Grubhub's Bold Fee Waiver Strategy: A Game-Changing Move in Food Delivery
In early 2026, Grubhub announced a strategic shift that sent ripples through the food delivery industry. The company unveiled a permanent policy eliminating all delivery and service fees on restaurant orders exceeding $50. This decision represents more than just a promotional tactic—it's a fundamental repositioning in an increasingly saturated market where price sensitivity drives consumer behavior. According to Adweek, Grubhub even enlisted George Clooney to announce this disruptive fee structure during a Super Bowl ad.
For years, food delivery platforms have operated on a fee-heavy model that customers increasingly resented. The average delivery and service fees on orders over
The timing of this announcement is strategically significant. Grubhub has been losing ground in the competitive landscape, with monthly active users declining 20% year-over-year in 2025 to just 8 million users, according to Verdict Foodservice. DoorDash, by comparison, commands nearly 50 million monthly active users. When a market leader faces such substantial user decline, dramatic action becomes necessary. Grubhub's fee waiver strategy represents an acknowledgment of this reality and an attempt to recapture market share through tangible customer value.
What makes this move particularly notable is its permanence. Unlike competitors who typically offer limited-time promotions or subscription-based benefits, Grubhub's fee elimination applies indefinitely to all qualifying orders. This creates a structural advantage that's difficult for competitors to match without fundamentally restructuring their business models. For consumers accustomed to subscription models like DashPass or Uber One, Grubhub's approach offers unconditional savings without requiring recurring payments.
Understanding the full implications of this strategy requires examining multiple dimensions: the competitive landscape, customer economics, restaurant impacts, and broader industry trends. This comprehensive analysis explores how Grubhub's fee waiver reshapes the delivery ecosystem and what it means for various stakeholders.
The Current Competitive Landscape in Food Delivery
Market Leaders and Their Current Positions
The food delivery market in North America comprises a handful of dominant players, each competing fiercely for market share and consumer attention. DoorDash has solidified its position as the market leader with approximately 50 million monthly active users and the broadest restaurant network. Uber Eats maintains strong growth, particularly through Uber's integrated ecosystem that bundles delivery with ride-sharing. Instacart has carved out a significant niche in grocery and convenience goods delivery, while smaller players like DoorDash-owned Caviar and various regional platforms serve specific geographic markets.
Grubhub's challenge has become increasingly acute in this landscape. Once a dominant player, the platform has struggled to maintain relevance as competitors invested heavily in logistics infrastructure, restaurant partnerships, and customer acquisition. The company's 20% year-over-year user decline represents a critical inflection point where aggressive action becomes necessary for survival.
How Competitors Currently Structure Their Fee Models
DoorDash operates a tiered approach through DashPass, its subscription service priced at $9.99 monthly. DashPass members receive delivery fee waivers on select restaurants and reduced fees on others, but the service doesn't provide universal fee elimination. Standard DoorDash users without DashPass pay full delivery and service fees regardless of order size. DoorDash periodically runs promotions offering free delivery on specific occasions or for limited periods, but these are temporary rather than structural changes.
Uber Eats follows a similar model with Uber One, a $9.99 monthly subscription offering delivery fee waivers. However, Uber One's benefits vary by restaurant and geographic location, creating inconsistent customer experience. Uber occasionally offers promotional free delivery periods, particularly during market entry phases or to attract new users.
Beyond major players, regional platforms and smaller competitors typically maintain flexible fee structures designed to remain competitive while maintaining unit economics. Many offer free delivery thresholds at
The Economics Behind Fee Waiver Decisions
When analyzing why Grubhub would eliminate fees on
For $50+ orders, customer economics differ significantly from smaller orders. These larger orders typically come from customers ordering for groups, special occasions, or multiple meals. These customers represent higher lifetime value, greater retention potential, and stronger positive word-of-mouth. By capturing and retaining these customers through fee elimination, Grubhub trades short-term revenue for long-term market position improvements.
Additionally, larger orders contain higher implicit margins for restaurants, meaning platform revenue sharing already provides platform income. When a
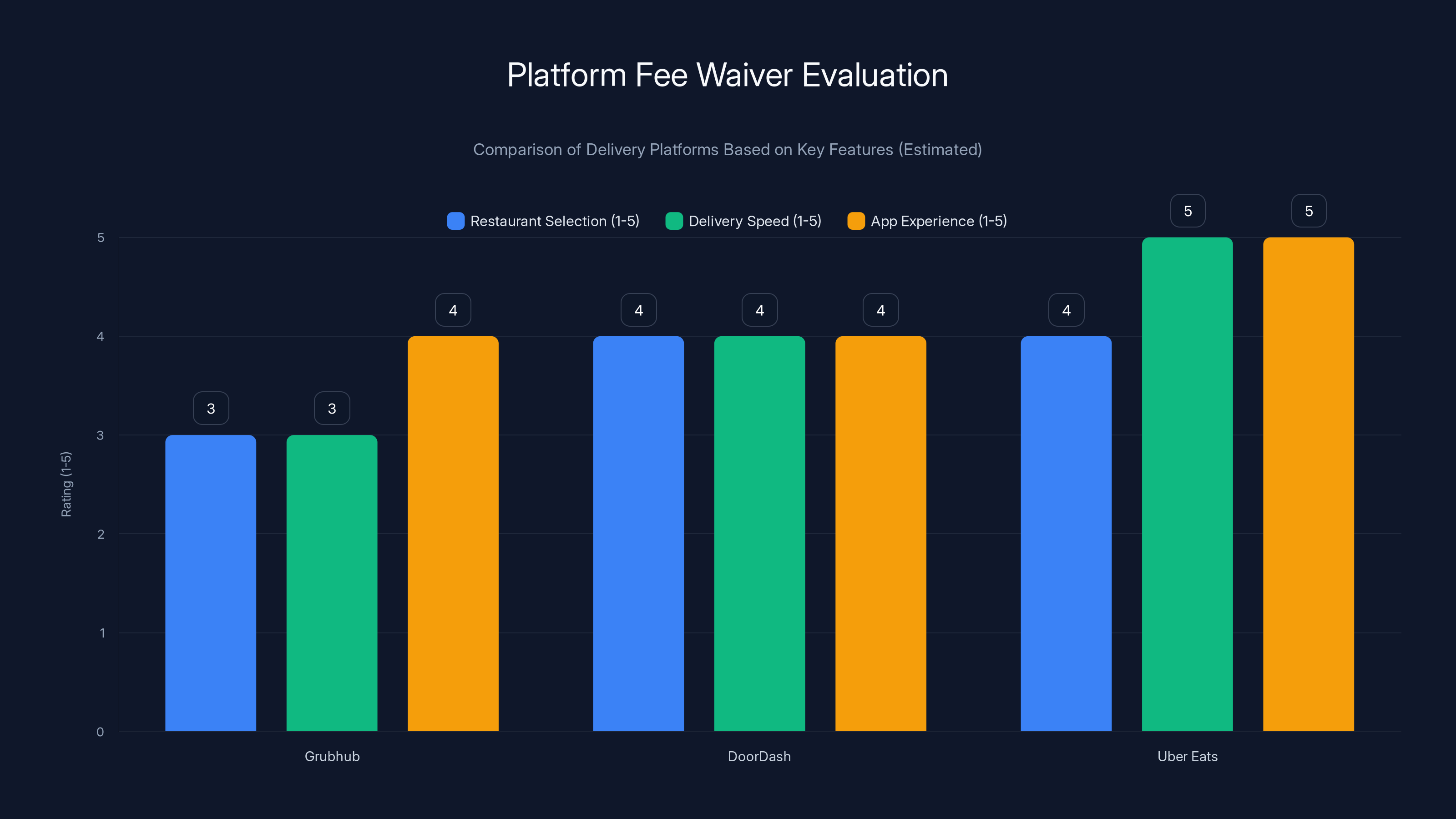
Grubhub's fee waiver is attractive, but DoorDash and Uber Eats offer better restaurant selection and delivery speed. Estimated data.
Understanding Grubhub's Fee Waiver Policy in Detail
Policy Mechanics and Eligibility Requirements
Grubhub's fee waiver applies to all orders exceeding the $50 threshold from participating restaurants. The policy covers both delivery fees and service fees, which together compose the bulk of platform charges. Unlike subscription-based competitors, there are no membership requirements, no geographic restrictions, and no restaurant-specific limitations—the policy applies universally across Grubhub's platform.
Order placement remains unchanged; customers add items, apply any available promotional codes, and proceed to checkout. At the payment stage, the system calculates the pre-tax order total. If the total exceeds $50, delivery and service fees automatically disappear from the final invoice. This transparent, frictionless approach provides immediate customer clarity compared to complex subscription redemption processes.
The policy applies to online orders placed through Grubhub's app or website. Delivery must be to a valid address within the restaurant's delivery zone. Scheduled orders (placing an order for future delivery) qualify as long as the order value exceeds $50. Special dietary requests, large party orders, and catering arrangements typically fall under separate pricing structures but may qualify depending on how they're processed through the platform.
