1 Password Phishing Protection: How the New Browser Feature Saves You [2025]
Introduction: The Phishing Crisis That AI Made Worse
You're sitting at your desk, coffee getting cold, checking your email. A message lands from what looks like your bank. The logo's perfect. The button says "Verify Account" and looks clickable. The urgency feels real.
Then your finger hovers. Something feels off.
Two years ago, this moment would've been easier. Bad phishing attempts had spelling errors. Weird fonts. Obvious tells that screamed "scam." Now? AI has changed everything. Scammers can generate perfect copy in seconds. Design tools spit out convincing layouts. The old rules don't apply anymore.
According to recent industry data, 60% of companies reported increased fraud losses between 2024 and 2025. That's not just a bump. That's a crisis accelerating in real time.
1 Password just released a feature that might actually matter in this fight. It's called phishing protection, and it does something almost elegant: it pauses the moment you're about to destroy your own security.
Here's what you need to know, and why it matters more than you probably think.
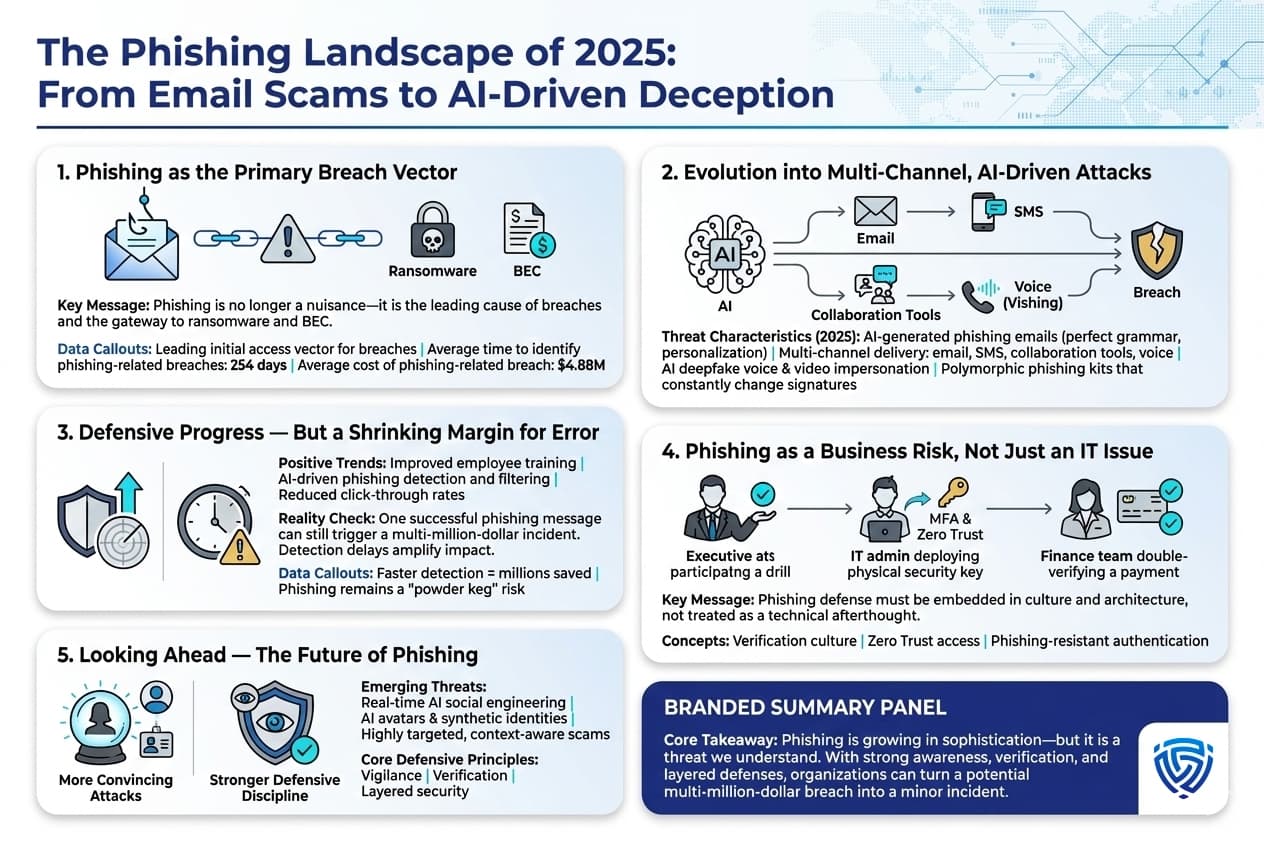
1Password's phishing protection can reduce phishing success rates by up to 50%, outperforming browser warnings and email filters. Estimated data based on typical effectiveness.
TL; DR
- What it does: The 1 Password browser extension now detects when you're trying to paste login credentials into a fraudulent website and blocks you with a warning
- How it works: Uses DNS checking and domain validation to catch spoofed sites before you hand over passwords
- When it helps most: That split-second decision point where you've already entered credentials but haven't committed yet
- The catch: Only works on websites, not on other contexts, and requires the 1 Password extension to be installed and active
- Bottom line: It's a genuinely useful second layer, not perfect defense, but absolutely worth having enabled
The Phishing Landscape in 2025: Why Old Protection Doesn't Cut It Anymore
Phishing isn't new. It's been around since the early days of email, and the concept is dead simple: trick someone into giving you their password, then use it to steal their identity or money.
What changed is the difficulty of execution. A decade ago, pulling off a convincing phishing attack required actual skill. You needed to understand web design. You needed to reverse-engineer login pages. You needed to host infrastructure and keep it hidden from authorities.
All of that created friction. Friction meant most attackers couldn't scale. They hit maybe a few hundred people with handcrafted attacks.
AI removed the skill requirement. Now, a moderately determined person can:
- Use Chat GPT to write a convincing email that sounds like it comes from their target's bank
- Use Canva or design AI to create logo-perfect graphics in under a minute
- Use Figma templates to build a login page that's pixel-perfect
- Spin up a domain that looks almost identical to the real one
- Deploy it all before breakfast
The barrier to entry collapsed. The volume exploded.
Traditional defenses broke, too. Email filters catch obvious stuff. But they miss the subtle things. Typos in unusual places. Slightly off domain names. Grammar that's almost perfect but not quite. When AI writes these, the filters can't distinguish them from legitimate mail.
That's where the human element still matters. You. Your eyeballs. Your instinct.
But you're tired. You're distracted. You have 147 emails in your inbox, and a message that says "Urgent: Verify your account" hits different when you're multitasking.
This is where 1 Password's new feature steps in.
