Introduction: A Pivotal Moment in AI Infrastructure Investment
In a strategic move that reverberates through the entire artificial intelligence infrastructure ecosystem, Nvidia announced a $2 billion investment in Core Weave during early 2026, marking one of the most significant capital injections into the data center sector in recent memory. This investment represents far more than a simple financial transaction—it signals Nvidia's commitment to building a vertically integrated AI infrastructure ecosystem and Core Weave's emerging role as a critical partner in deploying AI computing resources at scale.
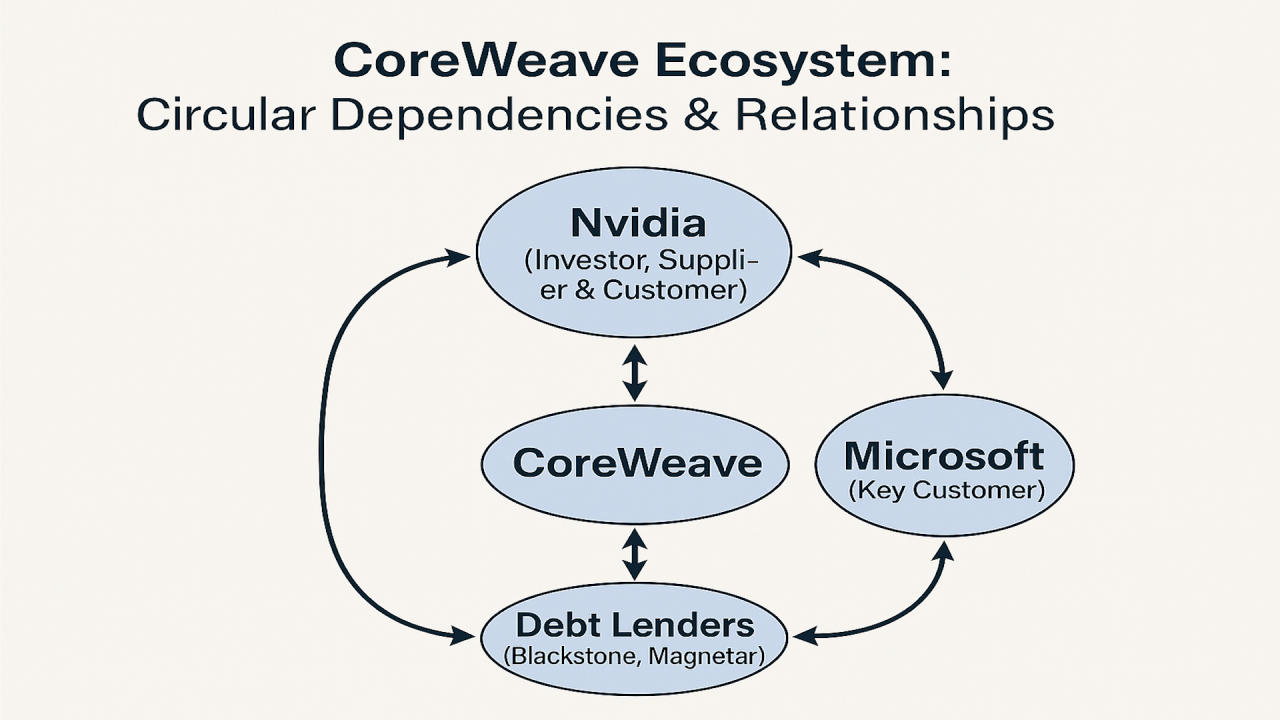
The timing of this investment carries substantial weight. Core Weave, a company that transformed from cryptocurrency mining infrastructure into an artificial intelligence data center provider, has faced increasing scrutiny regarding its debt obligations and business model sustainability. As of late 2025, the company carried approximately
Nvidia's investment acquisition of Class A shares at $87.20 per share provides both financial support and strategic alignment. Rather than viewing this as a traditional investment, market analysts have increasingly interpreted it as a partnership agreement that locks Core Weave into Nvidia's technology ecosystem while providing crucial capital for expansion. Core Weave's ambitious goal to deploy more than 5 gigawatts (5,000 megawatts) of AI computing capacity by 2030 has become achievable through this partnership, with Nvidia committing to assist in acquiring land and securing power supplies for new data center facilities.
This agreement reshapes the competitive landscape of AI infrastructure. The partnership extends beyond capital infusion into deep technological integration, with Core Weave committing to incorporate Nvidia's latest chip architectures, storage solutions, and CPU lines across its entire platform. Understanding the nuances of this deal—its financial implications, technological dimensions, competitive ramifications, and broader industry consequences—provides essential context for anyone seeking to understand the current state of AI infrastructure investment.
The broader context matters considerably. We're witnessing a period of unprecedented competition for AI computing resources. Companies like OpenAI, Meta, Microsoft, and Google have demonstrated insatiable appetite for computational capacity to train and deploy increasingly sophisticated language models and multimodal systems. This demand has created a supply-constrained market where data center operators can command premium pricing for GPU resources. Core Weave positioned itself to capitalize on this trend, but faced the classic challenge of rapid scaling: enormous capital requirements that exceed available venture funding.
The Financial Architecture of the Deal
Understanding the $2 Billion Capital Structure
What makes this investment strategically sophisticated is that Nvidia isn't simply providing cash to Core Weave for capital expenditures. Rather, it's demonstrating faith in Core Weave's execution capabilities while simultaneously ensuring that its own products—the GPUs, CPUs, storage systems, and software infrastructure that Core Weave deploys—generate recurring revenue. This creates what economists call a "complementary investment" scenario, where Nvidia's return depends not just on Core Weave's equity value appreciation but on the sustained deployment and utilization of Nvidia hardware.
The share purchase price of $87.20 reflects a valuation that was likely higher than Core Weave's previous fundraising rounds, validating the company's business model to other potential investors. This price point provides an anchor for future financing rounds and provides existing shareholders with exit optionality. For context, Core Weave completed its IPO in March 2025, and tracking the share price trajectory from IPO to this investment reveals investor sentiment evolution regarding data center infrastructure plays.
Debt Obligations and Financial Sustainability
The elephant in the room concerns Core Weave's $18.81 billion debt obligation. To contextualize this figure, it's helpful to calculate the debt-to-quarterly-revenue ratio: approximately 13.8x quarterly revenue, or roughly 55.2x annualized revenue (based on Q3 run-rate). This debt level would be catastrophic for most companies, but for a rapidly scaling infrastructure company, the metrics require deeper analysis.
Data center operators traditionally operate on lower margin economics than software companies. A typical data center achieves gross margins of 40-50%, and operating margins after capital depreciation, financing costs, and operational expenses of 15-25%. Core Weave's revenue growth trajectory suggests that if Q3 represented
Core Weave's CEO Michael Intrator has articulated a sophisticated defense of this debt model. Rather than viewing debt as a burden, he positions it as a feature of infrastructure scaling: companies can use their deployed GPU assets as collateral for debt financing, creating a virtuous cycle where deployed computing capacity generates revenue that services debt while simultaneously providing collateral for additional deployment. This model resembles how telecommunications companies financed network buildout in the 1990s or how renewable energy companies financed solar and wind farms in the 2010s.
The Nvidia investment provides debt service comfort. With Nvidia's backing, Core Weave gains access to favorable credit terms and additional financing capacity. Lenders view Nvidia partnership as significantly reducing execution risk—Nvidia has demonstrated commitment to ensuring Core Weave's success through capital injection and technological support.
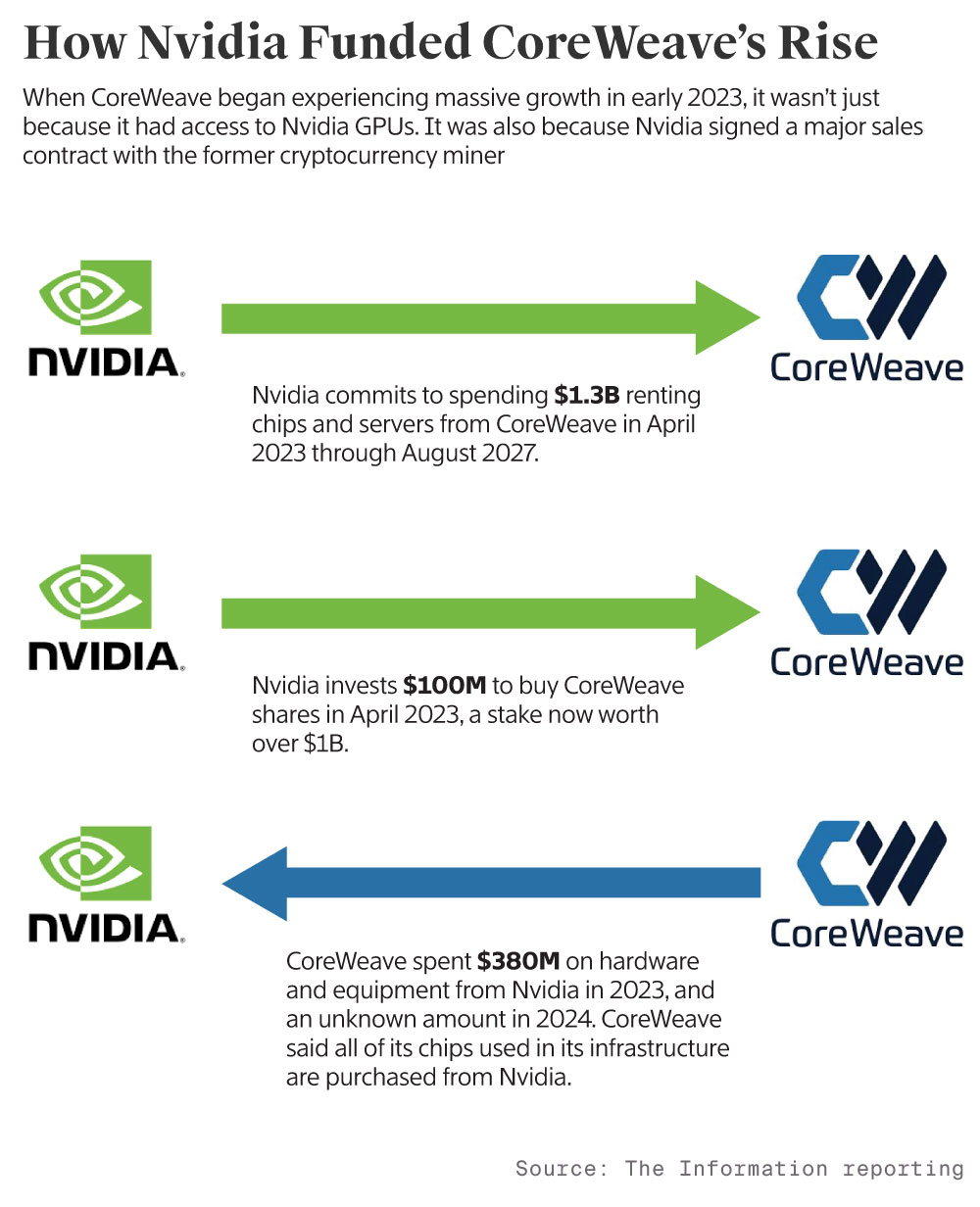
CoreWeave's expansion plan heavily relies on Nvidia GPU deployment, with power contracts and real estate acquisition also being critical components. (Estimated data)
The Technology Integration Strategy
Rubin Chip Architecture Adoption
At the heart of the partnership lies Nvidia's Rubin chip architecture, positioned as the successor to the current Blackwell architecture that dominates current AI data center deployments. The Rubin architecture represents the continuation of Nvidia's relentless pursuit of compute density and efficiency improvements. While detailed specifications for Rubin haven't been extensively disclosed at the time of this investment, historical trends suggest Rubin will offer improvements in tensor operations per watt, memory bandwidth, and multi-GPU scaling capabilities.
