Open AI's Enterprise Push 2026: Complete Strategic Analysis & Alternative Solutions
Introduction: The Enterprise AI Battle Heats Up in 2026
The artificial intelligence landscape is experiencing a dramatic shift as organizations worldwide grapple with how to integrate cutting-edge AI capabilities into their business operations. At the center of this transformation is Open AI, a company that once dominated the enterprise AI conversation but now finds itself in an increasingly competitive environment. In January 2026, Open AI announced a significant organizational restructuring, appointing Barret Zoph, a seasoned AI researcher and product leader, to spearhead its enterprise business division. This strategic move signals the company's recognition that it must intensify its efforts to capture and retain enterprise customers—a market segment that represents billions in annual revenue potential.
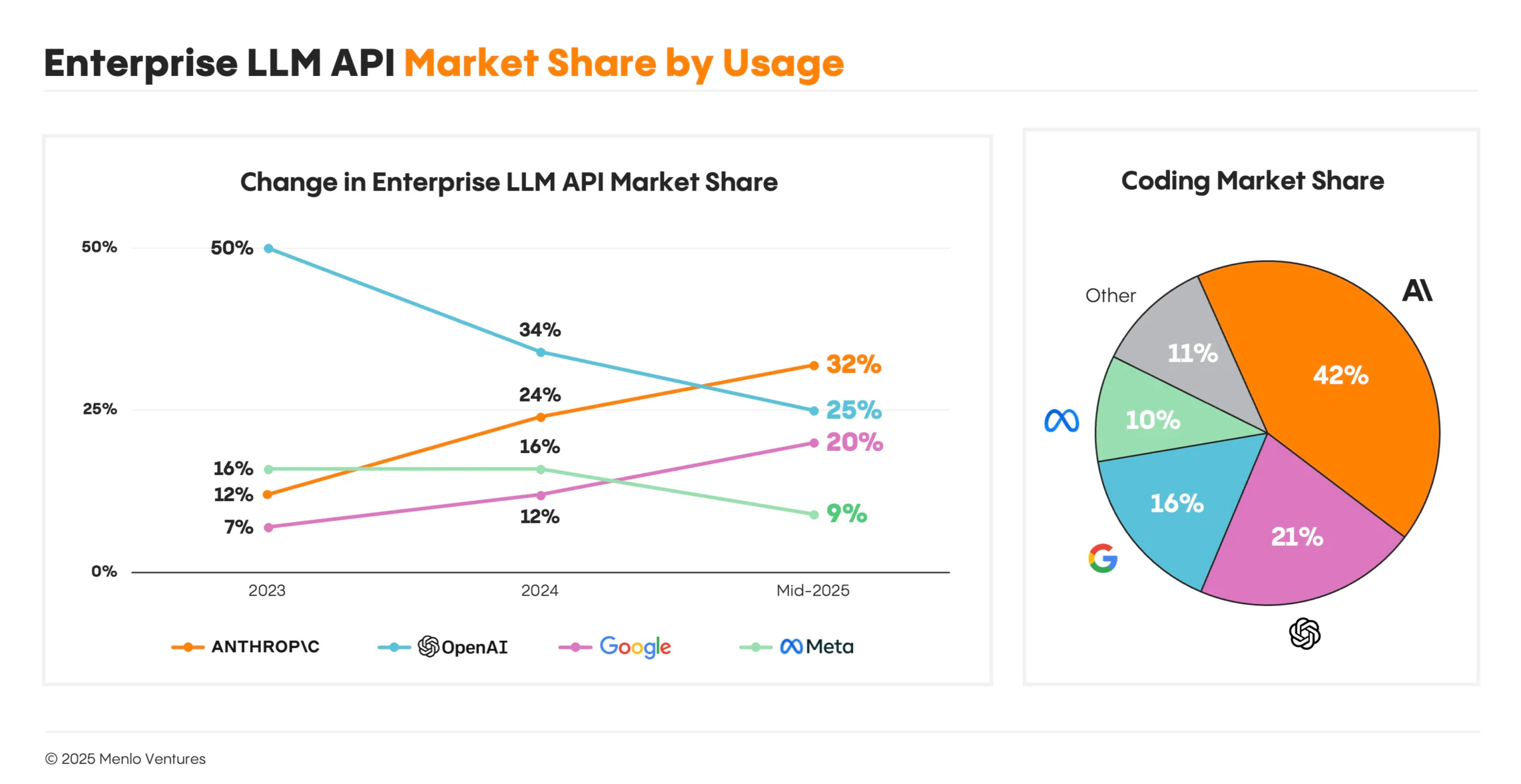
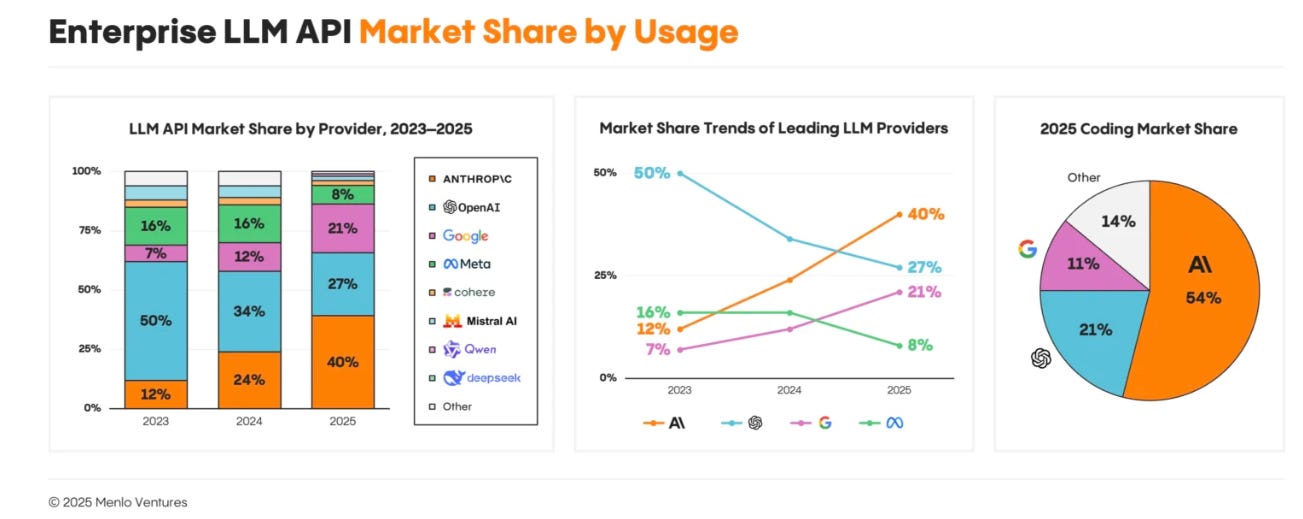
The decision to elevate enterprise sales reflects deeper market realities that have been developing over the past 18 months. Open AI launched its Chat GPT Enterprise product in September 2023, beating competitors like Anthropic by over a year and establishing itself as a first-mover in the enterprise AI space. The company boasted impressive early adoption metrics, claiming over 5 million business users and partnerships with major corporations including Soft Bank, Target, and Lowe's. However, impressive adoption numbers masked a troubling underlying trend: market share erosion. According to market research from venture capital firm Menlo Ventures, Open AI's enterprise AI market share collapsed from 50% in 2023 to just 27% by the end of 2025—a devastating 46% decline in relative market position over just two years.
This marketplace transformation occurred while competitors methodically built their enterprise capabilities and distribution networks. Anthropic, the company founded by former Open AI researchers, captured the dominant enterprise position with 40% market share by December 2025, up from 32% just five months earlier. Google, with its vast enterprise sales infrastructure and cloud platform integration, has maintained a steady and growing presence with 21% market share. The mathematical reality is striking: Open AI has lost nearly 23 percentage points of market share while its two primary competitors have captured that share and more. For a company that achieved its valuation partly on the strength of its enterprise momentum, this reversal represents an existential business challenge that demands immediate and comprehensive strategic response.
The appointment of Zoph as enterprise leadership carries particular significance because it demonstrates Open AI's commitment to treating enterprise as a core strategic priority rather than a secondary business line. Zoph's previous role as vice president of post-training inference at Open AI equipped him with deep technical knowledge about the company's AI model capabilities and limitations. His recent experience co-founding Thinking Machine Labs with Mira Murati exposed him to the challenges of building and scaling new AI products. The combination of technical credibility, product experience, and understanding of Open AI's capabilities positions him to drive meaningful enterprise initiatives.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of Open AI's enterprise strategy, the market dynamics driving the company's repositioning, competitive threats from Anthropic and Google, and practical alternatives that organizations should consider when evaluating enterprise AI solutions. For enterprises evaluating multiple options, understanding the strategic landscape helps inform better decision-making about which platforms and solutions best serve specific business needs.
