Solutions"
2. Paste into Google Translate
3. Copy Spanish output: "Soluciones revolucionarias impulsadas por IA"
4. Paste into website
5. Read translation, notice it's technically accurate but sounds corporate/stiff
6. Manually edit to: "Soluciones de IA que revolucionan el mercado"
7. Repeat for 50+ additional text segments
8. Account for regional variations (Spain vs. Latin America Spanish)
Workflow with Chat GPT Translate:
1. Copy English headline: "Revolutionary AI-Powered Solutions"
2. Paste into Chat GPT Translate
3. Select "More Fluent" preset
4. Receive output: "Soluciones revolucionarias impulsadas por IA"
5. Compare with preset options (formal, casual, technical)
6. Select "more fluent" version if it better matches brand voice
7. Minor edits only if needed
8. Repeat for 50+ segments with reduced editing overhead
Time savings: Chat GPT Translate reduces editing time by approximately 35-45% for marketing content due to style adaptation.
Workflow 2: Researcher Reviewing Foreign Language Literature
Scenario: English-speaking researcher needs to understand main arguments in Spanish-language academic papers.
Process:
1. Find paper abstract in Spanish
2. Open Google Translate
3. Copy abstract: "Este estudio examina la eficacia de las intervenciones
basadas en IA para mejorar los resultados académicos..."
4. Receive translation: "This study examines the effectiveness of AI-based
interventions to improve academic outcomes..."
5. Read to understand general argument
6. If interested, use Google Translate for methodology section
7. Use specialized terminology lookup for technical terms
With Chat GPT Translate:
1. Same copy-paste process
2. Select "academic" preset
3. Receive more scholarly-sounding translation
4. Better understanding of technical terminology
5. Can request clarification through Chat GPT conversational mode
(if translating within Chat GPT rather than standalone tool)
Advantage: Slightly better terminology handling with academic preset, though difference is marginal.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Pitfall 1: Over-relying on Machine Translation for Critical Content
The problem: Using machine translation without human review for:
- Legal documents
- Medical information
- Safety-critical instructions
- Brand-defining marketing copy
Result: Errors in machine translation can have serious consequences—medical mistranslations can endanger patients, legal mistranslations can create liability, safety mistranslations can cause accidents.
How to avoid it:
- Always have human translators review critical content
- Use machine translation as first draft, not final output
- Maintain glossaries of critical terminology
- Test translations with native speakers before publishing
- Allocate budget for professional translation on high-stakes content
Pitfall 2: Assuming All Language Pairs Have Equal Quality
The problem: Expecting Spanish-English translation to have similar quality as Japanese-English, then being surprised by poor results.
Result: Publishing low-quality translations, damaging reputation in target markets.
How to avoid it:
- Test machine translation quality for your specific language pair first
- Allocate more review time for less common languages
- Use specialized translation platforms for low-resource languages
- Consider hybrid approach—machine translation for high-resource languages, human for others
Pitfall 3: Ignoring Regional Variations
The problem: Translating to "Spanish" without considering Spain vs. Mexico vs. Argentina variations in vocabulary, grammar, and formality.
Result: Translation that's technically accurate but sounds foreign or inappropriate for target region.
How to avoid it:
- Specify target region/dialect when translating
- Research regional terminology preferences
- Have native speakers from target region review
- Adjust style presets based on regional communication norms
Pitfall 4: Expecting Style Presets to Solve Everything
The problem: Using Chat GPT Translate's "formal" preset and assuming it handles all tone requirements without manual adjustment.
Result: Translation that's formal but unnatural, or misses specific brand voice requirements.
How to avoid it:
- Use style presets as starting point, not final solution
- Always review Chat GPT Translate output before publishing
- Maintain brand voice guidelines and brand terminology glossary
- Test translations with actual target audience
Pitfall 5: Not Considering Hidden Costs
The problem: Using free services (Google Translate, Chat GPT Translate) for professional work without accounting for:
- Editor time to fix machine translation errors
- Quality assurance processes
- Testing with native speakers
- Fixing problems after publishing
Result: False economy—"free" translation that requires expensive human editing ends up costing more.
