Introduction: The Humanoid Robot Revolution Reaches Critical Mass
The humanoid robotics industry has entered an unprecedented growth phase, with venture capital flowing into the sector like never before. Apptronik, a University of Texas spinout, has just announced a remarkable
What makes Apptronik's funding announcement particularly significant is the composition of its investor base. Google, Mercedes-Benz, and B Capital have all committed capital across multiple funding extensions, alongside original investors and new participants entering the round. This diversified investor group spans technology giants, automotive manufacturers, and specialized venture firms, suggesting broad confidence in humanoid robotics' near-term commercial viability.
The company's trajectory over the past year reveals explosive demand that wasn't anticipated when the initial Series A was announced. Starting with a
Apptronik's focus areas—unloading trailers, picking warehouse inventory, and tending to machinery—represent the $3.2 trillion logistics and warehousing market in the United States alone. These tasks currently employ millions of workers globally and face significant labor shortages as demographic shifts continue. The company's embodied AI approach, developed in partnership with Google Deep Mind, positions autonomous humanoid robots as practical solutions to this structural market challenge.
Understanding Apptronik's funding success requires examining the convergence of several technological, market, and financial factors. The company's roots trace back over a decade, giving it both technical depth and institutional knowledge that newer competitors lack. Its partnerships with major corporations demonstrate real-world application potential beyond research labs. And its willingness to accept continued funding at increasingly higher valuations reflects investor confidence that the company can deliver on commercialization timelines.
The Apptronik Story: From NASA-DARPA to Commercial Robotics
Founding Origins and Technical Heritage
Apptronik's technical foundation runs surprisingly deep, extending back to 2013 when members of the Human Centered Robotics Lab from the University of Texas at Austin competed in the NASA-DARPA Robotics Challenge. This competition, established following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, aimed to accelerate robot development for disaster response scenarios. The UT Austin team worked on a robot called Valkyrie, which would become the experimental testbed for many of Apptronik's current technologies.
The formal founding of Apptronik occurred in 2016, but the company inherited over three years of research and development work from the university laboratory. This extended pre-history matters considerably because humanoid robotics requires solving fundamental research problems that cannot be rushed. Problems like bipedal balance in dynamic environments, manipulation with limited computational resources, and real-time perception represent multi-year research challenges. By the time Apptronik was formally established as a commercial entity, the team had already spent years solving core scientific problems.
The NASA-DARPA partnership has continued beyond the initial competition. Space agencies represent unique customers for robotics technology because they face extreme performance requirements, operate in environments where human presence is dangerous or impossible, and have budgets that can support cutting-edge technology. This relationship provides Apptronik with a customer base that values performance and reliability above cost, creating a market cushion while the company develops more cost-efficient versions for commercial applications.
The Apollo Robot: Embodied AI in Practice
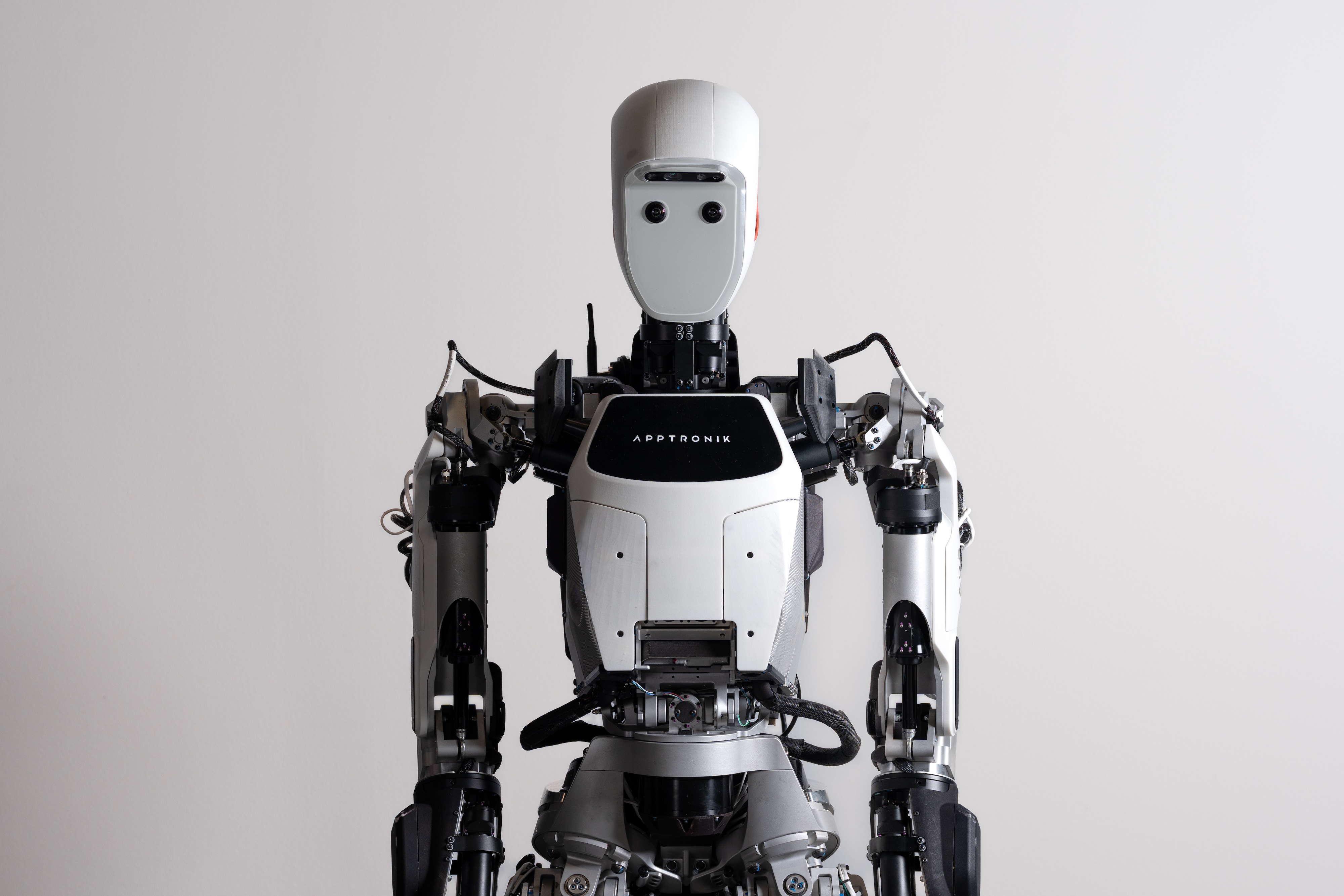
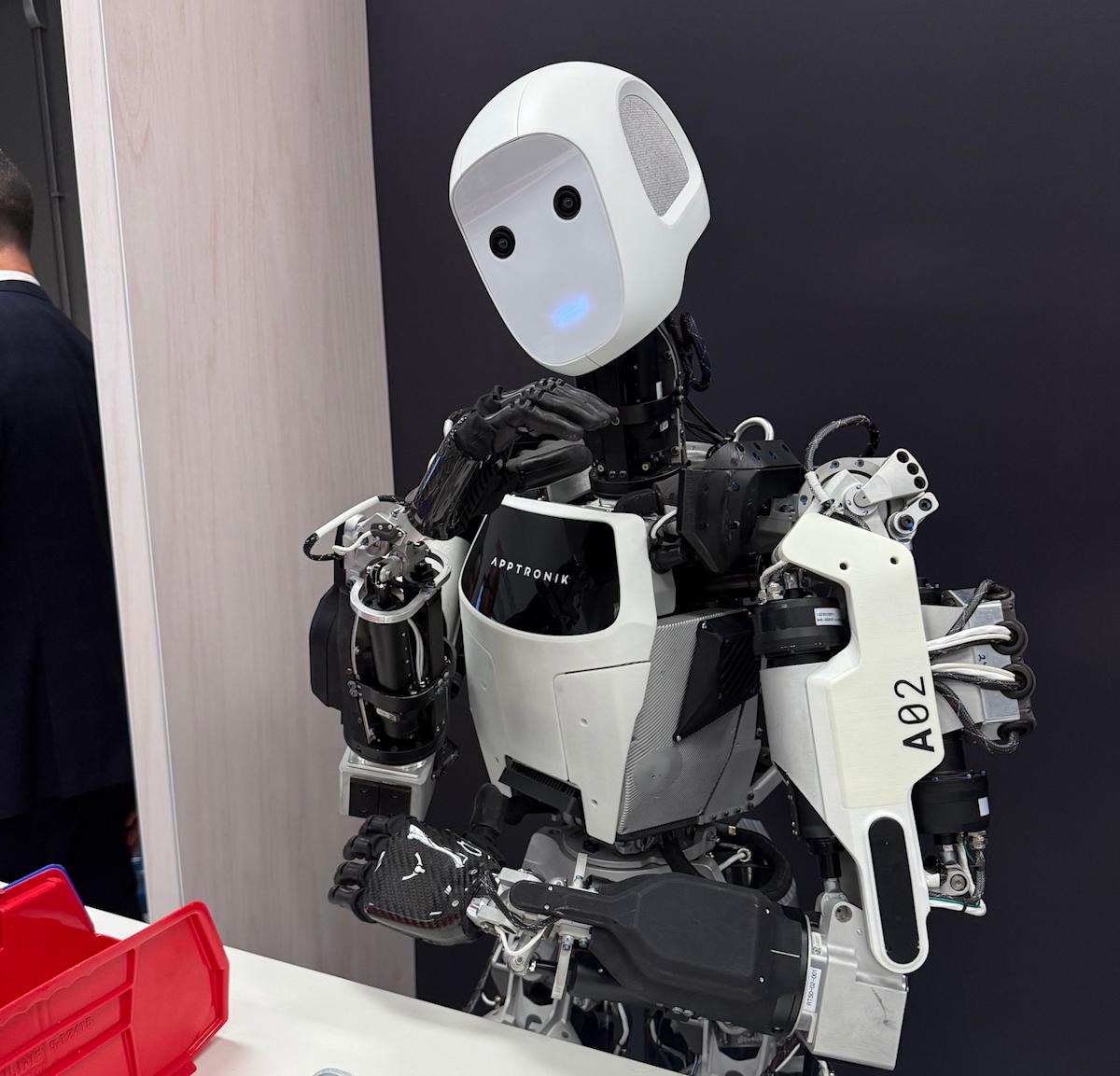
Apptronik's flagship platform is Apollo, a bipedal humanoid robot designed for commercial warehouse and logistics applications. Apollo stands approximately 5'8" tall and weighs around 150 pounds, dimensions chosen specifically to operate within human-designed workspaces without major infrastructure modifications. The robot features sophisticated sensory systems including stereo vision, tactile sensors, and inertial measurement units that provide real-time environmental awareness.