Core Weave's commitment to integrate Rubin across its platform represents a critical strategic choice. By standardizing on Nvidia's next-generation architecture, Core Weave ensures technology currency and customer satisfaction. AI research organizations and enterprises making multi-year commitments to training infrastructure want assurance that their chosen provider will maintain technological parity with competitors. Core Weave's willingness to deploy Rubin demonstrates this commitment.
The competitive implications matter. AMD and other GPU manufacturers have announced competing architectures, but Nvidia maintains architectural advantages in tensor operations, memory bandwidth optimization, and ecosystem maturity. Core Weave's exclusive focus on Nvidia (at least for GPU compute) simplifies its operational footprint while maximizing its bargaining power with Nvidia for support and favorable pricing.
Bluefield Storage Systems Integration
Beyond compute, Nvidia's Bluefield storage systems represent a critical piece of the puzzle. Modern AI workloads—particularly for large language model training—generate enormous I/O requirements. A model with hundreds of billions of parameters requires loading, caching, and manipulating massive datasets across multiple GPU clusters. Traditional storage architectures create bottlenecks that limit training efficiency.
Bluefield systems provide Smart NIC (Smart Network Interface Card) functionality that accelerates storage operations at the network level, removing CPU bottlenecks and improving throughput. Core Weave's integration of Bluefield across its platform enables it to deliver superior performance characteristics for storage-intensive workloads. This technological differentiation becomes crucial in competitive bidding situations where customers evaluate not just raw compute availability but sustained throughput for real-world training pipelines.
For Core Weave customers like OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft, Bluefield integration translates to reduced training time per model iteration, enabling faster experimentation cycles and quicker time-to-market for new model versions. In an era where AI capability leadership translates to competitive advantage, this acceleration matters enormously.
Vera CPU Architecture and System Completeness
Nvidia's introduction of the Vera CPU line completes the system architecture. Traditional x86 CPUs (from Intel and AMD) have historically served as the "management plane" in GPU clusters—orchestrating workloads, handling I/O, managing memory hierarchies, and running system software. Nvidia's decision to develop proprietary CPUs reflects strategic thinking: if Nvidia controls both compute (GPUs) and orchestration (CPUs), it can optimize the entire system stack for AI workloads.
Core Weave's adoption of Vera CPUs—rather than continuing with x86 alternatives—signals deep alignment with Nvidia's vision of fully integrated AI infrastructure. This technical standardization reduces complexity, improves system optimization, and further cements the Core Weave-Nvidia partnership. Customers deploying on Core Weave infrastructure increasingly rely on Nvidia-native tools and architectures end-to-end.
This vertical integration mirrors Apple's strategy of controlling silicon, firmware, and software. Just as Apple achieved performance and efficiency advantages by optimizing across the stack, Nvidia achieves AI infrastructure advantages by controlling compute, storage acceleration, CPU management, and increasingly, software frameworks and tools.
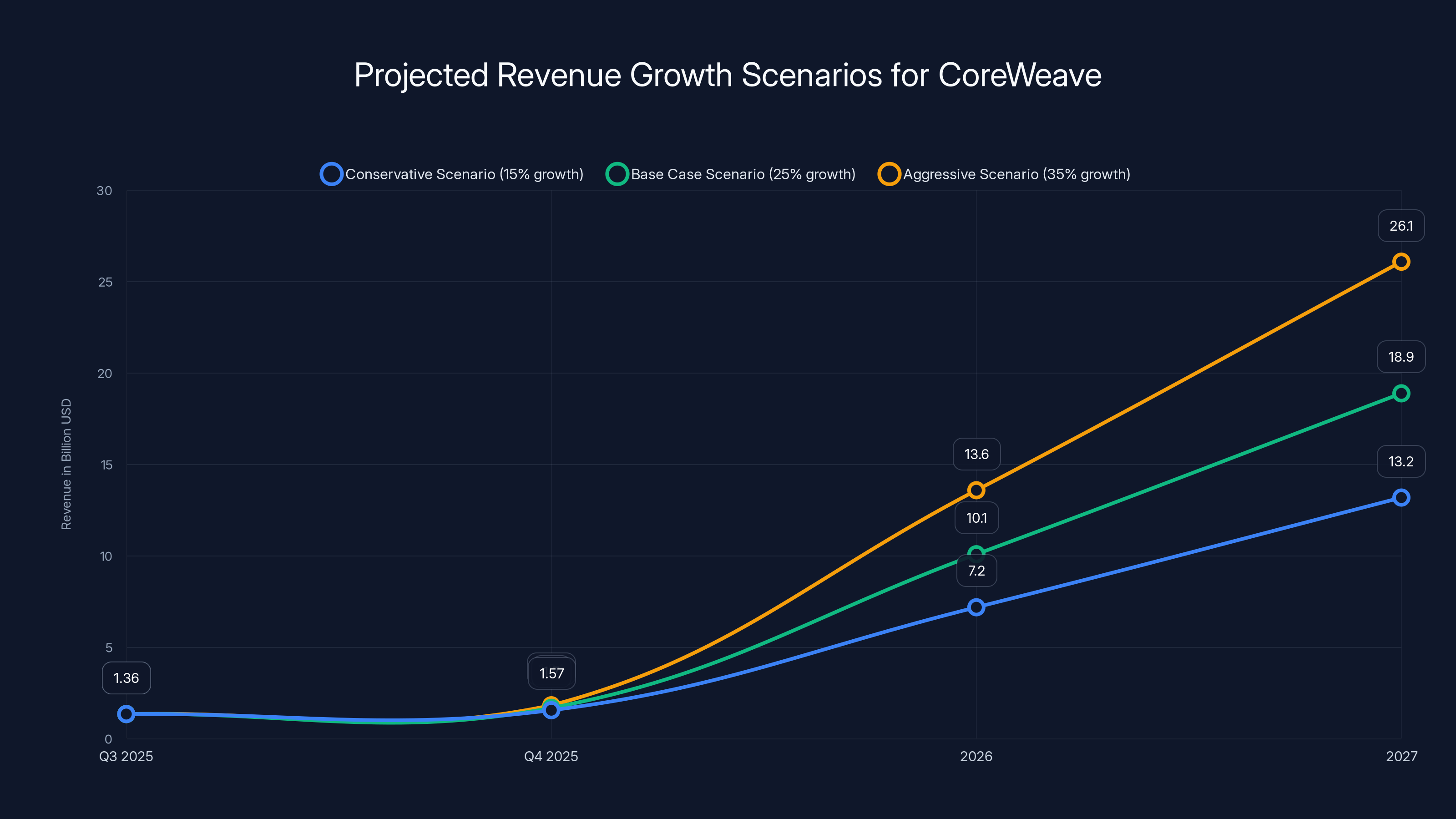
CoreWeave's revenue could reach $19 billion by 2027 in the base case scenario, achieving debt-to-revenue parity by late 2026. Estimated data based on growth assumptions.
Core Weave's Evolution and Business Model Transformation
From Crypto Mining to AI Infrastructure Provider
Core Weave's transformation from cryptocurrency mining infrastructure to AI data center provider represents one of the most successful business model pivots in recent technology history. During the cryptocurrency boom of 2017-2021, Core Weave operated GPU clusters optimized for mining operations—a commodity business with extremely tight margins and high operational complexity due to cooling requirements and electrical costs.
The transition to AI infrastructure proved prescient. Rather than chasing declining cryptocurrency profitability, Core Weave redeployed its engineering expertise and GPU inventory toward training and inference workloads. This pivot occurred precisely as AI researcher demand for computing resources exceeded available supply, creating a supply-constrained market where pricing could support healthier margins than mining ever provided.
Core Weave's competitive advantage in this transition stemmed from operational expertise in massive-scale GPU management, power delivery, and thermal management. These capabilities, developed during the mining era, directly transferred to AI workload optimization. The company understood how to pack GPUs densely, deliver adequate power and cooling, and manage the unique challenges of running thousands of GPUs in coordinated fashion—exactly what AI researchers required.