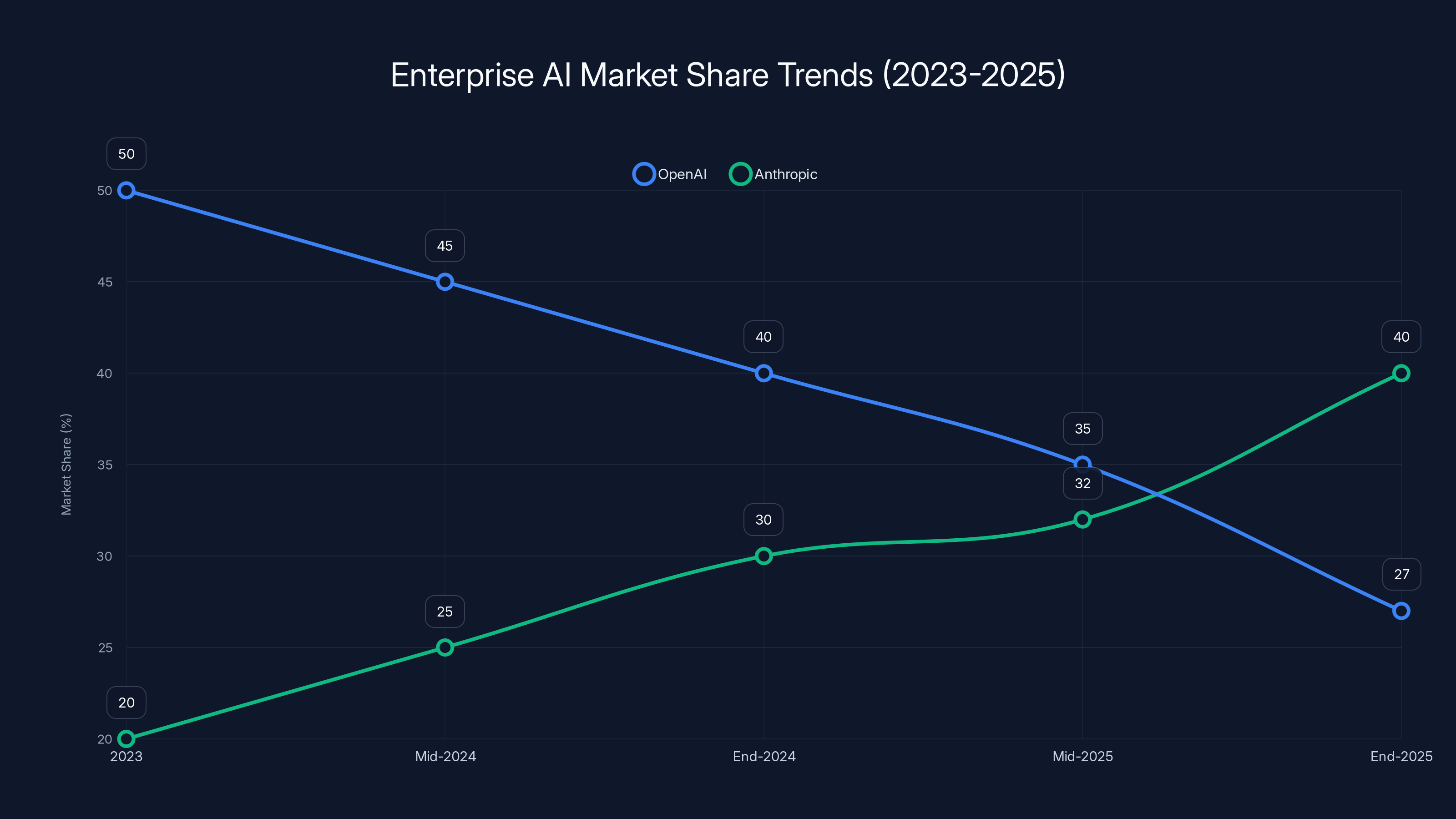
OpenAI's market share declined from 50% to 27% between 2023 and 2025, while Anthropic's share increased from 20% to 40%. Estimated data.
The Evolution of Enterprise AI Adoption: From Hype to Reality
Understanding the Enterprise AI Market Opportunity
Enterprise customers represent a fundamentally different segment than consumer AI users. While consumer adoption focuses on individual productivity and entertainment value, enterprise AI procurement involves complex buying processes, security requirements, compliance mandates, and integration with existing technology infrastructure. Enterprise deals typically range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars annually, with longer sales cycles averaging 6-12 months and rigorous vendor evaluation processes.
The enterprise AI market encompasses several distinct segments with different requirements and purchasing patterns. Infrastructure and platform services generate the largest revenue volumes, with enterprise customers paying for access to frontier AI models through APIs or cloud platforms. Vertical-specific solutions address particular industries like healthcare, financial services, and legal, where AI applications deliver measurable business value. Integration services and consulting help enterprises adapt their existing workflows to incorporate AI capabilities. Fine-tuning and customization services allow organizations to optimize generic AI models for their specific use cases.
Market research indicates that enterprise AI spending reached approximately $15-20 billion globally in 2025 and is projected to grow 25-35% annually through 2028. However, this growth masks significant distribution changes within the market. Organizations are increasingly consolidating their AI vendor relationships, preferring to work with 2-3 trusted providers rather than maintaining relationships with 5-10 vendors. This consolidation dynamic favors incumbents with strong existing enterprise relationships (like Google and Microsoft) and well-capitalized challengers with differentiated products (like Anthropic).
Why Open AI Lost Ground So Rapidly
Open AI's market share decline from 50% to 27% in two years didn't occur because of product inferiority. GPT-4 and its successors remain technically capable models that power sophisticated AI applications. The decline resulted from a complex interplay of strategic, organizational, and competitive factors that merit detailed examination.
First, Anthropic executed superior enterprise sales strategy. While Open AI maintained its focus on product excellence and platform reliability, Anthropic invested heavily in enterprise-focused business development. The company built dedicated enterprise sales teams, hired executives with deep enterprise Saa S experience, and invested in customer success functions that provided ongoing support and optimization for enterprise accounts. Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei made enterprise customers a personal priority, with quarterly business reviews and direct engagement with chief technology officers and chief information officers at major accounts.
Second, Google leveraged existing enterprise relationships. When Google launched Gemini Enterprise in late 2024, the company could immediately reach hundreds of thousands of enterprise customers through existing Google Cloud relationships. Enterprises already using Google Cloud for infrastructure could adopt Gemini through their existing vendor relationship with integrated billing, unified support, and native integration with Google Workspace and other Google services. This existing relationship advantage proved more valuable than Open AI's product leadership.
Third, Anthropic's product characteristics resonated with enterprise concerns. Enterprise customers expressed significant concerns about AI safety, alignment, and transparency. Anthropic's founding narrative—built on rigorous AI safety research and constitutional AI principles—addressed these concerns directly. The company's marketing emphasized responsible AI practices and built trust with enterprise customers who viewed AI governance as a strategic priority. Open AI, by contrast, faced perception challenges from its corporate reorganization and leadership transitions that created uncertainty about the company's direction.
Fourth, Open AI's enterprise offering lacked differentiation. Chat GPT Enterprise, while functional, represented a relatively thin wrapper around the consumer Chat GPT product with added admin controls and higher rate limits. Anthropic and Google offered more comprehensive enterprise platforms with deeper analytics, audit trails, API management, and integration capabilities that enterprise customers demanded. Open AI was selling a consumer product to enterprises rather than designing products specifically for enterprise requirements.
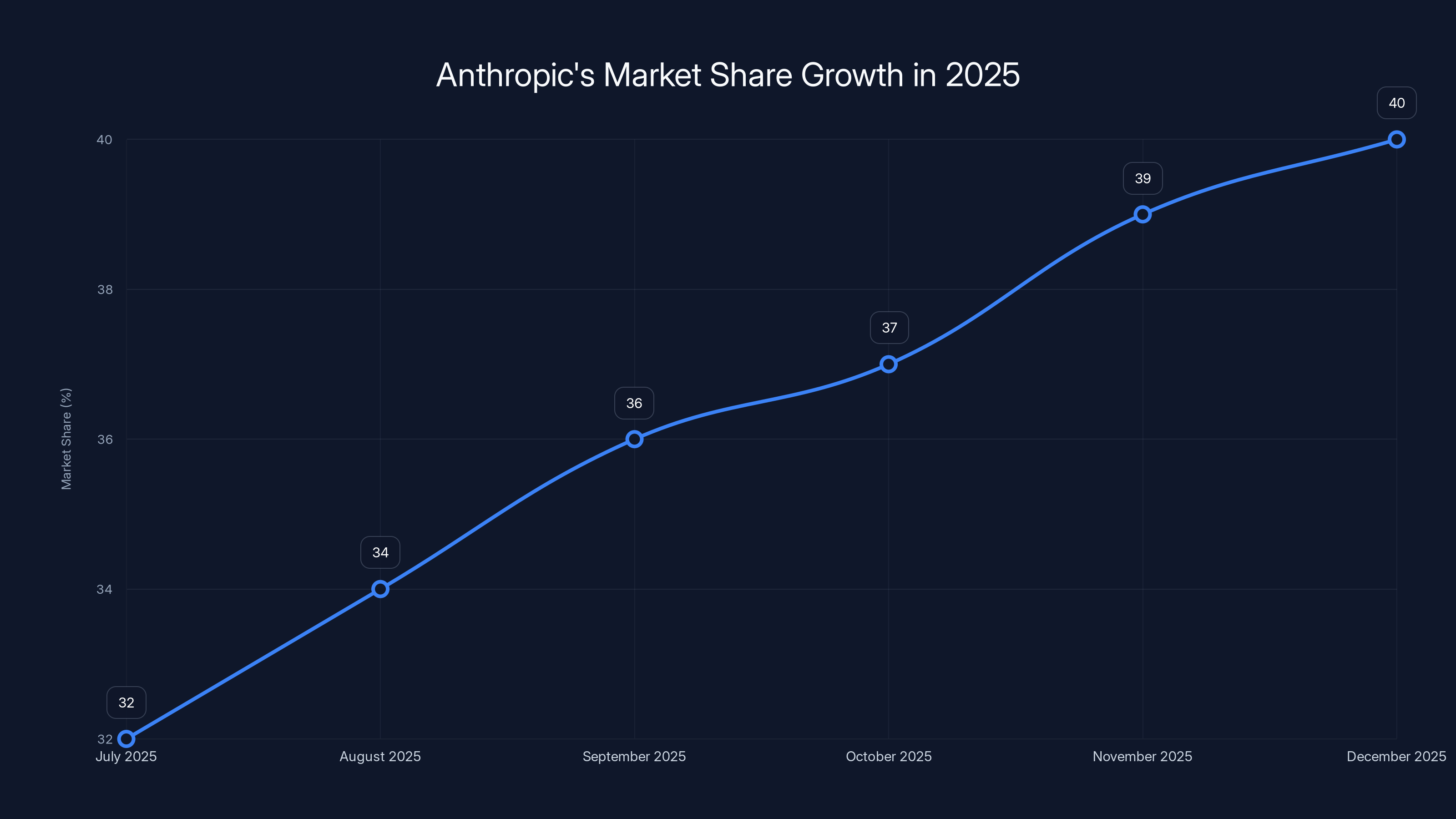
Anthropic's market share grew from 32% to 40% between July and December 2025, highlighting strategic execution and product capability alignment with enterprise needs.
