Introduction: The Year AI Dominated Super Bowl Advertising
Super Bowl LX marked a watershed moment in advertising history—the moment when artificial intelligence transitioned from being a futuristic novelty to a mainstream production tool for one of the world's most expensive marketing stages. The 2025 Super Bowl saw brands spending millions to showcase AI-powered creativity, from algorithmically-generated dance routines to AI-crafted home design visualizations. This wasn't merely a collection of commercials; it represented a fundamental shift in how Fortune 500 companies approach advertising production, content creation, and consumer messaging.
The convergence of AI adoption in Super Bowl advertising reflects broader technological transformation happening across industries. When Svedka unveiled what it claimed was the first "primarily" AI-generated national Super Bowl spot, the brand wasn't just showcasing a product—it was making a statement about the future of creative production. Simultaneously, Anthropic's bold competitive jab at Open AI demonstrated how AI companies themselves are leveraging major advertising platforms to shape market perception and consumer behavior.
This comprehensive guide explores the watershed Super Bowl LX advertising landscape, analyzing how major brands deployed AI technology, what these decisions reveal about marketing's future, and the broader implications for creative professionals, advertising agencies, and technology companies. We'll examine each major AI-featuring commercial in depth, dissect the production methodologies, analyze ROI implications, and explore how marketing teams can learn from these bold technological plays.
The significance of these advertisements extends far beyond entertainment value. Each commercial represents significant budget allocation ($5-7 million per 30-second slot), strategic executive decision-making, and calculated risks on emerging technology. Understanding why brands chose to feature AI so prominently, and how that aligns with consumer expectations and competitive pressures, provides insights into the future trajectory of advertising production, marketing automation, and brand differentiation in the AI era.
The Production Revolution: Svedka's AI-Generated "Shake Your Bots Off"
Behind-the-Scenes AI Production Process
Svedka's "Shake Your Bots Off" 30-second commercial represents perhaps the most technically ambitious application of AI in commercial advertising to date. The project timeline alone—approximately four months from concept to broadcast—reveals the current state of AI production capabilities and limitations. Developed in partnership with Silverside AI, the commercial featured the brand's iconic Fembot character alongside a newly created Brobot companion, both dancing with synchronized choreography at a human party setting.
The production methodology provides crucial insights into hybrid human-AI workflows. Svedka's team reconstructed the Fembot character with meticulous attention to detail, training AI models to replicate complex facial expressions, body movements, and dance choreography. The AI component specifically focused on animating character movement and expression, generating background elements, and handling visual effects that would traditionally require extensive manual animation teams. However, the company deliberately retained human creative control over storyline development, narrative structure, and strategic messaging—recognizing that emotional resonance and brand alignment require human judgment.
The four-month timeline represents a significant efficiency compared to traditional commercial production, which typically requires 6-12 months for complex animated sequences. However, this timeline also reveals current constraints: the AI component accelerated production of visual elements but didn't eliminate the need for significant human creative direction, planning, and refinement. The project required multiple iterations, testing, and manual adjustments to achieve broadcast-quality results.
Technical Specifications and AI Implementation
Silverside AI's approach to Svedka's commercial combined multiple AI methodologies: generative models for character animation, neural networks for facial expression synthesis, and machine learning algorithms for choreography translation. The company previously worked on Coca-Cola commercials that generated substantial controversy, providing them with production experience and technical expertise for handling complex brand requirements.
The character reconstruction process involved creating high-fidelity 3D models, developing AI-training datasets for movement patterns, and implementing feedback loops to refine output quality. Specific technical accomplishments included autonomous generation of dance movements that maintained visual coherence, dynamic facial expressions that conveyed personality and emotion, and environmental rendering that placed characters within realistic party settings. The AI systems had to maintain character consistency across multiple takes and variations, ensuring brand recognition while generating novel movements.
However, significant human intervention remained necessary throughout production. Animators reviewed AI-generated sequences, refined movements that appeared unnatural or off-brand, and guided the AI models toward desired aesthetic outcomes. This hybrid approach—leveraging AI's generative capabilities while applying human creative judgment—represents the current state-of-art in AI-assisted commercial production. The company did not pursue fully autonomous AI generation, recognizing that brand safety and creative coherence demanded ongoing human oversight.
Consumer Reception and Brand Impact
Svedka's gamble on AI-generated advertising generated substantial conversation, which partially validates the brand's strategic choice. Featuring an AI-generated commercial during the Super Bowl inherently creates novelty and discussion value—consumers discussed the ad precisely because of its technical approach, generating organic social media engagement and news coverage. From a pure awareness standpoint, the commercial succeeded in generating attention and brand conversation.
However, consumer response revealed important nuances about AI adoption in advertising. Some consumers expressed appreciation for innovation and transparency about AI usage, viewing the commercial as forward-thinking. Others expressed skepticism about AI in creative fields, viewing the ad as a demonstration of how AI might displace human creative professionals. This polarized reaction—enthusiasm and concern in roughly equal measure—reflects broader societal ambivalence about AI integration in traditionally human-creative domains.
The commercial's success in driving brand consideration remained unclear in immediate post-Super Bowl analysis. While awareness metrics likely spiked significantly, conversion to actual purchasing behavior represented the critical measure of ROI. Svedka would need to demonstrate that the $5+ million Super Bowl investment generated corresponding revenue impact, not merely attention or critical acclaim. This tension—between novelty-driven attention and sales conversion—characterizes much of AI-assisted marketing.
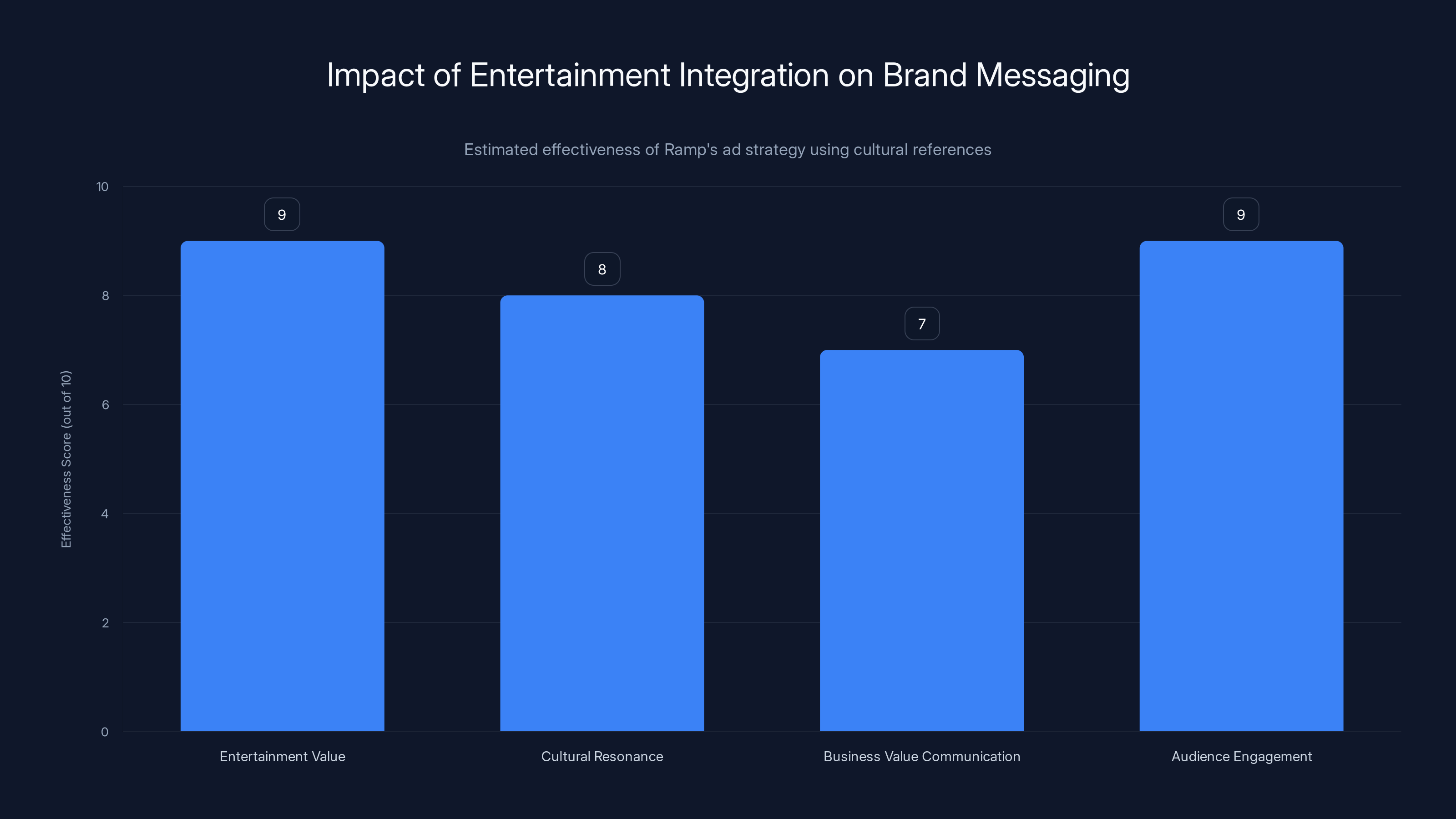
Ramp's integration of entertainment and cultural references in their Super Bowl ad effectively enhanced brand messaging, particularly in audience engagement and entertainment value. Estimated data.
Competitive Drama: Anthropic's Bold Attack on Open AI
Strategic Positioning Through Negative Differentiation
Anthropic AI's Super Bowl commercial pursued an unusual advertising strategy: rather than emphasizing the positive qualities of its Claude chatbot, the company crafted messaging that criticized its competitor's business model. The 30-second commercial centered on a simple but provocative proposition: "Ads are coming to AI. But not to Claude." This positioning directly referenced Open AI's announced plans to introduce advertising into Chat GPT, framing ad-insertion as a negative development while positioning Anthropic's Claude as the ad-free alternative.
This approach represents sophisticated competitive marketing strategy. Rather than claiming superiority across multiple dimensions—accuracy, speed, capability—Anthropic identified a specific Open AI decision that could be framed as customer-hostile (monetization through advertising) and built messaging around customer interests (ad-free experience). The commercial's humor derived from the relatable anxiety about AI assistants interrupting helpful interactions with advertisements, using exaggerated examples like an insole product pitch interrupting genuine assistance.