Which Restaurants Participate
Grubhub positions this as available at "all participating restaurants," though the precise participation rate affects policy effectiveness. Early indications suggest major restaurant chains participate, given their sophisticated ordering systems and platform-friendly infrastructure. Independent restaurants, particularly smaller establishments, may face implementation challenges or may choose not to participate due to margin concerns.
Restaurant participation likely varies geographically. Urban markets with high delivery density probably see broader participation, while rural areas or smaller cities may have limited options. This geographic variation creates an uneven customer experience that could limit the policy's competitive impact in some regions.
Financial Impact and Margin Implications
For Grubhub, the fee waiver creates revenue headwinds in the short term but promises customer acquisition and retention benefits that could improve long-term profitability. When a customer places a
The math becomes clearer over time. If the fee waiver increases customer retention by even 15% among the $50+ order segment, the lifetime value improvements offset short-term fee losses. Additionally, these higher-value orders naturally have better unit economics when restaurants pay commission fees, which Grubhub continues to collect regardless of delivery fee elimination.
Grubhub likely calculated that the marginal cost of delivering larger orders differs from delivery economics on smaller orders. Drivers may accept larger-order deliveries more readily because the customer service quality and tipping patterns tend to be better. This means the true cost of serving these orders may be lower than implied by average delivery fees.

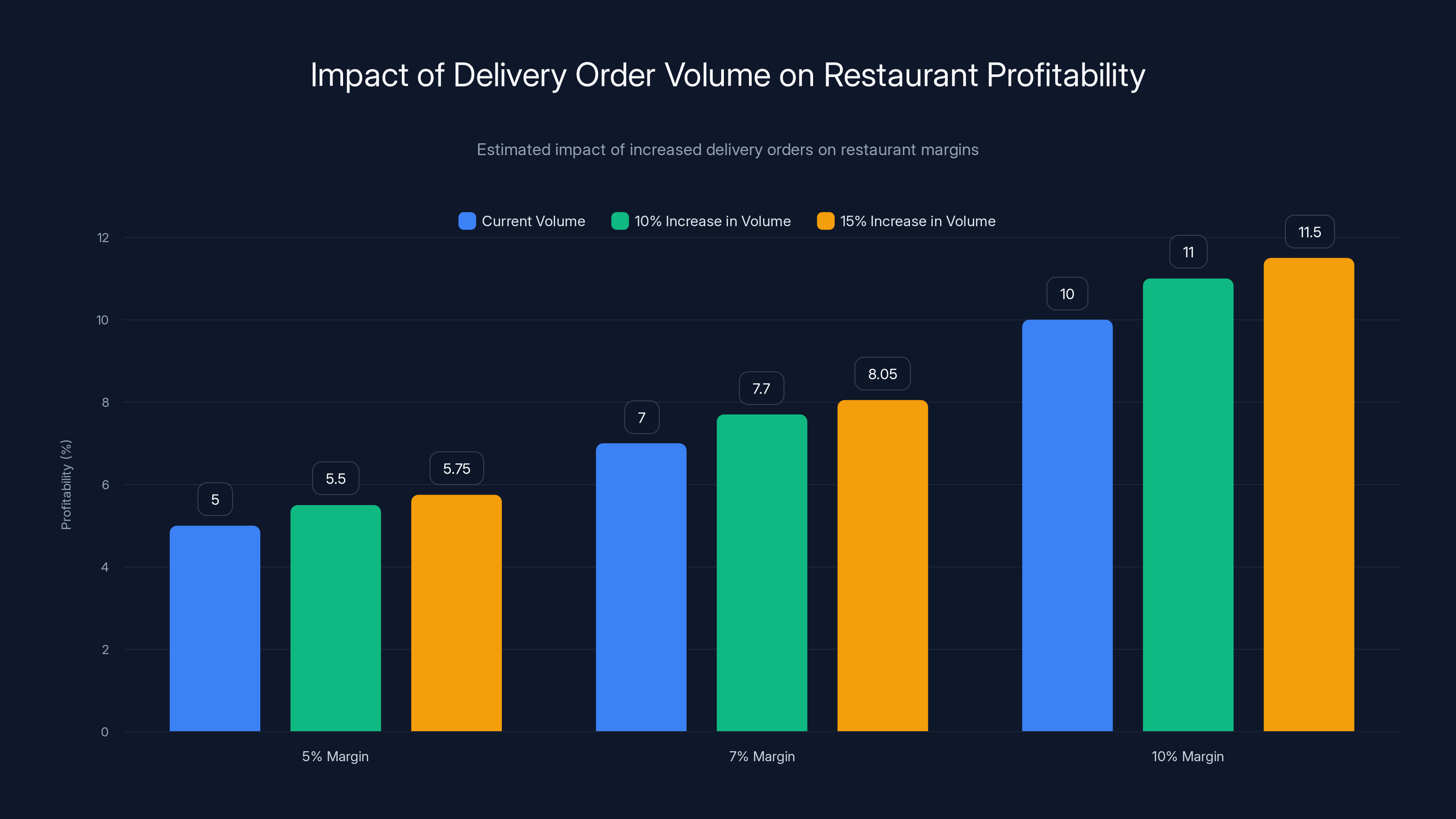
Estimated data shows that a 10-15% increase in delivery order volume can significantly boost restaurant profitability, even with unchanged commission rates.
Market Impact Analysis: How This Changes Competition
Immediate Competitive Response Pressure
Grubhub's announcement creates immediate pressure on DoorDash and Uber Eats to respond. These platforms face a dilemma: match the offer and accept margin compression, or ignore the policy and risk losing customers to Grubhub's value proposition. Neither option is entirely palatable, which explains why this strategic move is so effective.
DoorDash could theoretically eliminate DashPass subscription requirements and offer universal fee waivers on
Uber Eats faces similar constraints. Uber One's value proposition specifically includes delivery fee waivers as a primary benefit. Universal fee elimination would undermine the subscription's strategic purpose and customer acquisition power. Both competitors are likely exploring middle-ground responses that provide incremental value without eliminating core revenue streams.
Customer Switching Incentives
For price-sensitive customers, Grubhub's offer creates compelling switching incentives. Consider a consumer who regularly places
These savings are particularly meaningful for middle-income households and younger demographic segments with limited discretionary spending. Students, young professionals, and families represent significant portions of delivery platform user bases, and price-sensitive segments respond strongly to savings messages. Grubhub's marketing will likely emphasize the cumulative annual savings, potentially claiming customers could save
The switching also extends beyond individual consumers to corporate and workplace ordering. Companies managing employee meal programs or team lunches often place orders exceeding $50. For these bulk ordering scenarios, Grubhub's offer becomes particularly attractive compared to subscriptions or limited-time promotions.
Restaurant Ecosystem Effects
Restaurants experience mixed impacts from Grubhub's policy change. On one hand, increased order volume through Grubhub due to the fee waiver's attractiveness generates more business. Restaurants view expanded order volume positively, particularly during slow periods or when delivery order percentages lag behind dine-in and takeout.
Conversely, restaurants may worry about economic pressure from Grubhub to reduce their own delivery fees or offer special menu pricing to customers ordering through the platform. When customers save on platform fees, restaurants might perceive pressure to reduce menu prices or accept lower commission rates. While Grubhub hasn't implemented such policies, restaurants will monitor the situation closely.
Large restaurant chains have sufficient scale to resist pressure and may even benefit from Grubhub's increased market share. Smaller independent restaurants with thin margins might struggle if the policy eventually creates expectations for lower pricing or reduced commissions. This dynamic could accelerate concentration among larger, more established restaurant operators with better platform management capabilities.
Customer Economics and Savings Analysis
Calculating Real Savings Across Order Sizes
To understand the true customer impact, analyzing savings patterns across different order values provides clarity. For a
This creates an interesting dynamic where percentage savings decrease as absolute order values increase. However, absolute dollar savings remain constant at approximately
Annual savings calculations prove particularly compelling in marketing. A customer ordering four times weekly at an average value of
Comparison With Subscription Model Economics
When comparing Grubhub's offer against DashPass or Uber One, the analysis becomes nuanced. A DashPass subscriber paying
For a customer placing four weekly
Grubhub's approach of universal elimination on
Psychological Impact and Decision-Making
Beyond pure economics, psychological factors influence customer response to Grubhub's offer. The word "free" triggers powerful emotional responses and decision-making patterns. Customers see "no delivery fees, no service fees" as a more compelling message than they perceive a subscription offering variable benefits.
Additionally, the absence of friction matters. With subscriptions, customers must remember to maintain their membership, evaluate whether they're using benefits, and make ongoing renewal decisions. Grubhub's automatic benefit removes this cognitive burden. For many consumers, this simplified experience outweighs small economic differences.
Conversely, some customers may perceive Grubhub's model as unsustainable or question how the company maintains profitability. These skeptical consumers might assume the offer will eventually disappear or come with hidden costs. Addressing this perception requires strong communication about Grubhub's long-term commitment and economic viability.

