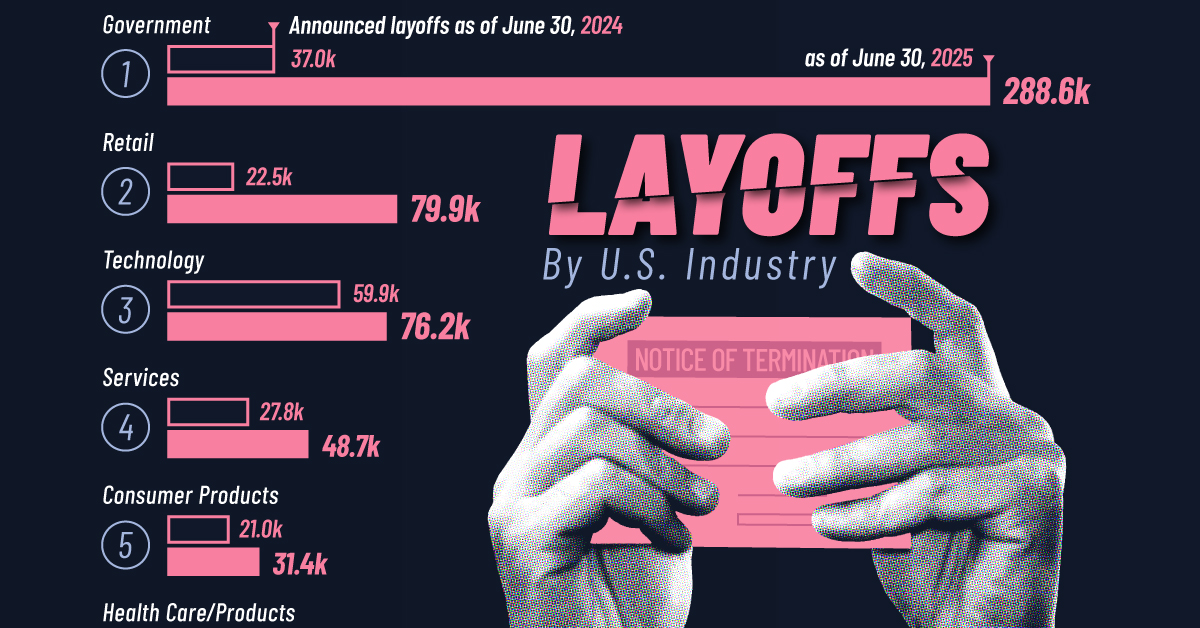
Pinterest Layoffs: How 700 Job Cuts Signal a Massive AI Shift
In early 2025, Pinterest announced it would lay off nearly 15% of its workforce. The numbers looked stark: roughly 700 employees out of a total staff of 4,666 would be affected by the restructuring. But the headlines missed the real story. This wasn't just another tech company tightening its belt. This was a company fundamentally repositioning itself around artificial intelligence.
The move revealed something crucial about where the tech industry is headed. When a platform with 430 million monthly active users doubles down on AI, it's not just about internal efficiency. It's about survival in a world where machine learning capabilities increasingly determine competitive advantage.
What made Pinterest's announcement different from the routine layoffs we've seen across Meta, Amazon, and Google wasn't the scale. It was the specificity of the pivot. Pinterest wasn't cutting costs and hoping to find new revenue streams later. It was explicitly stating that it would reallocate resources to AI-focused roles, reshape its product strategy around AI capabilities, and prioritize AI-powered features. The company expected to record pre-tax restructuring charges between
But what does this mean for users? For creators? For the future of the platform itself? And what does Pinterest's strategy tell us about how AI is reshaping the tech landscape in 2025?
These questions matter because Pinterest operates at a unique intersection. It's not a general social network like Meta. It's not a search engine like Google. It's a visual discovery platform built on the premise that users want to find, save, and shop for things. That specific mission makes it an ideal testing ground for AI capabilities, and it also makes the company's pivot especially instructive.
TL; DR
- Scale of layoffs: Pinterest cutting 700 employees (15% of workforce) to redirect resources to AI initiatives
- Financial impact: Company expecting $35-45 million in pre-tax restructuring charges through September 2025
- Strategic focus: Reallocating toward AI-focused roles, AI adoption, and AI-powered product capabilities
- Existing AI products: Pinterest Assistant already launched, with AI-powered personalized boards in testing
- Industry pattern: Reflects broader tech trend of prioritizing AI investment over traditional workforce expansion
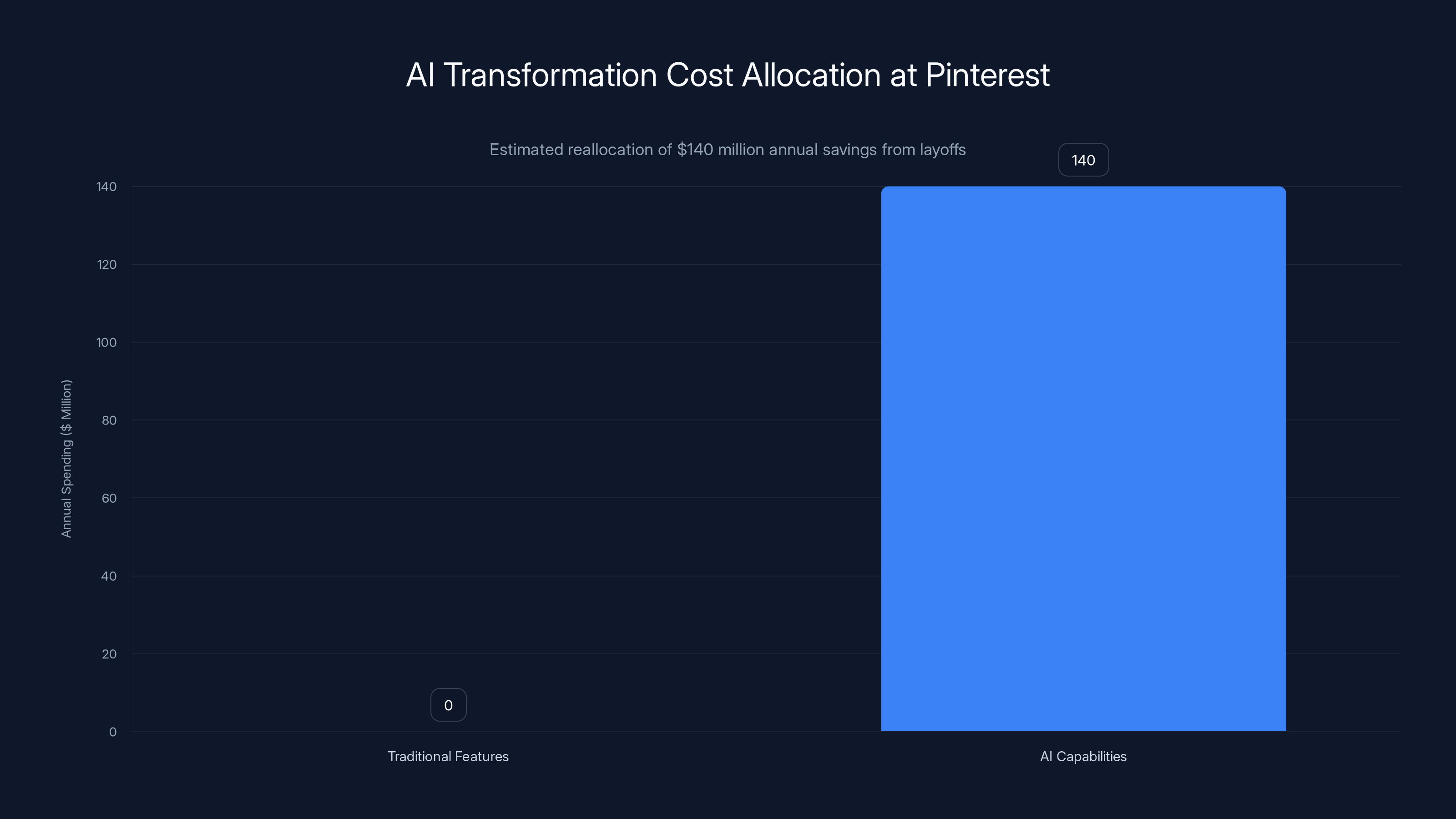
Pinterest is reallocating approximately $140 million from traditional features to AI capabilities, reflecting a strategic shift towards AI-native products. Estimated data.
