Mobile App Spending Surpasses Gaming in 2025: AI Adoption Trends & Complete Guide
Introduction: A Historic Shift in Mobile Economics
The mobile ecosystem experienced a fundamental turning point in 2025. For the first time in global history, consumers spent more money on non-game mobile applications than they did on gaming apps. This watershed moment represents far more than a simple revenue reallocation—it signals a profound restructuring of how users interact with mobile technology and where developers should focus their resources.
According to industry intelligence gathered from comprehensive market analysis, worldwide consumers deployed approximately **
What catalyzed this seismic shift? The primary driver wasn't incremental improvements to productivity tools or social platforms. Instead, generative artificial intelligence emerged as the dominant force, fundamentally changing user expectations and willingness to pay for mobile applications. Revenue derived from in-app purchases within AI-focused applications more than tripled, reaching **
This transformation extends beyond revenue metrics. Downloads of AI-powered applications doubled year-over-year, reaching 3.8 billion downloads. The user engagement patterns tell an even more compelling story: consumers spent an astounding 48 billion cumulative hours within generative AI applications during 2025. To illustrate the growth trajectory, this represents 3.6 times the total engagement seen in 2024 and represents a tenfold increase compared to 2023 levels.
The implications for developers, entrepreneurs, and technology investors are substantial. The market is clearly signaling that artificial intelligence capabilities have transitioned from "nice-to-have" features to "essential infrastructure" that justifies direct consumer spending. This article provides comprehensive analysis of this historic transition, examining the underlying factors, key market players, revenue dynamics, and what these trends mean for the future of mobile application development and business strategy.
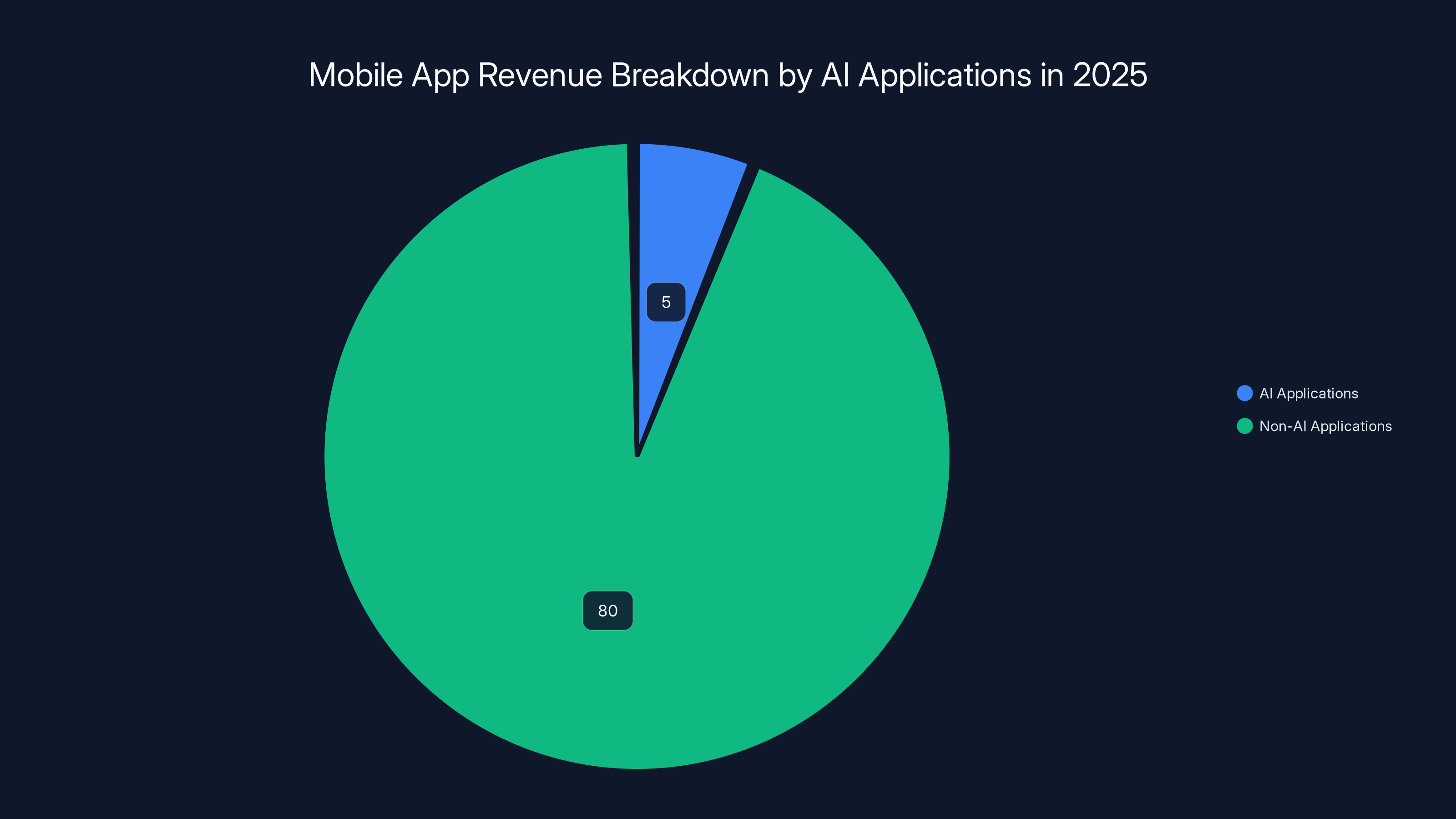
AI applications contributed approximately 6% to the total mobile app revenue in 2025, highlighting their significant role in driving market growth despite a smaller market share. Estimated data.
The Rise of Generative AI Apps: Market Dynamics and Disruption
How AI Apps Became Revenue Leaders
The ascendancy of generative AI applications to market dominance represents one of technology's fastest market adoption curves. What began as experimental interfaces to large language models in late 2022 transformed into a multi-billion-dollar category within just two years. This acceleration wasn't gradual—it was exponential.
The primary mechanism driving this adoption was the democratization of sophisticated AI capabilities. Previously, only well-funded enterprises possessed access to advanced natural language processing, image generation, and reasoning systems. Mobile applications transformed these enterprise-grade capabilities into consumer-accessible tools. Users could now access artificial intelligence assistants offering capabilities that previously required specialized technical knowledge or expensive subscriptions to enterprise software platforms.
OpenAI's Chat GPT emerged as the undisputed market leader, generating $3.4 billion in global in-app purchase revenue throughout 2025. This single application captured approximately 68% of all revenue generated within the AI assistant category. The scale of Chat GPT's mobile adoption illustrates the magnitude of market demand: Chat GPT's mobile interface surpassed the adoption velocity of essentially every historical software application category.
Competitors rapidly mobilized to capture their own share of the expanding market. Google deployed Gemini, integrating its advanced language models into an accessible mobile experience. Microsoft leveraged its partnership relationships and enterprise distribution channels. Chinese technology companies like Byte Dance introduced specialized AI applications focusing on content generation, video synthesis, and creative capabilities. Deep Seek, a newcomer to the market, achieved remarkable adoption velocity through optimized performance characteristics and distinctive reasoning capabilities.
The competitive intensity driving feature improvements created a virtuous cycle of rapid capability enhancement. Applications competed not through traditional distribution advantages or brand recognition, but through measurable improvements in factual accuracy, reasoning capabilities, coding assistance, image generation quality, and response speed. This competitive pressure accelerated the timeline for deploying new capabilities from years to months or even weeks.
Market Concentration and Publisher Consolidation
A striking characteristic of the AI app market is the extraordinary concentration of downloads and revenue among a small number of publishers. Among the leading AI application publishers, OpenAI and Deep Seek collectively captured nearly 50% of all global downloads. This represents a significant shift from 2024, when these two companies represented only 21% of total downloads.
This consolidation trend extended to major technology companies. Google, Microsoft, and other established technology publishers grew their collective market share from 14% in 2024 to nearly 30% in 2025. This growth came at the direct expense of earlier-stage AI assistant competitors that achieved initial popularity in 2023 and early 2024. Applications like Nova, Codeway, and Chat Smith—which previously held meaningful market positions—experienced significant user migration toward applications offered by more established publishers.
The consolidation pattern reflects several market dynamics. First, users demonstrated strong preference for AI applications backed by advanced capabilities and substantial computational resources. OpenAI's access to sophisticated GPT models, Google's Gemini architecture, and Microsoft's computational infrastructure translated into tangible user experience advantages. Second, major technology companies possessed distribution advantages through integration with existing ecosystems, pre-installation relationships with device manufacturers, and marketing resources. Third, users showed willingness to consolidate their AI assistant usage around a small number of primary applications rather than maintaining multiple competing tools.