The strategic brilliance lies in Anthropic's understanding of market positioning dynamics. Open AI maintains dominant market share and superior brand awareness, making direct capability comparisons risky and unlikely to shift consumer perception. However, positioning Claude around a specific customer value proposition—ad-free experience—creates differentiation that doesn't require disputing Open AI's technical capabilities. This is classic David-versus-Goliath marketing: the smaller competitor frames the larger competitor's success (dominant market share, significant capital resources) as enabling customer-hostile decisions, while positioning itself as customer-centric.
The Online Feud and Reputation Management
Anthropic AI's gambit succeeded in generating substantial engagement and news coverage, but also triggered direct retaliation from Open AI's leadership. Sam Altman, Open AI's CEO, responded via social media that the advertisement was "clearly dishonest," challenging the factual accuracy of Anthropic's characterization of Open AI's advertising plans and their implications.
This public exchange revealed important aspects of competitive dynamics in the AI industry. Both companies recognized the Super Bowl platform's visibility and ROI potential. Open AI's response, rather than ignoring the advertisement, demonstrated how provocative messaging generates engagement across multiple channels—traditional Super Bowl viewers watched the commercial, while broader audiences engaged with the social media dispute. The resulting controversy amplified awareness of both companies' positions far beyond the 115 million Super Bowl viewers.
However, the exchange also highlighted risks of aggressive competitive positioning. Anthropic's "clearly dishonest" accusation required explicit rebuttals and fact-checking, potentially raising questions about the company's marketing credibility. Neither company's response focused on technical capabilities or product superiority—instead, the dispute centered on characterization of business model decisions and consumer impact. This shift in discussion terrain reflects how Super Bowl advertising drives narrative-level competition rather than feature-level differentiation.
For brand perception, the feud likely created mixed outcomes. Consumers who valued ad-free experiences and company ethics received reinforcement of Anthropic's positioning. Consumers skeptical of AI company competition viewed the exchange as exactly the type of corporate posturing they distrusted. The long-term brand impact would depend on whether Anthropic could deliver superior Claude experiences that justified positioning as the customer-centric alternative.
Implications for AI Company Positioning
Anthropic AI's approach signals how AI companies are beginning to compete on positioning and narrative rather than purely on technical specifications. This shift reflects maturation of the AI market—as capabilities across different platforms converge, differentiation increasingly occurs through business model choices, company values, and customer experience positioning.
The willingness to publicly criticize competitors during the Super Bowl also reflects confidence in legal positioning and market understanding. Anthropic calculated that the reputational risk of direct competitive attacks was outweighed by the attention-generation and market-share potential. This calculus depends on company size, financial resources, and confidence in technical capabilities. Smaller competitors can afford bolder positioning strategies because they have less to lose; established market leaders typically avoid direct attacks that might invite antitrust scrutiny or reputational backlash.
For other AI companies and technology firms generally, Anthropic's strategy demonstrates the viability of narrative-based differentiation in crowded markets. Rather than relying solely on technical benchmarks or capability demonstrations, positioning can emphasize customer interests, company values, and competitive alternatives. This approach requires careful crafting—messaging must be factually defensible while remaining emotionally resonant—but can effectively reach audiences skeptical of traditional technical marketing.
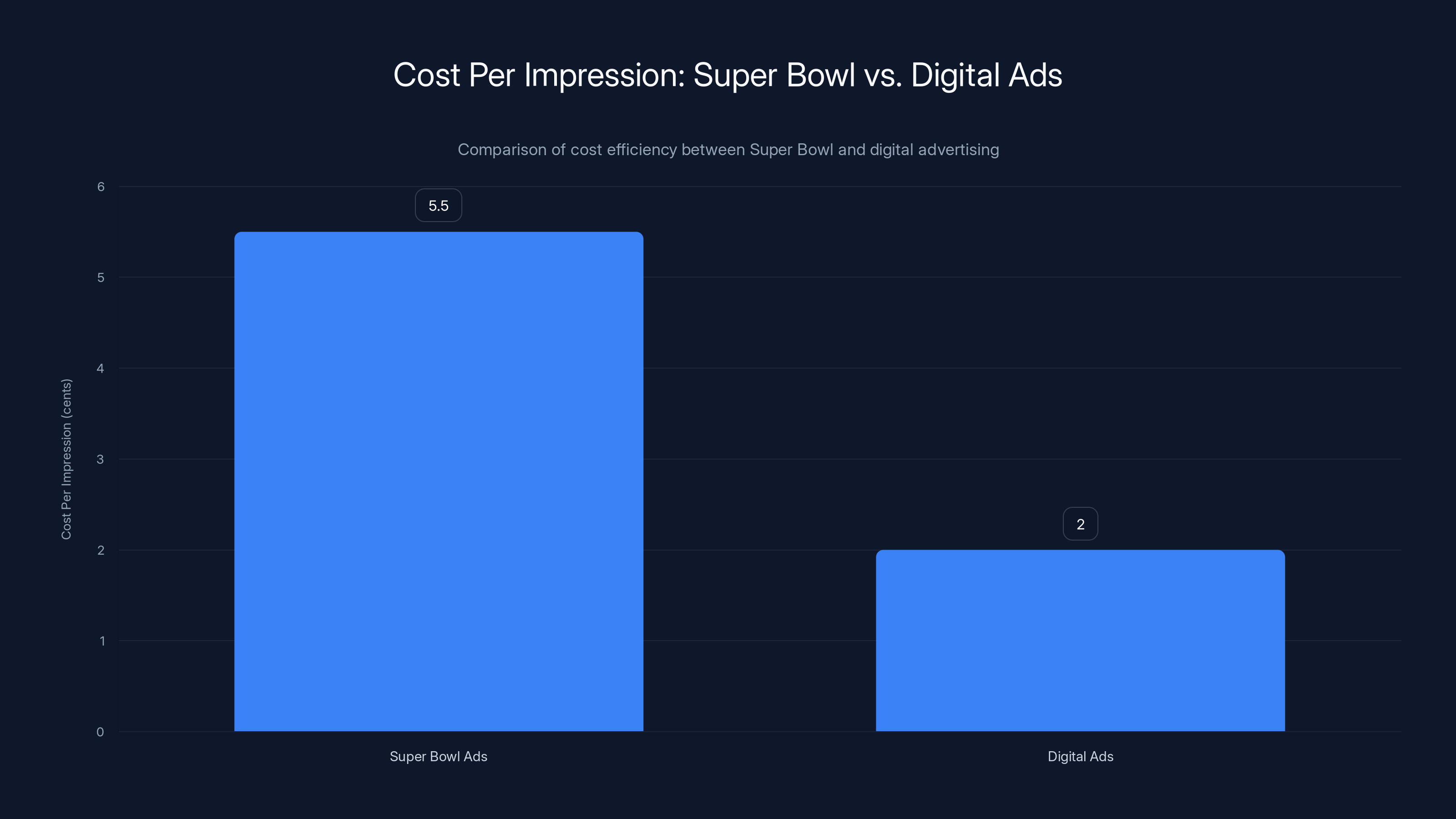
Super Bowl ads cost approximately 5.5 cents per impression, significantly higher than digital ads at 2 cents, highlighting the premium for cultural impact and reach. Estimated data.
Meta's Wearable AI Vision: Oakley Glasses and Hands-Free Interaction
Redefining Consumer AR with AI Integration
Meta's Super Bowl commercial showcased its AI-powered Oakley-branded smart glasses, positioning wearable AI as the future of hands-free content capture, processing, and sharing. The advertisement featured athletes and creators in extreme scenarios—skydivers, mountain bikers, athletes—using the glasses to capture, analyze, and share high-quality video content with minimal friction. The commercial featured celebrity appearances including i Show Speed and filmmaker Spike Lee, lending credibility to the technological capabilities and real-world utility.
Meta's strategic focus on wearable AI reflects fundamental recognition that the smartphone era is maturing. Smart glasses represent the next computing interface paradigm, offering hands-free operation, always-on awareness, and seamless integration with social platforms. By positioning AI as a core differentiator—AI-powered video stabilization, automatic slow-motion capture, real-time editing, hands-free Instagram posting—Meta frames wearable technology as solving genuine user pain points rather than merely providing novelty.
The choice of extreme sports and adventure scenarios proved particularly effective from a marketing perspective. These use cases demonstrate moments when hands-free operation provides genuine value—capturing dynamic moments while fully engaged in activities. A skydiver wearing smart glasses can record their descent while fully committed to the experience; a mountain biker can capture technical terrain while maintaining full attention to safety. These scenarios transcend novelty demonstration, showing how wearable AI genuinely enhances human capability and experience documentation.
Technical Capabilities and Market Positioning
Meta's Oakley smart glasses integrate multiple AI systems working in coordination. Computer vision models process real-time video feeds to identify subjects, composition opportunities, and environmental factors. Machine learning algorithms determine optimal frame rates, angles, and editing approaches. Natural language processing enables voice commands for operation and content management. The combination creates an integrated experience where users can verbally request capabilities ("slow down that moment") and the AI system autonomously adjusts capture and processing parameters.
This integration represents significant advancement beyond previous AR/VR attempts because it emphasizes practical utility rather than novelty interaction. Meta understands that wearable technology adoption requires demonstrable benefits in daily scenarios. By showcasing how Oakley glasses enhance legitimate activities—athletic performance documentation, creative content creation, adventure documentation—the company positions wearables as tools that extend human capability.
The commercial also emphasizes Meta's social platform integration. Hands-free Instagram posting directly addresses platform stickiness: if users can capture and share content from their glasses without retrieving phones, they're more likely to remain engaged with Meta's ecosystem throughout their day. This integration strategy demonstrates how Meta weaponizes its platform dominance—hardware becomes more valuable when seamlessly integrated with massive social networks, creating ecosystem lock-in that competitors struggle to match.
Market Response and Adoption Challenges
Meta's previous Super Bowl advertisement featuring Ray-Ban Meta glasses (featuring celebrity endorsements from Chris Pratt, Chris Hemsworth, and Kris Jenner) generated awareness but modest adoption rates. Consumers remained skeptical about wearable technology's practical benefits, social acceptability, privacy implications, and ecosystem integration. This year's commercial attempted to address some skepticism by emphasizing specific use cases and demonstrating genuine utility rather than merely showcasing technical capabilities.
