Why Chat GPT Can't Work in the Background: The Core Problem
Here's the thing that drives developers and power users absolutely crazy: once you close the Chat GPT window or move to a different message thread, everything stops. Any long-running task you started? Dead. Any calculation crunching through data? Gone. The AI simply cannot continue working in the background while you do something else.
This isn't a minor inconvenience. This is a fundamental architectural limitation that makes Chat GPT unsuitable for entire categories of work that require persistent, autonomous processing. According to Britannica, AI systems like Chat GPT are designed for specific tasks and lack the infrastructure for continuous background processing.
When you're actively chatting with Chat GPT, the conversation feels seamless. You ask a question, hit enter, and the AI streams back a response. But the moment that response completes, the session enters a kind of stasis. The system isn't designed to queue up tasks, schedule work, or maintain ongoing processes outside of active message turns. This limitation is highlighted in a Gizmodo article discussing Chat GPT's operational constraints.
Think about what this means in practice. You can't ask Chat GPT to analyze a massive dataset while you grab coffee. You can't request a 50-page report generation and come back in thirty minutes to a finished product. You can't set up a workflow that continuously monitors something and takes action based on what it finds. Everything has to happen inside that active reply window, in real-time, with you actively waiting.
The technical reason this limitation exists comes down to how Chat GPT's architecture works. The service operates on a request-response model. You send a message, servers process it, and you get a response back. Once the response completes, the connection state doesn't persist in a way that allows for background computation. This design choice simplifies the backend infrastructure and reduces operational costs, but it creates a massive usability problem for anyone trying to automate complex workflows.
Compare this to systems like Lang Chain or Runable, which actually support persistent agents and background task execution. These platforms allow you to set up autonomous workflows that continue processing even after you've logged off.
The Real-World Impact: Where This Breaks Down
Let's get specific about what fails when you bump into this limitation. Understanding the practical impact matters because it helps clarify why this isn't just a nice-to-have feature.
Data processing jobs that take more than a few minutes hit this wall immediately. You want Chat GPT to parse a 5GB CSV file and generate summary statistics? The timeout happens before the task completes. You ask it to cross-reference information across ten different documents? Somewhere in the middle of processing, the connection drops or the timeout triggers.
Content generation workflows break too. Imagine you're trying to generate a 200-page technical documentation from code comments. Chat GPT might generate the first thirty pages perfectly, but long before reaching page two hundred, the context window fills up or the session times out. You have to restart the entire process or somehow split it into smaller chunks and manually stitch them back together.
Scheduled automation doesn't exist at all. You can't say "every morning at 7 AM, summarize the news from these five sources and put it in a document." Chat GPT has no way to execute scheduled tasks. You'd need to manually prompt it each time, which defeats the entire purpose of automation.
Monitoring and alerting workflows are completely off the table. You can't ask Chat GPT to "watch this API endpoint and notify me if response times exceed 500ms." The bot can't maintain that kind of persistent listening state. It can only react to direct messages from you.
File processing at scale becomes a nightmare. You have fifty CSV files to process identically? Chat GPT forces you to either do them one at a time in the chat, or find external tools to handle the batch operation. There's no way to queue up ten parallel tasks and check back when they're done.
The real frustration emerges when you're building something that relies on AI automation. You start with Chat GPT thinking you've found your solution, then realize halfway through implementation that you need something with actual background task support.

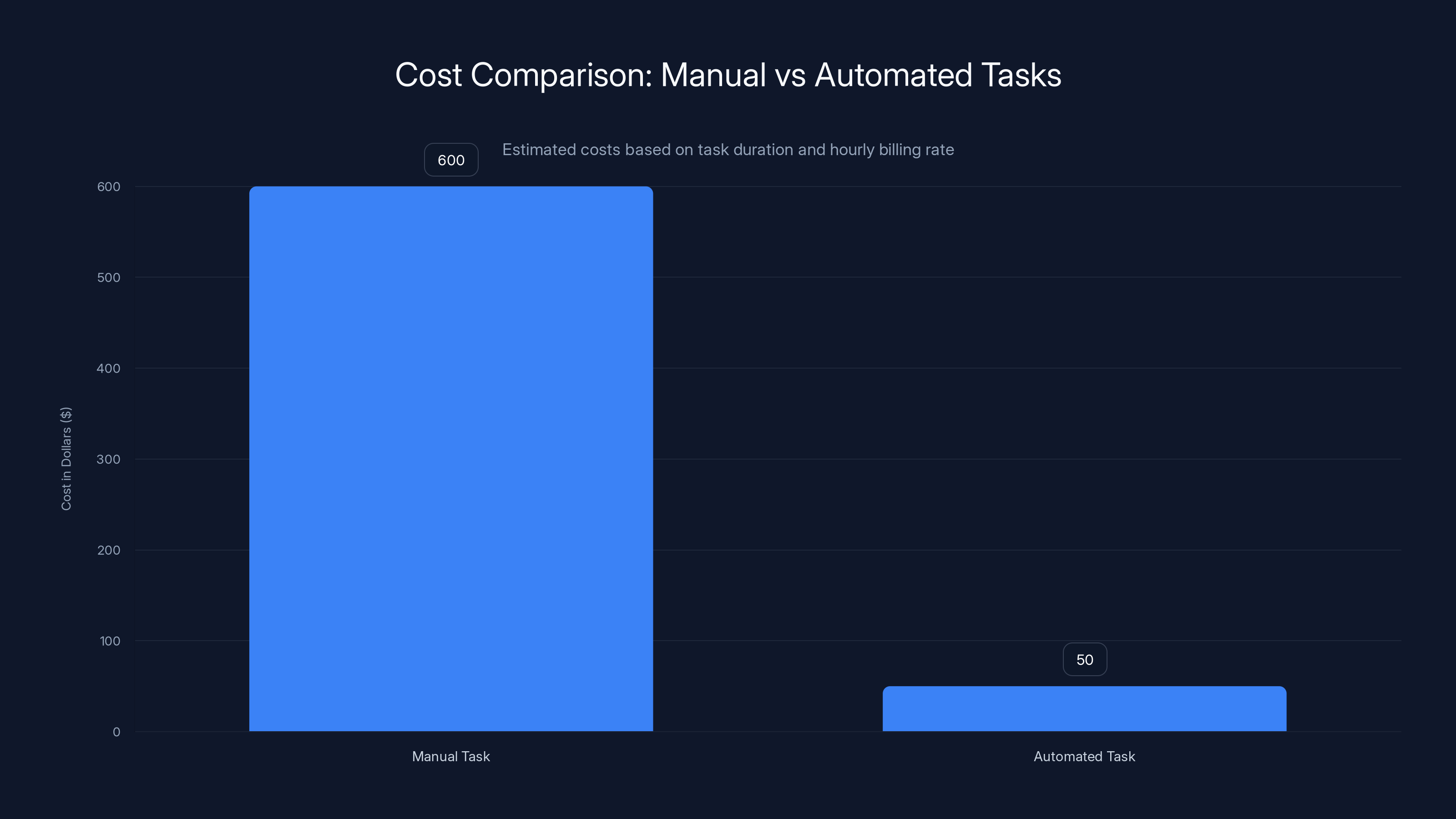
Estimated data shows manual tasks cost significantly more than automated ones, with a
Why This Limitation Exists: The Technical Reality
Understanding why this limitation exists actually helps you work around it better. It's not arbitrary. It's rooted in genuine architectural constraints and business decisions.