Barret Zoph's Appointment: Strategic Implications and What It Signals
Who Is Barret Zoph and Why Does His Role Matter?
Barret Zoph represents a particular profile of AI leader—technically credible, product-focused, and experienced in shipping enterprise-scale systems. Throughout his career at Open AI, Zoph contributed to core capabilities in the company's most sophisticated models. His work on post-training and inference optimization directly impacts model quality and deployment efficiency, the two factors that matter most to enterprise customers evaluating AI platforms.
Zoph's brief tenure at Thinking Machine Labs, the AI startup founded by Mira Murati following her departure from Open AI, provided him with valuable perspective on building AI companies outside of Open AI's ecosystem. He witnessed first-hand how startups approach product development, go-to-market strategy, and customer acquisition—insights that could prove valuable in transforming Open AI's enterprise organization. His decision to return to Open AI after just three months signals his belief that the opportunity at Open AI justifies leaving a position he helped create.
Expected Strategic Priorities Under Zoph's Leadership
Zoph's appointment likely signals Open AI's intention to pursue several strategic initiatives simultaneously:
Restructuring the Enterprise Sales Organization. Open AI historically maintained a relatively small enterprise sales team relative to competitors. This under-resourcing reflected the company's product-first philosophy—the theory that superior products sell themselves. Market share loss has clearly demonstrated this philosophy's limitations in competitive markets. Expect Zoph to build out dedicated enterprise sales teams, hire experienced Saa S sales leaders from competitors like Salesforce and Hub Spot, and establish regional sales organizations in key markets like Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Developing Enterprise-Specific Product Features. Chat GPT Enterprise needs substantial enhancement to compete with dedicated enterprise platforms. Priority enhancements should include advanced audit logging and compliance reporting for regulated industries, native integration with enterprise data sources and business applications, fine-tuning capabilities that allow enterprises to customize models for domain-specific use cases, and comprehensive API management and monetization tools.
Establishing Enterprise Customer Success Functions. Competitive analysis shows that Anthropic and Google both invest heavily in customer success operations that help enterprises derive maximum value from AI investments. Open AI likely needs to build similar capabilities, including dedicated customer success managers for enterprise accounts, regular optimization reviews, technical consulting services, and industry-specific best practice guidance.
Expanding Strategic Partnerships. Open AI's partnership with Service Now announced in early 2026 represents exactly the type of strategic distribution partnership that should accelerate enterprise adoption. Expect Zoph to pursue similar partnerships with other enterprise software companies—integration with Salesforce CRM for enterprise sales organizations, partnership with Workday for HR transformation, collaboration with SAP for enterprise resource planning customers, and integration with industry-specific platforms in healthcare, financial services, and legal technology.
Market Share Analysis: How Did Anthropic Capture Enterprise Dominance?
The Data Behind Anthropic's 40% Market Share Achievement
According to Menlo Ventures' market research tracking enterprise large language model usage, Anthropic grew from 32% market share in July 2025 to 40% by December 2025—an 8 percentage point gain in just five months. This rapid growth didn't occur randomly or accidentally but resulted from deliberate strategic execution across multiple dimensions simultaneously.
Anthropically's Claude models, particularly Claude 3 and subsequent iterations, established themselves as particularly capable for enterprise use cases. The models demonstrated superior performance on complex reasoning tasks, document analysis, and nuanced language understanding—precisely the capabilities that enterprise applications require. Enterprise customers conducting side-by-side model evaluations found Claude to be competitive with or superior to GPT-4 on their specific tasks. Subjective feedback highlighted Claude's superior ability to follow detailed instructions, resist prompt injections, and maintain consistency across long documents—all crucial for enterprise applications.
Beyond product capabilities, Anthropic invested in enterprise-focused go-to-market execution. The company hired Daniela Amodei, one of the company's co-founders, to lead business operations and enterprise strategy. This executive-level focus ensured that enterprise considerations shaped every strategic decision. The company established an enterprise board that included executives from major enterprise customers who provided feedback on product roadmap priorities, helping Anthropic align product development with actual enterprise needs rather than assumptions about those needs.
Google's Steady Enterprise Positioning
Google's enterprise strategy followed a different playbook that emphasizes integration and ecosystem lock-in rather than disruptive innovation. The company maintained relatively consistent market share around 20-21% by integrating Gemini deep into Google Cloud services. Enterprises using Google Cloud for computing infrastructure could access Gemini for AI workloads through their existing relationship with unified pricing and support.
Google's advantage stems from its installed base of enterprise customers and the breadth of its enterprise product portfolio. An enterprise already paying Google for cloud computing, workspace productivity tools, and analytics could layer Gemini AI capabilities into existing workflows. This integration advantage proves particularly powerful in large enterprises that already have significant Google relationships and don't want to manage additional vendors.
Open AI's Competitive Position in the Narrowing Market
Open AI's erosion from 50% to 27% market share in two years represents a loss of dominance but doesn't indicate irrelevance. With 27% market share, Open AI remains a significant player in enterprise AI. The company maintains relationships with thousands of enterprise customers and generates substantial revenue from enterprise API usage and Chat GPT Enterprise subscriptions.
However, the trend direction matters as much as the absolute position. Open AI is losing share while competitors gain it. Enterprise customers are increasingly adopting multiple models, a trend that dilutes Open AI's captive market position. Early Open AI dominance gave the company advantages in customer education, integration depth, and ecosystem development that competitors are now systematically capturing.
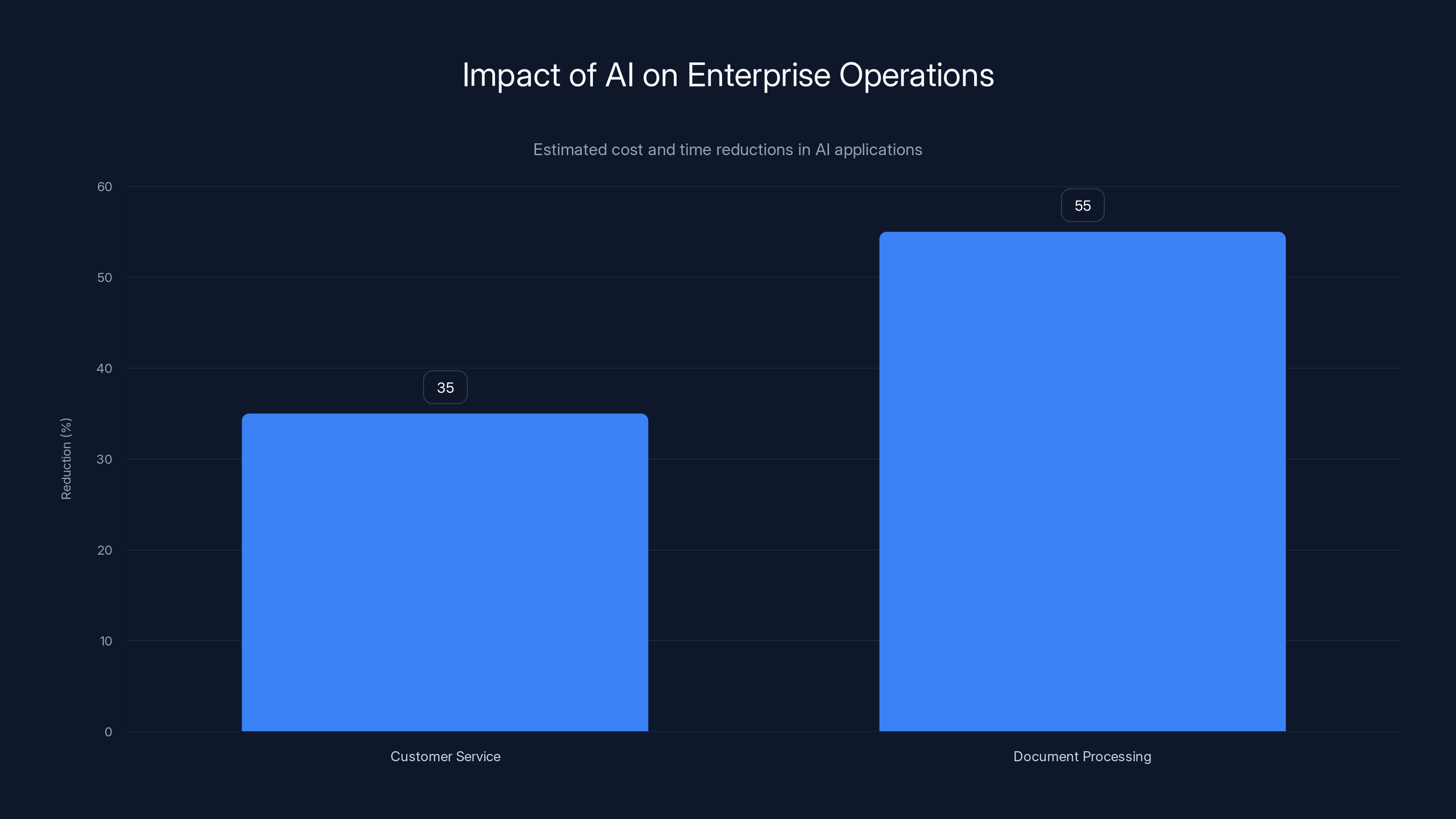
AI applications in customer service and document processing lead to significant reductions in costs and processing times, with estimates showing 35% and 55% improvements respectively.