This concentration pattern has important implications for new market entrants and emerging companies. The barriers to achieving meaningful market share in the AI assistant category increased substantially. Success increasingly required either differentiated capabilities unavailable through leading competitors, specialized focus on vertical-specific use cases, or partnership relationships with major distribution channels.
Geographic and Demographic Variations in AI App Adoption
While the global AI app market demonstrated explosive growth, adoption patterns varied significantly by geographic region and demographic segment. North American and Western European markets achieved earlier adoption and higher per-user spending. Asian markets, while demonstrating strong growth trajectories, showed different category preferences. For instance, text-to-video and music generation applications achieved disproportionate adoption in Asia relative to other regions.
Demographic patterns revealed that AI assistant adoption concentrated among internet-native populations with higher education levels and technology proficiency. However, the expansion of AI applications into specialized domains—coding assistance, content generation, creative tools—extended adoption across increasingly diverse demographic segments. Users in professional categories such as marketing, software development, graphic design, and content creation demonstrated particularly strong adoption of AI tools aligned with their professional workflows.
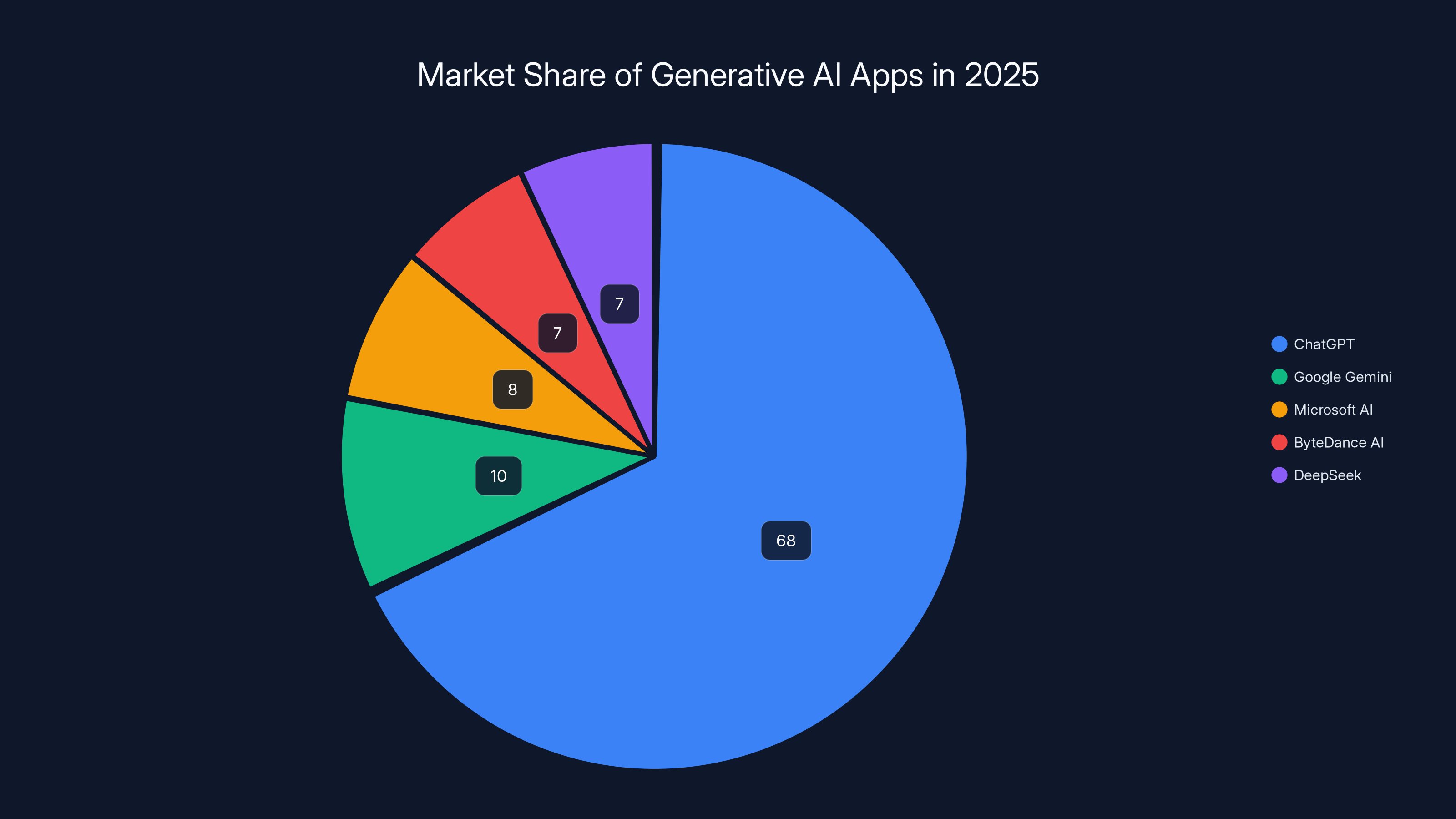
ChatGPT dominated the generative AI app market in 2025, capturing 68% of the revenue, with other players like Google Gemini and Microsoft AI sharing the remaining market space. (Estimated data)
Revenue Deep Dive: Understanding the $85 Billion Market
Total App Spending Growth and Year-Over-Year Trends
The $85 billion in global mobile app spending during 2025 represents a comprehensive victory for non-gaming applications. This figure encompasses all categories: AI assistants, productivity tools, social media platforms, video streaming applications, music generation tools, dating applications, financial software, health and fitness tools, and specialized vertical applications.
The 21% year-over-year growth rate significantly outpaced the growth rate of the overall global software market, illustrating the mobile channel's increasing importance within the broader technology ecosystem. For context, this growth rate implies that the mobile app market was expanding at approximately 4.2 times the rate of nominal global GDP growth, indicating substantial market-share gains from other software distribution channels and genuine expansion of consumer digital spending.
The growth acceleration compared to previous years deserves attention. In 2024, mobile app spending increased approximately 15% year-over-year. The 2025 acceleration from 15% to 21% growth suggests that AI-related applications created incremental demand that might not have otherwise materialized, rather than simply redirecting spending from existing categories. Users appeared willing to expand total digital spending to encompass AI capabilities they perceived as genuinely novel and valuable.
In-App Purchase Revenue Architecture
Approximately 68% of mobile app revenue derived from in-app purchases, with the remaining 32% distributed across subscriptions, ads, and alternative monetization models. The distinction between these revenue streams carries strategic importance. Subscription models typically generate recurring, predictable revenue streams but require sustained user engagement and perceived continuous value delivery. In-app purchases often generate higher initial revenue per transaction but require sophisticated user psychology and engagement optimization to achieve sustainable monetization.
AI applications predominantly employed subscription models or hybrid models combining low-friction initial access with premium subscription tiers. Chat GPT, for instance, offered free access to the base model with Chat GPT Plus subscriptions providing access to advanced models, priority access, and advanced features. This freemium model balanced user acquisition objectives against monetization requirements.
The shift toward AI applications specifically drove substantial growth in premium subscription adoption. Users demonstrated willingness to pay recurring subscription fees—often in the
Geographic Revenue Distribution and Market Concentration
North America and Western Europe collectively represented approximately 65% of total global mobile app spending, despite containing only approximately 12% of global population. This disparity reflects differences in average consumer wealth, digital payment infrastructure adoption, and technological literacy. Asian markets represented the second-largest revenue center at approximately 28% of total spending, while emerging markets collectively represented approximately 7%.
The geographic concentration of spending creates challenges and opportunities for application developers. Markets with the highest spending demonstrated the most competitive environments and often the most sophisticated user expectations regarding application quality and feature sophistication. Emerging markets presented larger user bases but lower average revenue per user, requiring different business model optimization.
The AI App Category: Detailed Segment Analysis
AI Assistants and Large Language Model Applications
AI assistants—applications built around conversational interfaces to large language models—comprised the dominant segment within AI applications. These applications enabled users to engage in text-based conversations with artificial intelligence systems, requesting information, writing assistance, coding help, creative content generation, analysis, research support, and countless other tasks. The category experienced virtually unlimited user demand discovery throughout 2025.
The leading AI assistants competed on multiple dimensions. Capability depth addressed the sophistication and accuracy of responses across different domains. Response speed affected perceived quality and user satisfaction. Integration capabilities allowed AI assistants to interact with other applications and data sources. Specialization features tailored applications toward specific professional or creative use cases. User interface design and accessibility influenced adoption among less technically sophisticated users.
Chat GPT's dominance stemmed from a combination of factors: OpenAI's access to advanced models, the company's focus on user experience refinement, aggressive product development timelines, and relatively transparent communication regarding model capabilities and limitations. Chat GPT's $3.4 billion in annual revenue represented extraordinary per-user monetization, suggesting not only high adoption but also premium feature adoption among users willing to pay for advanced capabilities.