Open AI architected Chat GPT as a conversational interface, not a task execution engine. The entire system is optimized for real-time chat interactions where users expect immediate responses. Maintaining long-running background processes would require completely different infrastructure.
Server-side compute management becomes significantly more complex with background tasks. You need to track state for each user's ongoing processes. You need persistent storage for intermediate results. You need ways to handle failures and retries. You need mechanisms to pause, resume, and cancel tasks. All of this adds operational overhead and complexity.
Cost structure plays a role too. Background task execution would consume server resources even when users aren't actively using the service. The current model charges per token used during active conversations, making it straightforward to bill users. Background processing would require different pricing models, capacity planning, and resource allocation strategies.
Timeout constraints are built into the system for good reason. HTTP requests have maximum execution times. Web Socket connections can drop. Networks are unreliable. Chat GPT's architecture assumes that any single response should complete within reasonable timeframes, typically measured in seconds to a few minutes.
Context window limitations compound this issue. Chat GPT operates with fixed context windows. GPT-4 has a 128K token window, which sounds enormous until you're actually processing massive datasets. A long-running task might need to maintain context across millions of tokens of intermediate processing. That's just not feasible with current token-based architecture.
The stateless nature of the service by design keeps things simple and scalable. Each request is independent. Each response completes and detaches. This design pattern works beautifully for conversational AI but fails catastrophically for persistent task execution.
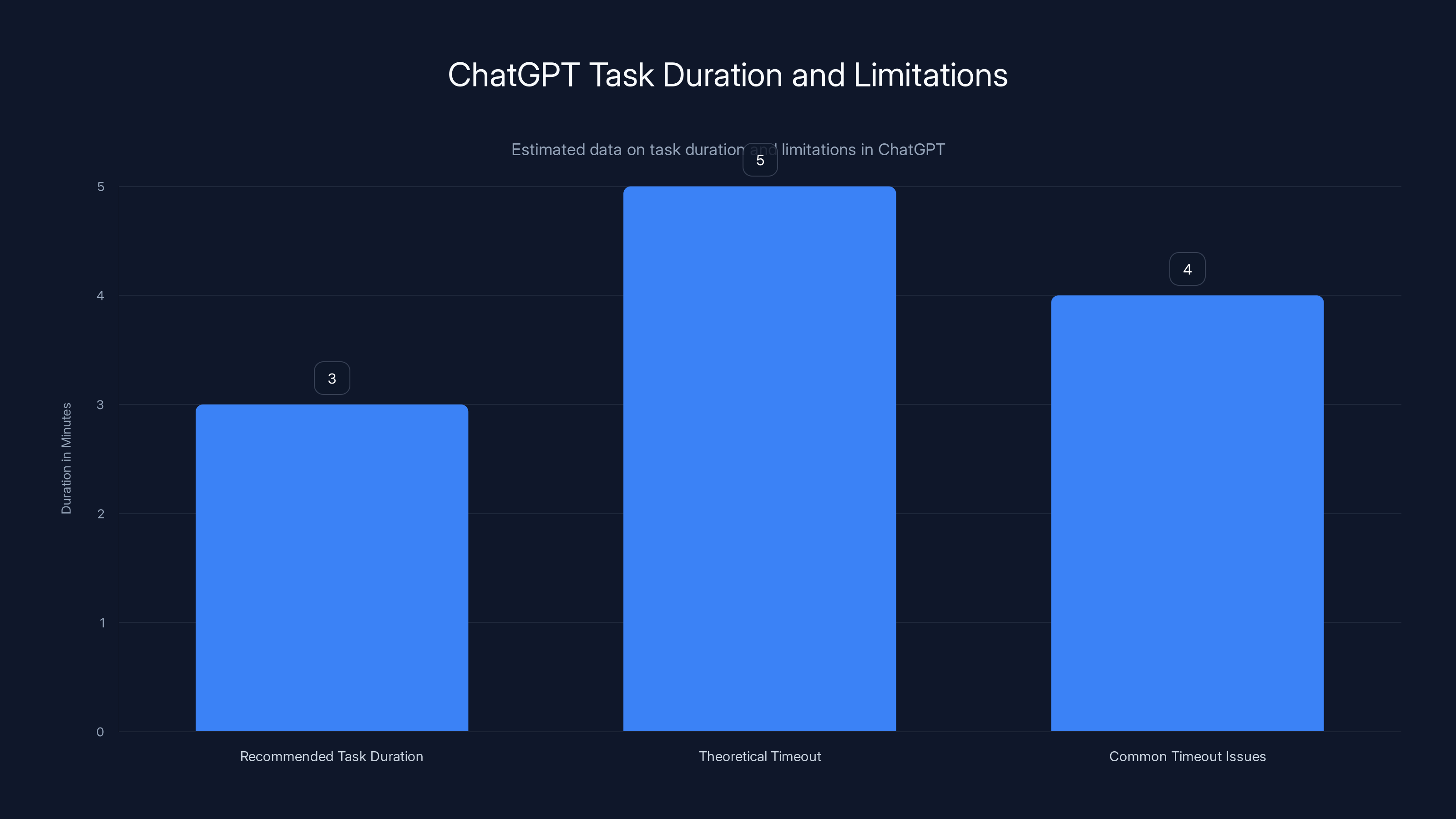
Estimated data suggests most tasks should complete within 3 minutes, with a theoretical timeout at 5 minutes. Common issues often arise around 4 minutes due to network and context constraints.
What Tasks Actually Fail (And When You'll Hit This)
You need to know exactly which kinds of tasks run into this wall. Some tasks work fine despite initial appearances. Others fail miserably in ways you might not anticipate.
Simple text generation usually succeeds because it completes quickly. You ask Chat GPT to write an email, a code snippet, or a short article, and you get back a result before any timeout triggers. The processing happens fast enough that the session duration isn't a constraint.
But complex multi-step text generation starts to break. You ask Chat GPT to write a 10,000-word research paper with citations, multiple sections, and original research integrated throughout. The token generation takes longer. The model has to maintain state across the entire document. Depending on load and your connection stability, this might timeout or get cut short.