The Enterprise Market Dynamics: Forces Reshaping Vendor Competition
Security, Compliance, and Governance Priorities
Enterprise customers evaluate AI platforms on dimensions that don't appear in consumer comparisons. Security and data governance rank among the highest priorities. Enterprise customers need assurance that proprietary business data won't leak to competitors or appear in training data for models. They demand detailed information about data retention policies, encryption approaches, and audit trail capabilities.
Anthropically's messaging aligned strongly with these concerns. The company emphasized constitutional AI principles and built its brand around responsible AI development. This positioning resonated with enterprise risk and compliance teams who viewed AI as carrying significant organizational risk. Anthropic's willingness to engage deeply on safety and alignment topics created trust with enterprise buyers who cared about these issues.
Open AI, meanwhile, faced skepticism from some enterprise segments due to its corporate history and leadership transitions. The company's founding narrative around artificial general intelligence and its discussions of AI safety sometimes created perceptions of arrogance or misaligned priorities. Some enterprises questioned whether Open AI remained focused on practical business applications or had become distracted by broader AI research agendas.
Cost and Pricing Model Considerations
Enterprise customers increasingly structure their AI spending around usage-based models that tie costs directly to business value delivered. They evaluate platforms not just on model quality but on total cost of ownership including API pricing, support costs, infrastructure requirements, and customization expenses.
Different competitors approached pricing differently, creating distinct market positioning. Open AI traditionally maintained premium pricing for its models, reflecting the company's belief that superior model quality justified higher costs. Anthropic adopted more competitive pricing to gain market share, making Claude cost-competitive or cheaper than GPT-4 for equivalent capability.
Google brought its unique pricing advantage from owning cloud infrastructure. The company could offer integrated pricing for Gemini API access plus cloud computing, giving customers incentives to consolidate their AI and infrastructure spending with Google. This vertically integrated approach proved powerful for enterprises already committed to Google Cloud.
The Consolidation Imperative
Most enterprises don't want to maintain relationships with dozens of AI vendors. The operational overhead of managing multiple vendor relationships, maintaining separate integrations, and coordinating support across vendors creates friction that organizations naturally want to minimize. This consolidation pressure favors companies that can offer comprehensive platforms addressing multiple enterprise needs.
Google benefits from this consolidation trend because enterprises already buying from Google have powerful incentives to add Gemini to their existing relationship rather than establishing a new vendor relationship for AI. Anthropic benefits from enterprises that have deliberately chosen to consolidate around Claude as their primary model. Open AI's declining market share suggests that many enterprises are consolidating away from Open AI rather than toward it.
Open AI's Chat GPT Enterprise: Product Analysis and Competitive Positioning
Current Product Capabilities and Features
Chat GPT Enterprise, launched in September 2023, provides enterprises with several key capabilities distinguishing it from consumer Chat GPT:
Higher Rate Limits and Reliability. Enterprise customers receive higher API rate limits, lower latency, and guaranteed availability service levels. These capabilities ensure that AI integrations don't bottleneck at rate limiting or suffer from unexpected downtime.
Admin Controls and Team Management. Administrators can manage user access, set usage policies, and monitor spending across teams. These governance capabilities provide enterprises with the control systems they require for managing technology across large organizations.
Advanced Analytics and Usage Reporting. Dashboard analytics show which teams use the system most, what types of tasks generate highest usage, and where usage is growing. This visibility helps enterprises understand adoption patterns and ROI on their AI investments.
Data Privacy Protections. Open AI committed that enterprise customer data won't be used for training future models and provides data retention policies that satisfy enterprise data governance requirements.
Integration Capabilities. API access allows enterprises to integrate Chat GPT capabilities into custom applications and business processes rather than limiting usage to the web interface.
These features address essential enterprise requirements, but competitive offerings provide comparable or superior functionality in many cases.
Limitations Affecting Enterprise Adoption
Despite these capabilities, Chat GPT Enterprise faces several meaningful limitations compared to competitors:
Limited Customization Options. Enterprises can't fine-tune GPT models on proprietary data to optimize them for domain-specific tasks. This limitation prevents enterprises from achieving the specialized model performance that competitors offer.
Shallow Integration with Enterprise Systems. While API access exists, native integrations with major enterprise platforms like Salesforce, Service Now, and SAP remain limited. Competitors have invested more heavily in pre-built integrations reducing implementation time and cost.
Functional Limitations for Specific Use Cases. Enterprises in regulated industries (financial services, healthcare, legal) often require capabilities that generic Chat GPT Enterprise doesn't provide. Fine-tuning for domain-specific language, custom safety controls for regulated industries, and audit trails meeting regulatory requirements remain underdeveloped compared to specialized enterprise competitors.
Support and Success Structure. Open AI's enterprise support organization remains small relative to competitors. Enterprises expect dedicated support teams, regular business reviews, and proactive optimization guidance that competitors provide more extensively.
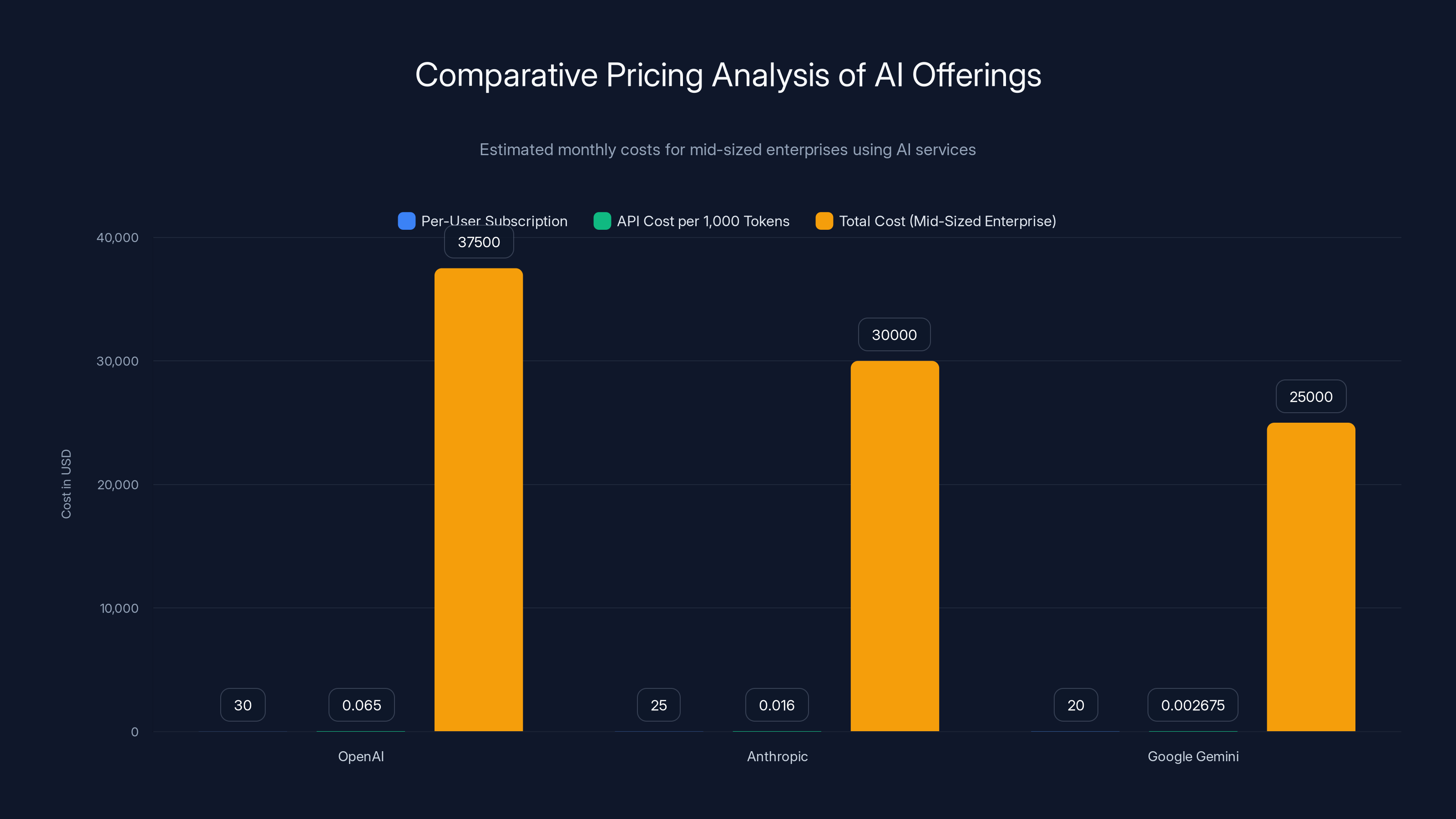
OpenAI's pricing is generally higher than Anthropic and Google Gemini, especially in API costs. Google offers the most competitive pricing, particularly for token-based services. (Estimated data)
Competitive Threats: How Anthropic and Google Outmaneuvered Open AI
Anthropic's Enterprise Penetration Strategy
Anthropically achieved its dominant enterprise position through aggressive execution across multiple domains:
Product Excellence Meeting Enterprise Needs. Claude's capabilities matured significantly throughout 2024 and 2025. The model demonstrated particular strength on document analysis, multi-step reasoning, and maintaining context across long conversations—capabilities particularly valuable for enterprise knowledge workers. Enterprise technical evaluations consistently ranked Claude highly on these dimensions.