The technical approach underlying Apollo represents a departure from traditional industrial robotics, which typically involves fixed installations and precisely controlled environments. Humanoid robots must operate flexibly within existing human spaces, adapting to variable conditions, unfamiliar objects, and dynamic situations. This requirement drives massive computational complexity—the robot must continuously solve inverse kinematics problems, balance while moving, perceive and classify objects, and make real-time decisions about movement strategies.
Apollo's embodied AI capability means the robot doesn't simply follow predetermined sequences of movements. Instead, it perceives its environment, reasons about task requirements, and determines optimal approaches to accomplishing objectives. When picking items from a warehouse shelf, Apollo must recognize items by appearance, estimate their weight and density, adjust its grip strength accordingly, navigate to correct positions, and manage its balance throughout the operation. All of these decisions occur in real-time with latency constraints that matter for practical efficiency.
Technology Development Roadmap
Apptronik has outlined a technology development roadmap that progresses from current capabilities toward increasing autonomy and capability. Current systems operate with substantial human supervision and intervention, but the roadmap targets progressive autonomy increases that would eventually enable unsupervised operation across broader task domains. The company's funding, combined with partnership resources from Google Deep Mind and other investors, accelerates movement along this roadmap.
The partnership with Google Deep Mind represents particularly significant technical resources. Deep Mind's expertise in artificial intelligence, reinforcement learning, and embodied AI directly addresses core technical challenges facing humanoid robotics. The collaboration likely involves knowledge transfer around perception systems, decision-making algorithms, and learning from demonstration techniques that could substantially accelerate capability development.
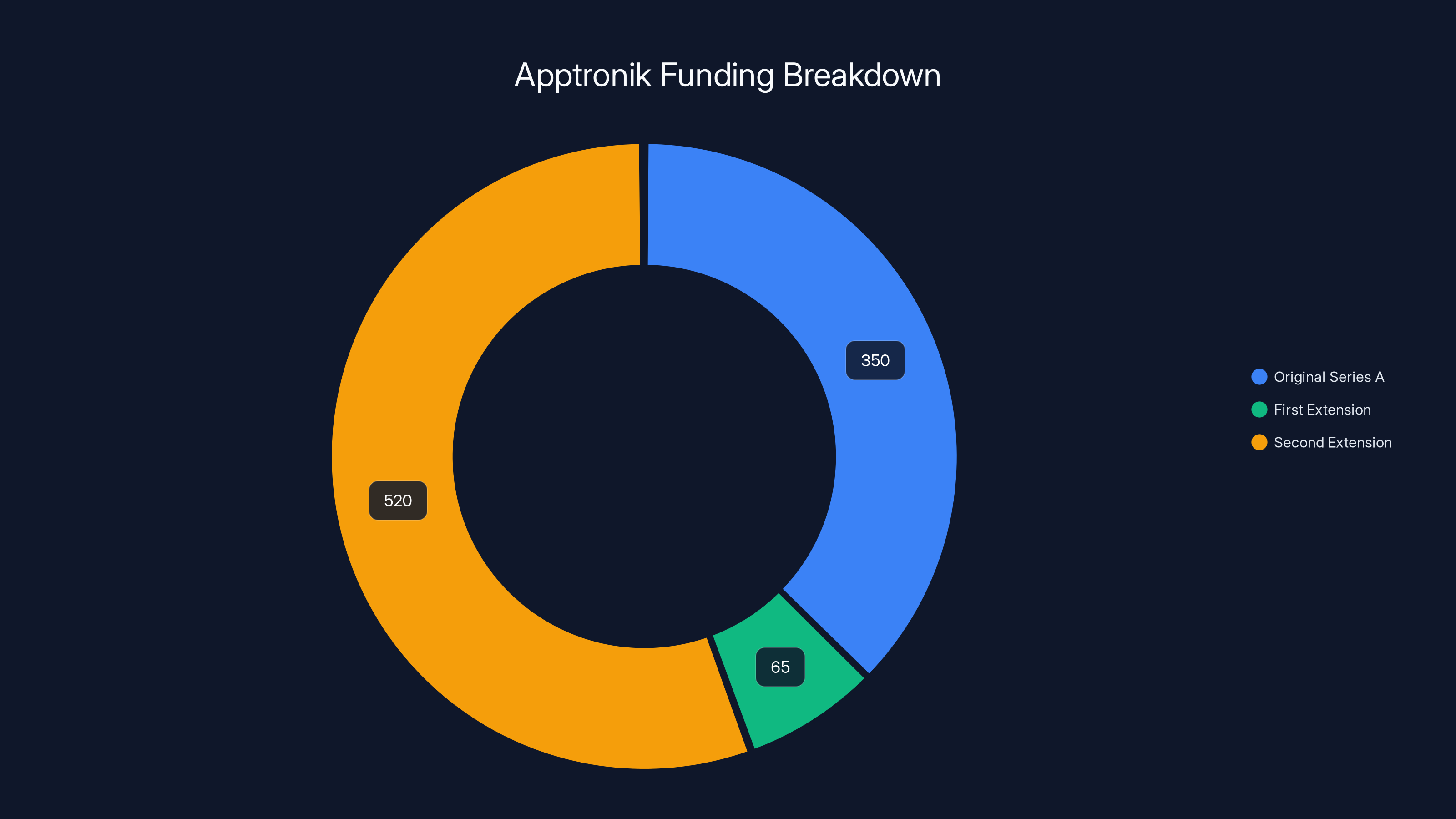
Apptronik's funding has grown significantly, with the largest contribution of $520 million in the second extension, highlighting strong investor confidence.
Market Opportunity: Why Humanoid Robots Matter Now
Structural Labor Shortages in Logistics and Warehousing
The market opportunity driving investor enthusiasm for Apptronik is fundamentally rooted in labor supply challenges. The United States logistics and warehousing sector employs approximately 3.5 million workers, with demand growth consistently outpacing labor supply. Demographic trends—aging population, declining birth rates, increasing educational attainment—all reduce the available pool of workers seeking physically demanding roles. Real wage requirements for warehouse and logistics positions have been increasing 5-7% annually as employers compete for limited labor supplies.
Warehouse work involves highly repetitive tasks where automation appears straightforward—unloading trucks, sorting items, placing goods on shelves. However, real warehouse environments include substantial variability. Items come in different shapes, sizes, weights, and packaging configurations. Shelves vary in height and depth. Pallets arrive in different orientations. These variables that humans handle intuitively remain challenging for traditional automation approaches.
Humanoid robots address this market gap by providing flexible automation that doesn't require major facility redesign or specialized infrastructure. A warehouse designed for human workers can integrate humanoid robots gradually, deploying them on specific task types while humans handle more variable or demanding work. This gradualist approach contrasts with traditional factory automation that often requires complete facility redesign.
The Economics of Warehouse Automation
From an economic perspective, warehouse automation demonstrates strong unit economics at current labor costs. A humanoid robot representing a capital investment of
Compare this to current warehouse wages of
Global Market Context and Competition
The global market opportunity for humanoid robots extends well beyond United States warehousing. European logistics faces similar labor constraints, with even stricter labor regulations and higher wage requirements. Japanese manufacturers face demographic challenges that make automation adoption essential for maintaining production. Chinese logistics operations benefit from scale that makes capital investment in robotics highly attractive.
Apptronik competes in this market against several other well-funded humanoid robot developers. Figure AI, mentioned in the original funding announcement, has raised nearly $2 billion and represents the most direct competitor. Boston Dynamics, owned by Hyundai, brings substantial resources and has demonstrated impressive robot capabilities. Sanctuary AI, Tesla's Optimus program, and several emerging Chinese competitors all pursue similar market opportunities. However, the market is large enough that multiple winners can emerge—current logistics automation penetration remains below 10% globally, suggesting abundant opportunity.