Data analysis tasks fail based on data size. Analyzing a 100KB CSV file works. Analyzing a 50MB file? The processing alone takes too long, and even if it doesn't timeout, you're using up massive amounts of context tokens. A 500MB file is completely unrealistic.
Iterative refinement workflows hit walls hard. You ask Chat GPT to refine something through five iterations, making specific changes each time. The first few iterations work. By iteration four or five, context limitations kick in. Timeouts might occur. The system might start forgetting earlier changes.
Parallel task execution simply doesn't exist. You can't ask Chat GPT to simultaneously process three different files and report results for all three. The system processes sequentially within single message turns. Any parallelization has to happen externally.
Scheduled or triggered execution is impossible. No matter what you try, you can't set up a workflow in Chat GPT that runs at specific times or in response to external events. The system has no way to be triggered. It only responds to direct user input.
The Timeout Problem: How Long Can Tasks Actually Run?
The exact timeout limits aren't officially published, but testing reveals practical constraints. Understanding these limits helps you predict when you'll hit the wall.
HTTP request timeouts typically max out around 5 minutes on consumer tier services. This means any single Chat GPT request that takes longer than 300 seconds to process might fail. In practice, you'll start seeing issues around 3-4 minutes because network latency, server processing, and token generation all eat into that window.
Web Socket connections, if Chat GPT uses them, have different timeout characteristics but similar practical limits. Connection drops after 10-15 minutes of inactivity are common across web services. Even if the server is actively processing, if no data flows across the connection for extended periods, the connection may drop.
Token generation speed matters enormously. Chat GPT generates approximately 50-100 tokens per second depending on system load. At 100 tokens per second, you can generate maybe 30,000 tokens in 5 minutes. That's roughly 20,000 words. Sounds great until you realize you need to include context for a task requiring 100,000 tokens of input. The math breaks quickly.
Context window exhaustion hits before timeout issues in many cases. If you load Chat GPT with 100K tokens of input data and ask it to analyze all of it, you've already consumed most of the available context. The model has only a small window left for output. It can't generate lengthy analysis because it would exceed the context limit.
Network interruptions happen constantly. Even if the Chat GPT backend could theoretically process for 30 minutes, your home internet connection might drop, your router might restart, or a middleman device might timeout. Any interruption forces you to start over.
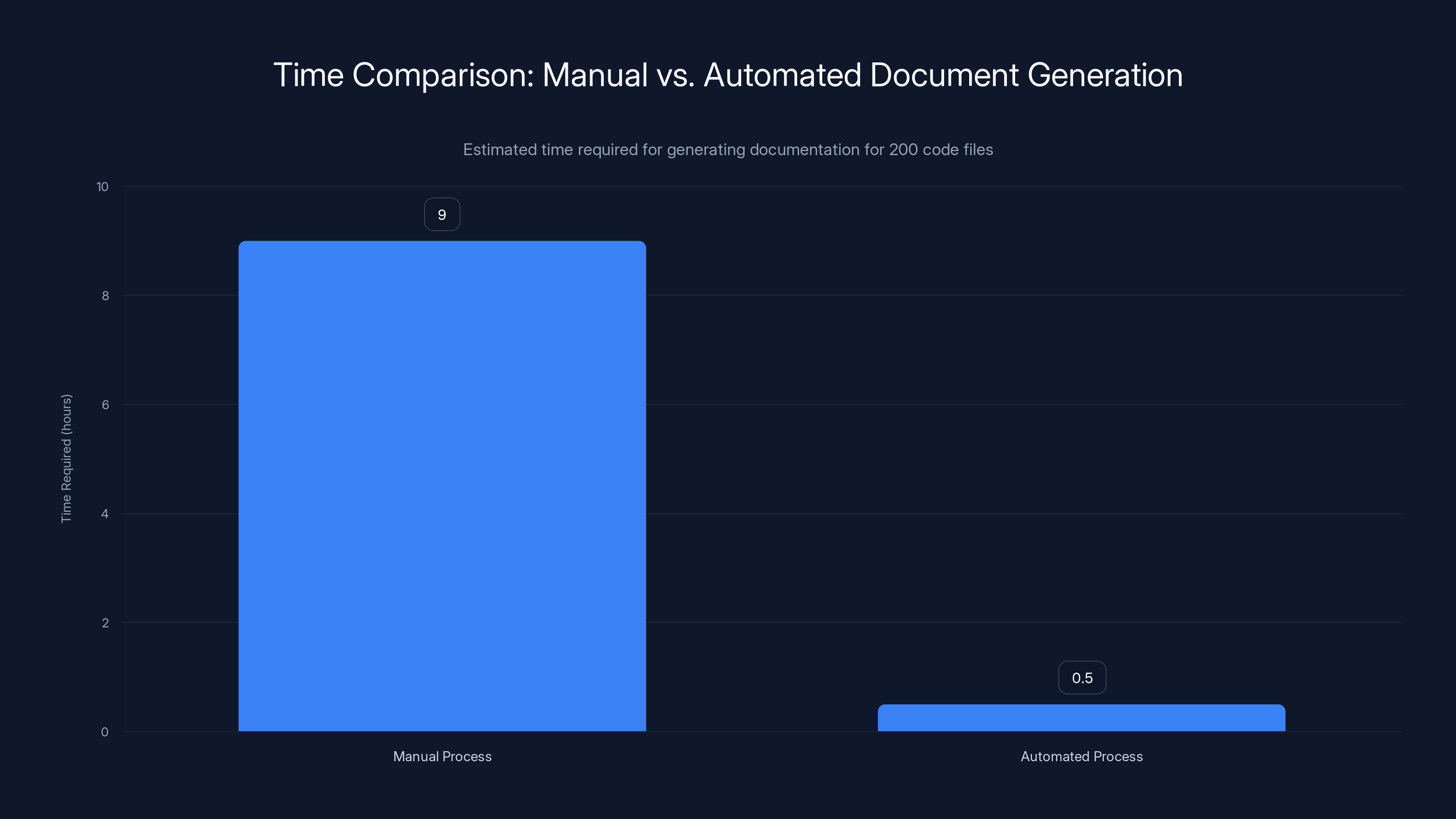
Automated document generation significantly reduces time from an estimated 9 hours to just 0.5 hours, highlighting the efficiency of background execution. Estimated data.
Session Persistence: Why "Continue Where I Left Off" Doesn't Really Work
You might think you can restart a task from where it left off. You're wrong, and understanding why is crucial.
Chat GPT does maintain conversation history within a single conversation thread. You can go back and reference earlier messages. You can ask the system to "continue from where we left off." But this isn't true persistence of task execution state. It's just conversation context.
The difference matters critically. Conversation history is metadata. Your earlier requests and Chat GPT's responses are stored. But the actual execution state, the intermediate variables, the partial results, the ongoing computation? None of that is preserved. It exists only in the context window of the current active message.