Google Gemini leveraged integration with Google's ecosystem, including Gmail, Google Docs, Google Calendar, and Google Drive. This integration strategy offered unique value propositions unavailable through standalone AI assistants. Users could request assistance with email composition, document editing, schedule management, and file organization—all within familiar interfaces. Microsoft's Copilot followed similar integration strategies, emphasizing Office suite integration and professional workflow optimization.
Specialized AI Applications and Vertical Solutions
Beyond general-purpose AI assistants, specialized applications targeting specific use cases achieved remarkable adoption and monetization. These included AI applications focused on image generation, video synthesis, music composition, coding assistance, and creative content production. The specialization approach often allowed developers to deliver superior user experiences within narrow domains compared to general-purpose assistants attempting to serve all use cases.
Suno, an AI music generation application, demonstrated the potential for specialized AI tools. Users could generate original musical compositions by describing desired musical characteristics, specifying genres, instrumentation, and mood. The application built communities of musicians, producers, and music enthusiasts experimenting with AI-assisted composition. Suno's success illustrated that substantial markets exist for AI applications addressing specific creative domains.
Byte Dance's Jimeng AI provided text-to-video synthesis capabilities, allowing users to generate video content from textual descriptions. This application aligned with the explosive growth in short-form video content and the shortage of skilled video production professionals. Users without video production expertise could generate compelling video content, expanding the addressable market for video creation tools.
Character.ai and similar AI companion applications offered persistent conversational experiences, allowing users to develop ongoing relationships with distinctive AI personalities. These applications explored the intersection of AI technology and human psychology, investigating whether users would value emotional connections with artificial entities. The category achieved meaningful adoption, suggesting genuine demand for this experience category.
Content Creation and Productivity AI Tools
AI applications addressing professional and creative productivity—such as writing assistance, image editing, code generation, and document synthesis—comprised a substantial market segment. These applications reduced barriers to entry for professional activities, enabling non-specialists to produce professional-quality output.
Writing assistance applications employed AI to improve writing quality, suggest structural improvements, offer synonym recommendations, and generate content outlines. These tools appealed to professional writers, content creators, students, business professionals, and anyone producing written communication. The accessibility of AI-powered writing assistance fundamentally altered content production workflows across numerous professions.
Image and video generation tools represented another high-growth category. These applications enabled users to create visual content without specialized design skills. Professionals could accelerate design workflows by using AI generation to create initial concepts, reducing the time required for design iteration. Non-professionals could generate professional-quality visual content, democratizing capabilities previously limited to specialized professionals.
Coding assistance tools like GitHub Copilot and similar applications transformed software development workflows. These tools suggested code completions, generated entire functions, identified bugs, and provided optimization recommendations. Professional software developers adopted these tools extensively, reporting 20-40% productivity improvements. For less experienced developers, coding assistance reduced barriers to entry and accelerated skill development.
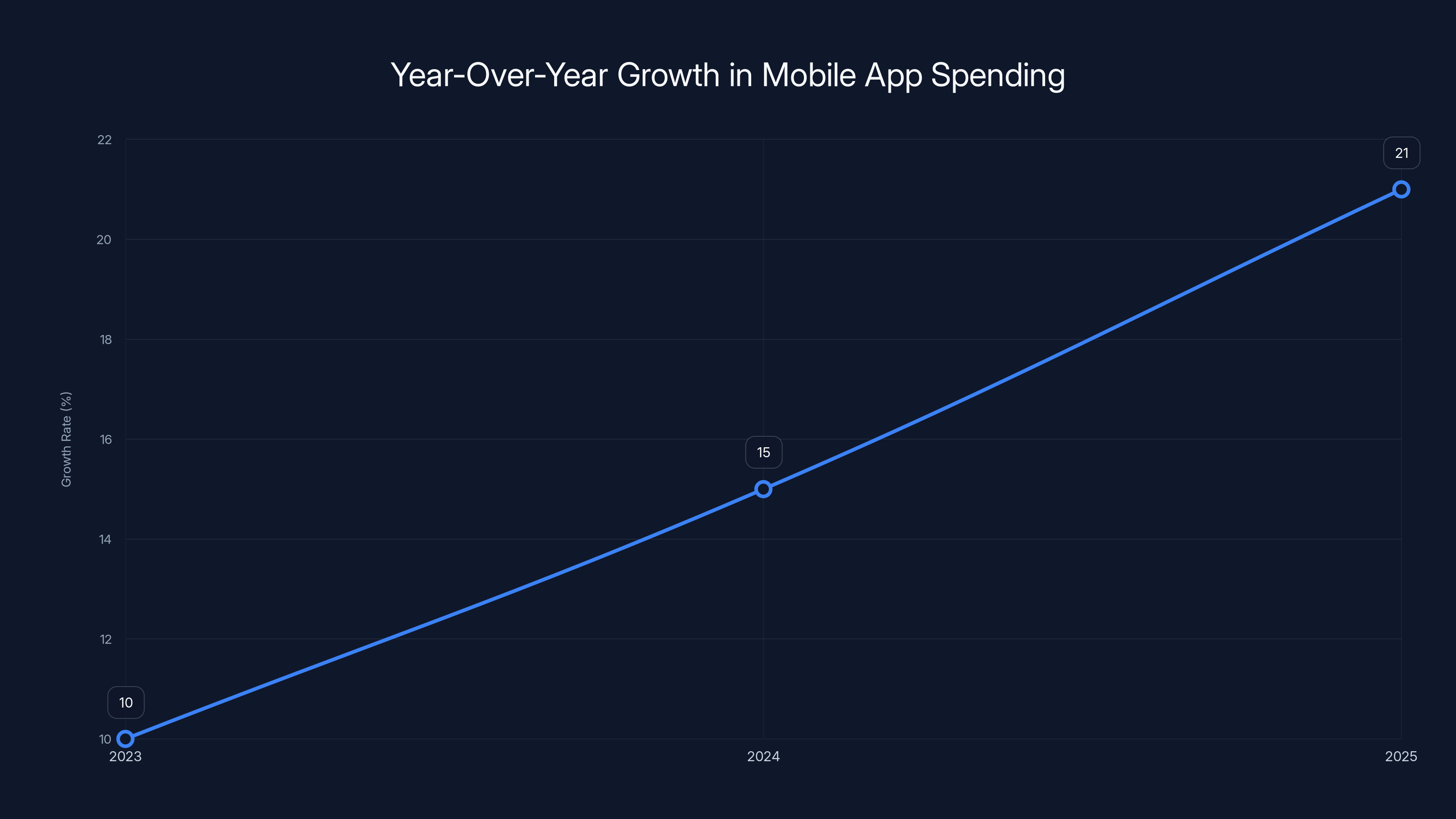
The mobile app market's growth rate accelerated from 15% in 2024 to 21% in 2025, driven by AI-related applications. Estimated data based on market trends.
User Engagement Metrics: Revealing Behavioral Patterns
Time Investment and Daily Active Usage
The sheer magnitude of user time investment in AI applications throughout 2025 provides powerful evidence of genuine utility delivery and engagement. Users collectively spent 48 billion hours in generative AI applications during the year. This figure represents far more than a vanity metric—it reflects genuine consumer choice about how to allocate limited leisure and work time.
To contextualize this engagement volume: if distributed evenly across the approximately 200 million monthly active users of AI assistants, this represents approximately 240 hours of annual engagement per user, or roughly 6 hours per week. For perspective, this exceeds the average weekly consumption of traditional streaming video platforms and approaches engagement levels with social media applications, historically the engagement leader in mobile applications.
The engagement concentration pattern deserves attention. Rather than spreading evenly across the user base, engagement concentrated among particularly engaged users. The most active 20% of users likely accounted for 60-70% of total engagement, reflecting classic power-law distribution patterns observed in digital applications. This concentration pattern indicates that a core group of professional users, hobbyists, and enthusiasts adopted AI applications as essential tools integrated into daily workflows, while the broader user base engaged more sporadically.
Session frequency metrics illuminated user behavior patterns. Session volume—measuring the number of times users opened AI applications—exceeded one trillion sessions during 2025. Remarkably, session volume grew faster than download growth, indicating that existing users deepened their engagement more rapidly than applications recruited new users. This pattern suggests strong retention and expanding use cases rather than churn toward alternative applications.
Mobile-Only Access Patterns
A particularly significant finding concerned the predominance of mobile-exclusive access. In the United States, where comprehensive data was available, AI assistant audiences exceeded 200 million users by year-end 2025. Most strikingly, 110 million users (55%) accessed AI assistants exclusively through mobile devices, without using desktop or web interfaces.