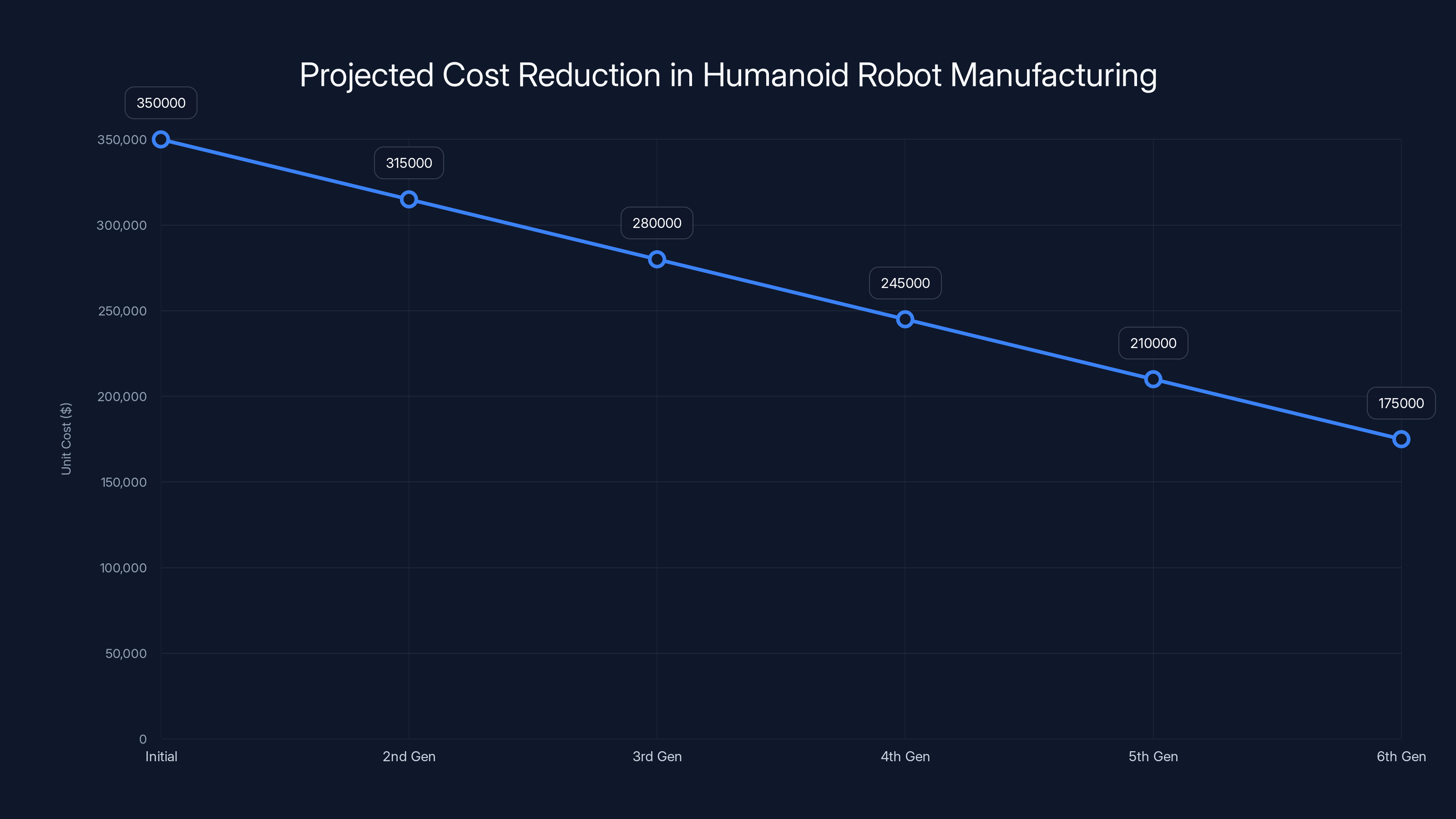
Estimated data shows a 40-50% reduction in unit costs over six production generations, aligning with commercial viability targets.
Understanding Embodied AI: The Technical Differentiator
Defining Embodied AI
Embodied AI represents a specific approach to artificial intelligence that emphasizes the integration of perception, reasoning, and physical action. Unlike conversational AI systems that process text inputs and generate text outputs, embodied AI systems must perceive physical environments through sensors, make real-time decisions about actions, and adapt based on feedback from physical interactions. The "embodied" dimension means the intelligence is grounded in actual physical interaction with the world rather than abstract information processing.
This distinction matters profoundly for humanoid robotics. A system could theoretically process images and generate movement commands without deeply understanding physical dynamics, but such a system would be brittle and ineffective in novel situations. Embodied AI approaches emphasize learning about physical properties—how objects fall, how friction behaves, how weight distributions affect balance—through interaction and experimentation. This experiential knowledge base enables robots to generalize beyond training scenarios.
Google Deep Mind's contribution to embodied AI development reflects the organization's leadership in reinforcement learning and robotics research. Deep Mind has published extensively on robot learning from demonstrations, self-supervised learning from unlabeled robot experience, and transfer learning that applies knowledge across different robot morphologies. These techniques directly enable the kind of flexible, adaptive behavior required for commercial humanoid robots.
Technical Implementation in Apollo
Apollo's embodied AI implementation involves several interconnected systems working in concert. The perception system processes sensor data to build real-time environmental models. The reasoning system uses these models to identify tasks, understand constraints, and plan action sequences. The control system translates high-level action plans into specific motor commands while continuously monitoring for execution errors or unexpected conditions.
Real-time decision-making is essential because warehouse environments change constantly. A shelf configuration that worked for one pick operation might be blocked for the next. Object properties that were assumed might be wrong. These variations require that the robot make continuous adjustments rather than rigidly following predetermined movements. The embodied AI approach enables this adaptive behavior by maintaining updated environmental models and continuously reasoning about task requirements.
Learning from human demonstration represents another critical embodied AI capability. Rather than programming every possible task variant, engineers can demonstrate desired behaviors and have the robot learn to generalize from these demonstrations. A human might demonstrate how to pick a fragile item, and the robot learns to adjust its grip strength and movement speed accordingly. This learning approach dramatically reduces engineering time required to deploy robots for new task types.
Advantages Over Traditional Automation
Traditional factory automation relies on rigid programming and carefully controlled environments. A robotic arm follows predetermined motion sequences with minimal sensing beyond confirmation that tasks completed. This approach works excellently in high-volume, low-variety manufacturing where the same operation repeats thousands of times identically. However, it fails in variable environments where flexibility matters.
Embodied AI approaches sacrifice some of the efficiency gains from rigid optimization to gain flexibility and adaptability. A humanoid robot might not pick items as quickly as a specialized gripper designed for a specific item type, but it can handle item variations that would require complete reprogramming of traditional systems. This flexibility has substantial value in logistics environments where item types, suppliers, and packaging configurations constantly evolve.
The economic implication is that embodied AI enables automation of tasks that were previously considered "too variable" for robotics. This expands the addressable market substantially beyond the narrow set of high-volume, low-variability operations that comprise most current industrial robotics.

The Investment Thesis: Why Investors Are Betting Big
Market Size and Growth Projections
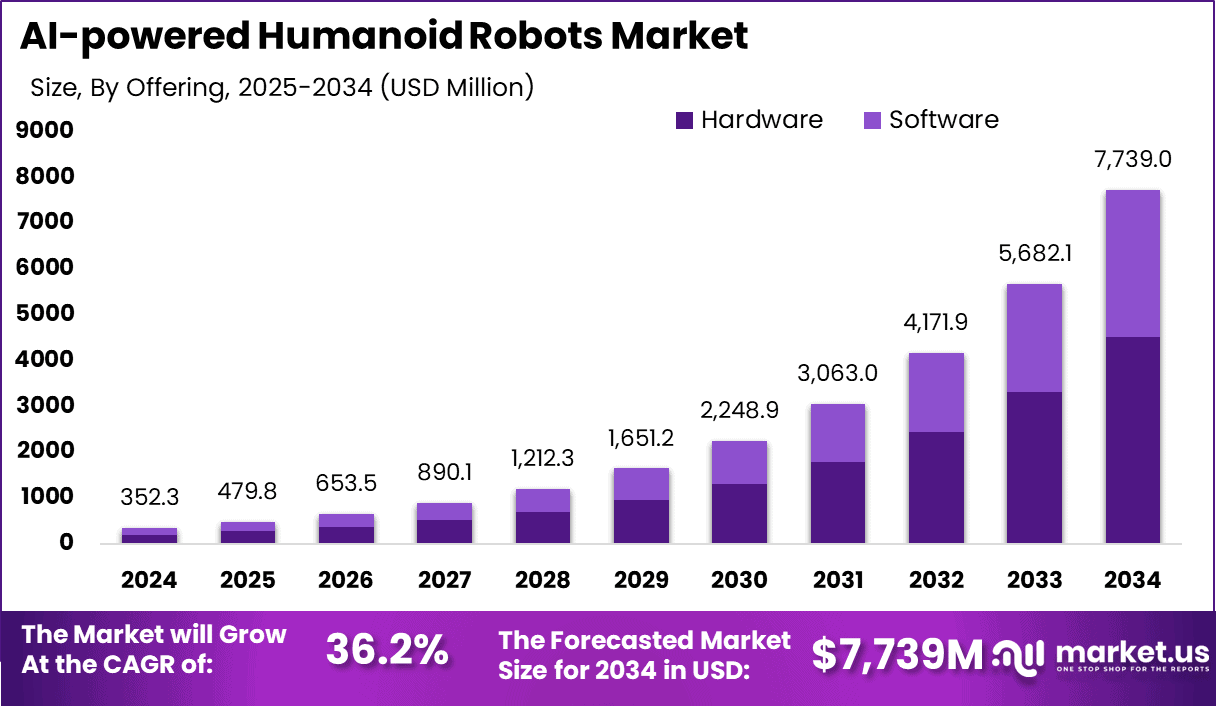
Venture capital investment in humanoid robotics exceeds
These projections rest on several key assumptions. First, that humanoid robot hardware costs will decline through manufacturing scale and component improvements, increasing the addressable market at lower price points. Second, that software capabilities will improve faster than hardware, enabling robots to handle increasingly complex tasks. Third, that regulatory frameworks will stabilize around safety standards that enable broader deployment. All three assumptions appear reasonable given current technological trajectories.
Apptronik's
Strategic Rationale for Corporate Investors
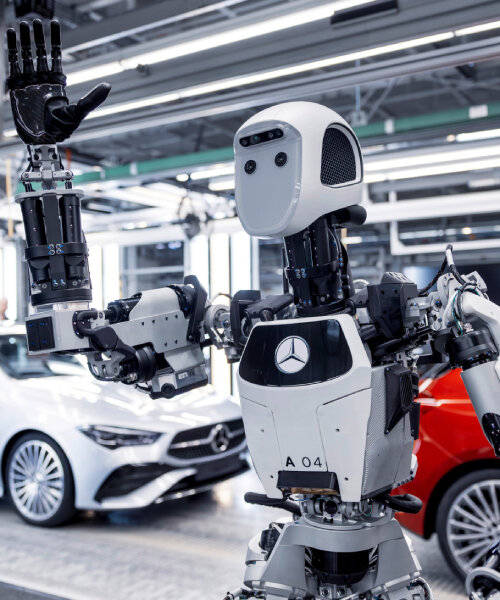
Corporate investors like Google and Mercedes-Benz bring different motivations than venture capital firms. Google's investment reflects strategic interest in embodied AI technology applicable across numerous product categories and use cases. Advances in robot perception and control potentially benefit autonomous vehicles, smart home devices, and various Google research initiatives. The investment provides access to technical talent and breakthrough capabilities in robotics and AI.