By 2025, Core Weave had established customer relationships with OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft—the three organizations most aggressively investing in frontier AI capability development. These relationships represent enormous recurring revenue commitments, providing the revenue visibility necessary to justify its debt structure.
Strategic Acquisition Strategy and Platform Expansion
Beyond its core data center operations, Core Weave has aggressively acquired complementary technology companies to build what might be characterized as a "platform" approach to AI infrastructure. In March 2025, Core Weave acquired Weights & Biases, an AI developer platform that provides experiment tracking, model versioning, and collaboration tools for ML teams. Shortly thereafter, it acquired Open Pipe, a reinforcement learning infrastructure company.
In October 2025, Core Weave announced acquisitions of Marimo (an open-source Jupyter notebook competitor) and Monolith (another AI infrastructure company). These acquisitions reflect Core Weave's strategic thinking: customers need not just compute infrastructure but entire software ecosystems to develop, train, optimize, and deploy models. By acquiring these companies, Core Weave can offer comprehensive solutions that reduce customer switching costs and increase their economic value.
Core Weave's acquisition strategy parallels Nvidia's own path to dominance. Nvidia initially competed as a GPU manufacturer, but increasingly invested in software frameworks (CUDA), development tools, and higher-level abstractions. Core Weave appears to be following a similar playbook—combine raw infrastructure with software tooling and platform services to create a comprehensive ecosystem that customers want to remain within.
OpenAI Partnership Expansion
Core Weave's recently expanded cloud partnership with OpenAI signals mutual confidence and dependency. OpenAI's computational requirements have grown exponentially as it trains larger models and serves increasingly diverse user bases. OpenAI's December 2024 announcement of cost reductions across its API pricing implied internal improvements in computational efficiency, yet paradoxically, the company continues expanding its compute footprint substantially.
OpenAI's willingness to expand partnership with Core Weave (rather than continuing exclusive reliance on Microsoft's Azure infrastructure) suggests that Core Weave offers unique capabilities or economics. Possible explanations include specialized infrastructure optimizations for OpenAI's particular workload characteristics, favorable pricing arrangements supported by Nvidia's investment, or geopolitical considerations (geographic redundancy outside Microsoft's ecosystem).
This partnership validates Core Weave's technical execution and customer satisfaction. Enterprise AI infrastructure relationships prove "sticky"—customers invest enormous effort in optimizing code and workflows for specific hardware configurations and software frameworks. If OpenAI expanded its Core Weave footprint in early 2025, it signals that Core Weave delivered the performance, reliability, and support quality necessary to attract additional workload volumes from an already demanding customer.
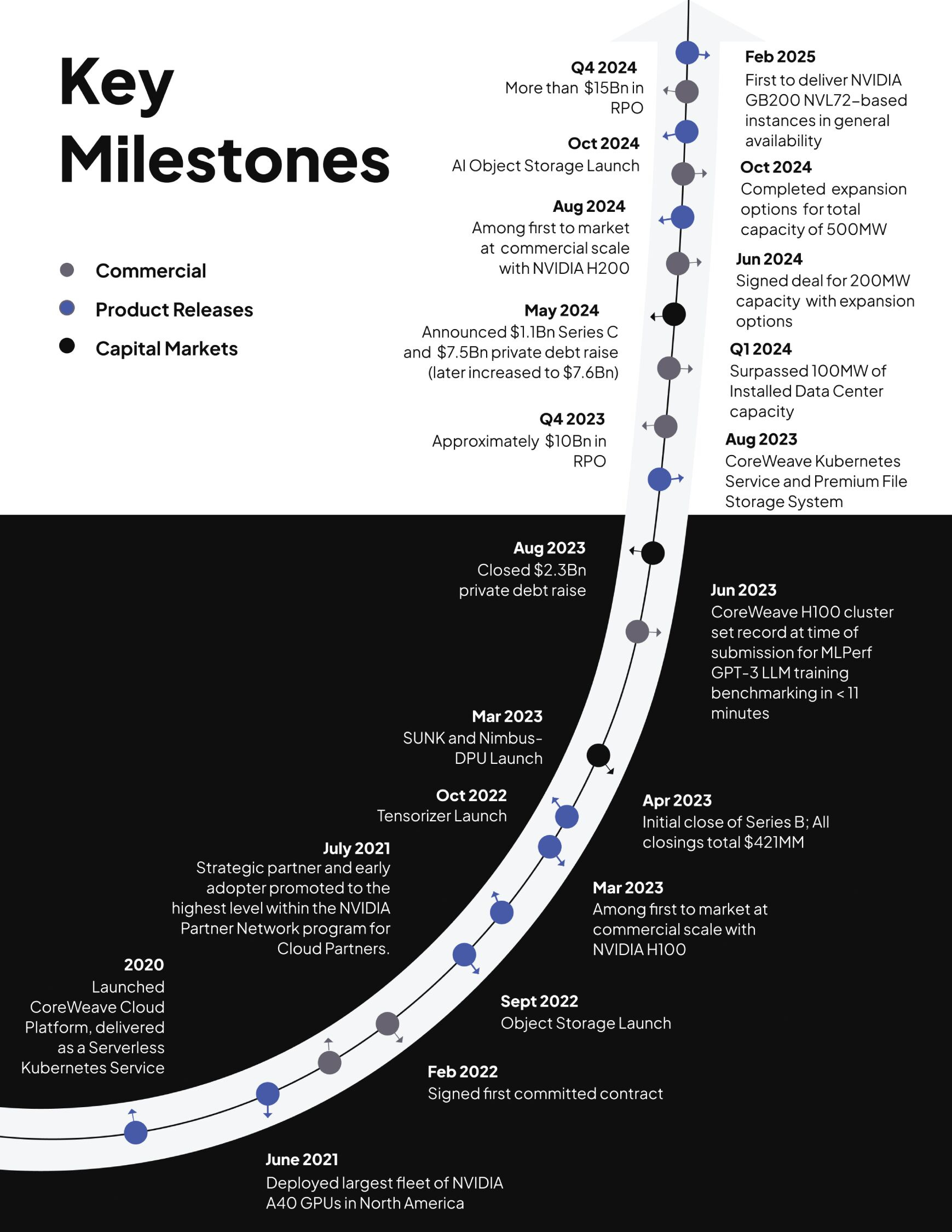
The 5 Gigawatt Expansion Plan: Technical and Logistical Dimensions
Scale and Capacity Context
The goal of deploying 5+ gigawatts of AI computing capacity by 2030 deserves grounding in concrete terms. One gigawatt equals 1,000 megawatts of continuous power supply. Five gigawatts represents approximately 5 million megawatts of annual energy consumption (assuming 8,760 hours of annual operation).
For context, this energy consumption rivals the total annual electricity consumption of many mid-sized countries. A single data center facility typically achieves 100-500 megawatts of capacity depending on design and customers served. Core Weave's plan therefore implies construction of 10-50 major data center facilities between 2025 and 2030—approximately 2-10 facilities per year depending on expansion curve acceleration.
This deployment rate vastly exceeds historical data center construction speeds. Traditional enterprise data center construction requires 18-36 months from site acquisition through operational deployment. Achieving Core Weave's goals requires compressed timelines, prefabricated modular designs, streamlined permitting processes, and substantial capital deployment. Nvidia's commitment to "help Core Weave buy land and power" addresses the two largest infrastructure constraints: real estate acquisition and power procurement agreements.
Power Infrastructure Requirements
Power represents the ultimate constraint on data center expansion. Unlike compute capacity, which Nvidia can manufacture, or real estate, which represents one-time acquisition costs, electrical infrastructure represents an ongoing operational commitment. Five gigawatts of continuous demand translates to approximately 44 terawatt-hours of annual energy consumption.
Core Weave's expansion therefore requires identifying and securing power sources adequate to support this scale. Options include grid connections to existing utility infrastructure, direct power purchase agreements with renewable energy operators (solar and wind farms), or natural gas generation partnerships. Each option carries different financial, environmental, and regulatory implications.
The most economically sustainable approach likely involves a portfolio strategy: leverage existing grid capacity in regions with favorable electricity pricing (particularly areas with abundant hydroelectric or other renewable capacity), simultaneously develop renewable energy partnerships to achieve corporate sustainability commitments, and potentially invest in or partner with power generation infrastructure directly.
Nvidia's support in this domain likely involves leveraging its existing relationships with utility companies and renewable energy operators. As the world's largest buyer of data center compute infrastructure, Nvidia has extensive experience negotiating power contracts and identifying geographically optimal deployment locations. This institutional knowledge proves invaluable for Core Weave's expansion planning.
Cooling and Thermal Management
Power delivery and cooling represent inseparable challenges in data center infrastructure. Modern GPUs convert electrical energy into computational output with approximately 80-85% efficiency; the remaining 15-20% dissipates as heat. A single GPU consuming 400 watts generates 60-80 watts of waste heat requiring active cooling.
At gigawatt scale, cooling becomes a dominant operational concern. Traditional air cooling (fans) remains the most economical approach but requires careful facility design. Liquid cooling offers superior heat transfer characteristics and lower overall facility power consumption (cooling requires less energy when liquid-cooled versus air-cooled), but increases complexity and capital costs.
Core Weave's expansion plan likely emphasizes increasingly sophisticated cooling architectures as it scales. Core Weave's heritage in GPU-intensive crypto mining operations provided expertise in thermal management that most traditional data center operators lack. This operational knowledge represents a competitive advantage in deploying high-density GPU clusters efficiently.
Advanced cooling technologies—including immersion cooling (submerging chips in dielectric liquids), spray cooling (misting systems that improve convective heat transfer), and hybrid air-liquid systems—offer potential for further efficiency gains. Core Weave's partnership with Nvidia provides access to architectural guidance on optimizing cooling for Rubin chips and other Nvidia systems.