When you ask Chat GPT to continue, the system has to reconstruct everything from conversation context. If you were processing step 47 of 100, Chat GPT doesn't have access to the results of steps 1-46 as structured data. It only has the conversation transcript, which is unstructured. Reconstructing execution state from unstructured conversation context is error-prone and inefficient.
Context window constraints amplify this problem. If your previous processing was extensive, you've accumulated a lot of conversation history. Add the new task you want to resume, and you quickly run out of space. Chat GPT has to either forget earlier context or abort the new task.
This is why many users experience weird behavior when trying to continue interrupted tasks. Chat GPT sometimes forgets earlier decisions. It sometimes re-does work unnecessarily. It sometimes produces slightly different results than before because it doesn't have perfect reconstruction of prior state.
Real task queuing systems, by contrast, maintain execution state in databases. They know exactly what's been completed, what's in progress, what failed, and what's queued next. They can pause work, resume it, and distribute it across multiple workers. Chat GPT has none of this infrastructure.
Workarounds That Partially Work (But Aren't Ideal)
You can't fully solve this limitation within Chat GPT, but some workarounds reduce the pain.
Breaking tasks into smaller chunks distributes processing across multiple message turns. Instead of asking Chat GPT to process a 500MB file in one go, you split it into ten 50MB chunks, process each separately, then consolidate results externally. This reduces pressure on timeouts and context limits. The downside? You do a lot of manual work stitching everything together, and parallelization remains impossible.
Externalizing computation shifts heavy lifting outside Chat GPT. You use Python scripts, shell commands, or other programming environments to handle the actual computation. Chat GPT orchestrates and guides the process, but doesn't execute long-running tasks itself. This works but requires technical skills most users don't have.
Using Chat GPT API with system tools allows more flexibility than the web interface. By writing a script that calls the Chat GPT API, you can implement retry logic, external persistence, and custom timeout handling. You can structure the flow to work around Chat GPT's limitations. This still doesn't give you true background task execution, but it's better than nothing.
Integrating Chat GPT with task runners like Zapier or Make creates workflows that continue working even if Chat GPT times out. You ask Chat GPT for analysis, the result triggers downstream automation, and that automation continues whether Chat GPT is still active or not. But this requires the downstream systems to do the heavy lifting.
Manual saving and resumption is tedious but sometimes necessary. You download intermediate results, save your progress, then manually ask Chat GPT to continue in a new conversation. This prevents loss of work but is labor-intensive and error-prone.

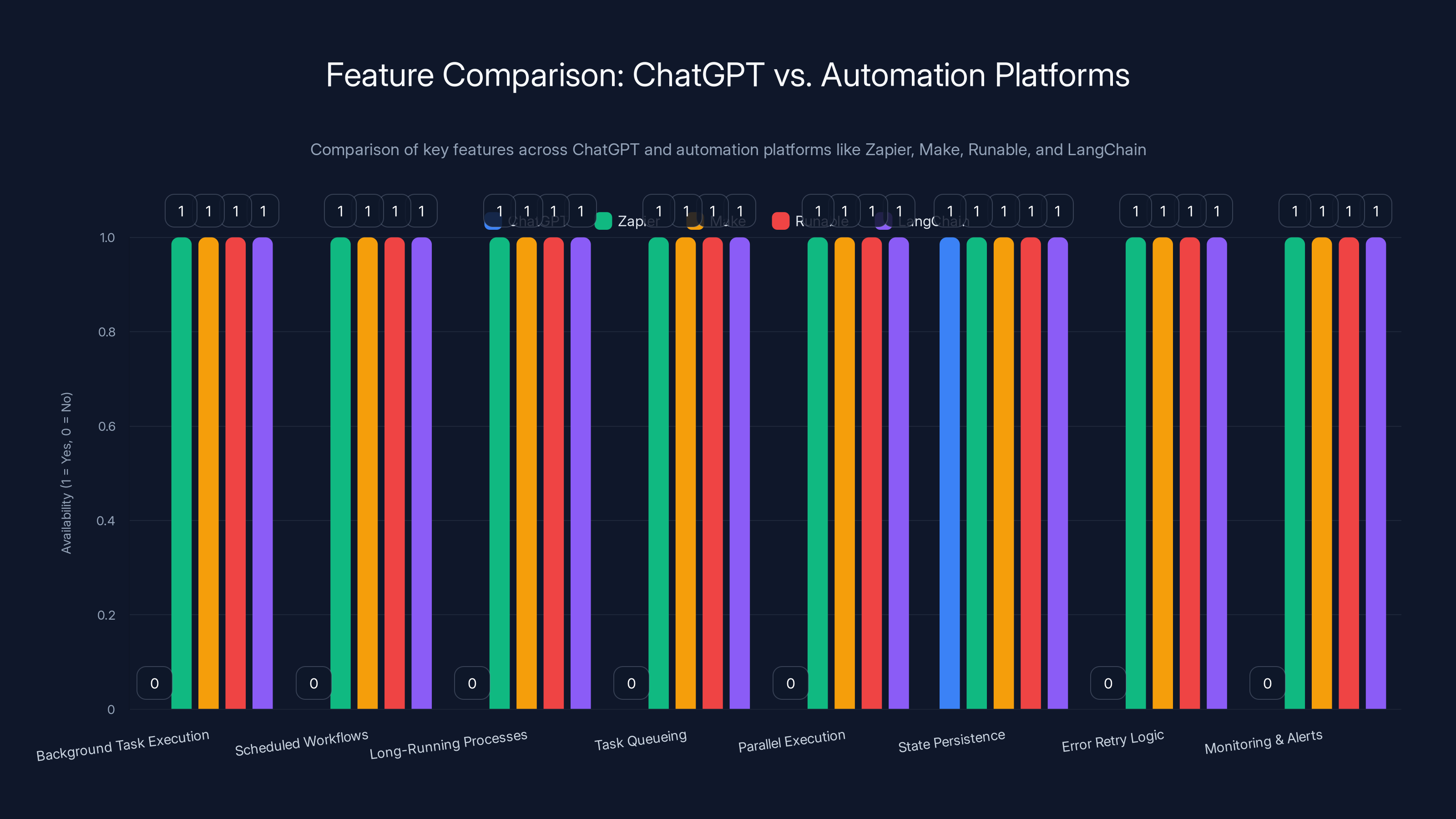
This chart highlights the feature availability across ChatGPT and other automation platforms. ChatGPT lacks many automation features that are standard in platforms like Zapier, Make, Runable, and LangChain.