Mercedes-Benz represents a different strategic calculation. The automotive manufacturer faces pressure to diversify revenue streams beyond vehicle manufacturing as electric vehicles commoditize the industry. Logistics robotics represents a potential growth vector, and direct investment in Apptronik provides optionality on acquiring capabilities and eventual M&A opportunities. The partnership likely includes discussions around manufacturing humanoid robots for Mercedes-Benz, creating downstream revenue opportunities.
GXO's involvement as a customer-investor creates a particularly compelling dynamic. As one of the world's largest logistics operators, GXO gains direct access to cutting-edge automation technology while simultaneously funding its development. GXO can deploy robots in real warehouse environments, providing Apptronik with invaluable operational feedback and learning opportunities. This customer-investor structure aligns incentives and accelerates development cycles compared to traditional vendor-customer relationships.
Timing and Market Readiness
Timing represents a critical factor in Apptronik's funding success. The convergence of several technological and market factors has created a favorable moment for humanoid robotics commercialization. AI capabilities, particularly in perception and reasoning, have reached thresholds where practical applications become possible. Manufacturing costs for robot components have declined substantially. And labor market conditions have created urgent demand for automation solutions.
Apptronik's willingness to accept continued funding at higher valuations demonstrates that the company's team believes near-term commercialization is achievable. Teams pursuing moonshot technologies often resist additional funding rounds that increase valuation pressure. Accepting progressively higher valuations signals confidence that revenue generation and adoption traction can support growing valuations. The team's comfort with this path suggests internal conviction about near-term commercial readiness.

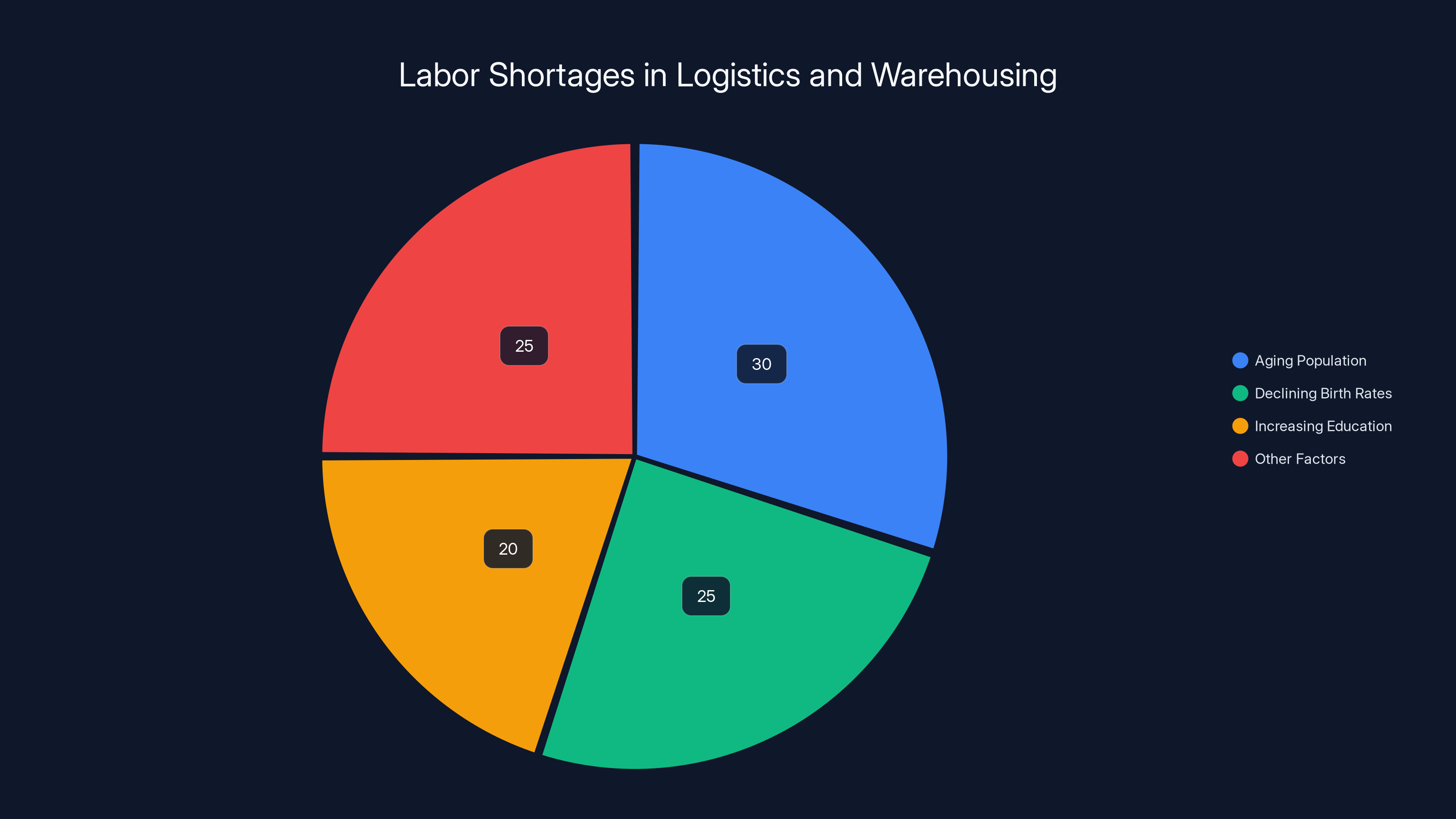
Estimated data shows that aging population and declining birth rates are major contributors to labor shortages in logistics and warehousing, each accounting for about 25-30% of the issue.
Partnership Ecosystem: Accelerating Commercialization
Google Deep Mind Collaboration
The partnership between Apptronik and Google Deep Mind represents one of the most technically significant aspects of the company's development. Deep Mind brings research capabilities and talent depth unmatched in the commercial robotics industry. The collaboration likely involves multiple dimensions including algorithm development, training methodology improvements, and access to Deep Mind's specialized hardware and infrastructure for robot learning.
Specifically, Deep Mind's expertise in reinforcement learning directly addresses core challenges in robot control and learning. Reinforcement learning enables systems to learn control policies through interaction and experimentation rather than requiring explicit programming. In robotics contexts, this approach allows robots to discover effective solutions to manipulation problems through trial and error, guided by reward signals indicating task success. This methodology has proven remarkably effective for learning complex behaviors that would be difficult to program explicitly.
The collaboration also likely leverages Deep Mind's work on multi-task learning and transfer learning. Robots deployed commercially must handle diverse task types—picking different items, operating in varied environments, responding to unexpected situations. Rather than training separate systems for each task type, multi-task learning enables a single system to develop generalizable capabilities. The robot learns that gripping strategies for fragile items differ from strategies for dense items, and transfer learning enables applying this knowledge to items encountered during training.
GXO Partnership: Bringing Automation to Real Logistics
GXO Logistics operates one of the world's largest third-party logistics networks, with over 750 facilities across multiple countries. The company handles logistics operations for numerous Fortune 500 companies, managing complex warehouse, transportation, and supply chain functions. GXO's partnership with Apptronik positions the robotics company to deploy humanoid robots in real operating environments rather than controlled laboratory or pilot facilities.
This partnership structure provides immense value to both companies. Apptronik gains access to diverse warehouse environments, operational data, and user feedback that accelerates product refinement. GXO gains early access to potentially transformative automation technology and maintains strategic optionality on eventual acquisition or deeper integration. Most importantly, customers of GXO's logistics services benefit from improved efficiency and service quality as robots augment human workers.
Real warehouse deployment involves challenges that laboratory environments don't capture. Dust, humidity, vibration, and temperature variations all affect robot performance. Equipment interacts with existing facility infrastructure in unexpected ways. Human workers adjust their behavior when robots are present. These practical factors force engineers to solve problems that theoretical analysis might miss, accelerating development maturity.
Mercedes-Benz Strategic Involvement
Mercedes-Benz's investment in Apptronik reflects the automotive industry's broader recognition that manufacturing and logistics automation will be central to future competitiveness. The partnership likely includes exploring humanoid robot applications within Mercedes-Benz manufacturing facilities, particularly in assembly operations where current automation is limited. Mercedes-Benz also potentially views humanoid robotics as a platform for technology development relevant to autonomous vehicles and smart facility operations.
The automotive manufacturer's involvement signals that major industrial corporations are moving beyond skepticism toward humanoid robotics toward active exploration and investment. This shift matters tremendously for market development because it suggests near-term commercial deployment opportunities at substantial scale. Mercedes-Benz facilities globally could represent thousands of robot deployment opportunities as capabilities mature and costs decline.