Understanding Pinterest's Position in the AI Era
Pinterest wasn't in crisis when it announced the layoffs. The platform remained profitable, with consistent user engagement and a loyal creator ecosystem. So why the dramatic restructuring?
The answer lies in competitive pressure. Every major tech platform discovered in 2024 that AI capabilities would define the next era of technology. Companies couldn't afford to move at a measured pace. Waiting meant falling behind. Allocating resources incrementally meant watching competitors pull ahead. The only option was aggressive reallocation.
For Pinterest specifically, the urgency was compounded by the nature of visual content discovery. A recommendation algorithm that understands what users want to find, create, and purchase is inherently more valuable when it's powered by modern AI. The difference between a decent recommendation system and an AI-native one could determine whether users spend ten minutes on the platform or an hour.
Bill Ready, Pinterest's CEO, emphasized this point during the company's earnings calls. He highlighted the potential of open-source AI models to help the company keep costs manageable while building capabilities that previously would have required massive infrastructure investments. This wasn't just about efficiency. It was about fundamentally changing how Pinterest could deliver value.
The 15% workforce reduction targeted roles that weren't essential to the new strategy. This meant some divisions faced heavier cuts than others. Teams working on legacy features, older monetization approaches, or non-core product areas bore the brunt. Teams working on AI integration, product personalization, and new AI-powered features either maintained headcount or grew.
What's striking about this approach is that it's not just defensive. Yes, companies cut costs during uncertain times. But Pinterest's restructuring was aggressively offensive. It wasn't about survival. It was about establishing dominance in a new competitive landscape.
The Rise of Pinterest Assistant and AI-Powered Discovery
Pinterest didn't start from zero with its AI strategy. The platform launched "Pinterest Assistant" months before the layoff announcement, giving users an AI companion they could talk to for shopping advice, product recommendations, and inspiration. This wasn't a minor feature update. It was a fundamental expansion of how users could interact with the platform.
Think about what Pinterest Assistant does. Instead of just scrolling through a feed of pins, users can ask a question. "I need ideas for a small bathroom renovation that won't break the bank." The AI assistant doesn't just return a list of results. It understands intent, context, and preference. It synthesizes information from across the platform's catalog of billions of pins and provides curated, contextual recommendations.
That capability is pure AI. It requires natural language understanding, semantic search, knowledge of visual content patterns, and synthesis of complex information into coherent recommendations. A human curator couldn't do this at scale. A traditional algorithm couldn't either.
Pinterest also began experimenting with AI-powered personalized boards. These aren't static collections. They're dynamic, adaptive boards that learn user preferences over time and adjust to match emerging interests. The AI doesn't just show you what you've saved before. It predicts what you might want to save next, based on patterns, trends, and the behavior of similar users.
These products aren't finished. They're generation one. But they establish the foundation for everything Pinterest plans to build next. Every employee hired or retained in the restructuring needed to understand how to build on this foundation, extend these capabilities, and create new products that users couldn't imagine before they existed.
The investment wasn't just financial. It was philosophical. Pinterest was saying: "This is what matters now. This is where we're going. Align with it or move on."