Comparison: Chat GPT vs. True Automation Platforms
Understanding how Chat GPT compares to purpose-built automation tools illuminates why this matters.
| Feature | Chat GPT | Zapier | Make | Runable | Lang Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background Task Execution | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scheduled Workflows | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Long-Running Processes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Task Queueing | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Parallel Execution | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| State Persistence | Limited | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Error Retry Logic | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Monitoring & Alerts | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cost for Heavy Usage | Per token | Per task | Per task | Per month | Self-hosted |
| Ease of Setup | Very Easy | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Hard |
Zapier excels at connecting services. You create a workflow where action in one app triggers action in another. Thousands of integrations exist. The UI is approachable. But Zapier isn't designed for computationally intensive AI tasks.
Make offers similar functionality with more power under the hood. You can write custom code, implement complex logic, and handle advanced scenarios. But it's still not specifically optimized for AI-powered automation.
Runable bridges the gap between Chat GPT's conversational simplicity and infrastructure platforms' complexity. It supports AI agents that can work autonomously, execute long-running tasks, and process data at scale. Starting at $9/month, it's cost-accessible for teams and individuals. You can set up AI workflows that generate presentations, documents, reports, images, and videos without manual intervention. The AI agents persist across sessions and continue working even when you're not actively monitoring.
Lang Chain is the developer's choice if you want maximum control. It's a framework for building applications with language models. You write Python code to orchestrate complex workflows. Lang Chain handles context management, tool integration, memory persistence, and agent orchestration. The tradeoff is that you need solid programming skills.
The key difference: Chat GPT assumes humans will ask questions and read answers. Automation platforms assume workflows will run independently with human oversight.

How Runable Solves the Background Task Problem
Since background task execution is critical for serious automation, understanding how modern tools solve it matters.
Runable approaches this problem from first principles. The platform is built specifically for AI-powered automation, not adapted from a conversational interface.
You describe what you want done: "Generate a monthly sales report from Q4 data, include trend analysis, create a presentation deck, and notify the team when it's ready." Runable's AI agents break this into discrete tasks, queue them, and execute them autonomously. You don't wait in a chat window. You get a notification when it's done.
The platform maintains persistent state throughout execution. If one step requires output from the previous step, Runable tracks that. If an error occurs midway through a 50-step workflow, Runable remembers which steps completed and which need retry. You can resume interrupted jobs without restarting from the beginning.
Parallel task execution means multiple workflows run simultaneously. You can generate ten different reports at once, create five presentations from different data sources, and process batches of images all in parallel. The system scales the work across available resources.
Scheduling is built in. You set up a workflow that runs every Monday morning, daily at 3 PM, or on specific triggers. The system executes without human intervention. You just review the results.
Integrations with external data sources let you pull information from APIs, databases, and files. Runable can fetch your latest sales data, analyze it, generate insights, create documents and presentations, and push the results back to your destination systems. The entire cycle runs autonomously.
Use Case: Automate your weekly sales reports—fetch data, analyze trends, generate a presentation, and email it to stakeholders—all while you focus on actual work.
Try Runable For FreeThe cost structure reflects heavy usage. At $9/month, Runable is designed for teams that need persistent automation. For occasional use, free tiers in various platforms might suffice. For serious automation, the monthly fee is negligible compared to the time you save.
What really differentiates Runable is the combination of capabilities. You're not just getting a task runner. You're getting an AI-powered system that understands context, can generate complex outputs (presentations, documents, reports, images, videos), can integrate with your existing tools, and can persist autonomously. It's Chat GPT's intelligence with actual automation infrastructure behind it.

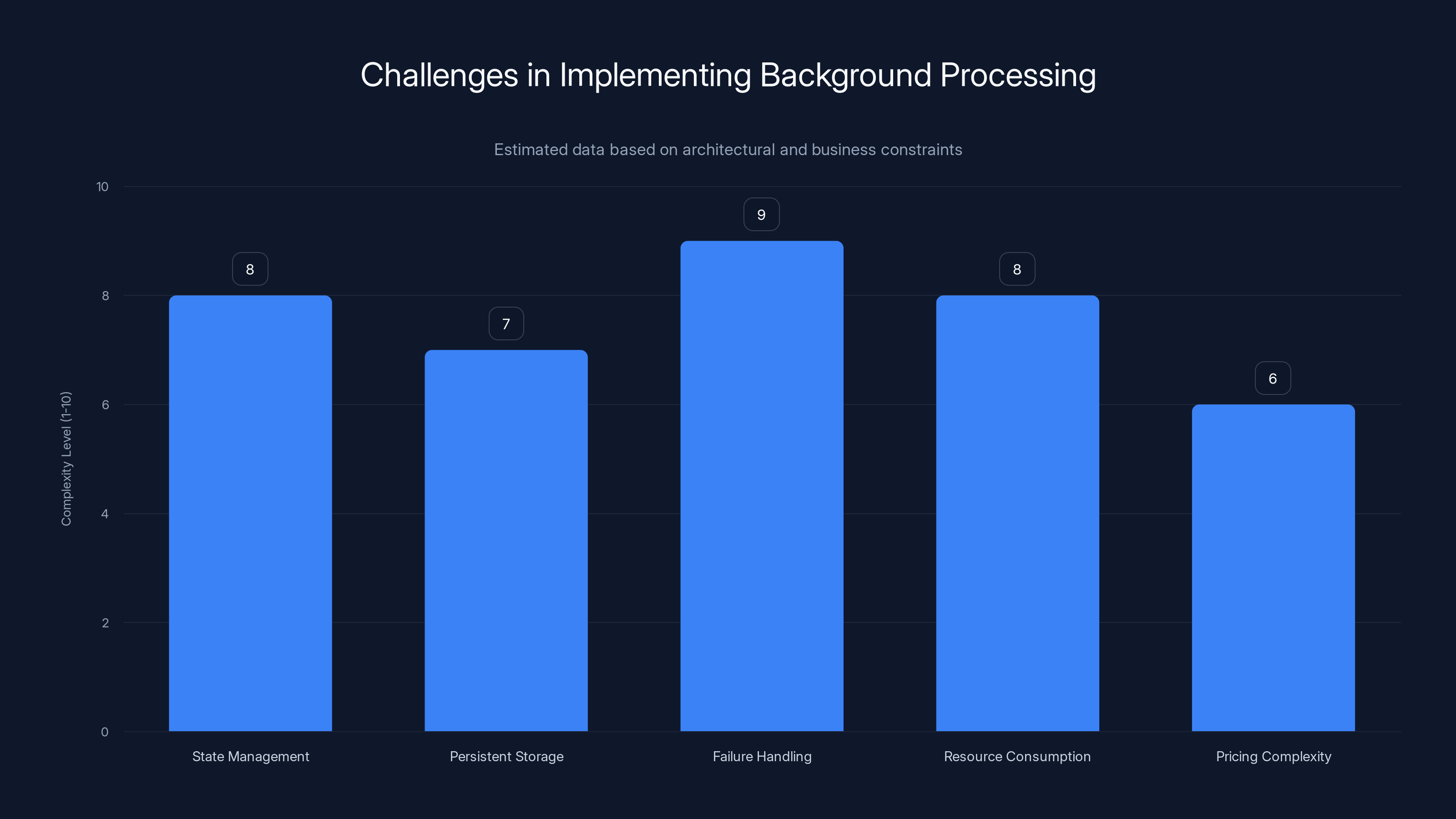
Implementing background processing in ChatGPT involves high complexity in state management, failure handling, and resource consumption. Estimated data.