Regulatory and Land Acquisition Strategy
Expanding data center footprint to five gigawatts requires navigating complex regulatory environments across multiple jurisdictions. Different regions impose varying environmental impact assessment requirements, power availability certifications, zoning compliance, and environmental sustainability mandates. A facility in California faces different regulatory constraints than facilities in Texas, Virginia, or international locations like the Netherlands or Singapore.
Nvidia's commitment to "help Core Weave buy land" likely involves leveraging its real estate partnerships and regulatory expertise. Nvidia has extensive experience identifying optimal data center locations that balance power availability, cooling water access, seismic stability, regulatory environment, and customer proximity. The company's expansion of its own data center operations and reference architectures provided foundational knowledge applicable to Core Weave's geography selection.
Core Weave's expansion timeline of five years until 2030 compresses what would normally be a 10-15 year buildout timeline. This compression requires pre-identifying and securing sites, negotiating power purchase agreements, and obtaining regulatory approvals in parallel rather than sequentially. Nvidia's support accelerates this process substantially.

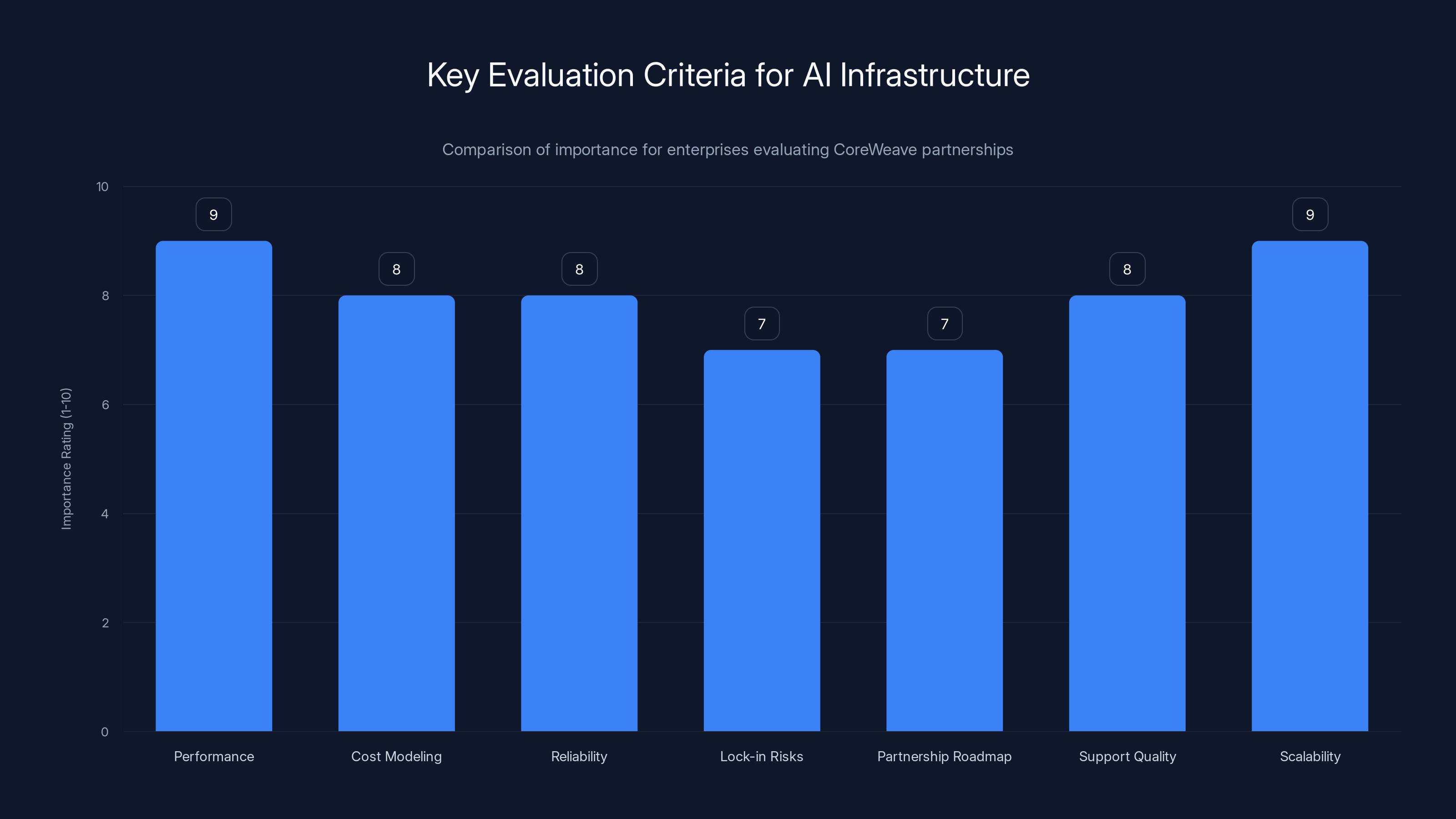
Performance and scalability are rated highest in importance for enterprises considering CoreWeave partnerships, indicating a strong focus on operational efficiency and future growth capabilities. (Estimated data)
AI Factories: The Partnership's Core Vision
Defining "AI Factories"
The term "AI factories" emerged prominently in the Nvidia-Core Weave partnership announcement, representing a conceptual evolution beyond traditional data centers. An AI factory represents an integrated facility optimized end-to-end for artificial intelligence workloads—from raw electrical input through compute nodes to final model output.
This differs meaningfully from traditional data centers that typically accommodate diverse workload types (web hosting, databases, gaming, storage, etc.). AI factories optimize for the specific characteristics of machine learning workloads: long-running training processes with high compute density, sophisticated multi-node communication patterns, specialized storage access patterns, and increasingly, hybrid compute requirements mixing different GPU types.
Nvidia and Core Weave's AI factory vision incorporates compute (GPUs and Vera CPUs), storage (Bluefield systems), networking (Nvidia HDR Infini Band), software frameworks (Nvidia CUDA and emerging AI software stacks), and operational orchestration. By standardizing on Nvidia technology throughout, the partnership enables optimizations that proprietary vendors operating within closed ecosystems cannot achieve.
Operational Architecture and Efficiency Gains
AI factories promise efficiency improvements over traditionally heterogeneous data center environments. When storage, compute, and networking components come from a single vendor ecosystem, integration becomes simpler and optimization opportunities expand. Rather than optimizing for generic workload patterns, AI factories optimize explicitly for GPU cluster communication, model training workloads, and inference serving.
Efficiency gains manifest in multiple dimensions:
- Network latency reduction: Nvidia's HDR Infini Band networking provides lower-latency node-to-node communication than Ethernet alternatives, enabling more efficient distributed training across hundreds or thousands of GPUs
- I/O throughput improvement: Bluefield storage acceleration systems reduce CPU bottlenecks and improve sustained data delivery rates
- Power efficiency: System-level optimization reduces power consumption for equivalent computational output
- Operational simplicity: Standardized architectures reduce management complexity and training requirements for operations teams
These efficiency gains translate directly to customer value. Training a model 10% faster on Core Weave infrastructure than a competitor's facility represents enormous value when multiplied across thousands of model training runs. A customer organization might complete model experimentation cycles 10-15% faster, accelerating time-to-market for production systems.
Reference Architecture Importance
Nvidia's commitment to "include AI software and architecture within Nvidia's reference architecture to sell to cloud businesses and enterprises" represents equally important value. Reference architectures serve as blueprints that other organizations can implement. When Core Weave's AI factory design becomes part of Nvidia's official reference architecture, it achieves validation and visibility that multiplies its influence.
Enterprise data center architects and cloud infrastructure providers consult Nvidia's reference architectures as authoritative guidance when planning infrastructure investments. Inclusion of Core Weave's approach in these reference architectures implicitly recommends Core Weave as a deployment partner. This effectively gives Core Weave brand visibility and credibility exceeding what Core Weave could achieve through direct marketing.
For enterprises considering outsourced AI infrastructure, the reference architecture provides confidence that they're adopting industry-standard approaches rather than custom bespoke solutions. This reduces perceived risk and accelerates purchasing decisions.

Competitive Implications and Market Positioning
Nvidia's Vertical Integration Strategy
The Core Weave investment represents the latest step in Nvidia's long-term vertical integration strategy. Nvidia's evolution from GPU manufacturer toward software and platform company occurred gradually over decades—from CUDA programming framework through cuDNN (deep learning library) through TensorRT (inference optimization) through RAPIDS (data processing framework).
The Core Weave partnership accelerates this vertical integration toward comprehensive infrastructure solutions. Rather than Nvidia simply selling GPUs to data center operators, the company now partners deeply with operators to shape their entire infrastructure architecture. This creates multiple revenue streams: GPU sales, software licensing, and increasingly, infrastructure consultation and optimization services.
This strategy mirrors Intel's decades-long approach. Intel didn't simply sell processors; it shaped entire server architectures through reference designs, software optimization, and ecosystem partnerships. Nvidia appears to be applying similar thinking to AI infrastructure. By controlling the reference architecture and partnering closely with major infrastructure providers, Nvidia influences purchasing decisions and standards-setting across the entire ecosystem.
Implications for Competing Infrastructure Providers
The Core Weave-Nvidia partnership creates strategic challenges for competing data center operators. Alternative providers (like Lambda Labs, Crusoe Energy, or others) cannot offer Core Weave's advantage of direct partnership with the world's dominant GPU manufacturer. Competing providers must differentiate through superior operational execution, more favorable pricing, specialized workload optimization, or geographic advantages.
Moreover, Nvidia's investment signals market confidence that Core Weave will remain a viable long-term partner. This makes Core Weave's competitive position more defensible. Customers who might have hesitated choosing Core Weave due to concerns about financial sustainability now face a more confident competitive landscape.
Core Weave's competitors must respond to this competitive dynamic. Some may accelerate diversification into AMD or other GPU architectures. Others may pursue niche specialization (e.g., inference-specific infrastructure, edge computing, specific geographic regions). The competitive intensity in AI infrastructure markets is rising substantially.