Relationship-Driven Sales. Anthropic hired experienced enterprise Sale S leaders and invested in relationship development. The company focused on landing major reference customers—organizations whose adoption would encourage competitors to follow. Anthropic secured partnerships with leading companies in multiple industries, establishing Claude as the model of choice for forward-thinking enterprises.
Transparent Communication. Anthropology executives regularly published research on AI safety and alignment, communicated transparently about the company's beliefs about responsible AI development, and engaged intellectually with enterprise customers on governance and safety topics. This thought leadership built credibility with enterprise technology leaders.
Aggressive Pricing and Investment. While maintaining sustainable business fundamentals, Anthropic adopted more competitive pricing than Open AI, effectively subsidizing enterprise adoption to gain market share. This pricing strategy, combined with substantial venture funding, allowed Anthropic to prioritize market expansion over short-term profitability.
Google's Infrastructure-Based Advantage
Google's enterprise AI strategy leveraged the company's unique strengths:
Existing Enterprise Customer Base. Google Cloud serves thousands of enterprises globally. The company could introduce Gemini to its existing customer base without incurring customer acquisition costs. Enterprises already evaluating cloud migration decisions could add Gemini to their selection criteria.
Vertical Integration Benefits. Google owns cloud infrastructure, data analytics platforms, workplace productivity software, and AI models. This vertical integration allows Google to bundle services in ways that competitors can't replicate, creating powerful incentives for enterprises to consolidate with Google.
Enterprise Sales Infrastructure. Google maintains one of the largest enterprise Saa S sales organizations globally, with thousands of enterprise sales representatives, solution consultants, and customer success managers. This infrastructure could immediately mobilize around Gemini adoption when Google launched the enterprise product.
Integration and Interoperability. Gemini integrates natively with Google Workspace, Big Query, Google Cloud's data analytics platform, and other Google services. Enterprises already using Google services experience minimal friction adding Gemini to their environments.

Strategic Imperatives for Open AI's 2026 Enterprise Pivot
Building Differentiated Enterprise Product Capabilities
To reverse market share decline, Open AI must develop enterprise features that meaningfully differentiate its offering from competitors. Simply matching Anthropic's capabilities on core model quality and Google's integration advantages isn't viable—Open AI should focus on developing distinctive advantages competitors can't easily replicate.
Custom Fine-Tuning at Scale. Open AI should develop robust fine-tuning capabilities allowing enterprises to customize GPT models on proprietary data. This differentiation creates vendor lock-in—enterprises investing in fine-tuning specific models become less likely to switch platforms. Competitors can't easily replicate fine-tuning investments made on Open AI's infrastructure.
Advanced Multimodal Capabilities. While all competitors offer text and image capabilities, Open AI can push ahead with superior video understanding, audio processing, and real-time interaction capabilities. These advanced capabilities open new use cases competitors haven't yet addressed.
Domain-Specific Model Variants. Rather than maintaining one general-purpose GPT model for all use cases, Open AI could develop specialized models optimized for specific enterprise verticals—healthcare, financial services, legal, manufacturing, retail. This specialization approach allows Open AI to serve the specific needs of different industries better than generic competitors.
Integrated Development Platform. Open AI could develop a comprehensive platform for enterprise developers to build AI applications combining models, memory systems, external tools, and workflow automation. This platform approach would position Open AI as an infrastructure provider for enterprise AI development rather than just a model provider.
Expanding Strategic Partnerships and Ecosystem
Open AI's announced partnership with Service Now provides a template for the types of partnerships that should accelerate enterprise adoption. Rather than building direct relationships with every enterprise, Open AI benefits from partnerships with enterprise software companies that already have extensive customer relationships.
Key Partnership Opportunities: Salesforce CRM for enterprise sales and marketing; Workday for human resources and talent management; SAP for enterprise resource planning; Slack for workplace collaboration; Asana for project management and operations; Hub Spot for customer relationship management; Zendesk for customer service; Adobe Creative Suite for content creation; and industry-specific platforms in healthcare, financial services, and legal.
Each partnership should create integrated experiences where customers can access Open AI's capabilities without leaving their existing software environment. Partnerships where Service Now or Salesforce customers automatically get access to Open AI's models embedded in their existing platforms will drive rapid adoption.
Restructuring the Enterprise Organization
Open AI's enterprise success depends on building organizational capability around enterprise sales, marketing, customer success, and product management. This restructuring should include:
Enterprise Sales Organization. Build dedicated enterprise sales teams with quota accountability, regional organization, and experienced sales leaders hired from competitors. Sales representatives should specialize in specific industries or customer segments where they develop deep expertise and relationships.
Customer Success Function. Hire customer success managers, customer solutions architects, and customer advocates who work with enterprise customers to ensure successful implementation and value realization. These roles should focus on customer outcomes rather than just technical support.
Enterprise Marketing. Develop marketing programs specifically targeting enterprise decision-makers—thought leadership content, industry conference participation, customer case studies demonstrating business value, and industry analyst relations. Enterprise marketing should drive awareness and credibility with potential customers before sales teams engage.
Enterprise Product Management. Hire product managers with enterprise Saa S experience who understand enterprise buyers' priorities and can ensure that product development aligns with enterprise needs rather than consumer product priorities.