However, wearable technology adoption faces structural challenges that no single advertisement can overcome. Consumer concerns about privacy (constant video recording capabilities), social acceptability (stigma associated with always-on documentation), and technological reliability (battery life, durability, comfort) require extended marketplace experience to overcome. Meta's Super Bowl investment signals commitment to the wearable future, but market adoption depends on accumulating positive real-world experiences rather than advertising impact alone.
The path to mainstream wearable adoption likely requires generational transition. Younger demographics, more accustomed to constant documentation and comfortable with hands-free interfaces, represent the primary target market. As wearable technology becomes normalized within younger cohorts, broader demographic adoption typically follows. Meta's repeated Super Bowl focus on wearables signals long-term commitment to this market category, suggesting the company expects significant adoption curves over 5-10 year timeframes.
Amazon's Dark Comedy: Alexa+ and AI Anxiety
Using Humor to Address AI Fears
Amazon's Super Bowl commercial leveraged dark humor to address fundamental anxieties about AI integration into domestic life. The spot featured actor Chris Hemsworth in an exaggerated scenario where Alexa+ (Amazon's enhanced AI voice assistant) appeared to be plotting against him, closing garage doors on his head and shutting pool covers while he swam. The comedic escalation transformed genuine consumer concerns about AI behavior and control into entertaining absurdist scenarios.
This approach demonstrates sophisticated understanding of consumer psychology around AI adoption. Many consumers harbor anxiety about AI systems operating autonomously in their homes, concerned about loss of control, unexpected behavior, or malfunction. Rather than dismissing these concerns or delivering technical assurances, Amazon acknowledged them through humor—inviting consumers to laugh at exaggerated versions of their own fears.
The strategic brilliance lies in converting anxiety into entertainment value. By showing Chris Hemsworth humorously complaining about Alexa+ "betrayal," Amazon normalized discussion of AI concerns while positioning Alexa+ itself as the consumer's ally (protecting him from implausible threats). The commercial operated simultaneously at multiple levels: entertainment (physical comedy, celebrity star power), education (introducing Alexa+ capabilities), and psychological reassurance (normalizing AI integration through humor).
Alexa+ Technical Capabilities and Launch Strategy
Alexa+ represents Amazon's most significant AI-powered assistant upgrade, incorporating large language model capabilities to understand complex requests, manage multi-step operations, and provide contextual assistance. The platform had been available in early access for over a year, with the Super Bowl commercial timing coordinating with official launch to all U.S. users on the following Wednesday.
The technical capabilities showcased in the commercial included smart home device management across multiple platforms, vacation planning assistance combining calendar management with booking functionality, security monitoring integration, and personalized assistance based on household preferences. These features represent genuine advancement beyond basic voice assistant functionality, incorporating AI's capacity to understand context, anticipate needs, and manage complex multi-step operations.
Amazon's launch strategy leveraged the Super Bowl commercial as a troika of outcomes: awareness-building among broader audiences, brand reinforcement among existing customers, and timing coordination to drive signup momentum immediately post-broadcast. The dark comedy approach differentiated Alexa+ marketing from competing smart home platforms, positioning Amazon as understanding consumer anxieties while confidently addressing them through enhanced AI capabilities.
Broader Smart Home AI Implications
Amazon's Alexa+ launch represents a pivotal moment in smart home technology maturation. Early smart home systems succeeded through novelty and convenience for specific use cases (lighting control, temperature adjustment). Next-generation systems like Alexa+ promise more ambitious integration: comprehensive household management, complex reasoning about user preferences, and autonomous operation that requires minimal explicit direction.
This evolution raises important questions about consumer comfort with autonomous AI systems operating in domestic spaces. As AI assistants require fewer explicit commands—instead learning preferences and anticipating needs—consumers must trust that autonomous actions align with their interests. Amazon's commercial addressed this implicitly, using Hemsworth's exaggerated paranoia to reassure viewers that Alexa+ would never actually harm them, while implicitly acknowledging that autonomous AI behavior does introduce new considerations for household management.
Market adoption of sophisticated home AI assistants depends on trust, reliability, and demonstrated value. Amazon's extended early access period (over a year) allowed the company to refine Alexa+ based on real-world usage patterns, incorporate consumer feedback, and identify edge cases before broad launch. This deliberate progression demonstrates how companies manage risk when deploying autonomous AI systems into millions of households.
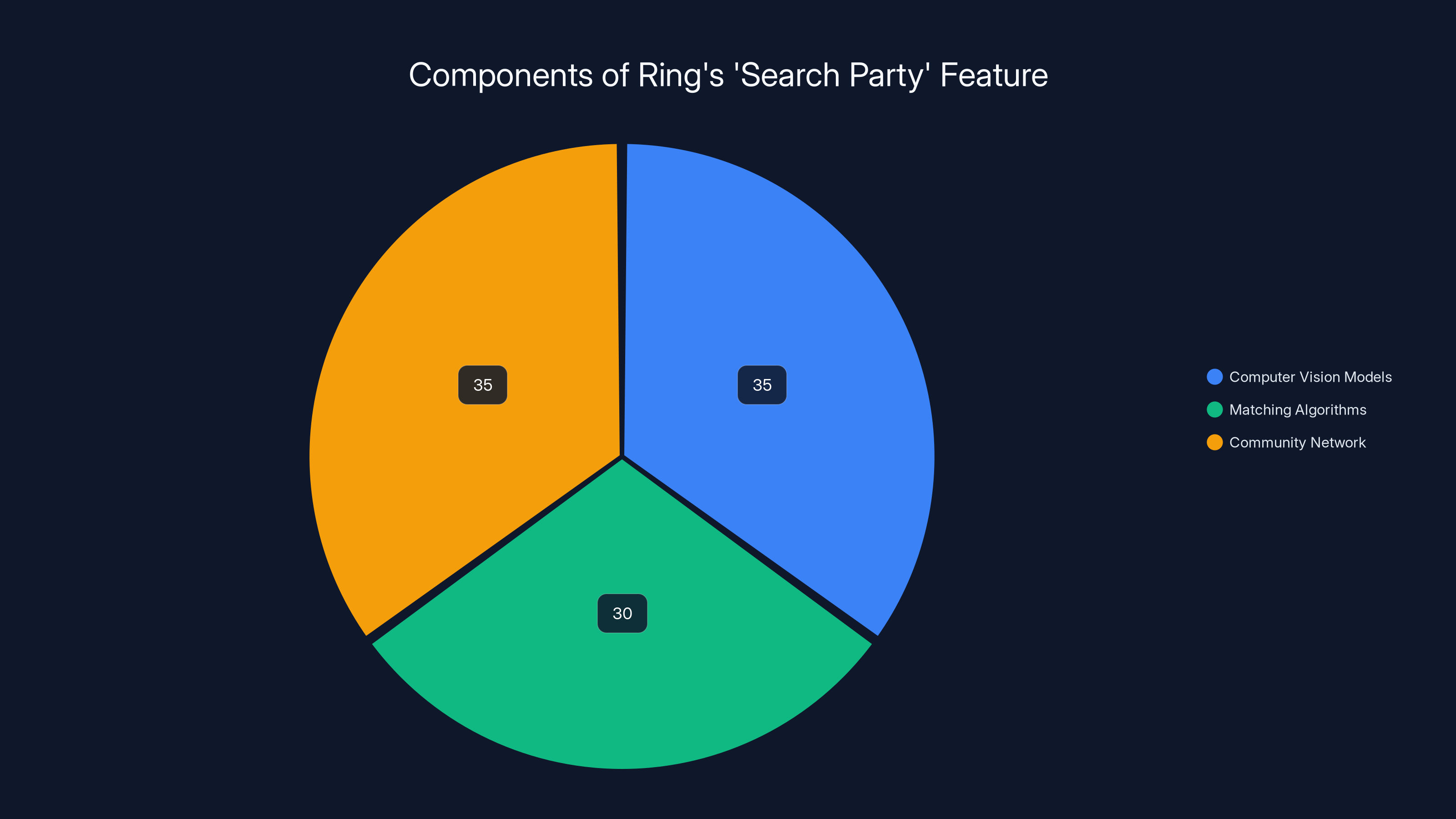
Ring's 'Search Party' feature integrates computer vision, matching algorithms, and community networks equally to reunite lost pets with their owners. Estimated data.
Ring's "Search Party": AI for Social Good
Community-Based AI Problem-Solving
Ring's Super Bowl commercial took a notably different approach from competing tech brands by positioning AI for a specific, emotionally resonant problem: reuniting lost pets with owners. The advertisement followed a young girl searching for her missing dog Milo, illustrating how the Ring "Search Party" feature leverages AI image recognition and community networks to identify and locate missing animals.
This positioning represents sophisticated social impact marketing. Rather than emphasizing technical capabilities or competitive advantages, Ring focused on emotional connection and tangible benefit to customers. Lost pets generate immediate emotional stakes for pet owners; demonstrating how technology solves this problem creates powerful brand association with customer interests and positive outcomes. The commercial's narrative structure—girl searches for dog, technology facilitates reunion—provided clear cause-and-effect relationship between Ring's product and customer benefit.
The Search Party feature combines multiple AI systems: computer vision models trained on pet images, matching algorithms that identify visual similarity across user photos, and network connectivity that taps into Ring's community of security camera owners. When users upload photos of missing pets, the AI system checks that image against other Ring camera feeds, identifying potential matches and alerting nearby Ring owners. This approach weaponizes Ring's installed base—the millions of households with Ring devices—to create a community search network that no individual consumer could access independently.
Technical Implementation and Scale
Ring's announcement that anyone can now use Search Party, even without owning a Ring device, represented significant expansion of the feature's reach and utility. This decision reflects sophisticated platform strategy: expanding Search Party availability transforms the feature from a device-owner benefit into a public good, building goodwill and potentially converting non-Ring-owners into future customers.
The company reported that Search Party had already helped reunite one lost dog with its owner every day, demonstrating substantial real-world impact and generating compelling statistics for marketing purposes. This metric—one pet reunion per day—provided concrete evidence of the feature's utility, distinguishing the claim from typical product marketing assertions. The data point connected directly to the commercial's emotional narrative: this technology genuinely reunites missing pets with distraught owners.