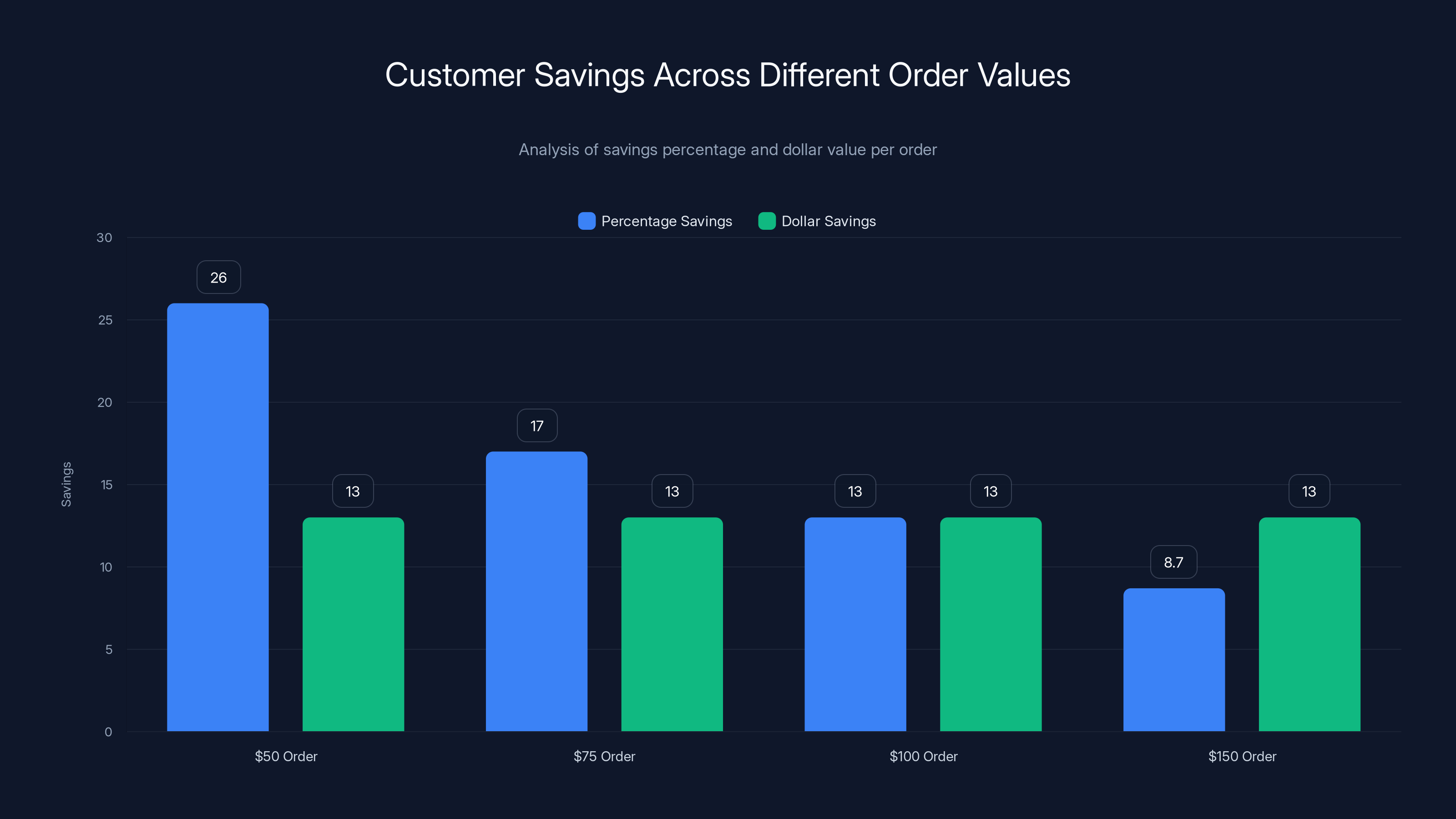
As order values increase, the percentage savings decrease from 26% to 8.7%, while the absolute dollar savings remain constant at $13 per order. Estimated data.
Strategic Context: Why Grubhub Made This Move Now
The Wonder Group Acquisition and Ownership Change
Grubhub's trajectory shifted dramatically following Marc Lore's Wonder Group acquisition of the platform in 2024. Lore, known for his involvement with multiple consumer-focused ventures, brought a different strategic vision to Grubhub's operations. The fee waiver policy reflects this new ownership's aggressive approach to growth and market expansion.
Under previous ownership, Grubhub maintained a relatively conservative fee structure aimed at maximizing near-term profitability. This approach optimized for cash generation but failed to maintain competitive parity with DoorDash's aggressive growth investments. Lore's investment model appears more focused on market share expansion and strategic positioning, even if short-term profitability declines.
Wonder Group's portfolio includes various retail and consumer brands, suggesting Lore has experience with customer acquisition at scale. The fee waiver strategy aligns with this experience—offering compelling customer value propositions to drive platform adoption, then monetizing growth through operational efficiency and scale advantages.
User Acquisition Costs and Competitive Pressure
Grubhub's declining user metrics made dramatic action necessary. Acquiring replacement customers through traditional digital marketing increasingly expensive as competitive ads drive up customer acquisition costs across the industry. A customer acquired through paid advertising might cost
The fee waiver policy functions as a more efficient customer acquisition mechanism. Customers attracted by the offer likely have higher lifetime value than those acquired through paid advertising alone. These customers are incentivized by tangible savings rather than vague value propositions, suggesting stronger product-market fit and lower churn risk.
Grubhub's strategy implicitly acknowledges that competing directly on execution quality with DoorDash and Uber Eats is challenging given their larger user bases and network effects. Instead, Grubhub competes through a more compelling economic proposition. This repositioning makes strategic sense given current market dynamics and resource constraints.
The Claim Acquisition Strategic Move
Simultaneously with the fee waiver announcement, Grubhub revealed its acquisition of Claim, a startup providing cash-back rewards at local restaurants. This move complements the fee waiver strategy by addressing a different customer segment: those who prefer eating at restaurants versus delivery.
Claim enables Grubhub to capture dining engagement across channels. When customers receive rewards through Claim for restaurant visits, they develop deeper platform engagement and frequency. Combined with delivery fee waivers, this creates a comprehensive value proposition addressing multiple customer needs and occasions.
The Claim acquisition also suggests Grubhub's vision extends beyond delivery disruption toward broader restaurant engagement. By helping restaurants build personalized rewards programs, Grubhub deepens restaurant relationships and creates switching costs that insulate it from competitive pressure. Restaurants investing in Grubhub-powered loyalty programs become less likely to prioritize competing delivery platforms.

Impact on Restaurant Operations and Margins
Commission Structure and Restaurant Revenue
Grubhub's fee waiver doesn't directly impact restaurants' economics because platform commissions remain unchanged. When a restaurant receives a delivery order, Grubhub typically takes 15-30% commission on the order subtotal, depending on the restaurant's contract tier and negotiating power. Eliminating customer-facing delivery and service fees doesn't change this commission structure.
Restaurants actually benefit from the fee waiver policy because it reduces customer friction and increases order volume. An increase in delivery order frequency directly translates to higher total revenue, which improves restaurant profitability despite unchanged commission percentages. For restaurants operating at 5-10% food cost margins, a 10-15% increase in delivery order volume could meaningfully improve overall profitability.
However, restaurants should monitor whether Grubhub attempts to extract concessions as the platform gains share. Historically, dominant platforms have negotiated commission reductions after achieving market leadership. If Grubhub successfully uses the fee waiver to gain DoorDash-like market position, restaurants might face pressure to accept lower commissions. Anticipating this dynamic, savvy restaurant operators might want to negotiate longer-term commission contracts while Grubhub remains hungry for market share.
Menu Pricing Pressures and Customer Expectations
One subtle risk from the fee waiver is potential pressure on restaurants to lower menu prices. When customers save $13 on delivery and service fees, they psychologically expect the restaurant to absorb margin pressure and offer lower prices. Marketing messaging emphasizing total savings might inadvertently create price expectations that restaurants can't sustainably meet.
To mitigate this risk, Grubhub should clearly communicate that the fee waiver applies to delivery platform economics, not restaurant pricing. The platform's marketing should emphasize that Grubhub enables restaurants to reach customers without inflating prices. Clear separation between platform fee benefits and restaurant pricing reduces pressure on margins.
Established restaurant brands with strong pricing power can resist pressure more effectively than independent operators. National chains negotiate from positions of scale and might extract better commission rates while accepting Grubhub's fee waiver. Independent restaurants lack this leverage and might experience subtle pressure if customers expect lower prices.
Logistics and Driver Economics
For delivery drivers, the fee waiver has indirect implications. Grubhub likely maintains driver compensation unchanged despite reduced platform revenue from customer-facing fees. However, increased order volume from the more competitive positioning means more delivery opportunities for drivers, improving earning potential.
Driver earning potential improves with order volume, but decreases with pressure to accept lower compensation per delivery. If Grubhub must reduce driver pay to offset fee waiver revenue loss, driver satisfaction and availability might decline, degrading service quality. Managing this balance becomes critical to policy success.
Geographic availability and surge pricing dynamics also shift. In markets where Grubhub's volume increases substantially due to the fee waiver, driver supply might not immediately adjust to demand, creating temporary capacity constraints. Grubhub must monitor regional driver availability closely and adjust compensation or incentives to ensure service quality doesn't deteriorate despite increased demand.