This mobile-first access pattern represents a fundamental shift in how users interact with sophisticated technology. Traditional perception viewed mobile devices as secondary interfaces—useful for consuming content or quick interactions, but limiting for complex tasks requiring significant input, output, or computational sophistication. AI applications inverted this paradigm. Users discovered that conversational interfaces suited mobile interaction patterns perfectly. Users could pose questions, receive responses, and continue conversations through mobile devices as effectively as desktop experiences.
The mobile-first adoption pattern has strategic implications for developers and infrastructure providers. It indicates that cloud computing infrastructure, sophisticated algorithms, and complex computational models can deliver value through mobile interfaces without requiring local computational resources. The mobile interface abstraction allows users to leverage powerful remote systems through familiar mobile interaction paradigms.
The growth trajectory of mobile-exclusive users provides perspective on adoption velocity. In 2024, approximately 13 million users in the US accessed AI assistants exclusively through mobile interfaces. By 2025, this figure reached 110 million. This represents an 8.5x multiplication in a single year. Such velocity suggests that substantial additional growth remained possible as mobile technology continued improving and AI application interfaces continued evolving.
Competitive Dynamics and Market Consolidation
The Rise of Big Tech and Market Leadership
The 2025 mobile app market demonstrated the enduring competitive advantages of established technology companies. Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Byte Dance all achieved meaningful positions in the mobile app economy. These companies possessed multiple competitive advantages: massive existing user bases providing distribution channels, substantial financial resources enabling rapid capability development, technical talent depth, existing relationships with device manufacturers, and ability to integrate AI capabilities across multiple products and services.
Google's strategy emphasizes ecosystem integration. Gemini's mobile presence expands through integration with core Google services—Gmail, Google Maps, Google Search, YouTube, and Google Photos. Users experiencing Gemini within familiar interfaces require less onboarding compared to standalone applications. Ecosystem integration also provides network effects: as Gemini capabilities expand across more Google services, incentives increase for users to engage with Google's ecosystem.
Microsoft pursued similar integration strategies through Copilot integration across Windows, Office applications, and cloud services. Apple developed Siri capabilities incorporating AI functionality while maintaining privacy-focused positioning. Meta integrated AI capabilities across WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook. Byte Dance deployed AI applications across TikTok and subsidiary services.
Challenges for Independent and Startup Competitors
The consolidation pattern created substantial headwinds for independent software companies and startups attempting to establish meaningful market positions. Earlier competitors that achieved initial traction in 2023-2024 found their competitive advantages eroding as big technology companies deployed resources and capabilities.
Several factors contribute to this dynamic. First, the shift toward vertical integration—where large companies bundle AI capabilities into existing products—provides distribution advantages that pure-play AI application companies cannot match. Users experience AI capabilities within applications they already use frequently, reducing friction and engagement barriers. Second, big technology companies can afford to offer AI capabilities at reduced prices, using revenue from other business segments to subsidize consumer-facing AI applications. This pricing power makes profitability challenging for dedicated AI companies. Third, major technology companies possess technical talent and computational resources that allow continuous capability improvements, making it difficult for smaller competitors to maintain differentiation based on model capabilities alone.
However, opportunities persist for specialized and vertical-specific applications. Applications addressing narrow use cases, serving specialized professional communities, or providing distinctive experiences unavailable through general-purpose assistants can achieve meaningful success. The key differentiator involves delivering clear, measurable value that users perceive as superior to general-purpose alternatives. Additionally, privacy-focused, open-source, and locally-hosted alternatives appeal to segments prioritizing data control and transparency.
International Variations in Market Leadership
While OpenAI and Google dominated global market share, regional variations existed. In China, Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, and Byte Dance achieved dominant positions, with Deep Seek emerging as a notable challenger. In Japan, LINE and other local companies maintained competitive positions. In India, local language and region-specific applications achieved meaningful adoption.
These geographic variations reflect multiple factors: regulatory differences, user preference for local language interfaces and cultural adaptation, existing distribution relationships with local device manufacturers, and network effects within local technology ecosystems. Understanding regional dynamics becomes essential for companies pursuing international expansion strategies.
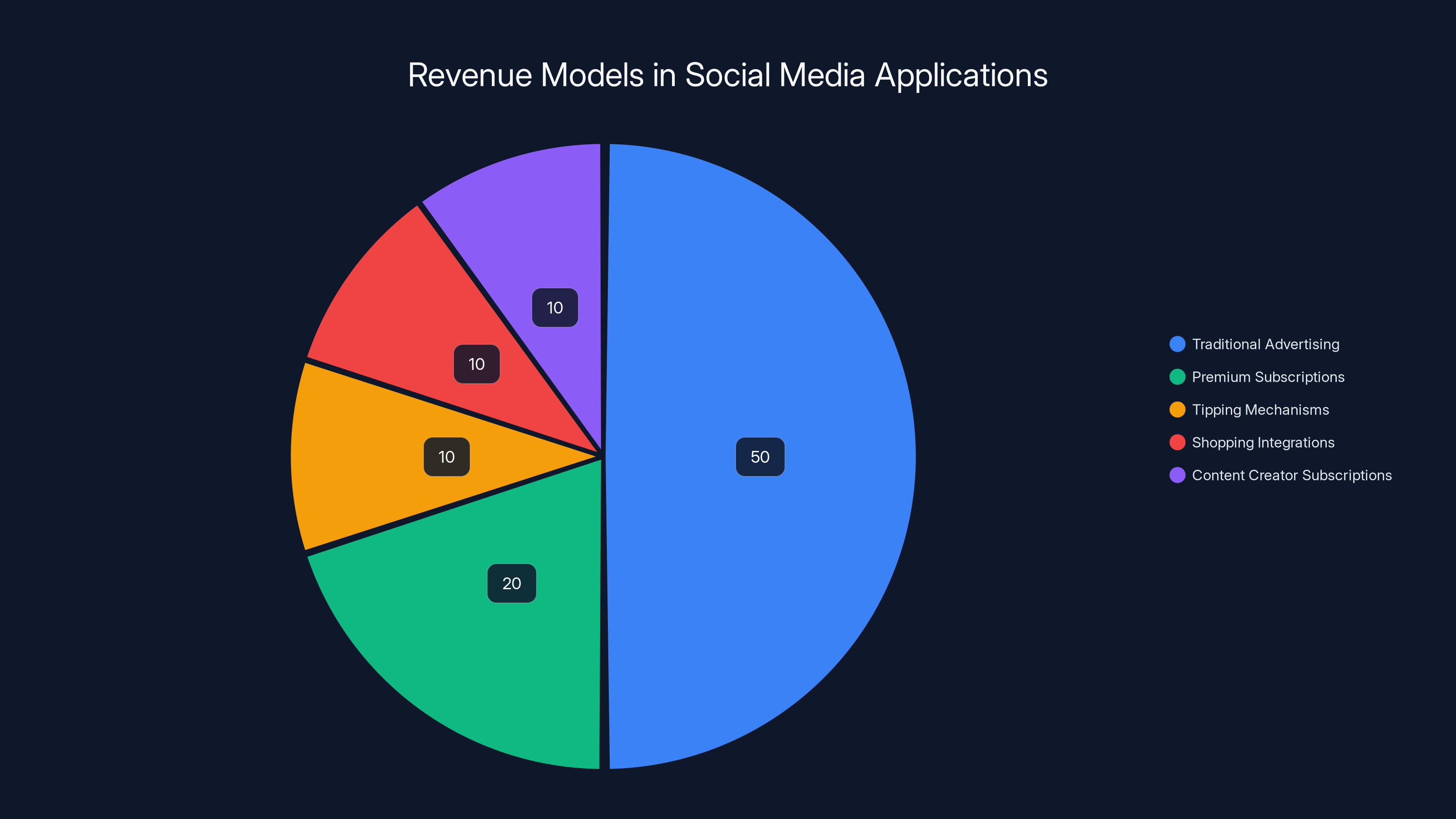
Traditional advertising remains the dominant revenue model in social media applications, accounting for an estimated 50% of revenue. However, alternative models like premium subscriptions and shopping integrations are gaining traction. Estimated data.
Beyond AI: Revenue Drivers in Other App Categories
Social Media Applications and Time Investment
While AI applications dominated growth narratives, established app categories continued generating substantial revenue and engagement. Social media applications demonstrated remarkable resilience and continued growth despite decades of maturity. Users spent an average of 90 minutes daily on social media applications, translating to approximately 2.5 trillion hours annually. This engagement increased 5% year-over-year, maintaining steady growth trajectories.