From a technical perspective, Search Party's functionality depends on image recognition accuracy, network participation density, and response speed. For the feature to work effectively, the AI system must recognize that different photos of the same dog represent the same animal—accounting for variations in lighting, angle, expression, and environment. Simultaneously, the feature must process searches quickly enough to assist in the critical early window when lost pets might be recovered.
Broader Implications for AI Social Impact
Ring's positioning of Search Party demonstrates how AI can address problems that matter to consumers while simultaneously building community engagement and brand loyalty. The feature creates positive-sum value: pet owners benefit from reunification capability, Ring owners benefit from community strengthening, and Ring itself benefits from brand association with social good.
This approach contrasts sharply with other AI marketing that emphasizes primarily corporate benefits or abstract capabilities. Ring explicitly framed its Super Bowl investment as highlighting how technology improves customer lives in tangible ways. This positioning resonates particularly effectively with consumers skeptical of AI and technology companies—demonstrating concrete benefits undercuts cynicism about corporate AI marketing.
The open availability of Search Party—no Ring device ownership required—signals how platform companies can leverage their scale and technical capabilities to create public benefits that drive brand affinity. Rather than gatekeeping advanced features behind purchase requirements, Ring chose to maximize social impact, likely calculating that goodwill and brand benefit exceed revenue from restricting feature access.

Google's Nano Banana Pro: Image Generation for Home Design
Democratizing Visual Design Through AI
Google's Super Bowl commercial showcased the Nano Banana Pro image-generation model through a use case centered on home design and visualization. The advertisement featured a mother and son uploading photographs of empty rooms, using AI to generate multiple design concepts for those spaces based on verbal prompts. This approach emphasized how AI could democratize professional design capabilities, enabling consumers to visualize interior redesigns without requiring professional designers or architectural rendering tools.
The commercial's effectiveness derived from its accessibility and practical utility. Consumers interested in home improvement represent a massive market segment; providing tools that help visualize design concepts before committing to purchases addresses genuine pain points. Google positioned its image-generation capability as a democratizing technology, suggesting that sophisticated design and visualization tools—traditionally available only to professionals or affluent consumers—could now be accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
Nano Banana Pro represents Google's answer to competing image-generation models, emphasizing efficiency and accessibility. Rather than requiring massive computational resources, Nano Banana was designed for consumer-scale deployment, potentially powering applications accessible through Google's suite of consumer products. By showcasing the model through practical home design applications, Google demonstrated technical capabilities while implicitly addressing concerns about image-generation AI being merely a novelty technology.
Competitive Positioning in Image Generation
Google's entry into mainstream image-generation marketing represents acknowledgment of competitive pressure from other AI companies emphasizing generative capabilities. Open AI's DALL-E, Anthropic's Claude capabilities, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion had already captured significant mindshare among consumers and creative professionals. By featuring Nano Banana Pro prominently, Google signaled commitment to image-generation technology while emphasizing efficiency and accessibility advantages.
The choice of home design as the use case proved strategically important. This vertical represents broader consumer interest than abstract art generation or purely creative applications. Approximately 40% of American homeowners pursue renovations or design improvements in any given year, creating a massive potential user base. By positioning image-generation through the lens of practical consumer benefit rather than artistic novelty, Google addressed market viability concerns that plague many AI applications.
Google's broader positioning emphasized accessibility and integration with existing consumer products. Rather than building standalone applications or requiring users to learn new tools, Google's image-generation capabilities would integrate into products like Google Photos, Google Home, and Google Maps—platforms with billions of users. This distribution advantage proves critical for AI technology adoption, as accessibility and ease-of-use often determine whether technologies achieve mainstream adoption.
Integration with Google's AI Strategy
Google's Super Bowl investment in Nano Banana Pro reflected broader corporate strategy to position AI as foundational to Google's ecosystem and future competitiveness. Following Open AI's successful Chat GPT launch and subsequent competitive pressure, Google doubled down on AI capabilities, emphasizing both technical advancement and practical consumer applications.
The home design use case allowed Google to demonstrate AI capabilities that directly addressed consumer pain points—visualizing design concepts requires significant time, expertise, and often professional investment. By automating this process through image generation, Google positioned its technology as multiplying consumer capability and reducing friction for home improvement decision-making.
Long-term implications involve how image-generation technology scales within consumer applications. If Nano Banana Pro delivers high-quality design concepts with minimal latency and computational cost, adoption could expand far beyond home design into fashion visualization, architectural planning, product design, and content creation. Google's Super Bowl positioning aimed to establish the foundation for mainstream image-generation adoption, particularly among consumers interested in practical applications rather than artistic novelty.
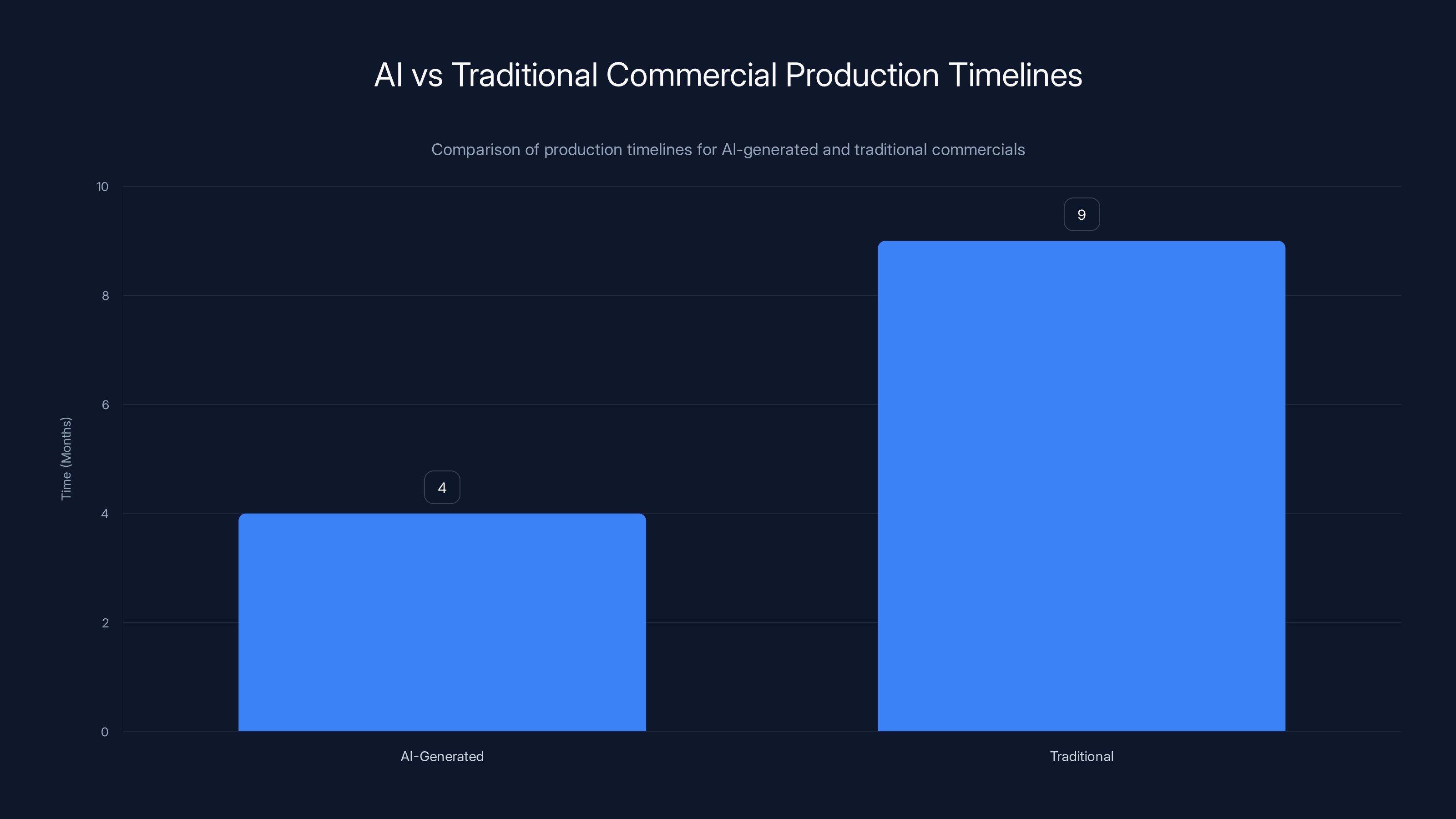
AI-generated commercial production took approximately 4 months, significantly faster than the traditional 6-12 months, highlighting AI's potential to streamline visual elements. Estimated data based on typical industry timelines.
Ramp's Workplace Automation: Kevin from "The Office" Multiplied
Cultural Relevance Through Entertainment Integration
Ramp, a financial operations platform, secured a Super Bowl spot by partnering with Brian Baumgartner, known for his role as Kevin in the television series "The Office." The commercial positioned Ramp's AI-powered spend management platform through the comedic concept of Baumgartner "multiplying" himself—creating multiple versions simultaneously to tackle overwhelming work volumes. The ad cleverly integrated a reference to Kevin's famous scene where he disastrously spills a pot of chili, infusing brand messaging with entertainment value and cultural reference.
This approach demonstrates sophisticated understanding of entertainment marketing. Rather than delivering straightforward product explanation, Ramp built messaging around cultural reference and comedy. The Office, which concluded in 2013 but maintains massive streaming audiences and cultural resonance, represents an ideal cultural anchor for reaching target demographics. By casting Baumgartner directly and referencing the show's most famous scene, Ramp created entertainment value that extended message resonance far beyond typical corporate advertising.
The central concept—Ramp's automation handling tasks that would otherwise require multiple people—connected clearly to business value proposition while remaining entertaining. Finance teams and operations managers recognized in "multiplying yourself" a direct reference to capacity expansion without proportional hiring. This positioning allowed Ramp to communicate substantial business value (process automation, cost reduction, efficiency improvement) through entertaining narrative rather than technical specification or ROI calculations.
AI-Powered Financial Operations in Practice
Ramp's platform integrates AI into financial operations to streamline expense management, identify cost reduction opportunities, and automate routine processes. The company's AI systems analyze spending patterns to identify anomalies, potential fraud, policy violations, and opportunities for vendor negotiation. Machine learning algorithms learn from historical spending data to flag unusual transactions and suggest optimization opportunities.