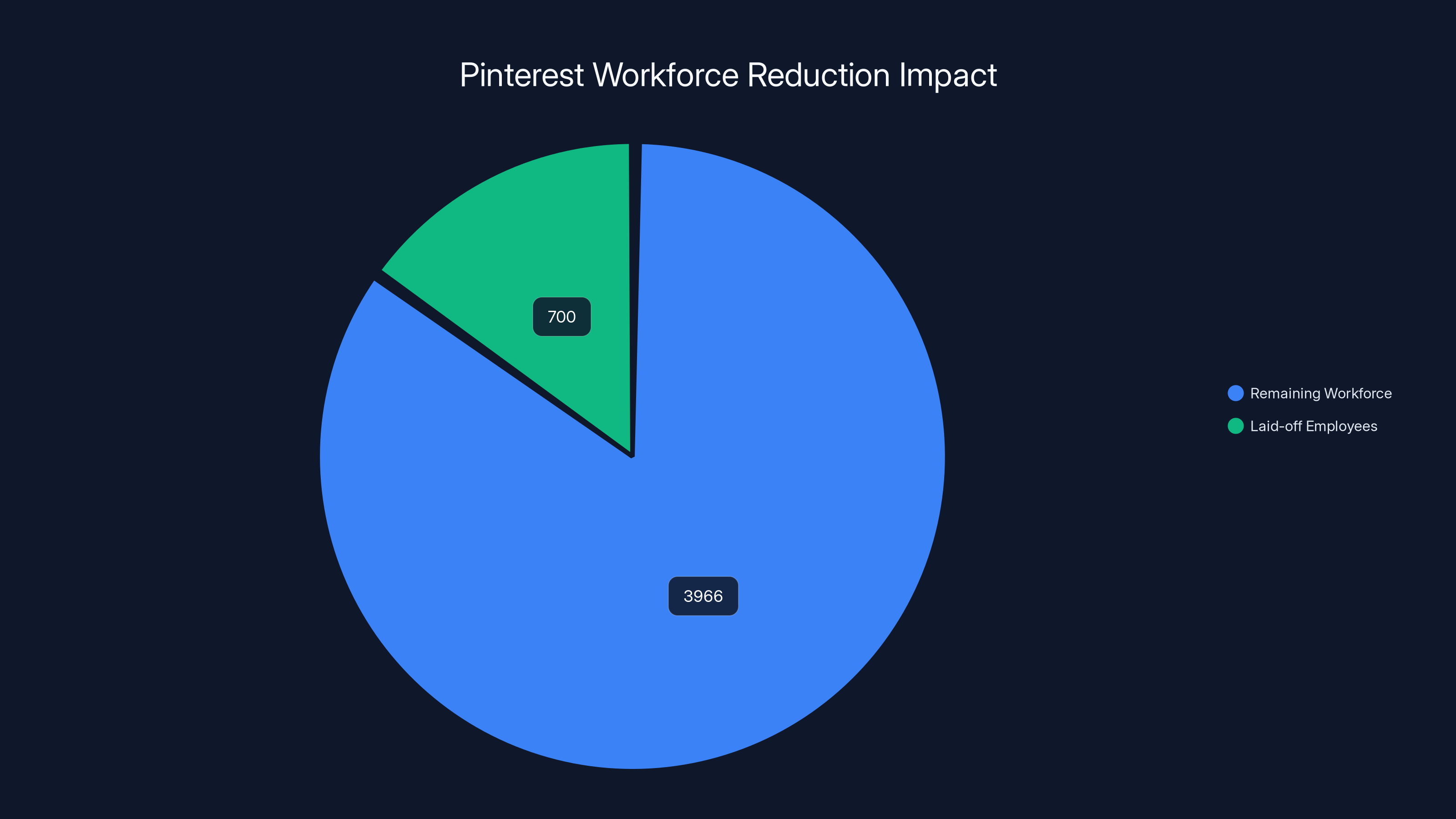
Following a 15% workforce reduction, approximately 700 Pinterest employees were laid off, leaving around 3,966 employees to focus on AI initiatives. Estimated data based on 2024 figures.
Why Layoffs Signal Strategic Conviction
Here's what many observers missed: layoffs are an expensive way to signal commitment. If a company wanted to shift strategy, it could do so gradually. Hire new talent in priority areas. Let underutilized teams shrink naturally through attrition. Slowly migrate resources.
Instead, Pinterest took the painful, costly route. They announced layoffs, incurred severance obligations, destroyed institutional knowledge, and faced morale challenges. Why? Because gradual shifts don't move fast enough in the AI era. By the time you've repositioned through attrition, your competitors have already built their next-generation capabilities.
The decisiveness signals three things to the market. First, the company is serious about AI. Second, leadership is confident enough to make big bets. Third, the strategy has staying power. This isn't a pivot that will reverse in six months if it doesn't immediately show results.
For Pinterest, that conviction is essential. The platform competes against Tik Tok for user attention, against Amazon for e-commerce traffic, and against Google for visual search queries. Each of those competitors has massive AI capabilities and larger budgets. The only way Pinterest wins is by moving faster, being more focused, and making bolder choices.
The Economics of AI Transformation
Pinterest expected restructuring charges of
With 4,666 employees before the layoff, even a full salary average of
But here's the thing: Pinterest isn't saving that money to boost profit margins. It's reinvesting it. The company will hire AI specialists, machine learning engineers, and product managers focused on AI capabilities. These roles typically command premium salaries. A senior ML engineer costs more than the average engineer across a company.
So the real economics aren't about cost reduction. They're about reallocating $140 million in annual spending from teams building traditional social features toward teams building AI-native products. That's a massive shift in resource allocation, and it's exactly what the market demanded from social platforms in 2024 and 2025.
Expecting $35-45 million in restructuring charges means the net savings in year one might be minimal or even negative when you factor in hiring costs and transition expenses. But in year two and beyond, the company operates with a fundamentally different cost structure and capability profile. That's when the economics turn positive.
What This Means for Pinterest Creators
Creators on Pinterest had questions. Would AI features cannibalize the audience for human-created content? Would the platform prioritize AI-generated recommendations over creator-curated collections? Would creators' roles become obsolete?
The honest answer: it's complicated. AI capabilities like Pinterest Assistant and AI-powered boards don't eliminate the need for human creators. They change how creators win attention.
A creator in 2024 succeeded by publishing pins that resonated with existing audience segments. Followers saw new pins in their feed. If the pins were good, they got engaged. The algorithm boosted visibility to similar audiences.
With AI-powered personalized boards, the dynamic shifts. Users don't just passively consume what the algorithm serves them. They actively ask the AI assistant for help. "I'm planning a kitchen remodel. Show me options under $50,000." The AI pulls together pins from thousands of creators, synthesizes them into curated collections, and presents them in context.
For creators, this is actually opportunity. Their pins now have multiple discovery pathways. They're not just competing in the feed algorithm. They're competing in AI-powered recommendation systems. Pins that answer specific questions, solve specific problems, or fit specific aesthetic preferences perform better.
But it also means the old strategies don't work. Clickbait pins, low-effort reposts, and engagement-farming tactics don't survive in an AI-curated environment. The AI is optimized for value to users, not engagement metrics. That's better for the platform long-term and better for creators who take quality seriously.
The shift also creates opportunity for a new type of creator: AI-native creators who understand how to collaborate with AI tools, create content optimized for semantic search, and build collections that AI systems naturally want to recommend.