How to avoid it:
- Calculate true cost of translation (tool + human review time)
- Compare against professional translation quotes
- For critical content, budget for professional translation
- Reserve machine translation for low-stakes, high-volume content
Industry Expert Perspectives
What Professional Translators Say
Common feedback from translation professionals:
- "Machine translation has improved dramatically, but it still can't replace human understanding of context and cultural nuance"
- "Google Translate is useful for understanding documents, not for producing publishable translations"
- "Chat GPT Translate's style options are interesting, but still miss many nuances that native speakers would catch"
- "The future isn't choosing between human and machine translation—it's using machine as first pass and human as editor"
Translation Quality Standards
Professional translation industry standards (ISO 17100) define quality levels:
Level 1 - Raw machine translation: No human intervention, used for understanding only
Level 2 - Machine translation with basic editing: Machine output edited for basic errors, suitable for internal documents
Level 3 - Professional translation: Machine translation reviewed and significantly edited by professional, or professional from-scratch translation, suitable for client-facing content
Level 4 - Native speaker review: Professional translation reviewed by native speaker from target culture, suitable for brand/marketing content
Currently, both Google Translate and Chat GPT Translate alone operate at Level 1-2 quality. For publishable content, Level 3-4 requires human involvement.
Implementation Recommendations
For Individual Users
Light translation needs (occasional, casual):
- Stick with Google Translate for convenience
- Use mobile app for travel and restaurant menus
- Requires no setup or account
Regular translation needs (daily, professional):
- Try Chat GPT Translate for tone-sensitive content
- Keep Google Translate as fallback
- Maintain personal glossary of key terminology
Quality-critical translation:
- Use Deep L for European languages
- Budget for professional translation service
- Use machine translation as reference only
For Teams and Organizations
Small team (1-5 people, basic translation needs):
- Combine Google Translate (for coverage) + Chat GPT Translate (for quality)
- Zero additional cost
- Owner creates brand terminology glossary
Growing team (5-20 people, regular translation work):
- Evaluate Runable if documentation automation is primary need
- Combine machine translation with occasional professional translator
- Implement translation memory for consistency
Large organization (50+ people, high translation volume):
- Implement Crowdin or Lokalise for workflow management
- Use multiple machine translation engines (Google, Deep L) with quality comparison
- Maintain professional translation team or service provider
- Establish translation standards and glossaries
- Train team on machine translation limitations
For Developers
MVP/Prototype phase:
- Use free Chat GPT Translate for quick localization
- Don't invest in infrastructure yet
- Gather user feedback on language quality
Growth phase (preparing for production):
- Evaluate Google Translate API for comprehensive language coverage
- Implement glossary management
- Set up translation QA process
Production phase (multiple languages, many users):
- Use Crowdin or Lokalise with Google Translate or Deep L
- Maintain professional translation relationships for critical languages
- Implement continuous localization pipeline
- Consider specialized models for domain-specific terminology
FAQ
What is Chat GPT Translate and how does it differ from Google Translate?
Chat GPT Translate is Open AI's standalone web translation service that prioritizes style customization and contextual accuracy. Unlike Google Translate's simple literal translation approach, Chat GPT Translate includes style presets like "more formal," "academic," and "business formal" that adapt the tone of translated text. Google Translate excels in ecosystem integration, language coverage (133 languages), and speed, making it ideal for casual use. Chat GPT Translate trades some convenience for better control over translation tone and register, particularly useful for brand-conscious marketing content and professional communication.
How does the accuracy of Chat GPT Translate compare to Google Translate?
For common language pairs like English-Spanish and English-French, both services deliver comparable accuracy (95%+). Chat GPT Translate shows marginal advantages for complex sentences and contextual understanding, particularly for Asian languages where the broader semantic knowledge of large language models provides benefits. Google Translate maintains advantage for rare languages and highly technical terminology due to specialized optimization. Testing specific language pairs is recommended before committing to either service for professional work.