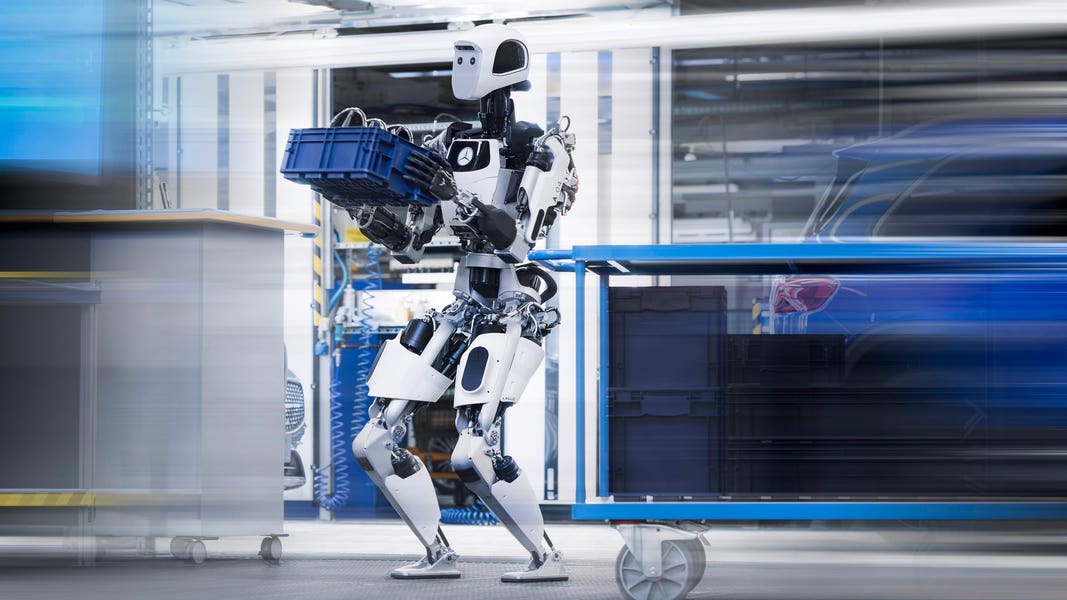
Competitive Landscape: Apptronik in Context
Figure AI: The Closest Competitor
Figure AI represents Apptronik's most significant competitor in the commercial humanoid robotics space. Founded in 2022, Figure AI developed rapidly through exceptional recruitment of robotics talent and aggressive fundraising. The company has raised nearly
Figure AI's funding trajectory differs from Apptronik's in important ways. Rather than extending a Series A round multiple times with progressively higher valuations, Figure AI completed larger, more distinct funding rounds. This approach suggests investors believed the company had reached inflection points warranting new valuation assessments, in contrast to Apptronik's approach of incremental extensions. Both approaches have merit—Figure's approach signals milestone achievement, while Apptronik's signals continued investor enthusiasm without requiring dramatic team expansion or organizational restructuring.
Competitively, Figure AI and Apptronik target similar markets but with potentially different technical approaches. Figure AI has emphasized manipulation capabilities and has pursued partnerships with automotive manufacturers and logistics operators. Apptronik's embodied AI emphasis and Google Deep Mind partnership suggest an approach centered on learning and adaptability rather than pure hardware performance. Both approaches will likely succeed in different segments of the market.
Boston Dynamics: Research to Commercialization
Boston Dynamics, now owned by Hyundai, occupies a unique position in robotics. The company demonstrated remarkable robot capabilities through videos and public demonstrations, building substantial mindshare around humanoid and quadruped robotics. Boston Dynamics' acquisition by Hyundai provided substantial capital resources but also integrated the company into an established manufacturing and logistics conglomerate, fundamentally changing its business model.
Boston Dynamics' recent focus has shifted toward commercial applications in inspection, maintenance, and logistics. The company is developing robot platforms for specific use cases rather than general-purpose humanoids. This focus aligns better with near-term commercial viability than pursuing general-purpose robots, but potentially limits total addressable market and growth potential. Hyundai's ownership provides manufacturing expertise and distribution channels that Boston Dynamics lacked independently.
Emerging Competitors and International Entrants
Beyond Figure AI and Boston Dynamics, numerous other companies pursue humanoid robotics opportunities. Tesla's Optimus program, though not yet commercially available, benefits from Tesla's massive engineering resources and manufacturing expertise. Chinese companies including Unitree and DEEP ROBOTICS are developing humanoid systems with emphasis on cost reduction and rapid iteration. Saudi Arabia's NEOM has funded multiple robotics initiatives. The competitive landscape is crowded and rapidly evolving.
These diverse competitors suggest that the humanoid robotics market will likely support multiple winners, particularly if each company establishes differentiation in specific task domains or market segments. Apptronik's differentiation centers on embodied AI capabilities and partnerships with leading technology and logistics companies. This positioning appears defensible, but success ultimately depends on executing commercialization and achieving positive operational experience with deployed robots.

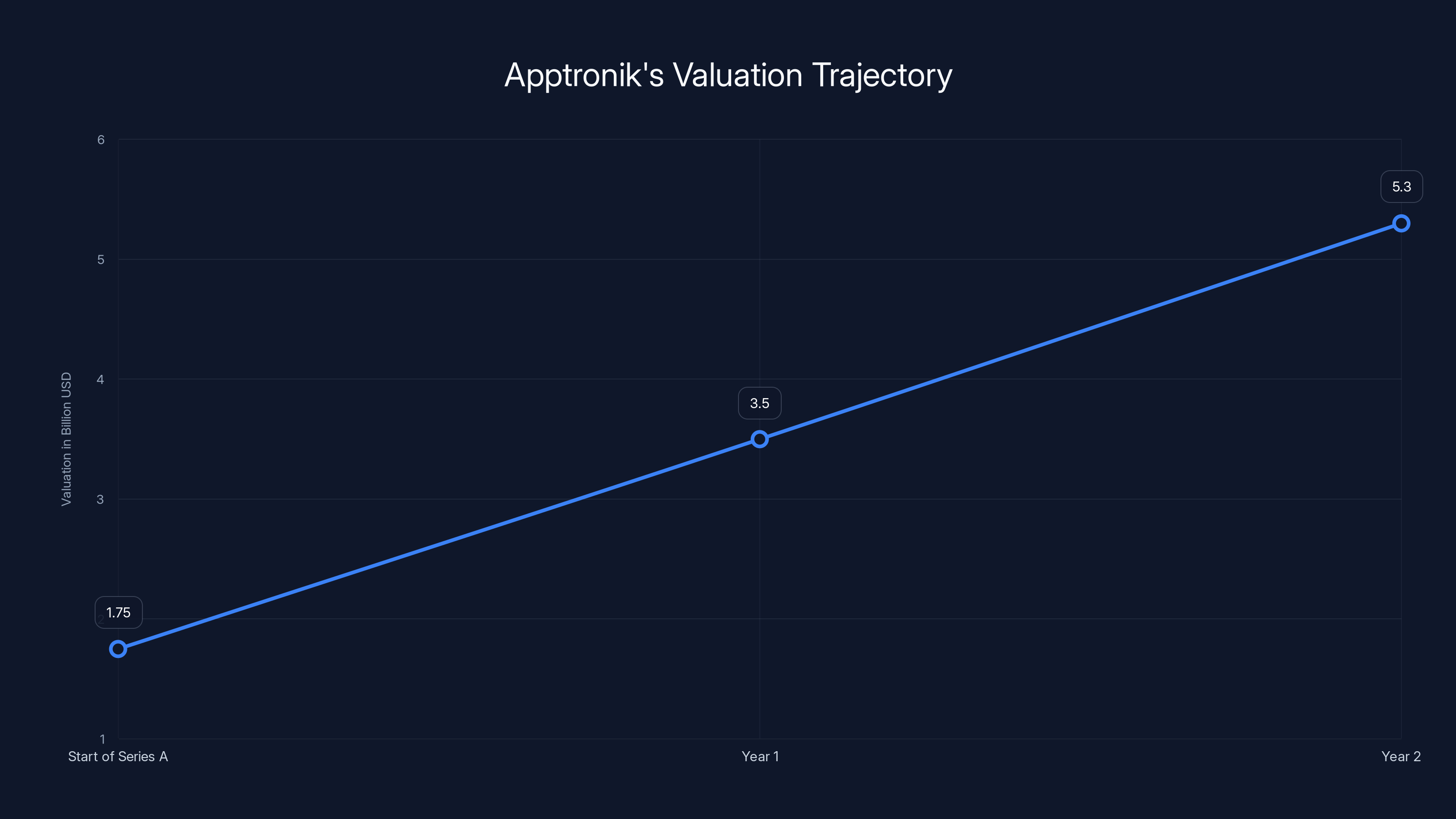
Apptronik's valuation increased from
Funding Strategy and Valuation Dynamics
Why Series A Extensions Over Series B?
Apptronik's decision to extend the Series A rather than complete a traditional Series B round reflects specific strategic considerations. From a corporate governance perspective, extending existing round terms simplifies cap table management and avoids setting new valuation precedents that might constrain future fundraising. From an investor perspective, extending the round allows existing investors to maintain ownership proportions while enabling new investors to participate.
The company's statement that it was "not actively seeking funding" but rather "dealing with inbound interest" suggests investors were pushing for participation rather than the company aggressively pursuing capital. This inbound interest dynamic strengthens Apptronik's negotiating position and implies high investor demand relative to limited allocation capacity. When investment demand exceeds supply, companies can be more selective about investor partners and potentially negotiate better terms.
Maintaining the Series A designation also carries strategic implications. Series B typically implies transition toward revenue generation and commercial traction. By remaining in Series A, Apptronik preserves narrative flexibility around development timelines and early-stage status. This approach reduces pressure for near-term commercialization milestones while accepting higher valuations that imply growth expectations.
Valuation Trajectory and Investor Returns
Apptronik's valuation progression from approximately
For investors in earlier rounds, this valuation trajectory generates substantial paper returns. An investor who participated in the initial Series A at $1.75 billion valuation has seen their investment appreciate to a current value approximately 3x higher. This performance motivates investor enthusiasm for subsequent rounds and creates reputational benefits for investors who backed the company early. However, it also creates challenges—current investors need compelling reasons to accept continued dilution, and exit paths must eventually materialize.
The progressive valuation increases with each extension suggest investors' confidence in Apptronik's execution is growing. If valuation had remained constant across extensions, it would suggest investors viewed earlier rounds as overvalued. Instead, consistent upward valuation movement demonstrates that investor conviction is increasing, likely based on company milestones, partnership announcements, or demonstration of technical progress.
Capital Efficiency and Use of Proceeds
Apptronik has now raised approximately $935 million cumulatively, representing substantial capital for a company still maintaining early-stage status. How effectively the company deploys this capital will significantly influence ultimate investment outcomes. Key allocation priorities likely include manufacturing capacity expansion, talent recruitment, software development, and demonstration of commercial viability through limited production runs and partnerships.
Manufacturing capacity represents a critical bottleneck for humanoid robotics commercialization. Current production is likely measured in dozens or low hundreds of robots annually. Scaling to thousands of annual production requires substantial manufacturing infrastructure investment, supplier development, and quality control systems. Apptronik likely needs to establish or substantially expand manufacturing capability to support near-term growth projections.