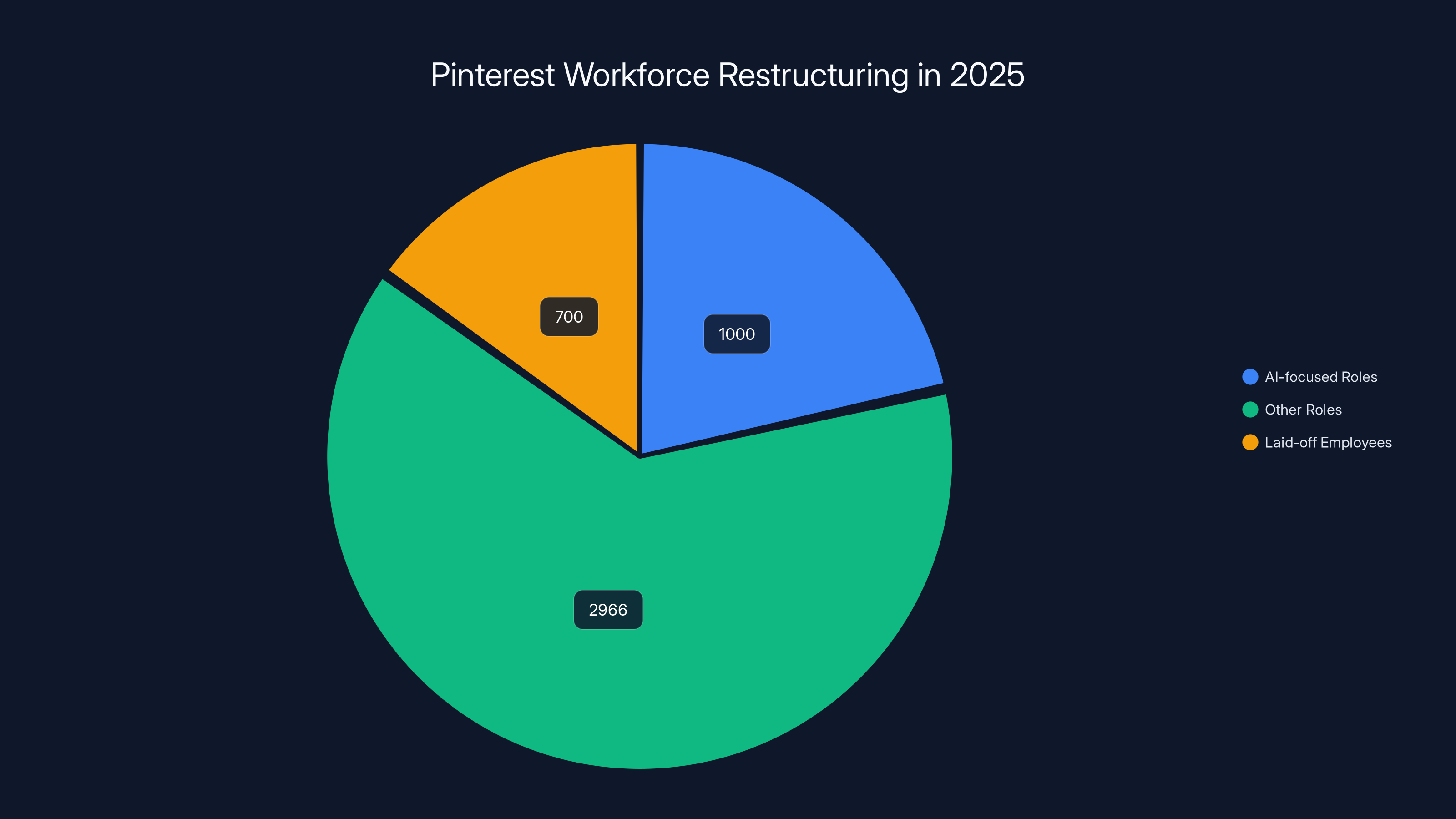
Post-layoff, Pinterest's workforce is expected to have a significant portion dedicated to AI-focused roles, highlighting a strategic pivot towards AI. Estimated data based on workforce restructuring.
The Open-Source AI Advantage
Bill Ready's emphasis on open-source AI models was telling. Why did it matter?
Open-source models like Llama, Mistral, and others democratized access to capable AI. A company no longer needed to build proprietary models from scratch or license from Open AI at premium rates. You could download a proven model, fine-tune it on your data, and run it on your infrastructure.
For Pinterest, this changed the economics dramatically. Building a proprietary visual search AI or recommendation system at scale might cost $500 million or more. Licensing a commercial model might cost tens of millions annually. Fine-tuning and deploying an open-source model costs millions, not hundreds of millions.
This meant Pinterest could afford to distribute AI capabilities across the platform rapidly. Multiple teams could experiment with AI. Features could include AI components without massive infrastructure costs. The company could move from "we're exploring AI" to "every surface has AI" without financial catastrophe.
The open-source strategy also meant Pinterest wasn't dependent on any single vendor. If Open AI changed pricing or introduced competing features, Pinterest had alternatives. That independence mattered strategically.
Of course, there were trade-offs. Open-source models might not match the capabilities of cutting-edge proprietary systems. They require engineering expertise to deploy and optimize. But for Pinterest's use cases, especially personalization and recommendation, they were sufficient and increasingly preferred.

Industry Context: Every Major Platform Is Making Similar Moves
Pinterest wasn't unique in making this shift. The timing and scale varied, but the pattern was universal across major tech platforms.
Google announced layoffs and restructuring around the same period, explicitly citing AI priorities. Meta completed a round of layoffs in 2024 and restructured around "efficiency and AI." Amazon, Microsoft, and others announced significant reallocations toward AI investment.
What distinguished Pinterest was the clarity of the message. Most companies announced layoffs and then vaguely mentioned AI. Pinterest said: "We're cutting positions that don't align with our AI strategy, and we're building an organization optimized for AI development and deployment."
That transparency revealed something uncomfortable for traditional tech employees: having a job in tech now requires being connected to AI in some way. If your role doesn't directly support AI capabilities or operate in an AI-native way, you're vulnerable.
This created a strange dynamic. Technical talent that previously had options across many companies now gravitated toward companies with the clearest AI strategies and the biggest AI budgets. Generalist product managers found themselves less valuable than product managers who understood AI. Marketing professionals who couldn't speak to AI-powered features became less hireable.
For Pinterest, this meant the restructuring would likely improve the average quality of the workforce. The company would retain and attract people who were excited about AI. It would lose people who wanted to build traditional social features. That's not necessarily better overall, but it's better aligned with the company's strategy.

The Timeline and Implementation
Pinterest announced the layoffs in early 2025, with completion expected by late September. That timeline mattered.
Early announcement meant affected employees could start job searches immediately. It meant Pinterest had time to manage the transition carefully rather than rushing. It meant the company could retain key people in critical roles during the restructuring period.
Late September completion meant Pinterest would enter 2026 with its new organizational structure fully implemented. By then, the company would have new AI teams in place, new product directions established, and new product launches planned. The company could announce new capabilities and features from a position of strength rather than explaining ongoing disruption.
The six-month timeline also matched the calendar of tech hiring cycles. Companies typically plan hiring for the fall cycle starting in summer. Pinterest's early announcement meant the company could be ready to make significant hires before competitors had fully committed their budgets.
This wasn't accidental. It was strategic timing designed to maximize the advantage of the restructuring while minimizing the downside.