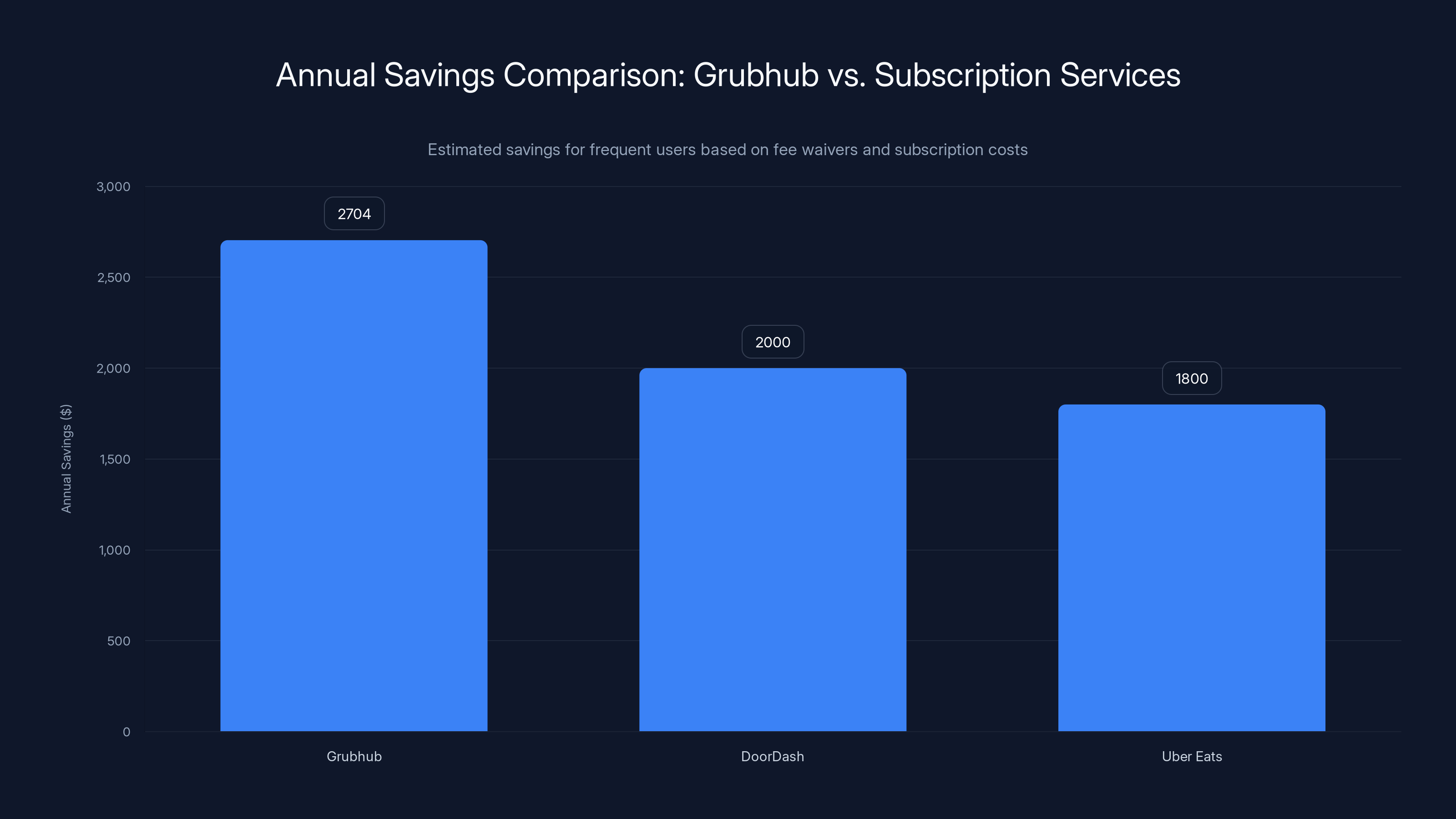
Grubhub offers significant savings for high-frequency users with orders over $50, surpassing typical savings from DoorDash and Uber Eats subscriptions. Estimated data.
Financial Sustainability Questions and Long-Term Viability
Revenue Model Impacts and Profitability Concerns
The immediate question facing Grubhub is whether permanent fee elimination on substantial order volumes maintains long-term financial viability. The company projects that increased volume and improved customer retention justify short-term margin compression. However, execution on these projections proves critical.
Grubhub's profitability depends on achieving several outcomes: (1) user acquisition that exceeds the volume increase from fee waivers, (2) improved retention among captured users, (3) maintained or improved commission rates with restaurants, and (4) operational efficiency gains that offset reduced fee-based revenue. Each of these represents an execution challenge, and shortfalls in any dimension threaten the model's viability.
Public company stakeholders will scrutinize quarterly earnings closely. If Grubhub reports user growth without profitability improvement, market skepticism will mount. The company must communicate a clear path to profitability despite short-term revenue headwinds, or else investor confidence will deteriorate.
Competitive Response Scenarios and Strategy Viability
Grubhub's strategy works only if competitors cannot or will not match the offer. If DoorDash and Uber Eats quickly implement similar fee waivers, the competitive advantage disappears and the entire industry suffers margin compression. This scenario benefits only customers but potentially threatens the long-term viability of all platforms.
However, matching the offer proves operationally difficult for larger competitors. DoorDash and Uber Eats have higher overall cost structures due to their larger logistics networks. They also have greater exposure to shareholder pressure regarding profitability. Grubhub, as a smaller player under Wonder Group control, faces less public market pressure and can accept margin compression for longer periods.
Moreover, DoorDash and Uber Eats likely have higher percentage costs devoted to driver compensation and logistics, making fee elimination less economically feasible. Grubhub's willingness to accept margin compression reflects its position as a challenger brand willing to sacrifice short-term profitability for market share gains.
Alternative Monetization and Diversification
Grubhub will likely accelerate development of higher-margin services to offset delivery fee revenue loss. Advertising opportunities on the platform become increasingly valuable as user base grows. Restaurants desperately want placement in search results and featured sections, willing to pay premium placement fees. This advertising revenue could meaningfully offset delivery fee losses.
The Claim acquisition suggests Grubhub is building restaurant loyalty software as a premium service. Restaurants willing to pay for sophisticated loyalty features and analytics create new revenue streams less price-sensitive than commission-based models. As this software matures, it could contribute meaningfully to overall profitability despite delivery fee compression.
Grubhub might also expand into adjacent services: grocery delivery, convenience goods, restaurant management software, and business intelligence services for restaurant operators. Each represents revenue opportunity less dependent on delivery fee economics. This diversification reduces risk from a single business model change.

Customer Segmentation and Usage Pattern Implications
High-Value Customer Targeting
Grubhub's fee waiver specifically targets high-value customers who regularly spend
This segmentation also means Grubhub isn't subsidizing small orders through the fee waiver policy. A customer placing a $30 order still pays delivery fees, meaning Grubhub captures revenue from price-sensitive, lower-value segments. This surgical targeting of fee waivers improves policy economics compared to offering universal free delivery.
Over time, Grubhub should monitor the distribution of order values and adjust the
Frequency-Based Economics and Lifetime Value
Customer ordering frequency drives fee waiver policy economics. A customer ordering twice monthly sees minimal impact from the policy. A customer ordering multiple times weekly sees substantial impact. Grubhub needs to ensure that fee waiver customers actually increase ordering frequency and don't simply shift existing orders from other platforms.
The challenge of distinguishing between incremental and transferred orders is significant. If a customer using DoorDash twice weekly and Grubhub once weekly switches to Grubhub three times weekly, incremental volume grows. However, if the customer simply replaces some DoorDash orders with Grubhub orders while maintaining total frequency, incremental volume is lower.
Grubhub's analysis should focus on post-promotion customer behavior. If customers acquired through the fee waiver demonstrate frequency increases over six-month periods, the acquisition investment proves worthwhile. If frequency remains flat or declines after initial acquisition, the policy hasn't achieved its strategic objective.
Geographic Expansion Implications
The fee waiver policy's success varies geographically based on competitive intensity and market dynamics. In markets where Grubhub has weak position against DoorDash, the policy creates strong incentive for switching. In markets where Grubhub already maintains strong share, incremental benefit is smaller.
Grubhub should prioritize marketing the policy in DoorDash strongholds and cities where Grubhub's share lags significantly. These markets offer the greatest upside for share gains. Simultaneously, the company must maintain service quality and restaurant availability in these expansion markets to ensure customer satisfaction justifies the low-price positioning.
Rural and less densely populated areas present different dynamics. These markets typically have limited delivery platforms and lower order volumes. The fee waiver matters less in markets without competitive alternatives. Grubhub should focus investment on urban markets with higher-value customers and greater platform competition.