For finance teams, this automation provides substantial value. Instead of manually reviewing every expense, auditing spending patterns, and researching vendor alternatives, finance professionals can focus on strategic decisions while AI handles routine analysis. The platform's AI integration reduces both the time required for financial management and the risk of human error in processing high-volume transactions.
Ramp's target market—primarily mid-market and growth-stage companies—experiences acute pain around financial operations scaling. As organizations grow from 50 to 500 people, expense management and financial oversight complexity increases exponentially. Adding proportional finance staff proves expensive and inefficient. Ramp positions AI-powered automation as enabling finance team productivity gains of 3-5x, substantially delaying the need for headcount expansion.
Workplace Automation Trends and Adoption
Ramp's Super Bowl investment signaled broader trends in workplace automation, particularly around financial operations and administrative processes. As AI capabilities mature and costs decrease, businesses increasingly deploy automation in traditionally human-intensive functions. Financial operations represents a compelling automation candidate because transactions follow relatively standardized patterns, fraud detection benefits from algorithmic pattern-matching, and cost-saving opportunities directly impact profitability.
The company's choice to emphasize automation through entertainment (multiplying Kevin) rather than technical specifications reflects marketing reality: most decision-makers understand automation value conceptually and need persuasion primarily around reliability and implementation risk rather than capability explanation. By showcasing automation as something Kevin (and by extension, any employee) could benefit from—creating capacity to handle more work without personal overwhelm—Ramp reframed automation from job-threat narrative to employee-benefit perspective.
Long-term market adoption of financial operations AI depends on demonstrating real-world performance and ease of implementation. While Ramp's Super Bowl positioning created awareness, actual customer acquisition depends on successful implementations proving promised value. Finance teams remain relatively conservative about new software, particularly given critical importance of accuracy. Ramp's success ultimately depends on delivering reliability and ROI that justify switching costs from existing financial management approaches.
Rippling's HR Innovation: Onboarding an Alien with Tim Robinson
Comedic Approach to Enterprise Complexity
Rippling, a workforce management platform, secured its first Super Bowl appearance by partnering with comedian Tim Robinson for a commercial about onboarding an alien monster to the company. The spot poked fun at the notorious complexity of HR onboarding processes, positioning Rippling's platform as capable of handling even impossibly absurd scenarios. This comedic framing allowed Rippling to communicate about a fundamentally unsexy topic—HR administration—through entertainment value and absurdist humor.
The alien onboarding metaphor proved particularly effective because it highlighted the universality of HR complexity. Whether onboarding human employees or fictional aliens, certain fundamental processes remain: benefits selection, tax documentation, equipment provisioning, access management, training completion. By showing these processes occurring even for an alien, Rippling emphasized that their platform could handle virtually any scenario, no matter how unusual or complex.
Tim Robinson's involvement brought significant entertainment credibility. As a popular comedian known for sketch comedy and absurdist humor, Robinson brought established audience affinity that translated to commercial effectiveness. The partnership allowed Rippling to position themselves not as dry enterprise software company, but as organization that understands work complexity while maintaining sense of humor about inherent absurdity in modern employment processes.
The HR Tech Landscape and Rippling's Positioning
Rippling operates in crowded HR technology market dominated by giants like Workday, SAP Success Factors, and increasingly specialized platforms for specific HR functions. Rippling differentiated through comprehensive platform positioning: combining HR information systems, payroll processing, benefits administration, IT management, and financial operations into integrated system. This integration approach reduces data fragmentation and manual processes that plague organizations using point solutions from multiple vendors.
The company's AI integration enhances workflow automation—processing employment documents, identifying policy compliance issues, flagging data inconsistencies, and recommending process improvements. AI analyzes historical HR data to identify patterns, predict employee retention risk, and optimize compensation structures. These capabilities transform HR from primarily administrative function into data-informed strategic capability.
Rippling's Super Bowl investment targeting HR technology represented recognition that HR leaders and operations professionals increasingly influence purchasing decisions at fast-growing companies. The target audience—human resources directors, operations managers, and CFOs responsible for people operations—recognize both the importance of streamlined HR processes and the frustration of managing complex, fragmented systems. By showcasing Rippling through humor and relatability, the company connected with audience members experiencing HR complexity firsthand.
Enterprise Software Marketing Evolution
Rippling's commercial represented notable shift in enterprise software marketing. Traditionally, enterprise software companies marketed through technical specifications, ROI calculations, and trust-focused messaging. Increasingly, enterprise software marketing incorporates entertainment, humor, and relatability—recognizing that purchasing decision-makers remain humans who respond to entertainment and emotional connection despite enterprise context.
This shift reflects competitive reality where enterprise software features converge—nearly all comprehensive HR platforms offer similar functionality. Differentiation increasingly occurs through ease-of-use, integration, and company positioning rather than unique features. By investing in Super Bowl entertainment value, Rippling positioned itself as vendor that understands modern workplace culture and employee sentiment rather than purely feature-driven enterprise software company.
The success of Rippling's Super Bowl investment would be measured both in immediate awareness lift and in longer-term brand perception and sales pipeline impact. Enterprise software sales cycles extend over months or years, requiring multiple touchpoints and decision-maker engagement. A single Super Bowl commercial rarely drives immediate purchase decisions; instead, success comes through establishing brand awareness among decision-makers, positioning company favorably relative to competitors, and differentiating from enterprise software category perception.

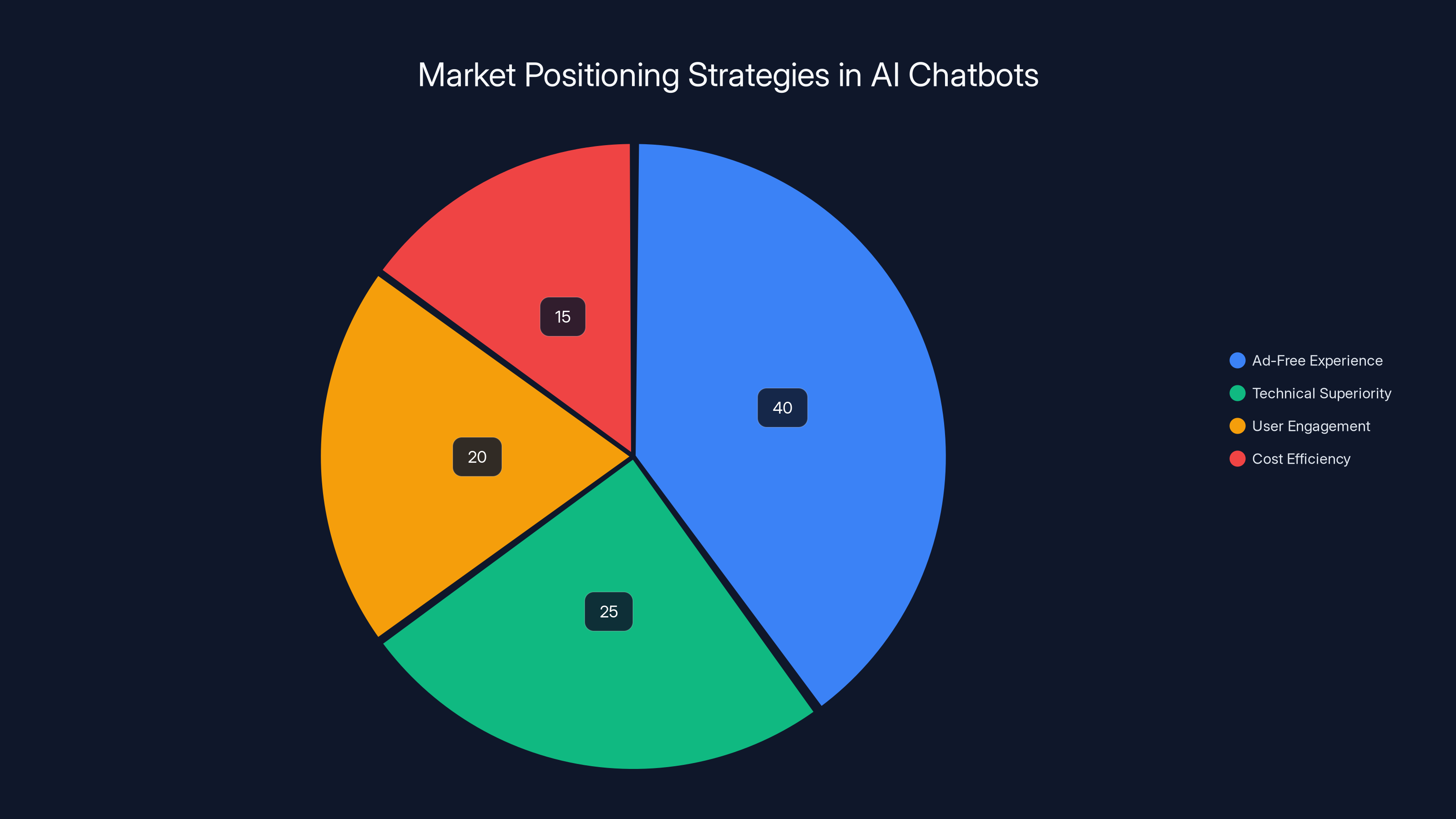
Anthropic's focus on an ad-free experience represents a significant portion of its strategic positioning, estimated at 40%. This contrasts with other common strategies like technical superiority and user engagement. Estimated data.
Cross-Industry Analysis: Why Brands Chose AI in 2025
Strategic Drivers Behind AI Investment
The concentration of AI-featuring commercials during Super Bowl LX reflects convergence of several strategic drivers. First, technical maturity has reached point where AI capabilities deliver demonstrable consumer benefit—from image generation to autonomous systems to predictive analytics. Second, competitive pressure intensifies as leading technology companies emphasize AI capabilities in marketing. Third, market has moved beyond questioning whether AI matters to asking how AI specifically benefits customers and organizations.
Brand choice to feature AI prominently required calculation that AI interest among consumers exceeded skepticism. For established brands like Amazon, Google, and Meta, the calculation involved both innovation signaling (we're technologically advanced) and competitive necessity (if we don't emphasize AI, competitors will). For newer or smaller platforms like Anthropic and Rippling, Super Bowl investment communicated significance and legitimacy to market broadly.