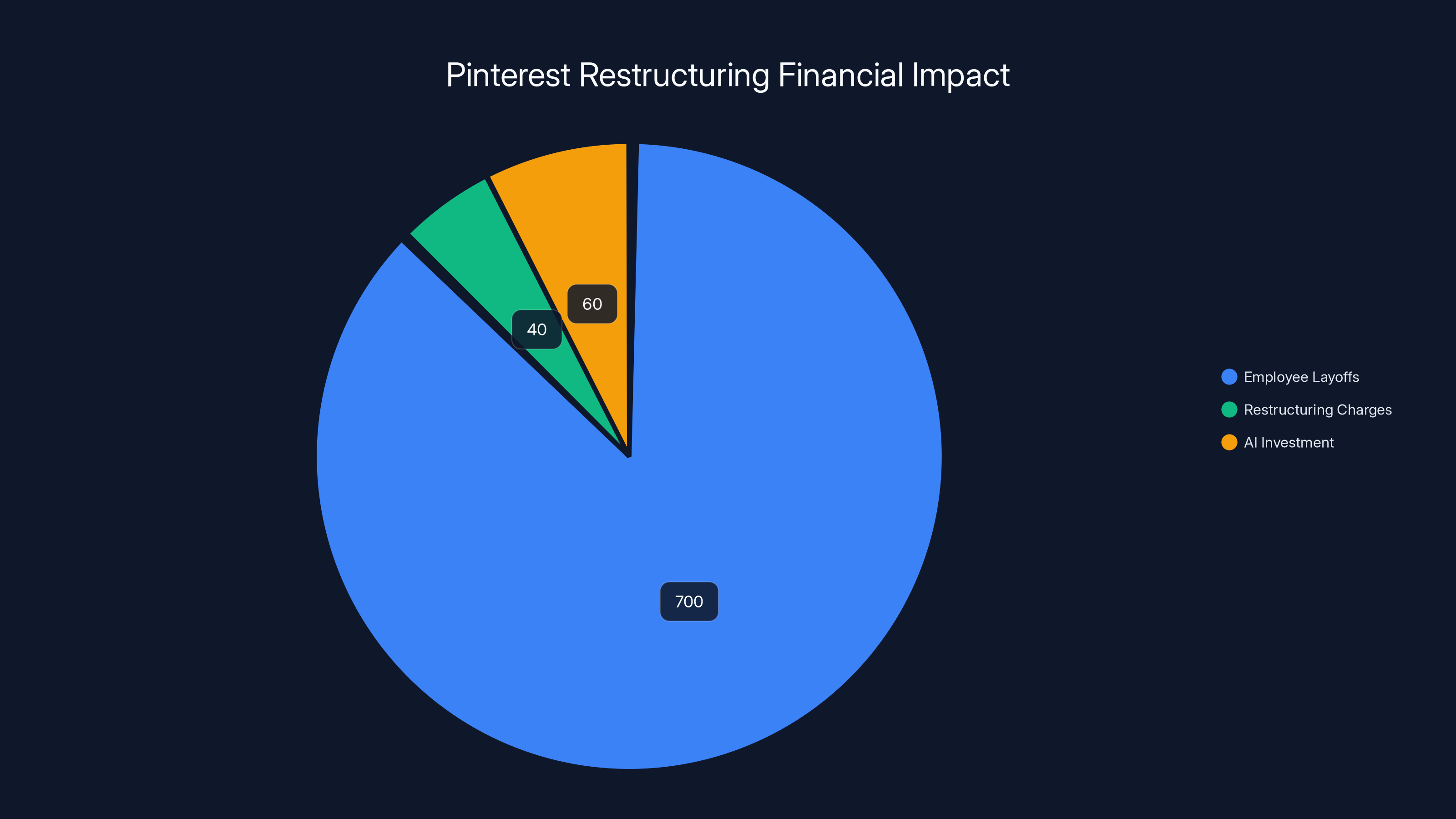
The restructuring involved laying off 700 employees, incurring $35-45 million in charges, and reallocating significant resources towards AI investment. Estimated data.
What About User Experience Changes?
Layoffs often result in product slowdowns. Fewer engineers means fewer features shipped, fewer bugs fixed, fewer customer issues resolved. Would users see a degraded experience during the restructuring?
The risk was real, but Pinterest had some advantages. The company had been investing in automation and AI-powered development tools. Some of the capabilities that new AI teams would build were designed to accelerate engineering productivity. Automated testing, AI-assisted code generation, and ML-powered deployment could offset some of the engineering capacity loss.
Still, there was likely a period where Pinterest shipped less, responded slower to bugs, and moved cautiously on new features. Users might notice longer resolution times on technical issues. Feature launches might slow. But the company counted on the new AI-powered products generating enough excitement to offset these frictions.
Long-term, the restructuring should improve the user experience. AI-powered search, better recommendations, more personalized collections, and smarter content discovery should make the platform more valuable. But there would be a transition period where the platform felt like it was treading water.

The Competitive Implications
Pinterest's move signaled something to competitors. The platform was willing to make dramatic changes to remain competitive in the AI era. It wasn't going to incrementally adopt AI. It was going to build it into everything.
For Tik Tok, this meant Pinterest was becoming a more formidable competitor for visual content discovery. Tik Tok had better real-time video, better social dynamics, better creator tools. But Pinterest was now betting that AI could personalize the experience so well that users would spend more time on Pinterest.
For Google and other search platforms, this meant Pinterest was investing in competing on AI-powered visual search and recommendations. Google had more resources, but Pinterest had focus.
For Instagram and other Meta properties, this meant Pinterest was differentiating through AI rather than trying to copy Meta's social features. Meta would eventually have better AI too, but Pinterest had a head start on this specific application.
The competitive dynamics were shifting. Companies couldn't win on feature parity anymore. They won on capability, personalization, and innovation velocity. Pinterest's restructuring was a bet that the company could outrun competitors on all three dimensions.

The Broader Narrative About Tech Employment
The layoffs also told a story about tech employment that many workers didn't want to hear. The era of building features for feature's sake was over. The era of hiring generalists and figuring out roles later was over. The era of company loyalty and multi-decade tenures at a single company was increasingly anachronistic.
Pinterest's restructuring was just one data point, but it fit a pattern. Tech companies were becoming more ruthless about organizational design. Roles that didn't drive metrics didn't survive. Strategies that didn't generate revenue faced cuts. And most critically, the company's strategic priorities determined employment, not the other way around.
For workers, this meant fewer safety nets. For managers, it meant tougher conversations. For the industry, it meant a faster pace of change and less room for tradition.
Was this sustainable? That was the question hanging over the industry in 2025. Aggressive restructuring generated short-term efficiency gains. But it also damaged culture, hurt morale, and sometimes eliminated institutional knowledge that would be needed later.
Pinterest was betting that the gains from AI investment would be large enough to offset those downsides. Time would tell if that bet paid off.