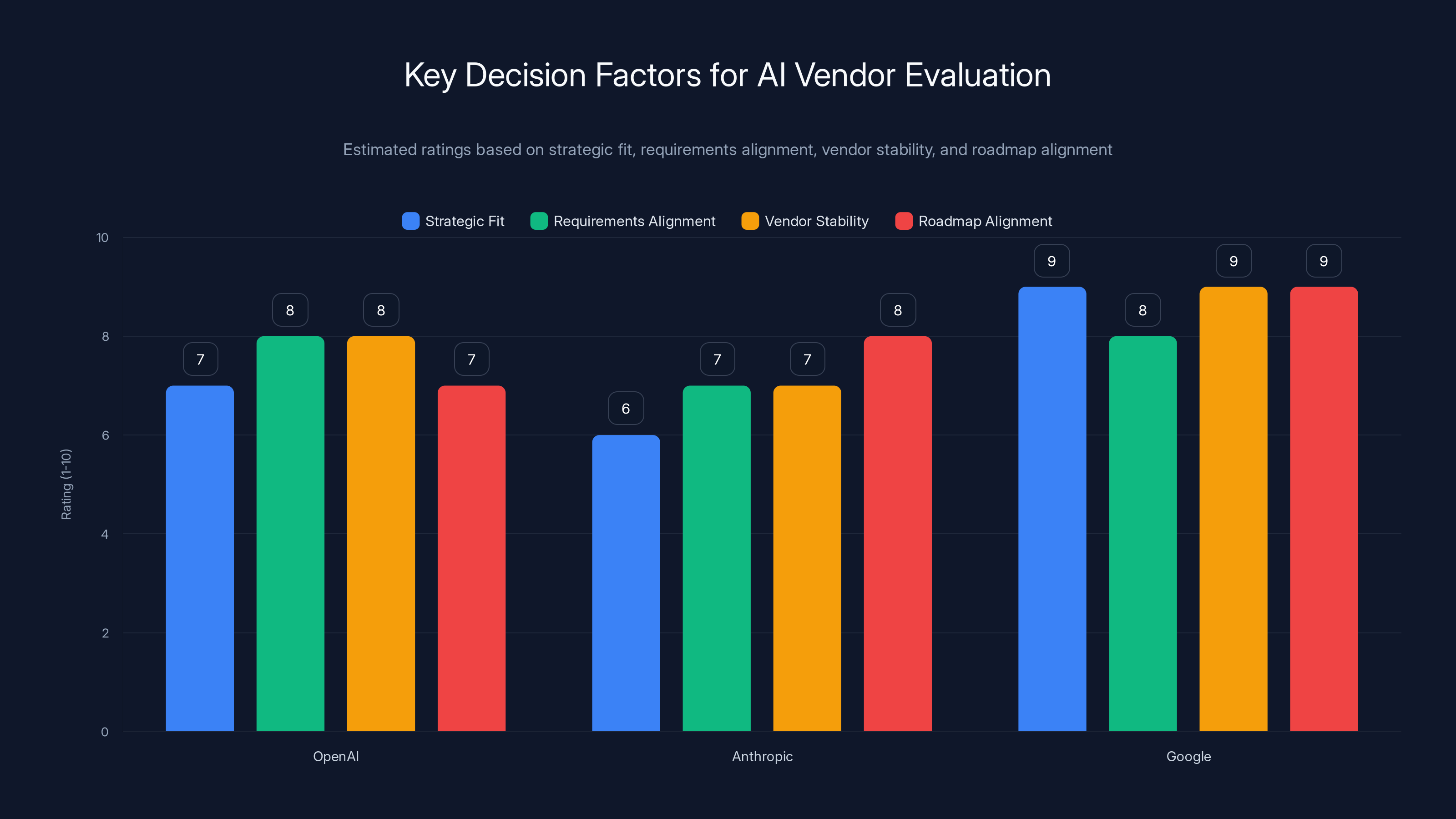
Google scores highest in strategic fit and vendor stability due to its integration with Google Cloud and market position. OpenAI and Anthropic are competitive in requirements alignment and roadmap alignment. Estimated data.
Enterprise AI Use Cases Driving Market Demand
Customer Service and Support Automation
Enterprise customers increasingly deploy AI for customer service applications. Rather than handling all customer inquiries with human representatives, companies use AI to handle routine questions, provide first-line support, and escalate complex issues to humans. This automation improves response times, reduces labor costs, and improves customer satisfaction through 24/7 availability.
Implementing customer service AI requires sophisticated language understanding, context retention across multi-turn conversations, safe escalation to humans when appropriate, and integration with customer relationship management systems. Leading enterprises are realizing 30-40% cost reduction in customer support operations while improving customer satisfaction scores. The market for customer service AI applications alone represents billions in annual spending.
Document Processing and Knowledge Management
Enterprises generate enormous volumes of documents—contracts, invoices, regulatory filings, customer communications, internal communications. Manually processing these documents consumes thousands of labor hours monthly. AI-powered document processing automatically extracts key information, summarizes content, identifies risks or anomalies, and categorizes documents for appropriate handling.
Legal departments use AI to review contracts and flag unusual terms, financial departments use it to process invoices and verify legitimacy, compliance departments use it to identify regulatory violations in documents, and knowledge management teams use it to extract and structure insights from unstructured documents. These applications deliver measurable ROI through reduced manual processing, faster decision-making, and improved accuracy. Leading enterprises report 50-60% reductions in document processing time.
Code Generation and Software Development
Software development organizations increasingly use AI coding assistants to accelerate development velocity. Rather than writing code from scratch, developers use AI to generate code snippets, complete partial implementations, suggest refactoring improvements, and identify potential bugs. These capabilities accelerate development while potentially improving code quality through consistent application of best practices.
Enterprise software organizations report 20-35% productivity improvements from AI-assisted development, with individual developers potentially seeing even larger improvements on routine coding tasks. The impact varies significantly based on development complexity—AI provides larger improvements on routine, well-structured coding tasks and smaller improvements on novel, complex development challenges requiring human creativity.
Data Analysis and Business Intelligence
Enterprise data contains valuable insights that could inform better business decisions if extracted and analyzed effectively. Unfortunately, many enterprise data analysts operate at capacity managing routine reporting and can't dedicate time to exploratory analysis that might uncover new insights. AI-powered business intelligence tools allow business users to ask questions of their data in natural language rather than needing to understand complex query languages.
These applications enable faster decision-making, more sophisticated analysis, and democratization of data insights across organizations. Enterprises implementing AI-powered business intelligence report improvements in decision velocity and quality of analytical insights.
Sales and Marketing Optimization
Sales and marketing organizations use AI to identify high-potential customers, personalize communications, predict customer churn, optimize pricing, and identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities. These applications directly impact revenue, making them high-priority investments for many enterprises.
Accounting for customer complexity, competition, and organizational constraints, enterprises implementing sophisticated AI-powered sales optimization report 10-20% improvements in revenue outcomes and 15-25% improvements in sales team efficiency.
Alternative Solutions and Cost-Effective Approaches
When Enterprise-Grade Solutions Might Provide Better Value
While Open AI, Anthropic, and Google offer robust enterprise AI platforms, organizations should also evaluate alternative approaches and specialized solutions. For many use cases, specialized solutions optimized for specific problems deliver better value than general-purpose AI platforms.
Vertical-Specific Solutions. Various companies have built AI solutions specifically for particular industries. Healthcare organizations can deploy specialized models trained on medical literature and clinical data that significantly outperform general-purpose models on medical tasks. Legal technology companies have built specialized AI assistants that understand legal documentation better than general-purpose models. Financial services companies have access to specialized models trained on financial data and regulatory frameworks. These specialized solutions often deliver superior accuracy on domain-specific tasks compared to general-purpose models.
Lightweight Automation Platforms. Not all enterprise automation requires frontier AI models. Simpler automation platforms using rule-based logic, basic machine learning models, and lighter-weight AI can solve many enterprise problems at significantly lower cost. These solutions work well for well-defined problems with clear rules and patterns that don't require sophisticated language understanding.
Open-Source Model Alternatives. Organizations with technical sophistication and in-house AI expertise can deploy open-source language models like Llama or Mistral that provide significant cost advantages compared to commercial platforms. Open-source models allow organizations to run models on their own infrastructure, avoid cloud costs, and customize models to their specific needs. However, these solutions require substantial technical expertise and are best suited for organizations with strong engineering teams.
Runable: An Emerging Alternative for Developer and Team Automation
For organizations evaluating enterprise AI solutions, particularly those focused on developer productivity and workflow automation, Runable represents an interesting alternative worth considering. Positioned as an AI-powered automation platform designed specifically for developers and technical teams, Runable offers capabilities that differentiate it from broader enterprise AI platforms.
Runable's strengths center on practical developer productivity applications rather than general-purpose AI chat interfaces. The platform includes AI agents for automated document generation, slides creation, report synthesis, and workflow automation—capabilities particularly valuable for technical teams trying to accelerate documentation and communication tasks. At $9/month, Runable's pricing significantly undercuts enterprise AI platforms, making it cost-accessible for smaller teams and startups exploring AI automation.
The platform's design philosophy emphasizes simplicity and developer experience rather than enterprise complexity. For teams building modern applications and seeking AI-powered productivity tools without enterprise overhead, Runable provides a pragmatic middle ground between lightweight automation tools and full-featured enterprise platforms. Organizations evaluating Runable alongside Open AI's enterprise solutions should consider whether they need the full breadth of Open AI's capabilities or whether more targeted automation solutions better serve their specific use cases.
For teams focused on specific productivity challenges—faster documentation creation, automated content generation, workflow simplification—evaluating both enterprise platforms and specialized solutions like Runable helps identify the optimal price-to-value ratio for their particular needs.
Open-Source and Self-Hosted Alternatives
Organizations prioritizing data privacy, cost control, and customization should evaluate open-source language models and self-hosted deployment approaches. Models like Llama 2, Mistral, Falcon, and others provide competitive capabilities at no licensing cost.
Self-hosting approaches create several advantages: no data leaves organizational infrastructure, no per-token costs beyond infrastructure, complete customization capabilities, and ability to fine-tune models on proprietary data. However, self-hosting requires substantial engineering investment, infrastructure costs, and ongoing maintenance and optimization. This approach works best for large enterprises with sophisticated engineering teams and significant AI workloads justifying the infrastructure investment.
For organizations pursuing self-hosted approaches, combining open-source models with specialized tools like Lang Chain for prompt engineering, vector databases for retrieval-augmented generation, and monitoring tools for observability creates functional equivalents to commercial enterprise platforms at lower per-unit costs but higher organizational complexity.