Social media monetization evolved throughout 2025. Traditional advertising remained the dominant revenue model, but applications increasingly explored alternative monetization: premium subscriptions offering ad-free experiences or exclusive features, tipping mechanisms compensating creators, shopping integrations enabling commerce, and subscription services for content creators.
The dominance of social media in time investment reflects fundamental psychological and social drivers. Humans possess intrinsic motivation to maintain social connections, observe social hierarchies, understand peer activities, and participate in community identity. Social media applications fulfill these motivations through digital interfaces, explaining persistent engagement despite critics' concerns regarding well-being impacts.
Video Streaming Services and Subscription Economics
Video streaming applications—Netflix, YouTube, Disney+, Amazon Prime Video, and numerous regional competitors—generated substantial revenue through subscription models. The category's profitability improved substantially as streaming services achieved scale economies, secured content efficiently, and optimized technology infrastructure costs.
Streaming services increasingly adopted ad-supported tiers as differentiation strategies. Users could access content at lower prices in exchange for advertising exposure. This tiering expanded addressable markets by serving cost-conscious segments previously priced out by premium-only offerings. The ad-supported model also improved profitability for many services, as incremental advertising revenue often exceeded customer acquisition costs for economically marginal users.
The competitive intensity among streaming services drove content differentiation and exclusive original programming investment. Services competed partly on content libraries, but increasingly on exclusive originals, specialized genres, and differentiated user experiences. This competition benefited consumers through content expansion but created challenges for profitability as content costs escalated.
Productivity and Utility Applications
Productivity applications—note-taking, task management, file storage, collaboration tools—maintained steady adoption and monetization. These applications typically targeted professional or ambitious consumer segments willing to pay for functionality enhancing personal productivity or professional effectiveness.
The integration of AI capabilities into productivity applications accelerated throughout 2025. Note-taking applications incorporated AI-powered search, summarization, and organization features. Project management applications employed AI to suggest resource allocation, identify risks, and optimize schedules. These integrations enhanced perceived value and justified premium pricing.

Technical Infrastructure and Computational Requirements
Cloud Computing and Scaling Challenges
The massive scale of AI application usage created unprecedented computational requirements. Serving one trillion sessions—each potentially requiring queries to sophisticated language models—demanded extraordinary infrastructure. Processing queries from 200 million monthly active users in the US alone, combined with global users, required thousands of data centers operating continuously at high capacity utilization.
OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and other leading AI companies invested billions into computational infrastructure. These investments encompassed GPU and TPU acquisitions, data center construction, network infrastructure, and power generation. The infrastructure requirements represent genuine barriers to entry, as establishing competitive computational capacity requires multi-billion-dollar capital commitments and sustained operational expertise.
Optimization became critical to profitability. Every millisecond of latency reduction, every efficiency improvement in token processing, and every reduction in computational requirements per query directly impacts profitability at scale. Companies pursuing AI applications at scale invested heavily in optimization research, model distillation, and inference efficiency improvements.
Model Architecture and Performance Innovations
Throughout 2025, leading AI companies released improved model architectures and performance innovations. OpenAI released GPT-4o with enhanced image generation capabilities. Google deployed improved Gemini architectures. Deep Seek introduced novel reasoning approaches. These improvements drove competitive dynamics, as users migrated toward applications offering superior capabilities.
The pace of innovation reflected competition intensity and substantial resource deployment. Companies conducted research, executed model training, evaluated performance, refined approaches, and deployed improvements on timescales of weeks to months—far faster than historical software development cycles.
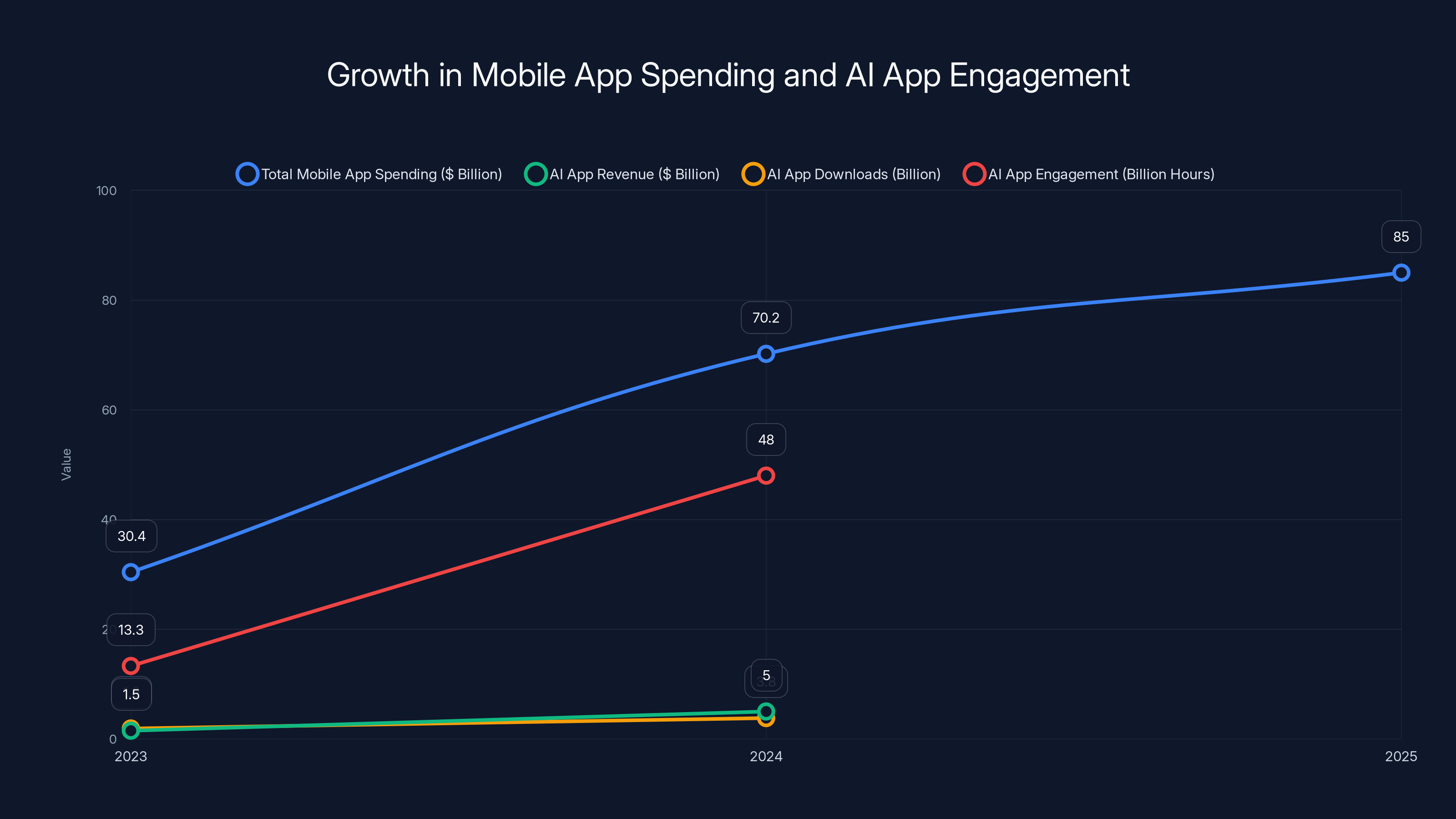
The mobile app market nearly tripled from 2020 to 2025, driven by a surge in AI app engagement and spending. Estimated data highlights the rapid growth in AI app downloads and user engagement.
Monetization Models and Revenue Optimization
Subscription Tier Architecture and Pricing Strategy
Successful AI applications employed sophisticated tiered pricing models. These models typically included free tiers providing basic functionality, mid-tier paid subscriptions offering enhanced capabilities, and premium tiers or specialized products for power users or professionals.
Chat GPT's pricing architecture exemplifies this approach: free access to base models, Chat GPT Plus ($20/month) providing access to advanced models and features, Chat GPT Team for team collaboration, and specialized enterprise offerings. This tiering allows Chat GPT to serve diverse market segments—from casual users discovering AI capabilities, to professionals and organizations integrating AI into workflows.
Pricing strategy balanced revenue optimization against user acquisition and retention. Excessively aggressive pricing alienates casual users, limiting the user base supporting premium conversions. Insufficiently aggressive pricing fails to capitalize on users' willingness to pay and undermonetizes engaged segments.
In-App Purchase Monetization and Impulse Drivers
While subscription models dominated AI application monetization, in-app purchases played meaningful roles. These purchases included advanced features accessed through tokens or points, expedited service delivery, cosmetic customization, or specialized capabilities. In-app purchase psychology—exploiting behavioral economics, social comparison, scarcity, and status signaling—drives engagement among engaged user segments.