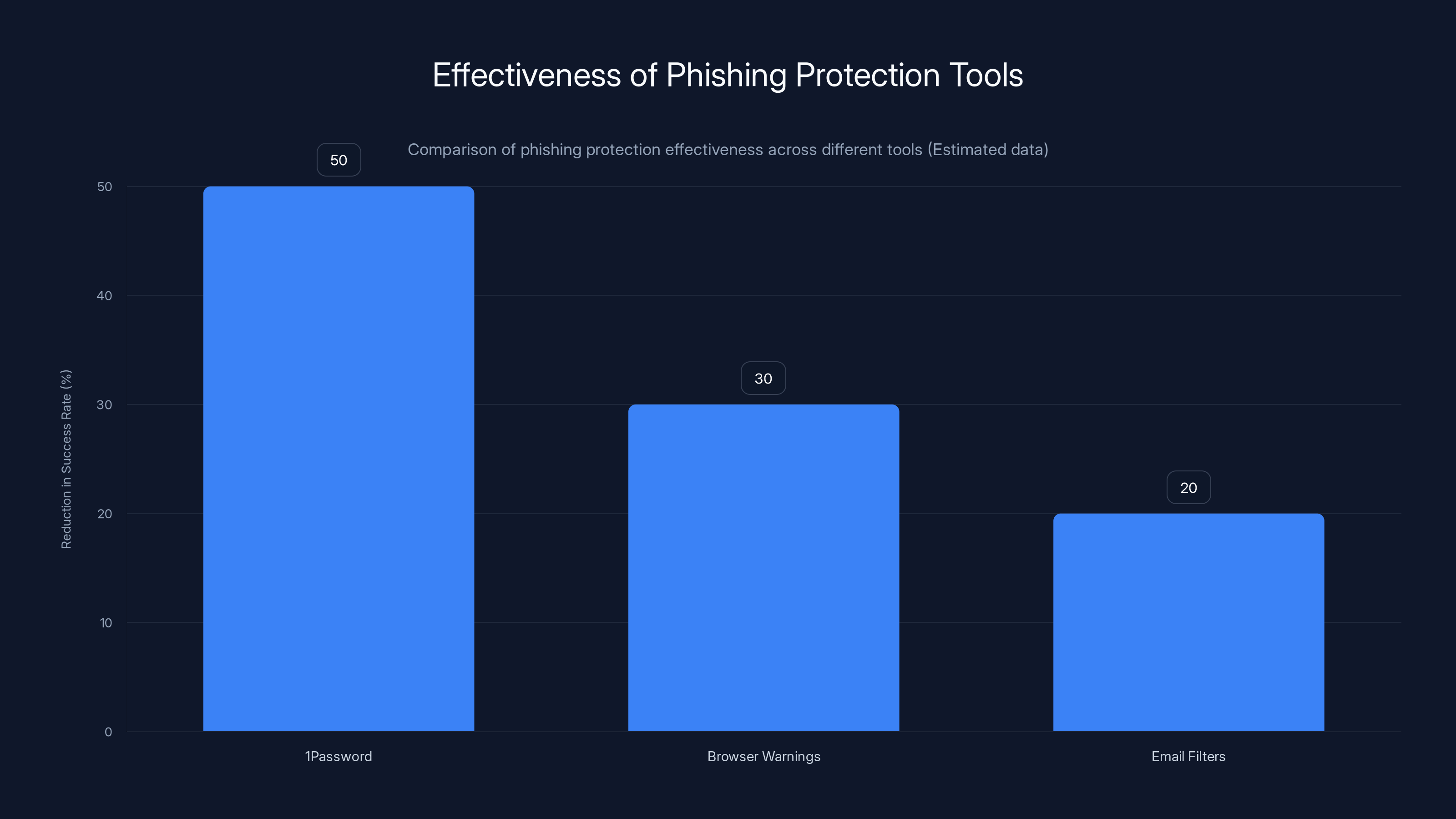
The annual cost of 1Password is $60, while the benefits, including time savings, security, and stress reduction, can provide significant value, with an ROI of 8:1 just from preventing one phishing attack. Estimated data.
How 1 Password's Phishing Detection Actually Works
The feature is deceptively simple in concept, but the engineering underneath is more interesting than you'd think.
When you use the 1 Password browser extension (available for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari), it's doing something in the background. It's watching.
Specifically, it's watching your clipboard. Not in a creepy way (well, not more creepy than every other extension). When you copy your password from 1 Password and go to paste it somewhere, the extension intercepts that moment. That's the crucial second.
Here's what happens next:
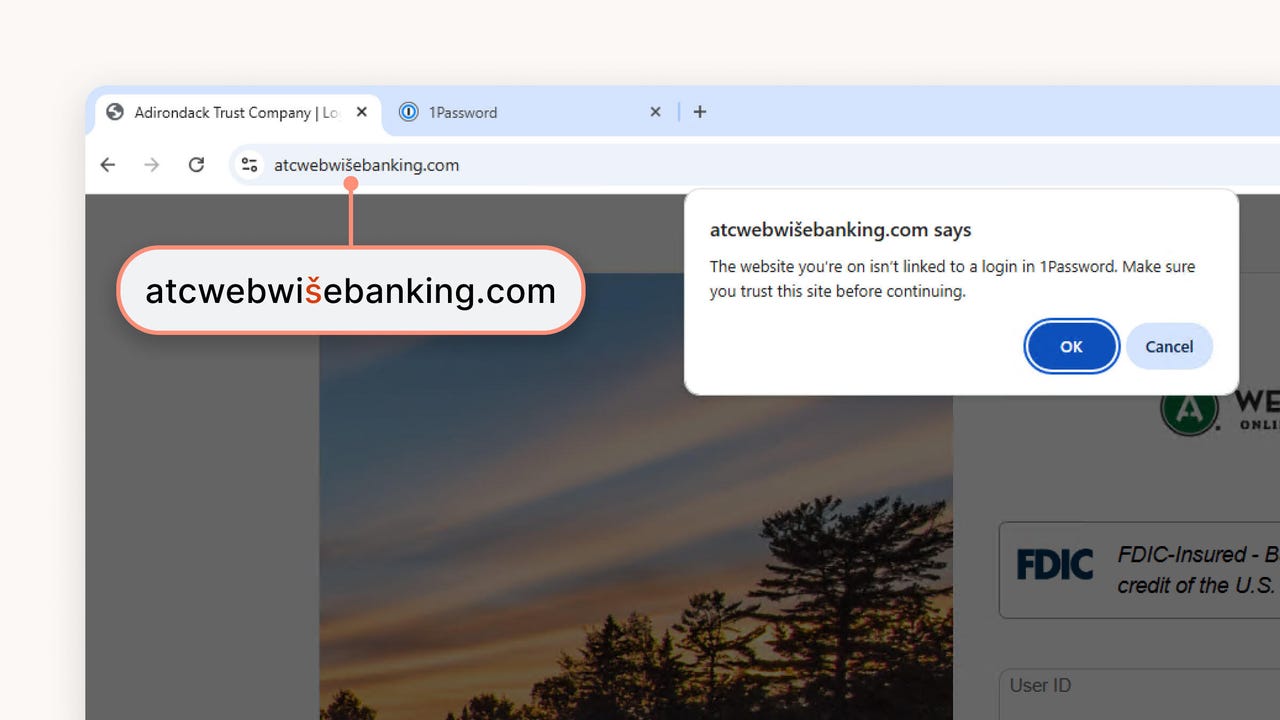
The extension checks the domain you're currently on. It compares it against known legitimate domains for the service you're about to log into. It checks SSL certificates. It verifies that the website's DNS record actually resolves to the company's real servers, not some attacker's infrastructure in a data center halfway around the world.
If everything checks out: you paste. Life continues. You never notice it happened.