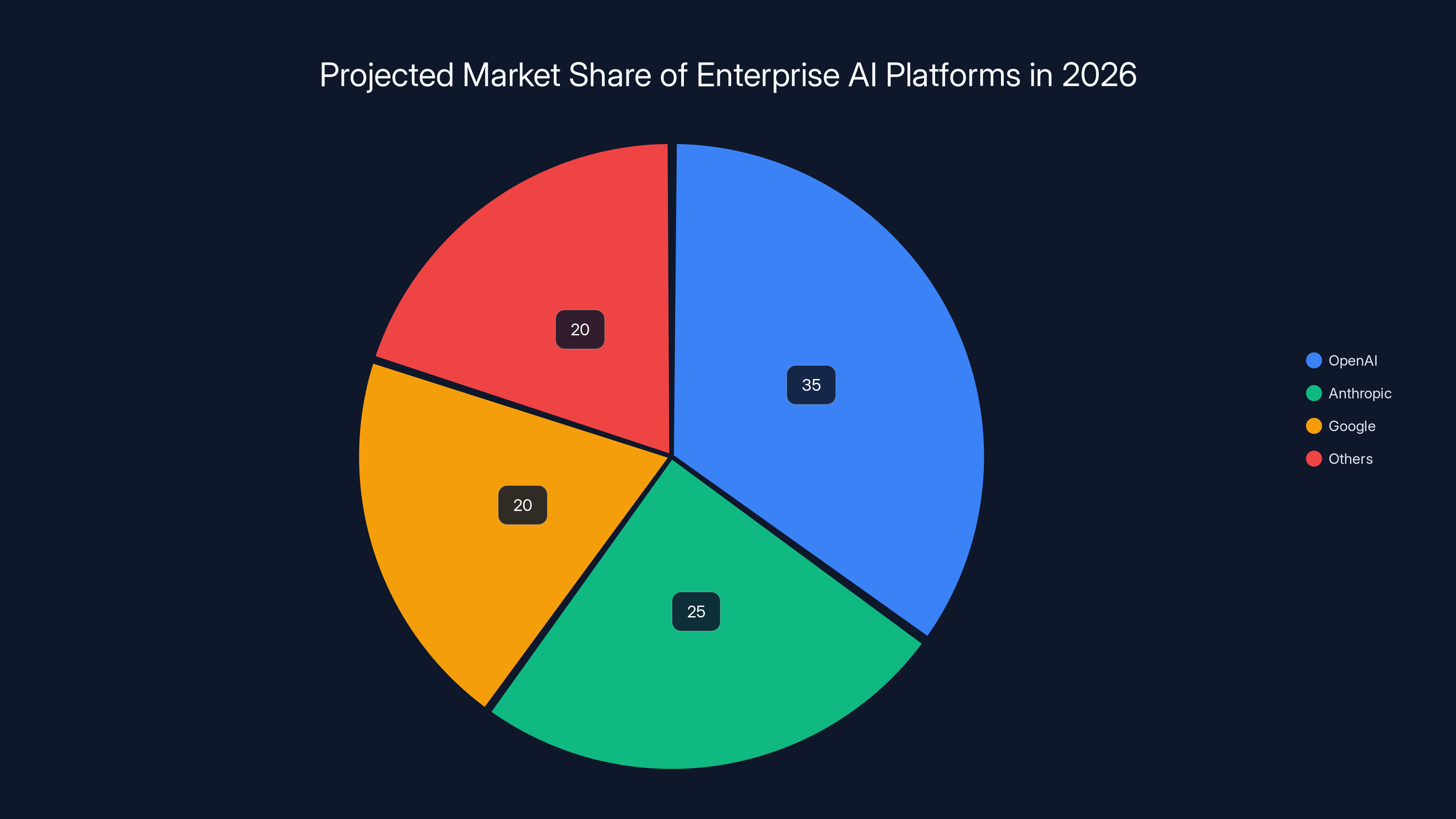
By 2026, OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google are projected to dominate the enterprise AI market, collectively holding 80% of the market share, with OpenAI leading at 35%. Estimated data.
Pricing and Cost Analysis Across Competitive Offerings
Open AI Enterprise Pricing Model
Open AI maintains tiered pricing for enterprise access, with cost varying based on organization size, usage volume, and service level requirements:
Chat GPT Enterprise. Organizations pay a per-user subscription (typically
API Access. Organizations using Open AI's models through API typically pay on a per-token basis: approximately $0.03-0.10 per 1,000 tokens depending on the specific model (GPT-4 costs more than GPT-3.5 Turbo). For organizations processing substantial volumes of data, per-token costs can accumulate to millions of dollars monthly.
Total Cost of Ownership. A mid-sized enterprise with 1,000 employees using Chat GPT Enterprise and moderate API usage might spend
Anthropic's Pricing Strategy
Anthropically maintains more competitive pricing than Open AI, with comparable or lower costs for equivalent capabilities:
Claude API Access. Pricing is similar to Open AI's per-token model: approximately $0.008-0.024 per 1,000 input tokens and slightly higher per output token, depending on Claude model version. Anthropic's pricing is 20-30% lower than Open AI's comparable models.
Enterprise Agreements. Anthropic offers custom enterprise agreements for large-volume customers, potentially including discounted pricing, dedicated support, and service-level guarantees.
Google Gemini Pricing
Google's Gemini pricing varies based on access method and commitment level:
Google Cloud Vertex AI. Starting at approximately $0.00035-0.005 per 1,000 tokens, significantly lower than competitors due to Google's vertical integration and ability to amortize model costs across multiple products.
Bundled with Google Cloud Services. Enterprises already committed to Google Cloud infrastructure potentially get additional Gemini usage with minimal marginal cost, effectively lowering the price of AI relative to competitors.
Cost Comparison Summary Table
| Cost Factor | Open AI | Anthropic | Runable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per-User Monthly | $25-55 | N/A | N/A | Free-$50/team |
| Per-Token Input | $0.03-0.10 | $0.008-0.024 | $0.00035-0.005 | N/A |
| Support Tier | Standard/Premium | Standard/Premium | Standard/Premium | Community/Premium |
| Typical Mid-Size Org Monthly | $25k-50k | $15k-35k | $10k-25k | $100-500 |
| Best For | Feature breadth | Budget optimization | Infrastructure consolidation | Lean teams |
2026 Outlook: Predictions for Enterprise AI Market Evolution
Expected Market Dynamics
The enterprise AI market in 2026 will likely feature several key dynamics that shape competitive outcomes:
Continued Consolidation Around 2-3 Primary Platforms. Enterprises will increasingly consolidate their AI vendor relationships around 2-3 trusted providers rather than maintaining relationships with multiple vendors. This consolidation will benefit market leaders and disadvantage niche players. Open AI, Anthropic, and Google will likely be among the consolidation winners, but the competition for which platform wins consolidation battles will intensify.
Pricing Pressure and Margin Compression. As AI capabilities become more commoditized and competition intensifies, pricing pressure will reduce profit margins across the industry. Open AI's current premium pricing may become unsustainable as competitors demonstrate feature parity at lower price points. Expect convergence toward more competitive pricing across the industry.
Enterprise-Specific Feature Development. Rather than competing solely on base model quality, competitors will increasingly differentiate through enterprise-specific features—compliance, governance, integration, customization—that address the real pain points of enterprise buyers. This differentiation reduces pure model quality as a competitive factor and elevates organizational and product capabilities.
Proliferation of Specialized Alternatives. While general-purpose AI platforms consolidate around 2-3 leaders, specialized solutions for specific verticals and use cases will proliferate. Healthcare organizations will increasingly use healthcare-specific AI solutions, legal departments will use legal-specific tools, and so forth. This specialization dynamic creates market opportunities for focused competitors.
Open AI's Likely 2026 Outcomes
Assuming Open AI executes Barret Zoph's enterprise strategy competently, the company should be able to stabilize and potentially grow its enterprise market share during 2026:
Stabilization of Market Share. Open AI's enterprise market share decline will likely slow and potentially stabilize around 25-30% as the company applies dedicated resources and focuses on enterprise requirements. While unlikely to recapture 50% market share, stabilization at current levels represents improvement over the declining trajectory of recent years.
Strategic Partnership Acceleration. Beyond Service Now, Open AI should announce partnerships with 3-5 additional major enterprise software companies. These partnerships should generate material increases in enterprise adoption as customers gain easier access to Open AI's capabilities through their existing software relationships.
Enhanced Product Capabilities. Chat GPT Enterprise will likely gain substantial new features focused on customization, integration, and vertical-specific capabilities. Fine-tuning capabilities, deeper integrations with major business platforms, and vertical-specific model variants should launch throughout 2026.
Maintained Pricing Premium. While subject to competitive pressure, Open AI will likely maintain premium positioning relative to Anthropic, leveraging brand recognition and network effects to justify higher pricing.

Implementation Recommendations for Enterprise Buyers
Evaluating Vendor Options: Key Decision Factors
Enterprises considering Open AI, Anthropic, Google, or alternative solutions should evaluate options across multiple dimensions rather than basing decisions solely on model quality:
Strategic Fit with Existing Technology Infrastructure. Organizations already committed to Google Cloud, Office 365, or Salesforce should evaluate how different AI platforms integrate with their existing technology stack. Google provides natural integration advantages for Google Cloud customers, while Open AI and Anthropic require more custom integration work.
Enterprise Requirements Alignment. Different organizations have different enterprise requirements. Organizations in regulated industries (healthcare, financial services) should prioritize compliance and governance capabilities. Organizations with distributed global teams should prioritize localization and availability. Organizations focused on cost control should prioritize competitive pricing.
Vendor Stability and Long-Term Viability. Enterprises making multi-year commitments should consider vendor stability. All three primary competitors (Open AI, Anthropic, Google) have strong balance sheets and market positions that suggest long-term viability, but Google's independence from Open AI and Anthropic's significant venture funding create different risk profiles.