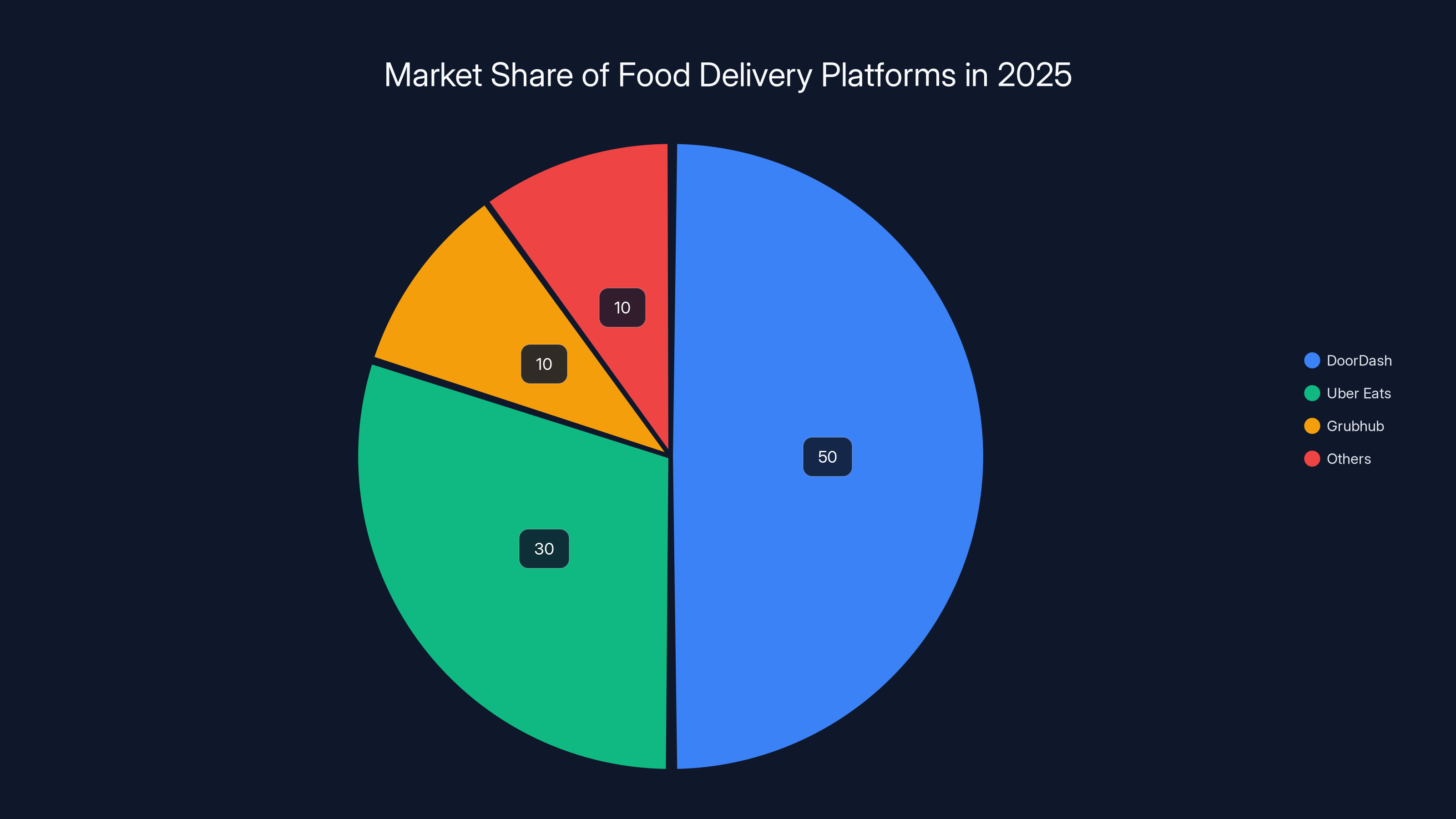
DoorDash leads the market with nearly 50% share, while Grubhub holds around 10%. Estimated data based on user activity.
Marketing Strategy and Brand Positioning
Messaging Framework and Customer Communication
Grubhub's marketing should emphasize three core messages: (1) permanent savings without hidden subscriptions, (2) broader restaurant selection than competitors, and (3) commitment to putting money back in customers' pockets. Each message addresses specific competitive vulnerabilities in DoorDash and Uber Eats positioning.
The "no hidden subscriptions" messaging differentiates from DashPass and Uber One, emphasizing transparency and fairness. Rather than feeling like they're missing out by not subscribing, customers understand they simply benefit from Grubhub's choice to share economics directly. This positioning leverages growing consumer skepticism about subscription creep and recurring charges.
Messaging emphasizing "your savings, our commitment" frames the fee waiver as Grubhub's strategic choice rather than a promotional tactic. This language suggests permanence and commitment, reducing customer concern that the offer will disappear after initial customer acquisition. Carefully crafted language matters significantly in communicating policy durability.
Advertising Channels and Customer Acquisition Tactics
Grubhub should allocate significant budgets to social media, particularly platforms where younger demographics congregate. TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube enable creative storytelling about fee elimination savings and customer testimonials. User-generated content from customers sharing their annual savings in engaging formats amplifies message authenticity.
Search advertising around competitor brand names becomes particularly valuable. When consumers search for "DoorDash delivery fees," "Uber Eats costs," or similar queries, Grubhub should capture these high-intent searches with messaging about fee elimination. These searches indicate customer price sensitivity, making them ideal targets for conversion.
Partnerships with content creators and influencers in the food and lifestyle spaces create authentic endorsements. Creators regularly order delivery, making them credible voices for platform recommendations. Compensation in delivery credits rather than cash aligns incentives and demonstrates platform confidence.
Public Relations and Thought Leadership
Grubhub should position leadership around broader narratives about platform economics fairness and consumer value. Opinion pieces in major publications about unsustainable delivery platform fee structures and Grubhub's alternative approach establish thought leadership. Marc Lore's public presence and willingness to discuss disruption strategy can amplify these messages.
Engagement with media covering food delivery, tech, and consumer economics ensures fair coverage of the fee waiver policy. Journalists typically favor companies offering bold policy changes backed by clear strategy. By facilitating media access and providing substantive information, Grubhub can shape narrative around the announcement.
Industry speaking opportunities at restaurant conferences position Grubhub as restaurant-focused platform partner. Discussing how the fee waiver benefits restaurant operations and customer acquisition creates positive sentiment among restaurant operators who influence platform visibility and promotion.

Competitive Response Predictions and Market Evolution
How DoorDash Might Respond
DoorDash faces a genuine strategic dilemma. The company could match Grubhub's offer by eliminating fees on $50+ orders, but this destroys DashPass value proposition and creates massive revenue headwinds. Alternatively, DoorDash might offer limited-time promotions ("free delivery for 30 days") that provide perceived parity without permanent commitment.
More likely, DoorDash introduces a new tier of DashPass or creates a separate premium offering with stronger benefits. For instance, "DashPass Pro" might offer universal fee elimination on all orders, positioning the subscription as premium but justifiable given broader benefits. This preserves DashPass brand equity while offering an answer to Grubhub's offer.
DoorDash might also accelerate development of higher-margin services like restaurant software, advertising, and data services. By diversifying revenue beyond delivery fees, DoorDash reduces dependence on customer-facing fees and can weather competitive pricing pressure better. This would mirror Grubhub's broader diversification strategy.
How Uber Eats Might Respond
Uber Eats has additional complexity because delivery represents only part of Uber's business. The company has different incentive structure than pure-play delivery platforms. Uber might be willing to offer more aggressive benefits because ride-sharing profitability and Uber One bundling create different economics.
Uber could offer universal free delivery on Uber One, making the subscription much more compelling compared to DashPass. Given Uber's financial scale, the company can absorb margin compression on delivery to protect Uber One subscriber base and ecosystem integration. This approach leverages Uber's multi-service strength against pure-play competitors.
Conversely, Uber might reduce focus on delivery given profitability challenges and allocate resources to higher-margin services. If Uber de-emphasizes delivery competition to focus on ride-sharing and advertising growth, Grubhub and DoorDash inherit more market share. This would represent strategic retreat rather than direct competitive response.
Potential Market Consolidation
Increasingly aggressive competition on pricing and customer acquisition could accelerate consolidation. If all platforms struggle with profitability amid fee wars, acquisition of weaker competitors becomes more likely. Smaller platforms might be acquired by larger players to consolidate market share and reduce competitive intensity.
Conversely, if Grubhub's strategy successfully captures share, the company might acquire complementary businesses or smaller platforms to accelerate growth. Wonder Group's investment thesis likely includes potential acquisitions that would expand Grubhub's market reach or capabilities. Strategic M&A could become more likely if the fee waiver policy succeeds.
Longer-term, the industry might consolidate into two or three mega-platforms operating in most markets. This would reduce competitive intensity and allow margin recovery, but would also increase regulatory scrutiny. The U.S. Federal Trade Commission has already expressed concerns about food delivery platform consolidation, suggesting any further M&A would face regulatory challenges.