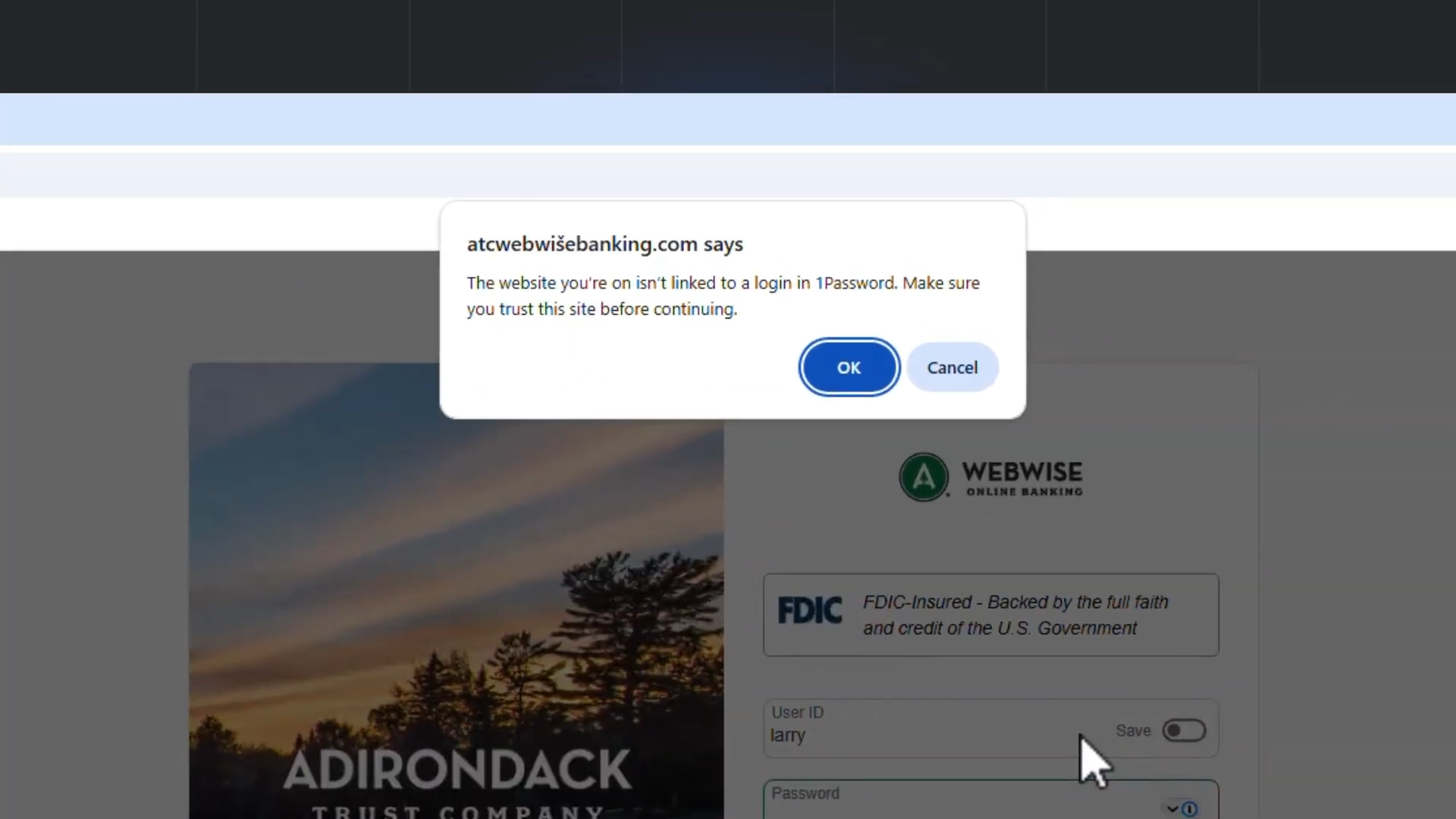
If something's off? The extension shows a warning. Not a soft suggestion. A real, impossible-to-miss warning that says "Hey, this might be fake. Are you absolutely sure?"
The key difference between this and other security warnings you ignore is timing. When you get a browser warning about an insecure certificate, you're already committing. You've already entered your password. The moment's passed. You click through or you don't, but the damage is already done either way.
1 Password's check happens before the paste. You haven't committed. You haven't exposed yourself. The friction is before the point of no return, not after.
This matters psychologically. When you're about to paste your password, you're in a high-stakes moment. Your brain's in "authentication mode." A warning at that exact second has maximum impact.
The Psychology of That One Moment
1 Password's own description of this feature uses language worth pulling apart: "That single moment of pause, that tiny bit of friction, is often all it takes to disrupt the attackers' entire plan."
There's real security thinking packed into that sentence.
Attackers count on momentum. They've worked to get you to this point. They've sent a convincing email. They've gotten you to click a link. They've convinced you that you need to verify your account, confirm your identity, or resolve some urgent problem.
You're moving at speed. You're not thinking clearly. You're reacting.
The best defense at this moment isn't complexity. It's friction.
A pause. A tiny doubt. A warning that makes you reconsider.
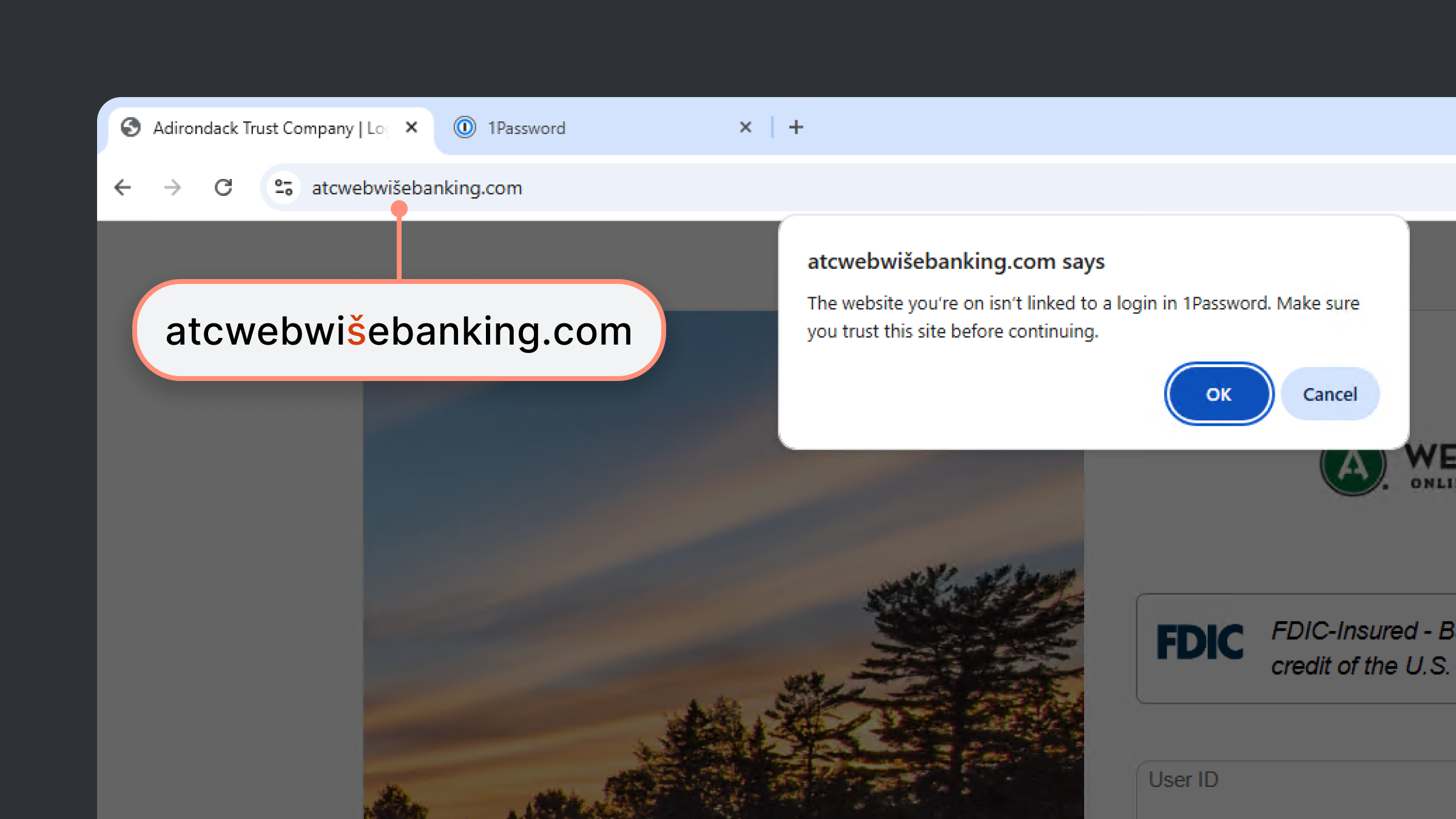
That's when you actually look at the URL. That's when you notice it says paypa 1.com not paypal.com. That's when your brain switches from reaction mode to analysis mode.