Applications balancing in-app purchases and subscriptions required careful psychology management to avoid user backlash regarding excessive monetization. Users tolerated monetization when perceiving genuine value delivery and fair pricing, but rejected applications perceived as exploitative.
Advertising as a Monetization Layer
Lower-tier applications increasingly incorporated advertising or sponsored content, creating friction-free access for cost-sensitive users while capturing advertising revenue. This model allows applications to serve users across broader economic spectrums while maintaining premium offerings for users willing to pay for ad-free experiences.
Advertising within AI applications requires careful implementation to avoid degrading user experience or accuracy. Injecting promotional content into AI-generated responses risks reducing perceived reliability. Advertising integration succeeded when placed adjacent to core content rather than within generated responses.
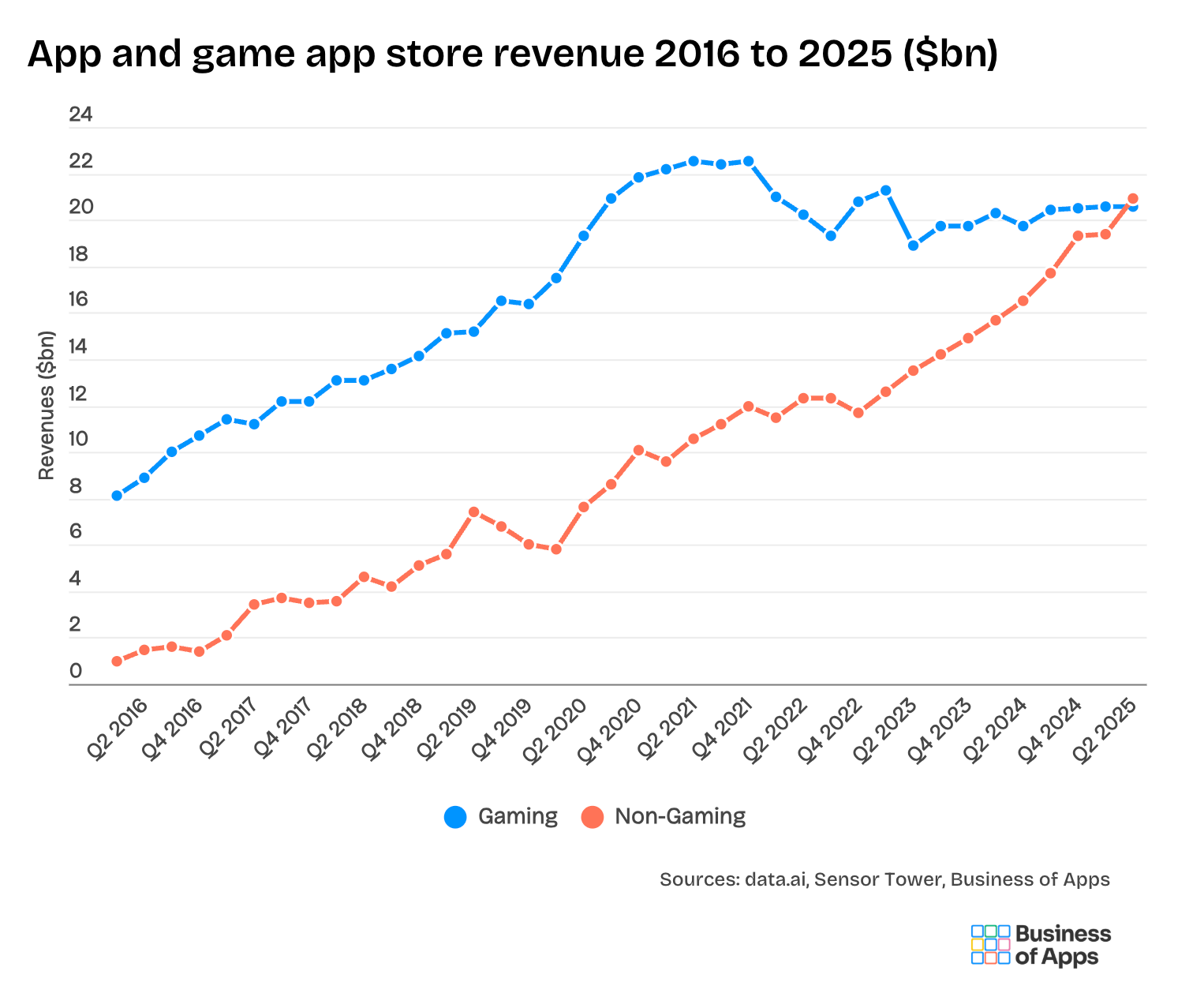
Impact on Developer Economics and Incentive Structures
Shifting Developer Priorities and Platform Focus
The explosion of AI application opportunities and revenue potential fundamentally altered developer incentive structures. Previously, developers pursuing lucrative mobile opportunities focused on social networks, games, and established productivity categories. The emergence of AI applications created fundamentally new opportunities with immediate monetization potential.
Developer attention shifted toward AI capabilities—learning machine learning fundamentals, understanding large language models, exploring prompt engineering, and experimenting with fine-tuning approaches. Online educational platforms, developer communities, and research institutions expanded AI education and training to meet surging demand.
The reallocation of developer attention from games toward AI applications contributed to revenue share shifts. Game development studios faced talent recruiting challenges as developers pursued AI opportunities. This talent reallocation had downstream effects on game development productivity and monetization, contributing to the historic shift where non-game app revenue exceeded gaming revenue.
Emergence of AI-as-a-Service Models
Providers of underlying AI capabilities—OpenAI through its API, Google through Gemini API, Anthropic, Mistral, and others—offered access to advanced models through API-based interfaces. This allowed independent developers to integrate sophisticated AI capabilities into applications without developing foundational models independently.
The API model democratized access to advanced AI capabilities, enabling smaller teams to compete against well-capitalized incumbents by focusing on superior user experience and specialized vertical applications rather than foundational model development. This architectural shift mirrors historical patterns in software where layered abstractions enable broader innovation.
Economic Returns and Unit Economics
Successful AI applications achieved extraordinary economic returns compared to historical software benchmarks. High-engagement users represented genuine monetization opportunities, with some users spending hundreds of dollars annually on AI subscriptions and capabilities. Viral coefficient assumptions—where engaged users recruit additional users—created exponential growth dynamics.
Unit economics for leading AI applications achieved ratios where customer lifetime value substantially exceeded customer acquisition costs. Chat GPT's
These unit economics support the venture capital and corporate investment flowing into AI applications. Investors perceived clear paths to profitability and meaningful scale despite competitive intensity.
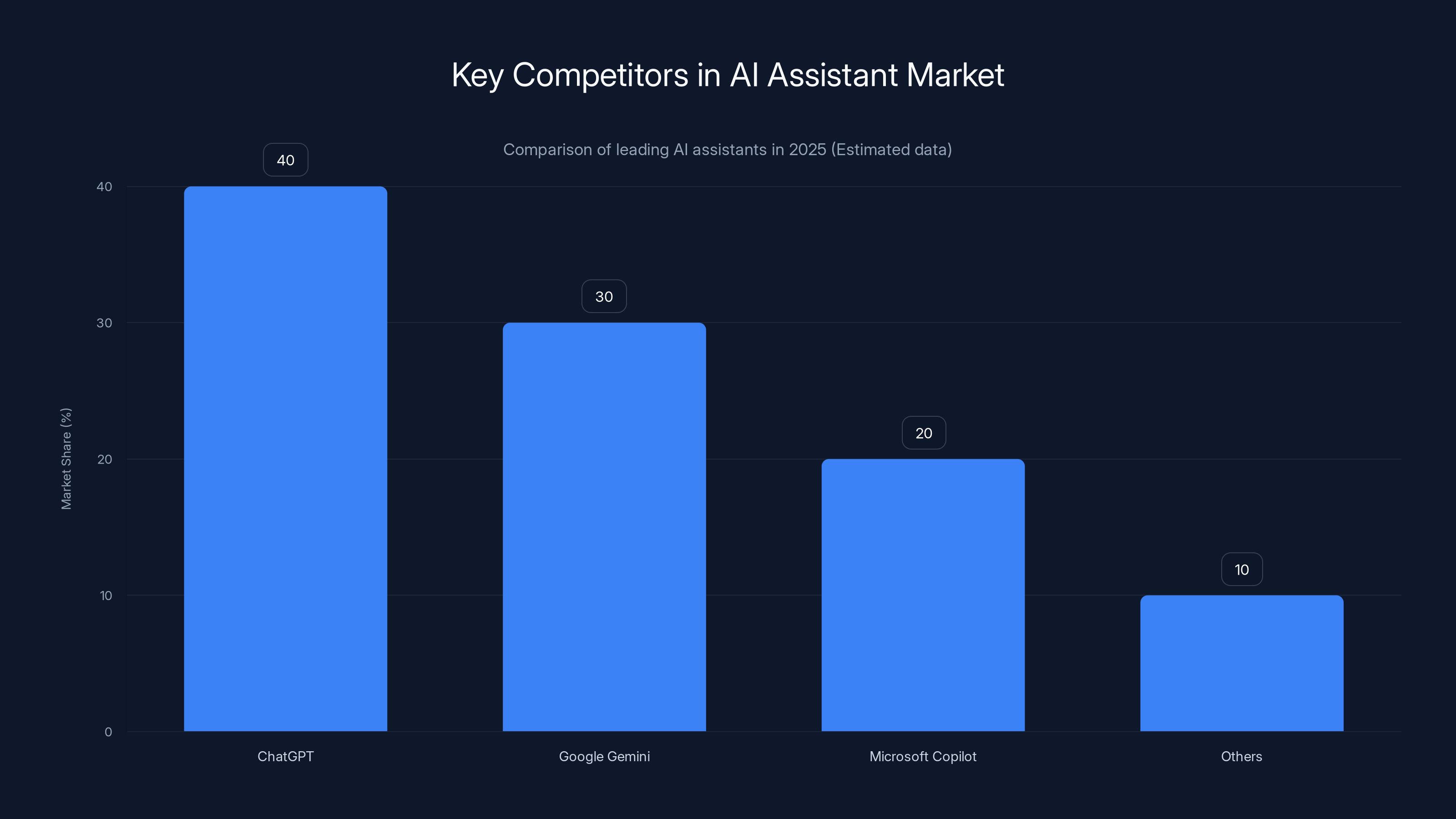
ChatGPT leads the AI assistant market with an estimated 40% share, driven by advanced models and user experience. Google Gemini and Microsoft Copilot follow with strong integration strategies. (Estimated data)
Looking Forward: Future Trends and Market Evolution
Artificial Intelligence Capability Trajectory
Artificial intelligence capabilities continue advancing rapidly. Reasoning capabilities, factual accuracy, domain-specific expertise, image and video generation quality, and multimodal capabilities all improved throughout 2025 and show no signs of plateauing. Continued advancement suggests that AI applications will progressively address increasingly complex tasks and specialized domains.