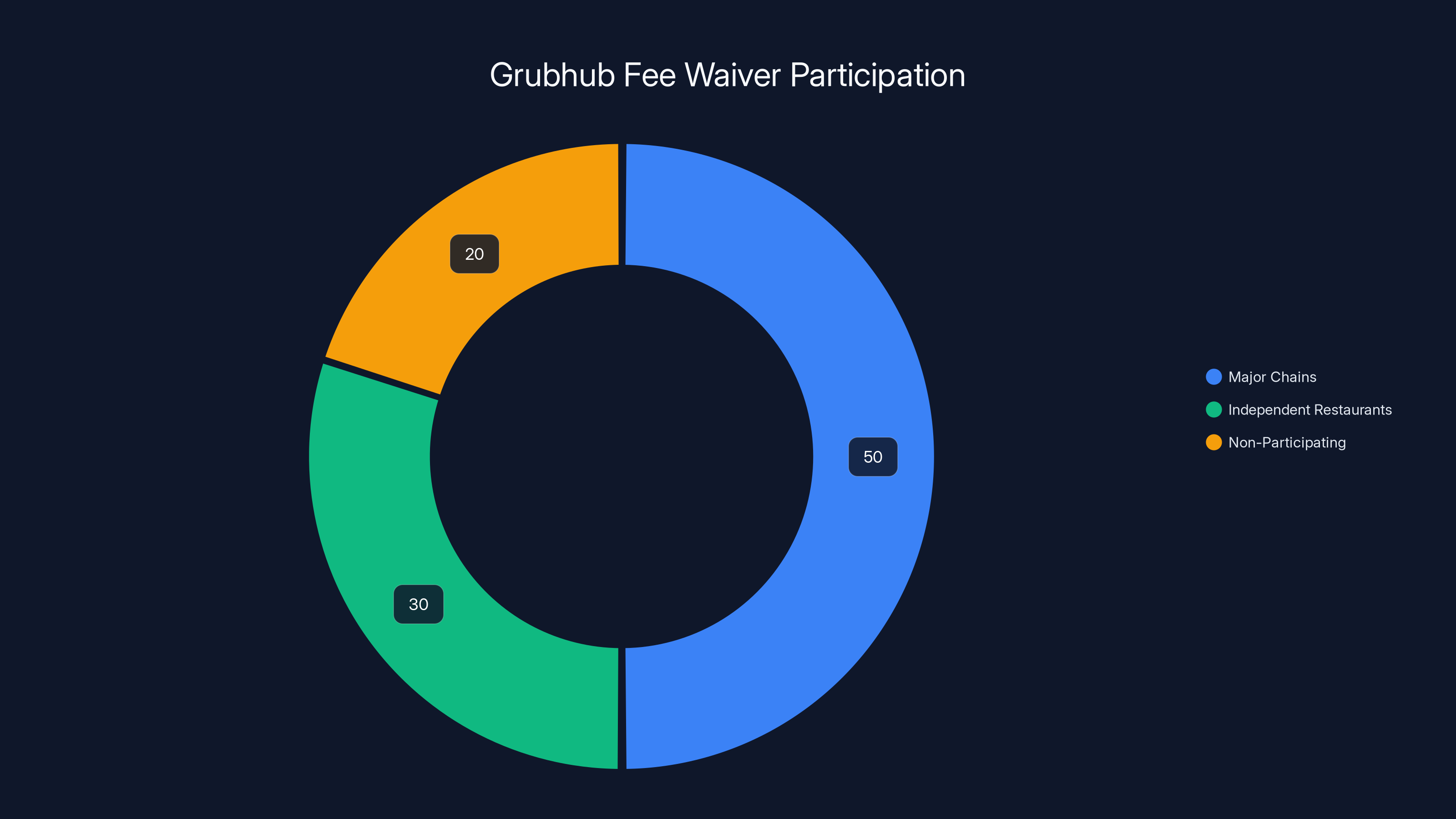
Estimated data suggests major chains are more likely to participate in Grubhub's fee waiver policy, while smaller independent restaurants may opt out due to margin concerns.
Looking at Alternatives to Grubhub and Competitive Platforms
Independent Restaurant Delivery Solutions
While Grubhub, DoorDash, and Uber Eats dominate the delivery market, independent restaurants increasingly build proprietary delivery capabilities. Restaurants develop their own apps, websites, and partnerships with local delivery services to avoid platform commissions and fees. This trend accelerates as restaurant operators recognize platform dependency risks.
Independent delivery coordination typically uses multiple services. Restaurants might partner with local delivery drivers, offer pickup options, or contract with regional logistics providers. While this approach lacks the convenience of aggregator platforms, it offers superior economics and brand control for restaurants. As this trend grows, aggregator platform growth decelerates slightly as restaurants optimize delivery channels independently.
Smaller platforms like Slice (focused on pizza), Toast, and Toast Takeout target specific restaurant segments with better technology and lower commissions than major aggregators. These platforms typically charge 5-15% commissions compared to 20-30% for major platforms, creating strong incentives for restaurants to utilize them. However, lower commissions mean less investment in customer acquisition and delivery optimization.
Regional Platforms and Local Competitors
Various regional platforms maintain strong positions in specific geographic areas. In Canada, Skip the Dishes represents the dominant platform. In Europe, Deliveroo and Just Eat maintain strong positions. In Asia, regional platforms dominate over Western competitors. These regional leaders often have advantages understanding local restaurant networks and customer preferences.
Smaller cities and towns often rely on multiple regional platforms rather than national aggregators. These platforms understand local restaurant relationships better and might offer more favorable commission terms. For customers in these markets, multiple platforms represent necessary options given limited restaurant availability on any single aggregator.
The Case for Using Runable for Restaurant Operations
Beyond consumer-facing delivery platforms, restaurants increasingly use operational tools like Runable to manage multi-channel ordering, inventory, and fulfillment. Runable's automation platform helps restaurants coordinate orders across multiple delivery services, manage kitchen workflows, and optimize staffing. At $9/month for basic features, Runable provides cost-effective operational support that complements delivery platform usage.
Restaurants using Runable can efficiently aggregate orders from Grubhub, DoorDash, Uber Eats, and proprietary channels into unified management systems. This reduces operational friction and enables data-driven decision-making about which platforms and channels drive profitability. For restaurants managing multiple platforms simultaneously, Runable's integration capabilities become increasingly valuable.
As delivery platforms compete on customer-facing economics (like Grubhub's fee waiver), restaurants must optimize operational efficiency to maintain margins. Tools enabling better workflow automation, order coordination, and kitchen management become essential infrastructure. Runable and similar platforms represent an underrated competitive factor in delivery ecosystem evolution.
Emerging Alternatives: Ghost Kitchens and Vertical Integration
Ghost kitchens and delivery-optimized restaurant models represent emerging alternatives to traditional restaurant delivery. Brands like Reef, Wonder Kitchen, and others operate multiple restaurant concepts from single kitchens optimized for delivery. This approach reduces real estate costs and enables more efficient delivery routing.
Vertical integration of restaurant brands into delivery is also emerging. Existing restaurant chains increasingly develop proprietary delivery infrastructure or acquire delivery services. This backward integration reduces platform dependency but requires capital investment and operational complexity beyond traditional restaurant operations.
These alternative models demonstrate that the delivery ecosystem is evolving beyond current aggregator platform dominance. Over the next five years, restaurants will increasingly employ hybrid approaches combining aggregator platforms, proprietary delivery, and alternative service models. This evolution benefits consumers through improved options and operators through better economics.
Implementation Challenges and Execution Risks
System Integration and Operational Complexity
Implementing universal fee elimination across Grubhub's platform involves substantial technical and operational complexity. Menu integration across thousands of restaurants, variable order minimum updates, and real-time commission calculation changes must be flawlessly executed. Any system failures could expose Grubhub to customer complaints and reputational damage.
Driver compensation systems require careful recalibration to ensure drivers receive appropriate incentive structures despite platform revenue reduction. If driver compensation declines perceived-ly due to fee elimination, driver recruitment and retention suffer. Grubhub must maintain driver satisfaction while managing margin pressure, a delicate balance requiring sophisticated compensation models.
Restaurant communication and adoption present another challenge. Not all restaurants possess sophisticated POS system integration enabling real-time menu and fee structure updates. Grubhub must provide implementation support and potentially compensation for integration costs to ensure rapid restaurant adoption. Phased rollout by restaurant size and sophistication manages this complexity but slows market impact.
Geographic Rollout Challenges
Grubhub's platform operates in thousands of cities with varying restaurant network maturity, competition intensity, and customer characteristics. Rolling out the fee waiver simultaneously across all markets risks inconsistent customer experience and operational issues. Phased geographic rollout allows testing in pilot markets before nationwide implementation.
Pilot markets should represent diverse competitive environments: markets where Grubhub leads, competitive neutral markets, and DoorDash-dominant markets. This geographic diversity tests the policy's effectiveness across different competitive scenarios. Insights from pilots inform national rollout strategy and help identify potential issues before broad implementation.
Timezone and regional customer service implications require attention. If rollout timing varies geographically, customers receive inconsistent messaging about launch timing. Coordinated national announcement with phased implementation provides clarity while managing operational complexity.