Talent acquisition represents another critical capital use. The humanoid robotics field faces intense competition for specialized expertise in control systems, mechanical engineering, perception software, and AI. Apptronik's ability to attract and retain top talent depends partly on compensation and equity packages funded by available capital. Companies that successfully recruit and retain exceptional teams typically outperform competitors with more capital but weaker talent acquisition strategies.
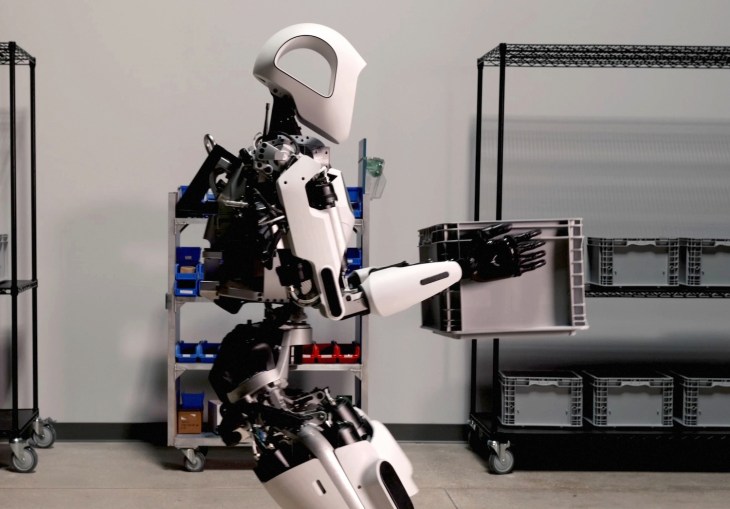

Technical Challenges and Development Roadmap
Bipedal Balance and Locomotion
Legend has it that walking on two legs is so computationally intensive that wheeled or quadruped robots represent better engineering choices. This conventional wisdom overlooks the reality that bipedal systems offer distinct advantages for operations in human-designed environments. However, achieving reliable bipedal locomotion in variable, unstructured environments remains technically challenging.
The core technical challenge involves maintaining balance while moving across uneven surfaces, navigating obstacles, and managing dynamic interactions with environmental elements. Human balance relies on extraordinarily sophisticated proprioceptive feedback, continuous micro-adjustments, and learned internal models of how the body responds to perturbations. Replicating these capabilities in robots requires combining multiple sensing modalities with real-time computational processing and adaptive control algorithms.
Apptronik's approach, informed by decades of research through NASA-DARPA partnerships, likely emphasizes learning-based control methods combined with classical control theory. Rather than designing controller algorithms manually, the team may use reinforcement learning to discover effective balance strategies. These learned controllers can adapt to novel situations and environmental variations that fixed controllers would struggle with.
Manipulation and Gripper Design
Robots require hands capable of manipulating diverse objects with varying sizes, weights, shapes, and fragility levels. Designing grippers that balance dexterity with robustness remains an open research problem. Anthropomorphic hands with multiple fingers offer flexibility but introduce mechanical complexity and control difficulty. Simpler grippers are easier to control and more robust but handle fewer object types.
Apollo likely employs gripper design that represents a compromise between these extremes—more sophisticated than parallel-jaw grippers but simpler than fully anthropomorphic hands. The specific design probably incorporates sensors providing feedback on grip force and contact state, enabling the control system to adjust grip strategies based on object properties. Over time, learning algorithms enable the robot to discover optimal gripper strategies for different object types.
Perception and Scene Understanding
Manipulating objects in real warehouse environments requires accurately perceiving objects, understanding their properties, and predicting how they will respond to applied forces. Current perception systems can identify object categories, estimate positions, and measure basic properties, but struggle with complex scenes involving occlusions, lighting variations, and object categories not represented in training data.
Apptronik's embodied AI approach addresses perception challenges through learning. Rather than requiring perfect initial perception, the robot can interact with objects, observe results, and update its understanding. If initial perception was inaccurate, feedback from manipulation attempts reveals the error and enables correction. This iterative learning approach is more robust than systems requiring perfect perception to function effectively.
Energy Management and Battery Technology
Humanoid robots moving dynamically through warehouses require substantial electrical power. Battery technology represents a practical constraint on operating duration and work intensity. Current lithium-ion battery technology limits operation duration to 8-12 hours per charge, requiring regular recharging that interrupts work schedules. Improved battery technology, either through advances in lithium-ion chemistry or adoption of next-generation battery types, could dramatically improve practical utility.
Apptronik's development roadmap likely includes exploring optimizations in motor efficiency, mechanical design to reduce energy waste, and battery integration. However, fundamental improvements probably require battery technology advances beyond what any individual company can achieve. The company likely bets on battery technology improvements continuing on historical trajectories while optimizing robot efficiency to work within current battery constraints.
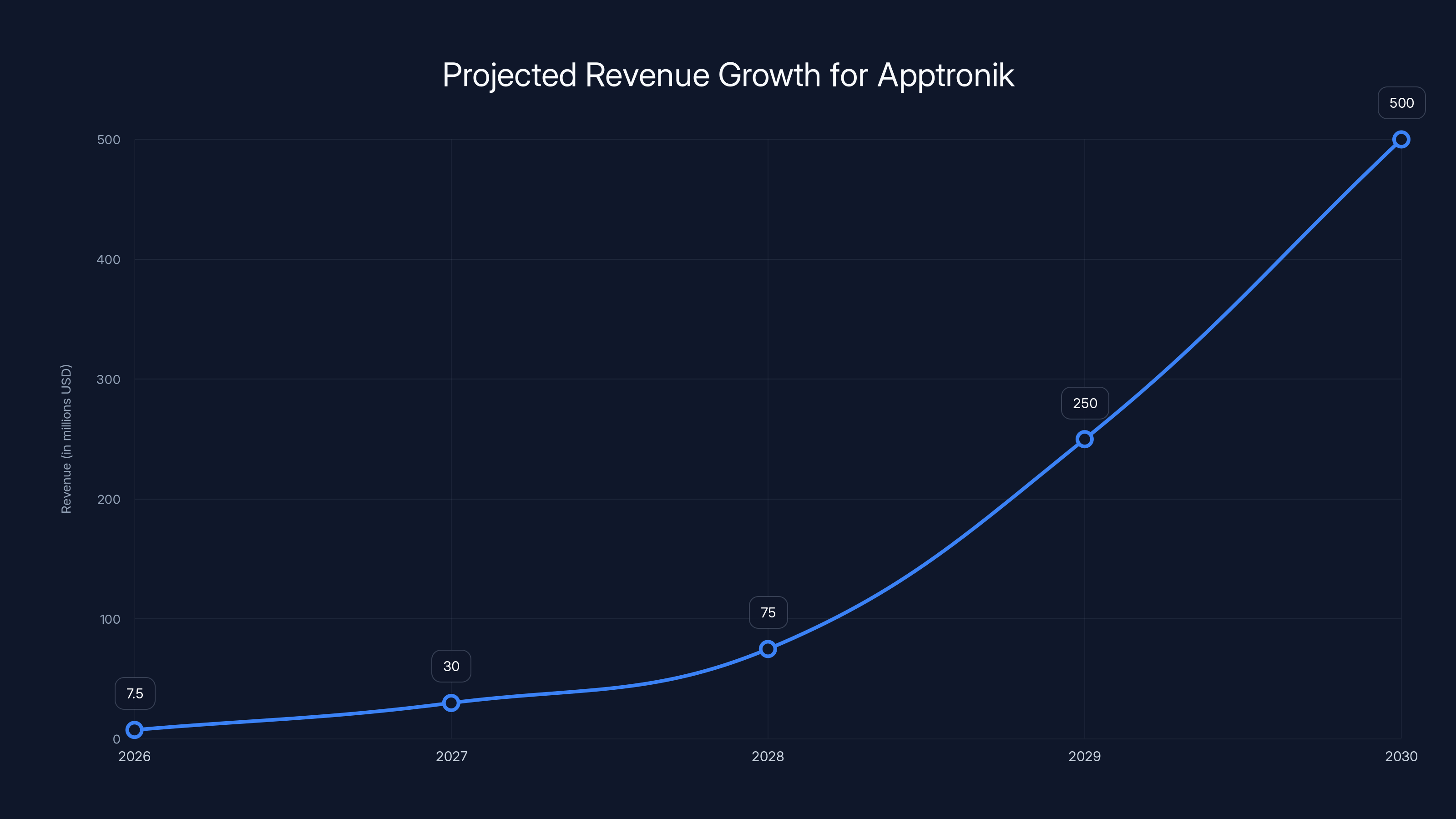
Estimated data shows Apptronik's revenue could grow from
Market Adoption and Deployment Challenges
Manufacturing Scale and Cost Reduction
Current humanoid robots represent low-volume manufacturing, with unit costs estimated in the
Apptronik's manufacturing roadmap likely involves establishing assembly operations, developing supply chain relationships for key components, and implementing manufacturing process improvements. Early production probably involves small batches assembled carefully with significant manual work. Subsequent generations aim for increasing automation of assembly, reducing direct labor and improving consistency. By fifth or sixth production generation, manufacturing costs typically decline by 40-50% from initial levels.
Partnerships with established manufacturers could accelerate cost reduction. Mercedes-Benz's involvement potentially includes discussions around manufacturing humanoid robots leveraging Mercedes's existing production capabilities, supplier relationships, and manufacturing expertise. Such partnerships could compress cost-reduction timelines significantly, improving commercialization prospects.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Deploying autonomous robots in human-occupied workspaces raises legitimate safety concerns. How should robots interact with humans who enter robot work areas? What safety standards apply to human-robot collaboration? How are injury liabilities assigned when robot actions cause human injuries? These questions require regulatory frameworks that provide clear guidance while enabling productive innovation.