AMD and Alternative GPU Ecosystems
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) represents the primary viable alternative to Nvidia in the GPU ecosystem. AMD's MI300 series and upcoming architectures offer competitive performance characteristics at potentially lower total cost of ownership. Some data center operators and customers have expressed interest in AMD alternatives to reduce Nvidia dependency and improve negotiating leverage.
However, AMD faces substantial disadvantages in software ecosystem maturity, developer tool sophistication, and established partnerships like Core Weave-Nvidia. AMD's software stack, while improving, lacks the maturity of Nvidia's CUDA ecosystem. Developers who invested years building expertise in CUDA-based workflows face substantial friction switching to AMD's ROCm alternatives.
Core Weave's exclusive focus on Nvidia architectures potentially forecloses opportunities for AMD to gain traction in the data center market. If Core Weave becomes the preferred infrastructure provider for AI workloads (as Nvidia's investment suggests), AMD would struggle to reach the customer base developing on Core Weave infrastructure.

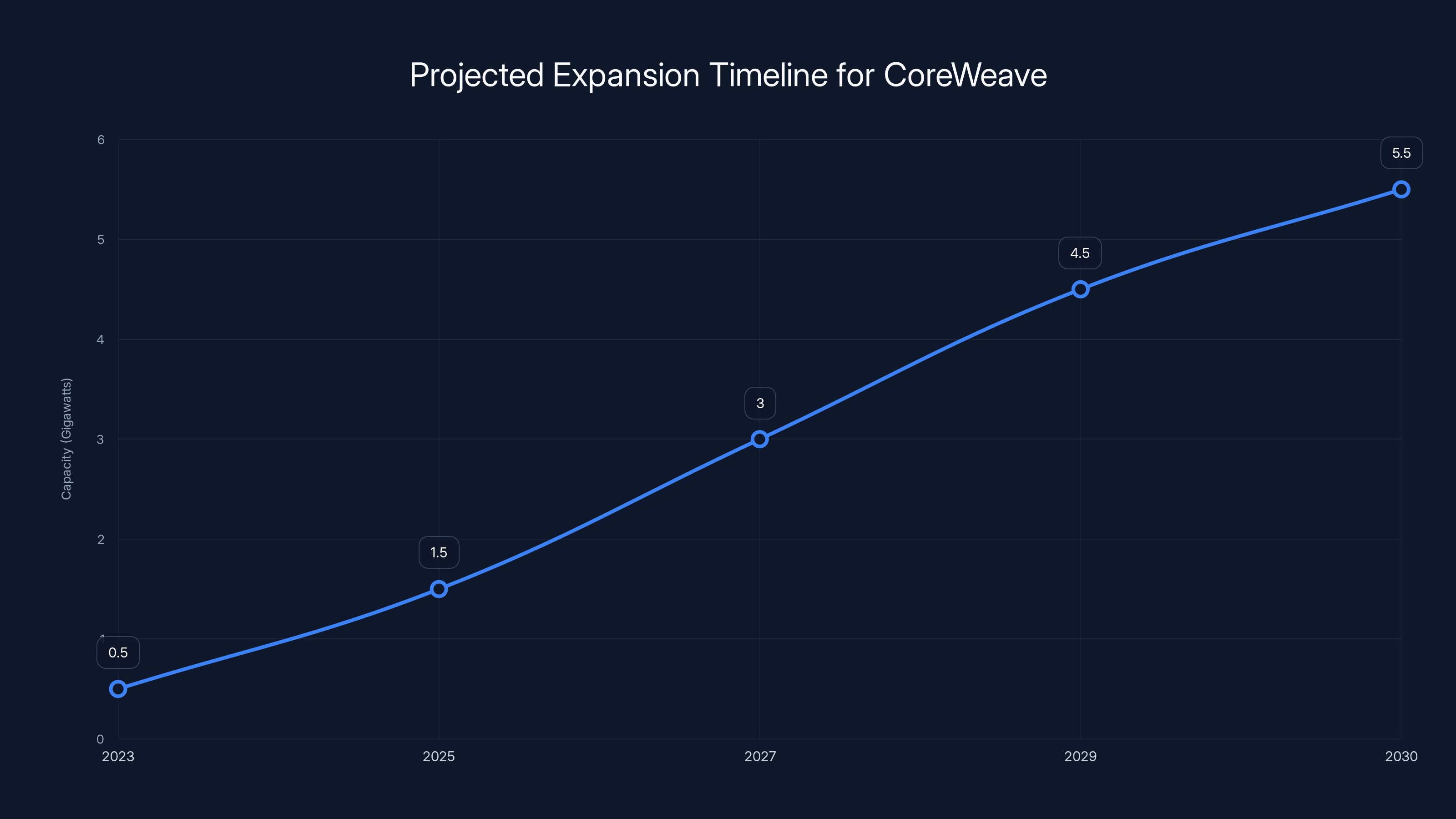
CoreWeave aims to expand its data center capacity to over 5 gigawatts by 2030. This ambitious timeline faces execution risks such as delays in power contracts and regulatory changes. Estimated data.
Customer Impact and Value Delivery
Benefits for Hyperscale AI Companies
Core Weave's major customers—OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft—benefit substantially from the Nvidia investment and partnership. These organizations have unprecedented computational demands for training frontier models. OpenAI, for example, likely requires tens of thousands of GPUs deployed simultaneously to train its largest language models. Even fractional improvements in infrastructure efficiency or reliability cascade to enormous cost and time savings.
The Nvidia partnership provides several concrete benefits. First, Core Weave gains access to Nvidia's latest hardware and architectural guidance, ensuring customers like OpenAI receive leading-edge infrastructure for their most demanding workloads. Second, Nvidia's involvement implicitly guarantees access to priority GPU supply chains—Nvidia can allocate GPU inventory to ensure Core Weave's customer commitments are fulfilled. Third, the Nvidia partnership provides technical support resources that Core Weave alone might lack.
For hyperscale companies, infrastructure reliability and performance predictability matters enormously. A single hardware failure in a 10,000-GPU training cluster causes the entire distributed training to restart from the last checkpoint. Nicer infrastructure with higher reliability translates directly to improved training efficiency and reduced compute waste. Nvidia's partnership likely improves Core Weave's reliability characteristics.
Enterprise and Mid-Market Accessibility
Beyond hyperscale customers, Core Weave's expansion benefits enterprise organizations that lack sufficient in-house AI infrastructure expertise or capital to build internal data centers. The reference architecture approach means enterprises can outsource AI infrastructure to Core Weave with confidence they're adopting industry-standard approaches.
For a mid-market company developing enterprise AI applications, outsourcing to Core Weave eliminates the need to hire specialized data center engineers, negotiate GPU supplier relationships, or invest hundreds of millions in facility construction. Instead, the company can focus its engineering resources on model development and application integration while relying on Core Weave for underlying infrastructure.
Core Weave's platform acquisitions (Weights & Biases, Marimo, etc.) amplify this value proposition. Enterprises no longer source individual point solutions but instead access integrated platform where compute infrastructure, development tools, collaboration platforms, and deployment frameworks come pre-integrated.
Cost and Performance Trade-offs
Core Weave's pricing strategy versus competitors remains a critical variable. Nvidia's investment might suggest willingness to subsidize Core Weave pricing to build market share, or conversely, Core Weave might maintain premium pricing due to superior technology and customer relationships. Industry observers should monitor pricing announcements carefully.
Performance advantages from specialized AI infrastructure justify some price premium. If Core Weave's AI factories deliver 10-15% superior training throughput compared to competitor infrastructure, customers can justify 10-15% price premium based purely on training efficiency. Additional value from platform integration (development tools, storage, software services) further justifies pricing.

Alternative Infrastructure Solutions and Competitive Options
Internal Data Center Development
Major technology companies including Meta, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon operate substantial internal data center infrastructure. These companies possess the scale, engineering expertise, and capital to build internal AI factories that rival or exceed Core Weave's capabilities.
However, internal development carries significant tradeoffs. Building data center infrastructure requires core competencies different from software development. Capital requirements to achieve Core Weave's scale exceed billions of dollars annually. For most organizations, partnering with Core Weave proves more capital-efficient than internal development.
Moreover, specialized providers like Core Weave achieve higher utilization rates than internal facilities. A company might size internal infrastructure for peak demand but experience substantial idle capacity during demand troughs. Outsourced infrastructure providers smooth demand across multiple customers, improving utilization. This translates to lower per-unit costs at scale.
Cloud Platform Infrastructure (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure)
Traditional cloud platforms offer generalized compute infrastructure including GPU options. AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and others provide managed GPU services that require minimal customer infrastructure development effort. Customers can launch GPU instances on-demand without capital expenditure or operational burden.
Cloud platforms offer substantial convenience advantages—no upfront capital, automatic scaling, integrated billing, and mature support ecosystems. However, cloud GPU pricing typically exceeds specialized providers' pricing for sustained workloads. A customer running training continuously for months might find specialized Core Weave infrastructure significantly more economical.
Additionally, cloud platforms optimize for diversity of workloads. Generalized infrastructure serves web applications, databases, and analytical workloads in addition to AI compute. Core Weave optimizes exclusively for AI workloads, potentially achieving superior performance at the cost of specialization.
Alternative Specialized Providers
Beyond hyperscale cloud, several specialized AI infrastructure providers compete for customer workloads:
- Lambda Labs: Offers GPU cloud services with human-friendly interfaces and data science-focused tooling
- Crusoe Energy: Emphasizes energy efficiency through innovative cooling and power management
- Paperspace: Provides managed notebooks and GPU compute for ML practitioners
- Vast.ai: Operates a marketplace connecting GPU supply with demand
These alternatives differentiate through specialized focus areas—some emphasize user experience, others emphasize cost, some emphasize energy efficiency. Collectively, they provide options for customers seeking alternatives to Core Weave or cloud platforms.