Research on phishing effectiveness bears this out. When users are forced to slow down, even slightly, phishing success rates drop dramatically. One study showed that adding a 2-second delay to login processes reduced phishing success by up to 50%.
The elegance of 1 Password's approach is that it creates that friction at exactly the right moment. Not before you've decided to enter your credentials, when you'd just get annoyed and turn off the protection. Not after you've committed, when it's too late. Right there, hand on the paste button.
Real Threats That This Feature Actually Prevents
Let's get specific. This isn't theoretical.
Scenario one: You're a small business owner. Your accountant's email gets compromised. An attacker sends you a message claiming there's been unusual activity on your business bank account. Click here to verify. The link looks right. The design looks right. You click.
The page loads. It looks like your bank. You enter your username. You paste your password from 1 Password.
The extension catches it. The domain is secure-banking-verification.com, not your actual bank's domain. It throws a warning.
You stop. You verify the real website by going directly to your bank's app instead. You realize you almost got robbed.
Scenario two: You work at a company with sensitive data. Your IT person sends an email about a critical security patch. Everyone needs to re-authenticate with new credentials. Click here.
You click. The page looks legitimate. You're about to paste your corporate password from 1 Password.
The extension warns you. The domain isn't your company's actual single sign-on server. You report it to your actual IT team, and they confirm it was a phishing attempt targeting your entire company.
Scenario three: You've been shopping online. An email arrives saying you need to verify your payment method. Click here.
The page loads. Credit card form looks standard. You're about to paste the card number from 1 Password.
It warns you. You check the actual website directly and realize the email was spam.
These aren't edge cases. These happen thousands of times a day.
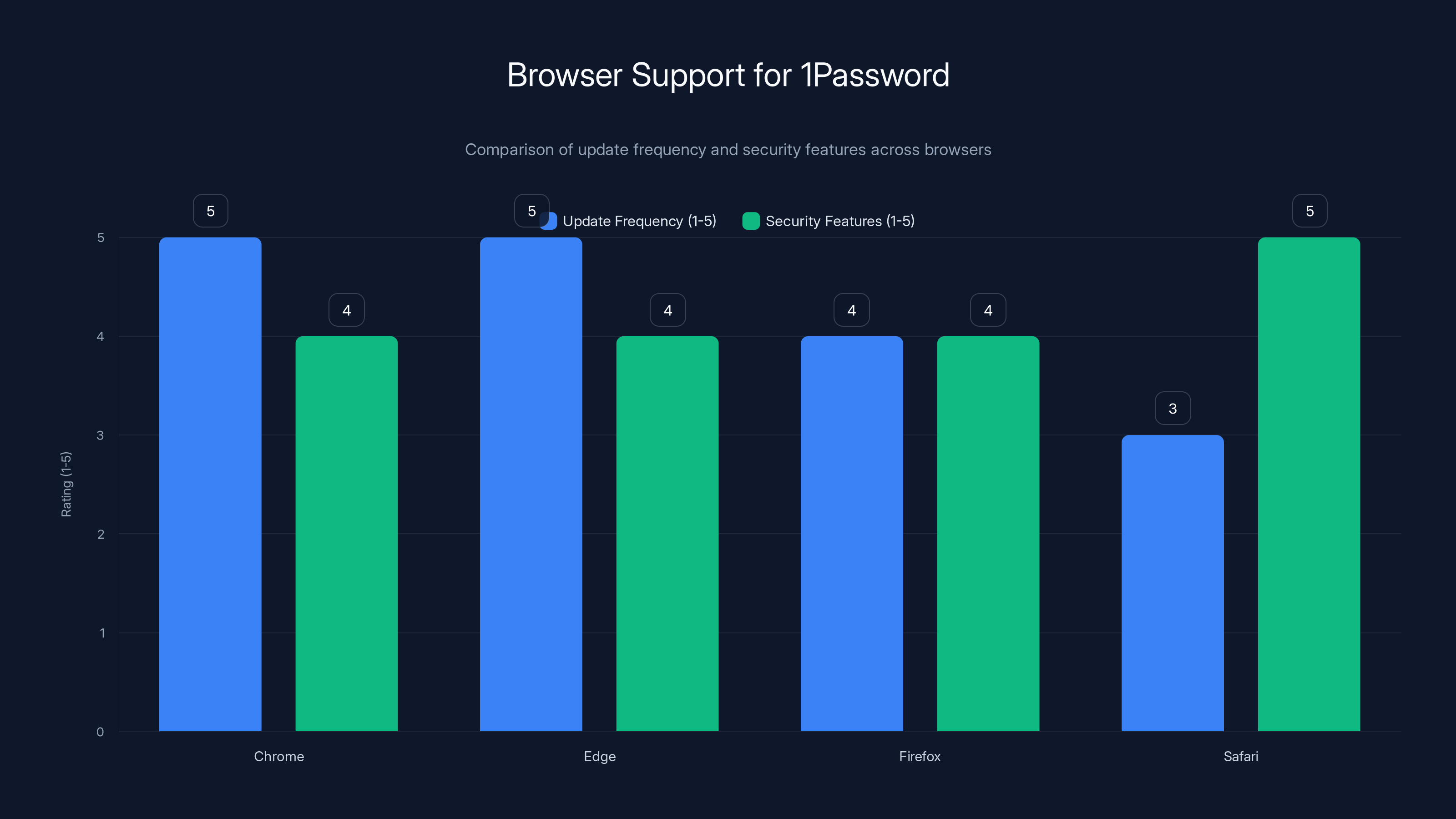
Chrome and Edge receive the quickest updates, while Safari offers the most restrictive security features. Estimated data based on browser characteristics.