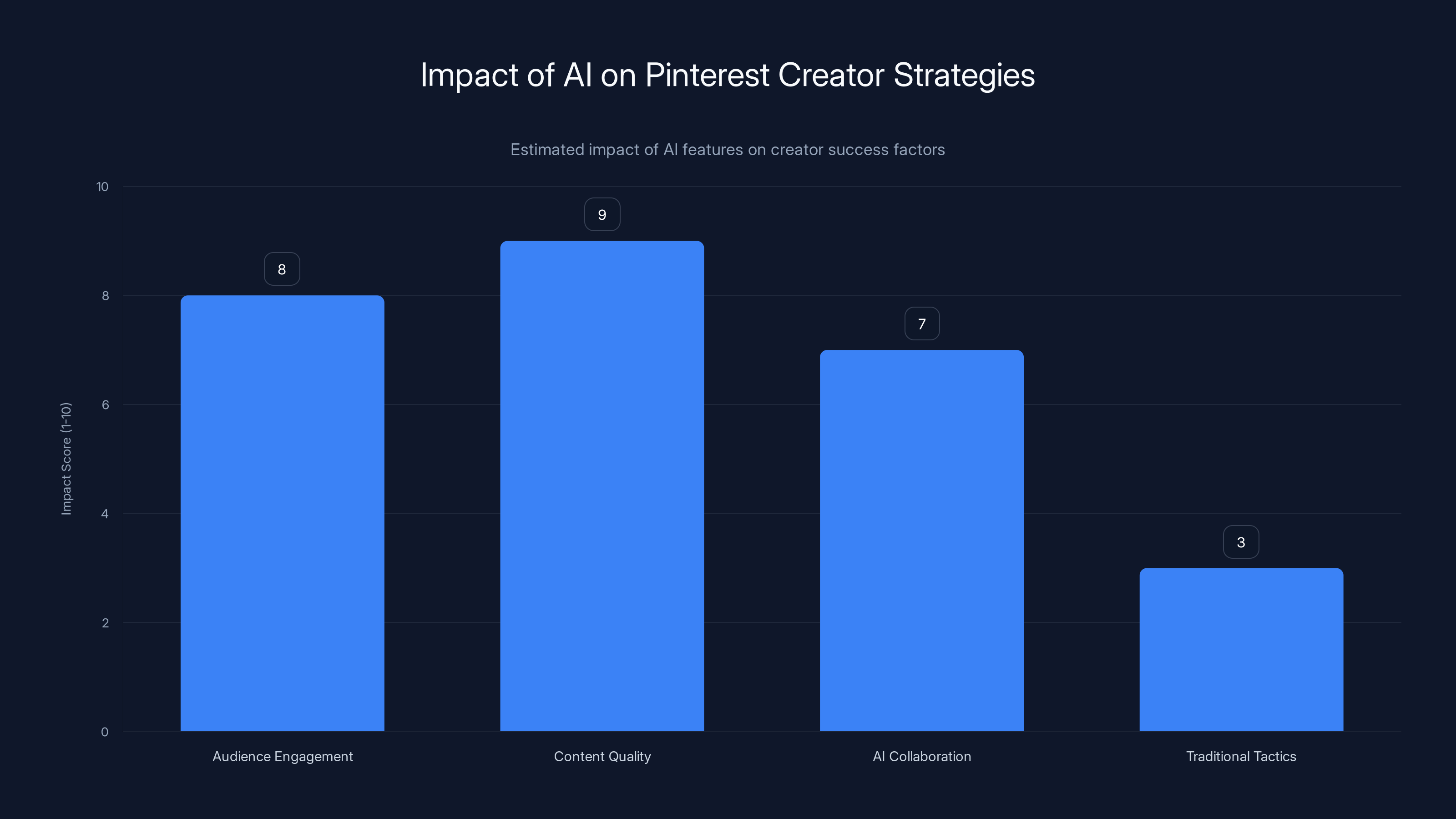
AI features on Pinterest shift focus towards quality content and AI collaboration, reducing the effectiveness of traditional tactics. (Estimated data)
Precedent: How Other Platforms Handled AI Shifts
Pinterest wasn't writing the playbook alone. Other companies had already made similar transitions, though not always as dramatically.
Google reorganized around AI after integrating Deep Mind and investing in transformer models. The company didn't do a single dramatic layoff, but it systematically shifted resources toward AI teams and away from lower-priority projects.
Meta invested billions in AI infrastructure and hired thousands of AI specialists while reducing headcount in other areas. The company's restructuring was explicit about AI priorities.
Amazon shifted toward generative AI capabilities across AWS, Alexa, and advertising while trimming traditional roles that weren't part of the strategy.
Microsoft essentially sold its future on AI by betting everything on the partnership with Open AI, and reorganized accordingly.
Pinterest's move followed the playbook established by these larger competitors. But the company executed with more clarity and speed, which was both an advantage and a risk. An advantage because it signaled conviction and generated faster change. A risk because it left less room for course correction if the strategy proved wrong.
The Role of Open Source in Pinterest's Strategy
We mentioned open-source models earlier, but they deserve deeper analysis because they're central to understanding how Pinterest can execute its AI strategy without competing directly with Open AI or Google on pure capability.
Open-source models democratized AI in a way proprietary systems never could. A company with 5,000 engineers and unlimited budget could build better models than a company with 100 engineers and $50 million. But a company with 100 good engineers and access to great open-source models could build better products than a company with mediocre engineers and proprietary models.
Pinterest falls into the second category. The company has talented engineers, but not Open AI-scale talent. It has a large budget, but not Google-scale budget. But with access to good open-source models, the company could build best-in-class products for its specific use case.
The strategy had another advantage: speed. Building proprietary models takes time. Licensing models takes negotiation. Using open-source models means you can start building immediately.
For Pinterest, this meant the company's AI roadmap could be aggressive because it didn't depend on developing fundamental breakthroughs. It depended on engineering: taking proven models, fine-tuning them on Pinterest's data, and integrating them into products.
This required specific skills. ML engineers who understood fine-tuning, data scientists who knew how to curate training data, product managers who understood where AI added value. These were the roles Pinterest would prioritize in hiring after the restructuring.
Financial Sustainability and Long-Term Viability
Some observers worried that Pinterest's pivot might threaten the company's financial model. Would AI-powered recommendations hurt monetization? Would the platform become less attractive to advertisers?
Actually, the opposite was likely. Better recommendations and smarter personalization improved advertiser value because ads could be more targeted and relevant. A user asking the AI assistant for product recommendations is in a buying mood. That's a premium advertising opportunity.
Pinterest's e-commerce focus (the platform had been building shopping features for years) aligned perfectly with AI capabilities. An AI that understood user preferences and could recommend products was essentially a salesperson for the brands advertising on Pinterest.
The restructuring also improved unit economics. Fewer employees meant lower overhead. Better AI meant better targeting, which meant higher advertiser willingness to pay. Together, these created a more sustainable business model.