The Document Generation Use Case: Why Background Execution Matters
Let's drill into a specific use case that highlights why background tasks matter.
Imagine you need to generate documentation for a software project. You have 200 code files totaling 50,000 lines. You want formatted documentation covering purpose, usage, parameters, return values, and examples for each function.
With Chat GPT in a chat window, you'd have to manually feed it code snippets one or two at a time. After each snippet, you copy the documentation it generates, paste it into a document, then go back and ask for the next snippet. This is mind-numbingly tedious. For 200 files, you're looking at 200+ back-and-forth exchanges. You have to stay actively engaged the entire time. It might take 8-10 hours of continuous work.
A system with background task support would work completely differently. You upload all 200 code files at once. You describe the documentation format you want. You click "generate." The system processes all 200 files in parallel, generates documentation for each one, assembles them into a coherent document, and notifies you when it's done. Total elapsed time? 15-30 minutes, depending on complexity. Your active involvement time? About 2 minutes to set it up.
The difference isn't just convenience. It's the difference between a task being feasible and a task being impossible. With Chat GPT, generating documentation for 200 code files is so tedious that you simply won't do it. You'll do partial documentation and call it done. With proper automation, you actually generate complete documentation.
Other document generation scenarios hit the same pattern. Generating reports from datasets, creating presentations from source material, assembling books from hundreds of chapters, synthesizing analyses from multiple sources. All of these are theoretically possible with Chat GPT. All of them are practically infeasible because of the session constraint.
Runable handles exactly these scenarios. You can set up an AI agent that ingests a code repository, generates documentation, creates tutorials, and builds a complete knowledge base—all autonomously, all in the background.

When Chat GPT Is Actually Sufficient
Not every task needs background execution. Understanding when Chat GPT is truly sufficient saves you from over-engineering.
One-shot questions where you need an answer and you're actively waiting. "What's the fastest way to learn Rust?" "Explain quantum entanglement simply." "Debug this code snippet." Chat GPT handles these perfectly.
Brainstorming and ideation where the value comes from iterative conversation. You explore ideas back-and-forth with Chat GPT. Each response sparks new thinking. This leverages Chat GPT's conversational strength.
Small content generation that completes quickly. Write me an email. Create a few paragraphs. Draft an outline. These happen fast enough that session constraints never matter.
Learning and explanation where understanding matters more than completion. You're exploring a complex topic, asking follow-up questions, diving deeper. Chat GPT's conversational nature shines.
Code generation for specific problems. Write a Python function to do X. Explain this regex. Help me fix this error. Single-function tasks complete quickly within session constraints.
Personal productivity tasks that don't require persistence. Making a grocery list, organizing notes, drafting an email. These don't need background execution.
The pattern is clear: if you can complete the task in a single active chat session and the task finishes quickly, Chat GPT works fine. If you need to step away, come back later, or process massive amounts of data, you need something else.
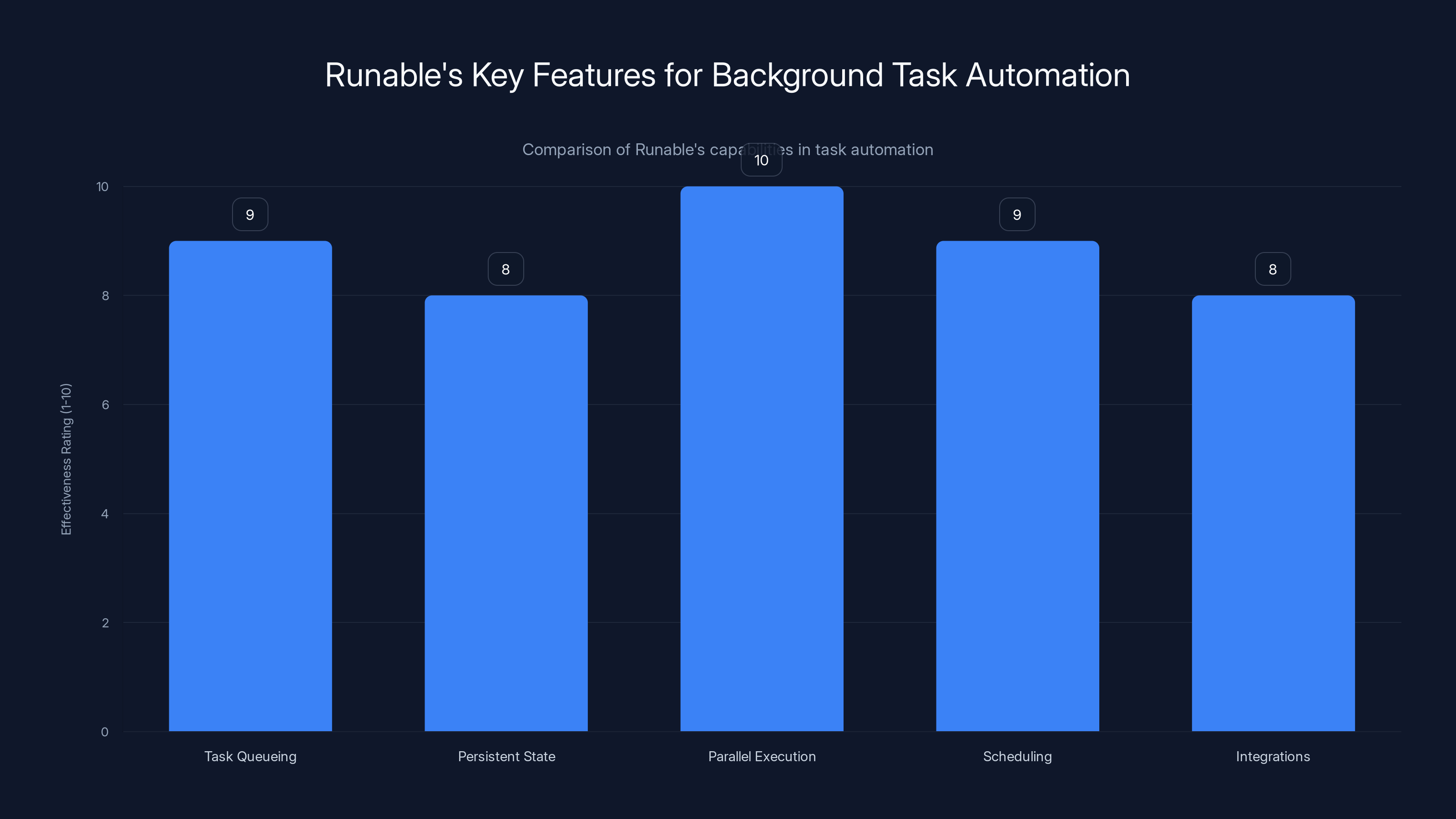
Runable excels in parallel execution and scheduling, offering robust automation capabilities. Estimated data based on feature descriptions.