What Makes 1 Password's Approach Different Than Other Tools
Other password managers exist. Bitwarden, Dashlane, Last Pass, and others all have browser extensions. Some of them warn you about breached passwords. Some block obvious domain mismatches.
But 1 Password's approach is different in a specific way.
Most warnings are passive. You see a notification, and then the action happens anyway. The browser still loads the page. The form still appears. You still have to actively dismiss the warning.
With 1 Password's implementation, the block happens at the paste moment. The extension isn't preventing you from accessing the website. It's preventing the specific action of pasting a credential into a suspicious site.
That's a crucial distinction.
It's also worth noting what this isn't: It's not a phishing filter that blocks you from visiting suspicious websites entirely. It's not a tool that prevents you from entering credentials by hand. It's specifically about the moment when you're using 1 Password's auto-fill or clipboard feature.
If you manually type your password into a phishing site, this won't help. If you get tricked and click a link that you then manually enter credentials into, this won't stop you.
It's a tool for a specific, common scenario: You trust the website enough to use your password manager, but the website might actually be fake.
Technical Deep Dive: How Domain Verification Works
Let's get into the actual security mechanisms at play here, because understanding them helps you understand why this matters.
When the 1 Password extension checks a domain, it's doing several things simultaneously:
DNS Verification: The extension queries the Domain Name System to see if the domain you're visiting actually resolves to legitimate servers. If you're on paypa 1.com and 1 Password knows that this domain resolves to a server in Bulgaria, but Pay Pal's real servers are in California, something's wrong.
SSL Certificate Validation: Modern browsers check SSL certificates, but 1 Password does its own check too. A legitimate site has a certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority. The certificate matches the domain name you're visiting. A phishing site either has no certificate (red flag), a self-signed certificate (bigger red flag), or a certificate for a different domain (biggest red flag).
Domain Similarity Analysis: Sometimes attackers register domains that look almost identical to real ones. rn instead of m. Numbers that look like letters. The extension can flag these. If you're about to paste credentials meant for facebook.com into faceb 00k.com, it should catch that.
Known Phishing Database Checks: 1 Password likely checks against databases of known phishing domains. Services like Google Safe Browsing maintain lists of malicious websites. If a domain appears on these lists, it gets flagged immediately.
Expected Domain Matching: When you're pasting credentials for a specific service, 1 Password knows which domains are legitimate for that service. If you're pasting your Facebook password, 1 Password knows it should go on facebook.com or a small set of legitimate Facebook-owned domains. If it tries to go anywhere else, that's a red flag.
The combination of all these checks is what creates the protection. No single one is perfect. Attackers can sometimes spoof DNS. They can sometimes get valid certificates. They can sometimes use legitimate domain variations.
But all of them together? That's much harder to fake.
The Economics of Phishing: Why This Matters at Scale
Here's something most people don't think about: Phishing is a numbers game, and it's an economics problem.
An attacker sends out 10,000 phishing emails. Let's say they have a 2% success rate. That's 200 people who fall for it. Even if each account is only worth
But if 1 Password's protection converts some of those 200 into successes that fail at the last moment, the economics change.
Let's say the protection stops half the attacks at the critical moment. Now the attacker only succeeds with 100 people instead of 200. The ROI drops in half. They might move on to easier targets or different attack vectors.
Multiply this across millions of users, and 1 Password's feature could genuinely shift the attacker economics for certain types of phishing.
Attackers aren't stupid. They optimize. If a particular attack method stops working consistently, they change tactics. A tool that creates friction at a specific point in the attack chain makes that attack vector less attractive.
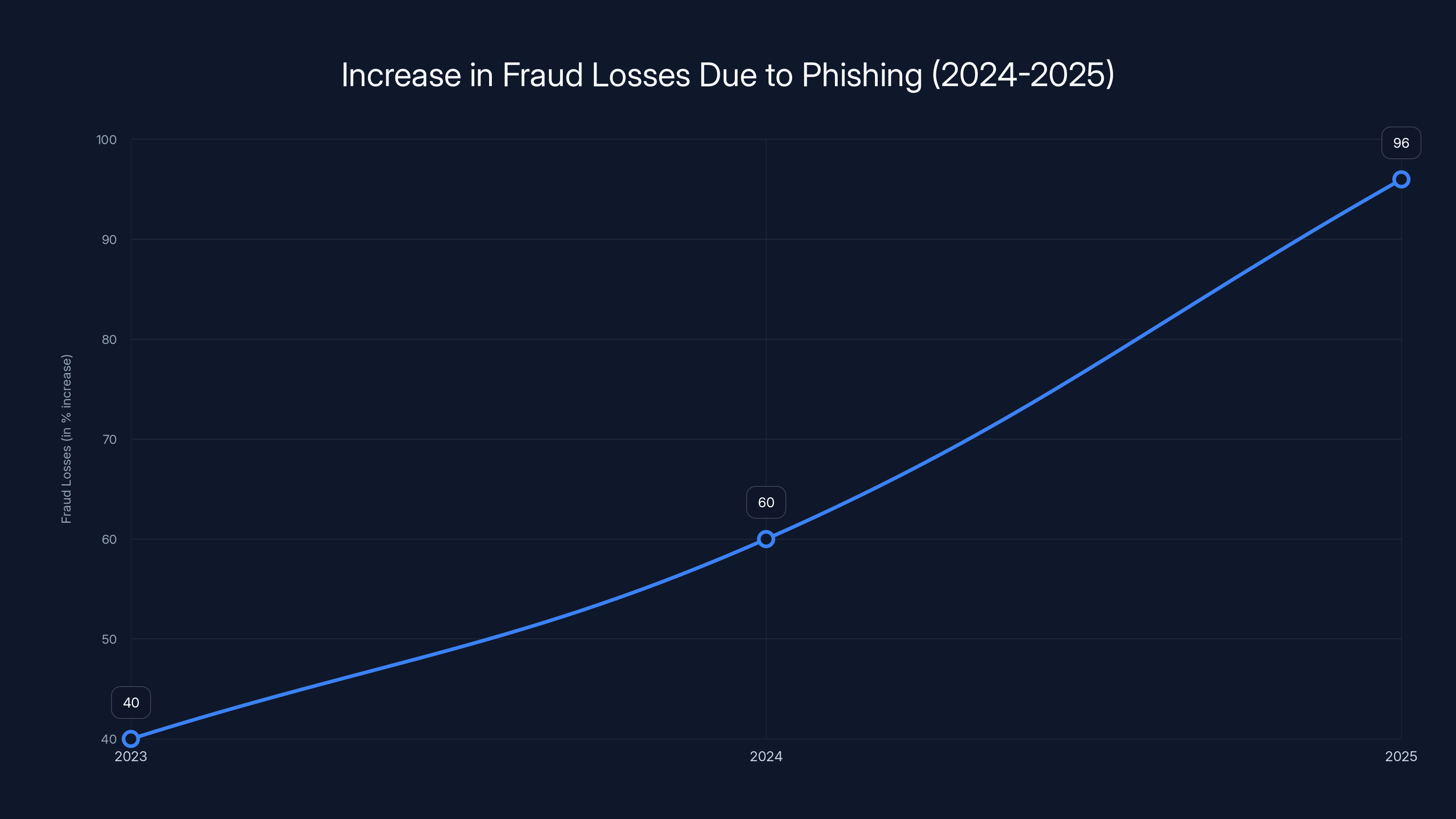
Fraud losses due to phishing increased by 60% from 2024 to 2025, highlighting the growing threat of AI-enhanced scams. Estimated data.