Apptronik's partnerships with major corporations provide some regulatory cover. Large companies like GXO and Mercedes-Benz have legal teams experienced in managing robotics deployment risks and likely already comply with applicable safety standards. This institutional knowledge and infrastructure smooths path to deployment compared to startup companies attempting initial robotics deployments independently.
Likely regulatory developments will establish safety standards around robot speed, force limitations, collision detection, and human-robot interaction protocols. These standards will probably evolve iteratively based on deployment experience and incident data, similar to how aviation safety regulations developed incrementally. Early deployment in partnership with major corporations provides data and experience that informs sensible regulatory development.
Workforce Transition and Labor Market Dynamics
Widespread humanoid robot deployment will substantially impact warehouse and logistics labor markets. While the industry faces current labor shortages, introducing robots creates long-term workforce displacement risks for workers in entry-level logistics roles. This societal impact matters for deployment acceptability and policy environment evolution.
Apptronik and other robotics companies would benefit from proactive engagement with labor unions, workforce development programs, and policy makers around transition planning. Rather than viewing robots as pure labor replacement, framing deployment as augmentation—robots handling the most dangerous, repetitive, or physically demanding tasks while humans focus on higher-value activities—provides more sustainable long-term positioning. In practice, robots likely enable warehouse workers to transition to supervisory, planning, and optimization roles requiring higher skills and commanding higher wages.
Government policy around robotics taxation, workforce transition support, and labor market management remains uncertain. Some jurisdictions have proposed taxes on automation or restrictions on robot deployment in certain sectors. Apptronik's success may ultimately depend on policy environment stability and societal acceptance of automation.
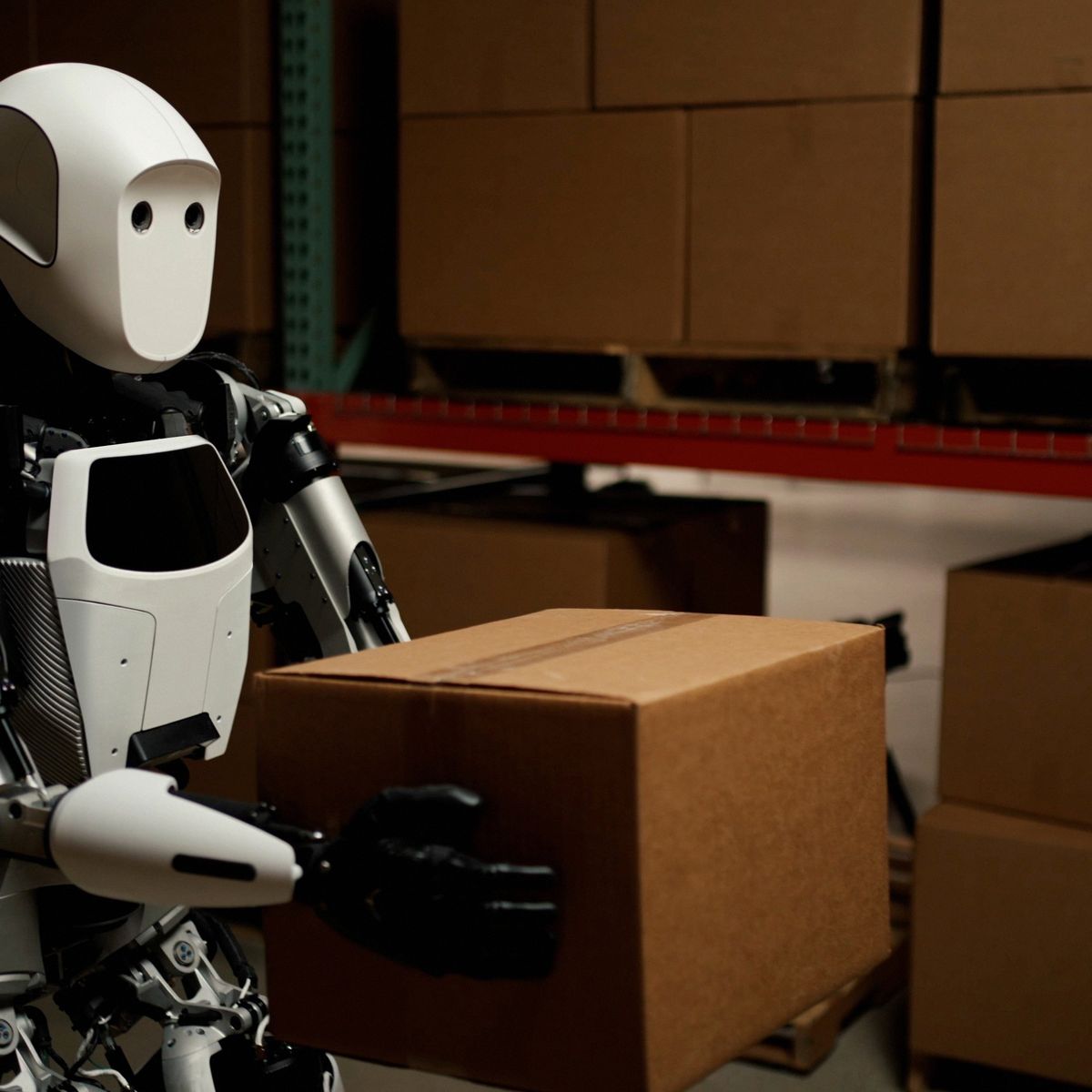

Financial Projections and Path to Profitability
Revenue Generation Timeline
Apptronik's path to profitability depends on several factors: manufacturing ramp, adoption acceleration, and per-unit economics. The company has likely outlined internal projections showing initial revenue generation from limited deployments with GXO and other partners, followed by accelerating adoption as manufacturing capacity increases and operational experience demonstrates value.
Typical projections might show minimal revenue in 2026 (
Unit Economics and Gross Margins
At current estimated robot costs of
To justify a

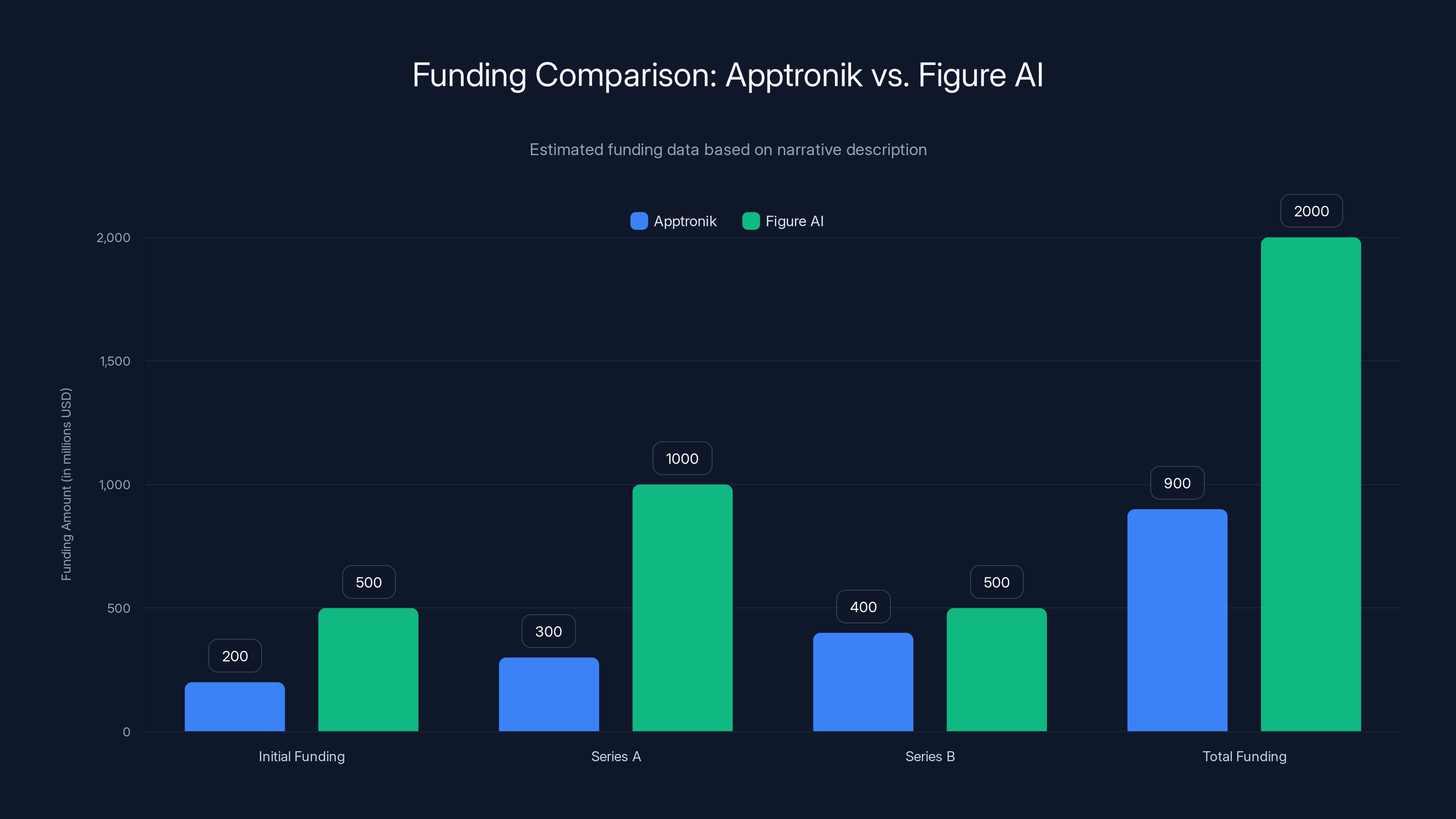
Figure AI has raised significantly more capital than Apptronik, with a total of
Lessons for Investors and Entrepreneurs
The Power of Persistent Innovation
Apptronik's success reflects over a decade of persistent technical innovation, starting from university research through formal company establishment and ongoing commercial development. The company didn't attempt to commercialize humanoid robots immediately upon founding, but rather spent years developing core technology through research partnerships and application experiences. This patient approach to building technical depth likely contributed to recent commercialization success.