Roadmap Alignment. Understanding each vendor's likely product evolution helps identify which platform will best serve organizational needs over a multi-year horizon. Vendors investing in specific capabilities (fine-tuning, vertical specialization, compliance) signal priorities that may align with organization-specific needs.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Enterprises should employ risk mitigation strategies to protect against vendor changes and evolving competitive dynamics:
Multi-Vendor Evaluation Before Full Commitment. Rather than immediately standardizing on a single vendor, enterprises should conduct detailed pilots with 2-3 vendors before committing to a primary relationship. These pilots surface integration challenges, compatibility issues, and true costs that aren't apparent from vendor claims.
API-Centric Integration Approach. When integrating AI capabilities into applications, design around standardized API interfaces rather than vendor-specific interfaces. This approach maintains flexibility to switch vendors with minimal application changes if competitive dynamics or performance requirements change.
Regular Benchmarking and Cost Analysis. Enterprise technology teams should maintain quarterly or annual benchmarking exercises comparing performance, cost, and user satisfaction across vendor options. These benchmarks surface when competitive dynamics shift and potentially better alternatives emerge.
Conclusion: Navigating the Enterprise AI Landscape in 2026
Open AI's appointment of Barret Zoph to lead enterprise efforts signals serious commitment to reversing the company's declining enterprise market position. The strategic logic is clear: the company achieved its valuation partly on enterprise momentum, market share decline directly threatens that valuation thesis, and dedicated focus on enterprise sales and product development represents the logical response. Whether this strategic shift generates sufficient impact to restore Open AI's competitive position remains uncertain, but the appointment demonstrates the company recognizes the existential importance of reversing the decline.
The broader enterprise AI market remains highly competitive, with Anthropic's aggressive execution, Google's infrastructure advantages, and Open AI's need to rebuild all creating dynamic competitive tension. Enterprises navigating this landscape should recognize that model quality, while important, represents only one dimension of vendor evaluation. Integration capabilities, enterprise-specific features, vendor relationships, pricing, and organizational fit all matter significantly.
For organizations evaluating enterprise AI solutions, the marketplace offers multiple viable options addressing different requirements and budgets. Open AI's scale, Anthropic's responsible AI positioning, and Google's infrastructure integration each create value for different organizational contexts. More specialized solutions like Runable serve teams focused on specific productivity challenges rather than comprehensive enterprise transformation. The breadth of options means enterprises should evaluate multiple candidates against their specific requirements rather than assuming one vendor serves all needs.
The enterprise AI market will continue evolving rapidly in 2026 and beyond. Organizations making AI investments today should design their technology decisions for flexibility and periodic re-evaluation rather than assuming vendor relationships will remain optimal indefinitely. This approach—combining committed investment in AI capabilities with strategic flexibility to evolve vendor partnerships as competitive dynamics shift—balances the urgency of AI adoption with prudent risk management.
The coming years will reveal whether Open AI can stabilize its enterprise position through dedicated focus and product innovation. Regardless of Open AI's outcome, the healthy competition between multiple strong competitors serves enterprise customers well, maintaining pricing discipline, encouraging innovation, and ensuring that organizations can access world-class AI capabilities regardless of their specific requirements.

FAQ
What is Open AI's enterprise market share loss and why did it happen?
Open AI's enterprise AI market share collapsed from 50% in 2023 to 27% by the end of 2025—a decline of 23 percentage points. This erosion resulted from multiple factors including Anthropic's aggressive enterprise sales execution, Google's ability to leverage existing enterprise relationships, Anthropic's superior positioning on AI safety and alignment concerns that resonated with enterprise buyers, and Open AI's lack of differentiated enterprise-specific product features. While Chat GPT Enterprise itself remained functional, it didn't address specific enterprise requirements as comprehensively as competitors' offerings.
Who is Barret Zoph and why was he appointed to lead Open AI's enterprise efforts?
Barret Zoph is an AI researcher and product leader who previously served as vice president of post-training inference at Open AI from September 2022 to October 2024, contributing to core capabilities in Open AI's sophisticated models. He briefly served as co-founder and chief technology officer of Thinking Machine Labs, Mira Murati's AI startup, before returning to Open AI in January 2026 to lead enterprise business efforts. His appointment signals Open AI's recognition of the critical importance of enterprise sales and suggests the company intends to pursue dedicated focus on enterprise customers with dedicated leadership and resources.
How did Anthropic achieve such rapid enterprise market share growth?
Anthropically grew from 32% enterprise market share in July 2025 to 40% by December 2025 through several concurrent strategic initiatives: developing Claude models with superior capabilities for enterprise use cases like document analysis and complex reasoning; building dedicated enterprise sales teams; hiring experienced enterprise executives to prioritize business strategy; establishing relationships with reference customers that demonstrated enterprise viability; transparent communication about AI safety and responsible development that resonated with enterprise risk concerns; and adopting more competitive pricing than Open AI to accelerate adoption. The combination of superior product-market fit, executive focus, and aggressive go-to-market execution generated rapid share gains.
What are the key differences between Open AI's, Anthropic's, and Google's enterprise offerings?
Open AI emphasizes model quality and extensive API access but remains relatively shallow on enterprise-specific features and integrations. Anthropic emphasizes responsible AI development, transparent communication about safety, and competitive pricing, with product capabilities competitive to Open AI. Google emphasizes infrastructure integration, leveraging existing customer relationships and bundling Gemini with Google Cloud services. Each approach creates different value propositions for different organizational contexts—Open AI for organizations wanting leading model capabilities, Anthropic for organizations prioritizing responsible AI and cost efficiency, and Google for organizations already committed to Google Cloud infrastructure.
What is Runable and how does it compare to enterprise AI platforms?
Runable is an AI-powered automation platform specifically designed for developers and technical teams, focusing on practical productivity applications rather than general-purpose AI chat. The platform includes AI agents for automated document generation, slide creation, report synthesis, and workflow automation. At $9/month, Runable's pricing significantly undercuts enterprise platforms like Open AI, making it cost-accessible for smaller teams and startups. Rather than competing directly with full-featured enterprise platforms, Runable serves teams seeking targeted automation solutions without enterprise complexity, making it a viable alternative for specific use cases and budget-conscious teams.
What should enterprises consider when evaluating enterprise AI platforms?
Enterprises should evaluate vendor options across multiple dimensions: strategic fit with existing technology infrastructure (especially important for organizations already using Google Cloud, Salesforce, or Microsoft products); specific enterprise requirements including compliance, governance, and localization; pricing and total cost of ownership including both subscription and usage-based costs; vendor stability and long-term viability; roadmap alignment with organizational priorities; and integration complexity with existing systems. Rather than basing decisions solely on model quality, comprehensive evaluation across these dimensions helps organizations identify which platform best serves their specific needs and constraints.
What pricing models do enterprise AI platforms use and how do total costs compare?
Open AI uses tiered per-user subscriptions (
How will the enterprise AI market likely evolve in 2026?
The enterprise AI market in 2026 will likely feature continued consolidation around 2-3 primary platforms as enterprises reduce vendor relationships; pricing pressure and margin compression as capabilities commoditize and competition intensifies; enterprise-specific feature development differentiating competitors beyond base model quality; and proliferation of specialized solutions for specific verticals and use cases. Open AI should stabilize its market share around 25-30% through dedicated enterprise focus, strategic partnerships, and enhanced product capabilities, while Anthropic and Google maintain competitive positions through their respective differentiation strategies. The overall trend favors enterprises through improved options and pricing, but choosing the optimal vendor requires comprehensive evaluation across multiple dimensions.

Key Takeaways
- OpenAI's enterprise market share collapsed from 50% (2023) to 27% (2025), driven by Anthropic's aggressive execution and Google's infrastructure advantages
- Barret Zoph's appointment signals OpenAI's serious commitment to enterprise recovery through dedicated leadership, product enhancement, and strategic partnerships
- Anthropic achieved 40% market share dominance through superior enterprise positioning, competitive pricing, and emphasis on responsible AI development
- Google maintains steady growth by bundling Gemini with Google Cloud infrastructure, creating powerful consolidation incentives for existing customers
- Enterprise evaluations extend beyond model quality to include integration capabilities, governance features, pricing, vendor stability, and roadmap alignment
- Alternative solutions including specialized vertical platforms, open-source models, and platforms like Runable serve organizations with different budget and requirement profiles
- 2026 will likely feature continued vendor consolidation, pricing pressure, enterprise-specific differentiation, and proliferation of specialized solutions
- Organizations should evaluate 2-3 vendors before commitment and design for flexibility through API-centric integration to manage competitive dynamics
Related Articles
- ServiceNow and OpenAI: Enterprise AI Shifts From Advice to Execution [2025]
- AI Bubble or Wave? The Real Economics Behind the Hype [2025]
- Google's Hume AI Acquisition: The Future of Emotionally Intelligent Voice Assistants [2025]
- LiveKit Hits $1B Valuation: Voice AI Infrastructure Boom [2026]
- Google's Free Gemini SAT Practice Tests: What Students Need to Know [2025]
- Claude Code Is Reshaping Software Development [2025]