However, none of these alternatives have achieved Core Weave's combination of scale (5GW expansion target), enterprise customer relationships (OpenAI, Meta, Microsoft), or strategic partnership with dominant GPU manufacturer (Nvidia). Core Weave's competitive position strengthens substantially due to the Nvidia investment.
For teams evaluating AI infrastructure providers, platforms like Runable offer complementary automation and orchestration capabilities that work alongside infrastructure services. Runable's AI-powered workflow automation tools help teams optimize their ML pipelines and automate repetitive infrastructure management tasks, reducing the operational burden of managing compute resources at scale.

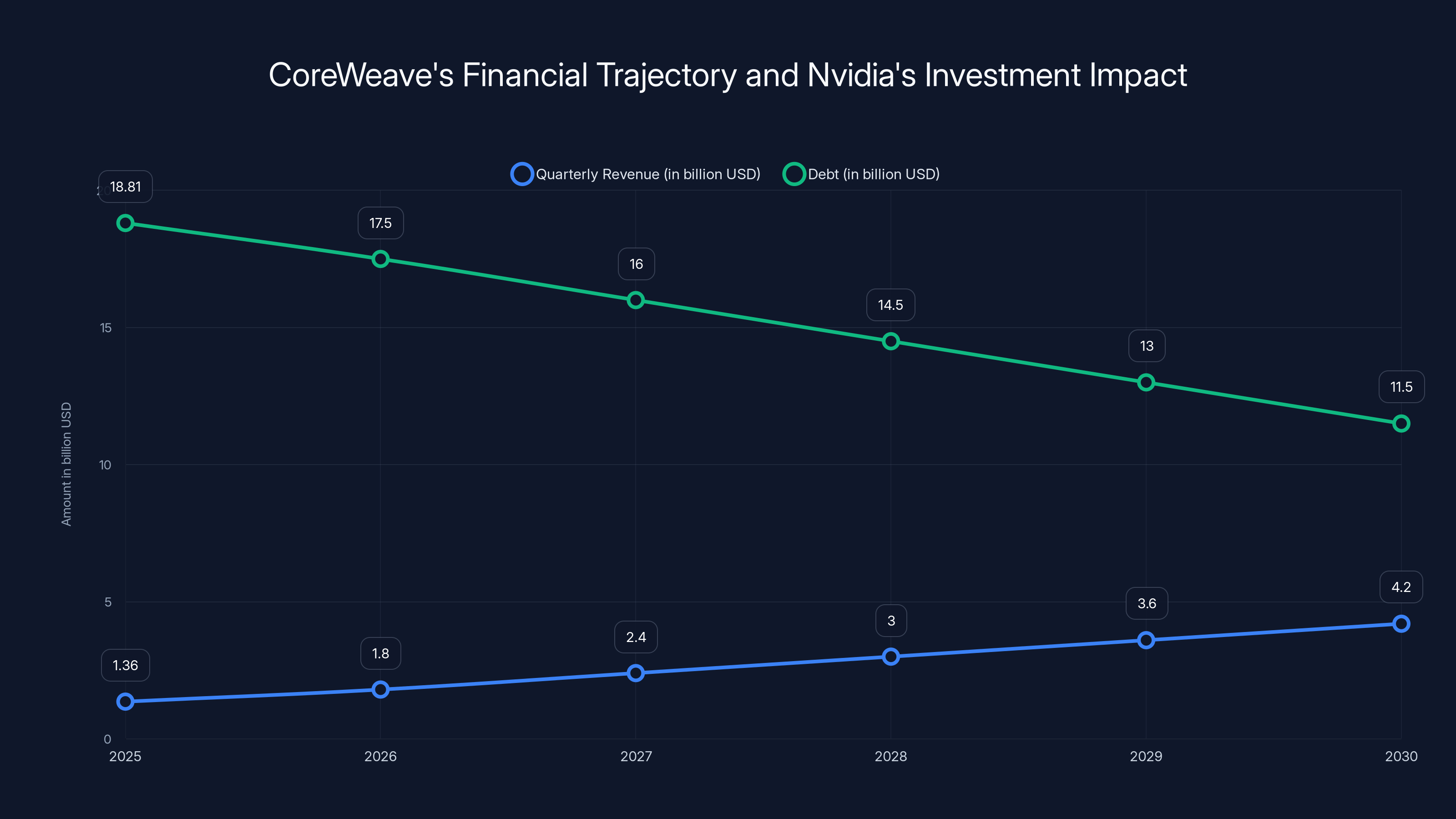
Nvidia's $2 billion investment in CoreWeave is projected to support significant revenue growth while aiding in debt reduction by 2030. Estimated data.
Financial Projections and Growth Scenarios
Revenue Trajectory Analysis
Based on Core Weave's reported Q3 2025 revenue of $1.36 billion, we can project forward under various growth scenarios. Assuming linear growth acceleration:
- Conservative scenario (15% quarterly growth): Q4 2025 7.2B → 2027 $13.2B
- Base case scenario (25% quarterly growth): Q4 2025 10.1B → 2027 $18.9B
- Aggressive scenario (35% quarterly growth): Q4 2025 13.6B → 2027 $26.1B
The base case scenario implies annualized revenue approaching
These projections assume sustained demand for AI infrastructure—a reasonable assumption given enterprise acceleration of AI deployment, but not guaranteed. Economic recession or slowdown in AI model training spending could moderate growth significantly.
Profitability and Path to Cash Flow Positivity
Data center businesses face substantial capital intensity but eventually achieve strong profitability. Core Weave's path to sustained profitability depends on achieving operational efficiency as it scales. Historically, data center operators achieve 20-30% operating margins once infrastructure fully depreciates and utilization reaches 80-90%+.
Assuming Core Weave achieves
The transition from current losses (necessary to fund growth) to sustained profitability requires approximately 2-3 additional years beyond 2027. This timeline aligns with industry-standard expectations for infrastructure scaling. The Nvidia investment provides confidence that Core Weave can reach this profitability milestone without additional distress financing.
EBITDA and Capital Return Analysis
Investors in data center infrastructure focus heavily on EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization) as a proxy for cash generation capability. Data center depreciation is substantial due to capital intensity, so operating profit underestimates cash generation.
Assuming Core Weave achieves
EBITDA generation at this level enables debt service of $18.81 billion over 2-3 years, providing clear path to financial sustainability. The Nvidia investment essentially purchases optionality to reach profitability without additional distress financing or dilutive equity raises.

Strategic Timing and Market Conditions
AI Compute Demand Dynamics
The timing of Nvidia's Core Weave investment reflects confluence of multiple market factors. AI model scaling has followed a clear empirical pattern for over a decade: models trained on 10x more compute achieve measurably superior capabilities. This relationship—scaling laws—continues driving demand for ever-larger compute footprints.
Competing AI companies (OpenAI versus Anthropic versus Google DeepMind) engage in implicit competition for compute resources. Whoever commands largest compute footprints can train larger models, potentially achieving superior capabilities faster. This competitive dynamic drives insatiable demand for GPU infrastructure.
Simultaneously, GPU supply has constrained due to Nvidia's manufacturing capacity limits. While Nvidia steadily increases production, demand growth exceeds supply growth, creating premium pricing for available GPU capacity. Core Weave benefits from this supply-constrained market dynamic.
Geopolitical Dimensions
Geopolitical considerations add another layer. U.S. export controls increasingly restrict sales of advanced GPUs to China and other entities perceived as competitive threats. This creates opportunity for non-U.S.-linked companies like Core Weave to serve non-U.S. customers who lack access to Nvidia GPUs through traditional channels.
However, Core Weave remains U.S.-based and Nvidia-dependent, limiting its ability to serve customers under export restrictions. Other data center operators based in allied nations might capture this market segment.
Conversely, Core Weave's U.S. basing provides value to U.S. government agencies and national security-conscious enterprises that require data center infrastructure within U.S. jurisdiction with trusted operators. Recent U.S. government initiatives to build sovereign AI capability might direct funding toward providers like Core Weave.
Cycle and Sentiment Trends
The AI enthusiasm cycle appears in mid-to-late innings of growth acceleration. While AI capabilities continue improving and use cases expanding, the media narrative has shifted from "AI hype" toward "AI deployment reality." Enterprise organizations increasingly view AI infrastructure investment as a necessary competitive capability rather than optional technology experimentation.
This maturation of sentiment supports sustained infrastructure investment. Companies that previously viewed GPU spending as optional experimentation now recognize it as strategic capital allocation. Core Weave's expansion plan aligns with this shift from experimentation to sustained deployment.