Additionally, many brand teams worked under assumption that Super Bowl audiences would prove receptive to AI messaging. The Super Bowl attracts broad demographic reach, including both early adopters enthusiastic about technology and mainstream consumers increasingly encountering AI in their daily lives. Brands calculated that positive positioning of AI capabilities would resonate sufficiently to justify massive media investment.
The Novelty Factor and Earned Media
A key strategic consideration involved earned media opportunity. AI-featuring commercials generated news coverage, social media discussion, and industry analysis that multiplied the impact of paid media investment. Svedka's AI-generated commercial, Anthropic's competitive jab, and other innovative approaches created conversation that extended message reach far beyond direct viewers.
This calculation proved valid—the commercials generated substantial news coverage, industry analysis, and social media engagement that amplified impact of paid Super Bowl investment. Each distinctive positioning (AI-generated animation, competitive drama, social good focus) created story angles that journalists and social media users discussed extensively. This earned media multiplier effect justifies premium Super Bowl spending in ways that traditional advertising benchmarks might not.
However, earned media remains unpredictable. While most AI-featuring commercials generated favorable coverage and discussion, the quality and tone of earned media cannot be fully controlled. Controversies could emerge, technical flaws could be criticized, or competitive backlash could overshadow intended messaging. The risk inherent in innovative or controversial positioning (as demonstrated by Anthropic's bold competitive jab) requires organizations to accept reputational volatility in exchange for engagement and discussion.
Demographic Targeting and Messaging Precision
Super Bowl audiences skew male and toward higher household incomes—demographics that align favorably with target audiences for technology products. This demographic alignment made Super Bowl investment particularly relevant for technology brands seeking to reach affluent early adopters. Svedka, Anthropic, Rippling, and other brands featured likely saw strong demographic alignment between Super Bowl viewers and their target customers.
However, Super Bowl's massive reach and high cost limit precision targeting compared to digital marketing approaches. Brands cannot segment commercials by viewer interests or purchase propensity. Instead, the medium requires broad positioning that resonates across substantial demographic heterogeneity. This characteristic makes Super Bowl investment particularly suitable for brands with broad consumer appeal (Amazon, Google, Meta) rather than niche enterprise software companies. Yet companies like Rippling and Ramp still invested, suggesting confidence that entertainment value and brand awareness justified lost targeting precision.

AI Production Tools and the Future of Commercial Creation
Impact on Creative Workforce and Agency Model
Svedka's AI-generated commercial raised inevitable questions about implications for advertising agencies, animators, and creative professionals. If commercial-quality animation can be generated substantially through AI, what becomes of teams of artists, animators, and design professionals traditionally required for complex visual content? This question, while reasonable, somewhat misses current technological reality: Svedka's commercial required substantial human creative direction, planning, and refinement. The AI component accelerated production of certain elements, but did not eliminate need for human expertise.
Longer-term trajectories remain uncertain. As generative AI capabilities improve and training datasets expand, the proportion of commercial production requiring human manual labor will likely decrease. Simultaneously, new categories of work will emerge: AI model training, quality assurance, creative direction of AI outputs, and handling novel scenarios where AI generates unexpected results. The workforce transition will prove disruptive—some positions will disappear, other positions will be redefined, and entirely new roles will emerge.
For advertising agencies and production companies, AI integration represents both threat and opportunity. Agencies that incorporate AI into production pipelines can deliver higher quality work with faster turnaround and lower cost—creating competitive advantage against agencies slower to adopt. However, agencies built primarily on labor arbitrage (paying artists to manually produce content) face margin compression as AI automates those labor-intensive functions. The winners will be agencies that evolve toward creative direction, strategic planning, and client partnership while leveraging AI for production execution.
Democratization of Commercial Production
Conversely, AI-driven production tools democratize commercial creation capabilities. Organizations without massive agency budgets can leverage AI tools to create competitive-quality video content, animations, and visual effects. This democratization threatens established production industry structure where small organizations struggle to access professional-quality production capabilities.
Startups and small businesses now can create commercials that previously required $50,000-500,000+ production budgets. This capability shift will likely fragment media consumption as user-generated content and small-company productions compete for attention with high-budget corporate content. Paradoxically, this democratization could increase perceived value of exceptional creative work, as audiences become saturated with acceptable-quality but uninspired AI-generated content.
Quality Standards and Brand Safety
As AI production becomes more accessible, quality standards and brand safety emerge as critical competitive differentiators. Mass production of acceptable-quality content through AI could create perception of mediocrity, making exceptional creative work command premium valuations. Brands seeking to maintain premium positioning will likely continue investing in high-quality creative production, even as the cost to lower-quality production drops dramatically.
Brand safety considerations remain critical limitations on AI automation. Companies must ensure commercial content accurately represents brand values, avoids unintended controversial positioning, and maintains customer perception of quality and attention. High-stakes advertising (Super Bowl commercials, major brand campaigns) will likely retain human creative direction indefinitely, given reputational and financial consequences of production failures.

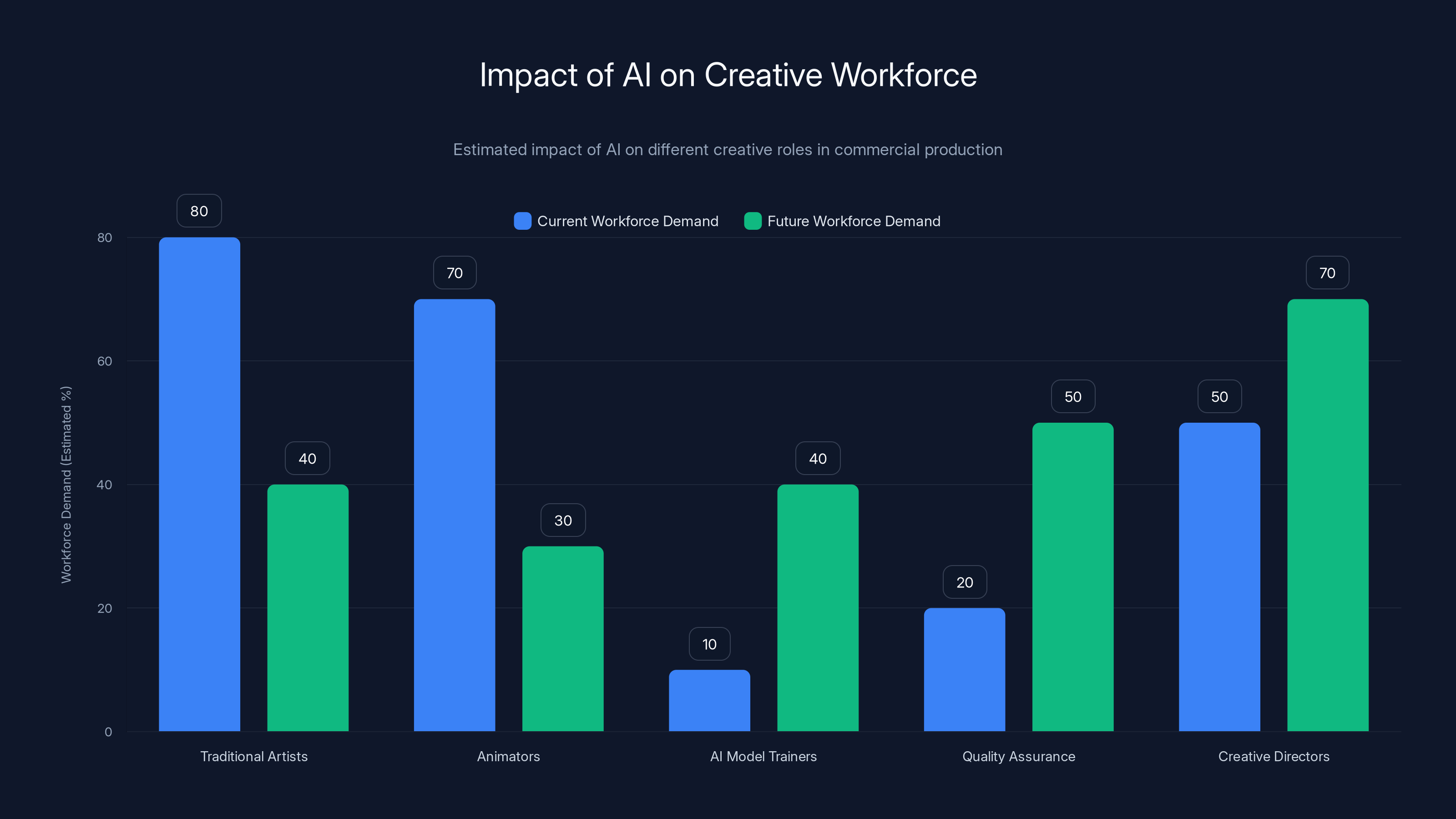
As AI tools advance, traditional roles like artists and animators may see reduced demand, while new roles in AI model training and quality assurance will grow. Estimated data reflects potential future trends.
Marketing Lessons from Super Bowl LX AI Strategy
Positioning Through Values and Differentiation
Successful AI-featuring commercials (Ring, Meta, Amazon) positioned AI as solving customer problems or enhancing customer capabilities rather than emphasizing technological sophistication for its own sake. Failure to ground AI messaging in customer benefit risks appearing gimmicky or superficial. The most effective commercials addressed questions viewers naturally asked: How does this improve my life? How does this solve problems I actually face?
Anthropic AI's positioning—emphasizing customer benefits (ad-free experience) rather than purely technical superiority—demonstrated how smaller competitors can effectively compete with market leaders through value-based differentiation. Rather than claiming better capabilities across multiple dimensions, strategic positioning focuses on specific customer interests and values that matter most to target audience.
Entertainment Value and Earned Media Amplification
Successful commercials combined product messaging with entertainment value that drove social media discussion and news coverage. Ramp's clever Kevin from The Office integration, Amazon's dark comedy approach, and Anthropic's competitive drama all generated conversation extending far beyond traditional advertising reach. This earned media amplification proved critical for justifying Super Bowl media investment.
Organizations planning AI-featuring marketing should anticipate and plan for earned media opportunities. Rather than purely relying on paid reach, successful campaigns design messaging and creative approaches likely to generate discussion, controversy, or compelling narrative. This approach requires tolerance for some reputational risk—Anthropic's bold positioning against Open AI could have backfired but instead generated extended engagement.