Future AI applications will likely incorporate real-time information access, deep integration with user data and contexts, personalization based on individual preferences and histories, and reasoning capabilities addressing complex multi-step problems. These capabilities will expand addressable markets and deepen engagement among existing users.
Integration with Physical World and Embodied AI
AI capabilities increasingly extend beyond digital interfaces toward physical world integration. Robots incorporating AI reasoning, autonomous systems deploying AI decision-making, and IoT devices leveraging AI processing represent expanding frontiers. While these technologies typically address enterprise or specialized domains, they represent the future evolution of AI from text-based conversational interfaces toward broader physical and digital integration.
Regulatory and Governance Challenges
As AI applications achieve scale and societal impact, regulatory scrutiny will intensify. Governments worldwide are developing frameworks addressing AI transparency, bias mitigation, data privacy, labor impact, and societal harms. Compliance requirements will increase operational costs and may limit certain use cases or approaches.
Regulatory frameworks will likely vary significantly by jurisdiction, creating challenges for applications pursuing global reach. Companies must balance regulatory compliance across diverse requirements while maintaining product coherence and operational efficiency.
Market Saturation and Specialization Dynamics
As AI application markets mature and competition intensifies, growth rates will likely decelerate from 2025's extraordinary levels. Market evolution typically progresses from explosive growth during emergence phases toward steady-state growth as markets mature and competitive intensity increases. The $85 billion market will likely grow, but at declining percentage rates as higher bases are achieved.
As growth decelerates in general-purpose AI assistant markets, specialization will accelerate. Applications addressing specific professional domains, cultural contexts, languages, or use cases will proliferate. Vertical-specific solutions will likely capture larger market shares relative to horizontal, general-purpose applications.
Accessibility and Democratization
AI application accessibility will expand toward less technically sophisticated users and emerging markets. User interfaces will simplify, assuming less technical knowledge. Localization into diverse languages and cultural contexts will expand addressable markets. Offline capability, reduced bandwidth requirements, and optimized performance for lower-end devices will enable adoption in regions with limited infrastructure.
This democratization will likely sustain market growth even as core markets saturate. Emerging markets represent substantial opportunities as billion-plus populations gain smartphone access and digital spending capacity.

Strategic Implications for Developers and Enterprises
When to Pursue AI Application Development
Developers evaluating opportunities in the AI application space should consider several strategic factors. First, assess genuine differentiation opportunities beyond general-purpose AI assistants. Second, identify underserved user segments or use cases where superior user experience or specialized capabilities provide meaningful advantages. Third, evaluate financial sustainability through clear paths to meaningful user monetization.
Opportunities exist in vertical specialization, privacy-focused alternatives, open-source approaches, integration capabilities, and user experience optimization. Success requires deep understanding of target user segments, willingness to invest in product refinement, and commitment to competing against well-capitalized incumbents.
Developers should also consider leveraging existing AI infrastructure through APIs rather than developing foundational models independently. This architectural approach reduces capital requirements and allows focus on user experience and vertical specialization where differentiation is achievable.
Enterprise Integration Strategies
Enterprises integrating AI capabilities face decisions regarding build-versus-buy approaches. Purchasing solutions from leading providers—Chat GPT, Google Workspace, Microsoft Copilot—provides rapid capability deployment, established support, and continuous improvement through vendor investment. Building custom solutions requires specialized talent and ongoing investment but provides greater customization and data control.
Most enterprises will likely employ hybrid approaches, combining vendor solutions for general-purpose capabilities with specialized internal systems addressing specific business requirements. This hybrid approach balances deployment speed against customization and control.
Skills Development and Talent Acquisition
Organizations increasingly require team members with AI literacy, prompt engineering skills, and understanding of AI capabilities and limitations. Forward-looking companies invest in training existing teams and recruiting talent with AI expertise. The talent shortage in AI skills continues intensifying, creating challenging recruiting environments and high compensation requirements for specialized talent.
Comparative Analysis: Understanding the Broader Technology Landscape
AI Applications Versus Traditional Software Categories
The emergence of AI applications as primary revenue drivers represents a significant inflection point for mobile app markets. Historically, social media and gaming dominated mobile economics. The shift toward AI applications reflects genuine technological capability improvements enabling new user experiences and addressing previously underserved needs.
Comparing AI application development economics against historical categories reveals important distinctions. AI applications typically require smaller teams and less continuous content creation compared to game development. User acquisition costs often prove lower as viral engagement driven by shared experiences accelerates adoption. However, computational infrastructure requirements substantially exceed historical mobile app economics.
For teams prioritizing innovation and rapid capability deployment in competitive landscapes, platforms offering automation and productivity tools can accelerate development cycles. Solutions like Runable, providing AI-powered automation for workflow and content generation ($9/month), enable teams to focus development resources on differentiated capabilities rather than foundational infrastructure or repetitive development tasks. Similarly, developers leveraging AI agent platforms for documentation generation and content automation reduce development friction, allowing faster iteration and market deployment.
Market Opportunities for Emerging Platforms
The expansion of AI application markets creates opportunities for infrastructure, enablement, and complementary solution providers. Platforms offering developer tools, automation capabilities, analytics, monetization infrastructure, and distribution channels all benefit from the expanding AI application market.
Alternatives and complementary tools addressing developer productivity needs gain relevance as teams scale AI application development. Automation platforms reducing repetitive development work, AI-powered documentation tools accelerating technical writing, and workflow automation solutions improving team collaboration all support the expanding AI application development ecosystem.
Conclusion: The Transformational 2025 and Implications for Tomorrow
The 2025 mobile app market milestone—where non-game app spending for the first time exceeded gaming revenue globally—represents far more than a statistical inflection point. This shift signals a fundamental reallocation of resources, user attention, and developer focus toward artificial intelligence capabilities. The $85 billion market, growing at 21% year-over-year, represents genuine expansion of consumer digital spending and user willingness to pay for sophisticated AI capabilities.
The drivers of this transformation are clear: generative AI represents genuinely novel technology delivering measurable value across professional and personal domains. Users demonstrated strong willingness to pay subscription fees—often exceeding $10-20 monthly—for continuous access to sophisticated AI capabilities. The achievement of 48 billion cumulative hours of user engagement validates that AI applications deliver not just novelty but sustained, genuine utility.
Market consolidation toward OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Deep Seek reflects predictable competitive dynamics as emerging categories mature. Well-capitalized companies with existing distribution advantages capture disproportionate market share. However, substantial opportunities persist for specialized applications, vertical solutions, and companies delivering differentiated user experiences or capabilities unavailable through leading competitors.