When This Protection Works (And When It Doesn't)
Let's be honest about the limitations, because security is about understanding what protects you and what doesn't.
This protection works when:
You're using 1 Password's extension and auto-fill features. You're trying to paste credentials into a website. The website's domain is actually different from what you think it is. You haven't disabled the warning feature.
This protection doesn't work when:
You manually type credentials instead of pasting them. The phishing website has somehow gotten a legitimate SSL certificate for its domain (possible but rare). You're on a mobile app instead of a browser. The phishing site has somehow cloned the legitimate domain's DNS records (requires more sophisticated attacks). You've disabled the feature. The attacker gains access through other means (malware, keyloggers, social engineering without phishing).
The honest assessment is this: It's a real security improvement, but it's not a complete solution. Nothing in security is.
How to Actually Use This Feature Effectively
Knowing a feature exists is different from actually benefiting from it. Here's how to make 1 Password's phishing protection actually work for you.
Step One: Install and Update
Make sure you have the latest version of the 1 Password browser extension. Go to your browser's extension store and verify you're on the current version. 1 Password updates happen regularly, and this feature might not exist in older versions.
Step Two: Enable Notifications
Go into 1 Password's settings. Look for security or warning preferences. Make sure phishing warnings are set to notify you. Some people turn off extension notifications to reduce spam. Don't do that for 1 Password. These warnings matter.
Step Three: Use Auto-Fill Consistently
This feature works best when you're actually using 1 Password to manage your credentials. If you use different password systems for different sites, you lose the protection on sites where you manage passwords manually.
The more you let 1 Password handle your credentials, the more protection you get.
Step Four: Read the Warnings
When 1 Password warns you, don't dismiss it casually. Take 5 seconds. Look at the domain. Verify that you're actually on the site you meant to be on. Open a new tab and go directly to the real site. Compare.
The warning is there for a reason.
Step Five: Report Bad Actors
If you encounter a phishing site, report it. Most browsers have "Report unsafe site" options. So do FBI cybercrime reporting systems. The more data security companies have about attacks, the better their defenses become.
The Broader Phishing Trend and Why AI Made It Worse
Phishing didn't start with AI, but AI absolutely accelerated it.
Before AI, there was a skill gradient. Simple phishing attempts came from low-skill attackers. Sophisticated attacks came from organized crime groups with resources. There was a middle tier that didn't really exist.
AI collapsed that gradient.
Now a teenager with no cybercrime experience can generate convincing phishing emails. Anyone can create a professional-looking fake login page. The skill bar went from "requires training and practice" to "requires a Chat GPT subscription."
What makes this especially bad is that traditional defenses relied partly on that skill gradient. Email filters looked for the kinds of mistakes that unskilled attackers made. Phishing sites had design flaws that tipped people off.
When the mistakes disappear, the filters struggle.
Security vendors are responding with AI-powered defenses. 1 Password's approach isn't ML-based; it's more traditional domain verification. But other tools are using AI to detect AI-generated phishing emails, looking for subtle patterns that still exist even in AI-written content.
It's an arms race, and the playing field got a lot more competitive when AI entered it.

Estimated data shows that 1Password's protection can reduce successful phishing attacks by 50%, significantly altering attacker ROI.
Comparing 1 Password's Protection to Other Security Layers
1 Password's phishing protection isn't the only tool in the security arsenal. Let's see how it compares to other approaches.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
This is still the gold standard. Even if you give your password to attackers, MFA stops them from accessing your account. The 1 Password feature prevents you from entering your password in the first place.
Both are valuable. MFA is more comprehensive. 1 Password's feature is more preventative.
Email Filters
Email filters catch obvious phishing emails before they reach you. 1 Password's feature handles cases where the email was convincing enough that you clicked it.
Email filters handle volume. 1 Password handles sophistication.
Browser Warnings
Modern browsers warn you about unsafe sites. But these warnings often come too late or are easy to ignore. 1 Password's warning is specifically timed to when it matters most.
DMARC, SPF, DKIM
These are email authentication protocols that make it harder to spoof email addresses. They're excellent but don't prevent people from creating phishing websites that look legitimate.
Antivirus and Malware Protection
These handle different threats. Phishing is social engineering. Malware is code. They're complementary approaches.
The reality is that security works in layers. No single tool stops all attacks. But each layer that you add increases the attacker's effort and decreases their success rate.
Setting Up 1 Password: Installation and Configuration
Getting 1 Password set up properly is straightforward, but there are choices that affect how much protection you actually get.
Browser Support
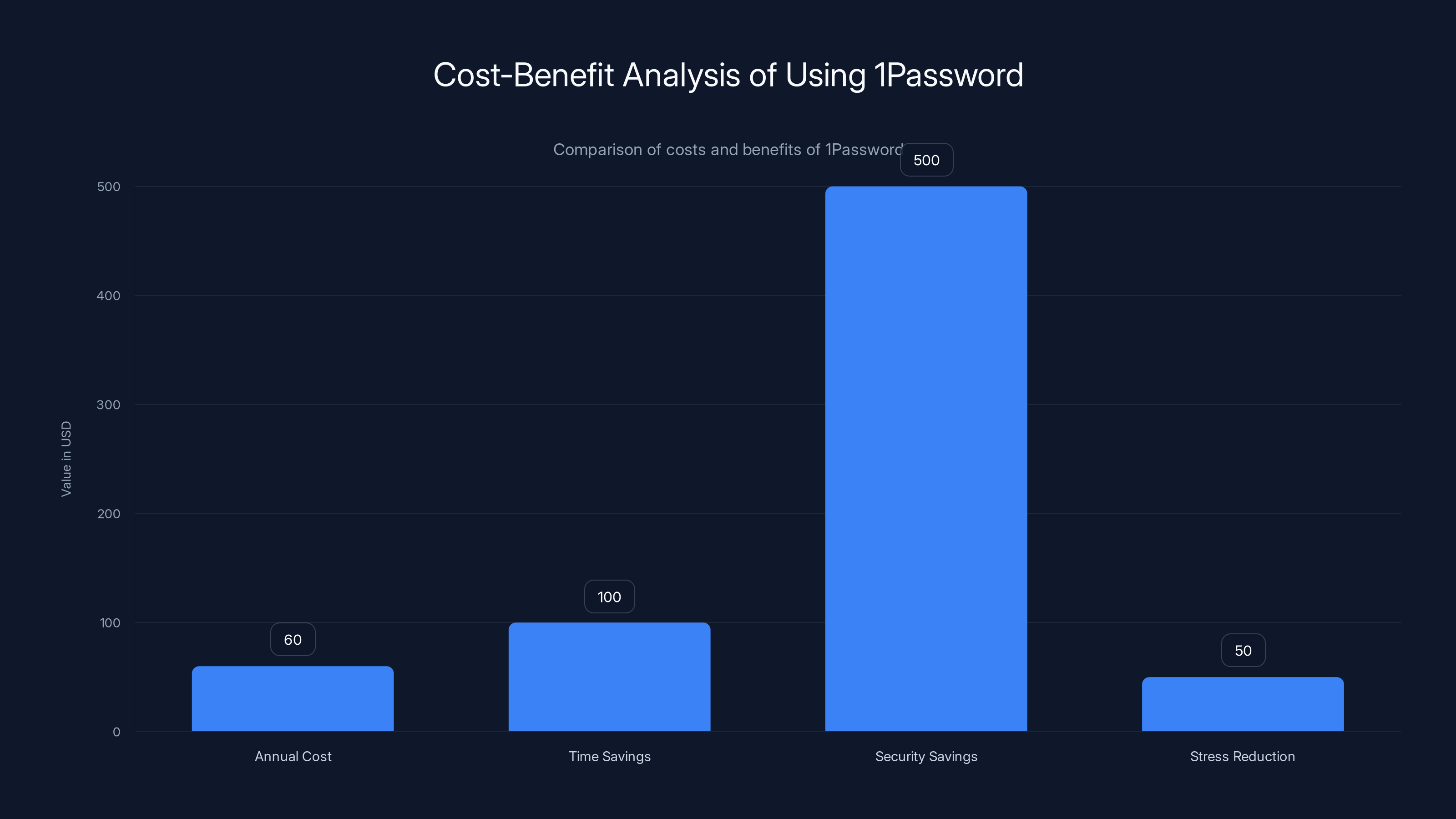
1 Password works on all major browsers. Chrome and Edge get the quickest updates. Firefox and Safari support is solid but sometimes lags. Safari's sandboxing model is most restrictive, which actually adds security but means some 1 Password features work slightly differently.