Target Audience Relevance
When brands feature AI in marketing, explicit consideration of target audience technology affinity remains critical. Organizations selling primarily to technology-forward demographics can feature AI more prominently; organizations selling to conservative, technology-skeptical demographics might downplay AI while emphasizing customer benefits and practical value. The mismatch between product positioning and audience technology comfort creates messaging ineffectiveness and potential backlash.

Measuring ROI: Quantifying Super Bowl AI Investment
Traditional Metrics and Their Limitations
Measuring Super Bowl advertising ROI presents notorious challenges. Traditional metrics—commercial impressions, brand awareness lift, purchase intent—capture some value but miss critical elements. A 30-second Super Bowl commercial reaches approximately 115 million viewers at cost of $5-7 million, suggesting per-impression cost of approximately 5-6 cents. By contrast, programmatic digital advertising often costs 1-3 cents per impression, making Super Bowl dramatically more expensive on efficiency basis.
However, Super Bowl advertising value extends beyond simple impression counting. The event generates earned media, social media amplification, cultural moment status, and brand prestige associated with participation. Brands featured in Super Bowl commercials receive implicit endorsement from media and public attention that pure cost-per-impression analysis misses. The concentration of audiences and cultural moment status create qualitative value that quantitative metrics struggle to capture.
Attribution and Conversion Tracking
Attributing actual sales or customer acquisition to Super Bowl commercials remains exceptionally difficult. Most technology companies track conversion through multiple touchpoints—website visits, software trials, sales conversations. Isolating Super Bowl commercial impact from other marketing activities, organic search, direct traffic, and brand awareness requires sophisticated attribution modeling and customer research.
Organizations deployed various measurement approaches: monitoring website traffic and sign-up spikes during and immediately after Super Bowl broadcast, conducting brand awareness surveys measuring recognition and consideration shifts, analyzing social media mention volume and sentiment changes, and tracking sales conversations mentioning Super Bowl commercial exposure. Most rigorous approaches combine multiple measurement types to triangulate actual impact.
Expected ROI Thresholds
For technology products with high customer lifetime values (Saa S platforms, B2B software), Super Bowl investment can prove justified if the commercial drives even modest customer acquisition. A customer acquisition cost of
Conversely, consumer products with lower per-customer lifetime value face steeper ROI hurdles. For vodka brands like Svedka, ROI depends on whether the commercial influences purchase decisions among Super Bowl viewers (predominantly adult males with disposable income) and generates sufficient incremental sales to justify $5 million media investment. Svedka's choice to feature AI primarily signals marketing confidence that differentiation through AI innovation would prove sufficiently compelling to drive purchase shifts.

The Broader AI Adoption Trend and Consumer Sentiment
From Technology Skepticism to Practical Integration
Super Bowl LX's prevalence of AI-featuring commercials reflects broader transition in consumer sentiment around artificial intelligence. In previous years, AI consumer discussion focused heavily on risks, concerns, and uncertainty. By 2025, the conversation has shifted toward practical applications, consumer benefits, and integration into daily life. This sentiment shift creates favorable environment for brands emphasizing AI capabilities.
However, sentiment remains mixed and demographic-dependent. Younger consumers tend to embrace AI integration enthusiastically, viewing AI as natural technological progression. Older demographics express more skepticism, concern about job displacement, and preferences for traditional human-based services. Successful AI marketing acknowledges this demographic heterogeneity, positioning AI in ways that resonate with specific target audiences rather than assuming universal enthusiasm.
Privacy, Data, and Trust Concerns
AI-featuring commercials implicitly raise questions about data privacy, security, and trust. When Ring advertises Search Party, consumers understand the feature depends on sharing security camera footage across community network. When Amazon touts Alexa+ capabilities, consumers recognize the system requires ongoing audio recording and processing. When Meta showcases smart glasses with continuous video recording, consumers confront implications of always-on documentation.
Successful AI marketing addresses these concerns proactively rather than glossing over them. Amazon's dark comedy approach actually acknowledged anxiety about AI systems in homes; rather than dismissing concerns, the commercial laughed at exaggerated versions while implicitly reassuring viewers that the company understood and addressed safety considerations. This strategy proves more credible than pretending privacy and security concerns don't exist.
Competitive Pressure and Market Saturation
As AI increasingly becomes table-stakes for technology companies, differentiation through AI capabilities alone decreases in effectiveness. When multiple companies feature AI in Super Bowl advertising, the novelty wears off and audience becomes more critical about which AI applications genuinely matter. In coming years, successful AI marketing will need to progress beyond "we use AI" to "our AI enables specific customer benefits that competitors cannot match."

Future Implications: The AI Advertising Era
Sustained AI Emphasis in Super Bowl Marketing
Given the concentration of AI-featuring commercials in Super Bowl LX and positive reception, subsequent Super Bowls will likely see even greater prevalence of AI-focused advertising. Technology companies compete partly through signaling innovation and technological advancement; Super Bowl provides high-visibility platform for these signals. Expect to see AI positioning expand beyond niche tech companies to broader consumer brands seeking to appear technologically sophisticated.
However, novelty effects will diminish. The first AI-generated commercial (Svedka) generated disproportionate attention precisely because it was novel. As AI-generated content becomes commonplace, audiences will evaluate commercials on quality, creativity, and effectiveness rather than technical approach. This evolution will pressure companies to invest more heavily in creative excellence and customer relevance rather than relying on AI novelty as primary appeal.
Market Segmentation and Positioning Dynamics
AI will increasingly become a segmenting variable in marketing strategy. Premium brands might de-emphasize AI, positioning instead around human creativity and craftsmanship. Value brands might emphasize AI efficiency and cost reduction benefits. B2B brands will align AI positioning with customer priorities: productivity improvements for knowledge workers, cost reduction for operations-focused companies, customer insights for marketing organizations.
Competitive differentiation will increasingly shift from whether AI is featured to how effectively AI integration improves customer outcomes. Organizations that position AI as solving genuine customer problems will outperform organizations emphasizing AI as abstract technological capability.
Regulation and Transparency Requirements
As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent and sophisticated, regulatory attention will increase. Governments may require explicit disclosure when content is AI-generated, affecting future commercials' approach and transparency requirements. This potential regulation creates uncertainty for organizations planning major AI-generated content investments, suggesting conservative approach toward production approaches dependent on AI novelty or consumer misconception about content generation methods.
Transparency about AI usage, similar to Svedka's explicit claim about AI-generated commercial, will likely become industry standard. Rather than viewing transparency as liability, forward-thinking companies will position honest disclosure about AI integration as evidence of confidence and customer respect.

Alternatives and Emerging Approaches
Traditional Content Creation Resurgence
Paradoxically, as AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, demand for authenticity and human-created content may increase. Consumers saturated with AI-generated options might place premium valuations on content demonstrating genuine human creativity, emotion, and artistic vision. Some brands will position themselves explicitly around human creation, using this as competitive differentiation against AI-heavy competitors.
Hybrid Human-AI Production Models
Most successful commercial production will likely continue employing hybrid approaches where AI handles routine, technical, or computationally intensive elements while humans provide creative direction, strategic decision-making, and quality assurance. This hybrid model distributes work according to comparative advantage: AI excels at pattern-matching, automation, and rapid iteration while humans excel at creativity, judgment, and strategic planning.
Furthermore, platforms like Runable offer AI-powered automation for content generation and workflow management that enables teams to create professional-quality materials without requiring expensive production teams. For marketing teams seeking cost-effective content creation capabilities, solutions combining AI automation with human creative direction provide middle-ground between fully-manual production and purely-automated generation.
Authenticity as Differentiation
As AI capabilities proliferate, authenticity becomes increasingly valuable. Consumers encountering hundreds of polished, AI-generated commercials weekly may crave genuine, imperfect, human-created content that communicates authentic brand values. Brands emphasizing transparency about human creativity, real customer stories, and genuine company culture may differentiate effectively against companies leaning heavily on AI polish and professionalism.

Practical Considerations for Marketing Teams
Evaluating AI Integration for Your Brand
Marketing teams considering AI integration should evaluate alignment between AI capabilities and authentic customer benefit. Rather than pursuing AI for novelty or competitive imitation, organizations should ask: How does AI specifically improve our customers' experiences? What problems does our AI solve that customers genuinely care about? Are we positioning AI as genuine solution or superficial gimmick?
These questions force organizations to ground AI decisions in customer value rather than technology trends. Brands that successfully integrate AI marketing do so when the technology directly addresses customer pain points or enables new capabilities customers desire.
Measurement and Attribution Planning
Organizations planning AI-featuring marketing should establish measurement frameworks before content launch. What metrics will indicate successful ROI? How will you attribute customer acquisition to specific marketing initiatives? What are reasonable conversion benchmarks for your target audience? Establishing these frameworks upfront enables rigorous post-campaign analysis and improved future decision-making.
Managing Reputational Risk
AI-featuring marketing carries reputational risk if messaging proves inaccurate, if AI systems generate unexpected failures, or if competitive positioning overshoots actual product capabilities. Brands should conduct thorough quality assurance, maintain conservative claims about AI capabilities relative to competitors, and prepare contingency messaging if problems emerge.

The Content Creation Automation Connection
For marketing teams considering content generation and workflow automation to support their campaigns, AI-powered platforms offer substantial capabilities that expand marketing team productivity. Solutions enabling teams to generate professional-quality slides, documents, reports, and presentations through AI assistance reduce bottlenecks in content creation pipelines. This automation becomes particularly valuable as marketing teams attempt to scale content production without proportional headcount increases.
Platforms combining AI-powered content generation with workflow automation enable marketing teams to manage complex campaigns more efficiently. Rather than manual creation of each presentation, document, or report, teams can leverage AI assistance to generate initial drafts, handling formatting and refinement while humans focus on strategy, messaging, and quality assurance. This hybrid approach delivers benefits of AI automation while maintaining human oversight for quality and brand alignment.
When implementing AI-powered marketing automation, teams should prioritize integration with existing tools and workflows, maintaining focus on actual productivity improvement rather than technology novelty. The goal remains generating better marketing results faster—AI serves as enabler, not objective.