For entrepreneurs pursuing ambitious technical goals, Apptronik's trajectory offers valuable lessons. Deep technical expertise and institutional knowledge matter tremendously in capital-intensive industries. Short-term capital raises matter less than building genuine technical capability that justifies investor confidence. Partnerships with research institutions and large enterprises provide resources and credibility that bootstrap smaller efforts.
Corporate Partnership Value in Deep Tech
Apptronik's success partnering with Google Deep Mind, GXO, and Mercedes-Benz demonstrates the value that strategic partnerships bring to deep technology companies. Rather than viewing these partnerships as losses of control or compromises on autonomy, treating them as opportunities for acceleration and shared learning creates tremendous value. Partners bring resources, expertise, market access, and credibility that early-stage teams cannot develop independently.
For entrepreneurs building deep technology companies, seeking partnership opportunities with established corporations or research institutions should be core strategy rather than afterthought. These partnerships provide validation that technology has genuine value, resources that accelerate development, and pathways to customers and commercialization that might take years to develop independently.
Investor Appetite for Moonshot Technologies
Apptronik's $935 million Series A demonstrates substantial investor appetite for technologies addressing massive markets with potential for transformative impact. While not all deep technology investments succeed, the sheer capital available for genuinely innovative approaches suggests that execution and timing matter more than capital availability for exceptional teams pursuing important problems.
For investors, Apptronik's trajectory illustrates the value of backing teams with deep technical expertise, demonstrated execution capability, and clear market validation. The company's funding success didn't depend on being first to market or having most capital, but rather on demonstrating real progress toward genuine commercialization of transformative technology.

Future Outlook: What Comes Next
2026-2027: Limited Deployment and Learning
The near term will likely see Apptronik focused on limited commercial deployments with GXO and potentially other early-adopter customers. These deployments serve as learning opportunities to refine hardware, improve software, and understand real-world operational challenges that laboratory testing doesn't reveal. The company will likely produce hundreds of robots rather than thousands during this period.
During this phase, Apptronik will continue advancing technical capabilities while building manufacturing infrastructure for scale. The team will recruit additional talent, establish supply chain relationships, and begin tooling for higher-volume production. Customer feedback from real deployments will inform product roadmap priorities and drive engineering focus.
2027-2029: Manufacturing Scale and Market Expansion
If early deployments prove successful and technical challenges are overcome, Apptronik will likely transition to manufacturing scale. Production volumes could grow from hundreds to thousands annually. The company might establish manufacturing partnerships or facilities in multiple geographies to serve different markets and overcome tariff and transportation constraints.
Market expansion during this period would likely broaden beyond logistics into other warehouse and manufacturing applications. Sorting facilities, manufacturing assembly, and packaging operations all represent potential application areas. The company might develop specialized variants optimized for specific task domains while maintaining a common technical foundation.
2030+: Market Leadership or Consolidation
By 2030, Apptronik will either establish itself as a market leader in humanoid robotics or face acquisition by larger corporations seeking to add robotics capabilities. The company's $5.3 billion valuation implies expectations of enormous future value creation, but achieving that requires sustained technical progress, successful commercialization, and market adoption. Companies that stumble in any of these dimensions might attract acquisition interest at valuations below current expectations.
Successful outcomes likely involve Apptronik becoming a multi-billion-dollar revenue company within 5-7 years, either as an independent enterprise or as part of a larger conglomerate. Less successful outcomes might involve the company being acquired at lower valuations or struggling to achieve positive unit economics and sustainable profitability.

Conclusion: Humanoid Robotics Reaches Inflection Point
Apptronik's
The company's funding success reflects multiple aligned factors. Technical progress on embodied AI, driven in part by partnerships with Google Deep Mind, has reached levels where commercial application seems plausible. Partnership structures with logistics operators like GXO and manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz provide real-world deployment opportunities and customer validation. Corporate investor participation demonstrates that major technology and manufacturing companies view humanoid robotics as strategically important beyond venture capital appetite.
Apptronik's trajectory also reflects broader trends in deep technology investment. Teams pursuing genuinely transformative technologies addressing massive markets continue attracting substantial capital, even when near-term profitability seems distant. The venture capital market's willingness to fund patient technical development, combined with corporate strategic investment, creates resources that enable ambitious technical visions. Apptronik has demonstrated both the technical capability and business strategy to capitalize on this capital availability.
For developers and teams exploring automation opportunities, Apptronik's funding and partnerships provide relevant strategic lessons. Deep partnerships with established technology companies and potential customers can provide resources and validation that accelerate commercialization. Focusing on solving genuine market problems—labor shortages in logistics—creates stronger investment rationale than pursuing technology for its own sake. And persistent focus on technical excellence, developed through research partnerships and iterative improvement, builds credibility that justifies investor confidence and customer adoption.
The humanoid robotics market remains nascent, with absolute certainty about ultimate deployment scale and commercial success still lacking. However, Apptronik's funding trajectory and partnerships suggest the market has progressed from speculative research domain to genuine commercial frontier. Investors, customers, and technology teams are now positioning themselves for what could be a transformative shift in how physical labor is performed globally. The outcomes of Apptronik's continued development will provide crucial data points for understanding how quickly this transformation might unfold.

FAQ
What is Apptronik and what do they do?
Apptronik is a University of Texas spinout specializing in developing humanoid robots for commercial applications, particularly in warehouse and logistics automation. The company builds Apollo, a bipedal robot designed to perform repetitive warehouse tasks like unloading trailers, picking inventory, and tending machinery. Apptronik's technology emphasizes embodied AI—enabling robots to perceive their environment and make adaptive decisions rather than simply following predetermined instructions.
How much funding has Apptronik raised and what is its valuation?
Apptronik has raised
What is embodied AI and why does it matter for humanoid robots?
Embodied AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that combine perception, reasoning, and physical action in real-world environments. Rather than following rigid programming, embodied AI enables robots to perceive their surroundings, make real-time decisions about actions, and adapt based on feedback from physical interactions. This capability is essential for humanoid robots to operate flexibly in variable warehouse environments where item types, configurations, and conditions constantly change.
Who are Apptronik's major partners and what do these partnerships provide?
Apptronik's major partners include Google Deep Mind, GXO Logistics, and Mercedes-Benz. Google Deep Mind contributes research capabilities and expertise in AI, perception, and robot learning. GXO, one of the world's largest logistics operators, provides real-world warehouse deployment opportunities and customer feedback for product refinement. Mercedes-Benz brings manufacturing expertise, supply chain resources, and potential applications in automotive assembly and logistics operations.
How does Apptronik's approach compare to other humanoid robot companies?
Apptronik differentiates itself through embodied AI capabilities developed with Google Deep Mind and partnerships with major commercial operators. Competitors like Figure AI have raised comparable funding but emphasize different technical approaches. Boston Dynamics, owned by Hyundai, focuses on specific use cases rather than general-purpose humanoids. Apptronik's strategy centers on learning and adaptability rather than pure hardware performance, positioning it for flexibility across diverse warehouse tasks.
What is the market opportunity for humanoid robots in logistics?
The logistics and warehousing market exceeds
When will Apptronik robots be available for widespread commercial deployment?
Apptronik is currently in limited deployment phase with partners like GXO, likely producing hundreds of robots annually. Widespread commercial availability probably extends 2-3 years into the future as manufacturing scales and operational experience validates product reliability. The company will likely announce growing deployment numbers and expanding customer partnerships over the next 12-24 months, providing signals about commercialization progress.
What technical challenges does Apptronik need to overcome for successful commercialization?
Key technical challenges include achieving reliable bipedal balance in variable environments, developing manipulation capabilities for diverse object types, improving perception in complex scenes with occlusions and lighting variations, and managing battery technology limitations affecting operating duration. Apptronik's embodied AI approach addresses several of these challenges through learning and adaptation rather than perfect initial capability, but execution across all these domains remains critical for commercial success.
How does Apptronik's funding progression compare to typical venture capital trajectories?
Apptronik's $5.3 billion valuation after approximately two years represents accelerated valuation growth compared to typical venture progression, but reflects genuine investor conviction driven by technical progress and partnership announcements. The company's decision to extend the Series A rather than complete a Series B round demonstrates investor demand exceeded capital requirements and allowed the company to maintain control of fundraising narrative while accepting higher valuations.
What could derail Apptronik's commercialization efforts?
Potential challenges include manufacturing scale-up difficulties, failure to achieve cost reduction targets, inability to generalize robot capabilities to diverse warehouse tasks, safety concerns limiting human-robot collaboration, regulatory barriers to deployment, and competitive developments from well-funded competitors. Even with substantial funding, deep tech companies pursuing transformative innovations face inherent execution risk that could significantly impact ultimate outcomes.

Key Takeaways
- Apptronik raised 5.3B valuation, demonstrating massive investor appetite for humanoid robotics commercialization
- Embodied AI enables robots to perceive environments and make adaptive decisions rather than following rigid instructions, differentiating Apptronik's approach
- Strategic partnerships with Google DeepMind, GXO Logistics, and Mercedes-Benz accelerate development and provide real-world deployment opportunities
- Warehouse labor shortages and economics (10.87/hour robot cost) create compelling market opportunity for automation
- Company faces technical execution risks around bipedal balance, manipulation, perception, and manufacturing scale that will determine ultimate commercial success
- Humanoid robotics market could grow from 200 billion by 2035, supporting multiple competitors alongside Apptronik
- Funding progression shows 3x valuation growth in two years, reflecting increasing investor conviction based on technical progress and partnership validation
Related Articles
- Robert Playter Steps Down as Boston Dynamics CEO [2026]
- AI Rivals Unite: How F/ai Is Reshaping European Startups [2025]
- Itch.io's Minnesota Bundle: 1,200+ Games for $10 [2025]
- Thomas Dohmke's $60M Seed Round: The Future of AI Code Management [2025]
- Humanoid Robots & Privacy: Redefining Trust in 2025
- Venture Capital Split Into Two Industries: SVB 2025 Report Analysis [2025]