The Architectural Fundamentals: Why Background Tasks Are Hard
Understanding why this limitation exists in detail helps explain why it's not getting fixed soon.
Stateless architecture is Chat GPT's design foundation. Every request is independent. The server processes it and returns a response. This simplicity enables enormous scalability. You don't need to maintain millions of user sessions in active memory. You don't need mechanisms to pause and resume processing. This design is elegant and cost-effective.
But statelessness and background tasks are fundamentally incompatible. Background tasks require tracking which tasks exist, which are running, which are paused, which failed. They require persistent memory of execution state. They require complex orchestration logic.
Building that infrastructure would require Open AI to redesign substantial portions of Chat GPT. They'd need persistent databases tracking every user's background tasks. They'd need job schedulers and task runners. They'd need failure detection and recovery systems. They'd need monitoring systems to ensure tasks complete reliably. All of this is operational complexity that the current system completely avoids.
Token-based pricing becomes messy with background tasks. Currently, you pay for tokens you use in active conversations. You see exactly what you're paying for. With background tasks, you'd pay for tokens used in work happening without your active monitoring. How do you price that? Do you charge by the task? By execution time? By tokens used? The pricing model becomes murky in ways Open AI probably doesn't want.
Reliability becomes harder to guarantee. In a stateless system, a failure in one request doesn't affect other requests. Each is independent. In background task execution, if a subtask fails, it affects dependent downstream tasks. You need complex error handling, retry logic, and rollback mechanisms. Scaling reliability to millions of simultaneous background tasks is genuinely challenging.
Competition matters too. If Chat GPT had flawless background task execution, there'd be no need for Zapier, Make, or specialized AI automation platforms. Open AI might see this as a reason to keep Chat GPT focused on its conversational strength while letting other companies build the automation layer on top.
Solutions on the Horizon: What's Changing
The AI landscape is moving toward better automation capabilities. Understanding what's coming helps you make decisions about what to use now.
AI agents with persistent memory are becoming more sophisticated. Tools like Lang Chain are making it easier to build agents that maintain state across sessions. Memory systems that let AI understand context accumulated over time are improving. This doesn't solve Chat GPT's architectural limitations, but it does enable better automation when you're willing to build custom solutions.
Function calling and tool use are giving large language models more capability to execute actions in external systems. Instead of just generating text, AI can now trigger workflows, call APIs, read databases, and execute code. Combined with persistent orchestration, this means AI can do real work autonomously.
Specialized automation platforms like Runable are emerging specifically to combine large language model capabilities with proper task execution infrastructure. Rather than waiting for Open AI to redesign Chat GPT, these platforms are building automation platforms from the ground up with background task execution as a core feature.
Mulri-agent systems where different specialized agents work together are becoming feasible. You might have one agent handling data ingestion, another handling analysis, another handling output formatting. These agents coordinate across time and maintain state. The architecture supports complex, long-running workflows.
Cloud infrastructure improvements are enabling longer execution windows. Better-optimized transformer implementations, improved GPU availability, and refined inference methods are all pushing the boundaries on how long AI processing can run without timeout issues.
Context window expansion helps too. As models get larger context windows, they can tackle bigger problems without running out of memory. GPT-4 has 128K tokens. Future models will likely have millions. This doesn't solve the background task problem directly, but it reduces how quickly you hit constraints on big tasks.
The missing piece still remains: built-in background task execution within Chat GPT itself. Don't hold your breath for this. Open AI's architecture and business model seem to actively resist it. But the broader AI ecosystem is adapting and building solutions that provide what Chat GPT won't.
Building Your Own Workarounds: Technical Approaches
If you're technically inclined, you can build workarounds that partially solve this limitation.
Using the Chat GPT API with Python gives you more control than the web interface. You can write a script that makes multiple API calls in sequence, manages state between calls, implements retry logic, and handles timeouts gracefully. You can persist intermediate results to a database. You can implement scheduling with something like schedule or Celery.
Here's a rough approach:
- Break your task into discrete subtasks that can each complete in under 5 minutes
- Write a Python script that processes subtasks sequentially or in parallel
- Save results from each subtask to a database or file
- If a subtask fails, implement retry logic
- Once all subtasks complete, assemble the final result
- Use a job scheduler to run this on a schedule if needed
This works but requires Python skills and server infrastructure (or a service like Heroku to run your scripts).
Integrating with Zapier or Make lets you orchestrate workflows that use Chat GPT for specific steps while other services handle persistence and orchestration. Chat GPT becomes one node in a larger workflow rather than the entire system.
Using Git Hub Copilot or similar tools to generate code that handles automation independently of Chat GPT shifts the burden. You use Chat GPT to understand what you want to build, then use other tools to actually build it.
Building with Lang Chain if you're serious about AI automation gives you a framework specifically designed for this. You write Python using Lang Chain's abstractions, and you get memory, tools, agents, and orchestration included.
For non-technical users, these approaches are unrealistic. That's why platforms like Runable exist. They provide the infrastructure and capability without requiring you to understand Python, databases, or APIs.
Real-World Costs of This Limitation
Let's quantify what this limitation actually costs you.
Time is the biggest cost. Every task that would run autonomously in a proper automation system becomes a manual drag in Chat GPT. You either spend hours babysitting the chat window, or you split the task into smaller chunks and do a lot of manual assembly.
For professionals, this time translates directly to dollars. If you bill
Tasks left undone is a hidden cost. Documentation doesn't get written. Reports don't get comprehensive. Analysis stays shallow. You operate with incomplete information because the manual effort required to do it right is too high.
Software licensing and infrastructure costs add up. You end up paying for Chat GPT Plus (
Opportunity cost is the real killer. Tasks that would unlock new capabilities—comprehensive documentation, detailed reporting, advanced analysis—don't get done because the friction is too high. You don't realize the opportunity cost until you see what's possible when you have proper automation.
Quality degradation happens subtly. You generate partial documentation instead of complete. You run analysis on sample data instead of entire datasets. You create reports monthly instead of weekly. You make good-enough decisions instead of data-driven decisions. The inability to automate complex tasks means you settle for simpler approaches.
For enterprises, this is even more pronounced. A company with fifty employees each losing three hours per week to manual AI-related tasks is losing 150 hours of productivity. At average salary, that's

The Bottom Line: When to Use Chat GPT vs. Automation Platforms
Clear decision rules help you choose the right tool.