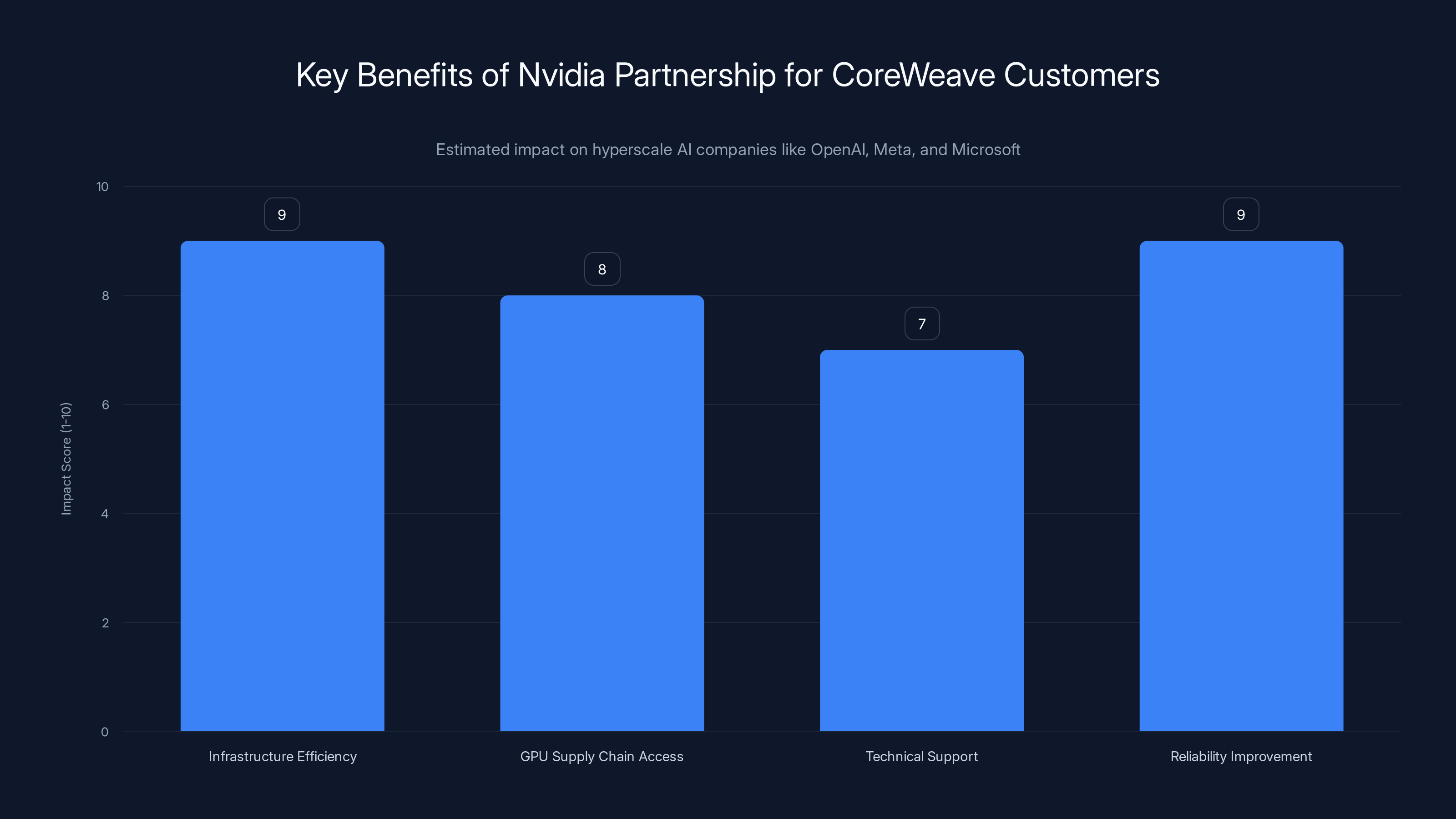
The Nvidia partnership significantly enhances CoreWeave's offerings, particularly in infrastructure efficiency and reliability, crucial for hyperscale AI companies. (Estimated data)
Risks and Challenges
Execution Risk and Timelines
Core Weave's ambitious expansion to 5+ gigawatts by 2030 faces execution risk. Deploying data center capacity at this scale requires flawless coordination of real estate acquisition, permitting, power infrastructure development, equipment procurement, and construction. Delays in any component cascade through the timeline.
For example, a six-month delay in securing power contracts for planned facilities could delay the entire expansion timeline proportionally. Regulatory changes could similarly impact expansion plans. The five-year timeline provides limited slack for addressing unexpected challenges.
Historically, large infrastructure projects experience delays and cost overruns. Core Weave's heritage as a relatively young company (compared to established data center operators like Equinix or Digital Realty) means it has less infrastructure deployment experience. This increases execution risk.
Technology Obsolescence and Architecture Risk
Core Weave's exclusive focus on Nvidia architectures creates technology risk. If AMD or other competitors achieve superior price-performance ratios, Core Weave customers might demand multi-architecture support. Core Weave's current commitments to Nvidia would limit responsiveness to this shift.
Moreover, if next-generation chip architectures move away from GPUs toward specialized AI processors (custom ASICs or neuromorphic processors), Core Weave's GPU-centric infrastructure might become stranded assets. While current AI roadmaps remain GPU-centric, long-term certainty cannot be guaranteed.
The partnership mitigates some of this risk—Nvidia influences AI architecture evolution through its research, partnerships, and product development. Core Weave's alignment with Nvidia provides some assurance that deployed infrastructure won't become obsolete. However, this risk remains non-trivial.
Market Demand Variability
AI compute demand might not grow as robustly as assumed. If frontier AI model scaling slows (e.g., due to reaching performance plateaus requiring new algorithmic innovations rather than scale), GPU demand might decelerate accordingly. Additionally, efficiency improvements in model training might require fewer GPUs for equivalent capability, reducing total addressable market size.
Conversely, if new AI applications emerge that require even greater compute (e.g., real-time video generation at scale), demand could exceed Core Weave's supply projections. The expansion plan was designed for forecasted demand, not worst-case scenarios.
Debt Service Vulnerability
While Core Weave's revenue growth trajectory supports debt service, vulnerability remains. Unexpected revenue deceleration (due to competitive pressure, economic recession, or technological disruption) would create debt service challenges. The company carries substantial leverage; profitability disruption would quickly threaten financial viability.
Nvidia's $2 billion investment provides comfort but doesn't guarantee unlimited support. If Core Weave continued underperforming, Nvidia would eventually face choice between continued support (potentially losing money) or allowing Core Weave to encounter distress.

Industry Implications and Future Outlook
Data Center Infrastructure Consolidation
The Core Weave-Nvidia partnership accelerates consolidation in data center infrastructure. Unlike cloud computing which consolidated toward a handful of hyperscalers, AI infrastructure might consolidate toward smaller number of specialized providers with unique partnerships and capabilities. Core Weave's Nvidia partnership creates competitive advantages that competitors cannot easily replicate.
We might expect increased M&A activity among smaller data center providers seeking scale, as well as potential exits of providers unable to compete with Core Weave's advantages. This consolidation improves efficiency but reduces competition and customer choice.
Software Stack Integration
Traditionally, infrastructure providers and software companies maintained clear boundaries. This separation is increasingly blurring. Core Weave's acquisition of Weights & Biases and other software companies reflects recognition that customer value increasingly comes from integrated stacks rather than point solutions.
Expect similar integration trends across the industry. Infrastructure providers will increasingly acquire or partner with software companies. Software companies will vertically integrate into infrastructure to ensure optimal performance. This blurring benefits customers who value integration but increases dependency on single providers.
Standard-Setting and Ecosystem Architecture
Nvidia and Core Weave's joint commitment to develop AI factories that become reference architectures suggests intentional standard-setting. When infrastructure providers and GPU manufacturers collaborate to establish standard architectures, they effectively shape entire ecosystem development.
This standard-setting authority carries both positive and negative implications. Standardization reduces integration complexity and improves compatibility. However, it also concentrates power and potentially forecloses architectural alternatives. Companies investing in non-standard approaches find themselves increasingly isolated.
Global Infrastructure Decentralization
Currently, AI compute infrastructure remains concentrated in a handful of geographic regions (U.S., China, EU) and limited number of providers. Core Weave's global expansion (implied by the gigawatt-scale goals) suggests potential decentralization of AI infrastructure globally.
Decentralization offers benefits—reduced latency for regional customers, improved disaster recovery, regulatory compliance with data localization requirements. However, it increases operational complexity and reduces the economies of scale that centralized facilities achieve.
Practical Implementation Guidance for Stakeholders
For Enterprises Evaluating AI Infrastructure
Enterprises considering Core Weave partnerships should evaluate multiple dimensions:
- Performance characteristics: Request benchmarks for your specific workload types (training, inference, data processing)
- Cost modeling: Build comprehensive total cost of ownership models comparing Core Weave versus alternatives
- Reliability commitments: Evaluate service level agreements, redundancy provisions, and disaster recovery capabilities
- Lock-in risks: Understand contractual terms and switching costs if relationship doesn't meet expectations
- Partnership roadmap: Understand Core Weave's product evolution and how Nvidia partnership influences your roadmap
- Support quality: Evaluate support team expertise, responsiveness, and track record with similar scale workloads
- Scalability: Confirm infrastructure can scale with your growth requirements without major re-architecture
Enterprises should negotiate terms carefully, particularly around pricing, capacity commitments, and exit provisions. Core Weave's growing confidence (enabled by Nvidia investment) might make pricing more rigid, but new customers should attempt to negotiate favorable terms.
For Infrastructure Operators Competing with Core Weave
Competitors face strategic choices:
- Specialize: Target specific workload types or geographies where Core Weave's general-purpose approach creates opportunities
- Diversify: Avoid exclusive dependence on single GPU architecture—offer multi-architecture options
- Partner: Develop partnerships with alternative GPU manufacturers (AMD) or software companies
- Optimize: Focus on superior operational execution, reliability, and customer support
- Niche down: Target underserved markets (edge computing, inference-specific, specific geographies)
- Integrate software: Acquire or partner with software companies to improve customer stickiness
Competing directly with Core Weave on general-purpose AI infrastructure proves increasingly difficult. Competitors must differentiate substantially or risk margin pressure and market share loss.
For GPU and Software Vendors
Nvidia's Core Weave investment signals its vertical integration intentions. Other vendors should expect Nvidia to increasingly develop partnerships with infrastructure providers, potentially creating preferred partner relationships. Vendors not aligned with Nvidia or other GPU manufacturers should seek partnerships to ensure representation in reference architectures and customer recommendations.
Software vendors should evaluate whether vertical integration with infrastructure providers benefits their market position or threatens their independence. Early partnerships with Core Weave might improve market access but could create dependency on Core Weave's success.

Conclusion: The Nvidia-Core Weave Partnership as Infrastructure Inflection Point
The $2 billion Nvidia investment in Core Weave represents far more than a financial transaction—it signals intentional reshaping of AI infrastructure competitive dynamics. By committing capital, providing technological support, and collaborating on reference architectures, Nvidia effectively endorses Core Weave as its preferred infrastructure partner while simultaneously deepening its own vertical integration into the infrastructure layer.