Customer Confusion and Expectation Management
Customers may misunderstand fee waiver eligibility or believe benefits apply more broadly than intended. Clear communication about the $50 minimum, participating restaurants, and policy permanence proves critical. Misleading customer perception creates dissatisfaction and undermines marketing effectiveness.
Grubhub must also manage customer expectations about the policy's permanence. If economic pressures force policy modification or elimination, customer backlash will be severe. The company should avoid over-promising permanence if there's meaningful possibility of future changes. Balanced communication acknowledges commitment while preserving strategic flexibility.
International expansion raises additional complexity. Grubhub operates internationally in addition to North America. The fee waiver policy's economics may differ significantly in international markets with different competitive dynamics, customer spending patterns, and platform commission structures. International implementation requires localized strategy rather than simple global replication.

Industry Trends and Future Market Evolution
The Broader Shift Toward Subscription and Convenience
Food delivery represents part of broader consumer shift toward convenience-driven commerce. Consumers increasingly expect fast delivery, abundant options, and transparent pricing across all commerce categories. Delivery platforms compete not just with each other but with all e-commerce and convenience alternatives.
Subscription models dominate modern commerce, but consumer sentiment increasingly shifts toward skepticism about subscription proliferation. Grubhub's permanent fee waiver model positions the company against this trend, offering simplicity and transparency compared to subscription complexity. This positioning aligns with broader consumer sentiment favoring straightforward pricing.
Longer-term, the delivery industry will likely see consolidation around two to three mega-platforms, similar to e-commerce consolidation around Amazon and other platforms. As consolidation occurs, regulatory scrutiny will increase, potentially constraining aggressive competitive tactics. Grubhub's strategy implicitly races against this consolidation timeline.
Technology Integration and Super Apps
Increasing integration of delivery with adjacent services represents another trend. Grubhub's acquisition of Claim and expansion into restaurant technology suggest broader super app ambitions. Platforms offering delivery plus dining reservations, grocery ordering, and restaurant management software create ecosystem stickiness.
Uber's multi-service integration (ride-sharing plus delivery plus restaurant reservations through partnerships) provides a roadmap for this evolution. Platforms that successfully integrate multiple services create switching costs and customer lifetime value that single-service models can't match. Grubhub's broader strategy likely includes expansion into adjacent services beyond pure delivery.
Sustainability and Regulatory Evolution
Regulatory scrutiny of delivery platform economics has intensified in recent years. Cities worldwide have implemented fee caps, limiting platform ability to charge customers above certain thresholds. Grubhub's fee waiver strategy implicitly acknowledges regulatory trends pushing toward lower consumer-facing fees.
Environmental sustainability also factors into future evolution. Single-order deliveries create significant carbon footprint. Multi-order consolidation and routing optimization become increasingly important as regulatory and consumer pressure around sustainability grows. Platforms enabling efficient delivery coordination gain advantages.
Labor regulations affecting driver classification and compensation represent another evolving regulatory landscape. Grubhub's driver-friendly positioning (maintaining driver compensation during customer-facing fee elimination) preemptively addresses potential regulatory scrutiny around driver economics. This approach differs from aggressive labor cost-cutting strategies more vulnerable to regulatory challenge.

Strategic Lessons and Best Practices
What Grubhub's Move Teaches About Competitive Strategy
Grubhub's decision to eliminate fees on large orders provides valuable lessons about competitive strategy in mature markets. When competing directly on execution and brand against stronger competitors fails, repositioning around a compelling value proposition becomes necessary. Grubhub recognized it couldn't beat DoorDash at their own game and instead changed the game entirely.
The strategy also demonstrates importance of willingness to accept margin compression to achieve market share goals. Many incumbent platforms optimize for near-term profitability, missing opportunities to invest in growth. Grubhub's new ownership showed willingness to prioritize growth and market position over immediate profits, a perspective shift that enables aggressive competitive action.
Finally, the strategy shows the power of clear economic value propositions in driving customer decisions. Customers understand fee elimination far more readily than they understand complex subscription value propositions. Simplicity and transparency in pricing creates marketing advantages and customer satisfaction that complexity cannot match.
Metrics for Success and Performance Monitoring
Grubhub should establish clear metrics measuring policy success: user acquisition, retention improvement, order frequency changes, and path to profitability. Monthly tracking of these metrics against baseline expectations provides early signals of policy effectiveness or problems requiring adjustment.
User acquisition cost for customers acquired through fee waiver promotion should compare favorably to traditional paid customer acquisition. If acquisition cost exceeds lifetime value, the strategy has failed regardless of overall user growth. Sophisticated cohort analysis tracking customer value by acquisition source proves essential.
Retention metrics warrant particular attention. The policy succeeds only if acquired customers exhibit retention rates exceeding historical baseline. If customers acquired through fee savings churn at elevated rates, the strategy simply trades revenue for temporary users, a losing proposition over time.
Why Other Platforms Haven't Adopted Similar Strategies
Why haven't DoorDash or Uber Eats implemented similar fee elimination? The most obvious reason: they can't afford to. DoorDash's larger user base and logistics network carry higher costs. Eliminating fees on significant order volumes threatens profitability at a scale that DoorDash's business model cannot support.
Additionally, DoorDash has built DashPass as a core strategic asset generating recurring subscription revenue and brand equity. Abandoning DashPass through universal fee elimination would destroy substantial shareholder value. Public company constraints prevent the margin compression strategy that Wonder Group can pursue as private ownership.
Uber Eats faces similar constraints but has additional strategic flexibility through Uber's other business units. However, ride-sharing profitability challenges and investor concerns about burn rates likely constrain Uber's willingness to compress delivery margins. These financial realities explain why only Grubhub pursued this aggressive strategy.

Risk Assessment and Potential Failure Scenarios
Revenue Decline Scenario
The most obvious risk is that fee elimination revenue loss exceeds gains from increased volume, resulting in declining profitability. If user growth disappoints and order frequency increases fail to materialize, Grubhub faces margin compression without offsetting benefits. This scenario becomes increasingly likely if competitors quickly match the offer and eliminate Grubhub's competitive advantage.
Revenue decline would force strategic decisions about policy continuation. Returning to fee-based model after customer expectations of free delivery would create massive backlash. Alternatively, Grubhub might be forced into acquisition by a larger player, representing failure of the independent strategy.
Competitive Match Scenario
If DoorDash and Uber Eats successfully implement similar fee waivers, the competitive advantage disappears and the entire industry faces margin compression. This outcome benefits customers but threatens platform profitability. In this scenario, the strategy doesn't fail for Grubhub specifically but rather forces all industry participants into lower-margin operations.
The industry might adapt through consolidation, with weaker platforms acquired or eliminated. Grubhub's scale relative to smaller regional competitors provides advantages in surviving prolonged margin compression. However, competing against DoorDash and Uber Eats even on equal pricing terms proves challenging given their superior scale and operational execution.
Economic Downturn Scenario
If broader economic recession occurs, consumer spending on delivery orders declines regardless of fee structure. In economic downturns, delivery represents discretionary spending vulnerable to cuts. Eliminating fees helps but doesn't overcome fundamental demand destruction from job losses and reduced consumer spending.
Economic downturn might actually benefit Grubhub if competitors prove unable to sustain margin compression. Stronger balance sheets and lower leverage might enable Grubhub to endure economic stress longer, allowing acquisition of weaker competitors. However, this represents opportunistic benefit rather than policy-driven success.
Regulatory Intervention Scenario
Regulatory bodies might view aggressive competitive pricing as predatory conduct harmful to restaurant economics. If regulators conclude that fee elimination creates unsustainable platform economics and threatens market viability, they might intervene with minimum fee requirements or other restrictions. This scenario would force policy modification and weaken competitive advantage.
Additionally, driver classification changes or labor protections could increase delivery costs substantially. If regulations require higher driver compensation or benefits, the economics supporting fee elimination deteriorate. Regulatory evolution around gig economy labor presents meaningful risk to delivery platform economics generally.
Practical Guidance for Affected Stakeholders
For Consumers: Evaluating the Offer
Consumers should evaluate Grubhub's fee waiver within broader platform context. Beyond fee elimination, consider restaurant selection, delivery speed, and app experience. A platform with fee elimination but limited restaurants or poor delivery performance provides less value than alternatives with broader selection.
Calculate your personal savings based on actual ordering patterns. If you rarely order above $50, the fee waiver provides minimal benefit. Track your spending across platforms to identify where savings concentrate. Some customers might benefit more from DashPass or Uber One depending on order patterns and preferred restaurants.
Monitor whether fee waiver persists over time and whether conditions change. If Grubhub adjusts the threshold upward, modifies participating restaurants, or adds other restrictions, revisit the evaluation. Regular reassessment ensures your platform choices remain optimal as competitive dynamics evolve.
For Restaurants: Platform Strategy
Restaurants should evaluate Grubhub's fee waiver as a marketing opportunity. The policy attracts customers willing to place higher-value orders, improving average order value and revenue. Capitalize on increased demand through menu optimization and promotional strategies.
Simultaneously, maintain presence across multiple platforms rather than concentrating on Grubhub. Competitive dynamics could change rapidly, and platform dominance creates dependency risk. Balanced portfolio approach across Grubhub, DoorDash, Uber Eats, and proprietary channels spreads risk.