Is Chat GPT Translate completely free to use?
Yes, Chat GPT Translate is currently free with no announced paid tier or usage limitations. This differs from Open AI's other paid services (Chat GPT Plus, API access). The sustainability of free access is uncertain—future versions may introduce premium features or monetization. For now, there are no costs to use the basic translation service, though this may change as the platform matures.
Which translation service should I use for business communication?
For business emails, proposals, and professional correspondence, Chat GPT Translate's style presets (especially "business formal") often produce more natural-sounding professional translations requiring less editing than Google Translate. However, for rapid translation of incoming emails from foreign clients or quick website reference, Google Translate's instant availability remains superior. For mission-critical business documents (contracts, formal proposals), professional human translation is still recommended regardless of machine tool choice.
Can I use these translation tools to translate an entire document or website?
Google Translate supports document upload (PDF, Word, Excel) and website translation through browser extension or direct URL input. Chat GPT Translate currently supports only text input, though image translation and document upload are planned features. For comprehensive document translation, Google Translate remains more capable. For website translation, Google Translate's browser extension provides instant translation of any website, functionality Chat GPT Translate hasn't yet replicated.
What languages do Chat GPT Translate and Google Translate support?
Google Translate supports 133 languages, providing comprehensive global coverage. Chat GPT Translate supports 50+ languages, covering all major languages (English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese, Japanese, Arabic, Hindi, Portuguese, Russian, Korean) and many regional languages. For rare, endangered, or regional languages, Google Translate offers superior coverage. For the most-spoken 50 languages representing 85%+ of global internet usage, both services provide adequate coverage.
Are there privacy concerns with using these translation services?
Both services retain translation data for service improvement purposes. Google Translate (enterprise version) offers data deletion guarantees and GDPR compliance. Chat GPT Translate's privacy documentation is less detailed, and translations are treated similarly to Chat GPT conversations with potential staff review. Neither service should be used for translating confidential information without verification of privacy terms. For highly sensitive content (medical, legal, financial), consult privacy documentation or use professional translation services with explicit confidentiality agreements.
Which alternative translation services offer the best quality?
Deep L consistently delivers the highest translation quality, particularly for European language pairs (German, French, Spanish, Dutch). Deep L's transformer-based neural machine translation approach produces more natural-sounding output than both Google and Chat GPT Translate. However, Deep L supports fewer languages (29), requires paid subscription for full features, and shows weaker performance on Asian languages. For European content translation and professional-grade quality, Deep L is worth the premium cost.
Can I integrate these translation services into my application or website?
Google Translate offers API access for developers through Google Cloud Console, starting at $15 per 1 million characters. Chat GPT Translate does not currently offer API access, though this is likely coming as Open AI expands its platform. For application developers needing translation integration, Google Translate API remains the primary option. Specialized platforms like Crowdin and Lokalise provide application-specific translation management and integrate with multiple machine translation engines.
What should I do if machine translation quality is insufficient for my needs?
For content where translation accuracy is critical (medical, legal, safety-critical, brand-defining marketing), supplement machine translation with professional human translation. Use machine translation as a first pass to save time, then have professional translators edit the output. This hybrid approach costs less than full professional translation while ensuring quality standards. Alternatively, evaluate specialized translation services, maintain comprehensive glossaries, and test translations with native speakers from your target market.
How can I improve the quality of translations I receive from these tools?
Provide clear, well-structured source text with proper grammar and punctuation. Avoid idioms, slang, and cultural references when possible. Include context about the translation purpose (formal vs. casual, technical vs. general audience). For Chat GPT Translate, explicitly select appropriate style presets. Maintain a glossary of key terminology and industry-specific terms. Always review machine translation output before publishing. For repetitive content, use translation memory tools to ensure consistency across documents.