Core Weave's transformation from cryptocurrency mining company to AI infrastructure powerhouse demonstrates remarkable adaptation and execution. The company seized opportunity in a supply-constrained market, built customer relationships with the world's most demanding AI organizations, and positioned itself as essential infrastructure provider. The Nvidia partnership validates this positioning and provides capital necessary to execute ambitious expansion plans.
The partnership creates a compelling value proposition for major AI organizations. Core Weave infrastructure optimized end-to-end for AI workloads, backed by Nvidia's technological roadmap and support, offers meaningful advantages over generalized cloud infrastructure or custom internal development. Organizations like OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft gain not just compute resources but integrated technology partnership supporting their AI capability development.
However, the partnership simultaneously increases concentration of infrastructure power. Core Weave's dominant position backed by Nvidia's heft creates meaningful barriers for competitors. The AI infrastructure landscape might consolidate toward fewer large players, reducing competition and customer choice while improving standardization and efficiency.
For enterprises, the Core Weave-Nvidia partnership provides confidence that outsourced AI infrastructure represents viable path. The partnership eliminates many risks that normally accompany reliance on emerging infrastructure providers. Customers can access leading-edge AI compute infrastructure without requiring massive internal capital investment or infrastructure expertise.
For competitors, the partnership presents substantial strategic challenges. Differentiating against Core Weave-Nvidia combination requires either specialization, superior execution, or partnership with alternative technology providers. Direct head-to-head competition on general-purpose AI infrastructure proves increasingly difficult.
Looking forward, the AI infrastructure market will likely experience rapid consolidation, standardization around Nvidia-influenced architectures, and continued vertical integration. These trends benefit large, well-capitalized operators with strong customer relationships and improving operations. They create challenges for smaller, specialized providers lacking scale or strategic partnerships.
The broader implication suggests that AI infrastructure—like cloud infrastructure before it—will become increasingly commoditized and consolidated. A small number of providers will dominate, offering specialized AI infrastructure optimized for specific workload types. Companies without scale or unique differentiation will struggle to compete.
Ultimately, the Nvidia-Core Weave partnership represents maturation of AI infrastructure from experimental startup business toward serious enterprise-grade infrastructure critical to global AI capability development. The partnership provides all stakeholders—Core Weave customers, Nvidia shareholders, competing infrastructure providers—clarity about the market's direction and the competitive dynamics that will shape infrastructure evolution in the 2026-2030 period and beyond.

FAQ
What does Nvidia's $2 billion investment in Core Weave accomplish?
Nvidia's investment provides Core Weave with critical capital to expand AI compute capacity while establishing a deep technological partnership. The investment is structured as a purchase of Class A shares at $87.20 per share, giving Nvidia significant shareholder influence while demonstrating confidence in Core Weave's business model and execution capabilities. Beyond capital, the partnership enables Core Weave to integrate Nvidia's latest chip architectures and provide customers with cutting-edge infrastructure optimized for AI workloads.
How does Core Weave plan to deploy 5 gigawatts of AI compute by 2030?
Core Weave's expansion plan requires constructing 10-50 major data center facilities across various geographic locations between 2025 and 2030. The expansion depends critically on three components: acquiring suitable real estate for data center locations, securing power contracts adequate to supply 5 continuous gigawatts of electricity, and deploying Nvidia GPU infrastructure at massive scale with advanced cooling systems. Nvidia's commitment to help Core Weave "buy land and power" addresses the two largest infrastructure constraints that would otherwise limit Core Weave's expansion speed.
What makes Core Weave's AI factories different from traditional cloud data centers?
AI factories represent purpose-built infrastructure optimized exclusively for artificial intelligence workloads rather than generalized computing. Traditional cloud platforms (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) optimize for diverse workload types including web applications, databases, and analytical processing. Core Weave's AI factories integrate compute (Nvidia GPUs and Vera CPUs), specialized storage systems (Bluefield), high-performance networking, and software frameworks designed explicitly for training and serving AI models. This specialization enables performance improvements and cost advantages for AI-intensive workloads compared to generalized infrastructure.
What are Core Weave's financial sustainability challenges and how does the Nvidia investment address them?
Core Weave carried approximately
How does the partnership affect competing data center providers and GPU manufacturers?
The partnership creates significant competitive advantages for Core Weave while constraining opportunities for competing infrastructure providers. Core Weave's exclusive focus on Nvidia architectures makes it the preferred deployment partner for Nvidia's technology roadmap. Competing infrastructure providers face strategic choices: specialize in underserved niches, develop partnerships with alternative GPU manufacturers like AMD, or pursue niche optimization (edge computing, inference-specific, specific geographies). For GPU manufacturers outside the Nvidia ecosystem, the partnership effectively forecloses access to one of the world's largest infrastructure providers.
What existing Core Weave customers benefit most from the Nvidia partnership?
Hyperscale AI organizations including OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft benefit substantially through guaranteed access to leading-edge infrastructure, priority GPU allocation from Nvidia, and deep technical support from both organizations. These customers gain infrastructure that can deliver computing efficiently at scales exceeding 10,000 GPUs. For these organizations requiring continuous infrastructure expansion to support model training growth, Core Weave's partnership with Nvidia ensures sustained technology currency and reliable supply availability critical to their AI capability development.
How does Core Weave's software acquisition strategy (Weights & Biases, Marimo, Monolith) complement the Nvidia investment?
Core Weave's acquisition strategy creates integrated platform where customers access compute infrastructure alongside development tools, collaboration platforms, and AI infrastructure software. The Nvidia investment provides capital enabling these acquisitions while establishing technological compatibility across the stack. Rather than forcing customers to integrate disparate point solutions, Core Weave increasingly offers cohesive ecosystem where infrastructure, development tools, and software frameworks are pre-integrated and optimized for each other. This vertical integration increases customer stickiness and creates switching costs that protect market position.
What geopolitical implications does Core Weave's expansion carry?
U.S. export controls increasingly restrict advanced GPU sales to certain countries and entities, creating geographic constraints on AI infrastructure deployment. Core Weave's U.S. basing and exclusive Nvidia partnership mean it cannot easily serve customers under export restrictions. However, Core Weave's expansion serves U.S. government agencies and national security-conscious enterprises requiring infrastructure within U.S. jurisdiction. Geopolitical fragmentation of AI infrastructure might create opportunities for Core Weave to serve as trusted provider for U.S. and allied nations while competitors potentially serve alternative geopolitical spheres.
How should enterprises evaluate whether Core Weave infrastructure makes economic sense versus internal development or cloud alternatives?
Enterprises should build comprehensive total cost of ownership models comparing Core Weave versus alternatives across multiple dimensions: capital expenditure (cloud typically has none; Core Weave outsourcing and internal development require substantial capex), operational expertise (cloud simplifies operations; Core Weave and internal require infrastructure expertise), performance characteristics (specialized infrastructure often outperforms generalized cloud for specific workloads), and long-term flexibility (internal development provides maximum flexibility; Core Weave creates some lock-in; cloud provides maximum switching ease). The optimal choice depends on organization size, in-house expertise, workload characteristics, and financial constraints. Larger organizations requiring sustained AI infrastructure investment often find outsourcing to specialized providers like Core Weave more efficient than internal development, while smallest organizations often prefer cloud simplicity despite higher marginal costs.
What risks could disrupt Core Weave's expansion timeline or financial viability?
Multiple risk categories could disrupt Core Weave's projections: execution risks (delays in facility construction, power procurement, regulatory approvals), demand risks (if AI model scaling slows or efficiency improvements reduce compute requirements), technology risks (if competing architectures displace Nvidia GPUs), and macroeconomic risks (if recession reduces enterprise AI investment). Additionally, Core Weave's debt obligations create financial fragility—unexpected revenue deceleration could quickly create debt service challenges. While Nvidia's investment provides some cushion, Core Weave remains highly leveraged with limited room for error. Stakeholders should monitor revenue growth trajectories carefully; sustained deceleration would signal emerging problems.

Key Takeaways
- Nvidia's $2 billion investment provides CoreWeave critical capital while establishing deep technological partnership and vertical integration into infrastructure
- CoreWeave plans to deploy 5+ gigawatts of AI compute capacity by 2030 through coordinated facility construction and power procurement with Nvidia support
- AI factories represent purpose-built infrastructure optimized exclusively for machine learning workloads, differentiating from generalized cloud computing platforms
- CoreWeave's debt obligations ($18.81B) remain sustainable if projected revenue growth of 20-35% quarterly is achieved, enabling path to profitability by 2027
- Partnership creates significant competitive advantages for CoreWeave while constraining opportunities for competing infrastructure providers without strategic alternatives
- Hyperscale AI organizations (OpenAI, Meta, Microsoft) gain preferred access to leading-edge infrastructure with Nvidia technology currency and priority GPU allocation
- Software acquisitions (Weights & Biases, Marimo, Monolith) complement partnership by enabling integrated platform approach and increasing customer switching costs
- Geopolitical dynamics create opportunities for CoreWeave to serve U.S. government and security-conscious enterprises requiring infrastructure under U.S. jurisdiction
- Enterprise evaluation of CoreWeave versus alternatives requires comprehensive total cost of ownership modeling across capital, operations, performance, and flexibility dimensions
- Infrastructure market consolidation, standardization around Nvidia architectures, and vertical integration will characterize competitive evolution through 2030
Related Articles
- AMI Labs: Inside Yann LeCun's World Model Startup [2025]
- Experian's AI Evolution: Credit Scores, Privacy & Data Ethics in 2025
- Hubristic Fundraising: Brex's $5.15B Acquisition & Lessons [2025]
- Rippling vs Deel Corporate Spying Scandal: DOJ Criminal Investigation
- Apple's Siri AI Chatbot Revolution: What Changed & Alternatives
- Apple's AI Chatbot Siri: Complete Guide & Alternatives 2026