The risk wasn't financial sustainability. It was execution. Could Pinterest actually build and deploy the AI capabilities it was planning? Would users adopt the new features? Would the company attract and retain the AI talent it needed?
These questions couldn't be answered until the products shipped and users responded. But the financial logic was sound.

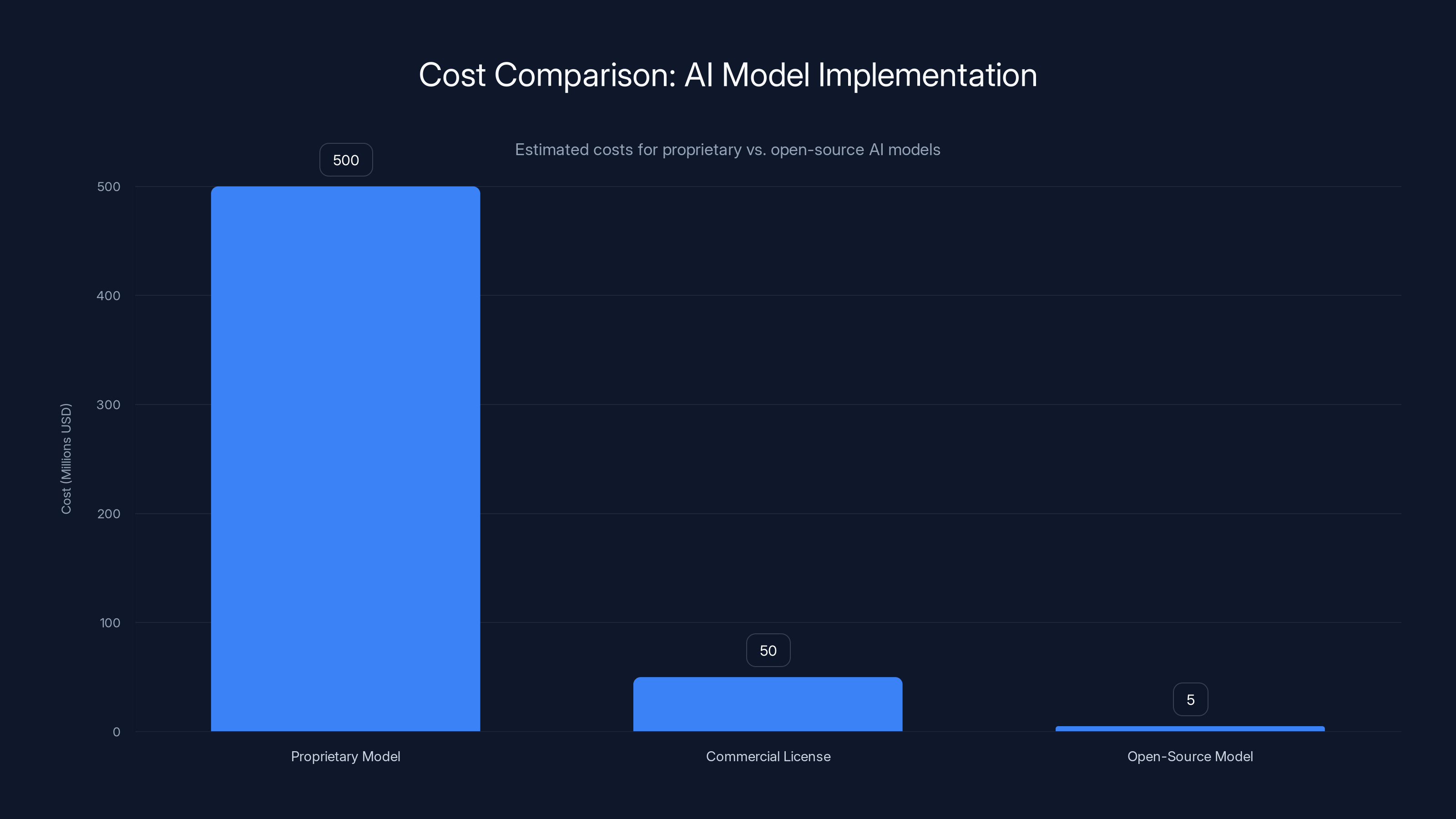
Estimated data shows that open-source AI models can be implemented at a fraction of the cost of proprietary models, enabling broader AI integration.
What the Restructuring Reveals About Company Culture
Layoffs are traumatic for the people affected and for the people who remain. Some companies try to soften the blow with generous severance, placement services, and communications designed to minimize guilt.
Pinterest took a different approach. The company was direct about why the layoffs were happening and what the company was betting on. This was actually more respectful in some ways. Affected employees understood that they were losing their jobs because of a strategic shift, not because they were bad at their jobs. They had a clear narrative.
For remaining employees, the message was equally clear: "You have a role in the AI future. The company is betting on you. Your skills matter now more than they did before."
This created a cultural split. There were the people who stayed (who might feel lucky and energized) and the people who left (who might feel resentful but understood the reason). Neither group would be confused about what happened or why.
The culture would change, though. A company that can make a decisive cut of 15% of its workforce will be perceived as ruthless. Employees will know that all jobs are contingent on remaining strategic. They'll be less inclined to plan long-term careers at the company. But they'll also be more focused on creating value.
This kind of culture is common in startup-like settings and in highly competitive industries. It's unusual in mature platforms, but the AI era made it necessary. Companies couldn't afford the luxury of managing through attrition or easing people into new roles.
Predictions: What Comes Next for Pinterest
Based on the restructuring's timing and focus, several developments were predictable.
First, Pinterest would launch new AI-powered features rapidly. Within six months of the layoff completion, expect announcements around AI-powered search, AI-powered recommendations, and possibly new forms of content creation assisted by AI.
Second, the company would announce new hires. Not to replace the people laid off, but to fill specific AI-focused roles. These announcements would emphasize deep learning expertise, data science skills, and product capabilities in AI.
Third, investor presentations would focus heavily on AI metrics. Monthly Active Users would still matter, but engagement, retention, and especially "AI feature adoption" would become the key metrics investors watched.
Fourth, Pinterest would explore partnerships with AI infrastructure companies. The company likely couldn't build all of its own AI systems. Partnerships with companies specializing in recommendation engines, NLP, or computer vision would accelerate development.
Fifth, creator communications would emphasize opportunity. Pinterest would message that AI-powered discovery was good for quality creators and bad for low-quality content. This would help creators understand the change and adapt.
Finally, competitive positioning would shift. Pinterest would stop competing on social features (where it could never beat Meta) and compete on discovery and shopping (where AI capabilities could create advantage).

The Regulatory and Ethical Dimensions
Pinterest's AI pivot raised questions about data usage, algorithmic bias, and market competition.