Use Chat GPT when:
- You need quick answers to specific questions
- You're actively engaged in the conversation
- Tasks complete within minutes
- You need iterative back-and-forth exchange
- You're learning or brainstorming
- You don't have technical infrastructure
Use automation platforms (like Runable) when:
- Tasks need to run independently while you do other work
- You need scheduled or triggered execution
- You're processing large datasets or files
- You need persistent state across multiple steps
- Tasks require parallel execution
- You need reliable error handling and retries
- Time savings matter financially
- You need output in multiple formats (documents, presentations, reports)
The truth is, most serious automation work needs the second category. Chat GPT is fantastic for thinking through problems and generating initial solutions. But once you're ready to actually automate and run at scale, you need infrastructure designed for that purpose.
Use Case: Set up daily automated reports from your sales data, generate presentation decks automatically, and get notified when everything's ready—without touching a chat window.
Try Runable For FreeThe emerging landscape of AI automation tools means you have real alternatives now. Chat GPT remains excellent for what it was designed for. But for background task automation, you have better options.
FAQ
What exactly is the background task limitation in Chat GPT?
Chat GPT cannot execute tasks in the background while the user is inactive or away from the chat interface. Every task must complete within an active message turn. Once you close the window or move to another conversation, any processing stops. This means Chat GPT is unsuitable for long-running processes, scheduled automation, or tasks that require maintaining state over extended periods.
Why doesn't Open AI just add background task support to Chat GPT?
Adding true background task execution would require fundamental architectural redesign. Chat GPT operates on a stateless, request-response model that's simple and highly scalable. Background tasks require persistent state management, task orchestration, complex error handling, and significantly different infrastructure. This would increase operational complexity and costs substantially. Additionally, it might cannibalize revenue Open AI sees from API access and their focus on conversational interactions.
How long can a single task run in Chat GPT before it times out?
Practically, most tasks should aim to complete within 3-5 minutes. Theoretical HTTP timeouts are around 5 minutes, but network latency, server load, and token generation speed all consume that window. Context window constraints also kick in well before timeout issues. Large tasks involving significant data processing often fail before reaching any hard timeout limit simply because they run out of context space.
Can I save progress and continue a task later in Chat GPT?
You can save conversation history, but true task resumption is limited. Chat GPT maintains conversation context, so you can reference earlier messages and ask it to continue. However, the system doesn't preserve actual execution state—only the conversation transcript. Reconstructing complex execution state from conversation history is error-prone and inefficient, often resulting in repeated work or inconsistent results.
What's the practical difference between Chat GPT and automation platforms like Runable for task execution?
Chat GPT is a conversational interface optimized for human interaction. Runable and similar platforms are specifically designed for autonomous AI execution. They maintain persistent state, support scheduling, enable parallel task execution, handle failures with retries, and can generate multiple output formats (documents, presentations, reports, images, videos) without user intervention. You set up a workflow once and it runs repeatedly, completing tasks while you focus on other work.
Is Chat GPT API any better than the web interface for background tasks?
The API offers more flexibility than the web interface, but it doesn't solve the fundamental limitation. You can write custom code to manage retries, persist intermediate results, and implement custom timeouts. You can orchestrate multiple sequential API calls and build some automation around them. However, the core constraint remains: Chat GPT itself cannot execute background tasks. You're just managing the workflow externally rather than having it managed by the service itself.
How does Runable handle background task execution differently than Chat GPT?
Runable is built from the ground up with persistent task execution as a core feature. It supports AI agents that continue working autonomously, maintains execution state across sessions, supports scheduling and triggering, enables parallel processing, handles errors with intelligent retry logic, and can generate complex outputs (presentations, documents, reports, images, videos). Starting at $9/month, it's designed specifically for teams needing reliable, scalable AI automation.
When should I stick with Chat GPT instead of upgrading to an automation platform?
Stick with Chat GPT for interactive tasks where you're actively engaged and the work completes quickly. Use it for brainstorming, learning, quick content generation, or one-shot questions. Upgrade to automation platforms when you have repetitive tasks, need scheduled execution, process large datasets, or want work to continue while you're doing other things. If you're asking "can this task run without me actively watching?" the answer should be yes, and Chat GPT won't provide that.
What would it cost Chat GPT to add true background task support?
Nobody outside Open AI knows exactly, but the costs would be substantial. Significant engineering effort to redesign core architecture, new infrastructure for task management and persistence, expanded database requirements, specialized job scheduling and monitoring systems, more complex billing systems, and increased operational overhead. The disruption to existing systems would be immense. This is likely why Open AI hasn't attempted it despite it being a frequently requested feature.
TL; DR
- The Core Problem: Chat GPT cannot work in the background once a message turn ends. Everything must happen within an active conversation window.
- Why It Matters: This limitation makes entire categories of automation impossible—scheduled tasks, long-running processes, data processing at scale, and background monitoring all fail.
- Why It Exists: Chat GPT's architecture is stateless and request-response based. Adding persistent background execution would require fundamental redesign.
- Real Cost: Professionals lose hours per week to manual task management. Teams operate with incomplete data and documentation because automation is too tedious.
- The Solution: Automation platforms like Runable (starting at $9/month) provide proper background task execution with AI-powered intelligence, document generation, presentation creation, and reporting automation—all autonomously.
- Bottom Line: Chat GPT is fantastic for conversations. If you need actual automation, you need infrastructure designed for it. The good news is that infrastructure exists and is finally accessible to non-technical users.

Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT fundamentally cannot execute tasks in the background—all processing must occur within active message turns and stops once sessions end
- This limitation eliminates entire automation categories: scheduled workflows, long-running processes, batch operations, and persistent state management
- The architectural reason is ChatGPT's stateless request-response design optimized for conversational interaction, not autonomous task execution
- Real-world cost is significant: professionals lose hours weekly to manual workarounds, incomplete automation, and reduced productivity
- Purpose-built automation platforms like Runable ($9/month) provide true background execution, persistence, scheduling, and output generation in multiple formats
Related Articles
- Voice-Activated Task Management: AI Productivity Tools [2025]
- ServiceNow and OpenAI: Enterprise AI Shifts From Advice to Execution [2025]
- Why Agentic AI Pilots Stall & How to Fix Them [2025]
- Google Gemini Meeting Scheduler: AI Calendar Optimization [2025]
- Claude MCP Apps Integration: How AI Meets Slack, Figma & Canva [2025]
- AI Coordination: The Next Frontier Beyond Chatbots [2025]
![ChatGPT's Critical Limitation: No Background Task Support [2025]](https://tryrunable.com/blog/chatgpt-s-critical-limitation-no-background-task-support-202/image-1-1769485198056.jpg)