Choose the browser that balances your workflow needs with your security preferences.
Extension Permissions
When you install the extension, your browser asks for permission to "read and change all your data on websites you visit." This sounds scary. It's necessary for the extension to work, but it's worth understanding.
1 Password needs to see form fields to auto-fill them. It needs to monitor your clipboard to check phishing warnings. It needs to know what page you're on to decide which credentials to suggest.
All of this requires those broad permissions.
The question is whether you trust 1 Password more than you trust malicious websites to not exploit that access. Most people do. 1 Password's code is extensively audited.
Account Setup
You'll need a 1 Password account. The free tier is limited. 1 Password Personal starts at
This feature is available in all paid tiers.
Master Password
Your master password is the key to everything. It unlocks your vault. It needs to be strong and unique. 1 Password generates suggestions if you want.
Don't use a password you've used elsewhere. Don't make it something you could type in your sleep. It needs to be genuinely random and complex.
Secret Key
1 Password uses something called a Secret Key in addition to your master password. This is a unique string that's generated when you create your account. You'll see it during setup.
Don't lose it. Keep it somewhere safe. You'll need it if you ever need to recover your account.
This dual-key system is more secure than password-alone systems.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is This Protection Worth It?
Security always involves trade-offs. Let's be quantitative about whether 1 Password makes sense for you.
The Costs
Financial: $4.99/month or higher for 1 Password service.
Complexity: You need to learn a new tool. Setup takes about 30 minutes. Migrating existing passwords takes longer.
Trust: You're trusting a company with all your passwords. That's a real consideration.
Performance: The extension adds a small amount of RAM and CPU usage.
The Benefits
Time saved: You no longer remember passwords. Average person spends 20+ minutes per month on password-related tasks. Over a year, that's 240 minutes. At even a modest hourly rate, that's real savings.
Security improved: You're using unique, strong passwords for every site. You're protected from phishing at the credential paste moment.
Stress reduced: You don't worry about what password you used where. You don't have the anxiety of breach notifications.
Accounts recovered: When a site gets breached (which happens constantly), attackers can't use your password on other sites because every password is unique.
The Math
Let's say you would catch a phishing attack on your own about once per year. That attack could cost you $500 in stolen money and hassle and account recovery.
1 Password costs roughly $60/year.
That's an ROI of 8:1 just on stopping one attack per year.
Most people can easily calculate higher ROI.


Introducing a delay in login processes can significantly reduce phishing success rates, with a 2-second delay cutting success by up to 50%. Estimated data.
Common Questions About 1 Password and Security
Can 1 Password itself be hacked?
A company was breached in 2023, but attackers didn't get password vaults. The encryption model that 1 Password uses means that even if attackers get your encrypted vault, they can't decrypt it without both your master password AND your Secret Key. The company has also been extensively audited by security researchers.
Is it possible? Theoretically. But it would require compromising multiple security layers, not just breaking the servers.
What if I forget my master password?
You're locked out. 1 Password can't help you. That's by design. If they could recover it, attackers could too.
This is why backing up your Secret Key matters.
Does 1 Password sell my data?
No. That's not their business model. They're a subscription service. Their incentive is to keep your passwords safe. If your data leaked, their business evaporates. There's alignment between your interests and theirs.
Is it better than free alternatives?
Bitwarden is free and open-source. It's excellent. The trade-off is that you're maintaining more of the infrastructure yourself.
For most people, 1 Password's convenience and polish justify the cost.
What about password managers built into browsers?
Chrome, Firefox, and Safari all have built-in password managers. They're better than no password manager. They're worse than dedicated tools.
The trade-off is that they're tightly integrated into your browser, which is convenient but means your passwords are only available in that browser.
Future of Phishing and Detection
Attackers will evolve. They always do.
The next frontier for phishing is probably accounts with MFA enabled. If a phishing site can't get your password to work (because you have MFA), attackers might try to socially engineer you into entering the MFA code yourself, or into authorizing an MFA request.
This is sometimes called "MFA bombing" or "prompt bombing."
Defense against this is different. You need to be skeptical of MFA prompts you didn't request. Tools like 1 Password can't really help here.
Beyond that, deepfakes might become more common. Video phishing where attackers create fake videos of executives requesting urgent actions. Or voice phishing with cloned audio.
The arms race will continue.
What won't change is that the human element matters. Slowing people down. Making them pause. Creating friction at the right moment.
That's what 1 Password's phishing protection does, and it's why it'll remain relevant even as attacks evolve.

Recommendations: Who Should Use This
Not everyone needs 1 Password.
You should use 1 Password if:
You have sensitive accounts (email, banking, work). You reuse passwords across sites (you need to stop doing this). You want built-in phishing protection. You access accounts across multiple devices. You share accounts with family members.
You might be okay without it if:
You have only a few accounts. You genuinely have unique, strong passwords for each. You use password managers built into your browser and you're comfortable with that. You only use one device.
But honestly, even people in the second category would probably benefit from 1 Password.
The phishing protection feature is a nice addition, but 1 Password's core value is password management. The phishing feature is the cherry on top.
Implementation Best Practices
If you decide to use 1 Password, here's how to maximize its benefits:
Start with critical accounts. Don't try to migrate all 200 of your passwords in one sitting. Start with your email, banking, and work accounts. These are high-value targets.
Use complex, unique passwords. Let 1 Password generate passwords. 20-character random passwords with mixed case, numbers, and symbols. Let it do the heavy lifting.