Conclusion: Making Your Translation Tool Decision
The emergence of Chat GPT Translate doesn't mean Google Translate is obsolete—instead, it signals healthy competition and specialization in the translation tools market. Each service excels in different scenarios, and the best choice depends entirely on your specific needs and workflow.
Choose Google Translate if you prioritize:
- Instant availability and ecosystem integration
- Comprehensive language coverage (133 languages)
- Website and document translation capabilities
- Mobile app experience with camera features
- Established reliability with minimal learning curve
Choose Chat GPT Translate if you prioritize:
- Tone and style customization for brand-conscious content
- Natural-sounding translations for professional communication
- Free access without API cost concerns
- Context-aware translation for complex sentences
- Voice input for mobile translation
Choose specialized alternatives (Deep L, Crowdin, Lokalise) if you:
- Need European language translation quality
- Manage software localization across teams
- Have domain-specific translation requirements
- Can justify premium pricing for superior results
The translation landscape in 2025 is genuinely competitive and user-centric. Rather than a single dominant service, we're seeing emergence of complementary tools serving different needs. Many professional workflows now use multiple translation services strategically—Google Translate for quick reference and high-volume low-stakes content, Chat GPT Translate for tone-sensitive material, Deep L for European quality, and professional translators for mission-critical content.
The most important principle remains unchanged: machine translation is a tool, not a replacement for human judgment. For publishable content, especially in professional, legal, medical, or brand-critical contexts, human review is non-negotiable. Machine translation excels at handling volume and providing initial translations for editing—exactly where professional translator workflow focuses.
As both Google and Open AI continue advancing their translation capabilities, expect convergence around key features (style customization, document handling, API access) while differentiation focuses on language quality for specific pairs, ecosystem integration, and cost structures. The question "which translation tool is best?" will increasingly be answered with "it depends on your specific use case." That's actually excellent news for users, as competitive pressure drives continuous improvement and forces each platform to genuinely solve user problems rather than simply maintain market dominance.
Your decision framework should account for not just current capabilities, but also trajectory and future plans. Chat GPT Translate's planned features (document upload, browser extension, mobile app, API access) suggest rapid evolution toward feature parity with Google. When and if those features launch, the competitive dynamics may shift significantly. For now, running parallel experiments with both services costs nothing and provides data for optimized workflows.

Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT Translate introduces style customization (formal, academic, casual) that Google Translate lacks, particularly benefiting marketing and professional communication
- Google Translate maintains significant advantages in language coverage (133 vs 50+ languages), mobile app ecosystem, and integration with browser/Office products
- For accuracy, both services perform comparably on common language pairs (95%+), but ChatGPT Translate shows marginal improvements for complex Asian languages requiring contextual understanding
- ChatGPT Translate is currently free with no usage limits, while Google Translate API costs start at $15 per million characters, making ChatGPT competitive for individual and small team use
- DeepL offers superior quality alternative for European languages but supports fewer languages overall and requires paid subscription
- Professional human translation remains essential for mission-critical content (medical, legal, safety-critical), regardless of which machine tool is selected
- Runable's AI document automation complements traditional translation tools by automating entire documentation workflows across languages
- The future of translation tools is likely hybrid—combining multiple machine translation services with human editing for optimal cost and quality balance
- Mobile translation landscape favors Google due to app ecosystem and camera features, while desktop professional work increasingly uses specialized platforms like Crowdin or Lokalise
- Implementation strategy should account for language pair quality, ecosystem integration needs, and total cost of ownership including human review time
Related Articles
- Google Gemini vs OpenAI: Who's Winning the AI Race in 2025?
- ElevenLabs $330M ARR: How AI Voice Disrupted SaaS Growth Curves
- MSI AI Edge Mini PC: Ryzen AI Max+ 395 Powerhouse Guide & Alternatives
- Claude Cowork: Complete Guide to AI Agent Collaboration [2025]
- Google Gemini Powers Apple AI: Complete Partnership Analysis & Alternatives
- Go-to-Market Strategies for the AI Era: Complete Guide [2025]