The geographic concentration of spending—with North America and Western Europe representing 65% of revenue—suggests substantial growth opportunities as adoption expands into emerging markets, different language contexts, and more diverse demographic segments. The mobile-exclusive access pattern, with 55% of US users in 2025 accessing AI assistants exclusively through mobile, confirms that sophisticated capabilities deliver value through mobile interfaces, potentially expanding addressable markets toward less technical user segments.
For organizations and developers, the implications involve recognizing that AI applications now represent fundamental categories requiring strategic attention. Whether pursuing new AI application development, integrating AI capabilities into existing products, or building infrastructure and tools supporting the AI application ecosystem, stakeholders must understand that the market dynamics have fundamentally shifted.
Developer attention and resource allocation increasingly focus on AI capabilities, creating downstream effects on other categories including games. This talent reallocation, combined with the $5 billion in AI application revenue, creates incentive structures favoring AI-focused development over traditional categories. This dynamic will likely sustain throughout coming years as AI capabilities continue improving and use cases expand.
The sustainability of this growth depends on continued AI capability improvement, expansion into adjacent domains and use cases, geographic market expansion, and identification of novel applications currently unimagined. Historical precedent suggests that transformational technologies capture increasingly larger market shares across technology spending as they mature, but also experience inevitable competitive consolidation and margin compression as markets mature.
The organizations best positioned for 2026 and beyond combine three characteristics: first, genuine understanding of AI capabilities and limitations; second, ability to identify and serve underserved user segments or use cases; and third, operational excellence in execution, user experience design, and monetization optimization. The market opportunity remains substantial, but competition will intensify as the transformational potential of AI applications becomes increasingly obvious to all market participants.

FAQ
What percentage of mobile app revenue came from AI applications in 2025?
While exact breakdowns weren't uniformly reported, in-app purchase revenue from AI applications reached
How did Chat GPT generate $3.4 billion in annual revenue?
Chat GPT achieved
What is the difference between in-app purchases and subscriptions in mobile apps?
In-app purchases typically represent one-time transactions where users pay for specific items, features, or content within applications—such as buying coins in games, accessing premium features, or purchasing advanced capabilities. Subscriptions represent recurring payments providing continuous access to features or services, often renewed monthly or annually. Many AI applications employ subscription models because they deliver recurring value (continuous access to AI capabilities) rather than discrete purchases. However, hybrid models exist where subscription tiers unlock the ability to make in-app purchases for additional features. Subscriptions generally provide more predictable and recurring revenue, while in-app purchases often generate higher transaction values but less predictable patterns. For AI applications, subscriptions aligned better with user expectations and business models, though in-app purchases supplemented core subscription revenue.
Why did mobile-exclusive AI app usage surge from 13 million to 110 million users in one year?
The dramatic increase in mobile-exclusive AI assistant users reflects several factors. First, mobile interfaces proved surprisingly well-suited for conversational interaction patterns, contrary to conventional assumptions that mobile devices were limiting for complex interactions. Second, improved mobile devices provided superior processing power, larger screens, and more responsive interfaces than previous generations. Third, AI application interfaces simplified accessing sophisticated capabilities, removing technical barriers that previously limited adoption to technical users. Fourth, awareness and cultural adoption of AI expanded substantially in 2024-2025, with mainstream media coverage and social proof driving adoption. Fifth, competitive improvements in mobile AI applications created better user experiences, improving retention and reducing friction. The 8.5x multiplication in a single year suggests that substantial additional growth remained possible as adoption continued expanding and interfaces continued improving.
What opportunities exist for independent developers competing against major technology companies?
Independent developers and startups can compete through vertical specialization (serving specific professional domains, creative niches, or underserved communities), privacy-focused approaches emphasizing data control and transparency, open-source solutions enabling customization and local deployment, superior user experience design in narrow domains, regional or cultural adaptation, or integration capabilities connecting AI to specialized data sources or workflows. The key distinction involves identifying specific user segments or use cases where major technology companies' general-purpose approaches prove suboptimal. Rather than competing directly with Chat GPT or Google Gemini as general-purpose assistants, successful independent applications differentiate through specialized capabilities, superior experiences for specific domains, or distinctive value propositions. Building on top of existing AI infrastructure (APIs from OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, etc.) rather than developing foundational models independently dramatically reduces capital requirements and enables focus on user experience and specialization.
How does AI application monetization differ from traditional mobile app monetization?
Traditional mobile apps typically monetized through advertising, in-app purchases (often for cosmetic items or convenience), or subscriptions at lower price points (
What does the future of mobile app spending look like beyond 2025?
Given historical market evolution patterns, mobile app spending will likely continue growing but at declining percentage rates as higher bases are achieved. The extraordinary 21% year-over-year growth of 2025 probably represents peak growth rates for AI applications as markets mature and competitive saturation increases. Geographic expansion into emerging markets, increased penetration among less technical user segments, and expansion of AI capabilities into new domains will sustain growth. However, consolidation around leading competitors will intensify as competitive barriers increase. Vertical specialization will likely accelerate as general-purpose markets mature, with specialized applications addressing professional domains, specific languages and cultures, and particular use cases capturing increasingly larger shares. Enterprise spending on AI capabilities will likely expand faster than consumer spending as organizations integrate AI into core business operations. Overall, mobile app spending will likely reach $100+ billion by 2027-2028 with growth rates moderating from 2025 levels toward 15-18% annually.
How does Runable compare to traditional AI assistant applications?
While leading AI assistants focus on conversational interactions and broad capability delivery, automation-focused platforms like Runable serve different user needs—specifically, developers and teams seeking to automate repetitive work, generate documentation, create presentations, and streamline workflows. Where platforms like Chat GPT excel at open-ended conversation and reasoning, Runable specializes in work automation and content generation through AI agents. At $9/month, Runable positions itself as an efficient alternative to complex enterprise automation tools, emphasizing developer productivity and workflow optimization rather than general-purpose conversation. Teams already using Runable for automation and content generation often use AI assistants for different purposes (research, writing, ideation), suggesting these categories serve complementary rather than directly competitive roles.
What role does artificial intelligence play in the broader software market shift toward mobile?
Artificial intelligence served as the primary catalyst accelerating the shift of software development and usage toward mobile platforms. AI applications provided genuinely novel capabilities that were immediately accessible through mobile interfaces, reducing friction compared to desktop-first applications requiring more complex interfaces. The ability to deliver sophisticated capabilities through simple conversational mobile interfaces demonstrated that mobile devices weren't merely secondary platforms but could deliver superior user experiences for certain use cases. AI applications achieving massive adoption primarily through mobile validated that mobile platforms could support sophisticated applications and justified continued developer investment in mobile-first approaches. This validation likely influences developer resource allocation across software categories for years forward, with implications extending beyond AI applications toward other emerging technologies and application categories.
Key Takeaways
- Consumer spending on non-game mobile apps exceeded gaming revenue in 2025 for the first time globally, reaching $85 billion with 21% YoY growth
- Generative AI drove market growth with in-app purchases in AI apps tripling to $5 billion and downloads doubling to 3.8 billion
- ChatGPT dominated AI application market with $3.4 billion in annual revenue, while OpenAI and DeepSeek captured 50% of downloads by year-end 2025
- Users spent 48 billion cumulative hours in AI applications (3.6x 2024 levels) across one trillion sessions, indicating strong retention and expanding use cases
- Mobile-exclusive AI app access surged from 13 million to 110 million users in the US alone, with 55% of users accessing AI assistants exclusively on mobile
- Big technology companies consolidated market share, growing from 14% to 30% as specialized competitors lost market positioning
- Social media remained engagement leader with 90 minutes daily per user (2.5 trillion annual hours) while AI applications achieved comparable engagement levels
- Geographic revenue concentration persisted with North America and Western Europe representing 65% of spending, creating opportunities in emerging markets
- Specialized AI applications in music generation (Suno), video synthesis (Jimeng AI), and companion services achieved notable adoption alongside general-purpose assistants
- Future market growth depends on geographic expansion, specialized vertical applications, regulatory compliance, and continued AI capability improvements
Related Articles
- Tesla's Dojo Supercomputer Restart: What Musk's AI Vision Really Means [2025]
- Jensen Huang's Reality Check on AI: Why Practical Progress Matters More Than God AI Fears [2025]
- ChatGPT Translate vs Google Translate: Complete Comparison Guide 2025
- Google Gemini vs OpenAI: Who's Winning the AI Race in 2025?
- ElevenLabs $330M ARR: How AI Voice Disrupted SaaS Growth Curves
- MSI AI Edge Mini PC: Ryzen AI Max+ 395 Powerhouse Guide & Alternatives