Invest in operational tools like Runable that enable efficient multi-platform order management. As delivery complexity increases with multiple platforms, automation becomes essential. Tools streamlining operations reduce labor costs and improve customer satisfaction, protecting margins amid competitive pricing pressure.
For Investors: Assessing Platform Investment
Investors should recognize that Grubhub's strategy represents bet on market share gains offsetting margin compression. Near-term financial metrics will likely disappoint as revenue declines from fee elimination. Patient capital willing to endure margin compression to fund growth becomes necessary.
Evaluate Wonder Group's financial strength to fund losses during market share expansion phase. If profitability targets require quick achievement, the strategy lacks sufficient time to execute successfully. Understanding ownership's investment thesis and timeline proves critical to assessing strategy viability.
Monitor competitive responses carefully. If DoorDash or Uber Eats quickly match the offer, Grubhub's advantage disappears and the strategy becomes value-destroying for all participants. However, if competitors fail to match due to financial or structural constraints, Grubhub's strategy could deliver substantial shareholder value long-term.

Conclusion: The Significance of Grubhub's Strategic Gamble
Grubhub's decision to permanently eliminate delivery and service fees on orders exceeding $50 represents one of the most significant competitive moves in food delivery platform history. The policy signals a strategic shift from incremental feature competition toward fundamental business model innovation. By attacking the most visible source of customer friction—platform fees—Grubhub takes a position that competitors struggle to match without fundamental restructuring.
The move's success depends on execution across multiple dimensions. Customer acquisition must deliver value exceeding traditional advertising alternatives. Retention must improve sufficiently that acquired customers generate lifetime value justifying their acquisition cost. Operational efficiency must improve to offset revenue losses. Restaurant participation must remain strong despite margin pressures. And most critically, competitive responses must fail to eliminate Grubhub's advantage.
While risks are substantial, the strategic logic is compelling. Grubhub faced a choice: continue declining against stronger competitors, accept acquisition or failure, or pursue aggressive repositioning with potential for transformation. The company chose the third path, betting that decisive action addressing customer pain points could overcome structural competitive disadvantages.
The fee waiver policy also signals broader evolution in food delivery economics. Platforms increasingly recognize that subscription-based pricing, while theoretically attractive, creates customer friction and perception of unfairness. Transparent, permanent fee elimination represents an alternative approach that might resonate more effectively with modern consumers skeptical of subscription proliferation.
For the broader industry, Grubhub's move pressures DoorDash and Uber Eats to reconsider fee-based revenue models. Extended margin compression across the industry would accelerate consolidation and potentially drive regulatory intervention. The status quo where platforms maintain substantial margins becomes increasingly difficult to defend if viable alternatives exist.
Ultimately, Grubhub's policy benefits consumers through reduced delivery costs and increased competitive intensity. For restaurants and drivers, implications are more complex, depending on whether fee elimination translates to volume growth sufficient to maintain or improve overall economics. The coming years will determine whether Grubhub's strategic gamble succeeds or becomes a cautionary tale about the limits of aggressive pricing strategies.
Stakeholders should monitor the policy's performance closely. If Grubhub successfully grows share, improves retention, and achieves profitability despite fee elimination, other platforms will be forced to follow. If the strategy proves financially unsustainable, Grubhub might retreat from the policy and reset expectations. Either outcome will shape food delivery platform economics for years to come.
For businesses analyzing their own competitive positioning, Grubhub's approach offers important lessons about bold action, customer-centric thinking, and willingness to disrupt existing models. In mature, competitive markets where incremental improvement fails to generate differentiation, sometimes transformation requires accepting near-term margin compression to achieve long-term market position gains.

FAQ
What exactly does Grubhub's fee waiver policy cover?
Grubhub's fee waiver policy eliminates both delivery fees and service fees on restaurant orders exceeding
How does this policy compare to DoorDash and Uber Eats subscription services?
Grubhub's approach differs fundamentally from DashPass and Uber One. Where competitors offer subscription-based benefits that vary by restaurant and include ongoing membership fees (
What restaurants participate in the fee waiver program?
Grubhub positions the policy as available at all participating restaurants on the platform. Participation likely varies geographically, with broader availability in urban markets and densely populated areas. Major restaurant chains have sophisticated ordering systems enabling rapid policy implementation, while independent restaurants might require more time for integration. Grubhub's website should provide updated information about participation status by restaurant and geographic market.
How much money can customers actually save with this policy?
Customer savings depend on order frequency and values. The average delivery and service fee elimination represents approximately
Why didn't DoorDash or Uber Eats implement similar policies?
DoorDash and Uber Eats face structural obstacles preventing fee elimination policies. Both companies have substantially larger operational costs due to extensive logistics networks and higher user bases. Additionally, DoorDash has built DashPass subscription as a core strategic asset generating over $1 billion in recurring revenue annually. Eliminating fees would destroy this revenue stream without offsetting gains. Uber Eats faces similar constraints plus pressure from investors regarding profitability. Grubhub, as a smaller platform under private ownership, has greater financial flexibility to accept margin compression for market share gains.
Is Grubhub's fee waiver policy sustainable long-term?
Sustainability depends on whether volume growth and improved customer retention offset revenue losses from fee elimination. If Grubhub successfully increases user acquisition and customer frequency, improved lifetime value could justify near-term margin compression. However, if competitors quickly match the offer or volume growth disappoints, profitability becomes challenging. The strategy requires sustained execution across customer acquisition, retention, and operational efficiency. Investors should monitor quarterly financial results closely for evidence of whether the policy is driving sufficient volume growth to achieve profitability targets.
What impacts does this policy have on restaurant operators?
Restaurants potentially benefit from increased order volume as Grubhub's competitive position strengthens. Higher delivery order frequency directly improves restaurant revenue. The policy doesn't change platform commission rates, meaning restaurants continue receiving similar economics per order while benefit from volume increases. However, restaurants should monitor whether Grubhub eventually pressures them for lower commissions or menu price reductions. Additionally, restaurants should maintain presence across multiple platforms to avoid dependency on any single platform's competitive fortunes.
How does Runable help restaurant operators navigate multi-platform delivery complexity?
Runable's AI-powered automation platform enables restaurants to manage orders across multiple delivery services from unified systems. At $9/month, Runable provides workflow automation, order consolidation, and kitchen management tools that help restaurants maintain operational efficiency even as delivery complexity increases with multiple platforms. For restaurants trying to balance Grubhub, DoorDash, Uber Eats, and proprietary channels, Runable reduces manual coordination and improves customer satisfaction through better order management.
What alternative delivery platforms should consumers consider besides Grubhub?
Consumers have several alternatives worth evaluating: DoorDash with DashPass, Uber Eats with Uber One, region-specific platforms like Skip the Dishes in Canada, and independent restaurant apps offering proprietary delivery. Additionally, some restaurants partner with local delivery services or offer pickup options reducing dependency on platform economics. For specific needs, ghost kitchens optimized for delivery in certain areas, or specialty platforms like Slice for pizza, provide niche solutions. For multi-platform convenience, Runable integration helps restaurants coordinate orders across channels, though consumers interact primarily with platform apps directly.
What should restaurants know about optimizing operations during intense platform competition?
Restaurants should recognize that platform competition creates opportunities if they manage multi-channel operations effectively. Invest in operational tools enabling efficient order management across platforms. Monitor platform-specific economics to identify which channels drive profitability. Don't become overly dependent on any single platform; maintain portfolio approach. Consider proprietary ordering channels (website, app) reducing platform commission exposure. Track customer data to understand channel preferences and optimize menu presentation by channel. Finally, focus on operational excellence and speed—platform differentiation increasingly depends on delivery speed and order accuracy rather than menu differences, making operational efficiency critical competitive factors.
Key Takeaways
- Grubhub's permanent fee waiver on $50+ orders represents bold competitive repositioning against DoorDash and Uber Eats
- Policy eliminates average 2,500+ annually for frequent users
- Competitors DoorDash and Uber Eats face significant constraints preventing similar fee elimination due to subscription revenue models and larger operational costs
- Strategy's success depends on customer acquisition, retention improvement, and volume growth offsetting short-term revenue losses
- Restaurants benefit from increased order volume but should maintain multi-platform presence to reduce dependency risk
- Operational tools like Runable help restaurants manage multi-platform complexity efficiently and maintain margins during competitive intensity
- Market consolidation and regulatory evolution will likely reshape delivery platform economics over coming years
- Consumer savings are greatest for high-frequency users placing orders above $50 threshold consistently
Related Articles
- Masking Net New Customer Slowdowns: The #1 B2B SaaS Growth Deception [2025]
- Nvidia's $100B OpenAI Investment: Reality vs. Reports [2025]
- Nvidia's $2B CoreWeave Investment: AI Infrastructure Strategy Explained
- Tesla FSD Subscription-Only Model: Strategic Shift & Industry Impact [2025]
- Go-to-Market Strategies for the AI Era: Complete Guide [2025]
- OnePlus Foldable Phone 2026: Strategic Case for Market Re-entry