Enable family sharing if relevant. If you're managing accounts for family members (kids' school logins, household services, etc.), 1 Password Family lets you share vaults without exposing everyone's passwords.
Use Categories and Tags. Organize your passwords. Having a clear system makes it easier to audit and manage.
Enable password strength reporting. 1 Password will scan your vault and tell you which passwords are weak, reused, or exposed in breaches.
Regularly review your vault. Every few months, spend 15 minutes looking at what passwords you're keeping. Delete accounts you no longer use. Update weak passwords.
Use the Travel Mode feature if you travel. You can temporarily hide certain vaults when crossing borders, reducing the risk of forced disclosure.
The Bigger Picture: Why Password Security Matters More Than Ever
We live in a world where most of your identity is tied to your email password. That password controls your email. Your email controls everything else.
Reset your email password and you can reset passwords for almost any other account.
Lose control of your email and attackers can reset all your other passwords.
This makes email password security absolutely critical.
Phishing is the leading attack vector against email accounts because it bypasses technical defenses. No firewall stops you from entering your password on a fake website. No antivirus stops social engineering.
The defenses have to happen at the human level: paying attention, slowing down, verifying.
1 Password's phishing protection tool is specifically designed to help at that moment.
It's not the most sophisticated attack defense that exists. But it's sophisticated in a different way: it's simple, it's automatic, and it works at the precise moment when human attention is most critical.
That's elegant security engineering.
Conclusion: A Simple Tool That Does One Thing Well
Let's step back. What did 1 Password actually do here?
They took the moment where you're about to paste a credential into a website. They added a check. They created a pause.
That's it.
It's not flashy. It doesn't involve machine learning or blockchain or any of the buzzwords that get venture capital excited.
But it's useful.
In a world where AI has made phishing attacks easier, where 60% of companies are reporting increased fraud, where the average person has dozens of accounts and dozens of reasons to be distracted when they're logging in, adding a single moment of friction at the right time actually matters.
It won't stop determined, sophisticated attackers targeting you personally. But it'll stop the bulk attack volume. It'll catch the case where you clicked a link thinking it was legitimate. It'll prevent the moment of distraction from turning into account compromise.
For most people, that's enough.
The security tools that work best are the ones that protect you without requiring you to remember to use them. Auto-filled passwords. Auto-filled forms. Auto-checked phishing warnings.
1 Password's phishing protection is in this category.
It's worth enabling. It's worth keeping enabled. And it's worth mentioning to people in your life who manage any sensitive accounts.
In the fight against phishing, this is one more layer. And in security, more layers, thoughtfully deployed, always help.
FAQ
What is 1 Password's phishing protection feature?
1 Password's phishing protection is a browser extension feature that detects when you're about to paste login credentials into a fraudulent website. When you attempt to paste a password into a website using the 1 Password extension, the feature performs a domain verification check to ensure you're on a legitimate site. If the website appears suspicious or doesn't match the expected legitimate domain for that service, 1 Password displays a warning to prevent you from compromising your credentials.
How does 1 Password detect phishing websites?
The phishing detection works by checking several security indicators simultaneously: verifying the website's SSL certificate validity, confirming the domain name matches legitimate services, checking DNS records to ensure they resolve to legitimate servers, and cross-referencing against databases of known phishing domains. The extension performs these checks at the critical moment when you're about to paste your password, catching potential attacks before you've committed your credentials to a malicious site.
Why is this protection better than other security tools?
1 Password's approach is different because it creates friction at the exact moment it matters most. Unlike browser warnings that appear after you've already entered credentials, or email filters that block messages before you see them, 1 Password warns you right when you're about to paste your password. This timing is crucial because psychological research shows that adding a moment of pause before a critical action significantly reduces the chance of falling for phishing attacks, with some studies showing up to 50% reduction in success rates.
Does 1 Password's phishing protection work on mobile devices?
The phishing protection feature is currently available primarily on desktop browsers where the 1 Password extension is installed and active. Mobile apps have different security architectures due to platform restrictions. 1 Password has launched mobile extensions on i OS and Android, but feature availability varies by platform. For maximum protection, using 1 Password on desktop browsers provides the most comprehensive phishing detection capabilities.
What should I do if 1 Password warns me about phishing?
If you receive a phishing warning from 1 Password, take it seriously by pausing before proceeding. Verify that you're on the correct website by visiting the official site directly through a new browser tab or app rather than continuing from your current location. You can also report the suspicious site to the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center or your browser's safety reporting feature to help protect other users from the same attack.
Is 1 Password itself safe from being hacked?
Yes, 1 Password maintains robust security practices. A 1 Password breach in 2023 resulted in attackers accessing encrypted vault backups, but user passwords remained protected because of the company's zero-knowledge encryption architecture. Your vault is encrypted with a combination of your master password and a Secret Key, meaning even if attackers access 1 Password's servers, they cannot decrypt your passwords without both pieces of information that only you possess.
What's the difference between 1 Password and free password managers?
1 Password charges
How do I set up 1 Password's phishing protection?
To enable 1 Password's phishing protection, first install the 1 Password browser extension from your browser's official app store for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or Safari. Create or sign into your 1 Password account, then ensure that security and warning notifications are enabled in the extension settings. The phishing protection works automatically once enabled; whenever you attempt to paste a password into a website, the extension will check the domain and warn you if it appears suspicious.
Can phishing attacks still succeed even with 1 Password protection?
Yes, 1 Password's protection is not absolute. If you manually type your password instead of using 1 Password's paste function, you won't get the warning. Additionally, sophisticated attackers using advanced techniques like malware, keyloggers, or social engineering tactics that don't involve fake websites can bypass this specific protection. This is why 1 Password protection works best as one layer in a comprehensive security strategy that also includes multi-factor authentication, regular password updates, and security awareness practices.
How often does 1 Password update its phishing detection capabilities?
1 Password regularly updates its security features and phishing detection mechanisms through browser extension updates. The company continuously monitors emerging phishing techniques and updates domain verification databases to catch new threats. Users receive automatic extension updates in most browsers, ensuring they have the latest protection without requiring manual intervention. Staying on the current version of the extension is important for maintaining access to the newest security features and protections.
Key Takeaways
- 1Password's phishing protection adds a security checkpoint at the exact moment you paste credentials, catching spoofed websites before account compromise
- AI has dramatically lowered barriers to creating convincing phishing attacks, with 60% of companies reporting increased fraud losses in 2024-2025
- The feature works through DNS verification, SSL certificate validation, and domain similarity analysis performed automatically in real-time
- 1Password's timing-based protection (at credential paste) is more effective than post-entry browser warnings or pre-entry email filters
- Layered security with 1Password, MFA, and security awareness training creates significantly stronger protection than any single tool alone
Related Articles
- 1Password's New Phishing Prevention Feature [2025]
- LastPass Phishing Scam: How to Spot Fake Support Messages [2025]
- SMS Sign-In Links: A Critical Security Vulnerability Affecting Millions [2025]
- Most Spoofed Brands in Phishing Scams [2025]
- UK VPN Ban Explained: Government's Online Safety Plan [2025]
- PcComponentes Data Breach Denial: What Really Happened [2025]
![1Password Phishing Protection: How the New Browser Feature Saves You [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/1password-phishing-protection-how-the-new-browser-feature-sa/image-1-1769092733128.png)