Data usage: Pinterest had billions of pins saved by hundreds of millions of users. Training AI models on this data generated value for the company. But did it compensate users for the value of their data? Did it protect privacy? These questions weren't unique to Pinterest, but they mattered for user trust.
Algorithmic bias: AI-powered recommendations could amplify biases in training data. If the platform had more data about certain demographics' preferences, the AI might serve biased results. Pinterest would need to monitor and correct for this.
Market competition: As Pinterest invested in AI, would it have advantages that competitors couldn't replicate? Or would open-source models level the playing field? This had implications for antitrust, platform power, and market concentration.
Pinterest didn't announce specific strategies around these issues. They were problems for later. But they would eventually need to be addressed as the AI features matured and faced user scrutiny.
The Macro Story: Why This Matters Beyond Pinterest
Pinterest's restructuring was a microcosm of a larger shift happening across the tech industry. Companies were reorganizing around AI. Talent was migrating toward AI-focused roles. Capital was flowing toward AI investment. The industry was making a bet that AI would be the primary driver of competitive advantage for the next decade.
Was that bet correct? Evidence suggested it was. Companies with better AI capabilities were growing faster, engaging users more deeply, and creating more defensible competitive positions. The companies that moved faster on AI in 2024 and 2025 would likely be the winners in 2030.
Pinterest, by making a decisive move, was positioning itself to be one of those winners. Or it was making a catastrophic mistake if AI turned out not to be as valuable as the company believed. But in the zero-sum competition of social platforms, there wasn't a safe middle ground. Companies had to bet big on the direction they believed the market was heading.
Pinterest bet on AI. The layoffs were the company putting its money where its mouth was.

Conclusion: The Restructuring as Strategic Inflection Point
Pinterest's decision to lay off 15% of its workforce and reallocate resources toward AI represented more than an operational adjustment. It was a strategic inflection point, the moment when the company committed to a new identity and capability set.
The numbers were significant: 700 employees, $35-45 million in restructuring charges, completion by late September. But the numbers were less important than the message. Pinterest was saying that the era of traditional social platform features was over, at least for the company. The future was AI-powered discovery, AI-assisted content curation, and AI-informed monetization.
Would the strategy work? Only time would tell. There were risks. The company might struggle to hire and retain AI talent. The new features might not resonate with users. Competitors might move faster or build better AI. The restructuring might damage the culture enough to hurt execution.
But there were also significant opportunities. Better personalization could increase user engagement. Smarter recommendations could increase advertiser value. AI-powered features could open entirely new use cases. The company could become a leader in applied AI for visual discovery and shopping.
For workers who lost their jobs, the restructuring was painful. For those who remained, it created both opportunity and uncertainty. For the industry, it was another signal that AI capabilities would determine success or failure.
Pinterest had spoken. The company was going all-in on AI. What that meant for the platform, the users, the creators, and the industry would unfold over the next one to two years. This wasn't just a layoff. It was a bet on the future.

FAQ
Why did Pinterest lay off 15% of its workforce?
Pinterest announced the layoffs to reallocate resources toward AI-focused initiatives. The company explicitly stated it wanted to redirect spending toward roles and teams that drive AI adoption and the development of AI-powered products and capabilities. Rather than gradual resource shifting, the company chose to make a decisive restructuring to move faster and signal strong commitment to AI strategy.
How many employees were affected by Pinterest's layoffs?
With Pinterest having 4,666 full-time employees at the end of 2024, the 15% reduction meant approximately 700 employees were affected by the layoffs. The company expected to complete the restructuring by late September 2025, meaning affected workers had several months to prepare and search for new opportunities.
What AI products has Pinterest already launched?
Pinterest launched "Pinterest Assistant," an AI companion that users can interact with for shopping advice, product recommendations, and inspiration. The platform was also experimenting with AI-powered personalized boards that dynamically learn user preferences and adjust recommendations over time. These products formed the foundation for the company's broader AI strategy.
How does this restructuring affect Pinterest creators?
Creators on Pinterest benefit from AI-powered discovery pathways beyond just the traditional feed algorithm. Instead of competing solely in the feed, creator content now competes in AI-powered recommendation systems. Quality, value-driven content that answers specific user questions performs better in AI-curated environments. However, the shift also means traditional engagement-focused tactics are less effective since AI optimizes for user value rather than engagement metrics.
Will Pinterest's AI strategy improve the user experience?
Long-term, the AI strategy should significantly improve user experience through better personalization, smarter recommendations, and more intuitive discovery. However, there may be a transition period where Pinterest ships fewer features and responds slower to issues as the new AI teams establish themselves. Once the AI-powered products fully launch, users should see dramatically better content discovery and product recommendations aligned with their preferences.
How does open-source AI fit into Pinterest's strategy?
Pinterest CEO Bill Ready emphasized the importance of open-source AI models in managing costs while building advanced capabilities. Rather than building proprietary models from scratch or licensing expensive commercial systems, the company can fine-tune proven open-source models on its own data. This approach gives Pinterest speed, cost efficiency, and independence from any single vendor while requiring specific engineering expertise to implement effectively.
What are the restructuring charges Pinterest expects?
Pinterest expected to record pre-tax restructuring charges of
How does this compare to other tech companies' AI pivots?
Pinterest's restructuring followed a pattern established by Google, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft, which all reorganized around AI investment in 2024 and 2025. However, Pinterest executed with more clarity and speed, explicitly tying the layoffs to AI strategy rather than vague efficiency goals. This directness and specificity distinguished Pinterest's approach and signaled stronger conviction about the company's AI-first future.
Key Takeaways
- Pinterest laying off 700 employees (15% workforce) to prioritize AI-focused roles and capabilities
- Restructuring reflects industry-wide pattern of major platforms reorganizing around artificial intelligence investment
- Open-source AI models give Pinterest cost-efficient path to advanced capabilities without massive R&D spending
- AI-powered features like Pinterest Assistant and personalized boards create new user engagement and monetization opportunities
- Companies moving fastest on AI in 2024-2025 are positioning themselves as winners in next-generation competitive landscape
Related Articles
- Pinterest Lays Off 15% for AI: What This Means for Tech [2025]
- Why AI Projects Fail: The Alignment Gap Between Leadership [2025]
- Enterprise Agentic AI Risks & Low-Code Workflow Solutions [2025]
- Modernizing Apps for AI: Why Legacy Infrastructure Is Killing Your ROI [2025]
- The AI Adoption Gap: Why Some Countries Are Leaving Others Behind [2025]
- BBC's YouTube Strategy and the TV Licence Crisis [2025]
![Pinterest Layoffs 15% Staff Redirect Resources AI [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/pinterest-layoffs-15-staff-redirect-resources-ai-2025/image-1-1769536180106.jpg)