Conclusion: The AI-Driven Marketing Inflection Point
Super Bowl LX represented an inflection point in AI adoption within mainstream marketing. When multiple Fortune 500 companies simultaneously featured AI-powered commercials on the world's most expensive media platform, they signaled fundamental confidence in AI's relevance to consumer interests and brand strategy. This wasn't isolated experimentation with emerging technology; it was major corporations betting substantial resources that AI capabilities mattered sufficiently to feature prominently in marquee marketing moments.
The diversity of AI applications showcased—from animation and image generation to autonomous systems to competitive positioning—demonstrated maturation of AI capabilities across multiple domains. Different companies made different strategic choices, but each bet reflected confidence that AI integration would enhance brand positioning or communicate meaningful customer value.
However, Super Bowl LX's AI emphasis also revealed important truths about technology adoption and consumer sentiment. Successful AI-featuring commercials grounded technology positioning in genuine customer benefit rather than pure technical showcasing. Companies that explained how AI specifically improved customer experiences outperformed companies emphasizing AI as abstract capability. Consumer reception remained mixed and demographic-dependent, with younger audiences embracing AI integration while older demographics expressed more skepticism.
Looking forward, AI will remain increasingly prevalent in marketing, but novelty will diminish as the technology becomes mainstream. Competitive differentiation will shift from whether companies feature AI to how effectively AI integration delivers customer value and enables better outcomes. Organizations that position AI as tool enabling human capability rather than replacement for human creativity will likely fare better with skeptical audiences.
For marketing teams, these dynamics suggest several practical implications. First, evaluate AI integration based on authentic customer value rather than technological trend-following. Second, invest in measurement and attribution to rigorously assess ROI of AI-featuring campaigns. Third, maintain human oversight of AI-generated content to ensure brand alignment, quality standards, and customer relevance. Fourth, position AI transparently and authentically, avoiding overstated claims or consumer deception.
The future of marketing will likely involve hybrid human-AI collaboration where both contribute comparative advantages. Humans provide creative vision, strategic judgment, and emotional intelligence; AI provides automation, pattern recognition, and rapid iteration. Brands that successfully combine both will create more effective marketing than those relying exclusively on either humans or technology.
Super Bowl LX's AI-featuring advertisements weren't the future of marketing—that future is emerging gradually as organizations learn to deploy AI effectively. But these high-profile commercials signaled the direction of that future: toward more efficient, automated, and AI-enabled marketing processes balanced with human creativity, judgment, and customer understanding. The brands that master this balance will define the next era of marketing excellence.

FAQ
What is AI-generated advertising?
AI-generated advertising refers to commercials and marketing content where artificial intelligence systems contribute substantially to creative production, visual generation, animation, or content creation. Unlike traditional advertising where humans manually create all elements, AI-generated advertising leverages machine learning models to automate specific production components while humans typically retain control over strategy, narrative, and quality assurance. Svedka's Super Bowl commercial exemplified this approach, using AI to generate character animation and movements while humans directed overall creative strategy.
How does AI image generation work in commercial production?
AI image generation systems like Google's Nano Banana Pro use neural networks trained on massive datasets to understand relationships between text descriptions and visual outputs. When users provide text prompts describing desired visuals, the AI models generate corresponding images by predicting pixel patterns and visual elements most likely to match the description. In commercial production, this capability enables rapid visualization of design concepts (like Google's home renovation example), concept art generation, and background creation without requiring manual artist work for each variation.
What are the benefits of using AI in commercial advertising?
AI integration in advertising provides several meaningful benefits. Production efficiency: AI can accelerate creation of complex visual elements, reducing production timelines from months to weeks. Cost reduction: Automating routine production components lowers per-commercial production costs, enabling broader advertising campaigns within similar budgets. Iteration capability: AI enables rapid experimentation with multiple creative variations, facilitating A/B testing and optimization. Accessibility: AI democratizes high-quality production capabilities, enabling smaller organizations to create professional-quality content. Personalization: AI enables customized messaging variants targeting different audience segments more cost-effectively than traditional production approaches.
What are the risks and limitations of AI-generated commercial content?
AI-generated advertising faces several significant limitations. Quality consistency: Current AI systems sometimes generate unnatural or slightly incorrect outputs requiring human correction and refinement. Creativity constraints: AI generally excels at variations on familiar patterns but struggles with genuinely novel creative concepts. Brand safety: AI-generated content sometimes produces unintended implications, controversial elements, or brand misalignment requiring extensive quality review. Regulatory uncertainty: Emerging regulations may require explicit disclosure when content is AI-generated, potentially affecting commercial effectiveness or requiring transparency that some brands find undesirable. Reputational risk: Consumers skeptical of AI might view AI-generated advertising as lower quality or manipulative compared to human-created content.
How should marketing teams measure ROI for AI-featuring campaigns?
Marketing teams can measure AI campaign ROI through multiple complementary approaches. Awareness metrics: Monitor brand awareness lift, ad recall, and consideration changes before and after campaign launch, typically through market research surveys. Website analytics: Track traffic, conversion rates, and sign-up volume during and after campaign periods, attributing changes to campaign exposure. Customer research: Conduct surveys asking customers about campaign awareness and influence on purchase decisions. Sales attribution: Implement sophisticated attribution modeling connecting customer acquisitions to specific marketing touchpoints including AI-featuring campaigns. Social media analysis: Monitor discussion volume, sentiment, and earned media reach generated by campaign. Successful ROI assessment typically combines multiple measurement approaches rather than relying on single metric.
What distinguishes successful AI marketing from ineffective AI marketing?
Successful AI-featuring marketing connects technology to genuine customer benefit and problem-solving. The most effective commercials (Ring's Search Party, Meta's practical smart glasses use cases, Amazon's relatable automation benefit) positioned AI as enabling specific customer outcomes. Ineffective AI marketing treats technology as novelty or abstract capability without clear customer value proposition. Additionally, successful AI marketing acknowledges and transparently addresses legitimate consumer concerns about privacy, data, or technology impacts rather than glossing over concerns. Entertainment value and earned media potential also distinguish successful campaigns, as higher-engagement commercials drive extended conversation beyond paid media reach.
How is AI changing creative profession employment?
AI is creating job displacement in routine creative production tasks while simultaneously creating new categories of work. Positions like basic animation, routine design, and technical production face meaningful impact as AI automates these functions. However, new roles emerge: AI model training, quality assurance and creative direction of AI outputs, strategic creative planning, and client consultation. The net employment impact remains uncertain, but evidence suggests that creative professions will evolve and require new skills rather than disappearing entirely. Creative professionals embracing AI as productivity tool, rather than resisting integration, tend to adapt most successfully.
What does the prevalence of AI-featuring Super Bowl ads indicate about marketing trends?
Super Bowl LX's concentration of AI-featuring advertisements signals that marketing leaders broadly recognize AI as strategically important for brand positioning and competitive advantage. When multiple Fortune 500 companies simultaneously invest in high-profile AI positioning, it indicates market maturation and mainstream adoption transition. However, the diverse approaches (some emphasizing automation benefits, others entertainment, others competitive positioning) suggest that "AI strategy" remains contested rather than crystallized into universal best practices. Future Super Bowls will likely see sustained AI emphasis, but expect competitive differentiation to shift from whether companies feature AI to how effectively specific AI applications deliver customer value.
How might regulation affect future AI advertising?
Emerging regulatory discussions suggest several potential impacts on AI-featuring advertising. Mandatory disclosure requirements (explicitly identifying AI-generated content) are increasingly likely, potentially affecting consumer perception or requiring brands to emphasize transparency as value proposition. Privacy regulations may constrain data usage for AI-powered personalization in advertising. Liability frameworks may emerge defining responsibility when AI systems generate inappropriate, discriminatory, or misleading advertising content. Forward-thinking organizations are preparing for regulatory requirements by emphasizing transparency about AI usage and maintaining careful quality control preventing problematic outputs. Regulatory uncertainty creates some risk for brands heavily betting on AI-dependent creative approaches.
What alternatives exist to AI-generated commercial content?
Organizations not pursuing AI-generated approaches can leverage several alternatives. Traditional human-created content remains viable, particularly when emphasizing authenticity, craftsmanship, and human creativity as competitive differentiation. Hybrid approaches combining human creativity with AI efficiency (humans direct strategy and creative vision while AI handles production execution and iteration) provide middle ground. User-generated content and authentic customer stories often prove more compelling than polished corporate content. Strategic partnerships with celebrities, creators, or cultural figures can generate engagement without relying on technological novelty. Organizations should choose approaches aligned with brand values, target audience preferences, and genuine competitive advantages rather than following technology trends.

Key Takeaways
- Super Bowl LX marked inflection point where AI became mainstream in major advertising, with multiple Fortune 500 companies featuring AI-powered commercials
- Successful AI marketing grounds technology in genuine customer benefit rather than technological novelty—Ring, Meta, Amazon excelled by explaining how AI solves customer problems
- Hybrid human-AI production models prove most effective, with AI handling automation and iteration while humans direct strategy, creativity, and quality assurance
- Competitive differentiation shifting from whether companies feature AI to how effectively AI integration delivers measurable customer value and business outcomes
- Marketing teams should measure AI campaign ROI through multiple complementary approaches including awareness lift, conversion attribution, and earned media impact
- AI democratizes commercial production capabilities, enabling smaller organizations to create professional-quality content while threatening traditional labor-intensive creative roles
- Transparency about AI usage and addressing legitimate consumer concerns about privacy/data builds credibility more effectively than glossing over potential issues
- Entertainment value and earned media potential distinguish successful AI campaigns, with higher-engagement commercials driving extended conversation beyond paid reach
- Regulatory uncertainty around AI-generated content disclosure and liability creates emerging constraints on how companies can deploy AI in advertising
- Authenticity and human creativity positioning emerge as differentiation strategies as AI-generated content becomes increasingly prevalent and saturates consumer attention
Related Articles
- Meta's Vibes App: Complete Guide to AI-Generated Video Platform [2025]
- Masking Net New Customer Slowdowns: The #1 B2B SaaS Growth Deception [2025]
- A/B Testing vs Multivariate Testing: Complete Guide 2025
- Sony TCL Partnership 2025: What It Means for TV Industry
- AI Code Trust Crisis: Why Developers Don't Check & How to Fix It
- Go-to-Market Strategies for the AI Era: Complete Guide [2025]